FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
|
|
|
- Frederick White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND BIO SCIENCES IMPACT FACTOR 2.093*** ICV 5.13*** Pharmaceutical Sciences REVIEW ARTICLE!!! FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW Smita S. Aher 1 *, Prashant R. Pagar 2, Dr. R. B. Saudagar 3 1 Department of Quality Assurance Techniques, R. G. Sapkal College of Pharmacy, Anjaneri, Nashik , Maharashtra, India. 2 Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, R. G. Sapkal College of Pharmacy, Anjaneri, KEYWORDS: Floating drug delivery system,gastric residence time, swelling index, buoyancy. For Correspondence: Prashant R. Pagar * Address: Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, R. G. Sapkal College of Pharmacy, Anjaneri, Nashik , Maharashtra, India. Nashik , Maharashtra, India. ABSTRACT Floating drug delivery system (FDDS) can retain the dosage form in the gastric region for several hrs. Designing the Floating drug delivery system for prolong gastric retention helps in improving bioavailability and improve solubility of the drug that are less soluble in a high ph environment. These are recent technological and scientific research has been devoted to the development of rate controlled drug delivery system to overcome physiological adversities such as unpredictable gastric emptying times and gastric residence time. FDDS are of particular interest of drugs that are locally active and have narrow absorption window in stomach or upper small intestine unstable in the intestinal or colonic environment and exhibit low solubility at high ph values FDDS in specific region of the GIT offers numerous advantages, specially the drugs having narrow absorption window in GIT, primary absorption in the stomach, stability problem in the intestine, poor solubility at alkaline ph, local activity in stomach. This review article is giving detailed information on the pharmaceutical basis of their design, classification, advantages, in vitro and in vivo evaluation parameter and future potential of FDDS. The present review deals with the concept, mechanism, recent innovations and applications of floating drug delivery system.
2 26 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): INTRODUCTION: The oral route is increasingly being used for the delivery of therapeutic agents because the low cost of the therapy and ease of administration lead to high levels of patient compliance. More than 50% of the drug delivery systems available in the market are oral drug delivery systems 1.Controlled release drug delivery system is capable of achieving the benefits like maintenance of optimum therapeutic drug concentration in blood with predictable and reproducible release rates for extended time period; enhancement of activity of duration for short half life drugs; elimination of side effects; reducing frequency of dosing and wastage of drugs; optimized therapy and better patient compliances 2,3. The successful development of oral controlled drug delivery systems requires an understanding of the three aspects of the system, namely. 1. The physiochemical characteristics of the drug. 2. Anatomy and physiology of GIT and Characteristics of Dosage forms 1 Good fundamental understanding of the anatomic and physiological characteristics of the human GIT is required to modulate the gastrointestinal transit time of a drug through FDDS for maximal gastrointestinal absorption of drugs and site specific delivery 2.Gastro retentive system can remain in thegastric region for several hours and hence significantly prolong the gastric residence time of drugs. Prolonged gastric retention improves bioavailability, reduces drug waste, and improves solubility of drugs that are less soluble in a high ph environment. It has applications also for local drug delivery to the stomach and proximal small intestines 1. Basic physiology of gastrointestinal tract Anatomically the stomach is divided in to three regions: Fundus, Body and Antrum(pylorus).The proximal part made of fundus and body acts as a reservoir for undigested materials, whereas the antrum is the main site for mixing motions and acts as a pump for gastric emptying by propelling actions (Figure 1). Gastric emptying occurs in both the fasting and fed states. During the fasting state an inter digestive series of electrical events take place which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2-3 hrs which is called as inter digestive myoelectric cycle or migrating myoelectric cycle which is further divided in to four phases After the ingestion of a mixed meal, the pattern of contractions changes from fasted to that of fed state which is also termed as digestive motilitypattern 3.
3 27 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Fig. 1: Physiology of stomach Gastrointestinal retention Gastro retentive systems can remain in the gastric region for several hours and hence significantly prolong the gastric residence time of drugs. Prolonged gastric retention improves bioavailability, reduces drug waste, and improves solubility for drugs that are less soluble ina high ph environment. To successfully modulate the gastrointestinal transit time of a drug delivery system through floating drug delivery system (FDDS) Formaximal gastrointestinal absorption of drugs and site specific delivery, one needs to have a good fundamental understanding of the anatomic and physiological characteristics of the human GIT 3. Stomach anatomy The main function of the stomach is to process and transport food. It serves as a short term storage reservoir, allowing a rather large meal to be consumed quickly. Substantial enzymatic digestion is initiated in stomach, particularly of proteins. The pattern of motility is however distinct in the 2 states. During the fasting state an inter digestive series of electrical events take place, which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2 to 3 hours. This is called the inter digestive myoelectric cycle or migrating myloelectric cycle (MMC), which is further divided into following 4 phases. 1. Phase 1-(Basic phase)-last from minutes with rare contractions. 2. Phase 2-(Preburst phase)-last for minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. 3. Phase 3-(Burst phase)-last for minutes which includes intense and regular contractions for short period also known as housekeeper wave.
4 28 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Phase 4-last for 0-5 minutes and occurs between phase 3 and phase 1of 2consecutive cycles (Period of transition) 3. Fig. 2: Motility pattern in GIT FACTORS AFFECTING GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF FDDS a) Formulation factors Size of tablets Retention of floating dosage forms in stomach depends on the size of tablets. Small tablets are emptied from the stomach during the digestive phase, but large ones are expelled during the house keeping waves 5. Density of tablets Density is the main factor affecting the gastric residence time of dosage form. A buoyant dosage form having a density less than that of the gastric fluids floats, since it is away from the pyloric sphincter, the dosage unit is retained in the stomach for a prolonged period. A density of less than 1.0g/ml i.e. less than that of gastric contents has been reported. However, the floating force kinetics of such dosage form has shown that the bulk density of a dosage form is not the most appropriate parameter for describing its buoyancy capabilities 7. Shape of tablets The shape of dosage form is one of the factors that affect its gastric residence time. Six shapes (ring tetrahedron, cloverleaf, string, pellet, and disk) were screened in vivo for their gastric retention potential. The tetrahedron (each leg 2cm long) rings (3.6 cm in diameter) exhibited nearly 100% retention at 24 hr 7.
5 29 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Viscosity grade of polymer Drug release and floating properties of FDDS are greatly affected by viscosity of polymers and their interaction. Low viscosity polymers (e.g., HPMC K100 LV) were found to be more beneficial than high viscosity polymers (e.g., HPMC K4M) in improving floating properties. In addition, a decrease in the release rate was observed with an increase in polymer viscosity 7. b) Idiosyncratic factors Gender Women have slower gastric emptying time than do men. Mean ambulatory GRT in meals (3.4±0.4 hours) is less compared with their age and race matched female counterparts (4.6±1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface 8. Age Low gastric emptying time is observed in elderly than do in younger subjects. Intrasubject and intersubject variations also are observed in gastric and intestinal transit time. Elderly people, especially those over 70 years have a significantly longer GRT 8. Posture i) Upright position An upright position protects floating forms against postprandial emptying because the floating form remains above the gastric contents irrespective of its size14. Floating dosage forms show prolonged and more reproducible GRTs while the conventional dosage form sink to the lower part of the distal stomach from where they are expelled through the pylorus by antral peristaltic movements 8. ii) Supine position This position offers no reliable protection against early and erratic emptying. In supine subjects large dosage forms (both conventional and floating) experience prolonged retention. On moving distally, these units may be swept away by the peristaltic movements that propel the gastric contents towards the pylorus, leading to significant reduction in GRT compared with upright subjects 8. Concomitant intake of drugs Drugs such as prokinetic agents (e.g., metoclopramide and cisapride), anti Cholinergics (e.g., atropine or propantheline), opiates (e.g., codeine) may affect the performance of FDDS. The coadministration of GI motility decreasing drugs can increase gastric emptying time 8.
6 30 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Feeding regimen Gastric residence time increases in the presence of food, leading to increased drug dissolution of the dosage form at the most favorable site of absorption. A GRT of 4 10 h has been reported after a meal of fats and proteins 9. SUITABLE DRUGS FOR GASTRO RETENTION Sustained release in the stomach is useful for therapeutic agents that the stomach does not readily absorb, since sustained release prolongs the contact time of the agent in the stomach or in the upper part of the small intestine, from where absorption occurs and contact time is limited. Appropriate candidates for controlled release gastroretentive dosage forms are molecules that have poor colonic absorption but are characterized by better absorption properties at the upper parts of the GIT. 1. Drugs that have narrow absorption window in gastrointestinal tract (GIT), e.g., riboflavin,para amino benzoic acid, furosemide and levodopa. 2. Basically absorbed from stomach and upper part of GIT, e.g., chlordiazepoxide and cinnarazine. 3. Drugs that disturb normal colonic bacteria, e.g., amoxicillin trihydrate. 4. Locally active in the stomach, e.g., antacids and misoprostol. 5. Drugs those are unstable in the intestinal or colonic environment e.g. captopril, ranitidine HCl and metronidazole. 6. Drugs that exhibit low solubility at high phvalues e.g. diazepam, chlordiazepoxide and verapamil HCl 4. APPROACHES TO GASTRORETENTION Several techniques are reported in the literature to increase the gastric retention of drugs ) High density systems These systems, which have a density of ~3g/cm3, are retained in the rugae of stomach and capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements. The only major drawback with these systems is that it is technically difficult to manufacture them with a large amount of drug (>50%)and achieve required density of g/cm3. Diluents such as barium sulphate (density= 4.9), zinc oxide, titanium oxide, and iron powder must be used to manufacture such high densityformulation 10. 2) Swelling and expanding systems These systems are also called as Plug type system, since they exhibit tendency to remain logged in the pyloric sphincters. These polymeric matrices remain in the gastric cavity for several hours even in fed state 10.By selection of polymer with the proper molecular weight and swelling
7 31 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): properties controlled and sustained drug release can be achieved. The extensive swelling of these polymers is a result of the presence of physical chemical cross links in the hydrophilic polymer network. On the other hand, a low degree of cross linking results in extensive swelling followed by the rapid dissolution of polymer. 3) Incorporating delaying excipients Another delayed gastric emptying approach of interest include feeding of digestible polymers or fatty acid salts that charges the motility pattern, of the stomach to a fed stage thereby decreasing the gastric emptying rate and permitting considerable prolongation of the drug release. Prolongation of GRT of drug delivery system consists of incorporating delaying excipients like trietanolamine myristate in a delivery system. 4) Modified systems Systems with non disintegrating geometric shape molded from silastic elastomers or extruded from polyethylene blends, which extend the GRT depending on size, shape and flexural modules of drug delivery device. 5) Mucoadhesive & bioadhesive systems Bioadhesive drug delivery systems are used to localize a delivery device within the lumen to enhance the drug absorption in a site specific manner. This approach involves the use of bioadhesive polymers, which can adhere to the epithelial surface in the stomach. Some of the most promising excipients that have been used commonly in these systems include polycarbophil, carbopol, lectins, chitosan, CMC and gliadin, etc. 6) Floating systems Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at the desired rate from the system. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach27. Floatation of a drug delivery system in the stomach can be achieved by incorporating floating chamber filled with vacuum, air, or inert gas 11. CLASSIFICATION OF FDDS BASED ON MECHANISM OFBUOYANCY A) Single unit Noneffervescent systems Effervescent systems or gas generating systems B) Multiple unit Noneffervescent systems
8 32 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Effervescent systems Floating microspheres C) Raft forming systems ADVANTAGES OF FLOATING DOSAGE FORM (1) These systems are particularly advantageous for drugs that are specifically absorbed from stomach or the proximal part of the small intestine, e.g., riboflavin and furosemide. (2) The fluctuations in plasma drug concentration are minimized, and concentration dependent adverse effects that are associated with peak concentrations can be prevented. This feature is of special importance for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index. (3) The efficacy of the medicaments administered utilizing the sustained release principle of floating formulation has been found to be independent of the site of particular medicaments. (4) Complete absorption of the drug from the floating dosage form is expected even at the alkaline ph of the intestine. The dissolution of the drug in gastric fluid occurs and then the dissolved drug is available for absorption in the small intestine after emptying of the stomach contents. (5) Poor absorption is expected when there is vigorous intestinal movement and a shorted transit time as might occur in certain type of diarrhea. Under such circumstances it may be advantageous to keep the drug in floating condition in stomach to get a relatively better response. (6) Drugs that have poor bioavailability because of site specific absorption from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract are potential candidates to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems, thereby maximizing their absorption. LIMITATIONS OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS (1) A high level of fluid in the stomach is required for drug delivery to float and work efficiently. (2) Drugs which have stability and solubility problems in GIT are not suitable candidates for these types of systems. (3) Drugs such as nifedipine, which under goes first pass metabolism may not be desirable for the preparation of these types of systems. (4) Drugs which are irritant to Gastric mucosa are also not desirable. (5) The drug substances that are unstable in the acidic environment of the stomach are not suitable candidates to be incorporated in the systems 14.
9 33 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): IN VITRO AND IN VIVO EVALUATION PARAMETERS OF STOMACH SPECIFIC FDDS: Different studies reported in the literature indicate that pharmaceutical dosage forms exhibiting gastric residence in vitro floating behavior show prolonged gastric residence in vivo. Although, in vitro floating behavior alone is not sufficient proof for efficient gastric retention so in vivo studies can provide definite proof that prolonged gastric residence is obtained. 1) Hardness, friability, assay, content uniformity (Tablets) These tests are performed as per described in specified monographs. 2) Floating lag time and total floating time determination The time between the introduction of the tablet into the medium and its rise to upper one third of the dissolution vessel is termed as floating lag time and the time for which the dosage form floats is termed as the floating or flotation time 14. 3) Drug release The test for in vitro drug release studies are usually carried out in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids maintained at 37 0 C. Dissolution tests are performed using the USP dissolution apparatus 14. 4) Drug loading, drug entrapment efficiency, particle size analysis, surface characterization, micromeritics studies and percentage yield (for floating microspheres and beads) Drug loading is assessed by crushing accurately weighed sample of beads or microspheres in a mortar and added to the appropriate dissolution medium which is then centrifuged, filtered and analyzed by various analytical methods like spectrophotometry 14. 5) Resultant weight determination. Bulk density and floating duration have been the main parameters to describe the adequacy of a dosage form s buoyancy Although single density determination does not predict the floating force evolution of the dosage form because the dry material of it is made progressively reacts or interacts with in the gastric fluid to release its drug contents 14. 6) Weight gain and water uptake (WU) Weight gain or water uptake can be studied by considering the swelling behavior of Floating dosage form 14. 7) XRay/ Gamma scintigraphy For in vivo studies, X Ray/Gamma Scintigraphy is the main evaluation parameter for floating dosage form 17.
10 34 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): ) Pharmacokinetic studies Pharmacokinetic studies include AUC (Area under Curve), Cmax, and time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) were estimated using a computer. Statistical analyses were performed using a Student t test with p, 0.05 as the minimal level of significance 16. 9) Specific Gravity Displacement method is used to determine the specific gravity of floating system using benzene as a displacing medium 19,20. Commercially available floating products Brand Name Drug Dosage form Polymers used Manufacturers Glumetza Metformin Hcl Tablet HPMC Depomed Cifran O.D Ciprofloxacin Tablet Xanthan gumand Ranbaxy sodiumalginate Liquid Gavison Mixture of Alginates Liquid Alginates Glaxo Smith Kline Madopar HBS Levodopa and Capsule HPMC Roche Benserazide FUTURE POTENTIAL FDDS approach may be used for various potential active agents with narrow absorption window, e.g. antiviral, antifungal and antibiotic agents (sulphonamides, quinolones, penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides and tetracyclines),and antidepresant which are absorbed from very specific regions of GI tract and whose development has been halted due to the lack of appropriate pharmaceutical technologies. In addition, by continual supplying the drug to its most efficient site of absorption, the dosage form may allow for more effective oral use of peptide and protein drugs such as calcitonin, erythropoetin, vasopressin, insulin, low molecular weight heparin, and LHRH. Some of the unresolved critical issues related to the rational development of FDDS include, the quantitative efficiency of floating delivery systems in the fasted and fed states and the correlation between prolonged GRT and SR/PK characteristics. However, we are as close as we have ever been to see a greater transition of gastric retention devices from developmental level to the manufacturing and commercial level. References: 1. Patel GM. Floating drug delivery system: An innovative approach to prolong gastric retention
11 35 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Koner P, Saudagar RB, Dharwal J. Gastro retentive drugs a novel approach towards floating therapy in drugs a novel approachtowards floating therapy, Dhole AR, Gaikwad PD, Bankar VH and Pawar SP. A Review on Floating Multiparticulate Drug Delivery System: A Novel Approach to Gastric Retention. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research. 2011; 6(2): Sharma M, Chaturvedi KA and Singh KU. A Review on Floating Multiparticulate System for Gastric Retention.American Journal of Pharmatech Research. 2012;2(6): Oth M, Franze M, Timmermans J, Moes A, The bilayer floatingcapsule: a stomach directed drug delivery system formisoprostol. Pharm Res 1992; 9: Li S, Lin S, Daggy BP, Mirchandani HL, Chien YW. Effect ofhpmc and Carbopol on the release and floating properties ofgastric floating drug delivery system using factorial design. Int JPharm 2003; 253: Mojaverian P, Vlasses PH, Kellner PE, Rocci ML. Effects ofgender, posture, and age on gastric residence time ofindigestible solid: pharmaceutical considerations. Pharm Res1988; 10; Timmermans J, Moes AJ. Factors controlling the buoyancy andgastric retention capabilities of floating matrix capsules: newdata for reconsidering the controversy. J Pharm Sci 1994; Singh B. N, Kim K. H. Floating drug delivery system: Anapproach to the controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. JControl Release 2000; 63: Kawashima Y, Nima T, Takeuchi H, Hino T, Itoh Y. Hollow microspheres for use as a floating controlled drug delivery system in the stomach. J Pharm Sci (USA) 1998; 81: Hilton A. K, Desai P. B. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of an oral sustained release floating dosage form of amoxicillin trihydrate. Int J Pharm 1992; 86: Mayavanshi A.V, Gajjar SS. Floating drug delivery systems to increase gastric retention of drugs: A Review. J Pharm Tech 2008; 1(14): Patel R. Recent development in floating drug delivery system for gastric retention of drugs: an overview. 2007; Gupta P, Virmani K, Garg S. Hydrogels: From controlled release to ph responsive drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today 2002; 7(10):
12 36 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): Desai S. A Novel Floating Controlled Release Drug Delivery System Based on a Dried Gel Matrix Network [master s thesis], Jamaica, N. Y: St John s University; Gambhire M. N, Ambade K. W, Kurmi S. D, Kadam V. J and Jadhav K. R; Development and In vitro Evaluation Of an Oral Floating Matrix Tablet Formulation of Diltiazem Hydrochloride, AAPS Pharma SciTech 2007; 8(3) Article Deshpane A. A, Rhodes C. T, Shan N. S and Malick A. W; Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems For Prolonged Gastric Residence: An over view, Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 1996; 22(6) Burns S. J. et al, Development and validation of an in vitro dissolution method of a floating dosage form with biphasic release characteristics. International Journal ofpharmaceutics, 1995; 121, Kathleen J. W, Obe W, Waugh A; The Digestive System, In: Anatomy Physiology in Health and illness. 8 th edition, Churchill Livingstone., New York, 1996; Ingani H. M, Timmermans J, Moes A. J; Conception and In vivo investigation of oral sustained floating dosage forms with enhanced gastrointestinal transit. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 1987; 35:
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
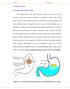 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.4 (2), April-June, 2014 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate
 Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences
 Srujana G. L.V et al / J Global Trends Pharm Sci, 2016; 7( (2):3065-3073 An Elsevier Indexed Journal ISSN-2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM-
Srujana G. L.V et al / J Global Trends Pharm Sci, 2016; 7( (2):3065-3073 An Elsevier Indexed Journal ISSN-2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM-
Factors responsible for the impaired bioavailability and instability rifampicin FDC
 Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH
 ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review
 Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual,
 Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets of lisinopril
 Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Suppl 2, 2011 Research Article GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY JUÁREZ
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 3, Suppl 2, 2011 Research Article GELUCIRE 39/01 AS EXCIPIENT FOR GASTRORETENTIVE METRONIDAZOLE SUSTAINED DELIVERY JUÁREZ
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Research Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF GLIPIZIDE AS FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM WITH NATURAL POLYMER (GUAR-GUM)
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF GLIPIZIDE AS FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM WITH NATURAL POLYMER (GUAR-GUM)
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Conferencia Inaugural
 Conferencia Inaugural UNDERSTANDING GASTRIC DIGESTION TO DEVELOP NEW FOODS FOR HEALTH R. Paul Singh Distinguished Professor of Food Engineering Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering University
Conferencia Inaugural UNDERSTANDING GASTRIC DIGESTION TO DEVELOP NEW FOODS FOR HEALTH R. Paul Singh Distinguished Professor of Food Engineering Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering University
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems
 Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
A New Venture in Drug Delivery: Bilayer Floating Tablet of Loop Diuretics with Potassium Supplement: A Review
 Human Journals Review Article December 2016 Vol.:8, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Mangal Gahandule et al. A New Venture in Drug Delivery: Bilayer Floating Tablet of Loop Diuretics with Potassium Supplement:
Human Journals Review Article December 2016 Vol.:8, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Mangal Gahandule et al. A New Venture in Drug Delivery: Bilayer Floating Tablet of Loop Diuretics with Potassium Supplement:
FORMULATION AND EVALUATIONOF AMOXYCILLIN: THREE-LAYER GUAR GUM MATRIX TABLET
 Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems
 Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 26 CMYK Research Paper Possible Use of Psyllium Husk as a Release Retardant ANGIRA DESAI, SUPRIYA SHIDHAYE*, V. J. KADAM Department of Pharmaceutics, Bharati Vidhyapeeth s College of Pharmacy, Sector-8,
26 CMYK Research Paper Possible Use of Psyllium Husk as a Release Retardant ANGIRA DESAI, SUPRIYA SHIDHAYE*, V. J. KADAM Department of Pharmaceutics, Bharati Vidhyapeeth s College of Pharmacy, Sector-8,
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES, ST AUGUSTINE
 UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES, ST AUGUSTINE FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES SCHOOL OF PHARMACY BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PHARMACY DEGREE COURSE SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE: COURSE CODE: BIOPHARMACEUTICS, NEW DRUG DELIVERY
UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES, ST AUGUSTINE FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES SCHOOL OF PHARMACY BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PHARMACY DEGREE COURSE SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE: COURSE CODE: BIOPHARMACEUTICS, NEW DRUG DELIVERY
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Determination of bioavailability
 Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Patel Tejas B et al / Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 5(5), Sep - Oct Research Article.
 Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
Research Article www.ijrap.net DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF NOVEL MUCOADHESIVE GASTRORETENTIVE FORMULATION OF GLIPIZIDE Patel Tejas B*, Patel Tushar R, Suhagia B. N, Patel Mehul N Faculty of Pharmacy, Dharmsinh
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
 Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
Available online through ISSN
 Kumar D et al / IJRAP 2011, 2 (3) 767-774 Review Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 APPROACHES, TECHNIQUES AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW
Kumar D et al / IJRAP 2011, 2 (3) 767-774 Review Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 APPROACHES, TECHNIQUES AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW
Controlled Delivery of Biologics NBC 22 June 2009
 Controlled Delivery of Biologics NBC 22 June 2009 ivery System Overview, Chris Rhodes, Amylin ulatory Perspectives, Mei-Ling Chen,FDA tained Circulation Strategies, Tim Riley, Nektar nsdermal Microporation,
Controlled Delivery of Biologics NBC 22 June 2009 ivery System Overview, Chris Rhodes, Amylin ulatory Perspectives, Mei-Ling Chen,FDA tained Circulation Strategies, Tim Riley, Nektar nsdermal Microporation,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES
 Research Article [Dhakar et al., 3(2): Feb., 12] ISSN: 9767126 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of floating tablet of rosiglitazone malate Koushlendra Singh,
Research Article [Dhakar et al., 3(2): Feb., 12] ISSN: 9767126 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of floating tablet of rosiglitazone malate Koushlendra Singh,
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
