A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Letitia Shaw
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
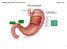
1 ISSN: Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Suresh Rewar* Shakya.V Department of Pharmaceutics, Rajasthan University of Health Sciences, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT The purpose of writing this review on floating drug delivery system (FDDS) was to compile the recent literature with special focus on the principal mechanism of floatation to achieve gastric retention. These systems are useful to several problems encountered during the development of pharmaceutical dosage form. Our review article suggests that gastro retentive dosage forms can be the possible way to improve patients compliance and robustness. This triggered an increased interest towards formulation of novel delivery systems which retained in the stomach for prolonged and predictable period of time. Several approaches such as floating drug delivery systems (FDDS), swelling and expanding systems, bio-adhesive systems, modified shape systems, effervescent system, high density systems or other delayed gastric emptying devices have been discovered till now. Various pharma companies opted advance technologies to make FDDS commercialized in large scale despite of several limitations. So, in future we hope to have a rational GRDF that s promises to be a potential approach for gastric retention Keywords: floating drug delivery system, effervescent system, non-effervescent system, gastric retention. The most preferred route is the oral route especially for the administration of therapeutic drugs because low cost of therapy and ease of administration leads to higher level of patient compliance. More than 50% of the drug delivery systems available are to be administered through oral route. Reasons behind using oral route are that it is the most promising route of the drug delivery and effective oral drug delivery may depend upon many factors such as gastric emptying process, gastrointestinal transit time of the dosage form, drug release from the dosage form and site of absorption of drug. High level of patient compliance is the major advantage of using the oral route. 1 To date, a number of FDDS involving various technologies, carrying their own advantages and limitations were developed such as, single and multiple unit hydro dynamically balanced systems (HBS), single and multiple unit gas generating systems, hollow microspheres and raft forming systems 2. Address for correspondence Mr. Suresh Rewar* Research Scholar, Department of Pharmaceutics, Rajasthan University of Health Sciences, Jaipur, Rajasthan, Mobile No ID: sureshrewar1990@gmail.com The hydrodynamic balanced system (HBS) also called Floating drug delivery system (FDDS) is an oral dosage form (capsule or tablet) designed to prolong the residence time of the dosage form within the GIT. It is a formulation of a drug with gel forming hydrocolloids meant to remain buoyant in the stomach contents. Drug dissolution and release from the dosage form retained in the stomach fluids occur at the ph of the stomach under fairly controlled conditions 3. These systems are useful in case of those drugs which are best absorbed in stomach for e.g. Albuterol. From the formulation and technological point of view, floating drug delivery system (FDDS) is considerably easy and logical approach in development of GRDDS. Therefore, this review article focuses on the current technological development in FDDS with special emphasis on the principal mechanism of floatation and advantages to achieve gastric retention and its potential for oral controlled drug delivery 4. The retentive characteristics of the dosage form are not significant for the drugs that: Act insoluble in intestinal fluids, Act locally & Exhibit site-specific absorption. However, the system can be used for most of the drugs where controlled (sustained) release of the dosage form is desired by the oral route. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE STOMACH: The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the digestion system which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals 2417
2 including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects (mid-gut), and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication (chewing). The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. It secretes proteindigesting enzymes called proteases and strong acids to aid in food digestion, (sent to it via esophageal peristalsis) through smooth muscular contortions (called segmentation) before sending partially digested food (chyme) to the small intestines. 5 Fig. 1 Sections of the stomach The capacity of the average stomach is about liters. it normally expands to hold about one litre of food. 5 The stomach is continuous with the esophagus at the cardiac sphincter and with the duodenum at the pyloric sphincter. It has two curvatures, the lesser curvature and greater curvature. The stomach can be divided into three parts: the fundus, the body and the pylorus or antrum. The distal end of the pyloric antrum is the pyloric sphincter, guarding the opening between the stomach and duodenum. When the stomach is inactive the pyloric sphincter is relaxed and open, and when the 6,7 stomach contains food the sphincter is closed. Bolus (masticated food) enters the stomach through the esophagus via the esophageal sphincter. The stomach releases proteases (protein-digesting enzymes such as pepsin) and hydrochloric acid, which kills or inhibits bacteria and provides the acidic ph of two for the proteases to work. Food is churned by the stomach through muscular contractions of the wall called peristalsis reducing the volume of the fundus, before looping around the fundus and the body of stomach as the boluses are converted into chyme (partially digested food). Chyme slowly passes through the pyloric sphincter and into the duodenum of the small intestine, where the extraction of nutrients begins. Depending on the quantity and contents of the meal, the stomach will digest the food into chyme anywhere between forty minutes and a few hours. 8 GASTRIC EMPTYING: 6,10,11 The passage of a drug from stomach to the small intestine, called as gastric emptying, can also be a ratelimiting step in drug absorption because the major site of drug absorption is intestine. For better drug dissolution and absorption, the gastric emptying can be promoted by taking the drug on empty stomach. Since gastric emptying is altered by several factors due to which large inter subject variations are observed, all biopharmaceutical studies. That require the drug to be taken orally are performed in volunteers on empty stomach. Several parameters are used to quantify gastric emptying: 1. Gastric emptying rate: is the speed at which the stomach contents empty into the intestine. 2. Gastric emptying time: is the time required for the gastric contents to empty into the small intestine. Longer the gastric emptying time, lesser the gastric emptying rate. 3. Gastric emptying t1/2: is the time taken for half the stomach contents to empty. APPROACHES TO GASTRIC RETENTION 11,12,13,14 Several approaches have been attempted in the preparation of gastro-retentive drug delivery systems. These include floating systems, swellable and expandable systems, high density systems, bioadhesive systems, altered shape systems, gel forming solution or suspension systems and sachet systems. Various approaches have been followed to encourage gastric retention of an oral dosage form. Floating systems have low bulk density so that they can float on the gastric juice in the stomach. The problem arises when the stomach is completely emptied of gastric fluid. In such a situation, there is nothing to float on. HYDRO DYNAMICALLY BALANCED SYSTEMS (HBS) It is also considered as a floating drug delivery system.these systems are designed to prolong the stay of the dosage forms in the gastric intestinal tract and aid in enhancing the absorption. Drugs having a better solubility in acidic environment and also having specific site of absorption in the upper part of small intestine is achieved by these HBS systems. To retain in stomach for a prolonged period of time the dosage form must have bulk density of less than 1 and has to maintain its structural integrity and release drug constantly from the dosage form. Among all the advantages single-unit formulations are associated with some limitations/problems such as sticking together or being obstructed in the GIT which may lead to potential danger of producing irritation. Hydro Dynamically balanced system (HBS) can be divided in the following: 1. Effervescent floating dosage forms 2. Non Effervescent floating dosage forms 3. Low density approach Effervescent Floating Dosage forms: These are matrix type systems prepared with the help of swellable polymers such as Hydroxypropyl methyl-cellulose or polysaccharides and chitosan and various effervescent components like sodium bicarbonate, calcium carbonate, citric acid or tartaric 2418
3 acid. These dosage forms are developed in such a way that, when they come in contact with gastric juice in the stomach, Carbon dioxide is liberated and is trapped in the swollen hydrocolloids. This provides buoyancy to the do-sage form. The liberated carbon dioxide may intimately get mixed within the tablet matrix in case of single layered tablet. 15 Non-Effervescent FDDS: It is also known as swellable system. The non-effervescent FDDS works on the mechanism of polymer swelling, bioadhesion of the polymer to mucosal layer of GI tract. The most commonly used excipients for the preparations of noneffervescent FDDS are gel forming or swellable type hydrocolloids, poly-saccharides and matrix forming polymers like poly methacrylates, polycarbonates, polyacrylates polystyrenes and bioadhesion polymers like chitosan and carbopols. Hydro dynamically balanced tablets containing mixture of drug and hydrocolloids. Upon contact with gastric fluid, the tablet shell dissolved in gastric fluid followed by swelling of mixtures, formation of a gelatinous barrier and maintains bulk density less than 1.0, which remained buoyant on the gastric fluid for an extended period of time. Low density approach: Floating systems come under low density approach. In this approach, the density of pellets should be less than 1 g/ml, so as to float the pellets or tablets in the gastric fluid and, release the drug slowly for a longer period of time. This type is also called as Hydro dynamically Balanced System (HBS). High density approach: For preparing such type of formulations, the density of the pellets should be higher than the stomach fluid. It would be at least 1.50 g/ml. In this type, the drug can be coated or mixed with heavy, nontoxic materials such as barium sulfate, titanium dioxide, etc. The GI transit time can be extended from an average of hours, depending more on density than on diameter of the pellets, although many conflicting reports Stating otherwise also abound in literature. Commonly used Excipients are barium sulphate, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide and iron powder, etc. These materials increase density by up to g/cm3. However, no successful high density system has made it to the market. Bioadhesive or mucoadhesive systems : These systems permit a given drug delivery system (DDS) to be incorporated with bio/mucoadhesive agents, enabling the device to adhere to the stomach (or other GI) walls, thus resisting gastric emptying. However, the mucus on the walls of the stomach is in a state of constant renewal, resulting in unpredictable adherence. Swelling and expanding systems: These systems are also called as Plug type system, since they exhibit tendency to remain logged in the pyloric sphincters. These polymeric matrices remain in the gastric cavity for several hours even in fed state 16. Raft forming system: Raft forming systems have received much attention for the drug delivery for gastrointestinal infections and disorders. The mechanism involved in the raft formation includes the formation of viscous cohesive gel in contact with gastric fluids, wherein each portion of the liquid swells forming a continuous layer called a raft. This raft floats on gastric fluids because of low bulk density created by the formation of CO 2. The system contains a gel forming agent (e.g. sodium alginate), sodium bicarbonate and acid neutralizer, which forms a foaming sodium alginate gel (raft), which when comes in contact with gastric fluids, the raft floats on the gastric fluids and prevents the reflux of the gastric contents (i.e. gastric acid) into the esophagus by acting as a barrier between the stomach and esophagus 52. A patent assigned to Reckitt and Colman Products Ltd., describes a raft forming formulation for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori) infections in the GIT The most important parameters affecting gastric emptying and, hence, the gastric retention time of oral dosage forms include: Density: Dosage form having density less than that of gastric fluid floats. Since it is away from the pyloric sphincter, the dosage unit is retained in the stomach for a prolonged period. Shape and size: The diameter of the dosage unit is equally important as a formulation parameter. Dosage forms having a diameter of more than 7.5 mm show a better gastric residence time compared with 9.9 mm. 19 Single or Multiple unit formulation 20 : Multiple unit formulations show a more predictable release profile and insignificant impairing of performance due to failure of units, allow co-administration of units with different release profiles or containing incompatible substances and permit a larger margin of safety against dosage form failure compared with single unit dosage forms; Particle size: To pass through the pyloric valve into the small intestine, the particle size should be 1 to 2 mm. 21 Caloric content: Gastric residence time can be increased by 4-10 hrs with a meal that is rich in proteins and fats. Body posture: Gastric emptying is favored while standing and by lying on the right side since the normal curvature of the stomach provides a downhill path whereas lying on the left side or in supine position retards Emotional state of subject: The influence of emotional factors on gastric motility and secretion may be either Augmentative or inhibitory depending upon whether the emotional experience is of an aggressive or a depressive. Effect of drugs: Drug that retard gastric emptying includes poorly soluble antacids (Aluminum hydroxide), narcotic analgesics (Morphine) and tricyclic antidepressants (Imipramine, amitryptiline), domperidom and Anti emetics stimulates gastric emptying. Exercise: physical activity retards gastric emptying. Age: Elderly people, especially those over 70 years have a significantly longer GRT. 27 Disease states: Diseases like gastroenteritis, gastric ulcer, pyloric stenosis, diabetes and hypothyroidism retard gastric emptying. Partial or total gastrectomy, duodenal ulcer and hyperthyroidism promote gastric emptying rate. Nature of meal: decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging drug release. 25 Fed or Unfed State: MMC is delayed and GRT is considerably longer
4 CLASSIFICATION: 8, 10, 11 Fig 2: Various Approaches to Gastroretentive systems of system ensures no passage from gastric sphincter Brand name Delivery system Drug Category Company name Topalkan Floating liquid alginate Al Mg Antacid Pierre Fabre Drug, France Conviron colloidal gel forming FDDS Ferrous sulphate Antianemic Ranbaxy, India Cifran OD Gas generating floating form Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Ranbaxy, India Valrelease Floating capsule Diazepam CNS depressant Roche, USA Madopar Floating CR capsule L Dopa Antiparkinsons Roche Products, USA Table 1: Marketed formulations available as GRDDS
5 ADVANTAGES 22 : a. Improves patient compliance by decreasing dosing frequency. b. Bioavailability enhances despite first pass effect because fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. c. Better therapeutic effect of short half-life drugs can be achieved. d. Gastric retention time is increased because of buoyancy. e. Drug releases in a controlled manner for a prolonged period. f. Site-specific drug delivery to the stomach can be achieved. g. Enhanced absorption of drugs which solubilize only in the stomach. h. Superior to single unit floating dosage forms such as microspheres, releases drug uniformly and there is no risk of dose dumping. i. Avoidance of gastric irritation, because of sustained release effect, floatability and uniform release of drug through multiparticulate system. DISADVANTAGES 23,24 1. Floating systems are not feasible for those drugs that have solubility or stability problems in gastric fluids. 2. There are limitations to the applicability of FDDS for drugs that are irritant to gastric mucosa. 3. One of the disadvantages of floating systems is that they require a sufficiently high level of fluids in the stomach, so that the drug dosages form float therein and work efficiently. 4. These systems also require the presence of food to delay their gastric emptying. 5. Drugs that cause irritation and lesion to gastric mucosa are not suitable to b e formulated as floating drug delivery Polymers and other ingredients: 28 Following types of ingredients can be incorporated into HBS dosage form in addition to the drugs: Hydrocolloids (20%-75%): They can be synthetics, anionic or non-ionic like hydrophilic gums, modified cellulose derivatives. E.g. Acacia, pectin, Chitosan, agar, casein, bentonite, Veegum, HPMC (K4M, K100M and K15M), Gellan Gum (Gel rite ), Sodium CMC, MC, HPC. Inert fatty materials (5%-75%): Edible, inert fatty materials having a specific gravity of less than one can be used to decrease the hydrophilic property of formulation and hence increase buoyancy. E.g. Beeswax, fatty acids, long chain fatty alcohols, Gelucires 39/01 and 43/01. Effervescent agents: E.g. Sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, tartaric acid, Di- SGC, CG (Citroglycine). Release rate accelerants (5%-60%): E.g. lactose, mannitol Release rate retardants (5%-60%): E.g. Dicalcium phosphate, talc, magnesium stearate Buoyancy increasing agents (upto80%): E.g. Ethyl cellulose Low density material: E.g. Polypropylene foam powder. 1. FUTURE POTENTIAL FDDS approach may be used for various potential active agents with narrow absorption window, e.g. antiviral, antifungal and antibiotic agents (sulphonamides, quinolones, penicillin s, cephalosporin, amino glycosides and tetracycline) which are absorbed from very specific regions of GI tract and whose development has been halted due to the lack of appropriate pharmaceutical technologies. In addition, by continual supplying the drug to its most efficient site of absorption, the dosage form may allow for more effective oral use of peptide and protein drugs such as calcitonin, erythropoietin, vasopressin, insulin, low molecular weight heparin, and LHRH. Some of the unresolved critical issues related to the rational development of FDDS include, the quantitative efficiency of floating delivery systems in the fasted and fed states and the correlation between prolonged GRT and SR/PK characteristics. However, we are as close as we have ever been to see a greater transition of gastric retention devices from developmental level to the manufacturing and commercial level. REFERENCE: 1. Shukla Shruti et al. ISSN Archives 2011; 2(6): Nasa et al.int J Pharmacy and Pharm Sci, Vol 2, Issue 3,pp Tripathy KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology. 6 th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee brothers medical publishers (p) Ltd. 2006; Deshpande AA, Shah NH, Rhodes CT, Malick W. Development of a novel controlled release system for gastric retention. Pharm Res 1997;14: Waugh A, Grand A. Ross and Wilson Anatomy and Physiology: In Health and Illness.10 th edi, Churchill Livinstone Elsevier; Edinburgh; 2006; Sherwood, Lauralee (1997). Human physiology: from cells to systems. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Pub. Co. ISBN OCLC Richard M. Gore; Marc S. Levine. (2007). Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology. Philadelphia, PA.: Saunders. ISBN Chein YW. Novel Drug Delivery Systems, 2 nd edition, Marcel Dekker, New York, 2005,
6 9. A. Arunachalam et al., Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci., 2(1), 2011, Shweta Arora, Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A Re-view, AAP. PharmSciTech 2005; 6 (3) Article 47, E Gangadharappa H.V, Pramod Kumar T.M and Shiva Kumar H.G, Gastric floating drug delivery systems. Indian J. Pharm. Educ.Res, 41(4), Oct-Dec 2007; Vyas. S.P and Khar Targeted and controlled drug deli-very novel carrier system Ist ed. CBS publishers and distributors, New Delhi, 2002, Jorgen F. Antacid composition.us Patent : Narang et al.int J App Pharm, Vol 3, Issue 1, 2011, Vedha hari b.n.et al, Development of a novel controlled-release system for gastric retention. Pharm Res.1997; 14: Robinson J, Lee R. In controlled drug delivery. 2nd ed. New York p Sasa Baumgartner,optimization of floating matrix tablets and evaluation of their gastric residence time, Int J Pharm, 195; (2000). 18. Tripathi, K.D., In: Essentials of medical pharmacology, th edition. JAYPEE Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd. New Delhi Jain Amit K, et,.al IJPSR/Vol. II/ Issue III/July- September, 2011/01-06.\ 20. Akash Yadav, Floating Controlled Drug Delivery Systems for Prolonged Gastric Retention: A Review the Pharma Research Vol: 01, (2009). 21. Binoy.B* Volume 1 Issue 3ISSN pp Kalus, Florey. Analytical profile of drug substances. Academicpree. Florida.1987.vol 4 p R.N.Brogden, R.M.Finder, Springer.com, april 1977,volume 13, issue 4, p.p Rouge N, Allémann E, Gex Fabry M. Comparative pharmacokinetic study of a floating multiple unit capsule, a high density multiple unit capsule and an immediate release tablet containing 25mg atenolol. Acta Pharm. Helv.1998; 73:81 87 PubMed DOI: /S (97) Sunil KJ, Govind PA, Narendra KJ. Evaluation of Porous Carrier -Based Floating Orlistate Microspheres For Gastric Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2006; 7(4) Article 90 ( 26. Ali, J., Arora, S., Ahuja,A., Babbar,K.A., Sharma,K.R., Khar,K.R., Baboota,S., European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics,Formulation and development of hydrodynamically balanced system for metformin In vitro and in vivo evaluation, 67 (2007), Robinson, J., Lee, R., In Controlled drug delivery nd edition, Nikita et.al. Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research 2011 ;7 (1): 6-20 How to cite this article: Suresh Rewar*,Shakya.V, A Novel approach for floating drug delivery system, 6(1): (2015) All 2010 are reserved by Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2422
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
EUDRATEC GRS. Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach.
 EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), 2013, 149-164 ISSN 2277-288X A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM MARINAGANTI RAJEEV KUMAR *, BONTHU SATYANARAYANA, NAGAKANYAKA DEVI PALADUGU,
ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), 2013, 149-164 ISSN 2277-288X A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM MARINAGANTI RAJEEV KUMAR *, BONTHU SATYANARAYANA, NAGAKANYAKA DEVI PALADUGU,
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating drug delivery system of Atenolol
 2014; 3(5): 11-18 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(5): 11-18 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 05-06-2014 Accepted: 12-06-2014 Kameswara Rao Sankula Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics,
2014; 3(5): 11-18 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(5): 11-18 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 05-06-2014 Accepted: 12-06-2014 Kameswara Rao Sankula Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics,
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
