INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
|
|
|
- Ashley Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Bhalla.Neetika*, Deep Arsh, Goswami Manish Akal College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutics, Mastuana Sahib, Sangrur, Punjab, India Article Received on: 10/02/12 Revised on: 28/03/12 Approved for publication: 18/04/12 * ABSTRACT In recent years scientific and technological advancements have been made in the research and development of oral drug delivery system. Oral sustained drug delivery system is complicated by limited gastric residence times (GRTs). In order to understand various physiological difficulties to achieve gastric retention, we have summarized important factors controlling gastric retention. To overcome these limitations, various approaches have been proposed to increase gastric residence of drug delivery in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract includes floating drug dosage (FDDS), swelling or expanding, mucoadhesive, magnetic, modified-shape, high density system and other delayed gastric emptying devices. Keywords: Gastroretentive ; Floating ; buoyant delivery Systems; Swelling System INTRODUCTION The oral route is the one, most frequently used for drug administration. Oral dosage forms are usually indicated for systemic effects resulting from drug absorption through various epithelia and mucosa of the gastro intestinal tract. Compared with other routes, the oral route is the simplest, most convenient and safest means of drug administration. 1 The treatment of illness has been accomplished by administrating drug to the human body via various pharmaceutical dosage forms like tablet, capsule, and microspheres. To achieve and maintain the therapeutics range extensive effort have recently been focused on targeting a drug or drug delivery system in a particular region of the body for extended period of time, not only for local targeting of drug but for better control of systemic drug delivery. To achieve and maintain the drug concentration in the body within the therapeutics range required for medication, it is necessary to take this type of drug delivery system several times a day this yield undesirable seesaw drug level in body. A number of advancement has been made recently in the development of new technique for drug delivery, the technique capable of regulating the rate of drug delivery system 2 To gain an appreciation for the value of controlled drug therapy it is useful to review some fundamental aspects of conventional drug delivery. Depending on the route of administration, a conventional dosage form of the drug, e.g. a solution, suspension, capsule, tablet etc. can produce a drug blood level versus time profile which does not maintain drug blood level within the therapeutic range for extended periods of time. An alternative approach is to administer the drug repetitively using a constant dosing interval, as in multiple dose therapy. There are several potential problems inherent in multiple dose therapy: The dosing interval is not appropriate for biological half life of the drug, large peaks and valleys in the drug blood level may result. The drug blood level may not be within the therapeutic range at sufficiently early times, an important consideration for certain disease states. Patient non compliance with the multiple dosing regimens can result in failure of this approach.however, these problems are significant enough to make drug therapy with conventional dosage forms less desirable than controlled release drug therapy. 2 Controlled release dosage form covers a wide range of prolonged action formulations which provides continuous release of their active ingredients at a predetermined rate and for a predetermined time. The majority of these formulations are designed for oral administration. The most important objective for the development of these is to furnish an extended duration of action and thus assure greater patient compliance. 3 Rationale of controlled drug delivery system The basic rationale for controlled drug delivery is to alter the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pharmacologically active moieties by using novel drug delivery or by modifying the molecular structure and/or physiological parameters inherent in a selected route of administration. Thus, optimal design of controlled release necessitates a thorough understanding of the 4 pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drug. However, when doses are not administered on schedule, the resulting peaks and valleys reflect less than optimum drug therapy. Extended release tablets and capsules are commonly taken only once or twice daily compared with counterpart conventional forms that may need to be taken three to four times daily to achieve the same therapeutic effect. Typically, extended release products provide an immediate release of drug which then is followed by the gradual and continual release of additional amounts of drug to maintain this effect over a predetermined period of time (Fig 1). 2 Fig.1 Characteristic representation of plasma concentrations of a conventional immediate release dosage form (IR), a sustained release dosage form (SR) and an idealized zero-order controlled release (ZOCR) dosage form (in combination with a start-up dose). Page 128
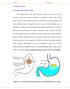
2 ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGS OF CONTROLLED RELEASE DOSAGE FORM The design of controlled release dosage forms holds many 5, 6, 7 advantages over conventional dosage forms like: Reduction in frequency of drug administration. Improved patient compliance. Reduction in drug level fluctuation in blood. Reduction in total drug usage when compared with conventional therapy. Reduction in drug accumulation with chronic therapy. Reduction in drug toxicity (local/systemic). Stabilization of medical condition (because of more uniform drug levels). Improvement in bioavailability of some drugs because of spatial control. Economical to the health care providers and the patient. Disadvantages of Controlled drug delivery system: Decreased systemic availability in comparison to immediate release conventional dosage forms; this may be due to incomplete release, increased first pass metabolism, increased instability, ph dependent solubility, etc. 8, 9 Poor in vitro-in vivo correlation. Possibility of dose dumping due to food, physiologic or formulation variables or chewing or grinding of oral formulation by the patients and thus, increased risk of toxicity. Retrieval of drug is difficult in case of toxicity, poisoning or hypersensitivity reaction. 8, 9 Higher cost of formulation. WHY IS CONTROLLED DRUG DILIVERY NEEDED? 1. To localize certain drugs at a specific site in the body. 2,4,12 2. The extend of drug absorption is limited by the residence time of the drug at the absorption site, localizing oral drug delivery system in the stomach or in the duodenum would significantly improve the extend of drug absorption. 3. They provide intimate contact between a dosage form and the absorbing tissue which may result in high concentration at a local area and hence drug flux through the absorbing tissue. 4. Maintenance of drug concentration within an optimal therapeutics range for prolongs duration of treatment. CLASSIFICATION OF ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Continuous Release Systems 1. Dissolution controlled release 2. Diffusion controlled release 3. Dissolution and diffusion controlled release 4. Ion-exchange resin-drug complexes 5. Slow dissolving salts and complexes 6. Osmotic pressure controlled 7. ph-dependent formulations 8. Hydrodynamic pressure controlled Delayed Transit and Continuous Release Systems 1. Altered density 2. Mucoadhesive 3. Size-based Delayed Release Systems 1. Intestinal release 2. Colonic release GASTRO-RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The limitations conferred by CRDDS have led to the development of gastro-retentive drug delivery (GR- DDS). Poor absorption or stability issue of many drugs in the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract necessitates controlled release dosage forms to be maintained in the upper GI tract, particularly the stomach and small intestine. GR-DDS are designed on the basis of delayed gastric emptying and controlled release principles. As rapid GI transit can prevent complete drug release in absorption zone and reduce efficacy of the administered dose, these are intended to restrain and localize the dosage form in the stomach or within the upper parts of the small intestine, for a prolonged and predictable period of time, until the system is devoid of the drug 8, 10, 11, 12. GIT Anatomy The GI tract is essentially a tube about nine meters long that runs through the middle of the body from the mouth to anus and include throat(pharynx), oesophagus,stomach, small intestine (consisting of duodenum, jejunum and ileum),and large intestine(consisting of the cecum, appendix, colon and rectum). The wall of GI tract has the same general structure throughout most of its length from oesophagus to anus, with some local variation for each region 8. Fig. 2 Human Stomach The stomach is an organ with a capacity of storage and mixing. The stomach is situated in the left upper part of the abdominal cavity immediately under the diaphragm 9, 33. Its size varies according to the amount of distention: up to 1500ml following a meal; after food is emptied a collapsed 20, 33, state is obtained with a resting volume of only 25-50ml 34. Anatomically the stomach is divided in to three region fundus, body and antrum (pylorus).the proximal part made of fundus and body acts as a reservoir for undigested materials, where as the antrum is the main site for mixing motions and acts as a pump for gastric emptying by propelling actions. The pattern of motility is however distinct in the 2 states. During the fasting state an interdigestive series of electrical events take place, which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2 to 3 hours 12,36. This is called the interdigestive myloelectric cycle or migrating myloelectric cycle (MMC), which is further divided into following 4 phases as described by Wilson and Washington 13, 35. Phase I (basal phase) lasts from 40 to 60 minutes with rare contractions. Phase II (preburst phase) lasts for 40 to 60 minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. As the phase progresses the intensity and frequency also increases gradually. Phase III (burst phase) lasts for 4 to 6 minutes. It includes intense and regular contractions for short period. It is due to Page 129
3 this wave that all the undigested material is swept out of the stomach down to the small intestine. It is also known as the housekeeper wave. Phase IV lasts for 0 to 5 minutes and occurs between phases III and I of 2 conse cutive cycles. Fig. 3 Gastrointestinal Motility Pattern After the ingestion of a mixed meal, the pattern of contractions changes from fasted to that of fed state. This is also known as digestive motility pattern and comprises continuous contractions as in phase II of fasted state. These contractions result in reducing the size of food particles (to less than 1 mm), which are propelled toward the pylorus in a suspension form. During the fed state onset of MMC is delayed resulting in slowdown of gastric emptying rate 14. ADVANTAGES OF GASTRO-RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The advantages associated with increased gastric residence time of drug can be listed as 8, 12, 14 : Retention of dosage form in the stomach for an extended period of time. Prolonged dosing interval. Controlled and continuous release of the drug. Site-specific drug delivery. Enhanced bioavailability of drugs. Reduced drug plasma level fluctuations. Improved pharmacotherapy of stomach through local drug release. Improved solubility for drugs that are less soluble in a high ph environment. Delivery of drugs with narrow absorption windows in the small intestinal region. Better in vivo-in vitro correlation have been observed in some cases. LIMITATIONS OF GASTRO-RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM GR-DDS like floating drug delivery system requires a sufficiently high level of fluids in the stomach for the delivery system to float and work efficiently. 8,13 GR-DDS are not feasible for drugs that have solubility or stability problems in the gastric fluid. Drugs which have nonspecific, wide absorption sites in the GIT, drugs that are well absorbed along the entire GIT are not suitable candidates for GR-DDS; e.g. nifedipine. 8,13 Similarly drugs that are irritant to the gastric mucosa and drugs that undergo significant first-pass metabolism are not preferred for GR-DDS. 8,13 FACTOR AFFECTING GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF DRUG 1. Density gastric retention time (GRT) is a function of dosage form buoyancy that is dependent on the density Size dosage form units with a diameter of more than 7.5 mm are reported to have an increased GRT compared with those with a diameter of 9.9 mm. 3. Shape of dosage form tetrahedron and ring shaped devices with a flexural modulus of 48 and 22.5 kilo pounds per square inch (KSI) are reported to have better GRT 90% to 100% retention at 24 hours compared with other shapes Single or multiple unit formulation multiple unit formulations show a more predictable release profile and insignificant impairing of performance due to failure of units, allow co-administration of units with different release profiles or containing incompatible substances and permit a larger margin of safety against dosage form failure compared with single unit dosage forms. 5. Fed or unfed state under fasting conditions, the GI motility is characterized by periods of strong motor activity or the migrating myoelectric complex (MMC) that occurs every 1.5 to 2 hours. The MMC sweeps undigested material from the stomach and, if the timing of administration of the formulation coincides with that of the MMC, the GRT of the unit can be expected to be very short. However, in the fed state, MMC is delayed and GRT is considerably longer. 6. Nature of meal feeding of indigestible polymers or fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging drug release. 7. Caloric content GRT can be increased by four to 10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats. 12 Page 130
4 8. Frequency of feed the GRT can increase by over 400 minutes when successive meals are given compared with a single meal due to the low frequency of MMC. 9. Gender mean ambulatory GRT in males (3.4±0.6 hours) is less compared with their age and race matched female counterparts (4.6±1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface). 10. Age elderly people, especially those over 70, have a significantly longer GRT. 14 APPROACHES TO GASTRO-RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Taking into consideration rapid transit of dosage form from stomach, various approaches such as mucoadhesive, expandable/swelling, high density, superporous hydrogel and floating drug delivery have been developed to 14, 15 increase gastric residence time of dosage forms. 1. Mucoadhesive The mucoadhesive are intended to extend the GRT by adhering them to the gastric mucosa membrane. Bioadhesion on soft tissues of certain natural or synthetic polymers has been exploited to control as well as to prolong the gastric retention of the delivery system. The adhesion of the polymers with mucous membrane may be mediated by hydration, bonding, or receptor mediated. In hydration mediated adhesion, the hydrophilic polymers become sticky and mucoadhesive upon hydration. Bonding mediated adhesion may involve mechanical or chemical bonding. Receptor mediated adhesion takes place between certain polymers and specific receptors expressed on gastric cells. The polymers could be anionic or cationic or neutral. Materials commonly used for mucoadhesion/ bioadhesion are poly (acrylic acid), carbopol, polycarbophil, chitosan, cholestyramine, HPMC, polylactic acid etc. Smart and Kellaway reported prolonged gastric retention of dosage forms coated with carbomer in mice 16. In vivo data of granules containing microcrystalline chitosan and furosemide showed higher AUC than that of the conventional dosage form. Also, the granules exhibited slow release characteristics with a marked lag time. It appeared that due to its mucoadhesive properties, chitosan retained the drug in the gastric mucosa for longer period of time Swelling / expandable The presence of polymers in the promotes their swelling to a size that prevents their passage through pyloric sphincter resulting in prolonged GRT. However, a balance between the rate and extent of swelling and the rate of erosion of the polymer is crucial to achieve optimum benefits and to avoid unwanted side effects. Agyiliraha 18 developed a polymeric coating system that formed an outer membrane on the conventional tablets. In the dissolution media the membrane detached from the core and swelled to form a balloon that kept the unit floating High- density High density are intended to lodge in the rugae of the stomach withstanding the peristaltic movements. Systems with a density of 1.3 g/ ml or higher are expected to be retained in the lower part of the stomach 19. The formulation of heavy pellets is based on the assumption that the pellets might be positioned in the lower part of the antrum because of their higher density. Devreux et al 20 reported that the pellets with density of at least 1.5 g/ ml have significantly higher residence time both in fasted and fed state. 4. Floating The floating system is intended to float in and over the gastric contents resulting in prolonged GRT. They have bulk density lower than the gastric content. Various patents have been granted on different floating including hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS) and gas generating. 21 I. Hydro dynamically balanced These are single-unit dosage forms, containing one or more gel-forming hydrophilic polymers. Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) is the most commonly used excipient; although hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC), hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC), sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC), agar, carrageen or alginic acid are also used. The polymer is mixed with drug and usually administered in a gelatin capsule. The capsule rapidly dissolves in the gastric fluid, and hydration and swelling of the surface polymers produces a floating mass. Drug release is controlled by the formation of a hydrated boundary at the surface. Continuous erosion of the surface allows water penetration to the inner layers, maintaining surface hydration and buoyancy 22. Incorporation of fatty excepients gives low-density formulations and reduced penetration of water, reducing the erosion. Effective drug delivery depends on the balance of drug loading and the effect of polymer on its release profile 23. II. Gas-generating Floatability can also be achieved by generation of gas bubbles. Carbon dioxide (co 2 ) can be generated in situ by incorporation of carbonates or bicarbonates, which react with acid, either the natural gastric acid or co-formulated as citric or tartaric acid. Gastric floating drug delivery system (GFDDS) offers numerous advantages over other gastric retention. These have a bulk density lower than gastric fluids and thus remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at desired rate from the stomach. Other approaches to extend gastric residence time are magnetic, geometric (modified-shaped ), co-administration of fatty acid salts, opiates and anticholinergics like propantheline, atropine, and 13, 24 polycarbophil or enzyme-digestible hydrogels. Fig. 4 Drug release from gas generating system Page 131
5 Table 1: Schematic representation for approaches to gastro retentive drug delivery 25,26,27 Approach Diagram Mechanism of action Floating Remains buoyant over gastric fluid for prolonged time as their density is less than that of the gastric contents, i.e. less than 1.0 g/ml. Expandable Swells or unfolds and increases in size, remains lodged at sphincter. Hence exit from stomach is prevented. Mucoadhesive Adheres to epithelial surface of GIT High-density/ Sedimentation Retains in rugae or antrum of stomach. CONCLUSION Based on the literature surveyed, it may be concluded that gastroretentive drug delivery offers various potential advantages for drug with poor bioavailability due their absorption is restricted to the upper gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and they can be delivered efficiently thereby maximizing their absorption and enhancing absolute bioavailability. Due to complexity of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics parameters, in vivo studies are required to establish the optional dosage form for a specific drug. All these gastroretentive drug delivery (high density, floating, expandable or unfoldable or swelling, superporous, bioadhesive, magnetic etc.) are interesting and present their own advantages and disadvantages. Now, a lot of work is running to develop different types of gastroretentive delivery of various drugs. In the future, it is expected that they will become of increasing importance, ultimately leading to improved efficiencies of various types of pharmacotherapies. ACKNOWLEDGMENT It is fathomless gratitude that I express my benevolent thanks to my reverend teacher and guide Manish Goswami, Principal, Akal College of Pharmacy and my Family for sharing their ideas and extending support during the course of study. REFERENCES 1. Garg S, Sharma S. Gastroretentive drug delivery system in drug delivery oral, Business Brief: Pharmatech 2003 : Rouge N, Buri P, Doeilkar E. Drug absorption sites in gastrointestinal tract and dosage form for site specific delivery. Int J Pharm, 1996; 136: Fell JT, Whitehead L, Collet H, Prolonged gastric retention using floating dosage forms. Pharm Technol.2000; 24(3): Matharu RS, Sanghvi NM. Novel drug delivery system of captopril. Drug Dev Ind Pharm, 1992; 18: Fell JT. Delivery system for targeting to specific sites in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharmacol. 1995; 51: Baumgartner S, Kristel J, Vreer F, Vodopivec P, Zorko B. Optimisation of floating matrix tablets and evaluation of their gastric residence time. Int J Pharm. 2000; 195: Moses AJ. Gastro Retentive Dosage Forms: Critical review. The Drug Carier Syst.1993; 10: Tortora GJ and Derrickson B. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology.11 th ed. John Wiley and Sons,Inc.2006: Washington N, Washington C, Wilson CG. Physiological Pharmaceutics.II. Taylor and Francis, New york, Singh BN, Kim KH. Floating drug delivery : an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J. Cont. Rel. 2000;63: Moes AJ. Drug Delivery Oral. Business Briefings- Pharmatech. 2003; Basak S, Chronicle Specials, Floatable Gastroretentives: Emerging Potentials, Mar Li X, Jasti BR. Gastric retentive dosage forms. In, Design of controlled release drug delivery. New York, McGraw-Hill; Chawla G, Bansal AK, Jain NK. Progress in Controlled and Novel Drug Delivery Systems. 1 st Edition. CBS Publishers and distributors; Swarbrick J, Boylan JC. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology, 2 nd Edition, New York, Marcel Dekker, I, Page 132
6 16. Arora S, Ali J, Ahuja A, Khar RK, Baboota S. Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A Review, AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 2005;6: Sakkinen M, Linna A, Ojala S, Jurjenson H, Veski P, Marvola M. In vivo evaluation of matrix granules containing microcrystalline chitosan as a gel forming excipient. Int. J. Pharm. 2003;250: Agyilirah GA, Green M, Cret R. Evaluation of gastric retention Properties of a cross-linked polymer-coated tablet versus those of a nondisintegrating tablet. Int. J. Pharm. 1991;75: Bechgaard H, Baggesen S. Propoxyphene and norpropoxyphene: influence of type of Controlled release formulation on intra-and intersubject variations. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980;69: Devereux JE, Newton JM, Short MB. The influence of density on the gastrointestinal transit of pellets. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990; 42: Rocca-Gutierrez J, Drug Delivery Oral. Business Briefings- Pharmatech. 2003: Bardonnet PL, Faivre V, Pugh WJ, Piffaretti JC, Falson F. Gastroretentive dosage forms: Overview and special case of Helicobacter Pylori. J. Cont. Rel. 2006;111: Wang SJ, Park H, Park K. Gastric Retentive Drug Delivery Systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Sys. 1998;15: Moes AJ. Gastroretentive dosage forms. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1993;10: Timmermans J, Moes AJ. The cut-off size for gastric emptying of dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 1993;88: Shah S, Qaqish R, Patel V, Amiji M. Evaluation of the factors influencing stomach-specific delivery of antibacterial agents for Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999;51: Chiou S, Riegelman WL. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971;60: Swarbick, J.,2007. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology. Informa health care, New York. 3 rd ed., 1, Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelkar E, Buri P, Peppas NA. Mechanism of potassium chloride release from compressed hydrophilic, polymeric matrices: Effect of entrapped air. J Pharm Sci. 1983; 72: Gander B, Gurny R, Doelkar E. Matrices for controlled liberation of drugs from polymers.1. Mechanism of penetration of solvents into polymers. Pharm Acta Helv.1986; 61: Doelkar E. Polymers. In: Peppas, N.A. (Ed) Hydrogel in medicine and pharmacy. CRC Press Inc. pp Vazquaz MJ, Porez-Marcos B, Gomez-Amoza JL, Peppas NA. Influence of technological variables on release of drug from hydrophilic matrices. Drug Dev Ind Pharm.1992; 21: Moes AJ. Drug Delivery Oral. Business Briefings- Pharmatech. 2003; Basak S, Chronicle Specials, Floatable Gastroretentives: Emerging Potentials, Mar Li X, Jasti BR. Gastric retentive dosage forms. In, Design of controlled release drug delivery. New York, McGraw-Hill; Chawla G, Bansal AK, Jain NK. Progress in Controlled and Novel Drug Delivery Systems. 1 st Edition. CBS Publishers and distributors; Page 133
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper
 D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE
 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 4
 (A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
(A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Asma Karameh. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة -
 -2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
-2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS
 BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS MOHSEN A. HEDAYA CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business Table of Contents Chapter
BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS MOHSEN A. HEDAYA CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business Table of Contents Chapter
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual,
 Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Determination of bioavailability
 Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Patel Krunal M et al. IRJP 2 (2)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 223 87 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF MODIFIED RELEASE TABLET OF MONTELUKAST SODIUM BY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 223 87 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF MODIFIED RELEASE TABLET OF MONTELUKAST SODIUM BY
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Revised European Guideline on PK and Clinical Evaluation of Modified Release Dosage Forms
 1st MENA Regulatory Conference on Bioequivalence, Biowaivers, Bioanalysis and Dissolution Jordan September 23 24, 2013 Revised European Guideline on PK and Clinical Evaluation of Modified Release Dosage
1st MENA Regulatory Conference on Bioequivalence, Biowaivers, Bioanalysis and Dissolution Jordan September 23 24, 2013 Revised European Guideline on PK and Clinical Evaluation of Modified Release Dosage
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Patel Tejas B et al / Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 5(5), Sep - Oct Research Article.
 Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE FORMS
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Factors responsible for the impaired bioavailability and instability rifampicin FDC
 Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
