The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
|
|
|
- Poppy Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a form of learning. Pavlov also discovered the phases of gastrointestinal secretions. He was awarded with the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for research on the nature of digestion in Ivan Petrovich Pavlov
2 3 sham feeding Bykov, 1960 small stomach Evans,
3 Classical (Pavlovian) conditioning detective mirror bell collecting saliva food The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion(lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role of gastric juice Mechanism of gastric juice secretion Control of gastric juice secretion Phases of gastric juice secretion Mechanisms contributing to mucosal defense Determination of gastic ph 3
4 Corpus Antrum Corpus (oxyntic region) Gastric juice secreting cells Antrum(regulation) Endocrine and paracrine cells Vitamin B12 4
5 Composition of gastric juice(1-1.5 L/day) Proteolytic enzymes pepsinogens Gastriclipase Mucus, intrinsic factor, alkaline fluid HCl(150 mmol/l vs mmol/l; ph: ) Activation of proteolytic proenzymes Protein denaturation Bactericid effect(but Helicobacter pylori) HCO 3- ; buffers(mucus, dietaryproteins) Ion transporters of parietal cells 5
6 Parietal cells in rest vs secreting Intracellular rearrangement- Amplification of the apical surface area is accompanied by an increased density of H/K-ATPase molecules at this site. Regulation of gastric HCl secretion 6
7 H + secretionmmol/10 min Feeding Hours The composition of gastric fluid depends on volume and flow rate. Potassium level remains relatively constant, but its concentration is greater in gastric secretions than in plasma. The rate of secretion lower in the morning and higher in the afternoon and evening. 7
8 Gastric acid measurements BAO=basal acid output MAO=mean acid output PAO=peak acid output 25 (Male) vs16 (Female) mmol/h Conventional aspiration tests via nasogastric tube Measuring the volume and the acidity of the gastric juice aspirated Test meals; pentagastrin augmented, Endoscopic methods Intragastric ph measurements Breath test Mg+2HCl MgCl2+H2 CaCO3+2HCL CaCl2+H2O+CO2 Ca 13 CO 3 Phases of gastric juice secretion Cephalic phase(40%) Gastric phase(50%) Intestinal phase(10 %) Stimulation and inhibition as well 8
9 ACh M rec parietalcell GRP (bombesinerg neurons) G cell gastrin PACAP ECL cell Pituitary adenylate cyclaseactivating polypeptide D cells- Somatostatine 9
10 Secretion of Gastrin underph 4 is progressively inhibited. (-feed back) 19 10
11 21 Mechanisms contributing to mucosal defense Tight junctions between the cells Mucus surface epithelial cells Bicarbonate and other buffers neutralize acids 22 11
12 Destruction of mucosal barrier Type: - erosion - ulcer - perforation stress vasoconstriction β2-receptor G-cell gastrin - HCl glucocorticoids; NSAID, aspirin alcohol Helicobacter pylori inflammation G-cell gastrin - HCl The Zollinger-Ellison syndrome uncontrolled gastrin secretion (tumor)..hcl large volumen of pancreatic juice fluid loss into the gut ph in the duodenum pancreatic enzymes fail to work maldigestion, malabsorbtion osmotic activity diarrhoea lipids (too) are not digested(fat soluble vitamins!!!) bacterial breakdown of carbohydrates in the colon.gases due to low ph, B 12 and intrinsic factor do not bind anemia multiple ulcers hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa cancer? 24 12
13 Urea breath test for the detection of Helicobacter pylori, serology, histology Other disorders affecting gastric juice secretion Zollinger-Ellison-syndrome gastrinoma HCl overproduction, ulcer, hypertrophy 13
14 Chief cells- secretion Pepsinogens proteolytic proenzymes Exocytosis H+ and autocatalitic process Gastric lipase: FFA + glycerin Regulation Vagalnerve(PSY) ACh M 3 gastrin(indirectly through acid secretion) Secretin; CCK 14
15 Exocrine pancreas: secretion and regulation (Lo. 65.) Exocrine pancreas Composition and significance of pancreatic juice Activation of pancreatic(pro)enzymes Neural and humoral control of pancreatic juice secretion Protection against self-digestion maintain integrity of pancreas Pancreatic juice productiom: ml/day 90% VITAL!! Lack of pancreatic function - Maldigestion and diabetes 15
16 Composition of pancreatic juice ml/day digestive(pro)enzymes Proteolytic enzymes Trypsinogenes Chimotrypsinogen Procarboxypeptidase Electrolites Acinar cells: Cl- secretion(small volume) Ductal cells: HCO3-(large volume) Lipases Pancreas lipase Prophospholipase cholesterine-esterase Regulatory molecules Pancreas α-amylase Procolipase Ribo- and dezoxyribonucleases Trypsine inhibitor Sequential-secretory mechanism 16
17 Vagal nerve- VIP, NO vasodilation in connection with secretion HCO 3- and Cl - transportsin pancreaticductcells ACh, Secretin 17
18 18
19 Control of pancreatic juice secretion Vagalnerve-ACh M 3 ; VIP -vasodilation CCK CCK1 Indirect vagovagal reflex Secretin Promotes the effectiveness of CCK on acinar cells PromotesHCO 3- productionin ductalcells (+AChand CCK) 19
20 Protection against self-digestion Trypsine inhibitors Pressure gradient promotes fluid flow toward the duodenum Secreted as pancreatic proenzymes (zymogens) Cell nucleus Pancreatic enzymes in granules Activation of pancreatic proenzymes in the duodenum 20
21 Bile: secretion, storage, mobilization, regulation (Lo. 66.) 600 ml/day Composition: primary& secondary bile salts phospholipids(e.g. lecithin) Cholesterine, bilirubin HCO 3 rich Hepatocytes liver parenchyma cells(60 %) bileproduction Cholangiocytes epithelial cells of thebileduct HCO 3- & water secretion(40%) VIP, secretin Significance: Promote lipid digestion and absorption (emulsification, micell formation) Excretionof endogenoussubstances, e.g. bilirubin; cholesterine Excretion of exogenous substances (drugs, copper, iron) Physiology of liver Permeability barrier Canalicular membrane with actin filaments 21
22 Hepatocellular transports Organicanion and cathion transporters Secondary active transporters ABC transporters MECHANISM OF BILE SECRETION GALLBLADDER Na + Cl - Bile from the gallbladder: dark green components in higher concentration ph slightly acidic Cl - HCO 3 - DUCT CELL HCO 3 - Na + H 2O Bile from the liver: golden yellow ph is close to neutral Na + Cl - B.A. H 2 O K + HEPATOCYTE Na + B.A. B.A. B.A. HCO
23 Enterohepatic circulation of bile salts Deconjugated bile acids reabsorption from the ileum 95% (primary and secondary) Binded with albumin in blood Na + /bileacidsecondaryactivetrp. intothe hepatocytes Conjugation ABC transporters used for secretion De novosynthesis 2-5% Regulation: negative feedback 23
24 Neural and humoral regulation of bile secretion Bile salts via enterohepatic circulation stimulate secretion of bile salts 24
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Ali Yaghi. Yaseen Fatayer. M.Khatatbeh
 6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Gastrointestinal Physiology. Secretion
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Gastric and Intestinal secretion
 Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Digestion and absorption (I)
 Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
Digestion and absorption (I) Jane Chao 1 Gastrointestinal tract upper gastrointestinal tract mouth pharynx esophagus stomach lower gastrointestinal tract small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) cecum
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT
 2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT
 2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT SECRETORY GLANDS AND CELLS The alimentary tract produces a large variety and quantity of substances which contribute to digesting the food, and protecting and regulating
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine.
 Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS
 1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine Masaryk University
 CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Michaela Králíkov ková,, MD Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine Masaryk University 2 major functions digestion and absorption of food digestion
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Michaela Králíkov ková,, MD Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine Masaryk University 2 major functions digestion and absorption of food digestion
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport. Lecture 2. Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients
 BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
BPK 312 Nutrition for Fitness & Sport Lecture 2 Digestion & Absorption of Food Nutrients 1. Overview of digestion & absorption of nutrients 2. Functional anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract 3. Digestion
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal Tract Fluid Professor A. S. Alhomida
 Disclaimer The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on: References supplied Atlases or The web King Saud University College
Disclaimer The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on: References supplied Atlases or The web King Saud University College
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Physiology 12. Overview. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Germann Ch 19
 Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Physiology 12 The Gastrointestinal Tract Germann Ch 19 Overview 1 Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
 Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
- Most nutrients are absorbed before reaching the ileum. - Colon is responsible for final removal of electrolytes and water.
 University of Jordan Department of physiology and Biochemistry Gastro-Intestinal physiology, Medical, Pt III. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Academic year:
University of Jordan Department of physiology and Biochemistry Gastro-Intestinal physiology, Medical, Pt III. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Academic year:
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION
 NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION NUTR 2050: Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Differentiate
NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION NUTR 2050: Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Differentiate
Overview. Physiology 1. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Guyton section XI
 Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Overview Physiology 1 The Gastrointestinal Tract Guyton section XI Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion Secretion Absorption Motility Basic functions of the GI tract Digestion: : Dissolving and breaking
Doctot: M. Khatatbeh Handout #2. Subject: Secretion 14/4/2013. System. t! Gastrointestinal. Lecture #: AJ N. The- Unlucr1ity of Jordan i!
 ~, ;:c-:;.. : "
~, ;:c-:;.. : "
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4)
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Chapter 02 The Digestive System Mechanism for Nourishing the Body
 Chapter 02 The Digestive System Mechanism for Nourishing the Body MULTICHOICE 1. Within the lamina propria, lying just below the epithelium, is the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), which. (A)
Chapter 02 The Digestive System Mechanism for Nourishing the Body MULTICHOICE 1. Within the lamina propria, lying just below the epithelium, is the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), which. (A)
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
Digestion. Generalized Digestive System. Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate. 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception.
 Digestion 24 Generalized Digestive System Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate 1 2 1 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception 3 3 4 4 (Eckert 25 15-13) 1 Foregut -Conducting, Storage, Digestion -Esophagus
Digestion 24 Generalized Digestive System Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate 1 2 1 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception 3 3 4 4 (Eckert 25 15-13) 1 Foregut -Conducting, Storage, Digestion -Esophagus
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Unit 2 : The Digestive System
 Unit 2 : The Digestive System Mind Map Components and Histology Digestion Oral Cavity Small Intestine Digestive System Digestion Stomach Large intestine Absorption Digestion Absorption Digestion Absorption
Unit 2 : The Digestive System Mind Map Components and Histology Digestion Oral Cavity Small Intestine Digestive System Digestion Stomach Large intestine Absorption Digestion Absorption Digestion Absorption
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Bile composition. Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis. Bile
 Bile composition Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis Robert F. Schwabe rfs2102@columbia.edu Phospholipids Miscellaneous (Pigment, Protein) (Lecithin) Bile Salts 0.7% 4% H 2 0 1% 12%
Bile composition Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis Robert F. Schwabe rfs2102@columbia.edu Phospholipids Miscellaneous (Pigment, Protein) (Lecithin) Bile Salts 0.7% 4% H 2 0 1% 12%
AP Biology. Animal Nutrition
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food oxygen food Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food oxygen food Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System Overview of GI Processes Functional Anatomy Digestion and Absorption General Principle of GI Regulation GI Secretion and Regulation GI Motility and its Regulation
Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System Overview of GI Processes Functional Anatomy Digestion and Absorption General Principle of GI Regulation GI Secretion and Regulation GI Motility and its Regulation
Overview of digestion
 Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Digestion Review V1 /36
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-w
 Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-water lysis-break apart) if not broken down, proteins
Summary break down long chain proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids into monomers recall hydrolysis (opposite of dehydration synthesis) (hydro-water lysis-break apart) if not broken down, proteins
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9.
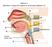 Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index
 Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index Digesting, absorbing and assimilating a meal requires precise coordination of a huge number of physiologic processes. Control over gastrointestinal function
Gastrointestinal Hormones: Introduction and Index Digesting, absorbing and assimilating a meal requires precise coordination of a huge number of physiologic processes. Control over gastrointestinal function
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed. Protein digestion and AA absorption
 Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed 1 Tuesday 18 April 2017 Protein digestion and AA absorption D S Jairajpuri 250 256 250 256 2 Wednesday 19 April 2017 Removal of nitrogen and urea cycle D S Jairajpuri
Day Date Title Instructor 5 th Ed 6 th Ed 1 Tuesday 18 April 2017 Protein digestion and AA absorption D S Jairajpuri 250 256 250 256 2 Wednesday 19 April 2017 Removal of nitrogen and urea cycle D S Jairajpuri
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 15 Digestive System 2 Stomach and Accessory Structures Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Stomach anatomy
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 15 Digestive System 2 Stomach and Accessory Structures Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Stomach anatomy
Study Aid for D1: Nutrition
 Study Aid for D1: Nutrition Essential nutrient Food only source. Ex. Some Amino acids, minerals, calcium, vitamins, water, some fatty acids Non-essential nutrient Can be made in body. Ex. Glucose, starch.
Study Aid for D1: Nutrition Essential nutrient Food only source. Ex. Some Amino acids, minerals, calcium, vitamins, water, some fatty acids Non-essential nutrient Can be made in body. Ex. Glucose, starch.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms.
 D2 Diges(on Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. This figure shows the main parts of the diges(ve
D2 Diges(on Essential idea: Digestion is the breaking down of food particles into smaller particles. It is controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. This figure shows the main parts of the diges(ve
Digestion and Absorption
 Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
-Mohammad Ashraf. -Anas Raed. -Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
-1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
