Lower extremity compartment syndrome in northern Ghana
|
|
|
- Richard Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(2): Lower extremity compartment syndrome in northern Ghana Kuubiere B. Callistus and Abass Alhassan ISSN: CODEN (USA): AASRFC Department of Human Biology, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, University for Development Studies, Tamale ABSTRACT Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within a closed compartment compromises circulation and function of the tissues within that space. This usually occurs in osseofascial compartment of the leg or forearm, but it may occur in the upper arm, thigh, foot, buttock, hand, and abdomen. The general cause of compartment syndrome is trauma, usually after a fracture. The incidence rate of acute compartment syndrome is up to 20% in acutely ischaemic limbs but can vary from one place to the other. Delays in treatment can result in significant disability including neurological deficit, muscle necrosis, amputation, and death. However, very little is known about the prevalence of this condition in the Northern part of Ghana. The aim of the study was to investigate the prevalence of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome and its causes in Northern Ghana over a five year period. The study setting was the Tania specialist orthopaedic hospital, Tamale, Ghana. Data regarding patient's age and sex, extremity involved, cause of injury from January, 2007 to December, 2012 were analysed retrospectively. The prevalence of compartment syndrome over the study period was 20.76%. Majority of the cases were a result of non-infected fractured limb (48.17%), followed by infected fractured wounds, 25.23%, Gun-shot wounds, 15.60%, burns, 7.34% and others 3.67%. Among the non-infected fractured wounds majority (52.38%) were a result of prolong immobility with back slap POP with gauze bandage. In conclusion the prevalence of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome in Northern Ghana is relatively high. High energy injuries such as those sustained from road traffic accidents and gunshots as well as traditional bonesetter splinting are the most predominant precursors for lower extremity compartment syndrome in this part of Ghana. Monitoring of compartment pressure in these patients as wells as early referrals for specialist orthopaedic and trauma management should be considered to allow for early detection and treatment Keywords: Compartment syndrome, lower limbs, fasciotomy, Fracture, Northern Ghana INTRODUCTION Compartment syndrome is said to occur when there is an increased pressure within a closed compartment which compromises the circulation and function of the tissues within that space [1, 2]. The most common occurrence is in an osseofascia compartment of the lower limb or forearm but may occasionally occur in the upper arm, thigh, foot and the abdomen. The causes of compartment syndrome are varied but the most common cause is trauma, usually after a fracture [1, 2]. Other causes included the use of inelastic gauze or bandages, and the use of inappropriate POP. It also occurs in ischaemia, burns and in poor positioning during certain prolonged surgical procedures (in lithiotomy) [1, 2]. Studies have shown that about 4.3% of all adult patients with tibial shaft fractures and 3.1% of diphyseal fracture of the forearm develops acute compartment syndrome. Acute compartment syndrome is said to occur most commonly among male patients under the age of 35 years [3-5].and can cause significant morbidity if not treated early but the diagnosis is often very challenging [6-8]. Delays in diagnosis and treatment can result in significant disability including neurological deficit, muscle necrosis, amputation and death. The diagnosis is very challenging because it requires a high index of suspicion usually by a trauma/orthopaedic specialist and severe pain is thought to be a cardinal feature of compartment syndrome [1, 2, 9]. 394
2 To the best of our knowledge there is virtually no literature on the prevalence and causes of compartment syndrome in the Northern part of Ghana. The purpose of the present study is to determine the prevalence and causes of lower extremity compartment syndrome in a specialist trauma/orthopaedic hospital which serve the Northern part of Ghana. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was conducted retrospectively over a five year period at the Tania Specialist orthopaedic/trauma hospital, Tamale from January 2007 to December This hospital is one of the very few Trauma/Orthopaedic hospitals serving the entire three Northern regions of Ghana with a population of about 5 million people. There were 177 males and 41 females representing 91.2% and 18.8% respectively. Acute compartment syndrome was diagnosed either clinically or by monitoring of compartment pressure. Normal pressure in the muscle compartment is below mm Hg [2]. The clinical diagnosis of acute compartment syndrome was made depending on the presence of some or all of the clinical indications (severe pain, stretch pain, sensory deficit, motor deficit), a differential pressure of less than 30 mmhg between the diastolic and compartment pressures [3] or a combination of both clinical and pressure indications. Majority (185 patients) of the patients had either been referred from the regional and district hospitals or they had sought treatment from traditional bonesetters before been admitted to our facility. RESULTS There were 218 patients with acute compartment syndrome in the lower extremity out a total of 1050 surgical cases recorded over the study period giving a prevalence rate of 20.76%. The study subjects included 41 females (18.8%) and 177 males (81.2%) with a mean age of 34.1 ± 11.7 years (mean ± SD). The mean age of the women was 31.8 ± 18.6 and that of the men was 34.5 ± More than 50.0% of the cases occurred among patients within the age so f 31 to 40 years with about 45% of those cases occurring in men as shown in table 1. There was a general decline in the number of case in both males and females above the age of 40 years (Table 1). Table 1: Prevalence of compartment syndrome stratified by age and sex Age Total n (%) Male n (%) Female n (%) (9.17) 13(6.0) 7 (3.21) (27.52) 50 (22.93) 10 (4.59) (53.67) 98 (44.95) 19 (8.72) (5.05) 8 (3.67) 3 (1.38) >50 10 (4.59) 8 (3.67) 2 (0.92) The primary condition causing lower extremity compartment syndrome among the patients was fracture occurring in about 73.4%. Non-infected fractures accounted for about 48% (105 patients) of all cases followed by infected fractures with 25.2% (55 patients) as shown in table 2. Penetrating wounds sustained as a result of gun-shot accounted for 15.6% (34 patients) (Table 2). Table 2: underlying causes of compartment syndrome among the patients Underlying condition Number of patients Percentage Non-Infected fracture Infected fracture Gun-shot wounds Others Majority of the non-infected cases were due to improper handling during immobilization of the fractures. Prolonged immobility of the affected part with back slap POP with gauze accounted for about 52.4% of the non-infected cases follow by prolonged immobility with circular POP with 38.1% and the remaining 9.5% was as a result of the application of traditional bonesetter splint (Table 3). Table 3: Sources of non-infected wounds Types of non-infected Number of patients Percentage prolong immobility with back slap POP with gauze bandage prolong immobility with circular POP traditional bonesetter splint
3 Figure 1 A show the initial causes of injury among the patients. Road traffic accident was the most common, accounting for over 70% of the cases follow by Gun-shot and fall from height. About 45% of the road traffic accidents involve Motorbike users and about 23% of the road traffic accident victims were passengers of vehicle involved in accidents. The rest of the road traffic accident cases were drivers of vehicles (4.7%) and pedestrian (7.3%). Other initial causes of injury as shown in figure 1 are Gun-shot injury (15.6%) and fall from height (5.1%). Figure 1 B show the laterality of the lower extremities involved. The right limb was the most affected part accounting for about 47.3% of the all the compartment syndrome cases and the left was involve in only 30.7% of the cases. Figure 1: The initial causes of injury among the patients and laterality of the injury. RTA; Road Traffic Accident, Pedest; pedestrian, PASS; passenger, FFT; Fall From Height DISCUSSION Compartment syndrome which is a condition in which increased pressure within a limited space compromises the circulation and function of tissues within that space can occur in any part of the body but is most often seen in the lower extremity especially in the lower leg. The lower extremity is frequently expose to trauma and has a typical predisposing anatomy where fascia, membranes, tibia and fibula enclose four compartments generally referred to as the anterior, lateral (or peroneal), deep- and superficial posterior compartment, each with specific muscles, vascular 396
4 structures and nerves, supplying the lower leg and foot [1, 9]. The general incidence and prevalence of compartment syndrome varies from one place to another likewise its causes [1, 2, 4]. In the present study the aim was to elicit the causes and general prevalence of lower extremity compartment syndrome in Northern Ghana. The study has shown the prevalence of lower extremity compartment syndrome among the study subjects to be about 20.7%. Studies have shown that the incidence rate of acute compartment syndrome is up to 20% in acutely ischaemic limbs but can vary from one place to the other depending on how prompt diagnosis are made and the early management [1, 2, 4, 10]. The result of the present studies has shown that young people within the ages of 31 to 40 years especially men have the highest incidence of lower extremity compartment syndrome. This finding is similar to the work of McQueen, et al [4] who also found acute compartment syndrome to be highest among this group. It is possible that young men have relatively large muscle volumes, while the compartment size does not change after growth is complete gives less space for swelling muscle in young men after injury. The communities in the catchment area of this study are male dominated in all aspect of their daily life and this could mean that males are more prone to injuries which could lead to the development of compartment syndrome. The area is also conflict prone zone resulting in lots of gunshot wounds as noted in the study. The finding also revealed that the incidence was low in older people. This could be due to the fact that older people have smaller hypotrophic muscles, and a relatively higher blood pressure which may provide tolerance for higher tissue pressure [8]. Despite the fact that there has been disagreement in deciding what pressures constitute an acute compartment syndrome the importance of the difference between perfusion pressure and tissue pressure has been shown both experimentally and clinically[1, 3, 6-8]. Hypertension has also been noted to have a protective effect against compartment syndrome [8] Our study have shown that while fracture in itself is not a prerequisite for compartment syndrome, its management especially prolonged immobilization with back slap POP, Circular POP and traditional bonesetter splint posses a greater risk of developing compartment syndrome in the lower extremities. Other studies have shown that complications such as avascular necrosis, contractures and ischaemic limbs as a result of fracture management by traditional bonesetter in Northern Ghana is very high [11] and could be responsible for the high incidence of compartment syndrome noted in this study. The present study has also shown that high-energy injuries such as road traffic accident and gun-shots accounted for majority of the initial caused of fracture and wounds. Previous studies have revealed that road traffic accident is very high in this part of Ghana especially involving motorbikes which the common means of transport for the people[10, 12]. The recent tribal conflicts in this part of the country could have accounted for the high number of gunshot injuries in the present study. During these conflicts young men are usually involve in the fighting and could explain the high number of men in the study. CONCLUSION The incidence of acute lower extremity compartment syndrome in Northern Ghana is relatively high. High energy injuries such as those sustained from road traffic accidents and gunshots as well as traditional bonesetter splinting are the most predominant precursors for lower extremity compartment syndrome in this part of Ghana. Monitoring of compartment pressure in these patients as wells as early referrals for specialist orthopaedic and trauma management should be considered to allow for early detection and treatment. Acknowledgements The authors will like to thank all the staff and patients of Tania Specialist Hospital in Tamale/Ghana for their support during the study. REFERENCES [1] Mar GJ, Barrington MJ, McGuirk BR: ABr J Anaesth 2009, 102(1):3-11. [2] Tuckey J: Br J Anaesth 1996, 77(4): [3] McQueen MM, Court-Brown CM: J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996, 78(1): [4] McQueen MM, Gaston P, Court-Brown CM: J Bone Joint Surg Br 2000, 82(2): [5] Schwartz JT, Jr., Brumback RJ, Lakatos R, Poka A, Bathon GH, Burgess AR: J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989, 71(3): [6] Dunwoody JM, Reichert CC, Brown KL: J Pediatr Orthop 1997, 17(3): [7] Hyder N, Kessler S, Jennings AG, De Boer PG: J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996, 78(3): [8] McQuillan WM, Nolan B: J Bone Joint Surg Br 1968, 50(3): [9] McQueen MM, Christie J, Court-Brown CM: J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996, 78(1): [10] Kuubiere CB, Alhassan A, Majeed SF: Journal of Medical and Biomedical Sciences 2013, 2(3):
5 [11] Alhassan A, Kuubiere BC, Issahaku M: FAdv Appl Sci Res 2013, 4(6): [12] Afukaar FK, Antwi P, Ofosu-Amaah S: Injuiry Control and Safety Promotion 2003, 10:
Rio Grande Trauma Conference December 1 st and 2 nd, 2016
 Rio Grande Trauma Conference December 1 st and 2 nd, 2016 Why is Acute Compartment Syndrome Important? It s a clinical emergency If left untreated, it can lead to severe morbidity and mortality. It triples
Rio Grande Trauma Conference December 1 st and 2 nd, 2016 Why is Acute Compartment Syndrome Important? It s a clinical emergency If left untreated, it can lead to severe morbidity and mortality. It triples
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
Topic 4: Fractures and External Fixation
 Topic 4: Fractures and External Fixation Acute Compartment Syndrome Prof. Dr. Andreas Platz Stadtspital Triemli, Zürich Demographics Incidence: Men 7.3/100,000 Women 0.7/100,000 69% due to trauma 36% fx
Topic 4: Fractures and External Fixation Acute Compartment Syndrome Prof. Dr. Andreas Platz Stadtspital Triemli, Zürich Demographics Incidence: Men 7.3/100,000 Women 0.7/100,000 69% due to trauma 36% fx
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Disclosure. Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program or presentation.
 Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Acute limb compartment syndromes
 Catherine Farrow FRCA Andrew Bodenham FRCA Max Troxler FRCS Matrix reference 2A06 Key points Compartment syndrome (CS) is a medical emergency, which needs to be recognized by those involved with the provision
Catherine Farrow FRCA Andrew Bodenham FRCA Max Troxler FRCS Matrix reference 2A06 Key points Compartment syndrome (CS) is a medical emergency, which needs to be recognized by those involved with the provision
Neurovascular Observations Nursing Clinical Guideline
 Reference (include title, Patel, k., & McCann, P. A. (2012). The emergent assessment of supracondylar fractures of the paediatric humerus. Hand Surgery, 17(2), 161-165. From Medline Evidence level (I-)
Reference (include title, Patel, k., & McCann, P. A. (2012). The emergent assessment of supracondylar fractures of the paediatric humerus. Hand Surgery, 17(2), 161-165. From Medline Evidence level (I-)
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Introduction Compartment syndrome can be a life or limbthreatening
 Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Measurement of compartmental pressure in a leg by Whitesides method in a Nepalese patients attending a tertiary care hospital in eastern region of Nepal P Chaudhary 1,
Original Article Chaudhary et.al. Measurement of compartmental pressure in a leg by Whitesides method in a Nepalese patients attending a tertiary care hospital in eastern region of Nepal P Chaudhary 1,
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Compartment Syndrome Associated with Tibial Fracture* 1
 Compartment Syndrome Associated with Tibial Fracture* 1 BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D4, BROOKLYN, NEW YORK, AND DAVID TEMPLEMAN, M.D.ij, MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA An Instructional Course Lecture, The American
Compartment Syndrome Associated with Tibial Fracture* 1 BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D4, BROOKLYN, NEW YORK, AND DAVID TEMPLEMAN, M.D.ij, MINNEAPOLIS, MINNESOTA An Instructional Course Lecture, The American
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome
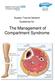 Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hennepin County Medical Center April 2016 Disclosure Information
Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hennepin County Medical Center April 2016 Disclosure Information
STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY
 STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY Peter Swift, PE SwiftLLC.com Fire vs. Vehicle Injuries and Fatalities 3,500,000.00 3,000,000.00 3,032,672.00 2,500,000.00 Incidents per Year 2,000,000.00 1,500,000.00 Fire Vehicle
STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY Peter Swift, PE SwiftLLC.com Fire vs. Vehicle Injuries and Fatalities 3,500,000.00 3,000,000.00 3,032,672.00 2,500,000.00 Incidents per Year 2,000,000.00 1,500,000.00 Fire Vehicle
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Acute Compartment Syndrome in Patients With Tibia Fractures Transferred for Definitive Fracture Care
 An Original Study Acute Compartment Syndrome in Patients With Tibia Fractures Transferred for Definitive Fracture Care Mark L. Prasarn, MD, Jaimo Ahn, MD, Timothy S. Achor, MD, Omesh Paul, MD, Dean G.
An Original Study Acute Compartment Syndrome in Patients With Tibia Fractures Transferred for Definitive Fracture Care Mark L. Prasarn, MD, Jaimo Ahn, MD, Timothy S. Achor, MD, Omesh Paul, MD, Dean G.
03/31/ Compartment Syndrome. Disclosure Information Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D.
 Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief of Orthopedic Surgery, Hennepin County Medical Center 50% Clinical 50% Basic Science Disclosure
Compartment Syndrome Andrew H. Schmidt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota Chief of Orthopedic Surgery, Hennepin County Medical Center 50% Clinical 50% Basic Science Disclosure
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Compartmental Syndromes: When the Pressure Gets Too Great
 FREDERICK A. MATSEN III, M.D. PROFESSOR AND CHAIRMAN UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER SHOULDER AND ELBOW WWW.ORTHOP.WASHINGTON.EDU/FACULTY/MATSEN Compartmental Syndromes: When the Pressure Gets
FREDERICK A. MATSEN III, M.D. PROFESSOR AND CHAIRMAN UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER SHOULDER AND ELBOW WWW.ORTHOP.WASHINGTON.EDU/FACULTY/MATSEN Compartmental Syndromes: When the Pressure Gets
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts
 Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
ACUTE COMPARTMENT SYNDROME
 ACUTE COMPARTMENT SYNDROME SHARON EDWARDS explores the definition of acute syndrome, its aetiology, sites and causes Sharon Edwards RGN, DipN(Lon), MSc, PGCEA is senior lecturer at the department of nursing
ACUTE COMPARTMENT SYNDROME SHARON EDWARDS explores the definition of acute syndrome, its aetiology, sites and causes Sharon Edwards RGN, DipN(Lon), MSc, PGCEA is senior lecturer at the department of nursing
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014
 Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014 The State of Florida now requires ALL Acute Care hospitals to submit data to the statetrauma Registry. Although Baptist Health hospitals are NOT Trauma Centers
Trauma Registry Documentation December 16, 2014 The State of Florida now requires ALL Acute Care hospitals to submit data to the statetrauma Registry. Although Baptist Health hospitals are NOT Trauma Centers
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
KNEE DISLOCATION. The most common injury will be an anterior dislocation, and this usually results from a hyperextension mechanism.
 KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field
 Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures
 CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures Francesco Maria Egro, MBChB, BSc (Hons), MRCS, MSc, Matthew Robert Frederick Jaring, MBBS, BSc (Hons), and Asif Zafar
CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures Francesco Maria Egro, MBChB, BSc (Hons), MRCS, MSc, Matthew Robert Frederick Jaring, MBBS, BSc (Hons), and Asif Zafar
REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC LOWER LIMB AMPUTATION
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Sanjitsingh R Sulhyan et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Sanjitsingh R Sulhyan et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved REPLANTATION OF POST-TRAUMATIC
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 34 (2003) 776 780 Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience B.G. Jones, R.D.D. Duncan The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 34 (2003) 776 780 Open tibial fractures in children under 13 years of age 10 years experience B.G. Jones, R.D.D. Duncan The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow
Case report. Your Diagnosis?
 Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma
 Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Upper extremity open fractures in hospitalized road traffic accident patients: adult versus pediatric cases
 Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
Rubin et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:157 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0657-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upper extremity in hospitalized road traffic accident : adult versus pediatric
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 International Trauma Life Support for Prehospital Care Providers Sixth Edition Patricia M. Hicks, MS, NREMTP Roy Alson, PhD, MD, FACEP Donna Hastings, EMT-P John Emory Campbell, MD, FACEP and Alabama Chapter,
International Trauma Life Support for Prehospital Care Providers Sixth Edition Patricia M. Hicks, MS, NREMTP Roy Alson, PhD, MD, FACEP Donna Hastings, EMT-P John Emory Campbell, MD, FACEP and Alabama Chapter,
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations
 Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Risk factors for acute compartment syndrome of the leg associated
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2015) 16:185 192 DOI 10.1007/s10195-014-0330-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for acute compartment syndrome of the leg associated with tibial diaphyseal fractures in adults Babak
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2015) 16:185 192 DOI 10.1007/s10195-014-0330-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for acute compartment syndrome of the leg associated with tibial diaphyseal fractures in adults Babak
Surgical Complications
 Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Surgical Complications Complications are common even with ideal management. Recently, Bashyal performed a retrospective review of 622 patients treated for supracondylar fractures and evaluated the complications
Spinal Cord Injury. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Cord Injury North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Cord Injury? A spinal cord injury is a condition that results from damage or trauma to the nerve tissue of the spine.
Spinal Cord Injury North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Cord Injury? A spinal cord injury is a condition that results from damage or trauma to the nerve tissue of the spine.
Compartment syndrome in infants and toddlers
 J Child Orthop (2016) 10:453 460 DOI 10.1007/s11832-016-0766-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Compartment syndrome in infants and toddlers Alexander Broom 1 Mathew D. Schur 1 Alexandre Arkader 2 John Flynn
J Child Orthop (2016) 10:453 460 DOI 10.1007/s11832-016-0766-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Compartment syndrome in infants and toddlers Alexander Broom 1 Mathew D. Schur 1 Alexandre Arkader 2 John Flynn
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
Popliteal artery injuries: Civilian experience with sixty-three patients during a twenty-four year period (1960 through 1984)
 Popliteal artery injuries: Civilian experience with sixty-three patients during a twenty-four year period (1960 through 1984) Allan R. Downs, M.D., F.R.C.S.C., and Peter MacDonald, M.D., Winnipeg, Manitoba,
Popliteal artery injuries: Civilian experience with sixty-three patients during a twenty-four year period (1960 through 1984) Allan R. Downs, M.D., F.R.C.S.C., and Peter MacDonald, M.D., Winnipeg, Manitoba,
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques
 TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures
 Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
A prospective study of functional outcome of primary intra-medullary nailing in type 3A and 3B open tibial diaphyseal fractures
 2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
2017; 3(3): 696-700 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 696-700 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 18-05-2017 Accepted: 20-06-2017 Dr. Deepak Shivanna Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics, BMCRI, Bengaluru,
ISPUB.COM. Prospective Study Of Limb Injuries In Calabar. N Ngim, A Udosen, I Ikpeme, O Ngim INTRODUCTION PATIENTS AND METHODS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 2 N Ngim, A Udosen, I Ikpeme, O Ngim Citation N Ngim, A Udosen, I Ikpeme, O Ngim.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 8 Number 2 N Ngim, A Udosen, I Ikpeme, O Ngim Citation N Ngim, A Udosen, I Ikpeme, O Ngim.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007
موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان
 8 موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان 1 P a g e Today we will talk about a new region, which is the leg. And as always, we will start with studying the sensory innervation of the leg. What is the importance
8 موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان 1 P a g e Today we will talk about a new region, which is the leg. And as always, we will start with studying the sensory innervation of the leg. What is the importance
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE REVIEW TRAUMA K. INABA, MD FACS LAC+USC MEDICAL CENTER
 SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE REVIEW TRAUMA K. INABA, MD FACS LAC+USC MEDICAL CENTER None DISCLOSURES OBJECTIVES CPMT SYNDROME ABDOMEN EXTREMITY OBJECTIVES CPMT SYNDROME ABDOMEN EXTREMITY Abdominal Compartment
SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE REVIEW TRAUMA K. INABA, MD FACS LAC+USC MEDICAL CENTER None DISCLOSURES OBJECTIVES CPMT SYNDROME ABDOMEN EXTREMITY OBJECTIVES CPMT SYNDROME ABDOMEN EXTREMITY Abdominal Compartment
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES
 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
Vascular dysfunction and vulnerable skin
 Vascular dysfunction and vulnerable skin Professor Peter Vowden Honorary Consultant Vascular Surgeon Clinical Director WoundTec HTC Bradford, UK 1 Exploring the clinical problem associated with the application
Vascular dysfunction and vulnerable skin Professor Peter Vowden Honorary Consultant Vascular Surgeon Clinical Director WoundTec HTC Bradford, UK 1 Exploring the clinical problem associated with the application
Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture
 214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus
 Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula
 Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Medial Malleolus Fracture Fixation in the Setting of Concomitant Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Medial Malleolus Fracture Fixation in the Setting of Concomitant Tibial Shaft Fractures Stephen R. Barchick 1, BA Andrew P. Matson 2, MD Samuel B. Adams 2, MD 1. Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
Medial Malleolus Fracture Fixation in the Setting of Concomitant Tibial Shaft Fractures Stephen R. Barchick 1, BA Andrew P. Matson 2, MD Samuel B. Adams 2, MD 1. Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS
 DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
 Geographia Napocensis Anul VI, Nr. 2, 2012 GEOCODING OF TRAUMA IN CHILDREN AS A MODELING OF CITY RISK ASSESSMENT AREAS (GIS BASED METHOD) DAMIAN ABSALON 1, BARBARA ŚLESAK 2, RYSZARD TOMASZEWSKI 2 Abstract:
Geographia Napocensis Anul VI, Nr. 2, 2012 GEOCODING OF TRAUMA IN CHILDREN AS A MODELING OF CITY RISK ASSESSMENT AREAS (GIS BASED METHOD) DAMIAN ABSALON 1, BARBARA ŚLESAK 2, RYSZARD TOMASZEWSKI 2 Abstract:
Case. 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds
 Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Management Of The Diabetic foot
 Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
ACUTE PAIN SECTION. M. Anthony Cometa, MD,* Andrea T. Esch, DO,* and André P. Boezaart, MD, PhD*
 Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 823 828 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. ACUTE PAIN SECTION Case Reports Did Continuous Femoral and Sciatic Nerve Block Obscure the Diagnosis or Delay the Treatment of Acute Lower Leg Compartment
Pain Medicine 2011; 12: 823 828 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. ACUTE PAIN SECTION Case Reports Did Continuous Femoral and Sciatic Nerve Block Obscure the Diagnosis or Delay the Treatment of Acute Lower Leg Compartment
We carried out a randomised, controlled trial in
 Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
Presented at 2015 TQIP conference. Developed by a panel of experts. Evidence based with expert opinion as needed
 Presented at 2015 TQIP conference Developed by a panel of experts Evidence based with expert opinion as needed Orthopaedic Trauma Best Practice Guidelines (BPG) Goals Offer guidance on what is practical
Presented at 2015 TQIP conference Developed by a panel of experts Evidence based with expert opinion as needed Orthopaedic Trauma Best Practice Guidelines (BPG) Goals Offer guidance on what is practical
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
 Session: L150 This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH Disclosures: This presenter has no financial relationships with
Session: L150 This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH Disclosures: This presenter has no financial relationships with
Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies
 Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies Joshua Crum M.D. Hill Country Sports Medicine San Marcos, TX Goals Define what constitutes and orthopedic emergency/urgency Know what conditions need
Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies Joshua Crum M.D. Hill Country Sports Medicine San Marcos, TX Goals Define what constitutes and orthopedic emergency/urgency Know what conditions need
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Please understand that the values set forth here estimated ranges of of value for New York pain and
 LOWER LEG INJURIES ISSUE 3 How New York Juries Decide the Value of obligation. You re invited to call John toll free at Pain and Suffering in Lower Leg Fracture 1-800-530-4660, or locally, 914-686-0900.
LOWER LEG INJURIES ISSUE 3 How New York Juries Decide the Value of obligation. You re invited to call John toll free at Pain and Suffering in Lower Leg Fracture 1-800-530-4660, or locally, 914-686-0900.
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound. William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017
 The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017 Disclosures: Financial I tried to find somebody to pay me to give this talk, but couldn t Disclosures: Intellectual
The Mangled Extremity: It s NOT Just a Flesh Wound William Hakeos, MD September 22, 2017 Disclosures: Financial I tried to find somebody to pay me to give this talk, but couldn t Disclosures: Intellectual
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations
 Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations
 Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Treatment of Acute Traumatic Knee Dislocations Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Hemorrhage Control. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
~, /' ~::'~ EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS. Leg-anterolateral :.:~ / ~\,
 TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Practice Changes I Hope You Make
 Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle.
 Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
The Pattern of Peripheral Nerve Injuries among Iraqi Soldiers in the War by using Nerve Conductive Study
 Research Article The Pattern of Peripheral Nerve Injuries among Iraqi Soldiers in the War by using Nerve Conductive Study Qaisar A. Atea, M.B.Ch.B, D.R.M.R. Safaa H. Ali, M.B.Ch.B, Msc, Ph.D. Date Submitted:
Research Article The Pattern of Peripheral Nerve Injuries among Iraqi Soldiers in the War by using Nerve Conductive Study Qaisar A. Atea, M.B.Ch.B, D.R.M.R. Safaa H. Ali, M.B.Ch.B, Msc, Ph.D. Date Submitted:
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Of approximately 2 million long bone fractures
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic
 Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital
 Original article: A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Mohammad Azmoddin 1, Surender Rao Yadagiri 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Original article: A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Mohammad Azmoddin 1, Surender Rao Yadagiri 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Dr Keith Holt Compartment syndrome is a relatively common disorder whereby pressure in one or more muscle compartments increases during exercise, causing progressively increasing pain,
Compartment Syndrome Dr Keith Holt Compartment syndrome is a relatively common disorder whereby pressure in one or more muscle compartments increases during exercise, causing progressively increasing pain,
Lower extremity acute compartment syndrome secondary to inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Lower extremity acute compartment syndrome secondary to inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report Keegan Devon Bradley, Hao Wang ABSTRACT
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Lower extremity acute compartment syndrome secondary to inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report Keegan Devon Bradley, Hao Wang ABSTRACT
Claw toes after tibial fracture in children
 J Child Orthop (2009) 3:339 343 DOI 10.1007/s11832-009-0200-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Claw toes after tibial fracture in children Frank Fitoussi Æ Brice Ilharreborde Æ Florent Guerin Æ Philippe Souchet
J Child Orthop (2009) 3:339 343 DOI 10.1007/s11832-009-0200-y ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Claw toes after tibial fracture in children Frank Fitoussi Æ Brice Ilharreborde Æ Florent Guerin Æ Philippe Souchet
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack
 1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
