OSCAR FARMATI, M.D., J. R. QtUNN, M.D., AND R. H. FENNELL, JR., M.D.~
|
|
|
- Stanley Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY OF THE INTUBATED LARYNX IN CHILDREN '* OSCAR FARMATI, M.D., J. R. QtUNN, M.D., AND R. H. FENNELL, JR., M.D.~ REPORTS OF SEQUELAE following endotracheal intubation initially appearing in the literature are characteristically in terms of gross consequences lending themselves to clinical classification. ~-~ Recent studies involve histologic changes and consequently utilize animal or post-mortem material. This is a study using cytologic evidence of injury to the respiratory epithelium obtained from selected cases in man at the time of extubation. METHOD Patients ranged in age from six months to ten years. A history of recent respiratory infection, evident nasopharyngeal congestion, or the suspicion of trauma during intubation excluded the patient from the series. Preoperative medication included atropine approximately 0.1 rag. per 10 pounds of body weight. Anaesthesia consisted of N20-O~-halothane. The endotracheal tubes were untufted For-Clear plastic tubes. The required size was estimated by using the French scale, and tubes were chosen equal in numerical size to the age of the patient plus twenty. The length of each tube was related to the diameter according to the scale of Marcy intended to produce a very short tube. 4 The tubes were gas sterilized.. Seventy patients were finally considered for evaluation. No lubricant was used on the tube in 50 patients. In the remaining 20 a thin layer of Xylocaine 5 per cent water soluble ointment was applied to the tube, and the larynx was sprayed using a Cordner needle and the volume of Xylocaine 2 per cent solution that would contain I mg. of drug per pound of body weight. The larynx was visualized with a laryngoscope and sta'aight blade following the administration of snccinylcholine intravenously or during deep planes of anaesthesia. The slide preceding intubation was prepared with a dry cotton applicator applied gently to the posteromedial aspect of the right vocal cord under direct visualization. A second slide was prepared similarly from the left vocal cord following extubation. The duration of anaesthesia varied from 20 to 200 minutes, during which a variety of otologic and ocular procedures were completed. No suction was applied to the airway preceding extxabation. Each smear was immediately coated with Spray-Cyte fixative and later Papanicolaou staining was applied. 5 *From the Departments of Anesthesiology and Pathology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and Eye and Ear Hospital, Pittsburgh, Pa. ~Dr. Farmati is Instructor, Department of Anesthesioliogy, and Clinical Research Associate, Department of Pharmacology, University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Quinn is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Anesthesiology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and Director of the Department of Anesthesiology, Eye & Ear Hospital, Pittsburgh. Dr. Fennell is Professor of Pathology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Can. Anaes. Soe. J., vol. 14, no. 4, July,
2 322 CANADIAN ANAESTI-I.ETISTS' SOCIETY JOURNAL I~StmTS The preintubation smear consisted of epithelial cells of squamous and columnar type, histiocytes and rare neutrophils, Mucus was present in some areas as a bluish background. Squamous cells of the superficial and intermediate type were the predominant epithelial cells, The columnar type cells tended to be ovoid, and cilia were difficult to see. Bacteria were occasionally present (Fig. I ), FmunE 1. Pap~ieolaou-stained.smear obtained from larynx prior to intubation. Scattered squamous cells are intermingled with respiratory type epithelium. The latter cells are swollen and cilia are difficult to visualize ( Smears following ext~fbation were similar, except that columnar cells were conspicuous, They tended to be in dumps or sheets and were well preserved. Cilia were obvious. There was no increase in neutrophils, and no fibrin was seen, There was no evidence of an inflammatory response regardless of the duration of intubation (Fig. 2 ). The smears after intubation in which Xylocaine was used were the same, except that columnar cells tended to be spread singly, with less conspicuous clumps. DISCUSSION The mucosa of the larynx is mainly ciliated columnar epithelium. Squamous epithelium covers the vocal folds adhering to the vocal ligament. It is also found at the entrance to the larynx covering the anterior and upper posterior surface of
3 FARMATI et al: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY O:F THE INTO BATED LARYNX 323 FIGURE 2. Papanicolaou-stained smear obtained after intubation. The predominant cell type is a slender colunmar cell with distinct cilia. No red blood cells or inflammatory cells,are visible (X450). the epiglottis and the upper portion of the aryepiglottic folds in continuity with similar epithelium of the pha~nx. 6 The vulnerability of the squamous mucosa of the vocal folds, particularly the mucoperichondrium in the area of the vocal process, is well establishedd Instrumentation is not necessarily the exclusive source of significant trauma related to intubation and the vocal cords. The constant activity of the cords, vocal trauma, infection, abnormal position of the head, and the size of the larynx are involved in cord lesions? 's~9 Long-term intubation in children illustrates ~e combination of several of these factors, In a recently reported series, seven of twenty-nine such patients surviving their primary disease developed laryngeal stenosis. 1~ The fragility of respiratory epithelium is documented by Hilding and Hilding. 11 The passage of gauze with moderate pressure over the surface of the trachea removed epithelium and injured the basement membrane. A single light passage of a dry swab was utilized in an effort to produce a lesser lesion. Lesions were always evident, although minimal if sufficient mucous was present to act as a lubricant. Cleavage of the epithelium was a striking finding in many specimens, and changes in the nuclei of separated columnar cells that were not detached primarily suggested subsequent sloughing31 Disruption of the epithelial layer is usually quickly restored by the regenerative
4 324 CANADIAN ANAESTHETISTS' SOCIETY JOURNAL properties of respiratory epithelium. 12 However, the occasional development of major complications following intubation demonstrates the possibility of other consequences. Way and Sooy consistently produced ulceration of the tracheal mucosa overlying the cricoid cartilage following two hours of intubation with an oversize tube in anaesthetized monkeys? 8 Debility, anaemia, vitamin deficiency, oedema, infection, reduced secretions, and the respiratory movement of tissue in contact with the tube are contributing factors enumerated by Dwyer et al. They found that ulceration of the respiratory epithelium during prolonged intubation overlaid the tracheal cartilages and was not seen in intubations of less than six hours' duration, x4 The frequent finding of tissue in aspirate removed by catheter suction through tracheostomies is further evidence of the susceptibility of respiratory epithelium to minimal trauma. 15 In the cases presented, unintentional trauma secondary to endotracheal intubation was not prevented by reducing antecedent factors and selecting only cases in which intubation was performed without difficulty. It continued relatively unchanged when lubrication was added in the form of topical anaesthesia to the larynx, and when anaesthetic ointment was applied to the tube. The vulnerability of ciliated columnar epithelium to damage is emphasized by the predominance of such cells in the cytology following extubation. Individuals performing procedures involving respiratory epithelium must use meticulous care to avoid enhancing injury and encouraging complications. SUMmArY The study uses exfoliative cytology to document injury to the respiratory epithelium following endotracheal intubation in a series of 70 children. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells occurring in clumps or sheets were conspicuous following extubation as compared with smears obtained in a similar way preceding intubation. This was interpreted as evidence of unintentional trauma and indicates the vulnerability of respiratory epithelium. RisuMi Nous avons &udi~ des cytologies exfoliatrices laryng6es chez 70 enfants avant et apr~s des intubations endotrach~ales de dur6es diverses. Nous avons fair des frottis de fa~on atraumatique avec un tampon de coton sec sur la r6gion post~rom6diale des cordes vocales et nous avons employ6 la coloration de Papanicolaou. La lame avant l'intubation &ait faite d'un pr61~vement venant de la corde vocale droite et celle qui suivait l'intubation, d'un pr61~vement de la corde vocale gauche. Nous avons exclus de l'exp6rience les malades qui avaient souffert r&emment d'une infection des voles respiratoires hautes ou qui avaient 6t6 bless6s au cours de l'intubation. Les frottis pr61ev6s avant l'intubation ont consist6 en cellules 6pith61iales de types squammeux et en colonnes avec des histiocytes muqueux et de rares neutrophiles. Les frottis pr61ev6s apr~s l'intubation ont montr~ ]a pr6sence de cellules 6pith61iales cili~es en colonnes en paquets ou en lames. Aucune 6vidence de r6ponse de cellule inflammatoire en d$pit de la duroc de
5 FAR2vlATI et al.: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY OF THE INTUBATED LARYNX 325 rintubation. L'interpr~tation: 6vidence de traumatisme involontafl'c et t6moignage de vuln~rabilit~ de l'~pith~lium des voles respirat:oires. REFERENCES 1. GILLESPIE, N. A. Endotracheal Anesthesia. 8rd ed., Madison: University of Wisconsin Press (1963). 2. JACKSON, C. Contact Ulcer Granuloma and Other Laryngeal Complications of Endotracheal Anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 14: 49.5 ( 1953 ]. 8. WOLFSON, B. Minor Laryngeal Sequelae of Endotracheal Intubation. Brit. J. Anaesth. 30:326 (1958). 4. SAFAri, P. Respiratory Therapy. 1st ed., Philadelphia: Davis (1965). 5. Koss, L. Diagnostic Cytology. 2nd ed., Philadelphia: Lippincott (1961). 6. ELLIS, H. Anatomy for Anesthetists. 1st ed., Philadelphia: Davis (1963). 7. MYEnSON, M. C. Granulornatous Polyp of the Larynx following Intratracheal Anesthesia. A.M.A. Arch. Otolaryng. 62:182 (1955). 8. HOWLAND, W. S. & LEWIS, j. s. Mechanisms in the Development of Post-intubation Granulomas of the Larynx. Ann. Otol. Rhin. & Laryng. 65:1006 (1956). 9. HOLINGEla, P. H. & JOHNSTON, K. C. Contact Ulcer of the Larynx. J.A.M.A. 172:511 (1960). 10. FEARSON, B.; MACDONALD, R. E.; SMITH, C.; & ~{ITCHELL, D. Airway Problems in Children following Prolonged Endotracheal Intubation. Ann. Otol. Rhin. & Laryng. 75: 975 (1966). 11. HILDING, A. C, & HmDINC, ]. A. Tolerance of the Respiratory Mucous Membrane to Trauma: Surgical Swabs and Intratracheal Tubes. Ann. Otol. Rhin. & Laryng. 71:455 (1962). 12. WILHELM, D.L. Regeneration of Tracheal Epithelium. J. Path. & Bact. 65:543 (1958). 13. WAY, W. L. & SooY, F. A. Histologic Changes Produced by Endotraeheal Intubation. Ann. Otol. Rhin. & Laryng. 74:799 (1965). 14. DwYER, C. S.; KnONNENnEnG, S.; & SAKLaD, M. Endotracheal Tube: Consideration of Its Traumatic Effect with Suggestions for Modifications Thereof. Anaesthesiology. 10: 714 (1949). 15. PLUM, F. & DUNNINC, M. F. Technics for Minhnizing Trauma to the Tracheobronchial Tree after Tracheotomy. New England J. Med. 254:193 (1956).
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
MINOR LARYNGEAL SEQUELAE OF ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION. Department of Anaesthetics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow
 Bnt. J. Anaesth: (1958), 30, 326 MINOR LARYNGEAL SEQUELAE OF ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION BY BERNARD WOLFSON Department of Anaesthetics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow THE laryngeal of endotracheal (1) There is
Bnt. J. Anaesth: (1958), 30, 326 MINOR LARYNGEAL SEQUELAE OF ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION BY BERNARD WOLFSON Department of Anaesthetics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow THE laryngeal of endotracheal (1) There is
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Upper Respiratory Histology
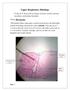 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY. Courtesy of Cook Critical Care
 PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
A VENTILATOR ADAPTER FOR FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY. R.E. NEEDS, M.B., B.CH., r.xa.c.p.(c)
 A VENTILATOR ADAPTER FOR FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY R.E. NEEDS, M.B., B.CH., r.xa.c.p.(c) THE INTRODUCTION of the flexible fibreoptic bronchoscope by Ikeda 1-2 has been a major advance in instrumentation
A VENTILATOR ADAPTER FOR FIBREOPTIC BRONCHOSCOPY R.E. NEEDS, M.B., B.CH., r.xa.c.p.(c) THE INTRODUCTION of the flexible fibreoptic bronchoscope by Ikeda 1-2 has been a major advance in instrumentation
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Airway Management in the ICU
 Airway Management in the ICU New developments in management of epistaxis. April 28, 2008 Methods of airway control Non surgical BIPAP CPAP Mask ventilation Laryngeal Mask Intubation Surgical Cricothyrotomy
Airway Management in the ICU New developments in management of epistaxis. April 28, 2008 Methods of airway control Non surgical BIPAP CPAP Mask ventilation Laryngeal Mask Intubation Surgical Cricothyrotomy
SORE THROAT AFTER ANAESTHESIA
 Brit. J. Anaesth. (1960), 32, 219 SORE THROAT AFTER ANAESTHESIA BY C. M. CONWAY, J. S. MILLER AND F. L. H. SUGDEN Department of Anaesthesia, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London, W.C.2 A sore
Brit. J. Anaesth. (1960), 32, 219 SORE THROAT AFTER ANAESTHESIA BY C. M. CONWAY, J. S. MILLER AND F. L. H. SUGDEN Department of Anaesthesia, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London, W.C.2 A sore
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
ACUTE TRACHEO-BRONCHITIS
 Thorax (1952X, 7, 36. ACUTE TRACHEO-BRONCHITIS B' V. E. NEGUS London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER 16, 1951) Considerable attention has been directed to acute tracheo-bronchitis of recent years, and
Thorax (1952X, 7, 36. ACUTE TRACHEO-BRONCHITIS B' V. E. NEGUS London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION NOVEMBER 16, 1951) Considerable attention has been directed to acute tracheo-bronchitis of recent years, and
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Respiratory System Structures and Gas Exchange
 A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
(ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital
 (ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital Pre-operative Assessment Clinical assessment of airway and risk of difficult intubation: (can be performed in a matter of seconds): 1. Mouth
(ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital Pre-operative Assessment Clinical assessment of airway and risk of difficult intubation: (can be performed in a matter of seconds): 1. Mouth
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Tracheostomy: Our Experience
 Research in Otolaryngology 201, 4(2): 29-33 DOI: 10.923/j.otolaryn.2010402.03 Tracheostomy: Our Experience R. K. Datta, B. Viswanatha *, P. J. Puneet, Merin Bobby, T. L. N. Kumari ENT department, Bangalore
Research in Otolaryngology 201, 4(2): 29-33 DOI: 10.923/j.otolaryn.2010402.03 Tracheostomy: Our Experience R. K. Datta, B. Viswanatha *, P. J. Puneet, Merin Bobby, T. L. N. Kumari ENT department, Bangalore
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Department of Otolaryngology, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol. 16, No. 3, 1969 PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES RELATING TO NEOPLASMS OF THE HYPOPHARYNX AND THE CERVICAL ESOPHAGUS IKUICHIRO HIROTO, YASUSHI NOMURA, KUSUO SUEYOSHI, SHIGENOBU MITSUHASHI,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol. 16, No. 3, 1969 PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES RELATING TO NEOPLASMS OF THE HYPOPHARYNX AND THE CERVICAL ESOPHAGUS IKUICHIRO HIROTO, YASUSHI NOMURA, KUSUO SUEYOSHI, SHIGENOBU MITSUHASHI,
Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage.
 [ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
[ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY METAPLASIA
 Metaplasia is the conversion of one adult differentiated cell type to another. Generally it is the result of persistent cellular trauma and serves as a protective mechanism. Thus anteriorly along the nasal
Metaplasia is the conversion of one adult differentiated cell type to another. Generally it is the result of persistent cellular trauma and serves as a protective mechanism. Thus anteriorly along the nasal
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
TRACHEOBRONCHIAL SUCTION IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 Brit. J. Anaesth. (1963), 35, 322 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL SUCTION IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY GORDON H. BUSH Department of Anaesthesia, University of Liverpool, England SUMMARY Angulated and straight catheters
Brit. J. Anaesth. (1963), 35, 322 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL SUCTION IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY GORDON H. BUSH Department of Anaesthesia, University of Liverpool, England SUMMARY Angulated and straight catheters
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
LARYNGEAL LESIONS FOLLOWING ENDOTRACHEAL ANESTHESIA: A REPORT OF TWELVE ADULT CASES
 Brit. J. Anasth. (1953). 25.32. LARYNGEAL LESIONS FOLLOWING ENDOTRACHEAL ANESTHESIA: A REPORT OF TWELVE ADULT CASES By NEVILLE YOUNG and SINCLAIR STEWART Manchester Royal Infirmary and Burnley and District
Brit. J. Anasth. (1953). 25.32. LARYNGEAL LESIONS FOLLOWING ENDOTRACHEAL ANESTHESIA: A REPORT OF TWELVE ADULT CASES By NEVILLE YOUNG and SINCLAIR STEWART Manchester Royal Infirmary and Burnley and District
Difficult Airway. Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital
 Difficult Airway Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital Difficult Airway Definition Predicting a difficult airway Preparing for a difficult airway Extubation
Difficult Airway Victor M. Gomez, M.D. Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine Medical City Dallas Hospital Difficult Airway Definition Predicting a difficult airway Preparing for a difficult airway Extubation
A COMPARISON OF VENTURI AND SIDE-ARM VENTILATION IN ANAESTHESIA FOR BRONCHOSCOPY
 A COMPARISON OF VENTURI AND SIDE-ARM VENTILATION IN ANAESTHESIA FOR BRONCHOSCOPY EDWARD CARDEN, M.A., M.B., B.CHm., F.R.C.P.(C), WALTER W. BURNS, M.D., NOEL B. MCDEvITr, M.D., AND TED CARSON, M.D. ~ EVER
A COMPARISON OF VENTURI AND SIDE-ARM VENTILATION IN ANAESTHESIA FOR BRONCHOSCOPY EDWARD CARDEN, M.A., M.B., B.CHm., F.R.C.P.(C), WALTER W. BURNS, M.D., NOEL B. MCDEvITr, M.D., AND TED CARSON, M.D. ~ EVER
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F
 Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
Review of Histopathological Changes in the Respiratory Tract of Rat Induced by Inhalation of the Mainstream Smoke of Standard Reference Cigarette 1R4F A. Teredesai LSRO Meeting, Dec., 13, 2001 Slide 1
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY VERTICAL PARTIAL LARYNGECTOMY Management of small tumours involving the true vocal folds can be contentious. Tumour control is achieved
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY VERTICAL PARTIAL LARYNGECTOMY Management of small tumours involving the true vocal folds can be contentious. Tumour control is achieved
DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT. Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr)
 DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr) AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND MAINTAINING OXYGENATION ARE THE FUNDAMENTAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF ANY BASIC DOCTOR. TO MANAGE A DIFFICULT AIRWAY,
DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr) AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND MAINTAINING OXYGENATION ARE THE FUNDAMENTAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF ANY BASIC DOCTOR. TO MANAGE A DIFFICULT AIRWAY,
The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes
 Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Gut, 1964, 5, 160 The permeation of gastric epithelial cells by leucocytes D. D. GIBBS From the Department of Medicine, The London Hospital EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS The cytological observations reported here
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Difficult Airway. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health Sciences Center (prepared by Brenda A. Bucklin, M.D.)
 Difficult Airway Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health Sciences Center (prepared by Brenda A. Bucklin, M.D.) Objectives Definition & incidence of the difficult airway Evaluation of
Difficult Airway Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health Sciences Center (prepared by Brenda A. Bucklin, M.D.) Objectives Definition & incidence of the difficult airway Evaluation of
Epithelial Tissue. By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: different types of epithelial membranes.
 Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies
 Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Hyoid Bone. Lower Airway. Aspiration. Larynx. Cartilages of the Larynx. Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles
 Lower Airway Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory Terminal Hyoid Bone Not part of the larynx. The Hyoid bone is an anchor for the anterior muscles of the neck
Lower Airway Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory Terminal Hyoid Bone Not part of the larynx. The Hyoid bone is an anchor for the anterior muscles of the neck
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E
 MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
How do you use a bougie as an airway adjunct for endotracheal intubation?
 Ruth Bird, MBBCh -Specialist Registrar: Anaesthesia & Paediatric Trauma Fellow Daniel Nevin, MBBCh -Consultant in Anaesthesia & Pre-Hospital Care The Royal London Hospital London s Air Ambulance (HEMS)
Ruth Bird, MBBCh -Specialist Registrar: Anaesthesia & Paediatric Trauma Fellow Daniel Nevin, MBBCh -Consultant in Anaesthesia & Pre-Hospital Care The Royal London Hospital London s Air Ambulance (HEMS)
CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY: A PHYSIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT DURING INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION IN RESPIRATORY FAILURE*
 CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY: A PHYSIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT DURING INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION IN RESPIRATORY FAILURE* A. K. LAWS, B.SC., M.B., B.S., F.F.A.R.C.S., and R. W. MCIrvrYRE, ~t.b., CH.B.,
CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY: A PHYSIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT DURING INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION IN RESPIRATORY FAILURE* A. K. LAWS, B.SC., M.B., B.S., F.F.A.R.C.S., and R. W. MCIrvrYRE, ~t.b., CH.B.,
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface
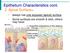 Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Angkana Lurngnateetape,, MD. Department of Anesthesiology Siriraj Hospital Perhaps the most important responsibility of the anesthesiologist is management of the patient s airway Miller
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues
 Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
Chapter 4 Histology: The study of body tissues https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zwxm2a0tfxm Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues = groups of cells with similar structure and
HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K.
 HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K. Razdan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Rachna Magotra, Sanjay Raina, Shyama K. Razdan.
HISTOGENESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS OF HUMAN LARYNGEAL EPITHELIUM: A PRENATAL STUDY Rachna Magotra 1, Sanjay Raina 2, Shyama K. Razdan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Rachna Magotra, Sanjay Raina, Shyama K. Razdan.
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
Endoscopy. Pulmonary Endoscopy
 Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
Tissues. Tissues. Four basic tissues. A collection of cells with a common function. 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4.
 Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Tracheal Stenosis or Tracheal Injury
 Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Nicolette Mosinski MPAS, PA-C
 Nicolette Mosinski MPAS, PA-C 1. Impaired respiratory effort 2. Airway obstruction Observe patient for detection Rate Pattern Depth Accessory muscle use Evidence of injury Noises Silent manifestations
Nicolette Mosinski MPAS, PA-C 1. Impaired respiratory effort 2. Airway obstruction Observe patient for detection Rate Pattern Depth Accessory muscle use Evidence of injury Noises Silent manifestations
Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein
 CLINICAL 09888888;rCYTOLOGY Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein objectives Define diagnostic cytology (clinical cytology). Explain the differences between histopathology and cytopathology. Recognize the methods for
CLINICAL 09888888;rCYTOLOGY Dr. Issraa Ali Hussein objectives Define diagnostic cytology (clinical cytology). Explain the differences between histopathology and cytopathology. Recognize the methods for
HUMIDIFICATION AND MUCUS FLOW IN THE INTUBATED TRACHEA
 Brit. J. Anaesth. (1973), 45, 874 HUMIDIFICATION AND MUCUS FLOW IN THE INTUBATED TRACHEA A. R. FORBES SUMMARY Observations of mucus flow in the trachea were made on greyhounds under barbiturate anaesthesia
Brit. J. Anaesth. (1973), 45, 874 HUMIDIFICATION AND MUCUS FLOW IN THE INTUBATED TRACHEA A. R. FORBES SUMMARY Observations of mucus flow in the trachea were made on greyhounds under barbiturate anaesthesia
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY LARYNGOMALACIA Laryngomalacia is characterised by collapse of the supraglottic tissues on inspiration, and is the most common cause of
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY LARYNGOMALACIA Laryngomalacia is characterised by collapse of the supraglottic tissues on inspiration, and is the most common cause of
Anatomy and Physiology. The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway.
 Airway management Anatomy and Physiology The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway. Non-instrumental airway management Head Tilt and Chin Lift Jaw Thrust Advanced
Airway management Anatomy and Physiology The airways can be divided in to parts namely: The upper airway. The lower airway. Non-instrumental airway management Head Tilt and Chin Lift Jaw Thrust Advanced
THE INTERPRETATION OF INFLAMMATORY REACTIONS IN THE VAGINA, CERVIX, AND ENDOCERVIX BY MEANS OF CYTOLOGIC SMEARS
 THE INTERPRETATION OF INFLAMMATORY REACTIONS IN THE VAGINA, CERVIX, AND ENDOCERVIX BY MEANS OF CYTOLOGIC SMEARS GEORGE L. WIED, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Chicago and the
THE INTERPRETATION OF INFLAMMATORY REACTIONS IN THE VAGINA, CERVIX, AND ENDOCERVIX BY MEANS OF CYTOLOGIC SMEARS GEORGE L. WIED, M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Chicago and the
Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral tube exchange: two case reports
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(3):219-223 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.3.219 Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(3):219-223 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.3.219 Fiberoptic bronchoscope and C-MAC video laryngoscope assisted nasal-oral
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
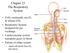 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
ANAESTHESIA FOR BLEEDING TONSIL
 ANAESTHESIA FOR BLEEDING TONSIL BY Dr.S.C.Ganeshprabu, MD., D.A., Professor of Anaesthesiology, Madurai Medical College & Govt. Rajaji Hospital, Madurai -652 020. A 5-year-old child who had tonsillectomy
ANAESTHESIA FOR BLEEDING TONSIL BY Dr.S.C.Ganeshprabu, MD., D.A., Professor of Anaesthesiology, Madurai Medical College & Govt. Rajaji Hospital, Madurai -652 020. A 5-year-old child who had tonsillectomy
Disease caused by herpes simplex virus
 Recurrence of herpes simplex virus in rabbit eyes: Results of a three-year study Peter R. Laibson and Sidney Kibrick Spontaneous reactivation of herpes simplex virus in rabbit ocular tissue was found on
Recurrence of herpes simplex virus in rabbit eyes: Results of a three-year study Peter R. Laibson and Sidney Kibrick Spontaneous reactivation of herpes simplex virus in rabbit ocular tissue was found on
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
8/8/2013. Disclaimer. Tracheostomy Care in the Home. Polling Question 1. Upper Airway and Respiratory System
 Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: Heather Murgatroyd RRT RPSGT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Tracheostomy Care in the Home Heather Murgatroyd, RRT, RPSGT
Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: Heather Murgatroyd RRT RPSGT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Tracheostomy Care in the Home Heather Murgatroyd, RRT, RPSGT
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Influence of laryngoscope design on heart rate and rhythm changes during intubation
 155 Demitri A. Cozanitis BSC PHARM MD, Kaarlo Nuuttila MD, J. Desmond Merrett PH D, Risto Kala MD Influence of laryngoscope design on heart rate and rhythm changes during intubation One hundred and t~enty
155 Demitri A. Cozanitis BSC PHARM MD, Kaarlo Nuuttila MD, J. Desmond Merrett PH D, Risto Kala MD Influence of laryngoscope design on heart rate and rhythm changes during intubation One hundred and t~enty
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS
 41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
CONCENTRATIONS OF DIETHYL ETHER IN THE BLOOD OF INTUBATED AND NON-INTUBATED PATIENTS
 Brit. J. Anaesth. (1954), 26, 111. CONCENTRATIONS OF DIETHYL ETHER IN THE BLOOD OF INTUBATED AND NON-INTUBATED PATIENTS BY A. MACKENZIE, E. A. PASK AND J. G. ROBSON Medical School, King's College, and
Brit. J. Anaesth. (1954), 26, 111. CONCENTRATIONS OF DIETHYL ETHER IN THE BLOOD OF INTUBATED AND NON-INTUBATED PATIENTS BY A. MACKENZIE, E. A. PASK AND J. G. ROBSON Medical School, King's College, and
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S
 UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer
 Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer Wojciech Golusiński Department of Head and Neck Surgery The Great Poland Cancer Centre, Poznan, Poland Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland Silver
Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer Wojciech Golusiński Department of Head and Neck Surgery The Great Poland Cancer Centre, Poznan, Poland Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland Silver
Domino KB: Closed Malpractice Claims for Airway Trauma During Anesthesia. ASA Newsletter 62(6):10-11, 1998.
 Citation Domino KB: Closed Malpractice Claims for Airway Trauma During Anesthesia. ASA Newsletter 62(6):1-11, 18. Full Text As experts in airway management, anesthesiologists are at risk for liability
Citation Domino KB: Closed Malpractice Claims for Airway Trauma During Anesthesia. ASA Newsletter 62(6):1-11, 18. Full Text As experts in airway management, anesthesiologists are at risk for liability
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005
 Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
