C HILDREN S knees can be studied by double contrast anthrography just as
|
|
|
- Cassandra Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APRIL, 197$ DOUBLE CONTRAST KNEE ARTHROGRAPHY IN CHILDREN* By ROBERT T. BRAMSON, and TOM W. STAPLE C HILDREN S knees can be studied by double contrast anthrography just as in adults. The paucity ofinformation in the literature regarding pediatric knee arthrography stimulated a review ofour experience in 24 children less than 12 years old. Compared to adults, the incidence and types of arthrographic abnormalities in children are unique. MATERIAL AND METHOD Twenty-four, on about I per cent, of slightly more than 2,500 anthrograms obtamed in the last years ( ), were studies of children to I 2 years of age. The 7 girls and 17 boys underwent either surgical confirmation or clinical follow-up. A review of teenage arthrograms (ages 13 through 19), showed that the indications for arthrography, the lesions found, and the technique were the same as in adults, so that they did not warrant independent study and analysis. TECHNIQUE ST. LOUIS, MISSOURI The anthrographic technique is similar to the double contrast method used in adults. Reassurance and gentle restraint of the patient during injection were sufficient to allow adequate examination of all the children. Neither heavy sedation nor general anesthesia was needed. The knee to be examined was extended and taped to a splint (Fig. i, ii and B). Both knees and the splint were then securely fastened to the x-ray table with adhesive tape. A restraining tape was placed across the child s chest to prevent sitting up during the injection (Fig. i,1 and B). This helped to relax the quadriceps muscle which allowed easier insertion of the needle behind the patella. An assistant reassured the child. It was not necessary for anyone to hold the knee and the sterile field was not disturbed. After sterile preparation and draping, I per cent Lidocaine was injected into the skin just medial to the middle third of the patelba. The tip ofthe needle was positioned behind the middle of the patebla and contrast material and then air were injected. Modifications of the adult injection technique were : (i ) the use of a 23 gauge, I inch needle for injection; (2) only i cc. of 76 per cent meglumine diatnizoate;* and (,) only io to i cc. of air to fill the companabby smaller joint of a child. Air was injected until the radiologist felt mild resistance. Glass syringes were preferred over plastic since they provided a greater sensitivity to resistance during the injection. After the injection, the needle was withdrawn and the straps removed. The knee was flexed 3 times to distribute the contrast material throughout the joint and the study was then continued in the same manner as with an adult knee. 4 RESULTS The normal pediatric knee arthrogram is similar to the adult with only a few exceptions. All the anticular cartilages in the child s knee are thicker than in the adult. The younger the child, the thicker the cartilage. The menisci have an adult configuration but are proportionately smaller (Fig. 2, 1 and B; and 3, 11 and B). Eleven studies were normal and 13 abnormal. No postexamination complications developed. Of the II patients with normal arthrograms, 8 were treated conservatively and are symptom free on clinical follow-up between 6 and 40 months. One 6 year old * Renografin-76, E. R. Squibb and Sons, Inc., P. 0. Box 4000, Princeton, New Jersey. * From the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. 838
2 VOL. 123, No. Double Contrast Knee Arthrography in Children 839 FIG. 4 Restraining tapes are then additionally placed across both knees and the chest. with a normal arthrogram was felt to have a medial collateral ligament strain. A year later his pain and medial collateral ligament tenderness persist. Another patient with a normal arthrogram underwent surgery 3 days later. He had only a hemar- 5 2 inch throsis with normal ligaments and cartilages, while a biopsy of the synovium showed chronic synovitis. A year later his symptoms subsided. The other patient with the normal study has been followed for 2 months and is becomingsymptom free.
3 840 Robert T. Bramson and Tom W. Staple APRIL, 1975 I - - I strated a projection ofnon-ossifled articulan k cartilage extending from the superior pole of each patebla (Fig. 6). The patient was not operated upon, since this abnormality was not considered the cause of the patient s symptoms. DISCUSSION FIG. 2. (1) Normal medial, and (B) lateral meniscus in a 10 year old child. The articular cartilages are thicker than in the adult. The menisci have an adult configuration. Three types of lesions form the bulk of the pathologic conditions, namely, discoid lateral meniscus, osteochondritis dissecans, and tears of the lateral meniscus. The 3 patients with discoid meniscus all underwent surgery which confirmed the roentgenographic diagnosis (Fig. 4, 44 and B). The symptoms of these 3 patients have resolved following excision of the involved meniscus. The 4 patients with osteochondnitis dissecans have been followed conservatively without surgery and are presently filling in their defects. The torn lateral menisci of 2 patients were confirmed and resected at surgery. These 2 patients are now asymptomatic. One II year old with an anthrographically demonstrated torn lateral meniscus was not operated upon and is now symptom free. One II year old child with a hemangioma of the knee joint has been previously reported (Fig. 5).3h1 One patient with disuse atrophy following derotational osteotomies of the femur had an underdeveloped patella with decreased ossification. Another patient with spondyboepiphyseal dysplasia had palpable masses about the patella in both knees suggesting loose bodies. Anthrography demon- - Congenital or developmental abnormalities constitute over half of the arthro- I. 3., meniscus and (B) lateral meniscus in a 3 year old boy. The articular cartilages of the femur ani tibia are even thicker than those of the patient in Figure 2. The menisci have an adult configuration.
4 VOL. 123, No. 4 Double Contrast Knee Anthrography in Children 84! graphic abnormalities found in our series. Discoid meniscus, tears of the lateral meniscus, and patellar abnormalities are all secondary to either developmental or congenital factors. The pathogenesis of a lateral discoid meniscus is not entirely settled. Certain authors originally felt that the discoid meniscus was an intrinsic congenital deformity.2 7 #{176}However, Kaplan,5 in an impressive embryologic and comparative anatomy study, concluded that the discoid meniscus was never found in the human fetus, but rather is acquired after birth as a consequence of congenital alteration in the attachment of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. The normal lateral meniscus is attached to the tibia at the anterior and posterior aspects of the lateral intencondylar tubercbe Fio.. Discoid lateral meniscus. (A) The apex of the anterior and (B) middle thirds of the meniscus are bulbous. The body of the meniscus extends well into the intercondylar notch. The lesion was surgically confirmed. FIG. 5. Hemangioma of the knee joint. Multilobulated mass occupying the apex of the suprapatellar bursa. and to the femur by the meniscofemoral ligament or the ligament of Wrisberg. According to Kaplan,5 patients who develop a lateral discoid meniscus lack a posterior attachment from the meniscus to the tibial plateau. During knee extension, the postenon meniscus horn dislocates into the intercondylar notch where it is held by the meniscofemorab ligament. As the knee flexes, the meniscus is pulled laterally by the coronary ligaments and popliteus tendon. Therefore, Kaplan5 postulates that the normal horn is trapped between the tibia and the femur and becomes thickened into a discoid meniscus. The discoid meniscus is an uncommon orthopaedic condition, most often discovered in children. It causes a clicking sensation during extension. Occasionally, the knee may lock and some authors feel that the discoid meniscus is more susceptible to tears than a normal meniscus.6 Roentgenographically, in place of the normal triangle, the discoid meniscus free margin bulges into the interarticular space in an oblong fashion. It is often torn and may be fragmented. If severely fragmented, it cannot be differentiated on occasion from an extensive tear with displacement of the
5 842 Robert T. Bramson and Tom W. Staple APRIL, 197$ - Fio. 6. A cartilaginous spur extends above the upper pole of the patella. This clinically simulated a loose body. free fragment into the intercondylar notch. All 3 patients with a torn menisci had involvement of the lateral meniscus (Fig. 7). This is in contrast to the situation in adults where a majority of tears present in the medial meniscus. The mechanism of meniscus tears has been the subject of extensive research and speculation. Rotational compression forces of the femonal condyle on the menisci during movement and stress result in cartilage tears. Most commonly in the adult, the medial meniscus is torn as the foot is held fixed in place and the femonal condyle rotates externally on the tibia. The normal adult usually has no varus or valgus deformity. On the other hand, children between the ages of 2 and 12 have varying degrees of genu valgus as a normal part of the growth process. After age I 2, this valgus deformity is corrected by normal growth.9 Perhaps the higher incidence of lateral meniscus tears in children is related to altered weight bearing and rotational forces transmitted to the lateral meniscus rather than the medial during the valgoid stage of normal knee development. The diagnosis of osteochondritis dissecans usually is evident on the plain roentgenograms. Arthrography may be of help in demonstrating the condition of the cartilage overlying the necrotic bone or to establish that meniscus injuries may or may not contribute to the symptoms. The anticular cartilage of the femoral condyle can be evaluated to establish whether it merely bulges from the underlying bone, is fractuned and nondisplaced, or presents as a loose fragment in thejoint. It is essential to demonstrate the overlying articular cartilage with a roentgenographic beam projected tangentially to the area of aseptic necrosis. The plain roentgenogram can establish the location of the lesion in relation to the anterior, middle, or posterior third of the condyle. If the lesion is in the middle third of the knee, it will be projected adequately on the standard arthrognaphic spot roentgenograms of the menisci. If it is located posteriorly, a vertical beam can be projected tangential to the posterior third of the femoral condyle when the patient is placed supine and the hip and knee are flexed (Fig. 8). The femoral condyle can be slightly rotated to obtain the maximal projection of the area of osteochondritis dissecans (Fig. 9). FIG. 7. Tear of the lateral meniscus. The meniscus has been separated from the joint capsule. The space between the meniscus and the capsule is not the popliteus tendon bursa.
6 VOL. 123, No. 4 Double Contrast Knee Arthnography in Children 843 p Fi8 -. i - dissecans. The knee is flexed at 90 degrees and the beam projected along the posterior surface of the femoral condyle. In regard to lateral meniscus tears, our results are similar to those of the extensive study of knee anthrognaphy in children carried out by Stenstrom. 2 Forty-eight per cent of his patients had tears of the lateral meniscus, which is much greaten than in the adult knee. Stenstrom studied patients between ages i and 18 years. A great majority of them were older than age 12 and it was impossible to determine whether an even larger percentage of those patients under age 12 may have had lateral rather than medial meniscus tears. The indications for pediatric knee anthrography differed somewhat from adults. However, in general, arthnography is used to exclude intra-anticular causes of abnormal joint motion. Its value in trauma is demonstrated by the patients in this group with torn lateral menisci. In osteochondritis dissecans, the location of any loose anticular cartilaginous bodies, and the exclusion of any additional lesions becomes important. Gait disturbances in children may be caused by intra-articular lesions, but are more likely to be the result of neunomuscular or growth disturbances such as cerebral palsy, congenital dislocation of the hip, or unequal leg length. Knee locking is a rare occurrence in children and may be caused by extra-articular lesions. We have been impressed by the locking which may be occasioned by fibrosis of the nectus femoris muscle which can prevent full flexion. A year old child recently referred to us for arthrography had in reality fibrosis of the rectus femoris muscle as the result of multiple intramuscular antibiotic injections during treatment for a prolonged severe systemic infection.8
7 8. Robert T. Bramson and Tom W. Staple APRIL, 197$ REFERENCES FIG. 9. Osteochondritis dissecans (arrows). The articular cartilage overlying the defect is intact. SUMMARY Knee arthrography in the pediatric patient can be performed without heavy sedation on general anesthesia. Lateral meniscus tears predominate oven those of the medial meniscus. The most common lesions found are tears of the lateral meniscus, osteochondnitis dissecans, and lateral discoid meniscus. Congenital on developmental factors apparently contribute to half of the demonstrated lesions. Extra-articular causes should be sought in the very young child with a locked knee. T. W. Staple, M.D., F.A.C.R. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology 510 South Kingshighway Boulevard St. Louis, Missouri I. BUTT, W. P., and MCINTYRE, J. L. Doublecontrast arthrography of knee. Radiology, 1969, 92, CAVE, E. F., and STAPLES, 0. S. Congenital discoid meniscus: cause of internal derangement ofknee. Am. 7. Surg., 1941,54, FORREST, J., and STAPLE, T. W. Synovial hemangioma of knee: demonstration by arthrography and arteriography. AM. J. ROENT- GENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., I97I, 1z2, FREIBERGER, R. H., KILLORAN, P. J., and CAR- DONA, G. Arthrography of knee by double contrast method. Avs. J. ROENTGENOL., RAD. THERAPY & NUCLEAR MED., 1966, 97, p 5. KAPLAN, E. B. Discoid lateral meniscus of knee joint, nature, mechanism, and operative treatment. 7. Bone & Joint Surg., 1957, 39-A, MIDDLETON, D. S. Congenital disc-shaped lateral meniscus with snapping knee. Brit. 7. Surg., 1936, 24, OBER, F. R. Discoid cartilage, trigger knee. Surgery, 1939, 6, RASK, M. R., and LATTIG, G. L. Traumatic fibrosis of rectus femoris muscle: report of five cases and treatment. 7.A.M.A., 1972, 221, SHOPFNER, C. E., and COIN, C. G. Genu varus and valgus in children. Radiology, I969, 92, SMILLIE, I. S. Congenital discoid meniscus. 7. Bone & Joint Surg., 1948,30-B, II. STAPLE, T. W. Extrameniscal lesions demonstrated by double contrast arthrography of knee. Radiology, 1972, 102, STENSTROM, R. Arthrography of knee joint in children. Acta Radiol., 1968, Suppl. 28!.
8 This article has been cited by: 1. Giovani Krolikowski, Carmen Lice Buchmann de Godoy, Luiz Carlos de Pellegrini, Stella Falkemberg Rausch, Ingrith Aparecida Mazuhy Santarosa, Josaine Cristina da Silva Rappeti, Fabrício Arigony Braga, Kleber Gomes, Daniel Muller, Luciana Brilhante Wolle, Maicon Pinheiro, Rômulo Rotilli Antonov Artrografia com meio de contraste positivo e duplo contraste na articulação do úmero de cães. Ciência Rural 39:1, [CrossRef] 2. Leon Root, Ulrich C. Liener Discoid Lateral Meniscus in Children; Long-Term Follow-up after Excision *. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume 77:9, [CrossRef]
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
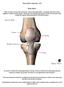
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
LOCALIZED NODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE KNEE: A REPORT OF TWO CASES WITH ABNORMAL ARTHROGRAMS*
 MARcH, i6 LOCALIZED NODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE KNEE: A REPORT OF TWO CASES WITH ABNORMAL ARTHROGRAMS* ABSTRACT: By THOMAS G. GOERGEN, M.D.,t DONALD RESNICK, M.D.,t and GEM NIWAYAMA, M.D4 SAN DiEGO, CALIFORNIA
MARcH, i6 LOCALIZED NODULAR SYNOVITIS OF THE KNEE: A REPORT OF TWO CASES WITH ABNORMAL ARTHROGRAMS* ABSTRACT: By THOMAS G. GOERGEN, M.D.,t DONALD RESNICK, M.D.,t and GEM NIWAYAMA, M.D4 SAN DiEGO, CALIFORNIA
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
KNEE EXAMINATION. Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective. EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine
 KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
What is Medial Plica Syndrome?
 What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks
 Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks _ The approach to examining the musculoskeletal system is the same no matter what joint or limb is being examined. The affected and contralateral region should both
Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks _ The approach to examining the musculoskeletal system is the same no matter what joint or limb is being examined. The affected and contralateral region should both
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective
 On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE?
 HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco
 Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the Advanced Tactical Practitioner (ATP) in the Austere Environment Part Two JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: The following
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the Advanced Tactical Practitioner (ATP) in the Austere Environment Part Two JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: The following
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
Examination of the Knee
 Examination of the Knee Wash your hands & Introduce the exam to the patient Positioning & Draping With the patient supine, make sure both legs are exposed in order to compare each side be sure to use draping
Examination of the Knee Wash your hands & Introduce the exam to the patient Positioning & Draping With the patient supine, make sure both legs are exposed in order to compare each side be sure to use draping
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
Please differentiate an internal derangement from an external knee injury.
 Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB.
 ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
Musculoskeletal Examination
 Musculoskeletal Examination Statement of Goals Know how to perform a complete musculoskeletal examination. Learning Objectives A. Describe the anatomy of the musculoskeletal system including the bony structures,
Musculoskeletal Examination Statement of Goals Know how to perform a complete musculoskeletal examination. Learning Objectives A. Describe the anatomy of the musculoskeletal system including the bony structures,
Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes.
 The injured knee Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes. J WALTERS, FC (Orth) SA Department of
The injured knee Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes. J WALTERS, FC (Orth) SA Department of
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Presents ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Multimedia Health Education
 HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES
 DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES INTRODUCTION: The knee is a common site of athletic injury. The knee injuries can be classified either into traumatic or acute and chronic, with overuse
DIAGNOSIS AND EARLY MANAGEMENT OF KNEE INJURIES INTRODUCTION: The knee is a common site of athletic injury. The knee injuries can be classified either into traumatic or acute and chronic, with overuse
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Differential Diagnosis
 Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
Case 31yo M who sustained an injury to L knee while playing Basketball approximately 2 weeks ago. He describes pivoting and hyperextending his knee, which swelled over the next few days. He now presents
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. OSCE 4: Knee Pain
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OSCE 4: Knee Pain This video format is designed to help you prepare for objective structured clinical examinations, or OSCEs. You are going to observe and participate
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OSCE 4: Knee Pain This video format is designed to help you prepare for objective structured clinical examinations, or OSCEs. You are going to observe and participate
JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD
 Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the Advanced Tactical Practitioner in an Austere Environment JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: The following article
Field Evaluation and Management of Non-Battle Related Knee and Ankle Injuries by the Advanced Tactical Practitioner in an Austere Environment JF Rick Hammesfahr, MD Editor s Note: The following article
MENISCAL INJURIES. (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION
 (copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
(copyright s h palmer 2009) MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL INJURIES Menisci are important for weight bearing, load distribution, joint stability and proprioception. Figure 1: A normal medial meniscus Any load
CASE REPORT GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT
 Journal of Musculoskeletal Research, Vol. 4, No. 2 (2000) 145 149 World Scientific Publishing Company ORIGINAL CASE REPORT ARTICLES GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT Mustafa Yel *,, Mustafa
Journal of Musculoskeletal Research, Vol. 4, No. 2 (2000) 145 149 World Scientific Publishing Company ORIGINAL CASE REPORT ARTICLES GIANT OSTEOCHONDRAL LOOSE BODY OF THE KNEE JOINT Mustafa Yel *,, Mustafa
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #2: Client History & The 23 Injuries Common to the Knee Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. Webinar Goals Understand the significance of
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO
 Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella
 CONTRACTURE OF THE QUADRICEPS MUSCLE A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella D. R. GUNN, SINGAPORE The objects ofthis paper are to suggest that an important
CONTRACTURE OF THE QUADRICEPS MUSCLE A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella D. R. GUNN, SINGAPORE The objects ofthis paper are to suggest that an important
Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review of Treatments
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):237-242 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.15.054 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Discoid Medial Meniscus Tear, with a Literature Review
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
An older systematic review looked at the evidence behind the best approach to evaluate acute knee pain in primary care (Ann Int Med.2003;139:575).
 There is so much we don't know in medicine that could make a difference, and often we focus on the big things, and the little things get forgotten. To highlight some smaller but important issues, we've
There is so much we don't know in medicine that could make a difference, and often we focus on the big things, and the little things get forgotten. To highlight some smaller but important issues, we've
What s your diagnosis?
 Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Case Study 58 A 61-year-old truck driver man presented with a valgus injury to the left knee joint when involved in a truck accident. What s your diagnosis? Diagnosis : Avulsion of Deep MCL The medial
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy
 Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Running Injuries. Lower Extremity
 Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
Chapter 20 The knee and related structures
 Chapter 20 The knee and related structures Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Bones & joints Femur, tibia, fibula, & patella Femur & tibia Weight bearing & muscle attachment Patella functions Anterior
Chapter 20 The knee and related structures Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Bones & joints Femur, tibia, fibula, & patella Femur & tibia Weight bearing & muscle attachment Patella functions Anterior
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Your Practice Online
 Your Practice Online Disclaimer P R E S E N T S - PATELLAR TENDON This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction.
Your Practice Online Disclaimer P R E S E N T S - PATELLAR TENDON This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction.
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis
 A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization
 evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
Objectives. The BIG Joint. Case 1. Boney Architecture. Presenter Disclosure Information. Common Knee Problems
 3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee
 Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip
 Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Lateral knee injuries
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
HANDS ON: Knee Evaluation J. Scott Delaney MD, FRCPC, FACEP, CSPQ
 HANDS ON: Knee Evaluation J. Scott Delaney MD, FRCPC, FACEP, CSPQ FACULTY DISCLOSURE Dr. Delaney has no affiliation with the manufacturer of any commercial product or provider of any commercial service
HANDS ON: Knee Evaluation J. Scott Delaney MD, FRCPC, FACEP, CSPQ FACULTY DISCLOSURE Dr. Delaney has no affiliation with the manufacturer of any commercial product or provider of any commercial service
American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013
 American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013 Paul J. Gubanich, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine/Sports Medicine Team Physician, Ohio
American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013 Paul J. Gubanich, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine/Sports Medicine Team Physician, Ohio
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM
 AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
