Integrating Critical Thinking & Argument Mapping into Education: Collaborative Evaluation. Dr. Christopher Dwyer
|
|
|
- Briana Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integrating Critical Thinking & Argument Mapping into Education: Collaborative Evaluation Dr. Christopher Thoughts on Thinking at psychologytoday.com
2 General Tips for Presenting Critical Thinking Instruction Be Personable Be Funny Utilise Active Learning Know your Audience Size Be Intellectually Honest with yourself and your students You cannot always be PC if you want to think critically Mode of Delivery Traditional, e-learning, Blended Learning Utilise Argument Mapping To teach critical thinking, you must think critically
3 Let s think about your modules Given that our last meeting took place mid-semester, it may not have been feasible to amend your course outline and assessment strategy. However, have you made plans for, or started to think about, future amendments?
4 4 Instructional Typologies for Delivering Critical Thinking (Ennis, 1989) 1. General Approach: Actual CT skills and dispositions are learning objectives, without specific subject matter content (Abrami et al., 2008, p. 1105). 2. Infusion Approach: Requires specific subject matter content upon which CT skills are practiced. In the infusion approach, the objective of teaching CT within the course content is made explicit. 3. Immersion Approach: Like the infusion approach, specific course content upon which critical thinking skills are practiced is required. However, CT objectives in the immersed approach are not made explicit. 4. Mixed Approach: Critical thinking is taught independently of the specific subject matter content of the course.
5 4 Instructional Typologies for Delivering Critical Thinking (Abramiet al., 2011) 1. General Approach: Medium effect 2. Infusion Approach: Medium to Large Effect 3. Immersion Approach: Very small effect 4. Mixed Approach: LARGE effect NB: The immersion approach is the only approach that does not make CT objectives explicit to students
6 Know you outcomes: How do I assess Critical Thinking? Continuously? Reflective judgment requires engagement opportunities to development. Give students those opportunities through continuous assessment! Final exam through what means? MCQ, fill-in-the-blank (long v. short), essay? Standardised CT assessment.
7 Understanding your students Causes of student stress? The amount of work The time in which to complete the work Procrastination is stressful. Whatever you want to do tomorrow, do today; whatever you want to do today, do it now.
8 Aggression is a serious problem in society. It is commonplace to hear of events involving violence, verbal abuse and other forms of aggression. Many factors influence aggressive behaviour. For years, psychologists have sought to understand whether an individual s behaviour emerges as a result of nature (i.e. their biology) or nurture (i.e. their environment). Aggressive behaviour falls into this argument. Is aggressive behaviour a by product of nature or nurture? Ethologists have shown that aggression in members of a species can aid survival of that species. They have shown, for example, that intra-specific aggression has several biological advantages. When accompanied by rivalry among males for mating opportunities, intraspecific aggression tends to perpetuate the genes of the healthier, more vigorous animals. Freud theorised that thanatos (the death instinct) and libido (the sexual drive) help to form personality by virtue of the way sexuality and aggression were channelled. However, Freud s ideas are merely theoretical and little scientific findings support these ideas. This is because psychoanalytic ideas (e.g. the death instinct) cannot be adequately tested or falsified in an empirical fashion. One piece of evidence to suggest that biology causes aggression is the fact that testosterone is correlated with aggression. For example, there is evidence that high levels of testosterone are correlated with aggression, as are depleted levels of serotonin. Men have higher levels of testosterone and are generally more aggressive than women (Knight et al., 1996). The role testosterone plays in aggression was exemplified when Dabbs et al. (1988) found that female prison inmates who displayed unprovoked violence and who had received several other convictions also showed high levels of testosterone. Genetic factors play a major role in aggression (e.g. in the breed of dogs). Inbreeding can create unstable temperaments, and hormones can contribute to aggressive tendencies in intact male dogs. However, an individual s environment can affect his or her testosterone level. For example, increases in testosterone have been found in Brazilian supporters who saw their team win the 1994 World Cup on television (Fielden et al., 1994). On the nurture side of things, various environmental factors may also influence aggression. For example, when parents habitually resort to aggression, their children are likely to do the same. In extreme cases of child abuse, parents who beat their children usually turn out to have been victims of child abuse themselves (Parke & Collmer, 1975). This can also be seen in work done by Bandura (1977) found that, after watching an adult interact with a Bobo Doll, children tended to imitate the observed behaviour. For example, if the adult beat the doll with a stick, children often did the same. Longitudinal studies tracing development from childhood to adolescence have found that long- term viewing of violence on television is associated with an increase in boys violent behaviour as adults (Lefkowitz et al., 1977). However, Feshbach & Singer (1971) found that being subjected to consistent violent television programmes, over six months, as a teenager, didn t increase levels of aggression and found that in some cases individuals were less aggressive. Displacement of responsibility is an important factor in aggressive behaviour. When people feel less responsibility for their behaviour (e.g., in mob situations), they are more likely to act aggressively. Aggression tends to increase in groups, which is a result of group polarization. Group attitudes often polarize (i.e., become more extreme) when individuals with similar attitudes get together. One outcome is extreme aggression. Dollard et al. (1939) proposed that aggressive behaviour results from frustration in attempts to achieve personal goals. Dollard said that aggression is always a consequence of frustration and frustration always leads to some form of aggression. However, experimental evidence for the frustration-aggression theory is mixed. According to Berkowitz (1962), frustration yields anger and anger only leads to aggression when a person is exposed to an aggressive cue, e.g. a gun. In conclusion, one acknowledges that aggression is a serious problem in society. It is commonplace to hear of events involving violence, verbal abuse and other forms of aggression. There are many influences on aggressive behaviour, such as various biological and environmental factors. For years, psychologists have argued about whether or not human behaviour is the result of nature or nurture. Aggressive behaviour falls into this argument. There is no 'clear-cut' answer here, as both environmental and biological factors influence aggression.
9
10 What is an Argument Map? All arguments share the characteristics of being composed of a network of propositions, prosebased or otherwise, that are structured via logical, inferential relationships: A central claim Reasons for why the central claim is true Objections to the central claim Rebutals that object to objections
11 What is an Argument Map? An argument map is a visual representation of that logically structured network of reasoning, in which the argument is made unambiguous and explicit. That is, there is no need for attention switching from paragraph to paragraph or from page to page in search of reasons and objections to the central claim around which the argument map is constructed.
12 Argument maps use a box and arrow design in which the boxes represent propositions (i.e. the central claim, reasons, objections and rebuttals) and the arrows among propositions indicate the inferential relationships linking the propositions together. Thus, the provision of an arrow between two propositions indicates that one is evidence for or against another.
13 Why would Argument Maps be able to facilitate improved learning? Maps are organised in a hierarchical structure, where propositions are identified as either reasons or objections. Colour (a Gestalt Grouping Principle of Similarity) allows the reader to easily differentiate reasons from objections. Argument Mapping removes the cognitive load (Sweller & Chandler, 1991) from thinking as the maps naturally chunk (Miller,1956) the propositions together in a close proximity, as opposed to text. Research suggests that argument maps not only improve memory (Dwyer, Hogan & Stewart, 2010; Dwyer, 2011), they also improve critical thinking (Alvarez-Ortiz, 2007; Butchart et al., 2009; Dwyer, 2011; van Gelder, 2000; 2001).
14
15 Consider the following dialogue: A: I think emotions make thinking irrational B: Why? A: Because in order to be rational one needs to be impartial. Positive emotions make one too agreeable and inclined to making risky decisions. Negative emotions make one too sceptical and inclined to reject all forms of evidence. B: But is not scepticism a critical part of good critical thinking? A: Yes, but rejecting all forms of evidence means one must also reject every belief, and that s not rational.
16 Now consider the structure of this argument. Arguments are hierarchical structures. We can continue to add more levels if we like. To increase COMPLEXITY. For example, we can offer a rebuttal to a but and construct a 4-level propositional structure.
17 Add a rebuttal and complete this 4-level propositional structure.
18 Consider arguments that reject the claim that emotions make thinking irrational: Paragraph 1 Paragraph 2 A commonly held belief is that emotions make thinking irrational. However, some people argue that neither emotion nor mood necessarily interfere with rational thought. For example, it has been found that low levels of positive emotion often maintain behaviour, not disrupt it. Thus, if a behaviour, such as reasoning, is associated with a pleasant, positive feeling, the behaviour is likely to continue. Emotion can enhance forms of cognition other than reasoning. For example, emotion can increase expressive communication. Also, a positive mood may actually help a person on creative kinds of tasks (Isen et al., 1985). However, these forms of cognition are not necessarily forms of rationality. Note how a good piece of prose puts related arguments into the one paragraph. This rule (one paragraph = one idea unit) often helps the reader to see and extract the structure of the argument.
19 There are two major objections to the central claim, both of which have a separate paragraph, both of which are supported by sub-claims, and one of which has a rebuttal. Paragraph 1 Paragraph 2
20 Argument Mapping in application Argument Maps are presented in a manner that represents all killer, no filler. However, good writing requires filler from time to time. For example, consider an argument map as, for the most part, the body of an essay, dissertation or thesis. Also consider an argument map as similar to an outline, which may enhance student appreciation of its use.
21 I. Introduction II. III. I. Something Quotable II. Central claim III. Why is it important? IV. Core Reasons Body I. Core Reason 1 I. Supporting Reason 1 II. Supporting Reason 2 III. Supporting Reason 3 II. Core Reason 2 I. Supporting Reason 1 II. Supporting Reason 2 III. Supporting Reason 3 III. Core Reason 3 I. Supporting Reason 1 II. Supporting Reason 2 III. Supporting Reason 3 IV. Core Reason 4 I. Supporting Reason 1 II. Supporting Reason 2 III. Supporting Reason 3 V. Core Reason 5 I. Supporting Reason 1 II. Supporting Reason 2 III. Supporting Reason 3 Conclusion I. Restatement of Central Claim, Importance & Core Reasons II. Summarise III. Implications, Limitations & Future Research IV. Concluding Points STRUCTURE Your weakest reason should go in the middle. Weakest, in this context, would refer to the least amount of support or the most easily criticised. In which case, you might consider providing an objection. Your strongest reasons should go first and last in the body.
22 Thank you for your time and attention! Dr. Christopher Thoughts on Thinking at psychologytoday.com
Integrating Critical Thinking into Educational Settings
 Integrating Critical Thinking into Educational Settings Dr. Christopher Dwyer cdwyer@nuigalway.ie @CogitoErgoDwyer Thoughts on Thinking at psychologytoday.com Things that cause cancer... according to the
Integrating Critical Thinking into Educational Settings Dr. Christopher Dwyer cdwyer@nuigalway.ie @CogitoErgoDwyer Thoughts on Thinking at psychologytoday.com Things that cause cancer... according to the
Aggression. Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental. Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz. Biological Theories
 Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 462 U2 AOS1: Interpersonal behaviour Research methods and ethics Case study 1 Emotional and behavioural responses to racism Kawakami and colleagues (2009) predicted that one reason why racism and prejudice
462 U2 AOS1: Interpersonal behaviour Research methods and ethics Case study 1 Emotional and behavioural responses to racism Kawakami and colleagues (2009) predicted that one reason why racism and prejudice
Chapter 12. Aggression: Why We Hurt Other People? Can We Prevent it?
 Chapter 12 Aggression: Why We Hurt Other People? Can We Prevent it? What Is Aggression? An aggressive action is intentional behavior aimed at causing either physical or psychological pain. What Is Aggression?
Chapter 12 Aggression: Why We Hurt Other People? Can We Prevent it? What Is Aggression? An aggressive action is intentional behavior aimed at causing either physical or psychological pain. What Is Aggression?
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
EIQ16 questionnaire. Joe Smith. Emotional Intelligence Report. Report. myskillsprofile.com around the globe
 Emotional Intelligence Report EIQ16 questionnaire Joe Smith myskillsprofile.com around the globe Report The EIQ16 questionnaire is copyright MySkillsProfile.com. myskillsprofile.com developed and publish
Emotional Intelligence Report EIQ16 questionnaire Joe Smith myskillsprofile.com around the globe Report The EIQ16 questionnaire is copyright MySkillsProfile.com. myskillsprofile.com developed and publish
Psychological Foundations of Curriculum. Kevin Thompson
 Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Kevin Thompson Focusing Questions 1. In what ways do psychological foundations enable curriculum workers (teachers, supervisors, and curriculum developers) to perform
Psychological Foundations of Curriculum Kevin Thompson Focusing Questions 1. In what ways do psychological foundations enable curriculum workers (teachers, supervisors, and curriculum developers) to perform
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn?
 Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Personality. Unit 3: Developmental Psychology
 Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
Syllabus AP Psychology
 Class Name: Syllabus AP Psychology AP Psychology Teacher Name: Mr. Myers Description: AP Psychology is a comprehensive study of the human mind and cognitive processes. Students will examine the many structures
Class Name: Syllabus AP Psychology AP Psychology Teacher Name: Mr. Myers Description: AP Psychology is a comprehensive study of the human mind and cognitive processes. Students will examine the many structures
Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists,
 DEVELOPING A SELF: A GENERAL SEMANTICS WAY MILTON DAWES Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists, and others have asked: Is there such a thing as a self? Does the self
DEVELOPING A SELF: A GENERAL SEMANTICS WAY MILTON DAWES Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists, and others have asked: Is there such a thing as a self? Does the self
Innate? Learned? Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Aggression and Violence. What is violence?
 Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
INDIAN HILL EXEMPTED VILLAGE SCHOOL DISTRICT Social Studies Curriculum - May 2009 Psychology Semester Course
 History and Methods of Psychology Big Idea: Psychology is the study of human behavior. Before it was as a science, psychology originates in the Stone Age. Since then, it has evolved into a scientific field
History and Methods of Psychology Big Idea: Psychology is the study of human behavior. Before it was as a science, psychology originates in the Stone Age. Since then, it has evolved into a scientific field
Module 5:Aggression Lecture 20: Perspectives on the causes of aggression. The Lecture Contains: Understanding aggression and its causes
 The Lecture Contains: Understanding aggression and its causes Freudian understanding of agression A critique of instinct theories of aggression Biological theory of aggression Effect of testosterone Testosterone
The Lecture Contains: Understanding aggression and its causes Freudian understanding of agression A critique of instinct theories of aggression Biological theory of aggression Effect of testosterone Testosterone
Chapter 3 Pseudoscience, Science, and the Medical Model of Deviance
 Chapter 3 Pseudoscience, Science, and the Medical Model of Deviance Student Study Guide This Study guide is read along with the text in the book. Throughout this Chapter you should take notes and be able
Chapter 3 Pseudoscience, Science, and the Medical Model of Deviance Student Study Guide This Study guide is read along with the text in the book. Throughout this Chapter you should take notes and be able
ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional defiant disorder and MERIM
 ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) ODD is very frequently associated with ADHD. People with ODD typically overreact with anger in response to minor frustration. The lack
ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) ODD is very frequently associated with ADHD. People with ODD typically overreact with anger in response to minor frustration. The lack
Lecture 9. Control and Personality. Professor Ian Robertson
 Lecture 9 Control and Personality Professor Ian Robertson SEE KELTNER ET AL PSYCH REVIEW (FROM LECTURE 8) Why does Power increase behavioural activation? Power is correlated with increased resources. Powerful
Lecture 9 Control and Personality Professor Ian Robertson SEE KELTNER ET AL PSYCH REVIEW (FROM LECTURE 8) Why does Power increase behavioural activation? Power is correlated with increased resources. Powerful
Introduction to CD2: September 6. Minodora Grigorescu Mothercraft College
 Introduction to CD2: September 6 Minodora Grigorescu Mothercraft College Agenda Early modern theorists Issues in development Reflection- why you are here What teaching skills do you have? Reflection cont
Introduction to CD2: September 6 Minodora Grigorescu Mothercraft College Agenda Early modern theorists Issues in development Reflection- why you are here What teaching skills do you have? Reflection cont
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline April 2011
 Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline April 2011 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Psychology Course Number: 1890 Grade Level: 11-12 Length of Course:
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline April 2011 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Psychology Course Number: 1890 Grade Level: 11-12 Length of Course:
Direct reinforcement. Demand characteristics. Phillips (1983) Mental representation. Demand characteristics. Bandura and Walters (1963)
 58 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Specifics of aggressive behaviour Direct reinforcement Bobo doll Demand characteristics Bandura et al. (1961) Phillips (1983) Context-dependent learning Specifics of aggressive
58 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Specifics of aggressive behaviour Direct reinforcement Bobo doll Demand characteristics Bandura et al. (1961) Phillips (1983) Context-dependent learning Specifics of aggressive
Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now
 Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) is a classic study demonstrating the acquisition of aggression through social learning. It is summarised in the box opposite. Bandura
Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) then and now Bandura, Ross & Ross (1961) is a classic study demonstrating the acquisition of aggression through social learning. It is summarised in the box opposite. Bandura
PSYC3017 Social Psychology
 PSYC3017 Social Psychology Unit of Study Code: Coordinator: PSYC3017 Dr Lisa Zadro Office: Room 455 Brennan MacCallum Building Phone: 90367059 E-mail: lisaz@psych.usyd.edu.au Other Lecturing Staff Dr Brian
PSYC3017 Social Psychology Unit of Study Code: Coordinator: PSYC3017 Dr Lisa Zadro Office: Room 455 Brennan MacCallum Building Phone: 90367059 E-mail: lisaz@psych.usyd.edu.au Other Lecturing Staff Dr Brian
Know and understand the assumptions
 Element SAMs Know and understand the assumptions The 3 assumptions named on the specification must be taught as they could be named in exam paper Easy to over-teach on this section Use examples from Psychology
Element SAMs Know and understand the assumptions The 3 assumptions named on the specification must be taught as they could be named in exam paper Easy to over-teach on this section Use examples from Psychology
PSYCHOLOGY. H567/02 Psychological themes through core studies Summer 2017 examination series A LEVEL. Exemplar Candidate Work
 Qualification Accredited A LEVEL PSYCHOLOGY H567 For first teaching in 2015 H567/02 Psychological themes through core studies Summer 2017 examination series Version 1 www.ocr.org.uk/psychology Contents
Qualification Accredited A LEVEL PSYCHOLOGY H567 For first teaching in 2015 H567/02 Psychological themes through core studies Summer 2017 examination series Version 1 www.ocr.org.uk/psychology Contents
Applied Social Psychology Msc.
 Applied Social Msc. Course Course names Course description codes MSPSY501* Applied Social This module will discuss, at advanced level: The cognitive system, conceptual systems, expectation, explanation
Applied Social Msc. Course Course names Course description codes MSPSY501* Applied Social This module will discuss, at advanced level: The cognitive system, conceptual systems, expectation, explanation
Critical Thinking Assessment at MCC. How are we doing?
 Critical Thinking Assessment at MCC How are we doing? Prepared by Maura McCool, M.S. Office of Research, Evaluation and Assessment Metropolitan Community Colleges Fall 2003 1 General Education Assessment
Critical Thinking Assessment at MCC How are we doing? Prepared by Maura McCool, M.S. Office of Research, Evaluation and Assessment Metropolitan Community Colleges Fall 2003 1 General Education Assessment
1. Temporal precedence 2. Existence of a relationship 3. Elimination of Rival Plausible Explanations
 Ci Criminology i 860 Experimentation: Deconstructing Donnerstein & Berkowitz Remember John Stuart Mill s 3 Criteria for inferring the existence of a causal relation 1. Temporal precedence 2. Existence
Ci Criminology i 860 Experimentation: Deconstructing Donnerstein & Berkowitz Remember John Stuart Mill s 3 Criteria for inferring the existence of a causal relation 1. Temporal precedence 2. Existence
Com 400 Dr. Raz. Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research
 Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts
 Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts HTTPS://WWW.JIGSAW.ORG/#OVER VIEW What do you think we are learning about today? LEARNING OBJECTIVE We are learning about the use of psychological knowledge
Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts HTTPS://WWW.JIGSAW.ORG/#OVER VIEW What do you think we are learning about today? LEARNING OBJECTIVE We are learning about the use of psychological knowledge
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2017
 Scheme (Results) January 2017 Pearson Edexcel International GCE In Psychology (WPS02) Paper 01: Biological Psychology, Learning Theories and Development Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC
Scheme (Results) January 2017 Pearson Edexcel International GCE In Psychology (WPS02) Paper 01: Biological Psychology, Learning Theories and Development Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC
PSYC 3018 Abnormal Psychology
 PSYC 3018 Abnormal Psychology Unit of Study Code: Coordinator: Other Teaching Staff: PSYC3018 Dr Marianna Szabó Office: 417 Brennan-MacCallum Building Phone: 9351 5147 E-mail: Marianna.szabo@sydney.edu.au
PSYC 3018 Abnormal Psychology Unit of Study Code: Coordinator: Other Teaching Staff: PSYC3018 Dr Marianna Szabó Office: 417 Brennan-MacCallum Building Phone: 9351 5147 E-mail: Marianna.szabo@sydney.edu.au
SUICIDE PREVENTION. Cassandra Ward, LCPC. Erikson Institute Center for Children and Families
 SUICIDE PREVENTION Cassandra Ward, LCPC Erikson Institute Center for Children and Families Overview of Today s Presentation Introduction CCF s School Mental Health Project What is Suicide What is Mental
SUICIDE PREVENTION Cassandra Ward, LCPC Erikson Institute Center for Children and Families Overview of Today s Presentation Introduction CCF s School Mental Health Project What is Suicide What is Mental
Understanding myself and others. Evaluation questions
 Understanding myself and others Evaluation questions This series of questions is drawn from a programme, SPECTRUM which is available on EvaluationStore.com. The site includes evaluations at organisational,
Understanding myself and others Evaluation questions This series of questions is drawn from a programme, SPECTRUM which is available on EvaluationStore.com. The site includes evaluations at organisational,
AP Psychology 12. Burnaby North Secondary Ms. Carey
 AP Psychology 12 Burnaby North Secondary 2016-2017 Ms. Carey Welcome to AP Psychology 12! The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and
AP Psychology 12 Burnaby North Secondary 2016-2017 Ms. Carey Welcome to AP Psychology 12! The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and
AP Psychology. Course Audit
 Ledyard High School 24 Gallup Hill Road Ledyard CT. 06339 AP Psychology Course Audit Daniel Mello Eric Van Frachen 1 AP Psychology Syllabus: The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the
Ledyard High School 24 Gallup Hill Road Ledyard CT. 06339 AP Psychology Course Audit Daniel Mello Eric Van Frachen 1 AP Psychology Syllabus: The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the
Outline how and why audiences have been researched in terms of effects and
 1.2 The Unshuffled Essay #1 Essay Question: Outline how and why audiences have been researched in terms of effects and uses. 3. When investigating the complex links between the media and the audience,
1.2 The Unshuffled Essay #1 Essay Question: Outline how and why audiences have been researched in terms of effects and uses. 3. When investigating the complex links between the media and the audience,
AP Psychology 12. Burnaby North Secondary Ms. Carey
 AP Psychology 12 Burnaby North Secondary 2017-2018 Ms. Carey Welcome to AP Psychology 12! The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and
AP Psychology 12 Burnaby North Secondary 2017-2018 Ms. Carey Welcome to AP Psychology 12! The purpose of AP Psychology is to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and
Logic Model. When do you create a Logic Model? Create your LM at the beginning of an evaluation and review and update it periodically.
 RRC Evaluation Tool Basket: Logic Model 1 Logic Model What is a Logic Model? A logic model is a series of if-then statements that outlines what you expect to happen in your program. For example, If these
RRC Evaluation Tool Basket: Logic Model 1 Logic Model What is a Logic Model? A logic model is a series of if-then statements that outlines what you expect to happen in your program. For example, If these
Personality. Chapter 13
 + Personality Chapter 13 + Personality An individual s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting. Each Dwarf has a distinct personality. + Psychodynamic Perspective Freud s clinical experience
+ Personality Chapter 13 + Personality An individual s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting. Each Dwarf has a distinct personality. + Psychodynamic Perspective Freud s clinical experience
Writing a Language Analysis Essay
 Writing a Language Analysis Essay Planning is CRUCIAL. 1. UNDERSTAND: Sit on hands reading. Read to understand the articles/image. Record the overall issue the material explores. As you finish each article
Writing a Language Analysis Essay Planning is CRUCIAL. 1. UNDERSTAND: Sit on hands reading. Read to understand the articles/image. Record the overall issue the material explores. As you finish each article
Unit 6 Learning.
 Unit 6 Learning https://www.apstudynotes.org/psychology/outlines/chapter-6-learning/ 1. Overview 1. Learning 1. A long lasting change in behavior resulting from experience 2. Classical Conditioning 1.
Unit 6 Learning https://www.apstudynotes.org/psychology/outlines/chapter-6-learning/ 1. Overview 1. Learning 1. A long lasting change in behavior resulting from experience 2. Classical Conditioning 1.
Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives. Chapter 3 Outline -Attitude Change
 Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives 1) An understanding of how both internal mental processes and external influences lead to attitude change 2) An understanding of when and how behavior which is inconsistent
Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives 1) An understanding of how both internal mental processes and external influences lead to attitude change 2) An understanding of when and how behavior which is inconsistent
Understanding the True Realities of Influencing. What do you need to do in order to be Influential?
 Understanding the True Realities of Influencing. What do you need to do in order to be Influential? Background and why Influencing is increasingly important? At Oakwood Learning we have carried out our
Understanding the True Realities of Influencing. What do you need to do in order to be Influential? Background and why Influencing is increasingly important? At Oakwood Learning we have carried out our
Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1
 Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1 A. Exercises 1. Write a brief characterization of each of the following professionals: A. Psychologist B. Astrologist C. Scientist 2. List the most interesting psychologist
Introduction Stanovich, Chapter 1 A. Exercises 1. Write a brief characterization of each of the following professionals: A. Psychologist B. Astrologist C. Scientist 2. List the most interesting psychologist
Contents. Chapter. A Closer Look at You. Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude. Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You
 Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
Evaluating a Claim. Identify and clarify key terms Highlight Major Debates Summarize your approach Thesis Statement: Take a Position
 AICE Long Essay Structure Evaluating a Claim Essay Element Argument in Favor of the Claim Argument Against the Claim Identify the subject Identify and clarify key terms Highlight Major Debates Summarize
AICE Long Essay Structure Evaluating a Claim Essay Element Argument in Favor of the Claim Argument Against the Claim Identify the subject Identify and clarify key terms Highlight Major Debates Summarize
Kantor Behavioral Profiles
 Kantor Behavioral Profiles baseline name: date: Kantor Behavioral Profiles baseline INTRODUCTION Individual Behavioral Profile In our earliest social system the family individuals explore a range of behavioral
Kantor Behavioral Profiles baseline name: date: Kantor Behavioral Profiles baseline INTRODUCTION Individual Behavioral Profile In our earliest social system the family individuals explore a range of behavioral
GCSE Psychology Topic A: How do we see our World?
 GCSE Psychology Topic A: How do we see our World? Tick the content covered box once your teacher tells you that a particular sub-topic has been taught. You then need to rate your understanding of that
GCSE Psychology Topic A: How do we see our World? Tick the content covered box once your teacher tells you that a particular sub-topic has been taught. You then need to rate your understanding of that
Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement. reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited
 OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
Psychology Stage 1 Modules / 2018
 Psychology Stage 1 Modules - 2017 / 2018 PSYC101: Psychology An Introduction - (Semester 1) 20 credits This module is an introduction to Psychology as a science. It includes elements which expose students
Psychology Stage 1 Modules - 2017 / 2018 PSYC101: Psychology An Introduction - (Semester 1) 20 credits This module is an introduction to Psychology as a science. It includes elements which expose students
Midterm Practice Examination Answer Key. Answer Key
 G r a d e 1 2 P s y c h o l o g y Midterm Practice Examination Answer Key Name: Student Number: Attending q Non-Attending q Phone Number: Address: For Marker s Use Only Date: Final Mark /100 = % Comments:
G r a d e 1 2 P s y c h o l o g y Midterm Practice Examination Answer Key Name: Student Number: Attending q Non-Attending q Phone Number: Address: For Marker s Use Only Date: Final Mark /100 = % Comments:
Audience research US Empirical traditions of audience research Effects research Bobo dolls and short term behavioural effects Results
 Audience research 1. This is about what happens when individuals, families, communities engage with media texts and technologies. 2. Most seek to analyse how media audiences are effected by pre-existing
Audience research 1. This is about what happens when individuals, families, communities engage with media texts and technologies. 2. Most seek to analyse how media audiences are effected by pre-existing
Writing in an Academic Style Module: Introduction
 Writing in an Academic Style Module: Introduction What is Academic Style? Writing tasks are different across different academic disciplines and to some extent the language use will be quite different from
Writing in an Academic Style Module: Introduction What is Academic Style? Writing tasks are different across different academic disciplines and to some extent the language use will be quite different from
Psychological Approaches to Counseling. Mr. Lema, Isaac Clinical Psychologist (MSc.) 25 th November 2015
 Psychological Approaches to Counseling Mr. Lema, Isaac Clinical Psychologist (MSc.) 25 th November 2015 Learning Objectives Explore different psychological approaches to counseling Adopt psychological
Psychological Approaches to Counseling Mr. Lema, Isaac Clinical Psychologist (MSc.) 25 th November 2015 Learning Objectives Explore different psychological approaches to counseling Adopt psychological
Check homework to determine depth of understanding. Daily questioning to check for comprehension of assigned work
 Immaculata Regional High School Course Outline Course: Psychology 11 Teacher: Mr. B. Oliveira Year: 2017 Content and Hours of Linkage with Learning Outcomes/Curriculum Organizers A. Introduction to Psychology
Immaculata Regional High School Course Outline Course: Psychology 11 Teacher: Mr. B. Oliveira Year: 2017 Content and Hours of Linkage with Learning Outcomes/Curriculum Organizers A. Introduction to Psychology
SPORT PSYCHOLOGY. Effective Communication and Dealing with Athletes with Low Self-Esteem
 SPORT PSYCHOLOGY Effective Communication and Dealing with Athletes with Low Self-Esteem 1 BIOGRAPHY Nicolas Allen, MA, BPE Provisional Registered Psychologist Master s of Counselling Psychology: City University
SPORT PSYCHOLOGY Effective Communication and Dealing with Athletes with Low Self-Esteem 1 BIOGRAPHY Nicolas Allen, MA, BPE Provisional Registered Psychologist Master s of Counselling Psychology: City University
Learning Approaches. Classical Conditioning Conditioned Stimulus (CS)... Conditioned Response (CR)... Acquisition... Extinction...
 Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
SSS 528 Human Sexuality 1 Credit Fall, 2011 Instructor: Dorothy Van Dam, LICSW
 Syllabus 1 SSS 528 Human Sexuality 1 Credit Fall, 2011 Instructor: Dorothy Van Dam, LICSW c This course is the property of NCSSS and the instructor and may be distributed only with written permission.
Syllabus 1 SSS 528 Human Sexuality 1 Credit Fall, 2011 Instructor: Dorothy Van Dam, LICSW c This course is the property of NCSSS and the instructor and may be distributed only with written permission.
IJPSS Volume 2, Issue 8 ISSN:
 Aggressive behavior in field soccer players: A comparative study Prof. Kalpana Sharma* Khalid Azim Khan** Zeeshan Haider*** Sartaj Khan*** _ Abstract Sports involve extremely complex behavioral issues.
Aggressive behavior in field soccer players: A comparative study Prof. Kalpana Sharma* Khalid Azim Khan** Zeeshan Haider*** Sartaj Khan*** _ Abstract Sports involve extremely complex behavioral issues.
Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams
 Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams From: Overcoming Depression: A Five Areas Approach. Chris Williams, Arnold Publishers (2002) 2 Section 1: Introduction. In this workbook you will: Find out
Workbook 3 Being assertive Dr. Chris Williams From: Overcoming Depression: A Five Areas Approach. Chris Williams, Arnold Publishers (2002) 2 Section 1: Introduction. In this workbook you will: Find out
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Learning. Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning.
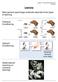 Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
WHAT IS SELF? MODULE-IV OBJECTIVES 16.1 CONCEPT OF SELF. What is Self? Self and Personality. Notes
 What is Self? MODULE-IV 16 WHAT IS SELF? Self is focus of our everyday behaviour and all of us do have a set of perceptions and beliefs about ourselves. This kind of self concept plays important role in
What is Self? MODULE-IV 16 WHAT IS SELF? Self is focus of our everyday behaviour and all of us do have a set of perceptions and beliefs about ourselves. This kind of self concept plays important role in
Student substance use is a considerable challenge
 W H AT no. W O R K S I E F B R SUBSTANCE USE AT SCHOOL Student substance use is a considerable challenge facing most high schools, both in terms of its ability to undermine school safety efforts and in
W H AT no. W O R K S I E F B R SUBSTANCE USE AT SCHOOL Student substance use is a considerable challenge facing most high schools, both in terms of its ability to undermine school safety efforts and in
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *1335707525* PSYCHOLOGY 9698/33 Paper 3 The Specialist Choices October/November 2016 No Additional Materials
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *1335707525* PSYCHOLOGY 9698/33 Paper 3 The Specialist Choices October/November 2016 No Additional Materials
Tros Gynnal Plant. Introduction. All of our services are:
 Families Plus 2016 Tros Gynnal Plant Introduction Most people know Tros Gynnal Plant as the Welsh Children s Rights Charity which provides Advocacy services for children and young people. However, as well
Families Plus 2016 Tros Gynnal Plant Introduction Most people know Tros Gynnal Plant as the Welsh Children s Rights Charity which provides Advocacy services for children and young people. However, as well
Your Growth and Development Chapter 2 Growth Patterns Typical growth patterns have been identified in the following four areas:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Your Growth and Development Chapter 2 Growth Patterns Typical growth patterns have been identified in the following four areas: growth follows a pattern but each person will will develop
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Your Growth and Development Chapter 2 Growth Patterns Typical growth patterns have been identified in the following four areas: growth follows a pattern but each person will will develop
CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
 CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Social Learning Theory explanation of Non- Verbal Communication Social learning theory (SLT) starts with the idea that we observe and imitate
CORE THEORY - NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION - SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY Social Learning Theory explanation of Non- Verbal Communication Social learning theory (SLT) starts with the idea that we observe and imitate
Hawaii Content and Performance Standards III Health Education
 Hawaii Content and Performance Standards III Health Education Hawaii s 7x7 Curriculum Focus for Standards Based School Health Education Build Knowledge and skills through teaching Promote Healthy Behaviors
Hawaii Content and Performance Standards III Health Education Hawaii s 7x7 Curriculum Focus for Standards Based School Health Education Build Knowledge and skills through teaching Promote Healthy Behaviors
MSc Criminology with Forensic Psychology
 Programme Specification for MSc Criminology with Forensic Psychology 1. Programme title MSc Criminology with Forensic Psychology 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching institution Middlesex
Programme Specification for MSc Criminology with Forensic Psychology 1. Programme title MSc Criminology with Forensic Psychology 2. Awarding institution Middlesex University 3. Teaching institution Middlesex
Inferences: What inferences about the hypotheses and questions can be made based on the results?
 QALMRI INSTRUCTIONS QALMRI is an acronym that stands for: Question: (a) What was the broad question being asked by this research project? (b) What was the specific question being asked by this research
QALMRI INSTRUCTIONS QALMRI is an acronym that stands for: Question: (a) What was the broad question being asked by this research project? (b) What was the specific question being asked by this research
Becoming New Me UK. Type of intervention. Target group, level of prevention and sub-groups: Target population. Delivery organisation
 Becoming New Me UK Type of intervention Prison Group Work Target group, level of prevention and sub-groups: Tertiary prevention Young Adults (18 20 Years), Adults (21 Years +) Males Interventions for those
Becoming New Me UK Type of intervention Prison Group Work Target group, level of prevention and sub-groups: Tertiary prevention Young Adults (18 20 Years), Adults (21 Years +) Males Interventions for those
Take new look emotions we see as negative may be our best friends (opposite to the script!)
 Tony Robbins - emotions Take new look emotions we see as negative may be our best friends (opposite to the script!) How do people deal? 1. They avoid them try not to feel them. a. Rejection 2. I ll endure
Tony Robbins - emotions Take new look emotions we see as negative may be our best friends (opposite to the script!) How do people deal? 1. They avoid them try not to feel them. a. Rejection 2. I ll endure
Assignment The professional context of counselling!
 - DO NOT COPY - THIS ASSIGNMENT EXEMPLAR IS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES ONLY Many organisations, including awarding bodies, use software to check that your content is original. Use this assignment exemplar
- DO NOT COPY - THIS ASSIGNMENT EXEMPLAR IS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES ONLY Many organisations, including awarding bodies, use software to check that your content is original. Use this assignment exemplar
Children's fitness testing: feasibility study summary
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Children's fitness testing: feasibility study summary This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Children's fitness testing: feasibility study summary This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER SUMMARY
 CHAPTER 14 PERSONALITY IN PERSPECTIVE: OVERLAP AND INTEGRATION CHAPTER OUTLINE Similarities Among Perspectives Psychoanalysis and Evolutionary Psychology: The Structural Model Psychoanalysis and Evolutionary
CHAPTER 14 PERSONALITY IN PERSPECTIVE: OVERLAP AND INTEGRATION CHAPTER OUTLINE Similarities Among Perspectives Psychoanalysis and Evolutionary Psychology: The Structural Model Psychoanalysis and Evolutionary
Chapter 13 and 16. Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text
 Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
Music and Emotional Expression in Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Thousand Oaks High School. April 20, 2017.
 1 Music and Emotional Expression in Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder Thousand Oaks High School April 20, 2017 Word Count: 4,014 2 Abstract This correlational study is intended to determine how exposure
1 Music and Emotional Expression in Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder Thousand Oaks High School April 20, 2017 Word Count: 4,014 2 Abstract This correlational study is intended to determine how exposure
3. Read the study by Grant. Underline psychology key words and add them to your glossary. 4. Make detailed notes on the study
 Getting ready to study Psychology: 1. Read the study by Loftus and Palmer. Underline psychology key words and look up what they mean. Get yourself a small exercise book and start to make a glossary. 2.
Getting ready to study Psychology: 1. Read the study by Loftus and Palmer. Underline psychology key words and look up what they mean. Get yourself a small exercise book and start to make a glossary. 2.
Research in Psychology MODULE DESCRIPTOR TITLE. Introduction to Psychology MODULE CODE S LEVEL 4 CREDITS 20 JACS CODE C800 DEPARTMENT
 MODULE DESCRIPTOR TITLE Introduction to Psychology MODULE CODE 77-4724-00S LEVEL 4 CREDITS 20 JACS CODE C800 DEPARTMENT Psychology, Sociology & Politics SUBJECT GROUP Psychology MODULE LEADER TBC DATE
MODULE DESCRIPTOR TITLE Introduction to Psychology MODULE CODE 77-4724-00S LEVEL 4 CREDITS 20 JACS CODE C800 DEPARTMENT Psychology, Sociology & Politics SUBJECT GROUP Psychology MODULE LEADER TBC DATE
How to use this recording
 Paragraphs That Pop How to use this recording Watch the video Do the activities Download the slides: http://sls.navitasprofessional.edu.au/webinar-recordings-materials/all Goals for this session Learn
Paragraphs That Pop How to use this recording Watch the video Do the activities Download the slides: http://sls.navitasprofessional.edu.au/webinar-recordings-materials/all Goals for this session Learn
COUNSELING THEORIES: Cognitive, Affective and Behavior Change with Children and Adolescents CPSY 512 Fall, 2007
 Steve Berman Office: (503) 238-5899 Office Hours by Appointment Email: berman@lclark.edu COUNSELING THEORIES: Cognitive, Affective and Behavior Change with Children and Adolescents CPSY 512 Fall, 2007
Steve Berman Office: (503) 238-5899 Office Hours by Appointment Email: berman@lclark.edu COUNSELING THEORIES: Cognitive, Affective and Behavior Change with Children and Adolescents CPSY 512 Fall, 2007
Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy
 Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy The media violence controversy basically centers around the questions of effects: Does watching violent media make
Entertaining Violence or Violent Entertainment? Mapping the Media Violence Controversy The media violence controversy basically centers around the questions of effects: Does watching violent media make
Programme Specification
 Programme Specification Title: Forensic Science Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Master of Science (MSc) Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) To be
Programme Specification Title: Forensic Science Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Master of Science (MSc) Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) To be
Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 15
 Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 5 Critical thinking is the ability and willingness to assess claims and make objective judgments on the basis of well-supported reasons. (Wade and Tavris, pp.4-5)
Critical Thinking and Reading Lecture 5 Critical thinking is the ability and willingness to assess claims and make objective judgments on the basis of well-supported reasons. (Wade and Tavris, pp.4-5)
PSYCHOLOGY IAS MAINS: QUESTIONS TREND ANALYSIS
 VISION IAS www.visionias.wordpress.com www.visionias.cfsites.org www.visioniasonline.com Under the Guidance of Ajay Kumar Singh ( B.Tech. IIT Roorkee, Director & Founder : Vision IAS ) PSYCHOLOGY IAS MAINS:
VISION IAS www.visionias.wordpress.com www.visionias.cfsites.org www.visioniasonline.com Under the Guidance of Ajay Kumar Singh ( B.Tech. IIT Roorkee, Director & Founder : Vision IAS ) PSYCHOLOGY IAS MAINS:
Programme Specification. MSc/PGDip Forensic and Legal Psychology
 Entry Requirements: Programme Specification MSc/PGDip Forensic and Legal Psychology Applicants for the MSc must have a good Honours degree (2:1 or better) in Psychology or a related discipline (e.g. Criminology,
Entry Requirements: Programme Specification MSc/PGDip Forensic and Legal Psychology Applicants for the MSc must have a good Honours degree (2:1 or better) in Psychology or a related discipline (e.g. Criminology,
Appendix A: NAPLaN Reading Skills by Proficiency Band
 Appendix A: NAPLaN Reading Skills by Proficiency Band NAPLaN Comprehension Skills by Proficiency Band PB Finds clearly stated information in the first sentence of an illustrated information text. 1 Locates
Appendix A: NAPLaN Reading Skills by Proficiency Band NAPLaN Comprehension Skills by Proficiency Band PB Finds clearly stated information in the first sentence of an illustrated information text. 1 Locates
OVERVIEW ANXIETY AND ANGER IN ADULTS AUTISM AND MENTAL HEALTH COMORBIDITIES WHAT YOU SEE AND WHAT THEY FEEL WHAT YOU SEE AND WHAT THEY FEEL 26/09/2015
 OVERVIEW ANXIETY AND ANGER IN ADULTS Autism and Mental Health Comorbidities What is anxiety? What is anger? Interaction between ASC, Anxiety and Anger Managing anxiety AUTISM AND MENTAL HEALTH COMORBIDITIES
OVERVIEW ANXIETY AND ANGER IN ADULTS Autism and Mental Health Comorbidities What is anxiety? What is anger? Interaction between ASC, Anxiety and Anger Managing anxiety AUTISM AND MENTAL HEALTH COMORBIDITIES
Advanced Placement Psychology Syllabus Ms. Bean
 Advanced Placement Psychology Syllabus 2015-2016 Ms. Bean (beanj@portlandschools.org) At Deering High School, our goal is to graduate students who are globally competent and college and career-ready. Welcome
Advanced Placement Psychology Syllabus 2015-2016 Ms. Bean (beanj@portlandschools.org) At Deering High School, our goal is to graduate students who are globally competent and college and career-ready. Welcome
Mr. Benjamin Walters ( or ext. 1333) AP Psychology Office Hours: Smart Lunch. Course Description:
 Mr. Benjamin Walters ( Bwalters@iss.k12.nc.us or 704-799-8555 ext. 1333) AP Psychology Office Hours: Smart Lunch Course Description: The purpose of the AP course in Psychology is to introduce the systematic
Mr. Benjamin Walters ( Bwalters@iss.k12.nc.us or 704-799-8555 ext. 1333) AP Psychology Office Hours: Smart Lunch Course Description: The purpose of the AP course in Psychology is to introduce the systematic
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Psychodynamic Assessment 1/1/2014 SESSION 6 PSYCHODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT
 THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Psychodynamic Assessment 1/1/2014 SESSION 6 PSYCHODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II SESSION 6: Psychodynamic Assessment Psychodynamic Assessment Assessing the specific
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Psychodynamic Assessment 1/1/2014 SESSION 6 PSYCHODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II SESSION 6: Psychodynamic Assessment Psychodynamic Assessment Assessing the specific
Implementing Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) Skills training on a male low secure ward
 Implementing Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) Skills training on a male low secure ward Dr Louise Roberts (Lead Clinical Psychologist) Viktoria Nagy (Assistant Psychologist) Robin Pinto Unit 12.06.2018
Implementing Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) Skills training on a male low secure ward Dr Louise Roberts (Lead Clinical Psychologist) Viktoria Nagy (Assistant Psychologist) Robin Pinto Unit 12.06.2018
Chapter 7. Learning From Experience
 Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
*Taken from the old syllabus. The new (2019) syllabus may have changes.
 I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
gender and violence 2 The incidence of violence varies dramatically by place and over time.
 gender and violence Everyone has the right to life, liberty, and the security of person (Article 3, UDHR, 1948; Articles 6.1 and 9.1, ICCPR, 1966). No one shall be subjected to... cruel, inhuman or degrading
gender and violence Everyone has the right to life, liberty, and the security of person (Article 3, UDHR, 1948; Articles 6.1 and 9.1, ICCPR, 1966). No one shall be subjected to... cruel, inhuman or degrading
Psychology Stage 4 Modules 2017 / 2018
 Psychology Stage 4 Modules 2017 / 2018 PSYC405 Psychology Dissertation - (All Year) 40 credits This module aims to consolidate and put into practice the research training carried out in earlier stages
Psychology Stage 4 Modules 2017 / 2018 PSYC405 Psychology Dissertation - (All Year) 40 credits This module aims to consolidate and put into practice the research training carried out in earlier stages
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介 COURSES FOR 4-YEAR UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES PSY2101 Introduction to Psychology (3 credits) The purpose of this course is to introduce fundamental concepts and theories in psychology
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介 COURSES FOR 4-YEAR UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES PSY2101 Introduction to Psychology (3 credits) The purpose of this course is to introduce fundamental concepts and theories in psychology
What is Psychology? Science versus Intuition 1 a. What is psychology? (from text) b. Note the revision from class:
 Lilienfeld et al. Chapter 1: Psychology and Scientific Thinking: A Framework for Everyday Life p. 1 of 12 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college- level courses.
Lilienfeld et al. Chapter 1: Psychology and Scientific Thinking: A Framework for Everyday Life p. 1 of 12 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college- level courses.
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Report JOHN SMITH 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The EIQ16 measures aspects of your emotional intelligence by asking you questions
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Report JOHN SMITH 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The EIQ16 measures aspects of your emotional intelligence by asking you questions
