The Bankart repair illustrated in crosssection
|
|
|
- Nathan Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Bankart repair illustrated in crosssection Some anatomical considerations RALPH B. BLASIER,* MD, JAMES D. BRUCKNER, LT, MC, USNR, DAVID H. JANDA,* MD, AND A. HERBERT ALEXANDER, CAPT, MC, USN From the *University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, Michigan, and the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Naval Hospital, Oakland, California ABSTRACT The Bankart repair for chronic anterior shoulder instability effectively addresses the pathologic components responsible for repeated dislocation or subluxation. However, contrary to popular belief, the Bankart repair does not precisely restore the premorbid anatomy. The capsule is reattached to the boney rim of the anteroinferior glenoid deep to and lateral to the torn cartilagenous labrum, thus excluding the labrum from the joint anteriorly. This was demonstrated by cross-sectional cadaver dissections performed to illustrate this complex surgical anatomy to orthopaedic residents in training. In addition, when correlated with double-contrast computerized axial tomography, we noted five predominant patterns of anatomical lesions which by common use have been collectively termed the "Bankart lesion." These are: 1) the rare "classic" Bankart lesion in which are torn the cartilagenous labrum and capsular origin from the glenoid rim; 2) the capsule stripped from the scapular neck and the labrum detached from the glenoid rim remaining fixed to the overlying capsule; 3) the capsule stripped from the scapular neck and the labrum separated from the glenoid rim, but separately; 4) the labrum abraded away and no longer radiographically detectable; and 5) glenoid rim fracture. The Bankart repair is very effective for the treatment of chronic, traumatic-onset, anterior or anteroinferior shoulder *t Address correspondence and repnnt requests to: Ralph B. Blasier, MD, University of Michigan Medical Center, 1500 East Medical Center Drive, Ann Arbor, MI The opinions or assertions expressed herein are those of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as necessary reflecting the views of the Department of the Navy or of the naval service at large. 630 instability.2,7 Many surgeons have settled on the Bankart repair or subtle modifications of the Bankart repair as their surgical treatment of choice for routine cases of anterior instability. Most descriptions of the Bankart repair are careful to state that it is a technically difficult and demanding procedure.6 The authors have encountered difficulty in teaching this procedure (exactly as popularized by Rowe4,7) to resident orthopaedic surgeons because of the complex anatomy involved and the limited operative exposure. Because ordinary teaching methods failed to achieve our educational goals, the authors embarked on a series of crosssectional cadaver dissections and correlative double-contrast computerized tomograms to illustrate the components of the Bankart lesion and the anatomical features of the repair. ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATIONS Computerized tomography Many lesions are associated with shoulder instability. Specifically we are here addressing the anterior labral and capsular lesions most often associated with chronic, traumatic-onset, anterior or anteroinferior shoulder instability. Excluded from this discussion is instability associated with psychiatric disturbances, collagen disorders such as the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, generalized joint laxity, glenoid hypoplasia, subscapularis rupture, and instability based on fractures such as greater tuberosity avulsions or the posterior humeral head impression fracture. Excluding these other associated lesions, there remain a number of patterns of injuries to the boney glenoid rim, the cartilagenous glenoid labrum, and the anterior joint capsule which are associated with and lead to anterior and anteroinferior instability of the shoulder. In order to define the precise pathologic lesions present in our patients, our pre-
2 631 Figure 1. A normal double-contrast computerized tomogram. The boney glenoid and the humeral head are well seen. A thin film of contrast coats and outlines the cartilagenous structures. The joint is distended with air. The triangular crosssection of the normal glenoid labral cartilage is clear (black arrowhead). The capsule (white open arrow) and its attachment to the scapular neck is obvious. The subscapularis muscle can be seen, but details are not apparent. Figure 3. The capsule stripped off the lateral scapular neck (white open arrow) &dquo;together&dquo; with the cartilagenous labrum which is off the boney glenoid (white arrowhead). The capsule (white open arrow) is not completely disrupted and maintains some capsular/periosteal connection, although much more medial than normal. Figure 2. A classic Bankart lesion. The cartilagenous labrum is clearly seen to be separated from the boney glenoid rim (white arrowhead). The capsule remains attached to the labrum and is no longer attached to the scapular neck (white open arrow). Figure 4. The capsule stripped from the scapular neck (white open arrow) and the labrum torn off the glenoid (black arrowhead), but separately. This is the pattern we see most commonly.
3 632 Figure 5. The anteroinferior labrum has been abraded away (black arrowhead). The capsule (white open arrow) is not completely disrupted and maintains some capsular/periosteal connection. Figure 7. A transverse section from a fresh cadaver, just inferior to the equator of the humeral head in its normal state. The major muscles are labeled for orientation: pectoralis (P); deltoid (D); subscapularis (S); and infraspinatisus (I). The boney glenoid and the humeral head are well seen. The triangular cross-section of the normal glenoid labral cartilage is clear. The capsule and its attachment to the scapular neck is well seen. Figure 8. An artificially created &dquo;bankart lesion&dquo; similar to that shown by computerized tomography in Figure 3. The labrum is separated from the glenoid, and the capsule is stripped from the scapular neck. Figure 6. Boney deformity from a malunited glenoid rim fracture. The boney rim is displaced 3 to 4 mm medial to its anatomical position (white arrow), and this loss of boney support allowed the dislocations. operative assessment includes double-contrast computerized tomography or occasionally arthroscopy. In many of our patients, this results in a decision to repair injured anterior structures by the Bankart procedure. In some cases in which the instability is found to be due to boney glenoid rim insufficiency or posterior humeral head impression fracture, another operation may be selected. In a few cases, however, no surgically repairable lesion is found. For these patients,
4 633 - Figure 9. Diagram of a cross-section of the capsule and labrum separated from glenoid rim. A popular misconception is that the dislocation occurs in the interval between the labrum and the rim (arrow). Figure 10. Diagram looking into the shoulder socket as if from the humeral head, showing labrum separated from the rim. Unless there are radial tears in the labrum (and there room for the dislocation usually are not), there is not enough to occur between the labrum and rim (&dquo;x&dquo;). surgery is delayed while more physical therapy is offered and further observation for psychiatric disturbance or generalized joint laxity is carried out by the surgeon. The physical therapy offered is a combination of internal shoulder rotator strengthening and &dquo;provocative&dquo; training in which the patient is taught the limits of his stable range of motion. The computerized tomograms have shown several patterns of anterior anatomical lesions, some of which will be illustrated here. The first double-contrast computerized axial tomogram discussed here is from a patient with shoulder pain not based on any anatomical lesion. A representative section from her normal double-contrast computerized tomogram is shown as Figure 1. The boney glenoid and the Figure 11. A, diagram of cross-section of capsule and labrum separated from glenoid rim showing labrum pushed medially and dislocation occurring over them labrum and into the overly capacious capsule. B, diagram looking into the shoulder socket as if from the humeral head showing where the dislocation occurs over the injured labrum and into the capacious capsule. humeral head are well seen. A thin film of contrast coats and outlines the cartilagenous structures. The joint is distended with air. The triangular cross-section of the normal glenoid labral cartilage is clear. The capsule and its attachment to the scapular neck is easily seen. The subscapularis muscle can be seen, but not in detail. The second patient was a previously well female in her late 20s who had her arm forcibly abducted and externally rotated in a minor boating accident. She never had any frank dislocation, but was severely troubled by frequent anteroinferior subluxation. Her double-contrast computerized tomogram (Fig. 2) shows a classic Bankart lesion as described in Bankart s second paper on the subject. We do
5 634 Figure 12. The deltopectoral interval has been opened. The cephalic vein has been taken medially. Figure 14. Medially, the division between the subscapularis tendon and muscle is clear and blunt dissection suffices. Figure 13. The development of the plane between the subscapularis tendon and muscle and the underlying capsule. In the lateral 2 cm, the tendon and capsule are confluent and the separation is done sharply. not see this pattern very often. The cartilagenous labrum is clearly seen to be separated from the boney glenoid rim. The capsule remains attached to the labrum and is no longer attached to the glenoid rim or scapular neck. The third patient was similarly troubled more by frequent subluxation than frank dislocation. His double-contrast computerized tomogram (Fig. 3) shows the capsule stripped off the lateral scapular neck in tight association with the cartilagenous labrum which is off the boney glenoid rim. The capsule is not completely disrupted and maintains a capsular/periosteal connection, although much more medial than normal. When we do see this pattern, it is commonly in a patient whose problem is chronic subluxation rather than frank dislocation. The fourth patient had recurring dislocations after an Figure 15. The capsulotomy. The capsule is opened vertically 4 to 8 mm lateral to and parallel to the glenoid rim. initial traumatic event. His double-contrast computerized tomogram (Fig. 4) shows the capsule stripped from the scapular neck and the labrum torn off the glenoid, but separately. This is the lesion we see most often in &dquo;typical&dquo; traumatic-onset, chronic anterior dislocation. The fifth patient under discussion had recurring dislocations, neglected for a prolonged period. His anteroinferior labrum has been abraded away (Fig. 5). This is also a pattern we see commonly on double-contrast computerized tomography. The last example patient was a healthy young Marine who sustained an anteroinferior glenoid rim fracture from a moderately severe injury. The fracture united promptly, but the patient had frequent subluxations and occasional dislocations. Due to a &dquo;dye&dquo; allergy, this patient had a singlecontrast (air) computerized tomogram (Fig. 6). It can be seen that his rim fracture is united 3 to 4 mm medial to its
6 635 Figure 16. The same capsulotomy diagrammed as if looking into the glenoid cavity. _ Figure 18. Treating this view into the glenoid cavity as the face of a clock, the suture fixation holes are seen at 2, 4, and 6 o clock. For patients in which inferior instability is especially prominent, the inferior hole may be carried around posteriorly toward 7 o clock. Figure 17. The needle demonstrates the location of the suture holes placed in the glenoid rim. anatomical position, and this loss of boney support allowed the chronic instability. Cross-sections For the cross-sectional demonstration of the anatomical details of the Bankart repair, a 6 mm thick section was taken from a fresh cadaver, just inferior to the equator of the humeral head. Figure 7 shows the section in its normal state. The boney glenoid and the humeral head are well seen. The triangular cross-section of the normal glenoid labral cartilage is clear. The capsule and its attachment to the scapular neck is obvious. Figure 8 shows an artificially created &dquo;bankart lesion&dquo; similar to that shown by computerized tomography in Figure 3. In this case, the labrum is separated from the glenoid, Figure 19. Sutures are placed through the holes in the rim to effect the repair. and the capsule is stripped from the scapular neck, but the two are left in close association. A popular misconception is that the dislocation occurs in the interval between the labrum and the rim (Fig. 9). Unless there are radial tears in the labrum, there is not enough room for the dislocation to occur between the labrum and rim (Fig. 10). During the dislocation, the labrum is pushed medially and the humeral head moves over the labrum and into the overly capacious capsule (Fig. 11). SURGICAL PROCEDURE To begin the Bankart repair, the deltopectoral interval is developed (Fig. 12). In this case, the cephalic vein has been
7 636 Figure 20. The medial edge of the lateral capsular flap is sutured to the glenoid rim, which has been roughened with an osteotome. Figure 22. The lateral edge of the medial capsule is tied into the same suture line to provide reinforcement. The cartilagenous labrum is incorporated providing an enhanced soft tissue buttress against anterior translation of the humeral head. Figure 21. Looking into the shoulder socket showing the medial edge of the lateral capsular flap being secured to the holes in the glenoid rim deep to and lateral to the cartilagenous labrum. The labrum is thus excluded from the anteroinferior aspect of the joint. This routine feature of the Bankart repair has not been emphasized in the past. mobilized medially as popularized by Henry, but it can be just as easily taken laterally if the surgeon prefers. The plane between the subscapularis tendon and muscle and the underlying capsule is then developed. In the lateral 2 cm, the tendon and capsule are confluent and the separation is done sharply (Fig. 13). Medially, the division is clear and blunt dissection suffices (Fig. 14). With the arm in external rotation, the glenoid rim is palpated through the intact capsule. The capsule is then opened vertically 4 to 8 mm lateral to and parallel to the rim (Fig. 15). This is shown as if looking into the glenoid cavity in Figure 16. Figure 23. The subscapularis insertion is repaired anatomically, without shortening or overlap. Holes are placed in the glenoid rim, usually at about the 2, 4, and 6 o clock positions (for a right shoulder) and perhaps even further around toward 7 o clock for patients in which inferior instability is prominent (Figs. 17 and 18). The sutures that will effect the repair are threaded through these holes (Fig. 19). The medial edge of the lateral capsular flap is sutured to the glenoid rim, which has been roughened with an osteotome (Fig. 20). This is quite straightforward in situations such as those illustrated here in which the labrum is torn from the glenoid rim, and is easily understood in cases in which the labrum has been abraded away. For cases in which the capsule is lax but the labrum is uninjured, Rowe and Zarins5 have developed a modification of the Bankart repair in which the medial edge of the lateral
8 637 further adding strength by providing an enhanced soft-tissue buttress against anterior translation of the humeral head. The subscapularis insertion is repaired anatomically (Fig. 23). The deltopectoral interval is reapproximated. Figure 24 shows the final result. It is important to note that this repair attaches the fibrous capsule directly to bone without intervening cartilage. Many other orthopaedic operations firmly fix fibrous tissue to bone, but few depend on the healing of fibrous tissue to cartilage or the healing of cartilage to bone. The cartilagenous labrum has been converted to an extraarticular structure in the anterior and anteroinferior aspects of the joint. CONCLUSION Figure 24. The final result. The repair attaches the fibrous capsule directly to bone without intervening cartilage. The cartilagenous labrum has been converted to an extraarticular structure in the anterior and anteroinferior aspects of the joint. capsular flap is brought down to the glenoid rim by sutures through the labrum rather than by sutures through bone. The medial edge of the lateral capsular flap ends up deep to and lateral to the cartilagenous labrum as in the standard Bankart repair. Figure 21 diagrams the medial edge of the lateral capsule being sutured to the boney glenoid rim deep to and lateral to the labral remnant. The resulting extracapsular position of the labral remnant (unless it has been abraded away) is a necessary feature of the standard Bankart repair, which is rarely described. The lateral edge of the medial capsule is tied into the same suture line to provide reinforcement (Fig. 22). The cartilagenous labrum is thus incorporated into the repair, In summary, the Bankart repair preserves the overall anatomy of the shoulder more than many alternative operations for shoulder instability. The Bankart operation repairs the capsule to the bone of the glenoid rim without intervening cartilage. The anatomy is distorted to the extent that the cartilagenous labrum, when present, is moved from its normal intraarticular position to an extraarticular position where it further butresses the humeral head against anterior translation. REFERENCES 1. Alexander AH, Grant JM: Provocative program for recurrent dislocation. Orthopaedics Today, page 8, March Bankart ASB: The pathology and treatment of recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint. Br J Surg 26: 26, Henry AK: Extensile Exposure. New York, Churchill Livingstone, 1970, pp Rowe CR: Bankart procedure for recurrent antenor dislocation of the shoulder. Strat Orthop Surg 2: 1-11, Rowe CR, Zarins B: Recurrent transient subluxation of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg 63A: , Rowe CR: Acute and recurrent dislocations of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg 44A: , Rowe CR, Patel D, Southmayd WW: The Bankart precedure: A long-term end result study. J Bone Joint Surg 60A: 1-15, 1978
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH Hospital
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH Hospital
The Shoulder. Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4
 The Shoulder Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4 Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Complex is the most mobile joint in the body. Scapula Clavicle Sternum Humerus Rib cage/thorax Shoulder Girdle It also includes
The Shoulder Anatomy and Injuries PSK 4U Unit 3, Day 4 Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Complex is the most mobile joint in the body. Scapula Clavicle Sternum Humerus Rib cage/thorax Shoulder Girdle It also includes
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX Tel#
 Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
The suction cup mechanism is enhanced by the slightly negative intra articular pressure within the joint.
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Stability A. The stability of the shoulder is improved by depth of the glenoid. This is determined by: 1. Osseous glenoid, 2. Articular cartilage of the glenoid, which is thicker at
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Stability A. The stability of the shoulder is improved by depth of the glenoid. This is determined by: 1. Osseous glenoid, 2. Articular cartilage of the glenoid, which is thicker at
Shoulder Instability
 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
Glenohumeral Joint Instability. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ
 1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM
 RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM D R. A M R I S H K R. J H A M S ( O R T H O ) A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R M E D I C A L C O L L E G E, K O L K A T A LABRUM Function as a chock-block,
RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM D R. A M R I S H K R. J H A M S ( O R T H O ) A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R M E D I C A L C O L L E G E, K O L K A T A LABRUM Function as a chock-block,
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
OBJECTIVES. Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability SHOULDER STABILITY SHOULDER STABILITY WHAT IS SHOULDER INSTABILITY? SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability Brian G. Leggin, PT, DPT, OCS Lead Therapist, Penn Therapy and Fitness at Valley Forge Adjunct Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, University
Therapists Management of Shoulder Instability Brian G. Leggin, PT, DPT, OCS Lead Therapist, Penn Therapy and Fitness at Valley Forge Adjunct Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, University
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai
 POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Orthopedics - Dr. Ahmad - Lecture 2 - Injuries of the Upper Limb
 The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Treatment of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Conflicting Study Outcomes. Prof. C. Milgrom Hadassah University Hospital Jerusalem, Israel
 Treatment of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Conflicting Study Outcomes Prof. C. Milgrom Hadassah University Hospital Jerusalem, Israel I. Natural history of shoulder dislocation and traditional
Treatment of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Conflicting Study Outcomes Prof. C. Milgrom Hadassah University Hospital Jerusalem, Israel I. Natural history of shoulder dislocation and traditional
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
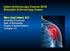
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
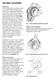 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder
 Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
The Upper Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
The Upper Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 11 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Sternoclavicular joint Double joint.? Each side separated by intercalating articular disc Grasp the mid-portion of your clavicle on one side
Body Planes. (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal
 Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
P.O. Box Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine
 P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
Shoulder Injuries. Glenoid labrum injuries. SLAP Lesions
 Shoulder Injuries functional anatomy clinical perspective impingement rotator cuff injuries glenoid labrum injuries dislocation Glenoid labrum injuries SLAP lesions stable or unstable traction/compression
Shoulder Injuries functional anatomy clinical perspective impingement rotator cuff injuries glenoid labrum injuries dislocation Glenoid labrum injuries SLAP lesions stable or unstable traction/compression
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER JOINT ANATOMY AND KINESIOLOGY
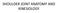 SHOULDER JOINT ANATOMY AND KINESIOLOGY SHOULDER JOINT ANATOMY AND KINESIOLOGY The shoulder joint, also called the glenohumeral joint, consists of the scapula and humerus. The motions of the shoulder joint
SHOULDER JOINT ANATOMY AND KINESIOLOGY SHOULDER JOINT ANATOMY AND KINESIOLOGY The shoulder joint, also called the glenohumeral joint, consists of the scapula and humerus. The motions of the shoulder joint
Chronic Shoulder Instability
 Chronic Shoulder Instability The shoulder is the most moveable joint in your body. It helps you to lift your arm, to rotate it, and to reach up over your head. It is able to turn in many directions. This
Chronic Shoulder Instability The shoulder is the most moveable joint in your body. It helps you to lift your arm, to rotate it, and to reach up over your head. It is able to turn in many directions. This
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Rehabilitation Protocol: Arthroscopic Anterior Capsulolabral Repair of the Shoulder - Bankart Repair Rehabilitation Guidelines
 Rehabilitation Protocol: Arthroscopic Anterior Capsulolabral Repair of the Shoulder - Bankart Repair Rehabilitation Guidelines Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington
Rehabilitation Protocol: Arthroscopic Anterior Capsulolabral Repair of the Shoulder - Bankart Repair Rehabilitation Guidelines Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography.
 Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
MUSCLES OF SHOULDER REGION
 Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
Patient ID. Case Conference. Physical Examination. Image examination. Treatment 2011/6/16
 Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Shoulder Instability
 Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
Shoulder Instability and Stabilisation
 Shoulder Instability and Stabilisation The benefit of the huge range of movements at the shoulder is that we are able to position the hand as required, the cost is that the shoulder is more likely to dislocate
Shoulder Instability and Stabilisation The benefit of the huge range of movements at the shoulder is that we are able to position the hand as required, the cost is that the shoulder is more likely to dislocate
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 789418, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789418 Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report Takeshi Kokubu,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 789418, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789418 Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report Takeshi Kokubu,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Arthroscopic Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Open Bankart Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Open Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction with Open Bankart Repair The anatomic configuration of the shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is often compared
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD
 Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
Surgical Treatment of Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability in American Football Players BY MICHAEL J. PAGNANI, MD, AND DAVID C.
 711 COPYRIGHT 2002 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Surgical Treatment of Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability in American Football Players BY MICHAEL J. PAGNANI, MD, AND DAVID
711 COPYRIGHT 2002 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Surgical Treatment of Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability in American Football Players BY MICHAEL J. PAGNANI, MD, AND DAVID
Subscapularis Avulsion in the Adolescent Athlete: Can Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques be used for Physeal-Sparing Surgical Repair?
 Subscapularis Avulsion in the Adolescent Athlete: Can Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques be used for Physeal-Sparing Surgical Repair? Alex L. Gornitzky, BS; Anish G.R. Potty, MD; James L. Carey MD, MPH; Theodore
Subscapularis Avulsion in the Adolescent Athlete: Can Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques be used for Physeal-Sparing Surgical Repair? Alex L. Gornitzky, BS; Anish G.R. Potty, MD; James L. Carey MD, MPH; Theodore
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum
 Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
Surgical Technique. Guide. Bristow-Latarjet Instability Shoulder System Open and Arthroscopic Techniques
 Surgical Technique Guide Bristow-Latarjet Instability Shoulder System Open and Arthroscopic Techniques a letter from dr. lafosse Dear Friends, Shoulder Instability has been treated differently with time
Surgical Technique Guide Bristow-Latarjet Instability Shoulder System Open and Arthroscopic Techniques a letter from dr. lafosse Dear Friends, Shoulder Instability has been treated differently with time
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Technical Guidelines SHOULDER
 Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines SHOULDER 1 Although patient s positioning for shoulder US varies widely across different Countries and Institutions reflecting multifaceted opinions and
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patien
 The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Shoulder Complex. Anatomy. Articulations 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas. Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus
 The Shoulder Complex Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Anatomy Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus Articulations Sternoclavicular SC joint. Sternum and Clavicle. Acromioclavicular AC
The Shoulder Complex Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Anatomy Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus Articulations Sternoclavicular SC joint. Sternum and Clavicle. Acromioclavicular AC
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Dislocations
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Dislocations 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Dislocations 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY PATIENT HANDBOOK Physical/Occupational Therapy 3755 Orange Place, Suite 101 Beachwood, OH 44122 216-312-6045 Therapist: Post-Op Visit: Anatomy and Function of the Shoulder The shoulder
SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY PATIENT HANDBOOK Physical/Occupational Therapy 3755 Orange Place, Suite 101 Beachwood, OH 44122 216-312-6045 Therapist: Post-Op Visit: Anatomy and Function of the Shoulder The shoulder
Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation
 Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint with tremendous flexibility and range of motion. The ball is the humeral head while the socket is the glenoid.
Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint with tremendous flexibility and range of motion. The ball is the humeral head while the socket is the glenoid.
REMINDER. Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns
 Understanding Shoulder Dysfunction REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns What is a healthy shoulder?
Understanding Shoulder Dysfunction REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns What is a healthy shoulder?
Congruent-Arc Latarjet Using the Glenoid Bone Loss Set with 3.75 mm Cannulated Screws Surgical Technique
 Congruent-Arc Latarjet Using the Glenoid Bone Loss Set with 3.75 mm Cannulated Screws Surgical Technique Congruent-Arc Latarjet The Arthrex Glenoid Bone Loss Set The Glenoid Bone Loss Set helps surgeons
Congruent-Arc Latarjet Using the Glenoid Bone Loss Set with 3.75 mm Cannulated Screws Surgical Technique Congruent-Arc Latarjet The Arthrex Glenoid Bone Loss Set The Glenoid Bone Loss Set helps surgeons
Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective
 Anatomic Considerations Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective Michael D. Loeb, MD Texas Orthopedics, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation Associates Austin, Texas Static Stabilizers Osseous
Anatomic Considerations Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective Michael D. Loeb, MD Texas Orthopedics, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation Associates Austin, Texas Static Stabilizers Osseous
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Type II SLAP lesions are created when the biceps anchor has pulled away from the glenoid attachment.
 Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Shoulder Pathologies
 Shoulder Pathologies In its early stages, AC joint osteoarthritis usually causes pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder around the joint. The pain is often worse when the arm is brought
Shoulder Pathologies In its early stages, AC joint osteoarthritis usually causes pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder around the joint. The pain is often worse when the arm is brought
Glenohumeral Joint. Glenohumeral Joint. Glenohumeral Joint. Glenohumeral Joint. Glenohumeral Joint. Glenohumeral Joint
 The Shoulder Joint Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 5-1 Shoulder joint is attached to axial skeleton
The Shoulder Joint Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 5-1 Shoulder joint is attached to axial skeleton
The Shoulder. By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson
 The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
Shoulder Trauma (Fractures and Dislocations)
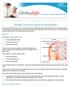 Shoulder Trauma (Fractures and Dislocations) Trauma to the shoulder is common. Injuries range from a separated shoulder resulting from a fall onto the shoulder to a high-speed car accident that fractures
Shoulder Trauma (Fractures and Dislocations) Trauma to the shoulder is common. Injuries range from a separated shoulder resulting from a fall onto the shoulder to a high-speed car accident that fractures
R. Frank Henn III, MD. Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine Residency Program Director
 R. Frank Henn III, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine Residency Program Director Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose 1. Labral anatomy 2. Adaptations of the throwing shoulder
R. Frank Henn III, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine Residency Program Director Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose 1. Labral anatomy 2. Adaptations of the throwing shoulder
D Degenerative joint disease, rotator cuff deficiency with, 149 Deltopectoral approach component removal with, 128
 Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
The Shoulder. Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information. The Shoulder
 1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
1 ! The most ACCESSIBLE to sonographic exam! The most MOBILE and VULNERABLE extremity AND Systematically scanning the shoulder provides extremely useful diagnostic information! The Goal for this section
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment
 SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.421 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(3): 421-426, 2010 The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.421 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(3): 421-426, 2010 The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior
Anatomy GH Joint. Glenohumeral Instability. Components of Stability. Components of Stability 7/7/2017. AllinaHealthSystem
 Glenohumeral Instability Dr. John Steubs Allina Sports Medicine Conference July 7, 2017 Anatomy GH Joint Teardrop or oval shape Inherently unstable Golf ball and tee analogy Stabilizers Static Dynamic
Glenohumeral Instability Dr. John Steubs Allina Sports Medicine Conference July 7, 2017 Anatomy GH Joint Teardrop or oval shape Inherently unstable Golf ball and tee analogy Stabilizers Static Dynamic
"Stability and Instability of RTSA"
 Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases
 Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Lexington, KY Broken screw s/p Bristow procedure
Intern Arthroscopy Course 2015 Shoulder Arthroscopy Cases Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Sports Medicine Lexington, KY Broken screw s/p Bristow procedure
Posterior Shoulder Instability
 Posterior Shoulder Instability Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor of Orthopaedics University of Connecticut USA Classification of Posterior Instability Dislocation -acute -chronic- fixed or locked Subluxation
Posterior Shoulder Instability Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor of Orthopaedics University of Connecticut USA Classification of Posterior Instability Dislocation -acute -chronic- fixed or locked Subluxation
Traumatic shoulder dislocation in the adolescent athlete: advances in surgical treatment Christopher R. Good and John D.
 Traumatic shoulder dislocation in the adolescent athlete: advances in surgical treatment Christopher R. Good and John D. MacGillivray Purpose of review The shoulder joint has the greatest range of motion
Traumatic shoulder dislocation in the adolescent athlete: advances in surgical treatment Christopher R. Good and John D. MacGillivray Purpose of review The shoulder joint has the greatest range of motion
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Instability
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Instability 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Instability 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of
Operative Technique Resurfacing Humeral Head
 EXACTECH SHOULDER Operative Technique Resurfacing Humeral Head TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS... 1 PATIENT POSITIONING... 2 SURGICAL APPROACH... 2 SIZING THE HUMERUS FOR A RESURFACING
EXACTECH SHOULDER Operative Technique Resurfacing Humeral Head TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 1 SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS... 1 PATIENT POSITIONING... 2 SURGICAL APPROACH... 2 SIZING THE HUMERUS FOR A RESURFACING
Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment. Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician
 Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician Apophyseal injuries; How to diagnose and manage? Goals for tonight Recognise
Football and netball season A review of the apophysis and the acute shoulder: assessment Simon Locke Sport and Exercise Physician Apophyseal injuries; How to diagnose and manage? Goals for tonight Recognise
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of Shoulder Instability must be made in conjunction with your
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of Shoulder Instability must be made in conjunction with your
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY
 UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Acute traumatic posterior shoulder instability is
 Arthroscopic Treatment of a Reverse Hill-Sachs Lesion Richard E. Duey, M.D., and Stephen S. Burkhart, M.D. Abstract: Acute traumatic posterior shoulder instability is a rare injury. Such injuries can result
Arthroscopic Treatment of a Reverse Hill-Sachs Lesion Richard E. Duey, M.D., and Stephen S. Burkhart, M.D. Abstract: Acute traumatic posterior shoulder instability is a rare injury. Such injuries can result
Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations.
 Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History/Demographics Bimodal: young-high energy, elderly-low energy(osteoporosis) 45% of all humerus fx. elderly females 4:1 over males
Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History/Demographics Bimodal: young-high energy, elderly-low energy(osteoporosis) 45% of all humerus fx. elderly females 4:1 over males
06/Μαρ/2013 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF. ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES
 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Types of shoulder Dislocation: Shoulder dislocation. 1. Anterior 2. Posterior 3. Luxatio erecta (inferior dislocation)
 Types of shoulder Dislocation: Shoulder dislocation 1. Anterior 2. Posterior 3. Luxatio erecta (inferior dislocation) Anterior Dislocation: head is dislocated anterior to the glenoid Most common among
Types of shoulder Dislocation: Shoulder dislocation 1. Anterior 2. Posterior 3. Luxatio erecta (inferior dislocation) Anterior Dislocation: head is dislocated anterior to the glenoid Most common among
Technique Guide Glenoid Latarjet System
 Technique Guide Glenoid Latarjet System Glenoid Grafting without the Grief The Glenojet Allograft System was created to replace and augment anterior glenoid bone loss associated with trauma, recurrent
Technique Guide Glenoid Latarjet System Glenoid Grafting without the Grief The Glenojet Allograft System was created to replace and augment anterior glenoid bone loss associated with trauma, recurrent
Secret shoulder secrets Dominik Meyer
 Secret shoulder secrets Dominik Meyer Head of the prostheses better too big or too small? In case of stiffness: smaller (loosening of capsule) In case of hyperlaxity / instability or strong correction
Secret shoulder secrets Dominik Meyer Head of the prostheses better too big or too small? In case of stiffness: smaller (loosening of capsule) In case of hyperlaxity / instability or strong correction
The shoulder girdle consists of the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular and scapulothoracic joints
 Anatomy of Shoulder Girdle The shoulder girdle consists of the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular and scapulothoracic joints Glenohumeral Joint A ball and socket synoval joint with a large
Anatomy of Shoulder Girdle The shoulder girdle consists of the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular and scapulothoracic joints Glenohumeral Joint A ball and socket synoval joint with a large
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Latarjet Protocol
 Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Latarjet Protocol Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. Shoulder instability may be caused from congenital deformity, recurrent overuse activity, and/or traumatic dislocation.
Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Latarjet Protocol Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. Shoulder instability may be caused from congenital deformity, recurrent overuse activity, and/or traumatic dislocation.
ANTERIOR SHOULDER STABILIZATION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
 ANTERIOR SHOULDER STABILIZATION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Background Ohio State s Anterior Shoulder Stabilization Rehabilitation Guideline is to be utilized following open or arthroscopic anterior shoulder
ANTERIOR SHOULDER STABILIZATION CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Background Ohio State s Anterior Shoulder Stabilization Rehabilitation Guideline is to be utilized following open or arthroscopic anterior shoulder
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide
 MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears:
 Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
Shoulder: Clinical Anatomy, Kinematics & Biomechanics
 Shoulder: Clinical Anatomy, Kinematics & Biomechanics Dr. Alex K C Poon Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Clinical Anatomy the application of anatomy to
Shoulder: Clinical Anatomy, Kinematics & Biomechanics Dr. Alex K C Poon Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Clinical Anatomy the application of anatomy to
Instability of the shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet. Under review. Page 1
 Instability of the shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Shoulder instability There is a balance between movements in the shoulder whilst maintaining stability. When the shoulder
Instability of the shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Shoulder instability There is a balance between movements in the shoulder whilst maintaining stability. When the shoulder
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention
 Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs
 Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs Mr Ilia Elkinson BHB, MBChB, FRACS (Ortho), FNZOA Orthopaedic and Upper Limb Surgeon Bowen Hospital Wellington Hospital Objectives Review pertinent anatomy of the
Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs Mr Ilia Elkinson BHB, MBChB, FRACS (Ortho), FNZOA Orthopaedic and Upper Limb Surgeon Bowen Hospital Wellington Hospital Objectives Review pertinent anatomy of the
Labral Tears. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
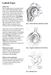 Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 January 19, 2012 John W. Hinchey, MD Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Shoulder & Elbow Service This live activity is designated for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit tm. Physicians should claim only
January 19, 2012 John W. Hinchey, MD Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Shoulder & Elbow Service This live activity is designated for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit tm. Physicians should claim only
The ball-and-socket articulation at the glenohumeral joint is between the convex
 SLAP Lesion Repair Emily Cotey, Emily Hurysz, and Patrick Schroeder Abstract SLAP lesion, which stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior, is a detachment tear of the superior labrum that originates
SLAP Lesion Repair Emily Cotey, Emily Hurysz, and Patrick Schroeder Abstract SLAP lesion, which stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior, is a detachment tear of the superior labrum that originates
