Gastrointestinal Physiology
|
|
|
- Jordan Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gastrointestinal Physiology
2 Digestion and Absorption
3 Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical digestion: Secreting digestive solution into the alimentary tract. t Absorption : The digestive products is moved from the lumen of alimentary tract across a layer of epithelial cells and enter the blood and lymph.
4 Functions of the digestive system Digestion and absorption Motility:physical digestion, propels food through the digestive system, elimination Secretion: chemical digestion Absorption: passage of the molecules into the body Immune function Endocrine function
5 Anatomy Components of the digestive system : Gastrointestinal (GI) tract plus the accessory organs
6 Structure of the alimentary canal
7 Histology
8 The gut wall has a layered organization, with the absorptive cells lining the lumen and neural and muscular components below. Blood and lymph vasculature is abundant.
9 Mechanical digestion smooth muscle
10 General properties of gastrointestinal Low excitability High distensibility ibilit Tonic contraction Autorhythmicity smooth muscle High sensitivity to temperature, stretch and chemical stimulation i
11 Electrophysiological properties of gastrointestinal smooth muscle Membrane resting potential (RP) 50~ 60 mv Slow wave (basic electrical rhythm, BER) The spontaneous rhythmic fluctuation of the RP. Initiated in the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC). Due to rhythmic changes in Na + K + pump pactivity. Frequency: 3~12 cpm. Spike potential (AP): Ca 2+ influx & K + efflux.
12 Rhythmic waves of smooth muscle contraction ti in the gut are the result of waves of action potentials moving along via gap junctions.
13
14 Normal BER frequencies of gastrointestinal system BER not generated by nervous activity
15 Neural control of gastrointestinal function Autonomic nervous system (extrinsic) Enteric nervous system (intrinsic)
16 Enteric nervous system Myenteric plexus (Auerbach s plexus) Submucosal plexus (Meissner s plexus) Neurotransmitters secreted tdby enteric neurons Ach, NE, ATP, serotonin, dopamine, cholecystokinin, substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, somatostatin, leu enkephalin, met enkephalin, enkephalin, bombesin, etc.
17 Function Myenteric plexus : control over GI motility Submucous plexus: regulate blood flow and control secretion
18
19
20 Gastrointestinal t ti reflexes Reflexes that are integrated entirely within the enteric nervous system Reflexes from the gut to the spinal cord or brain stem and then back to the gastrointestinal tract
21 Gastrointestinal hormones (Gastrointestinal peptide) pp The hormones synthesized by a large number of endocrine cells (APUD) within the gastrointestinal tract. Brain gut peptide Physiological functions Control of the digestive function Control of the release of other hormones Trophic action
22 Gastrointestinal hormones Four main types Gastrin Secretin Cholecystokinin (CCK) Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
23 (1) Gastrin: Synthesized in G cells; Regulator gastric acid secretion Proliferation of gastric epithelium (2) Cholecystokinin: I cells in the duodenum and jejunum contraction of the gallbladder Inhibits stomach motility Stimulates secretion of pancreatic enzymes (3) Secretin: Secreted by S cells in the duodenum and jejunum Inhibits the motility of gastrointestinal tract Stimulates secretion of water and bicarbonate from pancreas (4) Gastric inhibitory peptide :K cells in the duodenum, jejunum Inhibits gastric secretion and motility. Potentiates release of insulin in response to elevated blood glucose.
24 Splanchnic circulation
25 Blood supply to the intestines through the mesenteric web
26 Microvasculature of the intestinal villus
27 Physical digestion: Digestion in mouth Masticated (chewed) by teeth; mixed by tongue Functions : 1. Breaking large pieces into small pieces, resulting in an increase in surface area which is where digestive enzymes work. 2. Softening of food and transformation into a size conducive to swallowing. 3. lubrication of food by impregnating it with saliva.
28 Chemical digestion by saliva 1000 ml/d, ph 6.0~7.0 Composition of saliva H 2 O Na +, Cl -, K +, HCO - 3 Mucus (containing mucin) Amylase lysozyme, Function: Moisten and Lubricate food Dissolve food Antibacterial action: lysozyme Initiates starch digestion: amylase
29 Swallowing reflex The swallowing reflex is coordinated dby the medulla oblongata, which stimulates the appropriate sequence of contraction and relaxation in the participating i i skeletal lmuscle, sphincters, and smooth muscle groups.
30 Deglutition Esophagus peristalsis Peristaltic waves: Progressive wave of muscle contraction Heartburn Gastroesophageal reflux
31 Digestion in the stomach
32
33
34
35 Gastric juice Properties ph 0.9~ ~2.5 L/day Mj Major components Hydrochloric acid Pepsinogen Mucus Intrinsic factor
36 (1) Hydrochloric acid Secreted by the parietal cells Output Basal: 0~5 mmol/h Maximal: 20~25 mmol/h Mechanism HCl is actively secreted against a concentration gradient by H+/K+ ATPase or "proton pump"
37 H2 receptor antagonist M-type receptor antagonist Omeprazole
38 Role of HCl Acid sterilization Activation of pepsinogen Promotion of secretin secretion Beneficial to absorption of iron and calcium
39 (2) Pepsinogen MW: 42,500 Secreted by the chief cells as an inactive form. Activated initially by H + ions and then by active pepsin, autocatalytic activation. Active pepsin (MW: 35,000)
40 (3) Mucus Secreted by the epithelial cells all over the mucosa and by the neck mucus cells in the upper portion of the gastric glands and pyloric glands. A layer ~500 μm thick composed chiefly of mucins. Protection of the tissue from Mechanical damage by food particles and H+ damage.
41 Mucus HCO 3 barrier 3 Protecting the epithelium from acid and pepsin insults by traping HCO 3- in mucus layer to buffer chemically insulates.
42 If the mucus-hco 3- barrier is weak?
43 (4) Intrinsic factor A high molecular weight glycoprotein which synthesized and secreted by the parietal cells. The intrinsic factor binds to Vit B 12 and facilitates its absorption.
44
45 (5) other enzymes Gastric lipase Gastric amylase Gelatinase
46 Regulation of gastric secretion Basic factors that stimulate gastric secretion Acetylcholine (+ all secretory cells) Gastrin (+ parietalcells) Histamine (+ parietal cells)
47 Nervous regulation Short reflex pathways Short excitatory reflexes: mediated by cholinergic neurons in the plexuses Short inhibitory reflexes: mediated by non adrenergic noncholinergic (NANC) neurons Long autonomic pathways Long excitatory t reflexes: parasympathetic ti Long inhibitory pathways: sympathetic
48 Humoral regulation Excitatory ACh Histamine i Gastrin Inhibitory Somatostatin Secretin 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Prostaglandin
49 Phases of gastric secretion Cephalic phase Gastric phase Intestinal phase
50
51 30
52 Inhibition of gastric secretion Inhibition of gastric secretion by intestinal factors is presumably to slow the release of chyme from the stomach when the small intestine is already filled or overactive Mechanism Reverse enterogastric reflex: initiated by the presence of food in the small intestine Secretin secretion: stimulated by the presence of acid, fat, protein breakdown products, hyperosmotic or hypo osmotic fluids, or any irritating factors in the upper small intestine.
53 Motor function physical digestion Proximal stomach cardia fundus corpus (body) Distal stomach antrum pylorus pyloric sphincter
54 Motor function of the stomach Receptive relaxation Storage function (1.0~1.5 L) Vago vagal reflex Peristalsis BER in the stomach
55 Contractions in the empty stomach Migrating Motor Complex (MMC) Periodic waves of contraction, which hmove along the gastrointestinal tract from stomach to colon Purpose of this activity: to sweep debris out of the digestive tract during the interdigestive period MMCs can lead to hunger contractions, which are associated with discomfort, referred to as hunger pains
56 Emptying of the stomach Emptying rate Fluid > viscous Small particle > large particle Isosmotic > hyper & hypo osmotic Carbohydrates > Protein > Fat Regular meal 4~6 hrs
57
58 Regulation of stomach emptying Gastricfactors that promote emptying Gastric food volume Gastrin Duodenal factors that inhibit stomach emptying Enterogastric nervous reflexes Fat Cholecystokinin
59
60 Thank you!
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Overview of digestion
 Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
What part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is composed of striated muscle and smooth muscle?
 CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
 1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Asma Karameh. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة -
 -2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
-2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Gastrointestinal physiology II.
 Gastrointestinal physiology II. 62. Functions of the upper GI tract: chewing, salivation, swallowing. 63. Motor functions of the stomach. Vomiting (emesis). 1 Motor functions of the mouth and the oral
Gastrointestinal physiology II. 62. Functions of the upper GI tract: chewing, salivation, swallowing. 63. Motor functions of the stomach. Vomiting (emesis). 1 Motor functions of the mouth and the oral
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
,. 1\)... ubj«pcl: Doclo1: M. Khatatbeh Handout # 1 8/4/ Gastreintestinal System. Lecture#: 1. Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Lecture#: 1 Mc:di
Lecture#: 1 Mc:di
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Gastric and Intestinal secretion
 Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Gastrointestinal Physiology. Secretion
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
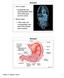 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
General principles of gastrointestinal motility
 General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion
 NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
Introduction to Digestion. Dr.sofiabadi 2015 qums
 Introduction to Digestion Dr.sofiabadi 2015 qums Digestive System is composed of: 1-Digestive tract AND 2- Accessory Organs Digestive System The primary function of the gastrointestinal (alimentary) tract
Introduction to Digestion Dr.sofiabadi 2015 qums Digestive System is composed of: 1-Digestive tract AND 2- Accessory Organs Digestive System The primary function of the gastrointestinal (alimentary) tract
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food
 UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Gastrointestinal Physiology Structure and Innervation of the Gastrointestinal Tract Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle Functions as a Syncytium.
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Structure and Innervation of the Gastrointestinal Tract Structure of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, Layers of the Gastrointestinal Tract 1. Mucosa: including A lining epithelium,
Gastrointestinal Physiology Structure and Innervation of the Gastrointestinal Tract Structure of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, Layers of the Gastrointestinal Tract 1. Mucosa: including A lining epithelium,
Digestion and absorption (I)
 Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Esophagus. Transport is achieved by peristaltic contractions and relaxation of the esophageal sphincters (upper and lower)
 GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63
 Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63 Types of GI movements: Propulsive movement-peristalsis Propulsion: controlled movement of ingested foods, liquids, GI secretions, and sloughed
Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63 Types of GI movements: Propulsive movement-peristalsis Propulsion: controlled movement of ingested foods, liquids, GI secretions, and sloughed
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System
 2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Notes on Digestive System by Qasim Page 1
 Digestion INTRODUCTION... 5 Function of Digestive System... 5 Parts of Digestive System... 5 Parts of Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)... 5 Accessory Organs of Digestive System... 5 Blood Supply... 6 Wall
Digestion INTRODUCTION... 5 Function of Digestive System... 5 Parts of Digestive System... 5 Parts of Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT)... 5 Accessory Organs of Digestive System... 5 Blood Supply... 6 Wall
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
1. Blood vessels that absorb the water and solutes leaving the filtrate of the nephron s tubules are called the
 Biology 2330: Lecture Test Five Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying
Biology 2330: Lecture Test Five Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT
 2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT
 2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
