Gastric ulceration in (race)horses. Mark Hillyer Newmarket Equine Hospital
|
|
|
- Magnus Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gastric ulceration in (race)horses Mark Hillyer Newmarket Equine Hospital
2 Mark Hillyer
3 Mark Hillyer
4 Mark Hillyer
5 Newmarket Equine Hospital
6
7 Anatomy
8 Anatomy
9 Anatomy
10 Equine gastric mucosa Squamous mucosa Glandular mucosa
11 Squamous mucosa Simple stratified epithelium No secretion or absorption Susceptible to acid/ peptic injury Good healing capacity
12 Glandular mucosa Many secretory cell types Mast cells and enterochromafin-like cells -> histamine Gastric G cells -> gastrin Parietal cells -> HCl acid Chief cells -> pepsinogen -> pepsin Mucus neck cells -> mucus barrier + HCO3
13 Acid Production Glandular Gastrin production by G cell stimulated by: Vagal stimulation Mucosa Histamine production by ECL cell is stimulated by: Gastrin A Choline Acid production by Parietal cell stimulated by: Histamine Gastrin Vagal tone (A Ch) Acid is secreted by proton pumps located on parietal cells Pepsinogen production by Chief cell stimulated by acid, Gastrin, Histamine, A Ch
14 Gastric ulceration in the racing Tb: Definition Primary squamous mucosa ulcer disease NOT Adjacent to margo plicatus (greater & lesser curvature) Secondary outflow obstruction ulcer disease (pyloric/duodenal stricture) Neonatal gastroduodenal ulcer disease NSAIDs induced ulcer disease Glandular mucosa ulcer disease
15 Definition No evidence of physical or functional obstruction of gastric outflow
16 Homeostasis Ulcerogenic factors Hydrochloric acid Pepsin Bile acids VFAs Lactic acid Protective factors Mucosal blood flow Mucus production Bicarbonate secretion Apical surface membrane transport» LEADING TO ACID INJURY TO THE STOMACH MUCOSA
17 Homeostasis Gradient of ph in stomach In-flow and Out-flow Fibrous raft floating in lumen
18 Squamous LOW DENSITY MAT; ph 6-7 Duodenum MEDIUM DENSITY MAT; Glandular ph 4-5 HIGH DENSITY LIQUID ph 1-2 ph > 4
19 Aetiology of ulcers Disruption to homeostatic balance Prolonged periods of low gastric ph (ph<4.0) Splash injury to squamous mucosa Currently little evidence for Helicobacter pylori involvement
20 Risk factors Intensive training activity Controlled irregular feeding Feed deprivation (intermittent during day) Prolonged extreme agitation Crib biting Periods of withdrawal of water High grain diet Low roughage diet Large high starch diets empty slowly from stomach allowing increased VFA and lactic acid production (>2 g/kg starch/day) Absence of forage other than straw Forage feeding interval > 6 hours
21 Protective factors Alfalfa as forage source Grazing Turnout with other horses
22 Risk factors ü Intensive training activity ü Controlled irregular feeding ü Feed deprivation (intermittent during day) Prolonged extreme agitation Crib biting ü Periods of withdrawal of water ü High grain diet ü Low roughage diet ü Large high starch diets empty slowly from stomach allowing increased VFA and lactic acid production (>2 g/kg starch/day) ü Absence of forage other than straw ü Forage feeding interval > 6 hours
23 Clinical signs Vague and nonspecific Poor appetite Failure to finish grain/concentrates Reluctance to train Poor/reduced performance or loss of performance Poor body condition Weight loss Rough hair coat Low-grade colic Girthing pain Cribbing/windsucking Attitude/behaviour changes
24 Prevalence in Thoroughbred Ireland racing Tb 60% of 40 had EGUS (Leadon 2000) Hong Kong post mortem survey noted gastric ulcers found in 66% of 195 racehorses (Hammond 1986) Newmarket racing Tb 71% of 72 had EGUS (McGladdery 2000) Newmarket endoscopic survey of racehorses 78% incidence (McGladdery 1997) USA racing Tb 81% of 185 (Vatistas 1994 & 1999) New Zealand racehorses in training 88.3% of 171 (Bell 2007) USA Tb racehorses 90% of 565 had EGUS (Johnson 2001)
25 Prevalence in Standardbred Standardbred 72-88% of 48 (Roy 2005) Standardbred in USA 87% of 224 (Rabuffo 2002) Standardbred in Italy 93.6% of 63 showed EGUS (Ferrucci 2003)
26 Prevalence in other horses Western performance horses 40% of 156 (Bertone 2000) Show horses 58% of 50 US show horses had EGUS (McClure 1999) Dressage horses 63% of 134 were affected with EGUS (Mitchell 2001) Endurance horses 67% (Nieto 2004)
27 Effect of exercise Increasing intensity of exercise is associated with an increasing prevalence of gastric ulcers
28 Effect of exercise Hypothesis Increased intra-abdominal pressure during exercise causes gastric compression, pushing highly acidic contents of glandular portion of stomach into squamous portion of stomach
29 PRESSURE BALLOON IN PROXIMAL STOMACH
30 Effect of exercise (N=3) Lorenzo-Figueras and Merritt. AJVR 2002;63:1481
31 ph ELECTRODE IN PROXIMAL STOMACH
32 Effect of exercise 7 6 Exercise Walk Trot + Gallop ph proximal stomach Walk 2 1 Fed Fasted 0 (n=3) Time blocks Lorenzo-Figueras and Merritt. AJVR 2002;63:1481
33 Squamous LOW DENSITY MAT; ph 6-7 VFA s MEDIUM DENSITY MAT; Glandular ph 4-5 Lactic Acid Duodenum HIGH DENSITY LIQUID ph 1-2
34 Squamous Duodenum Glandular HIGH DENSITY LIQUID ph 1-2
35 Aetiology Suggested that the primary cause is excessive exposure of the squamous mucosa to acidic gastric contents that are pushed up into the proximal stomach by the increased intra-abdominal pressure associated with gaits faster than a walk or any other situation where the horse may tense its abdominal muscles for extended lengths of time over a given day ( stressful stall environment? cribbing?)
36 Splash injury Fed Starved
37 Ulcer location
38 Diagnosis Endoscopic examination of the squamous mucosa Grade 1 Grade 0 Grade 2 Requires Feed/water withdrawal Sedation Grade 3 Grade 4
39 Equine gastroscopy
40 Equine gastroscopy
41 Equine gastroscopy
42 Equine gastroscopy
43 Equine gastroscopy
44 Endoscopic scoring Various scoring systems proposed Grade 0 Normal intact mucosa Grade 1 Mild reddening or hyperkeratosis Grade 2 Small single or small multifocal lesions Grade 3 Large single or multifocal lesions or extensive multifocal lesions Grade 4 Extensive (often coalescing) lesions with areas of deep ulceration
45 Diagnosis Sugar permeability tests Measure sucrose concentrations in plasma and urine Assay for sucrose is not readily available
46 Diagnosis Faecal occult blood tests Testing for Haemoglobin Haemoglobin Albumin
47 Diagnosis Serum alpha-1 antitrypsin assay (Taharaguchi et al. 2007) Released by damaged gastric tissue Higher concentrations found in foals with gastric ulcers compared to healthy foals Validation needed in adult horses with EGUS
48 Aims of treatment/prevention Keep the ph > 4.0 in squamous area 1. Raise the intra-gastric ph 2. Maintain the ph gradient 3. Prevent splashing 4. Provide local protectants
49 Medical management Lumen HCl Pepsin HCl Antacids Neighlox Mucosal Barrier Gastric Gland K + ~ X H + Parietal Cell Pepsin Chief Cell Protectants Proton Pump Inhibitors Sucralfate Pronutrin Omeprazole Gastrogard Gastrin Ach X H 2 H 2 Receptor Antagonists Ranitidine - Zantac Cimetidine Famotidine
50 Histamine receptor antagonists Cimetidine 25 mg/kg PO q 6-8 hours Ranitidine 6.6 mg/kg PO q 8 hours Famotidine Block parietal cell histamine receptors Only ranitidine shown to be effective in healing ulcers in horses
51 Intra-gastric ph: Adult Horse (electrode probe via naso-gastric route) R = ranitidine; 6.6 mg/kg PO Murray and Schusser. Eq Vet J 1993
52 Proton pump inhibitors Omeprazole (Gastrogard) Pantoprazole (Protonics IV) Potent inhibition of HCl secretion by parietal cells Increases ph in glandular portion of stomach 4 mg/kg PO q 24 hour for ulcer treatment 1-2 mg/kg PO q 24 hour for ulcer prevention
53 Non-glandular or Squamous LOW DENSITY MAT; ph 6-7 Duodenum MEDIUM DENSITY MAT; Glandular ph 4-5 HIGH DENSITY LIQUID ph 1-2 revised from Schummer et al., 1979
54 Omeprazole: Effect on gastric ph Exercise here N = 6 Hours Post-Treatment
55 Omeprazole studies Healed = score 0 Improved = score reduced by at least 1 grade McGladdery (2003) Tb s in UK & Eire
56 Omeprazole studies % horses day OME UK&Ire improved OME UK&Ire healed OME USA improved OME USA healed McGladdery (2003) UK & Ireland Andrews (1999) USA
57 Omeprazole studies Complete healing of squamous ulcers in up to 80% of Thoroughbreds in training with a 28 day course of omeprazole (Gastrogard) Day 0 Day 14
58 Proton pump inhibitors Omeprazole (GastroGard ) demonstrated greater efficacy than H 2 -antagonists in reducing incidence of primary squamous ulceration in athletically active horses Neito JE, Spier SJ, van Hoogmoed L, Pipers F, Timmerman B, Snyder JR. Comparison of omeprazole and cimetidine in healing of gastric ulcers and prevention of recurrence in horses. Eq Vet Educ 2001;13: Orsini JA, Haddock M, Stine L, Sullivan EK, Rabuffo TS, Smith G. Odds of moderate or severe gastric ulceration in racehorses receiving antiulcer medications. JAVMA 2003;122:
59 Long term use of proton pump Cost inhibitors Side effects (Delayed) Acute interstitial nephritis Toxic epidermal necrolysis Hypersensitivity reactions Rhabdomyolysis and hyponatraemic delirium Hypomagnesaemia Suppressed bone mineralisation (rats) Osteoporosis
60 Long term use of proton pump Cost inhibitors Side effects (Delayed) Acute interstitial nephritis Toxic epidermal necrolysis Hypersensitivity reactions Rhabdomyolysis and hyponatraemic delirium Hypomagnesaemia Suppressed bone mineralisation (rats) Osteoporosis (hip fractures n=13,556) AOR 1.44 with 1 year PPI tx AOR increased with each year of PPI tx (up to 1.6) AOR increased with long-term high dose PPI tx (2.65)
61 Omeprazole Gastrogard vs other formulations Formulation of omeprazole is vital for efficacy Generic omeprazole formulations Variable acid tolerance Low bioavailability 16% Gastrogard Very predictable and consistent response Curative in Tb in training
62 Mucosal protectants Combination of aluminium hydroxide and octasulfate (sucralfate) Adheres to ulcerated mucosa Forms proteinaceous layer Stimulates prostaglandin E1 synthesis Stimulates mucus production Inactivates pepsin + absorbs bile acids mg/kg PO q 8 hours Similar efficacy in one study to corn oil
63 Feed supplements
64 Neigh-Lox/Rite Trac Antacid Mixture of Aluminium and Magnesium hydroxide Acid neutralisation But Acid secretion and gastric emptying are continuous Require high dosing frequency increases gastric ph for 2 hours
65 Neigh-Lox/Rite Trac Feed supplement antacids shown to Reduce or prevent clinical signs in youngsters cribbing Ulcers may heal, but do not worsen Useful close to competition/ race day Wilson (2002)
66 Equitop Pronutrin Combination of pectin, glycerine and lecithin Pectin reduces gastric acidity and stabilises the protective mucus layer Glycerine/lecithin - enhances the water repellant protective layer g/day mixed in feed
67 Equitop Pronutrin Combination of pectin, glycerine and lecithin Clinical studies Stb and sport horses 10 day - significant improvement in ulcer score 30 day significant improvement in ulcer score and some healing glandular > squamous Ferrucci (2003) Venner (1999)
68 Corn oil Effect of feeding corn oil on equine gastric acid output
69 Forage Alfalfa - may help prevention Short chop fibre - maintains raft/mat and ph gradient Feed small quantity prior to exercise Multiple types/multiple locations Stimulate foraging activity and salivation Always present forage feeding interval > 6 hours is a risk factor
70 Treatment guidelines Omeprazole 4 mg/kg PO every 24 hours or Ranitidine 6.6 mg/kg PO every 8 hours Rite Trac every 2-4 hours Equitop Pronutrin g daily in feed Sucralfate mg/ kg PO every 8 hours Start prevention management
71 Management guidelines Grazing Forage Available at all times Alfalfa Multiple sources/types Short chop fibre with each feed (esp prior to exercise) Not solely straw Concentrate feeds at <2.5 kg q 6 hours Water available at all times Corn oil <500g daily Avoid feed or water deprivation Avoid hypertonic electrolyte pastes 1-2 mg/kg omeprazole PO q 24 hr Equitop Pronutrin
72 Welfare implications High prevalence of ulcers What is normal mucosal status for a horse in training? Is treatment or management needed? Welfare implications for horses used in sport?
73 Performance implications Association between presence of gastric ulcers and reduced performance 4 Tb NH horses History poor performance Treadmill exam normal Significant gastric ulceration 28 day Gastrogard Improved treadmill performance Improved raceform rating Treadmill expt study 56 days treadmill exercise +/- omeprazole Ulceration associated with Reduced aerobic development Earlier fatigue Less increase in stride length Nieto (2009) Franklin (2008)
74 Gastric ulcers in (race)horses Drugs may treat ulcers but Management prevents and controls ulcers
75 Equine gastroscopy
76
Introduction. Introduction. Equine Gastric and Pyloric Ulcer Syndrome. Equine gastric ulcer syndrome (EGUS) First described in 1986
 Equine Gastric and Pyloric Ulcer Syndrome Jenifer R Gold DVM, DACVIM-LA Assistant Professor-Colorado State University Colorado Veterinary Medical Association September 22, 2013 S Introduction Equine gastric
Equine Gastric and Pyloric Ulcer Syndrome Jenifer R Gold DVM, DACVIM-LA Assistant Professor-Colorado State University Colorado Veterinary Medical Association September 22, 2013 S Introduction Equine gastric
Equine Gastric Ulcer Factsheet
 Equine Gastric Ulcer Factsheet Equine Stomach Anatomy The equine stomach is a single large compartment that can be divided into two main regions. Top 1/3 is the non-glandular portion which is covered in
Equine Gastric Ulcer Factsheet Equine Stomach Anatomy The equine stomach is a single large compartment that can be divided into two main regions. Top 1/3 is the non-glandular portion which is covered in
Equine gastric ulcer syndrome
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Equine gastric ulcer syndrome Author : Nicola Menzies-Gow Categories : Vets Date : October 17, 2011 Nicola Menzies-Gow discusses
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Equine gastric ulcer syndrome Author : Nicola Menzies-Gow Categories : Vets Date : October 17, 2011 Nicola Menzies-Gow discusses
Current Ideas of Causes and Management A.M. Merritt, DVM, MS Professor Emeritus, University of Florida
 Current Ideas of Causes and Management A.M. Merritt, DVM, MS Professor Emeritus, University of Florida Some Essentials of Equine Gastric Anatomy and Function Relative to EGUS Anatomy In contrast to humans,
Current Ideas of Causes and Management A.M. Merritt, DVM, MS Professor Emeritus, University of Florida Some Essentials of Equine Gastric Anatomy and Function Relative to EGUS Anatomy In contrast to humans,
Frank Andrews is a graduate of Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. He completed an equine medicine and surgery residency at
 Frank Andrews is a graduate of Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. He completed an equine medicine and surgery residency at The Ohio State University and is Board Certified in Large
Frank Andrews is a graduate of Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. He completed an equine medicine and surgery residency at The Ohio State University and is Board Certified in Large
EFFECT OF TRACE MINERAL SUPPLEMENTATION ON GASTRIC ULCERS IN EXERCISING YEARLING HORSES. A Thesis ALEXA DAWN HAYES
 EFFECT OF TRACE MINERAL SUPPLEMENTATION ON GASTRIC ULCERS IN EXERCISING YEARLING HORSES A Thesis by ALEXA DAWN HAYES Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
EFFECT OF TRACE MINERAL SUPPLEMENTATION ON GASTRIC ULCERS IN EXERCISING YEARLING HORSES A Thesis by ALEXA DAWN HAYES Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
ULCERS. The Equine Stomach by Madalyn Ward, DVM
 ULCERS The Equine Stomach I was able to attend a fantastic lecture on the equine stomach at the 2003 AAEP convention. A. M. Merritt, DVM, MS shared the latest research on this topic. Here are just a few
ULCERS The Equine Stomach I was able to attend a fantastic lecture on the equine stomach at the 2003 AAEP convention. A. M. Merritt, DVM, MS shared the latest research on this topic. Here are just a few
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
Gastric Ulcer Prophylaxis in the Critically Ill Equine Neonate ( 6-Nov-2001 )
 In: Recent Advances in Equine Neonatal Care, P. A. Wilkins and J. E. Palmer (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Gastric Ulcer Prophylaxis
In: Recent Advances in Equine Neonatal Care, P. A. Wilkins and J. E. Palmer (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Gastric Ulcer Prophylaxis
Gastrointestinal diseases of performance horses Guy D. Lester
 CHAPTER 48 Gastrointestinal diseases of performance horses Guy D. Lester Equine gastric ulcer syndrome 1037 Right dorsal colitis 1043 Cecal emptying defect 1045 Stress-associated diarrhea 1045 References
CHAPTER 48 Gastrointestinal diseases of performance horses Guy D. Lester Equine gastric ulcer syndrome 1037 Right dorsal colitis 1043 Cecal emptying defect 1045 Stress-associated diarrhea 1045 References
-Mohammad Ashraf. -Anas Raed. -Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
-1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
Veterinarni Medicina, 54, 2009 (5):
 Veterinarni Medicina, 54, 2009 (5): 244 248 Case Report horses. Five horses showed frequent recumbency and poor performance. One horse had poor hair coat whilst the remaining one displayed intermittent
Veterinarni Medicina, 54, 2009 (5): 244 248 Case Report horses. Five horses showed frequent recumbency and poor performance. One horse had poor hair coat whilst the remaining one displayed intermittent
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Kelato GastroAID Technical Guide
 Key Features and Benefits Kelato GastroAID Technical Guide GastroAID is designed to maintain optimum gut health and function, and enhance digestibility and feed utilisation. Aids total digestive tract
Key Features and Benefits Kelato GastroAID Technical Guide GastroAID is designed to maintain optimum gut health and function, and enhance digestibility and feed utilisation. Aids total digestive tract
Purina Equine Gastric Health Program. Finding better ways to support your horses gastric comfort
 Purina Equine Gastric Health Program Finding better ways to support your horses gastric comfort Purina has a portfolio of products that are all part of an overall gastric health program designed to aid
Purina Equine Gastric Health Program Finding better ways to support your horses gastric comfort Purina has a portfolio of products that are all part of an overall gastric health program designed to aid
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
OSPAP Programme. Gastrointestinal Drugs. Dr. Adrian Moore Dale
 PAP Programme Dr. Adrian Moore Dale 1.03 Adrian.Moore@sunderland.ac.uk 0191 5152554 lide 1 of 26 PAP MPM14 Acid-Related Pathophysiology The stomach secretes: ydrochloric acid (Cl) aids digestion and also
PAP Programme Dr. Adrian Moore Dale 1.03 Adrian.Moore@sunderland.ac.uk 0191 5152554 lide 1 of 26 PAP MPM14 Acid-Related Pathophysiology The stomach secretes: ydrochloric acid (Cl) aids digestion and also
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease. By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease Learning objectives:
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease Learning objectives:
The foundation feed for a HEALTHY. Feed fibre first...feed Fiber Fresh
 The foundation feed for a HEALTHY HORSE Feed fibre first...feed Fiber Fresh Optimising Nature s Brilliance We established Fiber Fresh in 1984 in the belief that we could make a difference to the health
The foundation feed for a HEALTHY HORSE Feed fibre first...feed Fiber Fresh Optimising Nature s Brilliance We established Fiber Fresh in 1984 in the belief that we could make a difference to the health
Second term/
 Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Optimal Drugs for ICU Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis: Other. Grand Rounds Monday August 9, 2010 Teresa Jones R2
 Optimal Drugs for ICU Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis: Other Grand Rounds Monday August 9, 2010 Teresa Jones R2 Outline Options besides PPIs Comparison to PPIs Negative Effects of PPIs Conclusion Do we really
Optimal Drugs for ICU Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis: Other Grand Rounds Monday August 9, 2010 Teresa Jones R2 Outline Options besides PPIs Comparison to PPIs Negative Effects of PPIs Conclusion Do we really
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Chapter 63 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases
 Chapter 63 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases p1009 DRUGS USED IN ACID-PEPTIC DISEASES 1. classification of drugs 2. agents that reduce intragastric acidity Antacids,H 2 antagonists,proton
Chapter 63 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases p1009 DRUGS USED IN ACID-PEPTIC DISEASES 1. classification of drugs 2. agents that reduce intragastric acidity Antacids,H 2 antagonists,proton
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
- Ali Yaghi. - Sara Yaghi. - Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 -2 - Ali Yaghi - Sara Yaghi - Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e We ended the previous lecture with H2 receptor antagonists, which work by selectively inhibiting H2 receptors. They are widely used to treat: 1- GERD,
-2 - Ali Yaghi - Sara Yaghi - Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e We ended the previous lecture with H2 receptor antagonists, which work by selectively inhibiting H2 receptors. They are widely used to treat: 1- GERD,
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System. Antacids, Constipation, Increasing gastrointestinal motility
 Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antacids, Constipation, Increasing gastrointestinal motility Cells of the Gastric Gland parietal cells: produce & secrete HCl primary site of action for many
Drugs Affecting the Gastrointestinal System Antacids, Constipation, Increasing gastrointestinal motility Cells of the Gastric Gland parietal cells: produce & secrete HCl primary site of action for many
Case 4: Peptic Ulcer Disease. Requejo, April Salandanan, Geralyn Talingting, Vennessa Tanay, Arvie
 Case 4: Peptic Ulcer Disease Requejo, April Salandanan, Geralyn Talingting, Vennessa Tanay, Arvie Case 4: PUD Problem List: 1. Peptic Ulcer Disease SOAP Note: S Patient is complaining of abdominal pain
Case 4: Peptic Ulcer Disease Requejo, April Salandanan, Geralyn Talingting, Vennessa Tanay, Arvie Case 4: PUD Problem List: 1. Peptic Ulcer Disease SOAP Note: S Patient is complaining of abdominal pain
Gastric and Intestinal secretion
 Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Pthaigastro.org. Evolution of antisecretory agents. History. Antacids and anticholinergic drugs
 Evolution of antisecretory agents uthapong Ukarapol, MD. Division of Gastroenterology Chiang Mai University istory 1823- Prout discovered gastric hydrochloric acid 1875- eidenhain and 1893- Golgi identified
Evolution of antisecretory agents uthapong Ukarapol, MD. Division of Gastroenterology Chiang Mai University istory 1823- Prout discovered gastric hydrochloric acid 1875- eidenhain and 1893- Golgi identified
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
Nutritional Management of the Racehorse. Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky
 Nutritional Management of the Racehorse Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky Considerations Meet nutrient requirements Maintain normal GI tract Feeding the
Nutritional Management of the Racehorse Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky Considerations Meet nutrient requirements Maintain normal GI tract Feeding the
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Copy right protected Page 1
 DRUGS USED IN ULCERS AND GIT DISORDERS A peptic ulcer, also known as PUD or peptic ulcer disease is an ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful.
DRUGS USED IN ULCERS AND GIT DISORDERS A peptic ulcer, also known as PUD or peptic ulcer disease is an ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful.
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;21 Suppl:111-6. [Effect of antacids on intestinal motility]. [Article in German] Wienbeck M, Erckenbrecht J, Strohmeyer G. Abstract
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;21 Suppl:111-6. [Effect of antacids on intestinal motility]. [Article in German] Wienbeck M, Erckenbrecht J, Strohmeyer G. Abstract
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
ease&excel new gastric ulcers as part of a balanced diet low starch, high fibre, high oil blend targeted at Suitable for equines prone to
 new ease&excel ease&excel low starch, high fibre, high oil blend COMPOSITION Soya Bean Hulls, Oatfeed, Alfalfa Meal, Alfalfa & Green Oat Straw Chaff, Soya Oil, Distillers Grains, Ground Beet Pulp, Micronised
new ease&excel ease&excel low starch, high fibre, high oil blend COMPOSITION Soya Bean Hulls, Oatfeed, Alfalfa Meal, Alfalfa & Green Oat Straw Chaff, Soya Oil, Distillers Grains, Ground Beet Pulp, Micronised
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Gastric Pathology (16-Dec-2003)
 In: 8ème Congrès de médecine et chirurgie équine - 8. Kongress für Pferdemedezin und -chirurgie - 8th Congress on Equine Medicine and Surgery, P. Chuit, A. Kuffer and S. Montavon (Eds.) Publisher: International
In: 8ème Congrès de médecine et chirurgie équine - 8. Kongress für Pferdemedezin und -chirurgie - 8th Congress on Equine Medicine and Surgery, P. Chuit, A. Kuffer and S. Montavon (Eds.) Publisher: International
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
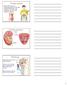 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Peptic ulcer disease. Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531
 Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Lab:2 Drugs acting on Gastrointestinal tract
 Lab:2 Drugs acting on Gastrointestinal tract Drugs that used to treat three common medical conditions involving the gastrointestinal tract: peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), chemotherapy-induced
Lab:2 Drugs acting on Gastrointestinal tract Drugs that used to treat three common medical conditions involving the gastrointestinal tract: peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), chemotherapy-induced
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Pharmacology
 Gastrointestinal Pharmacology Jan Kehr Department of Physiology and Pharmacology Gastrointestinal Pharmacology v Background v Peptic disorders v Constipation and Diarrhea v Chronic Bowel Disease Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal Pharmacology Jan Kehr Department of Physiology and Pharmacology Gastrointestinal Pharmacology v Background v Peptic disorders v Constipation and Diarrhea v Chronic Bowel Disease Gastrointestinal
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP)
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Active substance(s) (INN or common name): Esomeprazole Pharmaco-therapeutic group (ATC Code): A02B C05 Name of Marketing Authorisation Holder or Applicant: Strength and
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Active substance(s) (INN or common name): Esomeprazole Pharmaco-therapeutic group (ATC Code): A02B C05 Name of Marketing Authorisation Holder or Applicant: Strength and
August 2003 Peptic Ulcer Management H01
 W-F Professional Associates, Inc. 400 Lake Cook Rd., Suite 207 Deerfield, IL 60015 847-945-8050 August 2003 Peptic Ulcer Management 707-000-03-008-H01 MISSING A LESSON? IT S EASY TO GO TO OUR WEBSITE &
W-F Professional Associates, Inc. 400 Lake Cook Rd., Suite 207 Deerfield, IL 60015 847-945-8050 August 2003 Peptic Ulcer Management 707-000-03-008-H01 MISSING A LESSON? IT S EASY TO GO TO OUR WEBSITE &
Goals. The Hindgut 4/10/2014. Equine Digestive Tract. Week 2 Lecture 4
 Equine Digestive Tract Week 2 Lecture 4 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Know the main anatomical sections of the hindgut, their functions and purpose Sites of potential impactions
Equine Digestive Tract Week 2 Lecture 4 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Know the main anatomical sections of the hindgut, their functions and purpose Sites of potential impactions
April 2006 Peptic Ulcer Disease Volume 28 Number 4. W-F Professional Associates, Inc. 400 Lake Cook Rd., Suite 207 Deerfield, IL
 W-F Professional Associates, Inc. 400 Lake Cook Rd., Suite 207 Deerfield, IL 60015 847-945-8050 April 2006 Peptic Ulcer Disease 707-000-06-004-H01 FLORIDA PARTICIPANTS Be sure to provide your Florida License
W-F Professional Associates, Inc. 400 Lake Cook Rd., Suite 207 Deerfield, IL 60015 847-945-8050 April 2006 Peptic Ulcer Disease 707-000-06-004-H01 FLORIDA PARTICIPANTS Be sure to provide your Florida License
GI update. Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about
 GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
UPPER GI DISEASES 11/15/2014. Lesson Objectives. GI Tract Review. NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals. Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD
 UPPER GI DISEASES NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Describe causes and contributing
UPPER GI DISEASES NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Describe causes and contributing
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
Policy Evaluation: Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
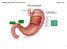 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
Proton Pump Inhibitors:
 Proton Pump Inhibitors: How bad could they be? Andrea Flanagan, Pharm.D. Iowa City VA Medical Center PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Objectives for Pharmacists At the end of this presentation PHARMACISTS should
Proton Pump Inhibitors: How bad could they be? Andrea Flanagan, Pharm.D. Iowa City VA Medical Center PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Objectives for Pharmacists At the end of this presentation PHARMACISTS should
Development of the Rodent Gastrointestinal Tract:
 White Paper Development of the Rodent Gastrointestinal Tract: The regulation of the development of the GI tract is unique and complex. With respect to the GI tract there are several considerations that
White Paper Development of the Rodent Gastrointestinal Tract: The regulation of the development of the GI tract is unique and complex. With respect to the GI tract there are several considerations that
PASTURE BASED NUTRITION FOR HORSES
 PASTURE BASED NUTRITION FOR HORSES Virginia State Feed Association & Nutritional Management Cow College DR. BRIDGETT MCINTOSH DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL SCIENCE M.A.R.E. CENTER MIDDLEBURG, VA FORAGE IS THE FOUNDATION
PASTURE BASED NUTRITION FOR HORSES Virginia State Feed Association & Nutritional Management Cow College DR. BRIDGETT MCINTOSH DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL SCIENCE M.A.R.E. CENTER MIDDLEBURG, VA FORAGE IS THE FOUNDATION
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus. Barbora Konečná
 Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms.
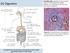 D2 Diges(on Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. This figure shows the main parts of the diges(ve
D2 Diges(on Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. This figure shows the main parts of the diges(ve
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ULCER DISEASE
 Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
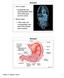 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP
 1234567890 10 210002 SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP DESCRIPTION Sucralfate is an -D-glucopyranoside, -D-fructofuranosyl-, octakis-(hydrogen sulfate), aluminum complex. It has the following structural formula:
1234567890 10 210002 SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP DESCRIPTION Sucralfate is an -D-glucopyranoside, -D-fructofuranosyl-, octakis-(hydrogen sulfate), aluminum complex. It has the following structural formula:
Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS. 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)?
 CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)? A. Chronic alcohol ingestion B. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)? A. Chronic alcohol ingestion B. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
Perforated peptic ulcer
 Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
Perforated peptic ulcer - Despite the widespread use of gastric anti-secretory agents and eradication therapy, the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer has changed little, age limits increase NSAIDs elderly
Nutrition #3 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education By Lezah Williamson
 Nutrition #3 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education By Lezah Williamson 1. Feed little and often 2. Feed plenty of bulk food 3. Feed according to size, age, breed, temperament, condition, season and
Nutrition #3 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education By Lezah Williamson 1. Feed little and often 2. Feed plenty of bulk food 3. Feed according to size, age, breed, temperament, condition, season and
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA. Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery
 AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery WHAT IS A GASTRINOMA? Gastrin secreting cells derived from multipotential stem cells of endodermal origin or enteroendocrine cells
AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery WHAT IS A GASTRINOMA? Gastrin secreting cells derived from multipotential stem cells of endodermal origin or enteroendocrine cells
PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE
 15 March, 2018 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Document Filetype: PDF 374.06 KB 0 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Among the oldest and cheapest drugs for diabetes are the drugs that
15 March, 2018 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Document Filetype: PDF 374.06 KB 0 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Among the oldest and cheapest drugs for diabetes are the drugs that
Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus
 Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP
 1234567890 10 210002-01 SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP DESCRIPTION Sucralfate is an -D-glucopyranoside, -D-fructofuranosyl-, octakis-(hydrogen sulfate), aluminum complex. It has the following structural formula:
1234567890 10 210002-01 SUCRALFATE TABLETS, USP DESCRIPTION Sucralfate is an -D-glucopyranoside, -D-fructofuranosyl-, octakis-(hydrogen sulfate), aluminum complex. It has the following structural formula:
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
