For more information about how to cite these materials visit
|
|
|
- Silvia McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers.
2 Citation Key for more information see: Use + Share + Adapt { Content the copyright holder, author, or law permits you to use, share and adapt. } Public Domain Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (USC ) Public Domain Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. Creative Commons Zero Waiver Creative Commons Attribution License Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike License GNU Free Documentation License Make Your Own Assessment { Content Open.Michigan believes can be used, shared, and adapted because it is ineligible for copyright. } Public Domain Ineligible: Works that are ineligible for copyright protection in the U.S. (USC (b)) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ { Content Open.Michigan has used under a Fair Use determination. } Fair Use: Use of works that is determined to be Fair consistent with the U.S. Copyright Act. (USC ) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ Our determination DOES NOT mean that all uses of this 3rd-party content are Fair Uses and we DO NOT guarantee that your use of the content is Fair. To use this content you should do your own independent analysis to determine whether or not your use will be Fair.
3 M1 - GI Sequence Stomach John Williams, M.D., Ph.D. Winter, 2009
4 STOMACH Functions of Stomach 1. Storage of ingested meal 2. Inhibition of bacterial growth 3. Mixing contents of stomach 4. Physical breakdown of food into small particles; some components solubilized 5. Regulates rate of emptying into small intestine. 6. Provides intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption Page 38 Page 39
5 Structure of Gastric Gland from the Body of the Stomach GASTRIC SECRETIONS Substance Cell Region HCl parietal cell fundus-body (oxyntic cell) Intrinsic Factor parietal cell fundus-body Pepsinogen chief cells fundus-body-antrum Mucus mucus cell volume: liters/day, isotonic The gastric mucosa contains a number of cell types which contribute to its function. Mucus epithelial cells and overlying mucus contribute to the gastric mucosal barrier. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid (and in the human, intrinsic factor) while chief cells produce and secrete the protease precursor pepsinogen. ECL cells do not contact the gland lumen synthesize and release the paracrine regulator histamine. Mucus neck cells include the stem cells which divide, differentiate and move up and down the gland in normal cellular turnover. basal rate: 1-5 mmoles H + /hr max rate: 6-40 mmoles H + /hr ph max: 1.0 Page 40 Page 41
6 Gastric Glands also Contain Endocrine Cells Fundus Somatostatin, Ghrelin Pylorus Gastrin, Somatostatin EM of Gastrin Cell Relationships Between the Concentrations of the Principal Ions in Gastric Juice and the Rate of Secretion Fig. 9 Johnson, L. Essential Medical Physiology. Raven Press, New York, NY; 1992: 484. Page 42 At low secretory rates most gastric secretion is by surface cells and is NaCl rich. A small amount of HCl is secreted by parietal cells but even at 10 mm results in a ph of 2.0. When secretion is stimulated the output of parietal cells increases 10 fold so H + increases to over 100 mm; the K + concentration also increases. Loss of gastric acid due to excessive vomiting can result in acid base abnormalities (alkalosis, hypokalemia). Page 43
7 Mechanism of HCl Secretion by the Parietal Cell (Diagram p.43) Plasma HCO 3 - Mechanism of HCL Secretion by Parietal Cells Na + CO 2 Cl - Cl - K + ~ CO 2 + H 2 O HCO 3 - K + Na + John Williams Parietal Cell H 2 CO 3 Carbonic anhydrase Cl - K + H + ~ Lumen K + H + Cl - Hydrochloric acid secretion by the parietal cell essentially involves separation of H + ions which are released into the gastric lumen and HCO 3 - released into the blood. CO 2 diffuses into the cell from plasma or is produced by cellular metabolism. It becomes hydrated to H 2 CO 3 (carbonic acid), a process facilitated by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. H 2 CO 3 dissociates into H + and H 2 CO 3-. At the apical membrane H + is transported out of the cell in exchange for K + by the H + -K + ATPase which is also known as the Proton pump. The K + taken into the cell recycles back out into the gastric lumen via a K + channel resulting in the elevated K + concentration of gastric juice. The final component of gastric HCl is Cl - which exits passively through a Cl - channel. Thus, the apical H + -K + ATPase drives the secretion of HCl. At the basolateral membrane of the parietal cell a Cl - HCO 3 - exchanger promotes HCO 3 - exit and Cl - uptake thus maintaining homeostasis of intracellular H + (ph) and Cl. The basolateral membrane also contains a Na + -K + ATPase which maintains intracellular Na + and K + as in other cells. The H-K ATPase is related structurally and functionally to the ubiquitous Na + -K + ATPase and the Ca 2+ ATPase present in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle. It contains a catalytic α subunit and a glycoprotein β subunit which is required for targeting. The H- K ATPase is the target for proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs) such as Omeprazole. PPIs are weak bases and concentrate in the low ph of the gastric gland where they are activated by molecular rearrangement in response to the low ph. The active drug then binds covalently to cysteine residues in the H-K ATPase, the predominant protein in the apical membrane of activated parietal cells, thereby inhibiting its function in a irreversible manner. PPIs are more potent inhibitors of acid secretion then H 2 blockers and are used to treat acid reflux disease, gastric acid hypersecretion, and as part of therapy to eradicate H. Pylori in the treatment of ulcers. Current PPIs include Prilosec (OTC), Nexium and Protonix. Page 44 Page 45
8 Schematic representation of the H+, K+ -ATPase Heterodimer in the Apical Membrane of the Parietal Cell Morphological Transformation of Parietal Cells Upon Stimulation The H +, K + ATPase is the molecular target of At rest, most of the H + -K + ATPase is present within the cell in proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole. The tubules and vesicles in an inactive form. Upon parietal cell molecules are activated in the acid environment stimulation these vesicles fuse with the luminal membrane of the gastric gland and covalently bind to which becomes greatly increased in surface area and now cysteine residues in the α subunit of the ATPase. includes the H + -K + ATPase in a location where it can transport H + into the lumen. This transformation requires an intact cytoskeleton and is reversed upon removal of the secretory stimulus. Page 46 Page 47
9 Secretory Transformation of Parietal Cells Page 48
10 Receptors and Intracellular Messengers Regulating Parietal Cell H+ Secretion Role of the ECL Cell in Peripheral Regulation of Gastric Acid Secretion Histamine H2 Adenylate cyclase Gastrin Vagalstimulation Acetylcholine ATP camp Ca 2+ Gastric hydrogen ion pump K + Potentiation Parietal Cell H + John Williams Secretion A B Sum A + B Alone A + B INTEGRATED CONTROL OF GASTRIC ACID SECRETION BY NEURAL AND HUMORAL PATHWAYS Gastric acid secretion is stimulated by Histamine acting on a H 2 receptor, Gastrin acting on a Gastrin receptor and Acetylcholine which acts on a M3 muscarinic receptor. All three receptors are 7 transmembrane domain, G protein coupled receptors. Specific antagonists exist for all three receptors and H 2 antagonists (prototype: Cimetidine) are used clinically to reduce acid secretion. Xantac (Ranitidine) is now sold over the counter. Histamine and Gastrin or Acetylcholine show potentiation of response, i.e., the response to the combination is bigger than the sum of the individual responses. It is this phenomenon that underlies the efficacy of H 2 blockers to inhibit secretion. Somatostatin (not shown) acts on a specific receptor which is coupled to an inhibitory G protein and inhibits adenylate cyclase and thereby the effect of histamine. Page Vagus acts directly on parietal cells and indirectly by effects on gastrin and histamine release. 2. Histamine released from enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL cells) reaches parietal cells by local diffusion. 3. Gastrin released from antral G cells reaches parietal cells by systemic circulation. 4. Inhibitory regulators include somatostatin released from D cells in the antrum and body of stomach, prostaglandins from surface cells, and intestinal hormones collectively termed enterogastrone. Page 50
11 Gastrin release from G cells of the antrum is stimulated by luminal acids and digested proteins, and is inhibited in a paracrine fashion by somatostatin released in response to luminal acid. Somatostatin is released when gastric ph <3.0. Page 51 Page 52
12 Cephalic Phase Gastric Acid Secretion sight, taste, smell, chewing, stress Vagus Nerve This acid secretion is mediated by the vagus. There is some increase in gastrin by neural release of GRP. GRP Enteric Nerve Plexus ACh Hist G-Cell ECL-Cell Parietal Cell GASTRIN John Williams HCL Mediated by gastrin and neural reflexes. Page 53 Page 54
13 Gastric Phase Acid Secretion Intestinal Phase Acid Secretion long and short reflexes inhibition of parietal cell and gastrin release + + gastrin G-Cell + somatostatin - ECL-Cell + histamine + Parietal cell ACh + Nerves Hormones enterogastrone GIP CCK secretin D-Cell + HCL peptides amino acids distension luminal stimuli fatty acids John Williams buffered by proteins in meal acid amino acids hypertonic solutions distension John Williams Page 55 Page 56
14 PEPSIN 1. Proteolytic enzyme secreted by chief cells as an inactive precursor, pepsinogen. 2. Release stimulated by vagal nerve and by presence of acid in stomach. 3. Activated by peptide cleavage at acid ph. 4. Initiates digestion of protein Pepsinogen is synthesized, stored in secretory granules, and released by exocytosis in response to increased intracellular Ca 2+ similar to pancreatic digestive enzyme secretion. After cleavage, pepsin is optimally active at ph 2 and is good proteolytic enzyme especially active on collagen. It is an endopeptidase acting on internal peptide bonds and its products are large peptides called peptones which are potent stimulators of gastrin and CCK release. INTRINSIC FACTOR 1. Glycoprotein of Mol. Wt. 55,000 which binds Vitamin B 12 ( cobalamin). 2. Produced by parietal cells. 3. After binding B 12 it binds receptors on ileal absorptive cells and is internalized by endocytosis. 4. Absent in pernicious anemia. THE MOLECULE OF INTRINSIC FACTOR AND ITS COBALAMIN COMPLEX Cobalamin in the diet is exclusively bound to animal protein. Adult requirement is about 2.5 µg/day. Involved in methione synthesis (methyl transfer) and in fatty acid metabolism. Deficiency leads to anemia and nervous system damage. Release of cobalamine from food requires acid ph. Thus can get deficiency with chronic use of PPIs. Page 57 Page 58
15 Sequential Steps in the Absorption of Cobalamin (Vit B 12 ) Fig Yamada, T, et al. Textbook of Gastroenterology. 4 th ed. Vol. 1 Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA; 2003: 453. Page 59
16 MECHANISMS CONTRIBUTING TO GASTRIC CYTOPROTECTION Gastric Mucosal Barrier Components of Barrier Mucus HCO 3 surfactant Tight junctions Barrier Breakers Bile Aspirin Ethanol Nonsteroidal Analgesics The gastric mucosa protects itself against acid and pepsin by a number of mechanisms that collectively are termed the gastric mucosal barrier. The barrier includes a prominent mucous layer and bicarbonate secreted by surface cells which sets up a ph gradient in the mucus. Other components of the barrier are the tight junctions between epithelial cells, surfactant like molecules secreted by mucosal cells and gastric mucosal blood flow which rapidly removes any penetrating acid. The mucosal cells can rapidly reconstitute any small break (within hours) by spreading into the space and reforming an intact layer. Substances that break the mucosal barrier include bile salts and lysolethicin (from biliary lethicin) if reflux across the pylorus occurs and exogenous substances such as ethanol and salicylates. Ethanol, being lipid soluble, is absorbed by the gastric mucosa and salicylates being weak acids are absorbed in the unionized form present in the lumen at low ph. Secretion of gastric mucous is stimulated by endogenous prostaglandins which explains the barrier breaking effect of nonsteroidal analgesics such as indomethacin. Page 60 Page 61
17 GASTRIC MOTILITY 1. Proximal Receptive relaxation as stomach fills (Fundus) 2. Distal Propulsive mixing and grinding (Antrum) 3. Pylorus Regulates outflow Fig. 4-9 Granger, D, et al. Clinical Gastrointestinal Physiology. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA; 1985: 84. Pressures within the body of the esophagus, the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), and the fundus region of the stomach. Resting pressure within the fundus is slightly above atmospheric pressure. With swallowing, the fundus relaxes before arrival of the bolus. After passage of the bolus into the stomach, fundic pressure returns to approximately the previous level. This relaxation after swallowing is mediated by vagal inhibitory fibers. The distal stomach mixes gastric contents with secretions and helps break down food into small particles. Only particles smaller than 1 mm can exit through the pylorus. The major motor activity is peristalsis initiated by pacemaker cells in the midportion of the greater curvature of the stomach. These cells initiate a basal electrical rhythm of slow waves propagating toward the pylorus 3 times per minute. Muscular contraction is brought about by action potentials occurring when the smooth muscle cell PD depolarizes below threshold. Action potentials and gastric contraction are increased by vagal or gastrin stimulation and decreased by vagotomy or sympathetic stimulation. (From Kelly, DA In: Johnson, L.R. (Ed) Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. New York, Raven Press, 1981). Page 62 Page 63
18 Relation of Contraction to Electrical Potential Regulation of Gastric Emptying Gastric emptying is regulated to prevent overload in intestine. Only particles less than 1 mm can pass through pylorus during digestive period. John Williams Jim Sherman In the top two panels the basal electrical rhythm or pacemaker potential is seen occurring 3 times/min but without muscle contraction. In the bottom two panels the pacemaker potential is generating action potentials and the resultant calcium influx induces contraction. Hinder, RA, Kelly, KA. Canine Gastric Emptying of solids and liquids. Am. J. Physiol. 233: E335, Page 64 Page 65
19 DISORDERS OF GASTRIC EMPTYING 1. Delayed Emptying a. Outlet obstruction (tumor, scarring) b. Diabetic neuropathy c. Use of prokinetic agents 2. Accelerated Emptying a. Dumping Syndrome Page 65A
20 Additional Source Information for more information see: Slide 4 Slide 5 Slide 6 (Left) Slide 6 (Right) Fig. 9 Johnson, L. Essential Medical Physiology. Raven Press, New York, NY; 1992: 484. Slide 7 John Williams Slide 8 (Both images) Slide 9 Slide 10 (Left) John Williams Slide 10 (Right) Slide 11 (Left) Slide 11 (Right) Slide 12 (Left top & bottom) Slide 12 (Right) John Williams Slide 13 (Left) John Williams Slide 13 (Right) John Williams Slide 14 Slide 15 - Fig Yamada, T, et al. Textbook of Gastroenterology. 4 th ed. Vol. 1 Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA; 2003: 453. Slide 16
21 Additional Source Information for more information see: Slide 17 (Left) Slide 17 (Right) Fig. 4-9 Granger, D, et al. Clinical Gastrointestinal Physiology. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA; 1985: 84. Slide 18 (Left) Jim Sherman Slide 18 (Right top) John Williams Slide 18 (Right bottom) Hinder, RA, Kelly, KA. Canine Gastric Emptying of solids and liquids. Am. J. Physiol. 233: E335, 1977.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
GI Secretion 1: Salivary and Gastric Secretion Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. List the volumes of secretion by various regions. 2. Predict the components of salivary secretion at different flow rates.
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastric and Intestinal secretion
 Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
What location in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has tight, or impermeable, junctions between the epithelial cells?
 CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
-Mohammad Ashraf. -Anas Raed. -Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
-1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
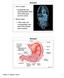 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
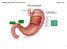 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Gastrointestinal Physiology. Secretion
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Gastrointestinal Physiology Secretion Fig. 24.26 Functions Provided by secretory glands which serve 2 functions: - Digestive enzymes. - Lubrication and protection of the mucosa. Types of secretory structures
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
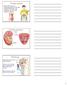 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ULCER DISEASE
 Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
Página 1 de 8 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Greenfield, Lazar J., Mulholland, Michael W., Oldham, Keith T., Zelenock, Gerald B., Lillemoe, Keith D. Surgery: Scientific Principles & Practice,
What part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is composed of striated muscle and smooth muscle?
 CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Asma Karameh. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة -
 -2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
-2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Figure Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore
 Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine.
 Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad
 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
In this chapter we will study gastrointestinal (GI)
 Chapter 28 The astric Phase of the Integrated Response to a Meal 1 CHAPTER 28 The astric Phase of the Integrated Response to a Meal In this chapter we will study gastrointestinal (I) tract physiology when
Chapter 28 The astric Phase of the Integrated Response to a Meal 1 CHAPTER 28 The astric Phase of the Integrated Response to a Meal In this chapter we will study gastrointestinal (I) tract physiology when
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment
 Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
OSPAP Programme. Gastrointestinal Drugs. Dr. Adrian Moore Dale
 PAP Programme Dr. Adrian Moore Dale 1.03 Adrian.Moore@sunderland.ac.uk 0191 5152554 lide 1 of 26 PAP MPM14 Acid-Related Pathophysiology The stomach secretes: ydrochloric acid (Cl) aids digestion and also
PAP Programme Dr. Adrian Moore Dale 1.03 Adrian.Moore@sunderland.ac.uk 0191 5152554 lide 1 of 26 PAP MPM14 Acid-Related Pathophysiology The stomach secretes: ydrochloric acid (Cl) aids digestion and also
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Gastrointestinal physiology II.
 Gastrointestinal physiology II. 62. Functions of the upper GI tract: chewing, salivation, swallowing. 63. Motor functions of the stomach. Vomiting (emesis). 1 Motor functions of the mouth and the oral
Gastrointestinal physiology II. 62. Functions of the upper GI tract: chewing, salivation, swallowing. 63. Motor functions of the stomach. Vomiting (emesis). 1 Motor functions of the mouth and the oral
PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE
 15 March, 2018 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Document Filetype: PDF 374.06 KB 0 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Among the oldest and cheapest drugs for diabetes are the drugs that
15 March, 2018 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Document Filetype: PDF 374.06 KB 0 PANCREATIC BETA CELLS PRODUCE AND SECRETE Among the oldest and cheapest drugs for diabetes are the drugs that
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System Overview of GI Processes Functional Anatomy Digestion and Absorption General Principle of GI Regulation GI Secretion and Regulation GI Motility and its Regulation
Chapter 20 The Gastrointestinal System Overview of GI Processes Functional Anatomy Digestion and Absorption General Principle of GI Regulation GI Secretion and Regulation GI Motility and its Regulation
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4)
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
