We have reviewed the cervical spine radiographs
|
|
|
- Marian Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY OF 180 PATIENTS TAKEO HARADA, SOHEI EBARA, MONZOOR M. ANWAR, ATSUKO OKAWA, ICHIRO KAJIURA, KAZUO HIROSHIMA, KEIRO ONO From Osaka Police Hospital and Osaka University Medical School, Osaka, Japan We have reviewed the cervical spine radiographs of 180 patients with athetoid cerebral palsy and compared them with those of 417 control subjects. Disc degeneration occurred earlier and progressed more rapidly in the patients, with advanced disc degeneration in 51%, eight times the frequency in normal subjects. At the C3/4 and C4/5 levels, there was listhetic instability in 17% and 27% of the patients, respectively, again six and eight times more frequently than in the control subjects. Angular instability was seen, particularly at the C3/4, C4/5 and C5/6 levels. We found a significantly higher incidence of narrowing of the cervical canal in the patients, notably at the C4 and C5 levels, where the average was 14.4 mm in the patients and 16.4 mm in normal subjects. The combination of disc degeneration and listhetic instability with a narrow canal predisposes these patients to relatively rapid progression to a devastating neurological deficit. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1996;78-B: Received 18 October 1995; Accepted after revision 11 January 1996 T. Harada, MD, PhD, Orthopaedic Surgeon Osaka Police Hospital, Kitayama-cho, Tennoji-ku, Osaka 543, Japan. S. Ebara, MD, PhD, Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Osaka University Medical School, 2-2 Yamadaoka, Suita 565, Osaka, Japan. M. M. Anwar, PhD, Senior House Officer Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma, Worcester Royal Infirmary NHS Trust, Newton Road, Worcester WR5 1JG, UK. A. Okawa, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon I. Kajiura, MD, PhD, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Bobath Memorial Hospital, Higashinakahama, Joto-ku, Osaka 536, Japan. K. Hiroshima, MD, PhD, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Osaka National Hospital, Hoenzaka, Chuo-ku, Osaka 540, Japan. K. Ono, MD, PhD, Director and Professor Emeritus Osaka Koseinenkin Hospital, Fukushima, Fukushima-ku, Osaka 553, Japan. Correspondence should be sent to Dr T. Harada British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery X/96/41205 $2.00 Patients with the athetoid type of cerebral palsy (athetoid CP) are considered to have a stable neurological condition, but many of them develop new functional deficits caused by cervical myelopathy and become progressively more disabled. These problems are crucial for the care of athetoid CP patients, but the disorders of the cervical spine are not widely recognised. Some patients may progress to a completely dependent state because of the lack of timely treatment. Several papers discuss degenerative changes in the cervical spine (Anderson et al 1962; Ebara et al 1989, 1990) and surgery at this level in athetoid CP (Nishihara et al 1984; Fuji et al 1987), but no previous reports address the cause of the high incidence of cervical myelopathy in these patients. We have made a radiological survey of the cervical spine in patients with athetoid CP and compared it with normal subjects to establish the characteristics and the factors leading to myelopathy. PATIENTS AND METHODS We invited 180 patients with a diagnosis of athetoid CP under treatment at five hospitals to participate in our study. We excluded all those who already had had cervical spine surgery. The mean age of the patients was 34.3 years (16 to 60); there were 102 men and 78 women (Table I). We considered them in two groups: an operative group who had surgical treatment for cervical myelopathy during our study and a non-operative group who had neither cervical myelopathy nor any operation for a cervical spine problem. The operative group included 24 men and 19 Table I. The age distribution of the 180 patients with athetoid CP and the 417 control subjects Athetoid CP (yr) Operative Non-operative Control to to to Total VOL. 78-B, NO. 4, JULY
2 614 T. HARADA, S. EBARA, M. M. ANWAR, ET AL Fig. 1a Fig. 1b The relationship between age and disc degeneration in patients with athetoid CP: (a) male; (b) female. women; their mean age was 37.9 years (19 to 60). The nonoperative group consisted of 78 men and 59 women; their mean age was 33.2 years (16 to 60). Our control group was 417 patients who attended for conditions other than spinal problems. All gave fully informed written consent for carefully screened radiography of the cervical spine. Their mean age was 36.4 years (15 to 64) (Table I). There were 230 men and 187 women. The age and gender distribution of the patients and the control group was not significantly different. We studied lateral radiographs in the neutral position and in maximum flexion and extension to detect disc degeneration, listhetic instability, angular instability and flattening of the vertebral body. We measured the sagittal diameter of the spinal canal. The CP patients were given 5 to 10 mg of diazepam orally about one to two hours before examination, and they were immobilised with a fixation device to the trunk which helped to obtain an extact lateral view of the cervical spine. All data were evaluated and statistical analysis used the chi-squared or Student s t-tests as appropriate. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Disc degeneration was assessed according to Lawrence (1969): grade 1 is slight anterior wear of the vertebral lip; grade 2 shows anterior osteophytes; grade 3 has both anterior osteophytes and narrowing of the disc space; and grade 4 is as grade 3 with sclerosis of the vertebral plates. The presence of a single osteophyte of less than 2 mm was recorded as a grade-1 change. Listhetic instability was diagnosed when flexion or extension caused movement of greater than 3 mm, either anteriorly or posteriorly, between two adjacent vertebrae. At the atlantoaxial joint listhetic instability was recorded when the atlantodental interval (ADI) was over 3 mm (Hinck and Hopkins 1960). Angular instability was recorded when excessive rotation in the sagittal plane was seen between two adjacent vertebrae during extension-flexion. Dvorak et al (1988), using Penning s superimposing method (Penning 1978), reported that the maximum range (mean plus 2 SD) of sagittal rotation in healthy adults is 20 at C1/2, 15 at C2/3, 23 at C3/4, 26 at C4/5, 28 at C5/6, and 26 at C6/7. The vertebral body ratio was recorded as the vertical diameter divided by the anteroposterior diameter of the vertebral body (Mochida, Hirabayashi and Satomi 1983). We calculated the mean value of the ratio minus 2 SD as the maximal flattening of normal vertebrae in the control group which showed no features of degenerative change or instability. We defined the sagittal diameter of the spinal canal as the distance between the posterior border of the vertebral body and the closest point on the cortical line at the junction of the laminae and the spinous process which is in the midline of the spinal canal (Wolf, Khilnani and Malis 1956). RESULTS Incidence of disc degeneration. The incidence and grade of disc degeneration increased progressively with age in both men and women (Fig. 1). In male patients cervical disc degeneration of grade 1 or more was found in 67% of patients aged between 15 and 24 years, in 97% in those between 25 and 34 years and in all over this age. Disc degeneration of grades 3 or 4 was present in half of all the patients. Gender made no difference to prevalence. Disc degeneration of grades 3 or 4 was found in 65% of operated and 46% of non-operated cases, a statistically significant difference (Table II). As expected, the control group showed a gradual increase in degeneration with age (Fig. 2) and again no significant gender difference. Disc degeneration of grades 3 to 4 was seen in only 6%. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY 615 Fig. 2a Fig. 2b The relationship between age and disc degeneration in control subjects: (a) male; (b) female. Fig. 3a Fig. 3b The relationship between disc levels and disc degeneration of grades 1 to 4 in patients with athetoid CP (a) and in the normal control group (b). Table II. Advanced disc degeneration, listhetic instability and angular instability in the operative and non-operative patients with athetoid CP Operative Non-operative p value (n = 43) (n = 137) of difference Advanced disc degeneration (+) 28 (-) 15 (+) 63 (-) 74 < Listhetic instability (+) 29 (-) 14 (+) 52 (-) Angular instability (+) 17 (-) 26 (+) 49 (-) Levels of cervical disc degeneration. In the patients, degeneration most often affected levels C3/4, C4/5, C5/6 and C6/7. In patients aged 15 to 34 years, the C5/6 disc was most frequently affected (Fig. 3). It seemed that degeneration started at the C5/6 disc level and progressed to other levels with increasing severity, eventually even affecting the C2/3 and C7/T1 levels (Fig. 4). In the control group, disc degeneration, usually of grades 1 or 2, was rare at C2/ 3, C3/4 or C7/T1 (see Fig. 3b). The sites of onset of disc degeneration were similar, usually at the C4/5, C5/6 and C6/7 disc levels, in both the control group and in the athetoid CP patients (Fig. 5a). In five of the athetoid CP patients, however, disc degeneration started at C3/4 (Fig. 5b), a pattern shown by none of the VOL. 78-B, NO. 4, JULY 1996
4 616 T. HARADA, S. EBARA, M. M. ANWAR, ET AL Fig. 4 Lateral radiograph of a 60-year-old man with athetoid CP, showing osteophyte formation, narrowing of the disc spaces from C2/3 to C7/T1 and remarkable flattening of the vertebral bodies. increased significantly with age (p = ). At other levels, listhesis was found mainly at C3/4 and C4/5, with increasing frequency at C2/3 over 35 years of age. It was rare at the C6/7 and C7/T1 disc levels for all age groups (Table III). At the C3/4 level the incidence was six times that seen in the control subjects and at the C4/5 level eight times greater. Again, there was a statistically significant difference between operative and non-operative groups (Table II). An increased incidence of angular instability was found at the C3/4, C4/5 and C5/6 disc levels in the patients (Table IV), and was very rare in the control group. Flattening. At all levels of the cervical spine in all age groups, the vertebral body ratio in the athetoid CP patients and the control group showed a statistically significant increase in flattening (p < ; Table V), with no significant difference between the operative and non-operative groups. Sagittal diameter. The cervical spinal canal in the athetoid CP patients at all levels was significantly narrower than that in the control group (Table VI). It was narrowest at C4 and C5, and narrower in the operative group. DISCUSSION Our findings show that patients with athetoid CP develop Figure 5a A 33-year-old man with athetoid CP. Cervical disc degeneration started at C4/5, C5/6 and C6/7. Figure 5b A 36-year-old man with athetoid CP. There is osteophyte formation and narrowing of the disc space only at the C3/4 level. Fig. 5a Fig. 5b control group. Instability. Listhetic instability of the atlantoaxial joint was not seen in control subjects, but was evident in 18 patients (Fig. 6), 11 in the operative group and 7 in the nonoperative group. Three of these patients showed an os odontoideum and the incidence of C1/2 instability disc degeneration in the neck at a younger age and that it progresses rapidly and involves more disc levels than in normal subjects. Angular and listhetic instabilities also appeared at a younger age (Fig. 7) and were much more frequent. In patients with athetoid CP, an already narrow spinal canal is further compromised by osteophyte forma- THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY 617 Table III. Incidence (percentage) of listhetic instability according to age and level in the athetoid CP patients and in the control group Level (yr) C1/2 C2/3 C3/4 C4/5 C5/6 C6/7 C7/T1 15 to 24 (n = 35/93)* 3/0* 3/0 9/0 34/0 6/0 0/0 0/0 25 to 34 (n = 66/103) 8/0 0/0 17/2 23/2 0/0 0/0 0/0 35 to 44 (n = 45/107) 9/0 7/0 18/2 24/6 4/2 0/0 0/0 45 to 54 (n = 21/76) 14/0 19/0 24/7 33/4 10/0 0/0 0/0 55 to 64 (n = 13/38) 38/0 15/0 23/8 31/8 15/0 18/0 0/0 * athetoid CP/control Table IV. Incidence (percentage) of angular instability according to age and level in the athetoid CP patients and in the control group Level (yr) C1/2 C2/3 C3/4 C4/5 C5/6 C6/7 15 to 24 (n = 35/93)* 9/4* 17/1 11/0 31/1 12/3 11/0 25 to 34 (n = 66/103) 6/2 9/2 18/0 24/4 9/3 0/0 35 to 44 (n = 45/107) 13/4 0/1 11/1 20/1 17/0 0/0 45 to 54 (n = 21/76) 10/1 0/0 0/3 0/4 0/0 0/0 55 to 64 (n = 13/38) 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/5 0/0 0/0 * athetoid CP/control Table V. Mean vertebral body ratio according to age and level in the athetoid CP patients and in the control group at all levels and in all age groups (p < ) C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 (yr) CP Control CP Control CP Control CP Control CP Control 15 to to to to to Table VI. Mean sagittal diameter (mm; ± SD) of the spinal canal at all levels in the athetoid CP patients and in the control group C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 Control 21.5 ± 2.6* 19.0 ± 2.0* 17.0 ± 1.8* 16.4 ± 1.7* 16.4 ± 1.7* 16.6 ± 1.7* 16.6 ± 1.4* Athetoid CP 19.7 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.5 Operative 19.7 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.2 Non-operative 19.6 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.6 * p < p < 0.01 p < VOL. 78-B, NO. 4, JULY 1996
6 618 T. HARADA, S. EBARA, M. M. ANWAR, ET AL canal stenosis. These changes are probably secondary to the excessive mechanical stress caused by involuntary cervical movement. Spinal degeneration is regarded as part of the normal ageing process (Lawrence 1969; Sasaki 1980; Kelsey 1982; Hayashi et al 1987), and the abnormal neck motion in athetoid CP patients accelerates this. Excessive neck motion may cause a fatigue failure of the cervical discs. The resulting degeneration and instability may lead to rapid neurological deterioration. Early surgical intervention can prevent irreversible neurological injury in these patients. We have used anterior decompression with fusion and laminoplasty with posterior fusion, usually from C3 to C7, in over 50 patients (Harada et al 1993,1994). There have been few problems in the early postoperative period after these stabilising procedures. Fig. 6 A 57-year-old woman with athetoid CP. The atlantodental interval is 7 mm and there is anterior listhesis of 4 mm at C3/4 and at C4/5. This study was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. Figure 7a Flexion view of an 18-year-old man with athetoid CP. The vertebral body ratios are: C3 0.55, C4 0.60, C5 0.63, C and C The atlantodental interval is 3.5 mm and there is anterior listhesis from C2/ 3 to C5/6. Figure 7b By contrast a normal 19-year-old man has vertebral body ratios of: C3 0.79, C4 0.75, C5 0.75, C6 0.75, C Fig. 7a Fig. 7b tion secondary to disc degeneration and instability. All these changes were statistically greater in those patients who had developed myelopathy requiring surgery. We have shown two developmental differences in the cervical spine in the athetoid CP patient. There is flattening of the vertebral bodies at all cervical levels and significant REFERENCES Anderson WW, Wise BL, Itabashi HH, Jones M. Cervical spondylosis in patients with athetosis. Neurology 1962;12: Dvorak J, Froehlich D, Penning L, Baumgartner H, Panjabi MM. Functional radiographic diagnosis of the cervical spine: flexion/extension. Spine 1988;13: THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
7 THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ATHETOID CEREBRAL PALSY 619 Ebara S, Harada T, Yamazaki Y, et al. Unstable cervical spine in athetoid cerebral palsy. Spine 1989;14: Ebara S, Yamazaki Y, Harada T, et al. Motion analysis of the cervical spine in athetoid cerebral palsy: extension-flexion motion. Spine 1990;15: Fuji T, Yonenobu K, Fujiwara K, et al. Cervical radiculopathy or myelopathy secondary to athetoid cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1987;69-A: Harada T, Ebara S, Hiroshima K, et al. Surgical planning for cervical spondylotic myelopathy and radiculopathy in patients with athetoid cerebral palsy. J Jpn Orthop Assoc 1993;67:S39. Harada T, Ebara S, Hiroshima K, et al. Surgical treatment for cervical spondylotic radiculopathy and myelopathy in patients with athetoid cerebral palsy. Cent Jpn J Orthop Traumatol 1994;37: Hayashi H, Okada K, Hamada M, Tada K, Ueno R. Etiologic factors of myelopathy: a radiographic evaluation of the ageing changes in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop 1987;214: Hinck VC, Hopkins CE. Measurement of the atlanto-dental interval in the adult. Am J Roentgenol 1960;84: Kelsey JL. Epidemiology of musculoskeletal disorders. In: Lilienfeld AM, ed. Monographs in epidemiology and biostatistics. Vol. 3. Oxford University Press, 1982: Lawrence JS. Disc degeneration: its frequency and relationship to symptoms. Ann Rheum Dis 1969;28: Mochida J, Hirabayashi K, Satomi K. The roentgenological study of the cervical canal stenosis: mainly make mention of the flat change of the vertebral body. Rinsho Seikei Geka 1983;18: (In Japanese). Nishihara N, Tanabe G, Nakahara S, Imai T, Murakawa H. Surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy complicating athetoid cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1984;66-B: Penning L. Normal movements of the cervical spine. AJR 1978;130: Sasaki A. Radiology of normal cervical spine. J Jpn Orthop Assoc 1980; 54: (in Japanese). Wolf BS, Khilnani M, Malis LI. Sagittal diameter of bony cervical spinal canal and its significance in cervical spondylosis. Mt Sinai Hosp J Med NY 1956;23: VOL. 78-B, NO. 4, JULY 1996
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Jing Tao Zhang 1, Lin Feng Wang 1, Yue Ju Liu 2, Jun Ming Cao 1, Jie Li 1, Shuai Wang 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine. European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82
 Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
Soccer causes degenerative changes in the cervical spine European Spine Journal, February 2004, 13(1):76-82 Alparslan Kartal, Brahim Yldran, Alparslan Enköylü and Feza Korkusuz FROM ABSTRACT: Background
THE SAGITTAL DIAMETER OF THE CERVICAL SPINAL CANAL
 8 SNGAPORE MEDCAL JOURNAL Vol. 5, No.. September, 974. THE SAGTTAL DAMETER OF THE CERVCAL SPNAL CANAL By C. L. Oon SYNOPSS The sagittal diameter of the cervical spinal canal was measured from radiographs
8 SNGAPORE MEDCAL JOURNAL Vol. 5, No.. September, 974. THE SAGTTAL DAMETER OF THE CERVCAL SPNAL CANAL By C. L. Oon SYNOPSS The sagittal diameter of the cervical spinal canal was measured from radiographs
Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of the Subaxial Cervical Spine between Athetoid Cerebral Palsy and Normal Control
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 61 (2) : 243-250, 2018 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0303.011 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of the Subaxial Cervical
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 61 (2) : 243-250, 2018 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0303.011 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of the Subaxial Cervical
Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011; 116: 133 137 ORIGINL RTICLE Lumbar radiculopathy caused by foraminal stenosis in rheumatoid arthritis TOMOKI KOKUTSU, NOKI MOROZUMI, YUTK KOIZUMI & YUSHIN ISHII
Matthew Colman, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Oncology Rush University Medical Center ACDF
 is the most reliable option for twolevel anterior cervical surgery Matthew Colman, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Oncology Rush University Medical Center Disclosures Medicrea:
is the most reliable option for twolevel anterior cervical surgery Matthew Colman, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery and Musculoskeletal Oncology Rush University Medical Center Disclosures Medicrea:
Radiographic Instability Report
 Prepared for: Bad Spine Insurance #: Gender: Male Date of Birth: 8/7/1954 Address: Evaluation Date: 6/29/2013 Date X-Ray Taken: 6/29/2013 Prepared by: Modern Chiropractic Someplace Drive Somewhere Cityville,
Prepared for: Bad Spine Insurance #: Gender: Male Date of Birth: 8/7/1954 Address: Evaluation Date: 6/29/2013 Date X-Ray Taken: 6/29/2013 Prepared by: Modern Chiropractic Someplace Drive Somewhere Cityville,
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Key Primary CPT Codes: Refer to pages: 7-9 Last Review Date: October 2016 Medical Coverage Guideline Number:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: ANTERI CERVICAL DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL POSTERI DECOMPRESSION WITH FUSION CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL DISC CERVICAL POSTERI
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Spinal Instrumented Fusion in Combination with Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in Patients with Athetoid Cerebral Palsy
 Spinal Instrumented Fusion in Combination with Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in Patients with Athetoid Cerebral Palsy Authors: Takeo Furuya, MD, PhD,* Masao Koda, MD, PhD,* Tuyoshi
Spinal Instrumented Fusion in Combination with Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in Patients with Athetoid Cerebral Palsy Authors: Takeo Furuya, MD, PhD,* Masao Koda, MD, PhD,* Tuyoshi
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Maximal rotation at atlanto-axial joint: analysis of changes in mid-sagittal space within atlas vertebra
 Eur J Anat, 14 (3): 127-132 (2010) Maximal rotation at atlanto-axial joint: analysis of changes in mid-sagittal space within atlas vertebra Niladri Kumar Mahato Department of Anatomy, SRM Medical College,
Eur J Anat, 14 (3): 127-132 (2010) Maximal rotation at atlanto-axial joint: analysis of changes in mid-sagittal space within atlas vertebra Niladri Kumar Mahato Department of Anatomy, SRM Medical College,
Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients
 Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up
 Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
Selective laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative study with a minimum 5-year follow-up Minori Kato*, Hiroaki Nakamura**, Koji Tamai**, Kazunori Hayashi**, Akira Matsumura**, Sadahiko
ELY ASHKENAZI Israel Spine Center at Assuta Hospital Tel Aviv, Israel
 nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
We performed CT myelography in 38 patients
 Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
Posterior movement and enlargement of the spinal cord after cervical laminoplasty Ikuo Aita, Koichiro Hayashi, Yasuyoshi Wadano, Takeshi Yabuki From the University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan We performed
PREPARED FOR. Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016. REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr.
 Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma. Cervical Spine Trauma. Imaging Standards. Canadian C. Spine Rule 11/28/2016
 Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Steven J. Gould, D.C. Board Certified Chiropractic Radiologist Cleveland Chiropractic College, KC. MO. Radiology Residency at CCC, KC Cervical Spine Trauma Vertebral
Radiology of Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Steven J. Gould, D.C. Board Certified Chiropractic Radiologist Cleveland Chiropractic College, KC. MO. Radiology Residency at CCC, KC Cervical Spine Trauma Vertebral
ISPUB.COM. Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Cervical Spine. B Dev, S wani., R Jindal, R Bahadur INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHODS RESULTS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 6 Number 2 Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Cervical Spine B Dev, S wani., R Jindal, R Bahadur Citation B Dev, S wani., R Jindal, R Bahadur. Rheumatoid
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 6 Number 2 Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Cervical Spine B Dev, S wani., R Jindal, R Bahadur Citation B Dev, S wani., R Jindal, R Bahadur. Rheumatoid
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Comparison between Radiological and Clinical Outcomes of Laminoplasties with Titanium Miniplates for Cervical Myelopathy
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:399-406 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.399 Comparison between Radiological and Clinical Outcomes of Laminoplasties with Titanium Miniplates
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:399-406 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.399 Comparison between Radiological and Clinical Outcomes of Laminoplasties with Titanium Miniplates
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
online ML Comm CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2014;10(2):60-65 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.60 Midline Splitting Cervical Laminoplasty Using Allogeneic
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement
 Rome Spine 2011 THE SPINE TODAY International Congress Rome 6-7th December 2011 Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement Prof. Dr. Karin Büttner-Janz Past President International Society for the Advancement of Spine
Rome Spine 2011 THE SPINE TODAY International Congress Rome 6-7th December 2011 Lumbar Facet Joint Replacement Prof. Dr. Karin Büttner-Janz Past President International Society for the Advancement of Spine
MRI of chronic spinal cord injury
 The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
EFSPINE CERVICAL COMBINED SET DISC PROTHESIS ORGANIZER BOX
 EFSPINE CERVICAL COMBINED SET INSTRUMENTS CERVICAL CAGE & DISC PROTHESIS ORGANIZER BOX Cervical Thoracic Thoraco - Lumbar Sacral EFSPINE CERVICAL COMBINED SET CERVICAL IMPLANTS INTRODUCTION Cervical Disc
EFSPINE CERVICAL COMBINED SET INSTRUMENTS CERVICAL CAGE & DISC PROTHESIS ORGANIZER BOX Cervical Thoracic Thoraco - Lumbar Sacral EFSPINE CERVICAL COMBINED SET CERVICAL IMPLANTS INTRODUCTION Cervical Disc
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion
 Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Introduction SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Radiological Examination of Postoperative Cervical Alignment and Stability in Patients with Dialysis-Associated Spondylosis Excluding Destructive Spondyloarthropathy:
Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine. Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland
 Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. *Shen et al.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Cervical Spine Radiology Rounds November 21, 2006 Derek Haaland Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. Laiho et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004:34;267. *Shen et al.
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA
 UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
UPPER CERVICAL MYELOPATHY WITH METATROPIC DYSPLASIA REPORT OF 4 SURGICAL CASES Yujiro Takeshita*, Kota Miyoshi**, Tomoaki Kitagawa** *Department of Orthopaedic and Spine Surgery, University of Tokyo, Japan
Ultimate Spinal Analysis PA USA-XRAY ( )
 Page: 1 Spine Atlas Angle 7.24 S Atlas Angle 21.67 S The Atlas Angle is a measurement of the stability of the Atlas. The Atlas Plane Line is compared to true horizontal. Any increase or decrease of this
Page: 1 Spine Atlas Angle 7.24 S Atlas Angle 21.67 S The Atlas Angle is a measurement of the stability of the Atlas. The Atlas Plane Line is compared to true horizontal. Any increase or decrease of this
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL
 SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
SPINAL CHAPTER, NESON DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE PRABIN SHRESTHA ANISH M SINGH B&B HOSPITAL INTRODUCTION DEGENERATIVE SPINAL DISEASE Gradual loss of normal structure and function of spine with time Also
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY
 PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, Besar, Akar and Abdelkader MD. 43 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion *Mohamed Abdulrahman Besar.MD;
Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, Besar, Akar and Abdelkader MD. 43 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion *Mohamed Abdulrahman Besar.MD;
Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion
 Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Complex Spine Symposium January 12th, Balgrist University Hospital
 DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
DEGENERATIVE CERVICAL MYELOPATHY CLINICAL DECISION MAKING Prof. Dr. Mazda Farshad Chair of Orthopedic Surgery Chief of Spine Surgery Medical Director CERVICAL MYELOPATHY - CAUSES degenerative cervical
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태
 KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
KNS Main Topic Session Spine Surgery : Case-Based Lecture of Spinal Disease Cervical Degenerative Disease - Surgical Approaches to CSM 가톨릭의대인천성모병원척추센터 김종태 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy ( CSM ) (1984,
Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE
 Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook Management of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) in pdf
Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook Management of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) in pdf
Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position
 275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
DIAGNOSTIC VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY IMPRESSIONS and BIOMECHANICS REPORT
 P.O. Box 6743 New Albany, IN 47151-6743 (812) 945-5515 (812) 945-5632 Fax WWW.KMX.CC DIAGNOSTIC VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY IMPRESSIONS and BIOMECHANICS REPORT Patient Name: Lubna Ibriham Date of Digitization and
P.O. Box 6743 New Albany, IN 47151-6743 (812) 945-5515 (812) 945-5632 Fax WWW.KMX.CC DIAGNOSTIC VIDEOFLUOROSCOPY IMPRESSIONS and BIOMECHANICS REPORT Patient Name: Lubna Ibriham Date of Digitization and
Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
National Imaging Associates, Inc. CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Original Date: July 2008 Cervical ACDF - Anterior Decompression with Fusion Single or Multiple Levels Page 1 of 13 Cervical Posterior Decompression
A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:189 193 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0082-y CASE REPORT A rare case of spinal injury: bilateral facet dislocation without fracture at the lumbosacral joint Kei Shinohara Shigeru Soshi
Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD
 CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
CSRS 21st Instructional Course Wednesday, November 30, 2016 Laminoplasty/Foraminotomy: Why Fuse the Spine at all? Christopher I. Shaffrey, MD John A. Jane Distinguished Professor Departments of Neurosurgery
Unanswered Questions. Laminoplasty is best
 Laminoplasty is best Wellington K. Hsu, MD Clifford C. Raisbeck Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Research Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Northwestern University Feinberg School
Laminoplasty is best Wellington K. Hsu, MD Clifford C. Raisbeck Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Research Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Northwestern University Feinberg School
Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of the Relation Between Flexion Angle and the Motion Axis of Fracture
 Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 139 143 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of
Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 139 143 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of
Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body lesions
 Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty
 Systematic Review 105 Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty John G. Heller 1 Annie L. Raich 2 Joseph R. Dettori 2 K. Daniel Riew 3 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Emory
Systematic Review 105 Comparative Effectiveness of Different Types of Cervical Laminoplasty John G. Heller 1 Annie L. Raich 2 Joseph R. Dettori 2 K. Daniel Riew 3 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Emory
CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY
 CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY ISADOR H. LIEBERMAN, JOHN K. WEBB From University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, England We reviewed 41 patients over the age of 65 years (mean 76.5)
CERVICAL SPINE INJURIES IN THE ELDERLY ISADOR H. LIEBERMAN, JOHN K. WEBB From University Hospital, Queen s Medical Centre, Nottingham, England We reviewed 41 patients over the age of 65 years (mean 76.5)
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
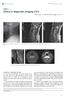 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
subluxation: a radiographic comparison
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty
 CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
CASE REPORT SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Catastrophic Dropped Head Syndrome Requiring Multiple Reconstruction Surgeries after Cervical Laminoplasty Seiichi Odate, Jitsuhiko Shikata and Tsunemitsu
Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy.
 Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Journal of the International Society of Head and Neck Trauma (ISHANT) Case report Misdiagnosis in cervical spondylosis myelopathy. Dr. Reinel A. Junco Martin. Neurosurgeon. Assistant professor Miguel Enriquez
Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse of a Lumbar Spine Vertebral Body
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 682075, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/682075 Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 682075, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/682075 Case Report Delayed Neurologic Deficit due to Foraminal Stenosis following Osteoporotic Late Collapse
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Cervical myelopathy is caused by spinal canal narrowing
 An Original Study Instrumented Open-Door Laminoplasty as Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in 104 Patients John R. Dimar II, MD, Kelly R. Bratcher, RN, CCRP, Dylan C. Brock, BS, Steven D. Glassman, MD,
An Original Study Instrumented Open-Door Laminoplasty as Treatment for Cervical Myelopathy in 104 Patients John R. Dimar II, MD, Kelly R. Bratcher, RN, CCRP, Dylan C. Brock, BS, Steven D. Glassman, MD,
Original Investigation. Byung-Wan CHOI. INTRODUCTION Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament ABSTRACT
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.16196-15.1 Received: 25.09.2015 / Accepted: 07.12.2015 Published Online: 01.06.2016 Original Investigation Clinical and Radiological Characteristics of Ossification of the Posterior
Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 508534, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/508534 Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty Brett
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 508534, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/508534 Review Article Operative Treatment of Cervical Myelopathy: Cervical Laminoplasty Brett
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
BIOMECHANICAL EFFECTS OF LAMINOPLASTY AND LAMINECTOMY ON THE STABILITY OF CERVICAL SPINE
 BIOMECHANICAL EFFECTS OF LAMINOPLASTY AND LAMINECTOMY ON THE STABILITY OF CERVICAL SPINE INTRODUCTION Relevant Anatomy: The spinal column is made up of series of motion segments, each of which contains
BIOMECHANICAL EFFECTS OF LAMINOPLASTY AND LAMINECTOMY ON THE STABILITY OF CERVICAL SPINE INTRODUCTION Relevant Anatomy: The spinal column is made up of series of motion segments, each of which contains
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Imaging of Trauma to the Spine. Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic
 Imaging of Trauma to the Spine Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Jefferson Fracture Yee, LL: The Jefferson Fracture, Radiology Cases in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
Imaging of Trauma to the Spine Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Jefferson Fracture Yee, LL: The Jefferson Fracture, Radiology Cases in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical
 Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Artificial Disc Replacement, Cervical Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.001 02/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 11/01/2011 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Title. CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement
 Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement Thomas T. Lee, M.D., Glen R. Manzano, B.S., and Barth A.
Modified open-door cervical expansive laminoplasty for spondylotic myelopathy: operative technique, outcome, and predictors for gait improvement Thomas T. Lee, M.D., Glen R. Manzano, B.S., and Barth A.
