Congenital dislocation of the patella
|
|
|
- Shanna Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:119 DOI /s ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Congenital dislocation of the patella Akifusa Wada Æ Toshio Fujii Æ Kazuyuki Takamura Æ Haruhisa Yanagida Æ Panya Surijamorn Received: 19 September 2007 / Accepted: 4 February 2008 / Published online: 4 March 2008 EPOS 2008 Abstract Purpose Congenital dislocation of the patella is permanent and manually irreducible, and it manifests immediately after birth with flexion contracture of the knee, genu valgus, external tibial torsion and foot deformity. We retrospectively reviewed the results of operative treatment of seven knees in six patients with congenital dislocation of the patella. Methods The age of the six patients at diagnosis ranged from 8 days to 3.6 years, with an average of 1.3 years, and their age at the time of ranged from 0.6 to 3.9 years, with an average of 2.1 years. Serial casting and/or a was attempted before surgery in five of seven knees, leading to improvement in the flexion contracture of the knee. All knees were treated operatively in combination with lateral release, medial plication, V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps, medial transfer of the lateral patellar tendon and posterior release of the knee. Results Although these deformities were noticed at birth in all seven knees, diagnosis was delayed in three knees due to the low suspicion of the disease and invisible patellae on radiographs. Ultrasonography confirmed the diagnosis of dislocation. The patella was centered in the groove of the femoral condyle after surgery in all knees, but subluxation of the knee with flexion was observed in one knee in which the was performed at 3.9 years. Genu valgus and external tibial torsion improved after surgery in all knees. The operated knee was mobile in A. Wada T. Fujii (&) K. Takamura H. Yanagida P. Surijamorn Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Fukuoka Children s Hospital, Tojinmachi, Chuo-ku, Fukuoka , Japan fujii.t@fukuoka-child.jp all cases, with less than 10 flexion contracture of the knee. Flexion contracture did not increase in any of the knees. Conclusion Congenital dislocation of the patella should be suspected in every patient with knee flexion contracture, genu valgus, external tibial torsion, foot deformity and delayed walking. Successful results were obtained when the was performed in younger children. Other procedures, such as the semitendinosus tenodesis or tendon transfer, might have to be combined to achieve better stability with flexion in older children. Keywords Congenital dislocation Patella Quadriceps malrotation Operative treatment Introduction Congenital dislocation is permanent and irreducible, and it manifests immediately after birth with flexion contracture of the knee, genu valgum and external tibial torsion. It should be distinguished from patellar instability, as well as from recurrent, habitual or permanent reducible dislocations [1 3]. Previous studies [4 7] have discussed patellar dislocation as a congenital dislocation associated with Down syndrome and nail-patella syndrome, but the onset of the former occurs after birth and should be distinguished from the latter [2, 3]. If these criteria are used, congenital dislocation is rare. We treated this condition using a combination of lateral release, medial plication, V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps, medial transfer of the lateral patellar tendon and posterior release of the knee. The purpose of the present study was to review and evaluate our experiences in the operative treatment of knees with congenital dislocation of the patella.
2 120 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:119 Patients and methods Between 1980 and 2005, seven knees in six patients (two boys and four girls) were operatively treated at our institution for congenital dislocation of the patella. The details of the six patients are shown in Table 1. There were five unilateral and one bilateral patella dislocations. The age of the patients at diagnosis ranged from 8 days to 3.6 years, with an average of 1.3 years, and their age at the time of ranged from 0.6 to 3.9 years, with an average of 2.1 years. Patellar dislocations associated with Down syndrome, nail-patella syndrome, Kabuki syndrome or Ellis-Van Crevald syndrome were excluded in the present study. Patellar dislocation was permanent and irreducible in all knees. Flexion contracture of the knee, genu valgus, external tibial torsion and foot deformity were present in all knees. Ultrasonography and MRI were performed to obtain a diagnosis and preoperative evaluation in all patients. Preoperative flexion contracture of the knee ranged from 5 to 60, with an average of 28. Associated calcaneovalgus foot deformity was present in four feet, congenital vertical talus was observed in two feet, and talipes equinovarus deformity in one foot. Three of six patients (cases 4, 5 and 6) who were operatively treated after walking had a severe limp before surgery. Treatment Serial casting and/or a was attempted in five of seven knees, leading to improvement in the flexion contracture of the knee. Serial casting and/or a was not used in one patient whose cardiovascular complications had been treated in another department. All knees were treated operatively in combination with lateral release, medial plication, V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps, medial transfer of the lateral patellar tendon and posterior release of the knee. Operative technique Under general anesthesia, the patient was placed in the supine position. A curved incision was made laterally starting from the distal third of the femur, extending superiomedially to the patella, and ending medially to the tibial tuberosity. Lateral release was performed by dividing the quadriceps from the fibrous adhesions to the iliotibial band and the lateral intermuscular septum. The lateral capsule was incised laterally to the dislocated patella and along the lateral border of the patellar tendon to the tibial tuberosity. The medial capsule and retinaculum were incised medially to the patella. The patella was released from the lateral aspect of the lateral femoral condyle and Table 1 Patient data Case Sex Side Underlying disease Age at diagnosis Treatment before Knee flexion contracture ( ) before Age (years) at Operative treatment Complications Duration (years) of postoperative follow-up Knee flexion contracture ( ) at follow-up 1 F L AMC 8 days Serial 2 F L Unknown 9 days Serial 3 M R Multiple congenital anomalies LR(PS), LR(PS), 8 days None LR(FG), PR L 8 days None LR(FG), PR 4 F L Chondrodysplasia punctata 5 M R Congenital fibular deficiency 6 F R Unknown 3.6 years Serial 2.6 years Brace LR(FG), MP 2.9 years Brace LR(PS), MP LR(FG), Subluxation with flexion AMC arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, LR lateral release, PS patch with a polytetrafluoroethylene (Gore-Tex) sheet, MP medial plication, QL V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps, medial transfer of the lateral patellar tendon, FG patch with a free graft taken from the abundant medial capsule and retinaculum, PR posterior release of the knee
3 J Child Orthop (2008) 2: reduced into the typically underdeveloped shallow groove of the femoral condyle. The tracking of the patella was checked carefully. In the five knees in which knee flexion was restricted due to the shortened quadriceps, the quadriceps tendon was lengthened proximal to the patella by V-Y plasty. In three of these five knees, in which mild lateral subluxation remained, the lateral half of the patellar tendon was carefully detached at its insertion from the cartilaginous tibial tuberosity and was sutured medially at the midline of the upper tibia. The lateral subluxation improved as a result of the lateral half of the patellar tendon transfer in all five knees. In the two knees with severe knee flexion contracture, posterior release was performed using two vertical incisions in the prone position after the anterior part of the surgery. Full extension was achieved by Z- or fractional lengthening of the hamstrings and semi-membrane and semitendinosus tendons; posterior capsular release was not performed. The lateral capsular defect was patched to prevent synovial fluid leakage in all knees. A free graft taken from the abundant medial capsule and retinaculum was used in four knees and a polytetrafluoroethylene (Gore-Tex) sheet (W.L. Gore and Associates, Flagstaff, AZ) was used in three knees. Medial plication was performed in all knees. The medial capsule and retinaculum with a part of the vastus medialis were drawn laterally and sutured anterolaterally to the patella. A long-leg plaster cast was applied to hold the knee in slight flexion for 2 3 weeks after surgery. Active and passive exercises of the knee were initiated after cast removal. Results The follow-up period ranged from 2.0 to 10.2 years, with an average of 4.8 years. Three of seven knees were not accurately diagnosed with patellar dislocation at our initial consultation. Ultrasonography was useful in all patients for evaluating the location of the non-ossified patellae and confirmed the diagnosis of dislocation. MR imaging was useful for preoperative evaluation and clearly visualized the malrotated quadriceps muscle with insertion of the patella tendon, the hypoplastic dislocated patella and the undeveloped intercondylar groove of the femoral condyle. Serial casting and/or s were attempted before surgery in five of seven knees and were effective in reducing flexion contracture. At the time of writing, the reduced patella was centered in the groove of the femoral condyle in all knees, but lateral subluxation with flexion persisted in one knee; the patient complained of femoropatellar pain after walking for long distances. Genu valgus and external tibial torsion improved after surgery in all knees. The operated knee was mobile in all cases, with less than 10 flexion contracture of the knee. Flexion contracture did not increase in any of the knees. The average flexion contracture of the knees was improved to 6 (0 10 ) with an average improvement of 22 (0 50 ). The preoperative limp in the three patients (cases 4, 5 and 6) improved after surgery. Two patients without the underlying disease (cases 2 and 6) had no limp at the time of writing. Discussion There has been great confusion regarding the classification of patellar dislocation in children [2, 3]. Many previous reports include patellar dislocations found in Down syndrome or nail-patella syndrome in the group of congenital dislocations of the patella [4 7]. The patellar dislocations associated with Down syndrome, nail-patella syndrome, Kabuki syndrome, and Ellis-Van Crevald syndrome are considered to occur after birth, during childhood or adolescence, and to gradually become permanent and irreducible; they were excluded from the present study. This condition was observed in children with joint laxity and occurs more or less late during growth, and much more frequently in teenagers [1]. The term developmental dysplasia of the patella (DDP) accurately reflects the variable characteristics of this condition [1]. Congenital dislocation of the patella is a different entity and should be distinguished from other patellar dislocations [1 3]. It is characterized by a relative stiffness, a short quadriceps, and a major femoropatellar dysplasia. Congenital dislocation is permanent and irreducible, and manifests immediately after birth with flexion contracture of the knee, genu valgum and external tibial torsion (Fig. 1a). Although these deformities were noticed at birth in all seven knees, diagnosis was delayed in three knees due to the low suspicion of the disease and, because the patella ossifies between 3 and 5 years of age, the invisibility of patellae on radiographs (Fig. 1b). When flexion contracture is severe, active extension of the knee is impossible because the quadriceps mechanism works as a knee flexor. In patients whose flexion contracture is mild or is improved by serial casting and/or a, active extension of the knee becomes possible with mild impairment of walking. Thus, patients with congenital patellar dislocation are often misdiagnosed with a neuromuscular disease or muscular dystrophy. Congenital dislocation of the patella should be suspected in every patient with arthrogryposis, skeletal dysplasia or other related syndromes, especially if the patient presents with knee flexion contracture, genu valgus,
4 122 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:119 Fig. 1 a A 9-day-old girl (case 2) presented with severe knee flexion contracture and external tibial torsion. Active extension of the knee was impossible. b Anteroposterior radiograph at 9 days showing left genu valgus and external tibial torsion. c Axial ultrasonography shows hypoplastic, laterally dislocated patella (arrowheads). d MR imaging at 0.5 years showing a laterally dislocated patella adherent to the lateral condyle and an underdeveloped, shallow groove of the femoral condyle. e Surgery at 0.6 years consisting of lateral release, medial plication and V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps tendon. The lateral capsular defect was patched with a polytetrafluoroethylene sheet. f Clinical photograph at 2.6 years showing no knee flexion contracture nor external tibial torsion. g MR imaging at 2.6 years showing the reduced patella in the groove of the femoral condyle external tibial torsion, foot deformity and delayed walking [4]. A careful physical examination is necessary, focusing on palpation of the patella, which is small, impossible to find at the anterior aspect of the knee, relatively fixed and lies laterally on the lateral condyle. Ultrasonography is easy to perform and is useful for locating the patella and confirming the diagnosis (Fig. 1c) [3, 8 11]. MR imaging allows visualization of fine anatomic details and relationships between the involved structures of the extensor mechanism and should be performed as a part of preoperative assessment and planning (Fig. 1d) [10, 11]. The only possible treatment for congenital dislocation of the patella is surgical. Serial casting and a are effective in reducing flexion contracture of the affected knee, but genu valgum, external tibial torsion and subluxation of the tibia inevitably develop without surgical
5 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:119 intervention. Stanisavljevic et al. [12] reported successful results of the extensive lateral release and anterior transposition of the entire quadriceps mechanism based on their suggested pathogenesis of malrotation of the quadriceps myotome during embryonic life. However, the entire release of the quadriceps requires a wide incision and extensive lateral dissection. The present operative technique of lateral release was less extensive than the Stanisavljevic procedure [12]. We did not extend the incision to the level of the greater trochanter and did not strip the quadriceps extraperiosteally. Our incision was limited to the mid-thigh, and our lateral release was performed by dividing the quadriceps from the fibrous adhesions to the iliotibial band and lateral intermuscular septum. V-Y lengthening of the quadriceps, medial transfer of the lateral patellar tendon and posterior release of the knee were combined according to the severity of the deformity. Bensahel et al. [1] and Eilert [9] also describe the effectiveness and good outcome of a similar procedure using a combination of lateral release, medial plication, lengthening of the quadriceps, and medial transfer of the patellar tendon. The operative findings in congenital dislocation of the patella have been described as follows [1 9, 12]: (1) malrotation of the quadriceps muscle with insertion of the patellar tendon on the anterolateral tibia, (2) contracture of the quadriceps and iliotibial band, (3) a hypoplastic patella with a flattened articular surface fixed on the lateral knee, (4) an undeveloped, shallow anterior intercondylar groove of the femoral condyle, (5) contracture of the lateral capsule and thickening of the medial capsule, (6) genu valgus and external tibial torsion and (7) lateral subluxation of the tibia. These were consistent with the findings in the present series. We used the polytetrafluoroethylene (Gore-Tex) sheet to make patches for the large lateral capsular defect to prevent synovial fluid leakage and adhesions to the quadriceps muscle and the surrounding tissues (Fig. 1e). The sheet has little reaction or adhesion to living tissue and has been used for dural repair, artificial vessels and patches for pericardium. To our knowledge, there is no orthopedic literature on the usage of the sheet except for our case report [13] in which the sheet was used in the ankle joint. Long-term follow-up is necessary to fully clarify the efficiency and safety of the sheet. The should be performed early, as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed, and preferably before 1 year of age [3]. In our two knees, which were operatively treated before 1 year of age, early made it possible to reconstruct almost normal knee function and to provide the patient with a normal gait without delay at the onset of walking (Fig. 1f, g). Neglected cases require more extensive excisions of contractures to ensure reduction of the patellar dislocation and more complicated surgical reconstructions to ensure patellar stability [3]. Subluxation of the knee with flexion recurred in the knee in which the was performed at 3.9 years. Other procedures, such as the semitendinosus tenodesis as described by Galeazzi [14] or tendon transfer as described by Uezaki [15], might have to be combined additionally to achieve better stability with flexion in older children. Acknowledgments for this study. References None of the authors received financial support 1. Bensahel H, Souchet P, Pennecot GF, Mazda K (1990) The unstable patella in children. J Pediatr Orthop B 9: Ghanem I, Wattincourt L, Seringe R (2000) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Part I: pathologic anatomy. J Pediatr Orthop 20: Ghanem I, Wattincourt L, Seringe R (2000) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Part II: orthopaedic management. J Pediatr Orthop 20: Gao GX, Lee EH, Bose K (1990) Surgical management of congenital and habitual dislocation of the patella. J Pediatr Orthop 10: Gordon JE, Schoenecker PL (1999) Surgical treatment of congenital dislocation of the patella. J Pediatr Orthop 19: Langenskiöld A, Ritsilä V (1992) Congenital dislocation of the patella and its operative treatment. J Pediatr Orthop 12: Paton RW, Bonshahi AY, Kim WY (2004) Congenital and irreducible non-traumatic dislocation of the patella a modified soft tissue procedure. Knee 11: Calisir C, Inan U, Yilmaz O (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging of bilateral lateral congenital dislocations of unossified patellae. Skeletal Radiol 35: Eilert RE (2001) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop 389: Koplewitz BZ, Babyn PS, Cole WG (2005) Congenital dislocation of the patella. Am J Roentgenol 184: Walker J, Rang M, Daneman A (1991) Ultrasonography of the unossified patella in young children. J Pediatr Orthop 11: Stanisavljevic S, Zemenick G, Miller D (1976) Congenital, irreducible, permanent lateral dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop 116: Wada A, Fujii T, Takamura K, Yanagida H, Matsuura A, Katayama A (2003) Physeal arrest of the ankle secondary to extravasation in a neonate and its treatment by the Gruca : a modern application of an old technique. J Pediatr Orthop B 12: Galeazzi R (1921) Nuove applicazioni del trapianto muscolare e tendineo. Arch Orthop 38: Uezaki N (1981) Luxations habituelles de rotule chez l enfant. Méthode personnelle utilisant le demi-tendineux (semi-tendinosus); méthode d Heusner modifiée. Rev Chir Orthop 67:
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Management of ACL Elongation in the Surgical Treatment of Congenital Knee Dislocation
 Management of ACL Elongation in the Surgical Treatment of Congenital Knee Dislocation Kevin E. Klingele, MD; Scott Stephens, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search:
Management of ACL Elongation in the Surgical Treatment of Congenital Knee Dislocation Kevin E. Klingele, MD; Scott Stephens, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search:
Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella Treated with a Different Method in Each Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA
 ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
A combined procedure for irreducible dislocation of patella in children with ligamentous laxity: a preliminary report
 OIGINA ATICE Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2015;49(5):530538 doi:.3944/aott.2015.15.0044 A combined procedure for irreducible dislocation of patella in children with ligamentous laxity: a preliminary report
OIGINA ATICE Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2015;49(5):530538 doi:.3944/aott.2015.15.0044 A combined procedure for irreducible dislocation of patella in children with ligamentous laxity: a preliminary report
A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella
 CONTRACTURE OF THE QUADRICEPS MUSCLE A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella D. R. GUNN, SINGAPORE The objects ofthis paper are to suggest that an important
CONTRACTURE OF THE QUADRICEPS MUSCLE A Discussion on the Etiology and Relationship to Recurrent Dislocation of the Patella D. R. GUNN, SINGAPORE The objects ofthis paper are to suggest that an important
HABITUAL DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA IN FLEXION
 HABITUAL DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA IN FLEXION NEIL R. BERGMAN, PETER F. WILLIAMS From the Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne Thirty-five patients with habitual dislocation of the patella in fiexion
HABITUAL DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA IN FLEXION NEIL R. BERGMAN, PETER F. WILLIAMS From the Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne Thirty-five patients with habitual dislocation of the patella in fiexion
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Chronic patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Using an iliotibial tract for patellar dislocation in children
 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:343 351 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0106-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Using an iliotibial tract for patellar dislocation in children Nguyen Ngoc Hung Received: 6 May 2007 / Accepted:
J Child Orthop (2008) 2:343 351 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0106-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Using an iliotibial tract for patellar dislocation in children Nguyen Ngoc Hung Received: 6 May 2007 / Accepted:
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy
 Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer``
 Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer`` Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS(C) McGill University Health Centre Intoeing Knock knees Bowlegs Flatfeet Toe walking Knee pain Hip click Intoeing Objectives
Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer`` Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS(C) McGill University Health Centre Intoeing Knock knees Bowlegs Flatfeet Toe walking Knee pain Hip click Intoeing Objectives
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Case Report Adult Congenital Permanent Bilateral Dislocation of the Patella with Full Knee Function: Case Report and Literature Review
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 182795, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/182795 Case Report Adult Congenital Permanent Bilateral Dislocation of the Patella with Full Knee Function: Case Report
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 182795, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/182795 Case Report Adult Congenital Permanent Bilateral Dislocation of the Patella with Full Knee Function: Case Report
7/20/14. Patella Instability. Alignment. PF contact areas. Tissue Restraints. Pain. Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint
 Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN. Guy BELLIER PARIS France
 BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN Guy BELLIER PARIS France TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN CONTROVERSIAL DIAGNOSIS clinical exam X-rays (stress) M.R.I. arthroscopy ACL TEARS
BAD RESULTS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN Guy BELLIER PARIS France TREATMENT OF ACL TEARS IN CHILDREN CONTROVERSIAL DIAGNOSIS clinical exam X-rays (stress) M.R.I. arthroscopy ACL TEARS
Peggers Super Summaries: PFJ
 Patellofemoral Joint: ANATOMY: Largest sesamoid ossifying at 3-5 years of age Multiple foci having a sec ossification centre SUPEROLATERAL Helps increase moment arm PATELLOFEMORAL OA Incidence 10% of knee
Patellofemoral Joint: ANATOMY: Largest sesamoid ossifying at 3-5 years of age Multiple foci having a sec ossification centre SUPEROLATERAL Helps increase moment arm PATELLOFEMORAL OA Incidence 10% of knee
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
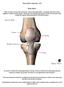 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
World Medical & Health Games
 Management of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome João Barroso Orthopaedic department ULS Matosinhos Portugal Introduction Anterior Knee Pain affects 1 in 4 athletes very common! (Knowles et al) Patellofemoral
Management of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome João Barroso Orthopaedic department ULS Matosinhos Portugal Introduction Anterior Knee Pain affects 1 in 4 athletes very common! (Knowles et al) Patellofemoral
Unilateral congenital dislocation of the knee and hip : a case report
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 134-138 CASE REPORT Unilateral congenital dislocation of the knee and hip : a case report Farhad TAJDAr, Jan ViCTOr From St-Lucas Hospital, Bruges, Belgium We report our experience
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 134-138 CASE REPORT Unilateral congenital dislocation of the knee and hip : a case report Farhad TAJDAr, Jan ViCTOr From St-Lucas Hospital, Bruges, Belgium We report our experience
Doron Sher. 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick Burwood Rd, Concord. MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA
 Doron Sher MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick 47 49 Burwood Rd, Concord www.kneedoctor.com.au www.orthosports.com.au Medial PatelloFemoral (MPFL) And AnteroLateral Ligament (ALL) Reconstruction
Doron Sher MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick 47 49 Burwood Rd, Concord www.kneedoctor.com.au www.orthosports.com.au Medial PatelloFemoral (MPFL) And AnteroLateral Ligament (ALL) Reconstruction
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016
 Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016 With many thanks to Beth Shubin Stein, MD What is the Problem??? THIS IS THE PROBLEM Patella Stability Factors contributing to stability Articular
Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016 With many thanks to Beth Shubin Stein, MD What is the Problem??? THIS IS THE PROBLEM Patella Stability Factors contributing to stability Articular
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes
 Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Congenital dislocation of the knee: a protocol for management based on degree of knee flexion
 J Child Orthop (2011) 5:143 149 DOI 10.1007/s11832-011-0333-7 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Congenital dislocation of the knee: a protocol for management based on degree of knee flexion Tarek Hassan Abdelaziz
J Child Orthop (2011) 5:143 149 DOI 10.1007/s11832-011-0333-7 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Congenital dislocation of the knee: a protocol for management based on degree of knee flexion Tarek Hassan Abdelaziz
HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES
 HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES Written by Philippe Landreau, Qatar The treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries remains challenging in young athletic populations. A residual
HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES Written by Philippe Landreau, Qatar The treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries remains challenging in young athletic populations. A residual
10/26/2017. Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP. Objectives. It s all about function. Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD
 Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD Objectives Understand varying levels of intervention are available to optimize function of children
Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD Objectives Understand varying levels of intervention are available to optimize function of children
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
CHRONIC PATELLOFEMORAL INSTABILITY
 INSTRUCTIONAL COURSE LECTURE DAVID J. DANDY From Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, England This article aims to discuss the many causes of patellofemoral instability so that an appropriate stabilisation
INSTRUCTIONAL COURSE LECTURE DAVID J. DANDY From Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, England This article aims to discuss the many causes of patellofemoral instability so that an appropriate stabilisation
Plaster-Wedging Technique:
 Plaster-Wedging Technique: An Appropriate, Safe, Quick, & Economical Method To Stretch Soft Tissue Contractures Of The Knee H.M. Steenbeek General Information. In the field of physical rehabilitation of
Plaster-Wedging Technique: An Appropriate, Safe, Quick, & Economical Method To Stretch Soft Tissue Contractures Of The Knee H.M. Steenbeek General Information. In the field of physical rehabilitation of
Acute patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 14 Acute patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for the first acute dislocation? How can we document the pathoanatomy? What is our treatment concept? Table CS14 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 14 Acute patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for the first acute dislocation? How can we document the pathoanatomy? What is our treatment concept? Table CS14 Patellofemoral joint
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Patellofemoral Joint. Question? ANATOMY
 Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique
 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique Medial Patellofemoral Ligament The medial patellofemoral complex, consisting of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) and the medial patellotibial
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique Medial Patellofemoral Ligament The medial patellofemoral complex, consisting of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) and the medial patellotibial
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES
 A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Knee Capsular Disorder. ICD-9-CM: Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified
 1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
AACPDM IC#21 DFEO+PTA 1
 Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
Toe walking gives rise to parental concern. Therefore, toe-walkers are often referred at the 3 years of age.
 IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula
 Chronic, Painful Ankle Instability in Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula Brian D. Busconi,* MD, and Arthur M. Pappas, MD From the Department of Orthopedics
Chronic, Painful Ankle Instability in Skeletally Immature Athletes Ununited Osteochondral Fractures of the Distal Fibula Brian D. Busconi,* MD, and Arthur M. Pappas, MD From the Department of Orthopedics
A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap for valgus knee TKA
 Jiang and Fernandes Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:173 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0316-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap
Jiang and Fernandes Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:173 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0316-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A lateral approach defect closure technique with deep fascia flap
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation
 Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation American Medical Society for Sports Medicine April 6, 2014 Beth E. Shubin Stein, MD Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery Beth E. Shubin
Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation American Medical Society for Sports Medicine April 6, 2014 Beth E. Shubin Stein, MD Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery Beth E. Shubin
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE
 PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO INDUSTRY CONFLICTS TO DECLARE I AM AN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON TRAINED IN
PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO INDUSTRY CONFLICTS TO DECLARE I AM AN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON TRAINED IN
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on
 ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD
 MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD Professor and Team Physician: Orthopaedic Surgery University of Kentucky School of Medicine Disclosure Institution: Research/Education Smith-Nephew
MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD Professor and Team Physician: Orthopaedic Surgery University of Kentucky School of Medicine Disclosure Institution: Research/Education Smith-Nephew
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018
 Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Hip and Knee Approaches
 Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Patellofemoral Pathology
 Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff),
 Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff), Consultant Knee Surgeon NHS: The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital & Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham MRI Knee:
Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff), Consultant Knee Surgeon NHS: The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital & Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham MRI Knee:
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
As for the forelimb, treatment of condition of the hindlimb may be treated by both localised therapy, applying the laser
 MLS Master Class - Veterinary Imaging Presented by CelticSMR Ltd Free Phone (UK): 0800 279 9050 International: +44 (0) 1646 603150 AUTHOR DETAILS Carl Gorman BVSc MRCVS PUBLISHER DETAILS Mike Howe B Vet
MLS Master Class - Veterinary Imaging Presented by CelticSMR Ltd Free Phone (UK): 0800 279 9050 International: +44 (0) 1646 603150 AUTHOR DETAILS Carl Gorman BVSc MRCVS PUBLISHER DETAILS Mike Howe B Vet
Early Reduction for Congenital Dislocation of the Knee within Twenty-four Hours of Birth
 Original Article 266 Early Reduction for Congenital Dislocation of the Knee within Twenty-four Hours of Birth Chun-Chien Cheng, MD; Jih-Yang Ko 1, MD Background: (CDK) is a very rare condition that comprises
Original Article 266 Early Reduction for Congenital Dislocation of the Knee within Twenty-four Hours of Birth Chun-Chien Cheng, MD; Jih-Yang Ko 1, MD Background: (CDK) is a very rare condition that comprises
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes
 Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Lateral knee injuries
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report
 Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Chronic Knee Dislocation: Reduction, Reconstruction, and Application of a Skeletally Fixed Knee Hinge
 0363-5465/98/2626-0591$02.00/0 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE, Vol. 26, No. 4 1998 American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine Chronic Knee Dislocation: Reduction, Reconstruction, and Application
0363-5465/98/2626-0591$02.00/0 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE, Vol. 26, No. 4 1998 American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine Chronic Knee Dislocation: Reduction, Reconstruction, and Application
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes.
 The injured knee Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes. J WALTERS, FC (Orth) SA Department of
The injured knee Knee injuries are probably one of the most common orthopaedic problems encountered in general practice, particularly among recreational athletes. J WALTERS, FC (Orth) SA Department of
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
10/30/18. Disclosures. Recurrent Patellar Instability. Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability
 Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability Miho J. Tanaka, MD Associate Professor Director, Women s Sports Medicine Program ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Disclosures None Recurrent Patellar Instability Lack of
Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability Miho J. Tanaka, MD Associate Professor Director, Women s Sports Medicine Program ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Disclosures None Recurrent Patellar Instability Lack of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
