Original Article. Abstract
|
|
|
- Cory York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Chagas-Neto FA et al. / Diagnostic performance of 3D TSE MRI of the knee at 1.5 T Diagnostic performance of 3D TSE MRI versus 2D TSE MRI of the knee at 1.5 T, with prompt arthroscopic correlation, in the detection of meniscal and cruciate ligament tears * Desempenho diagnóstico da técnica 3D-TSE de RM do joelho comparada com a técnica 2D-TSE em 1,5 T na detecção de rupturas meniscais e ligamentares com correlação artroscópica imediata Francisco Abaeté Chagas-Neto 1, Marcello Henrique Nogueira-Barbosa 2, Mário Müller Lorenzato 3, Rodrigo Salim, Maurício Kfuri-Junior, Michel Daoud Crema 5 Chagas-Neto FA, Nogueira-Barbosa MH, Lorenzato MM, Salim R, Kfuri-Junior M, Crema MD. Diagnostic performance of 3D TSE MRI versus 2D TSE MRI of the knee at 1.5 T, with prompt arthroscopic correlation, in the detection of meniscal and cruciate ligament tears. Radiol Bras Mar/Abr; 9(2):69 7. Abstract Resumo Objective: To compare the diagnostic performance of the three-dimensional turbo spin-echo (3D TSE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique with the performance of the standard two-dimensional turbo spin-echo (2D TSE) protocol at 1.5 T, in the detection of meniscal and ligament tears. Materials and Methods: Thirty-eight patients were imaged twice, first with a standard multiplanar 2D TSE MR technique, and then with a 3D TSE technique, both in the same 1.5 T MRI scanner. The patients underwent knee arthroscopy within the first three days after the MRI. Using arthroscopy as the reference standard, we determined the diagnostic performance and agreement. Results: For detecting anterior cruciate ligament tears, the 3D TSE and routine 2D TSE techniques showed similar values for sensitivity (93% and 93%, respectively) and specificity (80% and 85%, respectively). For detecting medial meniscal tears, the two techniques also had similar sensitivity (85% and 83%, respectively) and specificity (68% and 71%, respectively). In addition, for detecting lateral meniscal tears, the two techniques had similar sensitivity (58% and 5%, respectively) and specificity (82% and 92%, respectively). There was a substantial to almost perfect intraobserver and interobserver agreement when comparing the readings for both techniques. Conclusion: The 3D TSE technique has a diagnostic performance similar to that of the routine 2D TSE protocol for detecting meniscal and anterior cruciate ligament tears at 1.5 T, with the advantage of faster acquisition. Keywords: Knee; Menisci; ; Magnetic resonance imaging; Arthroscopy. Objetivo: Comparar o desempenho diagnóstico da técnica tridimensional turbo spin-eco (3D TSE) de ressonância magnética (RM) do joelho na detecção de rupturas meniscais e ligamentares em comparação com o protocolo bidimensional turbo spin-eco (2D TSE). Materiais e Métodos: A sequência 3D TSE foi adicionada ao protocolo de rotina 2D TSE em 38 pacientes que foram submetidos a cirurgia artroscópica do joelho em até três dias após a realização da RM. Usando os achados artroscópicos como referência padrão ouro, foram calculados o desempenho diagnóstico e a concordância entre os protocolos. Resultados: A técnica 3D TSE e o protocolo 2D TSE apresentaram, respectivamente, sensibilidade (93%/93%) e especificidade (80%/ 85%) semelhantes na detecção de rupturas do ligamento cruzado anterior, sensibilidade (85%/83%) e especificidade (68%/71%) semelhantes na detecção de rupturas do menisco medial, assim como sensibilidade (58%/5%) e especificidade (82%/92%) semelhantes na detecção de rupturas do menisco lateral. A concordância intraobservador entre os dois métodos foi de substancial a quase perfeita em todos os parâmetros avaliados para ambos os leitores. Conclusão: A técnica 3D- SE apresentou desempenho diagnóstico semelhante ao protocolo de rotina 2D TSE na detecção de rupturas meniscais e ligamentares em magneto de 1,5 T, com a vantagem de possibilitar uma redução significativa no tempo de aquisição. Unitermos: Joelho; Menisco; Ligamento cruzado anterior; Ressonância magnética; Artroscopia. * Study conducted in the Division of Radiology, Internal Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto da Universidade de São Paulo (FMRP- USP), Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil. 1. PhD, Professor of Radiology, Division of Radiology, Universidade de Fortaleza (Unifor) and Centro Universitário Christus; Section Head, Musculoskeletal Imaging, Hospital Antonio Prudente, Fortaleza, CE, Brazil. 2. PhD, Full Professor of Radiology, Division of Radiology, Internal Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto da Universidade de São Paulo (FMRP-USP), Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil. 3. MD, Radiologist, Radiologia Especializada de Ribeirão Preto, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil.. PhD, Department of Biomechanics, Medicine and Rehabilitation of the Locomotor Apparatus, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto da Universidade de São Paulo (FMRP-USP), Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brazil. 5. MD, Radiologist, Radiology Department, Saint-Antoine Hospital, University of Paris VI, Paris, France; Department of Radiology, Quantitative Imaging Center, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA; Department of Radiology and Teleimagem, Hospital do Coração (HCor), São Paulo, SP, Brazil. Mailing Address: Dr. Francisco Abaeté Chagas-Neto. Avenida Washington Soares, 1321, Edson Queiroz. Fortaleza, CE, Brazil, fabaeteneto@gmail. com. Received March 20, Accepted after revision June 11, Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2): Colégio Brasileiro de Radiologia e Diagnóstico por Imagem
2 INTRODUCTION Routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols for the knee often use fluid-sensitive sequences based on twodimensional (2D) acquisitions, acquired in three orthogonal planes (coronal, axial, and sagittal). These sequences are widely used in clinical practice as well as in clinical research (1 3). Although 2D sequences exhibit high spatial resolution, they are acquired with relatively thick slices (2.0.0 mm) and may present gaps between slices, which can generate partial volume artifacts. When 2D sequences are the source for reformation, it is also impossible to generate reconstructions in multiple planes without a significant loss of quality. Three-dimensional (3D) turbo spin-echo (TSE) MRI with isotropic or nearly isotropic resolution techniques has the potential to improve the depiction of pathology by reducing partial volume averaging as well as time efficiency of the MRI use in the musculoskeletal system (1, 7). Such volumetric acquisitions may be used in order to create multiplanar reconstructions, thereby eliminating the need to repeat sequences, providing spin-echo tissue contrast in different planes. In addition, the acquisition of source images is faster with 3D TSE than with the triplanar 2D TSE protocol (1, 7). If the 3D technique can provide at least the same quality of assessment as does the 2D technique and do it in less time, with the possibility of multiplanar reconstruction, the differences between 2D and 3D TSE could have a significant effect on clinical practice and research. The majority of studies assessing the diagnostic performance of 3D TSE MRI in detecting pathology of the knee have used 3.0 T scanners (1, 10), and there are therefore few data available regarding the application of the technique in the more widely available 1.5 T scanners. There are, however, some controversies and disadvantages that should be mentioned before one considers replacing the routine 2D TSE protocol with the 3D TSE technique in the assessment of the knee. Acquisition times are typically longer for the 3D technique than for the single-acquisition 2D technique, which makes the former more susceptible to motion artifacts. Decreasing the time of acquisition for 3D techniques, preferable for a busy clinical practice, is often challenging and will likely have an impact on the quality of the images acquired. Recent studies have demonstrated that routine 2D protocols are more reliable in depicting meniscal pathology than is the 3D protocol, that difference likely being related to decreased in-plane resolution and image blurring (10), as well as to a decrease in the number of signals averaged (to accelerate the acquisition time) and to suboptimal soft-tissue contrast (8). The main purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of 3D TSE MRI at 1.5 T in the detection of meniscal and ligament tears, in comparison with that of the standard 2D TSE protocol, using prompt surgical findings (arthroscopy) as the reference standard. Our hypothesis was that a single acquisition with the 3D TSE technique with multiplanar reconstructions would have a diagnostic performance similar to that of the 2D TSE routine protocol, at 1.5 T. MATERIALS AND METHODS Participants After approval by the local institutional review board, we recruited participants who agreed to take part after explanation of research methods and objectives. All participants gave written informed consent. We evaluated 38 consecutive patients who had been referred for knee arthroscopy and agreed to participate in this prospective study by having an MRI of the knee prior to surgery. There were three main indications for the patients scheduled for surgery and included in this study: knee instability, joint locking, and chronic joint pain without improvement after clinical management. The study sample comprised 28 men and 10 women, from 21 to 57 years of age (mean, 33.5 ± 10. years). MRI acquisition All knees were imaged with the same 1.5 T MRI scanner (Philips Achieva 1.5 T MRI System; Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) and an 8-channel SENSE knee coil. Routine 2D and 3D TSE images were acquired on the same day. The MRI parameters and acquisition time for both techniques are summarized in Table 1. Table 1 MRI parameters for the 2D and 3D techniques. All sequences were acquired with intermediate-weighted spectral adiabatic inversion recovery. MRI parameter Sagittal 2D TSE Coronal 2D TSE Axial 2D TSE Sagittal source 3D TSE Repetition time (ms) Echo time (ms) Matrix (pixels) Field of view (cm) Slice thickness (mm) Echo train (n) Excitations (n) Bandwidth (khz) Acquisition time min 3 sec* min 30 sec* min* min * Total 2D TSE multiplanar acquisition time: 8 minutes 13 seconds. Total 3D TSE single sagittal plane acquisition time: 5 minutes (approximately 0% less than in the 2D TSE protocol). 70 Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2):69 7
3 The sagittal source images from the 3D TSE technique were used in order to create sagittal, coronal, and axial reformatted images of the knee joint with a slice thickness of 1.5 mm. The reformatted images were used for the 3D TSE assessment of the knee. The post-processing of the 3D TSE sequence was performed by a fellow in musculoskeletal radiology on a Philips Achieva MRI workstation (Extended MR Workspace; Philips Medical Systems) immediately after the images had been acquired. MRI assessment Images were interpreted independently by two musculoskeletal radiologists. Reader 1 was a senior radiologist with ten years of experience, and reader 2 was a fellow in musculoskeletal radiology with one year of training. Both were blinded to all clinical information about the MRI. The 2D and 3D TSE images were assessed separately and independently by both radiologists. They assessed the 3D images first and the 2D images after a minimum interval of four weeks. The delay in the second reading was intended to minimize the risk of interpretation and recognition bias. The medial and lateral menisci were evaluated throughout their length (anterior horn, body, and posterior horn) and were classified according to the presence or absence of a meniscal tear. A meniscal tear was defined as either meniscal distortion or intermediate to high signal intensity extending into the articular surface of the meniscus on at least two consecutive sagittal or coronal images (11). Intrameniscal signal changes were not considered indicative of meniscal tears. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) were both analyzed according to the presence or absence of tears, regardless of whether the tears were partial or complete. The signs of cruciate ligament tear were an abnormal course, abnormal signal intensity, and partial or complete discontinuity (12 1). Arthroscopic knee surgery All knee arthroscopies were performed within three days after the MRI, 80% being performed on the same day. The arthroscopies were performed by one of two experienced knee surgeons at our institution with 5 and 20 years of practice, respectively. During all arthroscopies, a complete inventory of the joint was performed, with special attention to and documentation of menisci and cruciate ligaments, which were assessed according to the presence or absence of tears. Analytic approach The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy for the detection of meniscal and cruciate ligament tears were calculated separately for each of the MRI protocols, using surgical findings (arthroscopy) as the reference standard. To increase the statistical power for the comparison between the two imaging protocols (), the data from the independent reviews of both readers were assessed separately and then mathematically combined when calculating sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy. Kappa statistics were used in order to measure the interobserver agreement, as well as to determine the intraobserver agreement between the two methods, for each reader (15). To calculate the differences in diagnostic performance between the 3D TSE and the 2D TSE MRI techniques for dichotomized values (presence or absence of pathology), we used Fisher s exact test, with 95% confidence intervals, values of p < 0.05 being considered statistically significant. The statistical analysis was performed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). RESULTS The number of positive findings (tears) detected by each reader in each MRI technique is presented in Table 2, as is the number of positive findings detected by arthroscopy. The overall combined sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for the detection of tears of the ACL, the medial meniscus, and the lateral meniscus are displayed in Table 3. Table 2 Number of positive findings detected by each reader in each MRI technique assessed. Reader Technique 2D MRI 3D MRI 2D MRI 3D MRI tears (n = 2) n, number of positive findings at arthroscopy. tears (n = 13) ACL tears (n = 28) Table 3 Overall combined sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and agreement (kappa) for 2D and 3D MRI protocols in the detection of tears of the anterior cruciate ligament, medial meniscus, and lateral meniscus. 2D: both readers combined 3D: both readers combined Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Overall 2D vs. 3D agreement MRI feature 93 [83 98] 83 [70 93] 5 [33 73] 85 [62 97] 71 [51 87] 92 [81 98] 91 [82 99] 79 [67 91] 79 [67 91] 93 [83 98] 85 [72 9] 58 [37 77] 80 [56 9] 68 [8 8] 82 [69 91] 89 [80 98] 79 [67 91] 7 [63 9] 0.83 [ ] 0.89 [ ] 0.7 [ ] p-value range: Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2):
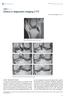
4 Regarding the detection of ACL tears, the overall combined sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were similar for the two techniques. For the 2D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 95% and 81%, respectively. For the 3D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 93% and 80%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the protocols for the detection of ACL tears. The kappa agreement between the two methods was 0.83 (range, ). Regarding the detection of medial meniscal tears, the overall combined sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were similar for the two techniques. For the 2D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 83% and 71%, respectively. For the 3D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 82% and 73%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the protocols for the detection of medial meniscal tears (Figure 1). The kappa agreement between the two methods was 0.89 (range, ). Regarding the detection of lateral meniscal tears, the overall combined sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were similar for the two techniques. For the 2D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 78% and 79%, respectively. For the 3D protocol, the overall combined positive and negative predictive values were 63% and 79%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the protocols for the detection of lateral meniscal tears. The kappa agreement between the two methods was 0.7 (range, ). Table shows the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and intraobserver agreement regarding the detection of ACL, medial meniscal, and lateral meniscal tears, for both readers A B C Figure 1. A 36-year-old woman with a tear of the medial meniscus. Sagittal MRI (A: 2D TSE; and B: 3D TSE volume isotropic turbo spin-echo acquisition [VISTA]) of the knee depicting a tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus (arrows). C: Corresponding arthroscopic correlation of the tear (arrow). Table Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and intraobserver agreement (kappa) for the 2D and 3D MRI protocols in the detection of anterior cruciate ligament, medial meniscus, and lateral meniscus tears for both readers separately. Reader 1 2D 3D Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Intraobserver agreement MRI feature 93 [77 99] 83 [63 95] 5 [25 81] 90 [56 100] 6 [35 87] 92 [7 99] 89 [7 100] 76 [58 95] 79 [59 9] 89 [72 99] 88 [68 97] 62 [32 86] 80 [ 97] 57 [29 82] 76 [55 91] 87 [71 100] 76 [58 95] 71 [9 85] 0.87 [ ] 0.88 [ ] 0.70 [ ] Reader 2 2D 3D Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity Accuracy Intraobserver agreement 93 [77 99] 83 [63 95] 5 [25 81] 80 [ 97] 79 [9 95] 92 [7 99] 89 [7 100] 82 [62 98] 79 [59 9] 96 [82 100] 83 [63 95] 5 [25 81] 80 [ 97] 79 [9 95] 88 [69 97] 92 [77 100] 82 [62 98] 76 [56 91] 0.79 [ ] 0.89 [ ] 0.79 [ ] p-value range: Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2):69 7
5 separately. There were no significant differences between the two protocols in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, or accuracy, in the separate or combined readings (p-values ranging from 0.25 to 1.00). The interobserver agreement for the detection of ACL, medial meniscal, and lateral meniscal tears, for both MRI techniques, is presented in Table 5. There were no significant differences between the two methods in terms of the kappa interobserver agreement (p-values ranging from 0.58 to 0.99). On 2D and 3D TSE images, both readers correctly detected the two PCL tears that were found by the surgeons, as well as correctly identifying normal morphology of the PCL in the remaining cases. Table 5 Interobserver agreement (kappa) for the 2D and 3D MRI protocols for detecting tears of the anterior cruciate ligament, medial meniscus, and lateral meniscus. MRI feature Interobserver agreement 2D TSE 0.80 [ ] 0.89 [ ] 0.56 [ ] 3D TSE VISTA 0.73 [ ] 0.77 [ ] 0.52 [ ] p-value range: VISTA, volume isotropic turbo spin-echo acquisition. DISCUSSION Imaging methods are essential for the evaluation of knee injuries (16,17). Among the various methods, MRI is one of considerable importance. Three-dimensional MRI sequences obtained with isotropic or nearly isotropic resolution techniques can be manipulated to provide high-resolution multiplanar reconstructions. The diagnostic performance of several 3D isotropic-type gradient-echo sequences has been previously tested in the evaluation of articular cartilage pathology (18 20) : spoiled gradient-recalled echo; double-echo steady-state; driven equilibrium Fourier transform; fast low-angle shot; and balanced steady-state free precession. However, 3D gradient-echo acquisition protocols are time consuming and cannot completely replace routine 2D TSE, because they do not allow accurate assessment of other important joint structures such as the menisci, ligaments and subchondral bone changes (18 20). Recently, 3D TSE MRI techniques were introduced that provide isotropic or nearly isotropic resolution. Previous studies have shown that this technique has good diagnostic performance for the detection of cartilaginous, meniscal, and ligament lesions with a 3.0 T magnet (1, 10). It should also be noted that acquisition of the source images was significantly faster with the 3D TSE protocol than with the triplanar 2D TSE protocol. The volume isotropic turbo spin-echo acquisition MRI technique provides high-resolution volumetric intermediate- weighted images acquired with 3D TSE and is clinically available for 1.5 and 3.0 T systems. To our knowledge, there have been no previous studies testing the diagnostic performance of this technique in detecting meniscal and ligament tears of the knee in a 1.5 T scanner and comparing the results promptly with arthroscopic correlation. We found that there were no significant differences between 2D and 3D TSE techniques regarding the detection of ACL and meniscal tears, with substantial to almost perfect intraobserver and interobserver agreement for medial meniscal and ACL tears. Similar results have been obtained in previous studies testing 3D TSE sequences (1, 7). The only discrepancy between our study and those in the current literature was the relatively lower sensitivity for lateral meniscal tears in both MRI techniques, with moderate interobserver agreement (1, 10). We retrospectively reviewed the six cases for which lateral meniscal tears were missed on MRI and found that four of them were very small peripheral flap tears in patients with complete ACL tears or extensive medial meniscal tears. The fact that those tears were subtle even in arthroscopy probably influenced our results. However, the purpose of the present study was to compare the diagnostic performance of the two techniques. Two previous studies presented different from ours results when testing the 3D TSE sequence in the knee joint and concluded that 2D TSE acquisitions are more reliable than are 3D TSE acquisitions (8,10). Van Dyck et al. suggested that, although 3D TSE may be a valuable component of a knee MRI protocol at 3.0 T, it cannot entirely replace routine 2D MRI in the assessment of the knee (10). However, other authors have tested 3D TSE MRI of the knee and concluded that its diagnostic performance is comparable to that of conventional 2D sequences in the detection of meniscal and ACL tears (6,7). Ai et al. stated that the 3D TSE sequence is comparable if not superior to conventional 2D imaging for comprehensive joint assessment of knee injuries and predicted that it is likely to replace the currently used 2D imaging protocols for the evaluation of knee injuries (7). This study has some notable strengths. We had the opportunity to optimize the time between MRI acquisition and arthroscopy, which were performed on the same day in 80% of the cases, with a maximum interval of three days. In previous studies, the mean time between imaging and arthroscopy has ranged from four weeks to four months, which could compromise the reliability of the imaging findings in relation to the surgical data (1, 10). In addition, the different experience levels of the readers in our study did not appear to have a significant effect on the final diagnostic performance, which suggests that the 3D TSE technique can also be successfully interpreted by readers with varying degrees of expertise. Our study has some limitations. We had a relatively small sample (38 subjects), which made it impossible to analyze the diagnostic performance of 3D TSE for PCL tears, because there were only two positive cases. In addition, we did not Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2):
6 evaluate the articular cartilage. The complexity of grading cartilage pathology and the potential assessment of cartilage pathology in different regions/compartments of the knee using the 3D TSE technique would require careful standardization, as well as the evaluation of a much larger sample, in order to achieve adequate statistical power. Furthermore, the relatively thick slices used for the standard 2D TSE sequences (.0 mm) could potentially reduce the sensitivity and specificity of that technique. Moreover, there was an inherent referral bias in that only patients referred for arthroscopy were included in the study. There was also a verification bias, because the readers knew which MRI technique they were reading (separate rolls of readings for each protocol and obvious imaging features). The minimum interval of four weeks between the two readings was intended to minimize interpretation and recognition bias. Another potential limitation was that we did not categorize in detail the types and locations of the meniscal and cruciate ligament tears. With such a small sample size, we would not have had enough statistical power to test the ability of the two techniques to depict different types and locations of tears, in comparison with that of arthroscopy. Although the readers had more previous experience with the 2D TSE sequences than with the 3D TSE technique, the novelty was reduced because they had been assessing 3D TSE images in clinical practice for at least 12 months prior to the study, as recommended in the literature (8). On the basis of the results of the present study, we cannot immediately recommend that radiologists replace the routine 2D TSE technique with the 3D TSE protocol for knee MRI, because our assessment was limited to the menisci and cruciate ligaments. However, we feel that the results of this study represent an important step toward implementing this technique in clinical practice. In conclusion, we demonstrated that 3D TSE is a reliable technique and has a diagnostic performance similar to that of the routine 2D TSE MR protocol for detecting meniscal and ACL tears at 1.5 T. The 3D TSE MRI technique has the advantage of faster acquisition times, which would be important in clinical practice to increase patient comfort and the efficiency of the MRI scanner. Acknowledgments This study received financial support from the Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (Finep) (Brazilian Financing Agency for Studies and Projects). REFERENCES 1. Kijowski R, Davis KW, Woods MA, et al. Knee joint: comprehensive assessment with 3D isotropic resolution fast spin-echo MR imaging diagnostic performance compared with that of conventional MR imaging at 3.0 T. Radiology. 2009;252: Peterfy CG, Gold G, Eckstein F, et al. MRI protocols for wholeorgan assessment of the knee in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;1 Suppl A:A Peterfy CG, Schneider E, Nevitt M. The osteoarthritis initiative: report on the design rationale for the magnetic resonance imaging protocol for the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16: Kijowski R, Davis KW, Blankenbaker DG, et al. Evaluation of the menisci of the knee joint using three-dimensional isotropic resolution fast spin-echo imaging: diagnostic performance in 250 patients with surgical correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;1: Ristow O, Steinbach L, Sabo G, et al. Isotropic 3D fast spin-echo imaging versus standard 2D imaging at 3.0 T of the knee image quality and diagnostic performance. Eur Radiol. 2009;19: Jung JY, Yoon YC, Kwon JW, et al. Diagnosis of internal derangement of the knee at 3.0-T MR imaging: 3D isotropic intermediateweighted versus 2D sequences. Radiology. 2009;253: Ai T, Zhang W, Priddy NK, et al. Diagnostic performance of CUBE MRI sequences of the knee compared with conventional MRI. Clin Radiol. 2012;67:e Subhas N, Kao A, Freire M, et al. MRI of the knee ligaments and menisci: comparison of isotropic-resolution 3D and conventional 2D fast spin-echo sequences at 3 T. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197: Jung JY, Jee WH, Park MY, et al. Meniscal tear configurations: categorization with 3D isotropic turbo spin-echo MRI compared with conventional MRI at 3 T. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012;198:W Van Dyck P, Gielen JL, Vanhoenacker FM, et al. Diagnostic performance of 3D SPACE for comprehensive knee joint assessment at 3 T. Insights Imaging. 2012;3: De Smet AA, Tuite MJ. Use of the two-slice-touch rule for the MRI diagnosis of meniscal tears. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187: Robertson PL, Schweitzer ME, Bartolozzi AR, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament tears: evaluation of multiple signs with MR imaging. Radiology. 199;193: Fischer SP, Fox JM, Del Pizzo W, et al. Accuracy of diagnoses from magnetic resonance imaging of the knee. A multi-center analysis of one thousand and fourteen patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73: Mink JH, Levy T, Crues JV 3rd. Tears of the anterior cruciate ligament and menisci of the knee: MR imaging evaluation. Radiology. 1988;167: Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33: Arend CF. Sonography of the iliotibial band: spectrum of findings. Radiol Bras. 201;7: Nakamura SA, Lorenzato MM, Engel EE, et al. Incidental enchondromas at knee magnetic resonance imaging: intraobserver and interobserver agreement and prevalence of imaging findings. Radiol Bras. 2013;6: Duc SR, Pfirrmann CW, Schmid MR, et al. Articular cartilage defects detected with 3D water-excitation true FISP: prospective comparison with sequences commonly used for knee imaging. Radiology. 2007;25: Duc SR, Koch P, Schmid MR, et al. Diagnosis of articular cartilage abnormalities of the knee: prospective clinical evaluation of a 3D water-excitation true FISP sequence. Radiology. 2007;23: Crema MD, Roemer FW, Marra MD, et al. Articular cartilage in the knee: current MR imaging techniques and applications in clinical practice and research. Radiographics. 2011;31: Radiol Bras Mar/Abr;9(2):69 7
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Key words: arthroscopy, orthopaedic examination, magnetic resonance imaging, knee injury.
 Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the Knee
 doi: 10.5505/actamedica.2016.81905 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 4 Issue 3 2016 Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the
doi: 10.5505/actamedica.2016.81905 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 4 Issue 3 2016 Quantitative Comparison of 2D and 3D MRI Techniques for the Evaluation of Chondromalacia Patellae in 3.0T MR Imaging of the
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Isotropic Resolution 3D FSE MRI of Articular Cartilage of Knee Joint Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Cristy N. Gustas 1 Donna G. Blankenbaker 2 Alejandro
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Isotropic Resolution 3D FSE MRI of Articular Cartilage of Knee Joint Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Cristy N. Gustas 1 Donna G. Blankenbaker 2 Alejandro
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
imri 2018;22:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
Original Article. José Luiz de Sá Neto 1, Marcelo Novelino Simão 2, Michel Daoud Crema 3, Edgard Eduard Engel 4, Marcello Henrique Nogueira-Barbosa 5
 Original Article Sá Neto JL et al. / MRI in the evaluation of periosteal reactions Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of periosteal reactions in bone sarcomas using
Original Article Sá Neto JL et al. / MRI in the evaluation of periosteal reactions Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of periosteal reactions in bone sarcomas using
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Original Article. Hyun Su Kim, MD 1, Young Cheol Yoon, MD 1, Jong Won Kwon, MD 1, Bong-Keun Choe, MD, PhD 2 INTRODUCTION
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.443 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(4):443-449 Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Isotropic Ankle Magnetic Resonance
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.443 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(4):443-449 Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Isotropic Ankle Magnetic Resonance
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy
 Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and
 MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
doi: /j.knee
 doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.04.016 Title page (a) title: Oblique coronal and oblique sagittal MRI for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears and evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament remnant tissue
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Frequency of Baker s Cysts in Cases of Meniscal Injury
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2016, PP 10-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0401003
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
 Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity
 Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak 1, Andrew Arjun Sayampanathan 2, Thean-Howe Bryan Koh 2, Hwee-Chye Andrew Tan 1. Original Article.
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Diagnosis of ligamentous and meniscal pathologies in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings Hamid
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Diagnosis of ligamentous and meniscal pathologies in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopic findings Hamid
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping
 The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
CLINICAL SCIENCE. Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre Vieira Guedes b
 CLINICS 2008;63(1):3-8 CLINICAL SCIENCE CHRONIC MULTIPLE KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES: EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MORE THAN ONE HUNDRED CASES Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre
CLINICS 2008;63(1):3-8 CLINICAL SCIENCE CHRONIC MULTIPLE KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES: EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MORE THAN ONE HUNDRED CASES Rosalvo Zosimo Bispo Júnior, a Cezar Teruyuki Kawano, b Alexandre
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 0, pp. 000 000 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee and Unjustified Surgery Peleg Ben-Galim, MD*; Ely
Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
Original Article Diagnostic Accuracy of 0.2 Tesla Open MR Imaging Unit in Detecting Meniscal Tears: Correlation with Arthroscopy Mustafa Koplay 1, Elif Aksakallı 2, Serdar Toker 3, Seda Özbek 1, Ali Sami
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation
 A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
A comparison of arthroscopic diagnosis of ramp lesion and pre-operative MRI evaluation Yasuma S, Nozaki M, Kobayashi M, Kawanishi Y Yoshida M, Mitsui H, Nagaya Y, Iguchi H, Murakami H Department of Orthopaedic
Differentiation between simple cyst and hepatic hemangioma utilizing T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with gradient-echo (b-ffe) technique*
 Original Article Artigo Original Differentiation between simple cyst and hepatic hemangioma Differentiation between simple cyst and hepatic hemangioma utilizing T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with
Original Article Artigo Original Differentiation between simple cyst and hepatic hemangioma Differentiation between simple cyst and hepatic hemangioma utilizing T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with
Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis?
 Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
Ultrasound assessment of internal derangement of the knee
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (10), Page 5490-5494 The Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Meniscal Injury Nada Sayed Mahdy*, Hossam Mousa Sakr, Allam Elsayed Allam Radiology
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Acute Injury of the Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone: A Common but Unrecognized Lesion in the Immature Knee
 Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Rachel S. Oeppen 1,2 Susan. Connolly 3 Jenny T. encardino 4 Diego Jaramillo 1 Received May 19, 2003; accepted after revision July 28, 2003. 1 Department of Pediatric Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital,
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
B one contusion is a finding substantiated by magnetic
 592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the
 CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging
 Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution
 MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional
 MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
MRI Findings of Posterolateral Corner Injury on Threedimensional Isotropic SPACE. Poster No.: C-1792 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S.-W. Lee, Y. M. Jeong, J. A. Sim, S. Ahn; Incheon/KR
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison between Pre-Contrast and Post-Contrast Images
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Graduating 4th year radiology residents perception of optimal imaging modalities for neoplasm and trauma: a pilot study from four U.S.
 Radiology ORIGINAL residents ARTICLE perception ARTIGO of optimal ORIGINAL imaging exams Graduating 4th year radiology residents perception of optimal imaging modalities for neoplasm and trauma: a pilot
Radiology ORIGINAL residents ARTICLE perception ARTIGO of optimal ORIGINAL imaging exams Graduating 4th year radiology residents perception of optimal imaging modalities for neoplasm and trauma: a pilot
Imaging assessment of glenohumeral dysplasia secondary to brachial plexus birth palsy*
 Imaging assessment of glenohumeral dysplasia secondary to brachial plexus birth palsy* The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Imaging assessment of glenohumeral dysplasia secondary to brachial plexus birth palsy* The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Index words : Bile duct radiography, technology Bile ducts MR Bile ducts surgery Liver, transplantation
 Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Imaging of the Elbow. Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich
 Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
Imaging of the Elbow Marco Zanetti Radiology Balgrist University Hospital Zurich Elbow Case 1 Case 8 Case 2 Case 9 Case 3 Case 10 Case 4 Case 11 Case 5 Case 12 Case 6 Case 13 Case 7 Case 14 Elbow Imaging
MRI Characteristics of Healed and Unhealed Peripheral Vertical Meniscal Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kijowski et al. MRI of Peripheral Meniscal Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Richard Kijowski 1 Humberto G. Rosas 1 Kenneth S. Lee 1 rnold Cheung
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
