Baseline Thickness of Proximal Femoral Epiphysis in the Diagnosis of Hip Diseases in Infants and Children in Nigeria
|
|
|
- Sydney Thornton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Surgical Research 2014, 3(2): DOI: /j.surgery Baseline Thickness of Proximal Femoral Epiphysis in the Diagnosis of Hip Diseases in Infants and Children in Nigeria Abiodun A. A. 1, Falana B. A. 2,*, Olatunbosun A. 3 1 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Health Sciences, University Ile-Ife, Nigeria 2 Department of Anatomy, College of Health sciences, Osogbo, Nigeria 3 Department of Anatomy, College of Health Sciences, University of Ilorin, Nigeria Abstract Backgroung/Introduction: This study investigated the baseline for the epiphyseal plate thickness of femoral head in infants and children in Nigeria. This was with a view to establishing the longitudinal growth rate, and monitoring the hormonal influence on longitudinal growth rate in infants and children studied, with a view to diagnosing effectively pathological conditions associated with it. Materials and Methods: Plain anteroposterior pelvic radiographs collected from the radiological department of the University Teaching Hospital Ilorin Kwara State Nigeria were used for this study. The film focal distance (FFD) was 100cm, and the retrieved radiographs were mounted on x-ray View Box and the measurement of the epiphyseal plate taken by measuring the vertical distance or height between the ossified epiphyses of the femoral head and neck. The epiphyseal plate is seen as the space between the ossified epiphysis of femoral head and neck. Other parameters recorded include the age and sex of the patients. The result was statistically analysed. Results: Results of the study showed no significant difference in both sexes as compared with age (p>0.05). The thickness was significant with values greater in males than in females (p<0.05). It was also observed that there is an earlier closure of the epiphyseal plate of femur in females when compared to that of males. The thickness when compared with age in both sexes have no significant difference for both the left and right sides (p>0.05). Conclusions: It was concluded that there is significant difference in the mean of the epiphyseal plate thickness of the femoral head between the male and the female infant and children, and these baseline thickness for different age groups will be useful in diagnosis of disorders and injuries like perthes disease and slipped upper femoral epiphysis which are common at a particular age group with the diseases affecting epiphyseal plates. Keywords Epiphyseal plates, Infant & children perthes disease Slipped upper femoral epiphysis 1. Introduction The epiphyseal plate (growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. The plate is found in children and adolescents, also found in adults, who have stopped growing, the plate is replaced by an epiphyseal endochondral ossification responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's chondrocytes are under constant division by mitosis. These daughter cells stack, facing the epiphysis while the older cells are pushed towards the diaphysis. As the older chondrocytes degenerate, osteoblasts ossify the remains to form new bone. In puberty increasing levels of * Corresponding author: benedict.falana@uniosun.edu.ng (Falana B. A.) Published online at Copyright 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved estrogen, in both females and males, leads to increased apoptosis of chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate. Depletion of chondrocytes due to apoptosis leads to less ossification and growth slows down and later stops when the entire cartilage have become replaced by bone, leaving only a thin epiphyseal scar which later disappears. Once the adult stage is reached, the only way to manipulate height is modifying bone length via distraction osteogenesis. Proximal femoral growth disturbance is a major complication associated with ischemic osteonecrotic conditions, such as Legg-Calvè-Perthes disease. The extent of ischemic damage and the mechanisms by which ischemic injury to the growing femoral head produces growth disturbance of the proximal femoral growth plate remain unclear. Disruption of the epiphyseal vasculature did not lead to diffuse growth plate damage in the majority of the ischemic femoral heads. [30] established the use of microfracture technique for the treatment of full thickness articular
2 International Journal of Surgical Research 2014, 3(2): cartilage lesions of the knee especially in high impact athletes. The distribution of chondrocytes throughout the total thickness of articular cartilage from the femoral condyles of infants, children and adults has been studied using serial sections cut parallel as well as perpendicular to the articular surface. The thickness of the articular cartilage was estimated in fixed sections in the work of [20-26] but reports on the deleterious effect of these fixatives has also been documented, thereby limiting the study to data interpretation rather than exploring using routine laboratory techniques..in the standing position the femora are oblique but there is also variation according to sex (greater in women), age, and stature [8]. In X-ray radiographs of the femoral bones of the infant, the bone consists of all the structures as specified above in adult but less developed with the presence of the epiphyseal plates in various region including the femoral head, trochanters (great and lesser) and the distal end of the femur. Observation on developmental patterns of this supply in late fetal and early post natal periods modifies the above description through medial and lateral circumflex arteries at first contribute equally, two major branches of the neck [9] supply from the lateral circumflex diminishes and arterial circle is interrupted. Growth plate fractures of the distal femur are challenging to treat, with complications that require a secondary surgery 40% to 60% of the time [29]. These fractures often necessitate operative intervention, even in the youngest patients and even with minimal apparent displacement. Treatment varies with the Salter-Harris (SH) classification and with the extent of initial displacement, ranging from simple casting for nondisplaced SH I fractures to open reduction and internal fixation for almost all SH III and IV fractures. The load bearing articular tissues have a stiffness gradient that safely transmits loads from the articular cartilage to the trabecular bone. Engineered tissue constructs and biomaterials combined with the recipient site properties should approximate this gradient. Biomechanical properties of the recipient site are dependent on parameters such as cartilage thickness, cartilage glycosaminoglycan and water content, and calcified cartilage/subchondral bone characteristics. [16-18, 1] observed growth disturbance after distal femoral growth plate fractures in children. Distal femoral physeal fractures in children have a high incidence of physeal arrest, occurring in a mean of 40% of cases. The underlying nature of the distal femoral physis was the primary cause, but other factors have been postulated to contribute to the formation of a physeal bar [7]. In general, the closer a child is to reaching skeletal maturity, the less risk they have of their tibia or femur growing at an abnormal angle if their growth plate is injured. Very young children, who still have a lot of growing to do, have a greater risk of permanent damage if their growth plate is injured. [4] Analysed histomorphometrically the human growth plate from birth to adolescence, in their study, development of trabecular bone racterized from growth plate cartilage in the human rib from birth to adolescence. The height of the proliferative and hypertrophic zones within the growth plate and the primary bone spongiosa decreased with increasing age, with the greatest change observed in the first year of postnatal life. Within these zones, an internal rearrangement of tissue structure occurred. The matrix volume fraction (either cartilage or bone) increased with age in each of the zones. A concomitant increase in cartilage septae thickness and bone trabecular thickness was observed. A decrease in cartilage septae number was seen in the proliferative zone and a decrease in bone trabeculae number was also observed in the primary spongiosa. However, no difference in cartilage septae number was noted in the hypertrophic zone, the region at which cartilage is transformed into bone. Together the proliferative and hypertrophic regions of the growth plate and the bone primary spongiosa appear to constitute the active growth region, with concomitant changes observed that result in longitudinal growth. In contrast, bone mineral volume in the secondary spongiosa was stable over the ages examined; however, trabecular architecture underwent consolidation as trabecular number decreased and trabecular thickness increased. The integration of the structural transformation from cartilage to bone is crucial in achieving the dual purposes of longitudinal growth and peak bone mass. The structure developed during childhood will have an important bearing on the response to bone-altering disease in later life. Bearing all these variation in mind about the epiphyseal growth plates both in the children and adults this present study investigates the baseline thickness between infants and children only. The absolute values for cartilage thickness depended on the method used, but in general total thickness was found to approximately double from late gestation to maturity. In the selected adult specimen, the cartilage was thickest just anterior and posterior to the main weight-bearing area of the condyles [19]. John Hunter studied growing chickens. He observed bones grew at the ends and thus demonstrated the existence of the epiphyseal plates. Hunter is considered the "father of the growth plate" [8]. Endochondral ossification: is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system by which bone tissue is created. Unlike intramembranous ossification, which is the other process by which bone tissue is created, cartilage is present during endochondral ossification. It is also an essential process during the rudimentary formation of long bones [11] the growth of the length of long bones [2] and the natural healing of bone fractures [3]. This tendency for bone to grow quickly in children explains why they often heal more quickly from fractures than adults do. It can also, unfortunately, put children at risk for cancers of the bone, because the rapid replication can allow cancer cells to spread quickly. In the standing position the femora are oblique but there is also variation in neck-shaft angle according to sex (greater in women), age, and stature [9]. The distal end comprises of two condyles, the medial and lateral condyles [9]. In plain radiographs of the
3 24 Abiodun A. A. et al.: Baseline Thickness of Proximal Femoral Epiphysis in the Diagnosis of Hip Diseases in Infants and Children in Nigeria femoral bones of the infant, the bone consists of all the structures as specified above in adult but less developed with the presence of the epiphyseal plates in various region including the femoral head, trochanters (great and lesser) and the end of the femur. The main blood supply to the femoral head is from the lateral epiphyseal artery. A small supply reaches the head along its ligament by the acetabular branches of obturator and medial circumflex arteries, these anastomose with the epiphyseal vessels [5]. Disruption of the epiphyseal vasculature did not lead to diffuse growth plate damage in the majority of the ischemic femoral heads [28]. The growth plates can clearly be seen on X-rays. Inspection of these areas is sometimes used to provide more information about bones. The plates fuse over at a stable and predictable rate, so someone with experience can examine a bone and make an estimate of its age. After about age 25, when the epiphyseal lines are fully formed, examination of this area of the bone can be less useful, as it may do little more than confirm that the bone belonged to a fully grown adult. It is possible to experience a fracture of the epiphyseal plate. 2. Materials and Methods Plain anteroposterior radiographs of the pelvis were collected from the radiology department of the teaching hospital. The radiographs were mounted on the X-ray viewing box and dimension of the epiphyseal plate taken by measuring the vertical distance or height between the ossified epiphysis of femoral head and neck. It is important to know that two measurements were taken, one at the point of the widest diameter and the other at the lowest diameter. The mean is then determined. Measurements were taken for right and left femoral epiphyseal plates in both sexes. Other parameters recorded include: i). Age and (ii) Sex of the patient. 3. Results From the tables 4 and 5 below, (see appendix) it was observed that changes in the thickness of the growing plate may be as a result of the factors in table 5. The femoral head growing plate thickness measured for infants and children shows that it ranges from 0.5mm-0.4mm and with mean values in male being 1.35±0.11 for both limbs and in female being 0.96±0.12. There are no changes in the value for both limbs. It closes earlier in male has compared with female. This baseline thickness values can also be used in diagnosis of disorders of proximal femoral epiphyseal plate among Nigerian infants and children. 4. Discussion Though the distal femoral epiphyseal plate and epiphyseal plate of the proximal part of the tibia contribute immensely to the longitudinal growth in the lower limb [6]. Nevertheless, the femoral head epiphyseal plate thickness contributed to overall longitudinal growth of the limb [11]. Since femoral epiphyseal plate contributed to racial and sexual difference in height. It was observed in this study that there was an earlier closure of epiphyseal plate of the femur in female as compared with age in both sexes has no significant difference for both left and right sides (P>0.05). The study observed that there is significant difference in mean of the epiphyseal or growth plate thickness of the femoral head between the female and male in infants and children because their values were found to be significantly higher in males than in females (P>0.05). This may be due to androgenic hormonal influence. The difference were not significant in values of both sides i.e. right and left in each sex. The difference in mean value between male and female epiphyseal thickness of the femur and its early closure may have contributed to the earlier differences in vertical diameter of femoral head, in female and male reported in various regions of the country and also in other parts of the world which was reported to be significantly higher in males than females. 5. Conclusions This study concluded that the baseline thickness for different age groups should be taken into consideration when making diagnosis of disorders affecting proximal femoral epiphyseal plate in Nigerian infants and children. Appendix Table 1. The comparison between the two sides in each sex for values of epiphyseal thickness in age Number of observation Mean Standard Deviation SEM (±) Actual Range of Age with Sex Male 3 weeks to 16 years Female 3 weeks to 14 years Table 2. The difference between male and female values of epiphyseal thickness for right and left femoral head with age Number of observation Mean Standard Deviation SEM(±) P-Value: >0.05
4 International Journal of Surgical Research 2014, 3(2): Table 3. The difference between the male and female values of the epiphyseal thickness for the right and left femoral heads Number of observations Mean Standard Deviation P-Value: <0.05 SEM(±) It was noted that each of the two thicknesses is significant and greater in male than in female (P>0.05), the calculated value was noted to be greater than the tabulated value (tn at α=0.05=2.36) Actual range of thickness 0.5mm-4mm Table 4. Range of values for epiphyseal thickness of femoral head in both male and female Age Group/ Years Range mm Table 5. Diagnostic calendar of Hip disorders Age of Onset (year) O birth Probable diagnosis Congenital dislocation 0-5 Infections 5-10 Perthes disease Slipped epiphyses (a) (b) Figure 1. Showing schematic representation of Osteogenesis
5 26 Abiodun A. A. et al.: Baseline Thickness of Proximal Femoral Epiphysis in the Diagnosis of Hip Diseases in Infants and Children in Nigeria growth plate from birth to adolescence. Bone (4): REFERENCES [1] Basener, CJ, Mehlman CT, Dipasquale, TG. Growth disturbance after distal femoral growth plate fractures in children: A meta-analysis. J. Orthop Trauma 2009 (9): [2] Brighton CT, Yoichi S, and Robert MH (1973), "Cytoplasmic structures of epiphyseal plate chondrocytes; quantitative evaluation using electron micrographs of rat costochondral junctions with specific reference to the fate of hypertrophic cells", Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 55-A: [3] Brighton CT, and Robert MH. (1986): "Histochemical localization of calcium in the fracture callus with potassium pyroantimonate: possible role of chondrocyte mitochondrial calcium in callus calcification", Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 68-A (5): [4] Byers S, Moore AJ, Byard RW, Faz. Quanlarri NL (2000) Quantitative histomorphometric analysis of the human growth plate from birth to adolescence. Bone 2000, (4): [5] Crock H.V (1965). A review of the anatomy of the arteries supplying the upper end of the human femur. J. Anat. (2): [6] Faucet D.W (1994). A textbook of histology 12 th edition Chapman and Hall [7] Garret BR Hoffman EB, Carrara H. The effect of percutaneous pin fixation in the treatment of distal femoral physeal fractures. J. Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011(5): doi: / X.93B [8] Hamilton W.J. textbook of human anatomy. McMillian Publishers (1987) Ltd [9] Ogden J.A Changing Pattern of Proximal femoral vascularity J. Bonest Sur A: [10] Seinsheimer F, Sledge CB. Parameters of longitudinal growth rate in rabbit epiphyseal growth plates. J Bone Joint surg., am. 1981, 63(4): [11] Netter, Frank H. Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation 1987 ISBN , p [12] Gilmore RS and Palfrey AJ Chondrocyte distribution in the articular cartilage of human femoral condyles J.Anat. 157: [13] Byers S, Moore AJ, Byard RW, Faz. Quanlarri NL (2000) Quantitative histomorphometric analysis of the human [14] Basener CJ, Mehlman CT, Dipasquale TG Growth disturbance after distal femoral growth plate fractures in children: a meta-analysis J.Orthop Trauma.2009 (9): [15] Ducheyne et al., J. Biomech., 1977, 10: [16] Hall et al., J. Bone Joint Surg. 1980, 3:408:413. [17] Treppo et al., J. Orthop Res., 2000, 18: [18] Gilmore, RS Palfrey AJ. A Histological study of human femoral condylar articular cartilage. J Anat.1987; 155: [19] Gilmore RS, and Palfrey AJ. Chondrocye distribution in the articular cartilage of human femora codyles J Anat. 1988;157: [20] Barnett CH, Cochran W, Palfrey AJ, Age changes in articular cartilages of rabbits. Ann Rheum Dis. 1963;22: [21] Davies DV, Barnett CH, Cochrane W, Palfrey AJ. Electron microscopy of articular cartilage in the young adult rabbit. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962;21: [22] Engfieldt B, Hjertquist So, The effect of various fixatives on the preservation of acid glycosaminoglycan in tissues. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(2): [23] Roy S, Meadrim G. Chondrocyte ultrastructure in the adult human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968;27(6): [24] Stockwell RA. The interrelationship of cell density and cartilage thickness in mammalian articular cartilage. J Anat.1971; 109(pt3): [25] Wilsman NJ, Van Sickle DC. Cartilage canals, their morphology and distribution. Anat Rec.1972;173(1): [26] Seinsheimer.F. Sledge C.B. Parameters of longitudinal growth rate in rabbit epiphyseal growth plates. J Bone Joint surg., Am. 1981, 63(4): [27] Netter, Frank H. Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation 1987 ISBN , p [28] Kim et al., Effects of disruption of epiphyseal vasculature on the proximal femoralgrowth plate J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(5): [29] Wall EJ, May MM. Growth plate fractures of the distal femur. J. Pediatr Orthop Suppl 1: [30] Mithoefer et al., High impact athletics after knee articular cartilage repair. A prospective evaluation of the microfracture technique. The Amer. J.Sports Medicine 34:
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Bone Development. V. Gilsanz and O. Ratib, Hand Bone Age, DOI / _2, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012
 Bone Development 2 Skeletal maturity is a measure of development incorporating the size, shape and degree of mineralization of bone to define its proximity to full maturity. The assessment of skeletal
Bone Development 2 Skeletal maturity is a measure of development incorporating the size, shape and degree of mineralization of bone to define its proximity to full maturity. The assessment of skeletal
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion
 Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
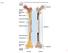 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Epiphyseal Injuries in Junior Rock Climbers The mind is stronger than the finger
 Epiphyseal Injuries in Junior Rock Climbers The mind is stronger than the finger Dr. med., Dr. rer. biol. hum. Isabelle Schöffl Klinik für Kinder und Jugendliche Sozialstiftung Bamberg Anatomy The growth
Epiphyseal Injuries in Junior Rock Climbers The mind is stronger than the finger Dr. med., Dr. rer. biol. hum. Isabelle Schöffl Klinik für Kinder und Jugendliche Sozialstiftung Bamberg Anatomy The growth
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Bone (2) Chapter 8. The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer.
 Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
 Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
Pathophysiology of fracture healing
 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
Change in Femur Shape during Postnatal Development and Growth of C57BL/6 Mice
 Change in Femur Shape during Postnatal Development and Growth of C57BL/6 Mice Introduction: Disorders of skeletal development, including hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, and Legg-Calve-Perthes
Change in Femur Shape during Postnatal Development and Growth of C57BL/6 Mice Introduction: Disorders of skeletal development, including hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, and Legg-Calve-Perthes
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Physeal fractures in immature cats and dogs: part 1 forelimbs
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Physeal fractures in immature cats and dogs: part 1 forelimbs Author : Lee Meakin, Sorrel Langley-Hobbs Categories : Canine,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Physeal fractures in immature cats and dogs: part 1 forelimbs Author : Lee Meakin, Sorrel Langley-Hobbs Categories : Canine,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
CHAPTER 9. Summary and general discussion.
 CHAPTER 9 Summary and general discussion. Chapter 9 Chapter 1 This thesis describes different aspects of slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE). Although rare, SCFE is the most common adolescent hip
CHAPTER 9 Summary and general discussion. Chapter 9 Chapter 1 This thesis describes different aspects of slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE). Although rare, SCFE is the most common adolescent hip
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
Disclosure. Learning ObjecAves. A Quick Review. Pediatric Fractures. The Developing Bone
 How to Bend but not Break Managing Pediatric Orthopedic Injuries in the Emergency Department Disclosure Nothing to disclosure No conflict of interest related to this topic Adam Cheng, MD, FRCPC Division
How to Bend but not Break Managing Pediatric Orthopedic Injuries in the Emergency Department Disclosure Nothing to disclosure No conflict of interest related to this topic Adam Cheng, MD, FRCPC Division
Disclosures. Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, Fracture vs. Break. Learning Objectives
 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES. Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium
 PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy
 Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy Surgically Induced canine OA models: Anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament transection model Pond MJ, Nuki G. Ann Rheum Dis 1973 (and > 100 others) Meniscal disruption
Why the dog? Analogy of the anatomy Surgically Induced canine OA models: Anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament transection model Pond MJ, Nuki G. Ann Rheum Dis 1973 (and > 100 others) Meniscal disruption
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures. Resources: - Lecture by dr.alboukai - Diagnostic imaging book
 Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!!
 Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2017; 3(2): DOI:
 2017; 3(2): 806-812 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 806-812 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-02-2017 Accepted: 28-03-2017 Sakher Alssayed Mohamedahmed Alwahbany Orthopedic Surgeon & Anatomist
2017; 3(2): 806-812 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 806-812 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-02-2017 Accepted: 28-03-2017 Sakher Alssayed Mohamedahmed Alwahbany Orthopedic Surgeon & Anatomist
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 309-313 ORIGINAL STUDY Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease : The importance of timing Alexander VAN TONGEL, Guy FABRY From the University
Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete
 Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete Tara J. Clark, Lindsey E. Eberman, and Michelle A. Cleary Abstract: Pediatric musculoskeletal trauma accounts for most childhood injuries.
Physeal Growth Plate Fractures: Implications for the Pediatric Athlete Tara J. Clark, Lindsey E. Eberman, and Michelle A. Cleary Abstract: Pediatric musculoskeletal trauma accounts for most childhood injuries.
SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES:
 SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES: DO THESE LIL GUYS SPRAIN OR BREAK? Process of growth Begins in utero Continues until the end of puberty Linear growth Result of multiplication of chondrocytes in the epiphyses
SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES: DO THESE LIL GUYS SPRAIN OR BREAK? Process of growth Begins in utero Continues until the end of puberty Linear growth Result of multiplication of chondrocytes in the epiphyses
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
THE Salter-Harris classification is a radiologic
 Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
, MD. physiologic. tibia varum. in utero (in. Disease in. variation. positioning. back and legs. instead of. Blount's. Infant with bowing in both legs
 North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
Posterior Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Posterior Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History 6 year old male with intermittent hip pain for several months, acutely worsened after climbing the sand dunes. Diagnosis
Posterior Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History 6 year old male with intermittent hip pain for several months, acutely worsened after climbing the sand dunes. Diagnosis
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
