A detailed Activity Information Chart for VersaTiles Science is provided on
|
|
|
- Kevin Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to Read the Activity Information Chart A detailed Activity Information Chart for VersaTiles Science is provided on pages It is intended to help you assign appropriate activities to your students and to help you integrate VersaTiles into your current curriculum. These two columns give the book title, grade level, and page number for each activity. Titles are listed in the order in which they appear in the book. Extend learning with these prompts for journal writing or class discussion. They are a good complement to the general science reading strategies offered on page 28. Earth Science: Learn About Your World Real Science: Reading Maps Sue Hendrickson: Modern Adventurer* Earth Systems: Four Spheres Volcanoes: Forces That Shape Earth Earth Materials: Rocks Rule* Identify topics of study in earth science. Interpret symbolic information to read a map. Recognize Sue Hendrickson's contribution to science. Define Earth s four systems and compare their components. Define a volcano and identify how it erupts and takes form. Identify the three main types of rock and how they form Properties of earth materials; objects in the sky; changes in the earth and sky K-4 Std. G History and Nature of K-4 Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives:Types of resources Properties of earth materials. Research the names of the seven continents, list them, and circle the name of the one you live on. 2. Write how meteorologists help you in everyday life.. Draw a map of your town or neighborhood. 2. Make a list of the types of people who might need to use maps on a daily basis.. Write a story of Sue the T-rex, from when it lived on Earth to when it was displayed in the museum. 2. Write about how you think Sue Hendrickson felt when she discovered the T-rex.. What is the nearest mountain range to you? How do you think it formed? 2. Which geosphere do you find most interesting? Why?. Which type of volcano would be most dangerous to live by? Why? 2. Research a famous volcanic eruption and write down some facts about it.. What rocks do you think are common in your area? 2 Pick up a rock Write a story of how it formed This column states the objective for each student activity. Use this column to identify the National Science Education Standards to which each activity is correlated.
2 Activity Information Chart, Level 3 2. Research the names of the seven continents, list them, and circle the name of the one you live on. 2. Write how meteorologists help you in everyday life.. Draw a map of your town or neighborhood. 2. Make a list of the types of people who might need to use maps on a daily basis.. Write a story of Sue the T-rex, from when it lived on Earth to when it was displayed in the museum. 2. Write about how you think Sue Hendrickson felt when she discovered the T-rex.. What is the nearest mountain range to you? How do you think it formed? 2. Which geosphere do you find most interesting? Why?. Which type of volcano would be most dangerous to live by? Why? 2. Research a famous volcanic eruption and write down some facts about it.. What rocks do you think are common in your area? 2. Pick up a rock. Write a story of how it formed.. How would a groundhog digging help the soil? 2. How would the soil in a forest be different from soil in a desert?. Research another popular flying dinosaur. Compare it to Archaeopteryx. 2. Write about an ordinary day in the life of an Archaeopteryx.. Which stage of the water cycle is the easiest to see? Why? 2. Imagine you are a drop of water. Write about your journey through the four stages.. What clouds are in the sky today? What weather can you expect from these clouds? 2. What would the world be like if clouds didn t exist?. Describe what it looks like outside when there is a strong wind blowing. 2. What other instruments do meteorologists use? Properties of earth materials; objects in the sky; changes in the earth and sky Identify topics of study in earth science. Earth Science: Learn About Your World Interpret symbolic information to read a map. Real Science: Reading Maps K-4 Std. G History and Nature of Recognize Sue Hendrickson's contribution to science. Sue Hendrickson: Modern Adventurer* K-4 Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives:Types of resources Define Earth s four systems and compare their components. Earth Systems: Four Spheres Define a volcano and identify how it erupts and takes form. Volcanoes: Forces That Shape Earth Properties of earth materials Properties of earth materials Identify the three main types of rock and how they form. Identify characteristics of soil, as well as how soil forms. Earth Materials: Rocks Rule* Soil:What s the Scoop? Explain how fossils provide information about prehistoric animals. Fossils: Flying Dinosaurs* 4-5 Identify stages of the water cycle. The Water Cycle: Water All Around Describe cloud characteristics and associated weather events. Observing Weather: Clues in the Clouds 8-9 Explain the use of an anemometer and the Beaufort Scale. Tools of Science: Anemometer* 20-2
3 30-3 Activity Information Chart, Level 3 The Solar System: Earth s Neighborhood* Earth s Axis:The Reason for Seasons Lunar Cycle:The Moon Through the Month Ocean Tides: Rise and Fall Stars and Constellations: Sky Pictures Earth Science Life Science: Plants and Animals All Around Characteristics of Life:You Can't Live Without Them Louis Pasteur: Pioneer Against Disease Tools of Science: Thermometers Real Science: Classification* Animal Classes: Creature Features Identify celestial objects and their organization in the solar system. Explain the cause of seasons. Identify and describe the phases of the Moon. Explain the cause of ocean tides. Define stars and constellations. Define and explain key earth Compare characteristics of plants and animals. Distinguish between living and non-living things. Describe Louis Pasteur s scientific contributions to society. Understand the use of a thermometer and its scales. Explain how classification is used to sort and group organisms. Identify major classes of animals and their distinguishing characteristics. Objects in the sky Objects in the sky Objects in the sky Properties of earth materials; objects in the sky; changes in the earth and sky ; life cycles of organisms; organisms and K-4 Std. G History and Nature of. Research some facts about the planet you find most interesting and write about it. 2. Compare one of the inner planets with one of the outer planets.. Describe what the weather is like today. Now describe what you think it is like on the opposite side of Earth. 2. Write what you think it would be like if Earth didn t tilt on its axis.. What is your favorite phase of the Moon? Why? 2. Can there be two full moons in one month? How?. How do you think the tides affect people living on an ocean shoreline? 2. What would the tides be like if Earth did not rotate?. What is your favorite constellation? Why? 2. Research and write about why people in the Southern Hemisphere cannot see the North Star.. Write a letter to your parents telling them what you have learned in this book. 2. What was your favorite activity in this book? Why?. What are the five main kingdoms of living things? To which kingdom do you belong? 2. Draw a picture of a plant and label its main parts.. Name one living thing and identify three characteristics that make it alive. 2. Explain the main differences between living and non-living things.. What do you think is the most interesting fact about Pasteur? Why? 2. How has Pasteur affected your life?. Make a list of all the places you see thermometers. Describe how the thermometer is used in each place. 2. How might a thermometer be used in life science?. Classify the students in your class based on a single characteristic. 2. Write about how you use classification in your life.. To which class do human beings belong? Why? 2. Do some research about the lesser known animal classes. Identify examples of each. 3
4 Activity Information Chart, Level 3 4. Have you ever seen a fossil? Describe what it looked like. 2. What do you think a fossil of a human being would look like?. Which biome would be the hardest to live in? Why? 2. Where on Earth would a tundra biome be located? Why do you think that?. Research five tropical rain forest animals and identify which rain forest layer they live in. 2. Look at a map. List some countries where tropical rain forests may be located.. Make a list of three animals from each diet category. 2. What is your favorite animal and why? To which category does it belong?. What animal has the best camouflage? Why? 2. Why do large animals like sharks and tigers need to use camouflage?. How do you think a beaver dam changes life below the dam? 2. Research another animal that changes its environment and explain how it does it.. Which honeybee s job is the most important to a colony? Why? 2. Imagine you are a scout bee. Write about what a day in your life would be like.. Do some research and find out why geese fly in a V formation. 2. Write a story about a flock of geese migrating north.. Write about what farmers do to help seeds grow. 2. What is your favorite fruit? Draw a picture of the kinds of seeds it has.. A man with brown eyes, thick brown hair, a small nose, and thin lips reproduces with a woman with blue eyes, red hair, a big nose, and thick lips. What would their offspring probably look like? 2. What traits did you inherit from your mother? From your father? List them.. Which part of life science would you like to learn more about? Why? 2. Write five facts you learned from completing these activities. Properties of earth materials Define fossils and describe how some fossils are formed. Fossils:A Record of Life* Identify and describe a habitat and Earth s major biomes. Habitats and Biomes: Nature s Homes 4-5 Describe the structure and biodiversity of a tropical rain forest. Rain Forest Life: It s a Jungle Out There Compare various ways animals obtain food for energy. Animal Diets: Eating for Energy 8-9 Animal Camouflage: Clever Colors* 20-2 Define camouflage; compare and contrast different types of camouflage. Recognize that living things affect their environment. How Animals Change the Environment:The Busy Life of Beavers Describe the behavior and social organization of honeybees. Animal Behavior:The Sweet Life of Bees Identify migration as a response to changes in the environment. Animal Migration: Making the Round- Trip Route Plant Structures:A Peek at Seeds* K-4 Std. C Life Science: Life cycles of organisms Identify seed anatomy and the stages of germination. K-4 Std. C Life Science: Life cycles of organisms Recognize that offspring inherit genetic traits from their parents. Genes: Parents Pass Them On 30-3 ; life cycles of organisms; organisms and Define and explain key life Life Science
5 Activity Information Chart, Level 3 Physical Science: Describing How the World Works Real Science: Solve a Science Mystery Matter: It Makes Up Your World* States of Matter: Liquids, Solids, Gases* Changes in Matter: Physical or Chemical?* Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter Lise Meitner: Discoverer of Nuclear Fission Force and Motion: Pushes and Pulls Newton s Laws:The Science of Stop and Go* Energy: Put It to Work Heat: Energy That Sizzles Identify topics of study in physical science. Deduce facts from observations. Define matter and explain some physical properties of matter. Identify three states of matter and understand that matter can change state. Distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter. Discuss atoms and molecules and their relationship with matter. Recognize how Lise Meitner s research contributed to our understanding of atoms and energy. Define force and identify common forces. Describe Newton s Laws of Motion and identify real-life examples of each law. Define energy and identify some of its different forms. Define heat and explain how it is transferred. of objects and materials; position and motion of objects; light, heat, electricity, and magnetism of objects and materials of objects and materials of objects and materials of objects and materials K-4 Std. G History & Nature of K-4 Std. B Physical Science: Position and motion of objects K-4 Std. B Physical Science: Position and motion of objects. What part of physical science sounds most interesting to you? Why? 2. What form of energy would you like to learn about?. How are scientists like detectives? How are they different? 2. Write a description of an object, and see if a classmate can guess what it is.. Pick an object and list its properties. 2. Make a list of your own physical properties.. Describe how water looks in its three states. 2. Describe what happens if you forget to put ice cream in a freezer.. Make a list of three physical changes and three chemical changes that happen in your home. 2. How much different would life be if chemical changes were not possible? Write about it.. How do you think scientists discovered atoms. 2. What do you find interesting about atoms?. Research something that uses nuclear fission and write about it. 2. Do you think Lise had a tough life? Why or why not?. What would happen to your body if you went to the Moon where the force of gravity is less? 2. What 7th-century scientist came up with theories of force and motion? Write about him.. Write your own example of each of the laws of motion. 2. How does gravity affect these laws?. Why does a stretched rubber band have potential energy? 2. Which form of energy do you think you come across the most during the day? Why?. Why is it usually cooler during the night than during the day? 2. How does convection help birds to fly? 5
6 Activity Information Chart, Level 3 6. Think about what happens when the power goes out in your home. Write about how difficult it is to live without electricity. 2. Make a list of the electrical devices you use every day.. Find out how a compass uses magnets and write about it. 2. Write about how magnets help you in your daily life.. Why do some objects appear to change color in different lights? 2. Make a list of objects that reflect light well.. How does the name ROY G BIV help you remember the colors of the rainbow? 2. What do you think the world would be like if white light didn't exist?. How do you think ear plugs work? 2. What happens when a person s vocal chords are damaged? Why does this happen?. What is the most interesting thing you learned about in physical science? 2. What part of physical science do you not understand? Define static electricity and current electricity. Electrical Energy: Charge It! Define magnetism and explain its use in a burglar alarm. Tools of Science: Magnets Light Energy: Let It Shine* Identify light as a form of energy and understand how it affects what we see. Identify what a light spectrum is and explain how rainbows form. Light and Color:What is a Rainbow?* K-4 Std. B Physical Science: Position and motion of objects Recognize sound as a form of energy and understand how it is made and heard. Define and explain key physical Sound Energy: Hear It Loud and Clear 30-3 of objects and materials; position and motion of objects; light, heat, electricity, and magnetism Physical Science
7 Activity Information Chart, Level 4 Earth Science: It s Your World! Real Science: Using Tables and Graphs* Dr. Mae C. Jemison: Countdown to Success World Oceans: Our Watery World Weather Changes: Trouble in the Air* Earthquakes: Living on Shaky Ground Volcanoes: Nature s Fury Weathering and Erosion: Shaping the Land* Fossils:The Record of Life on Earth* Classification of Rocks: Let s Rock! Identify topics of study in earth science. Explain how tables and graphs are used in science. Recognize Dr. Mae Jemison s contributions to science and society. Distinguish between the world s oceans in terms of geography, depth, and area. Describe the weather changes associated with the four types of fronts. Explain the cause of earthquakes. Describe the structure of a composite volcano and the conditions that cause an eruption. Define weathering and erosion, and identify agents of both. Explain how fossils are used to understand the history of life on Earth. Compare and contrast igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Properties of earth materials; objects in the sky; changes in the earth and sky K-4 Std. G History and Nature of Properties of earth materials Properties of earth materials. Research a famous earth scientist and write about him/her. 2. What part of earth science do you think will interest you the most?. Make a graph comparing the number of students in your class with brown, blonde, and red hair. 2. Find an example of a graph and write about it.. What part of Dr. Jemison s life did you find most interesting? Why? 2. How do you think Dr. Jemison felt on Endeavor?. Why is it hard for boats to sail in most of the Arctic Ocean? 2. Why do you think the Pacific Ocean is deeper than the other oceans?. What was the last front that moved through your area? How do you know? 2. What type of air mass is most likely to form in your area?. Have you ever been in an earthquake? Describe what it was like (or what you think it would be like). 2. What are you supposed to do if you are caught in an earthquake?. Find out about the biggest-ever volcanic eruption in the U.S. and write some facts about it. 2. Do you think scientists can predict when a volcano will erupt? Explain.. Write about how you think erosion formed the Grand Canyon. 2. What other things besides rocks undergo weathering?. Imagine you could travel back in time. Which time period would you visit. Why? 2. What is the most interesting fossil you have ever seen?. Which group of rocks has the most colorful rocks? Name some of them. 2. Is one type of rock harder to identify than the others? Why? 7
8 Activity Information Chart, Level 4 8. In your own words, describe how the rock cycle works. 2. What do you think causes more rocks to change: water, ice, wind, or gases? Why do you think that?. Which type of rock do you think is the easiest to identify? 2. What types of rocks do you think are most common around your home?. Explain why a year on Uranus is longer than a year on Earth. 2. Would you be older if you lived on Uranus or on Venus? How do you know?. Have you ever looked through a telescope? What was it like? 2. Which type of telescope did you use? What did you look at?. What are some ways that you can reduce solid waste? 2. Think of a unique way to reduce solid waste and write about it.. Look around your classroom. Make a list of all of the recyclable items you see. 2. Write down what you can do to increase recycling in your school.. What part of earth science interests you the most? 2. What part of earth science confuses you? Describe the rock cycle and the changes that a rock may undergo. The Rock Cycle:The Recycling of Rocks 20-2 Properties of earth materials Use a dichotomous key to identify rock samples. Rock Identification: Using a Key to ID! Objects in the sky Use the revolution period to calculate age on the planets of the solar system. Solar System Science: Your Age on Other Planets Compare and contrast reflecting and refracting telescopes. Tools of Science: Telescopes* K-4 Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives: Types of resources Cleaning Up the Environment:Trash, Trash Go Away! K-4 Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives:Types of resources Define the term solid waste, and describe some ways that communities deal with solid waste. Recognize the different kinds of recyclable items found at home. Recycling:Treasure from Trash 30-3 Define and explain key earth Earth Science. What type of biologist has the most interesting job? Why? 2. Pick a biologist and describe what a day in his/her life would be like.. What did Maria learn from her experiment? 2. Would it be an accurate experiment if Maria only watered one of the plants? Why or why not?. What kind of microscope have you used? Why do you think that? 2. Make a list of Leeuwenhoek s accomplishments.. In your own words, write a definition for each microscope part. 2. What object would you like to observe with a microscope? What do you think it would look like? Properties of earth materials; objects in the sky; changes in the earth and sky ; life cycles of organisms; organisms and environments Identify different specialties within the field of biology. Biology:The Living Science Describe how to perform a simple controlled experiment. Real Science: Solving Problems with Experiments* Anton van Leeuwenhoek: Microscope Master Tools of Science:The Microscope* K-4 Std. G History and Nature of Discuss the important scientific contributions of Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Identify the parts of a microscope and their functions.
9 Activity Information Chart, Level 4 The Kingdoms of Living Things: Life s Variety Microbes: Earth s Unseen Helpers* Decomposers: Doing the Dirty Work* Biodiversity:The Variety of Life Food Chains:Who Eats Whom?* Animal Teeth: Adaptations to Diet Animals Needs: Staying Alive Mammals: Our Furry Friends Varieties of Plants: It s A Green World After All* The Many Uses of Plants: Plant Products Identify and describe the five major kingdoms of living things. Identify some benefits of microbes. Explain decomposition and identify the four major groups of decomposers. Define biodiversity and explain how it is related to climate. Explain how food chains and food webs model the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Identify dietary adaptations in animals. Identify the four basic needs of animals. Distinguish between the three groups (subclasses) of mammals. Compare and contrast the four major groups of plants. Describe how people use plants in their daily lives.. Which kingdom did you know the least about? What did you learn about it? 2. In your own words, write a definition for each kingdom.. Make a list of places you might find bacteria or fungi. 2. Write about three things you learned about microbes.. What would Earth be like if there were no decomposers? 2. Have you ever seen any of the four decomposers at work? Describe what was happening.. Make a list of the different species of animals you can find in your back yard or in a park. 2. What animals do you think you could find in Brazil that you couldn t find here?. Imagine that humans were on the bottom of the food chain. How would life be different? 2. What do you think would happen if a plant/animal in a food chain dies out and becomes extinct?. Pick your favorite animal. Describe its diet and say which category it belongs to. 2. Make a list of three animals for each diet category.. Which of the basic needs do you think an animal could go without for the longest period of time? Why? 2. Do you have a pet? How are its four basic needs taken care of?. Make a chart that compares the traits of a human, a kangaroo, and a duck-billed platypus. 2. Invent a new animal. Give it characteristics that would make it a marsupial.. What types of plants grow near your home? Explain how you know. 2. Write a story about the life of a tree that grows near your home.. Make a list of plant products that you have used today. 2. Write a story that tells where your pencil came from. 9
10 Activity Information Chart, Level 4 Human Body Systems: Welcome to Your Machine! Describe the major structures and functions in the human body.. Which body system do you think is the most important? Why? 2. Describe how you would look without a skeleton Inherited and Acquired Traits: Is it Nature or Nurture? Life Science Physical Science: Let s Get Energized! Matter:What Everything Is Made Of! Changes in Matter: Is It Physical or Chemical? Classes of Matter: It s the Makeup That Matters! Dr. Marie Curie:The Science of Radioactivity Forces and Motion: Push Me, Pull Me Simple Machines: Making Work Easier* Distinguish between acquired and inherited traits. Define and explain key life Identify topics of study in physical science. Define matter and identify some properties of matter. Distinguish between a physical change and a chemical change. Distinguish between the three classes of matter. Examine Marie Curie s contributions to science and society. Distinguish between balanced and unbalanced forces. Identify the six types of simple machines and how they are used. K-4 Std. C Life Science: Life cycles of organisms ; life cycles of organisms; organisms and environments K-4 Std. B Physical Science: properties of objects and materials; position and motion of objects; light, heat, electricity, and magnetism of objects and materials of objects and materials of objects and materials K-4 Std. G History & Nature of Science: History and nature of science K-4 Std. B Physical Science: Position and motion of objects K-4 Std. B Physical Science: Position and motion of objects. What are some acquired traits you have? How did you get them? 2. Can you change your inherited traits? Your acquired traits? Why or why not?. What part of life science interests you the most? 2. Write a story using five of the vocabulary words from this activity.. Write a story using the vocabulary words from this activity. 2. Look at the activities in this book. Which one do you want to do the most? Why?. Pretend you are describing the properties of your favorite food to someone who has never seen it. 2. Compare and contrast the properties of water as a solid and water as a liquid.. Make a chart that shows the differences between physical and chemical changes. 2. What are some physical and chemical changes that go on within your own body?. What is the Periodic Table of Elements? What does it do? 2. How are mixtures and compounds used every day in a kitchen?. What part of Marie Curie s life do you find most interesting? Why? 2. Why is Marie Curie such an important scientist?. List examples of three balanced forces and three unbalanced forces. 2. Explain why gravity is a force.. Write about the last time you used a simple machine to help you do something. 2. Which simple machine do you find most helpful? Why? 20
11 Activity Information Chart, Level 4 Heat and Temperature: Is There a Difference?* Real Science: Interpreting Data* Sound Energy: Good Vibrations!* Sound and Hearing: What s the Frequency?* Electric Current: Let It Flow!* Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits* Energy: Renewable and Nonrenewable Sources Magnetism: A Magnetic Mystery Electricity and Magnetism: All in the Family Physical Science Distinguish between heat and temperature. Analyze data from an experiment and draw conclusions. Define sound and explain how sound waves travel. Examine the loudness and frequency (pitch) of sounds. Identify how an electric current flows through a circuit. Distinguish between series and parallel electrical circuits. Identify the major sources of energy. Define magnetism and explore how a compass works. Explore the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Define and explain key physical Understanding about scientific inquiry K-4 Std. B Physical Science:Position and motion of objects K-4 Std. B Physical Science:Position and motion of objects K-4 Std. F Science in Personal & Social Perspectives:Types of resources of objects and materials; position and motion of objects; light, heat, electricity, and magnetism. In your own words, describe the difference between heat and temperature. 2. Explain why a pot of boiling water will start to cool off when you stop applying heat to it.. Make a list of items in your home that use insulators. 2. What material would you use to insulate Robert s clubhouse? Why?. Find out how some high-pitched sounds can make glass shatter and write about it. 2. Is it possible to feel sound? If so, describe how.. Explain why dogs can hear things that humans can t. 2. Write a story about the loudest thing you ever heard.. You are drying your hair with a hair dryer. Explain what would happen if the cord was suddenly cut. Why would this happen? 2. In your own words, explain the difference between an open circuit and a closed circuit.. Explain why it is better for homes to be wired with parallel circuits instead of series circuits. 2. Why do you think people still use series circuits?. What renewable energy sources could be used in your area? 2. Why is it so important that we conserve our fossil fuel supply?. Make a list of the kinds of people who would use compasses. 2. Make up a story about how a compass could help save you.. In your own words, explain how a doorbell works. 2. How are electromagnets helpful in your daily life?. What was the most interesting activity in this book? 2. Write a summary of what you learned in this book. 2
12 Activity Information Chart, Level What activity in this book are you most looking forward to doing? 2. Write a sentence for each of the words in the Answer Box.. Write a conclusion to Matt s experiment. 2. What are the necessary elements to an experiment? Structure of the earth system; Earth s history; Earth in the solar system Identify topics of study in earth science. Earth Science: Discovering the Secrets 5-8 Std. A Science as Inquiry: Real Science: Science is an Everyday Experience! Rachel Carson: Crusader for the Environment Ocean Tides:Water in Motion. How are pesticides harmful? 2. What fact about Rachel Carson do you find most interesting?. Write an imaginary tide table showing when the ocean is at high tide and low tide. 2. How do you think tides affect people living on the ocean shore?. Draw a picture of what you think the Hawaiian Islands look like under the water. 2. Imagine you are an oceanographer about to go on an expedition. What tools would you bring and why?. What happens when large amounts of precipitation come down and the lakes and rivers can t hold all of it? 2. Write a story about how a puddle formed and then disappeared.. Is there a polluted body of water near you? What do you think caused it to become polluted? 2. What tests would you do to find out if a body of water near you is polluted? Why that test?. Why is the ozone layer so important? What would happen if it didn t exist? 2. Why can humans live only in the troposphere?. Which weather instrument do you think is used the most? How is it used? 2. Write a weather forecast for tomorrow with pretend readings from all the weather instruments.. What could be the most damaging form of precipitation? Why? 2. What weather conditions are needed for each type of precipitation to occur? 5-8 Std. G History and Nature of Structure of the earth system Discuss how science can be used to solve everyday problems. Discuss the life of Rachel Carson and her contributions to science. Examine the cause of ocean tides. 5-8 Std. G History and Nature of Oceanography: Exploring the Deep Blue Sea Structure of the earth system Describe the topography of the ocean s bottom, and explain common oceanographic instruments. Identify the stages of the water cycle. The Water Cycle: Water on the Move 5-8 Std. A Science as Inquiry: Examine how water quality tests can check for signs of pollution. Tools of Science: Measuring Water Quality* Structure of the earth system; Earth s history Structure of the earth system Identify the layers of the atmosphere. The Atmosphere: Earth s Protective Blanket Weather: Measuring the Atmosphere* 4-5 Identify how weather instruments are used to understand weather and climate. Explore the relationship between the states of water and types of precipitation. Structure of the earth system Rain, Snow, Hail, and Sleet: A Matter of State* 8-9
13 Activity Information Chart, Level 5 Weather Forecasting: Blue Skies Ahead? The Solar System: Space is the Place!* Planets: Homes Away from Home?* Phases of the Moon: First You See It,Then You Don t* Characteristics of the Sun: Our Star! Galaxies:The Milky Way and Beyond Earth Science Naming Species: Dinosaur Dilemma! Real Science: Analyzing Graphs Charles Drew: Saving Blood, Saving Lives Ecosystems: Connections and Balance Identify the symbols used in a weather observation report. Identify and describe the objects in our solar system. Identify and describe characteristics of the nine planets in our solar system. Discuss how the Moon s phases depend on the Moon s position around Earth. Identify and describe important features of the Sun. Distinguish between spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. Define and explain key earth Use Greek and Latin root words to find the English meaning of dinosaur names. Analyze information from a pie chart, a bar graph, and a table. Recognize Charles Drew s contributions to science and society. Discuss ecosystems, biotic and abiotic factors, and their interrelationship and balance. 5-8 Std. A Science as Inquiry: Earth in the solar system Earth in the solar system; Std. G History and Nature of Science: Science as a human endeavor Earth in the solar system Earth in the solar system Earth in the solar system Structure of the earth system; Earth s history; Earth in the solar system 5-8 Std. A Science as Inquiry: ; Std. C Life Science: Diversity and adaptations of organisms 5-8 Std. A Science as Inquiry: 5-8 Std. G History and Nature of Science: History of science 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Populations and ecosystems. Write about what a weather reporter might say about today s weather. 2. What would your ideal weather observation report look like?. Make a chart that compares comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. 2. What is the difference between planets and moons?. List the planets in order from largest to smallest. 2. Which planet has the longest day? How did you figure that out?. In what phase is the Moon the brightest? Why? 2. Explain why you can t see the Moon when it is in the New Moon phase.. Draw a picture of the Sun and label the parts. 2. In your own words, write a definition of each layer of the Sun.. Describe the differences in the three types of galaxies. 2. Why is the Hubble Telescope so important to astronomers?. What is your favorite part of earth science? Why? 2. Write a paragraph telling what you learned from the activities in this book.. Use Greek and Latin root words to make up names of five new dinosaurs. 2. Flip through this book. Which activity do you want to do first? Why?. Make a pie chart that compares the number of boys and the number of girls in your class. 2. Make a list of places you see charts and graphs.. Tell a story about a day in the life of a white blood cell. 2. Why is storing blood so important?. Pretend your classroom is an ecosystem. What would happen to your ecosystem if your teacher was removed? 2. Make a list of all the biotic and abiotic factors that affect your back yard or a park near your home. 23
14 Activity Information Chart, Level What biome do you live in? Explain why you think that. 2. Write a postcard from your biome, like Julia did.. Make a list of the different ways humans get nitrogen. 2. In your own words, explain the nitrogen cycle and why it is important.. Look out the window; list all of the plants you see and whether they are vascular or nonvascular. 2. Make your own fill-in-the-blank questions using vocabulary words from this activity.. What would happen to a tree if its roots became diseased? 2. How do plant roots help the soil?. What happens when your body temperature changes? Is it a good or bad thing? 2. Make a list of animals that are ectotherms and a list of animals that are endotherms.. Write a story from an insect s point of view as it passes through a complete metamorphosis. 2. Describe what an insect looks like in the larva stage.. What are some things that people can do to protect endangered species? 2. Make a list of animals that have become extinct.. Write a meal plan you should follow to have a balanced diet. 2. Which is your favorite food group? Why?. Tell a story about the trip your breakfast took through your digestive system. 2. What parts of the digestive system had you never heard of before? What do they do?. Make a chart that compares the characteristics of veins and arteries. 2. Explain how the circulatory system works with the respiratory system.. How are your leg muscles similar to the muscles in your arms? 2. What would the human body be like if it didn t have joints? 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Populations and ecosystems Compare characteristics of several biomes. Biomes: Biome, Sweet Biome 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Populations and ecosystems Nitrogen Cycle: Nothing Is Wasted, Not Even Waste. 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems; diversity and adaptations of organisms Describe how nitrogen circulates through the environment during the nitrogen cycle. Distinguish between vascular and nonvascular plants. Plant Classification: Vascular and Nonvascular Plants* 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems Identify the functions of plant roots. Plant Roots: Let s Get to the Root of the Matter!* Animals:Warm- Blooded or Cold Blooded? Std. C Life Science: Diversity and adaptations of organisms Distinguish between warmblooded and cold-blooded animals. 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Reproduction and heredity Distinguish between the three types of insect life cycles. Insect Life Cycles: What s the Buzz? Std. C Life Science: Diversity and adaptations of organisms Protecting Endangered Species: Saving the Sea Turtle The Food Pyramid: Healthful Choices* Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives:Personal health Define extinction and explain the purpose of the Endangered Species Act. Explain how following the food pyramid leads to a healthy diet. 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems Explain the function of the digestive system and its parts. Digestive System: Break It All Down!* 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems Explain the function of the heart and circulatory system. Circulatory System: Your Body s Superhighway* 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems; Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives: Personal health Explain how bones and muscles work together to produce body movement. Muscles and Bones: Moving the Body Machine
15 Activity Information Chart, Level 5 Tools of Science: X-Rays* Life Science: Discover the Elements: It s Elementary, My Dear Watson Physical and Chemical Properties: Identify Yourself! Atoms and Molecules: It Matters to Know Them! Hideki Yukawa: Atoms and the Strong Force Tools of Science: A Microscope for Seeing Atoms Elements and Compounds:Types of Matter Acids and Bases: Common Chemicals* Mixtures: Separating Crude Oil Identify what x-rays are and how they are used in medicine. Define and explain key life Identify the practical uses of common elements. Identify between physical and chemical properties of matter. Define atoms and molecules; describe the basic structure of the atom. Recognize Hideki Yukawa s contributions to science. Explain how a scanning tunneling microscope is used to see atoms. Distinguish between elements and compounds; identify the use of chemical symbols and formulas. Distinguish between acids and bases; explain the ph scale and how it relates to acids and bases. Explain how the ingredients of crude oil can be separated by their physical properties. 5-8 Std. E Science and Technology: Understanding about science and technology 5-8 Std. C Life Science: Structure and function in living systems; reproduction and heredity; regulation and behavior; populations and ecosystems; diversity and adaptations of organisms 5-8 Std. F Science in Personal and Social Perspectives:Populations, resources, and environments and changes of properties in matter and changes of properties in matter 5-8 Std. G History & Nature of 5-8 Std. E Science and Technology: Understanding about science and technology and changes of properties in matter and changes of properties in matter and changes of properties in matter. What are some reasons why people need to get x-rayed? 2. What is the difference between an x-ray photograph and a CT scan?. What are the major systems of the human body? What are their functions? 2. What aspect of life science interests you the most? Why?. Flip through this activity book. What activity do you most want to do? Why? 2. Which elements have you heard of before? How do you know them?. Why would it be helpful to know the chemical properties of an object? 2. Describe another chemical property of matter.. Describe in your own words the difference between atoms and molecules. 2. Describe the makeup of a water molecule.. Write your own description of one of the scientists from this activity. 2. Which discovery do you think was most important? Why?. In your own words, explain how a scanning tunneling microscope is like reading Braille. 2. Write a definition of what an STM is and how it works.. Use a periodic table to find the chemical symbols of your three favorite elements. 2. Describe the difference between an element and a compound.. What do you think would happen if you mixed an acid and a base? 2. Define a neutral substance. Find an example of one.. Name a mixture from everyday life. Tell why it is a mixture. 2. Write a definition for each of the vocabulary words in this activity. 25
16 Activity Information Chart, Level Write about an element you know something about. How is it used? 2. Write a story about how you think the first periodic table was written.. Write about a day in the life of a metallurgist. 2. Write about the last time you saw a metal used. Describe how it was being used.. Make a list of places where you can find each kind of biological compound. 2. Explain why carbohydrates and proteins are important in your diet.. Imagine that you took a trip in the rocket. Tell a story about it. 2. Name some other ways line graphs are used.. Name three things in your classroom that have potential energy. Explain why. 2. In your own words, explain the difference between kinetic and potential energy.. Explain how friction can be good and how it can be bad. Give specific examples. 2. Explain how magnetism and gravity are alike.. Make a diagram showing how electricity is produced. 2. Research how much electricity costs to use. What can you do at home to reduce your use of electricity and save money?. Write a story about what your life would be like if you had to give up the use of electricity. 2. Which fossil fuels are used in your home? How are they used?. What part of physical science do you find most interesting? Why? 2. Is there a part of physical science that confuses you? What confuses you? and changes of properties in matter Discuss the organization of the periodic table. The Periodic Table: Repeating Patterns and changes of properties in matter Identify characteristics of metals. Metals:A Class of Their Own* 8-9 and changes of properties in matter Discuss the function of biological compounds in living things. Carbon Compounds: The Secret of Life* Std. A Science as Inquiry: Interpret data from charts and line graphs. Real Science: Interpreting Graphs and Charts Potential and Kinetic Energy: Follow the Bouncing Ball 5-8 Std. B Physical Science:Transfer of energy Distinguish between potential and kinetic energy. 5-8 Std. B Physical Science: Motion and forces Identify and explain the forces of friction, gravity, and magnetism. Explain how electricity is produced in a typical power plant. Forces in Everyday Life: Can You Live Without Them?* How Electricity is Produced:Taking Charge* 5-8 Std. B Physical Science:Transfer of energy 5-8 Std. B Physical Science:Transfer of energy Identify the three main fossil fuels and their uses. Fossil Fuels: Everyday Uses 30-3 and changes of properties in matter; motions and forces; transfer of energy Define and explain key physical Physical Science
Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills
 Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills I Learn with My Senses The Mystery Seeds Living Things Are Everywhere! The Life of a Butterfly Our Earth What Is Weather? Tell Me All About It Watch What
Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills I Learn with My Senses The Mystery Seeds Living Things Are Everywhere! The Life of a Butterfly Our Earth What Is Weather? Tell Me All About It Watch What
SRS Achievement Statements. Science
 SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1
 2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and
2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and
Barlows Primary School Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and
 Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 Curriculum. The content for Year 1 is detailed below: During year 1, pupils should be taught to use the following practical
Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 Curriculum. The content for Year 1 is detailed below: During year 1, pupils should be taught to use the following practical
Science curriculum: Reception. Working Scientifically - Skills. Plants and Animals
 Science curriculum: Working Scientifically - Skills Reception Plants and Animals Identify and name common plants (green plants, wild plants and trees, deciduous and evergreen) Label parts of a plant Identify
Science curriculum: Working Scientifically - Skills Reception Plants and Animals Identify and name common plants (green plants, wild plants and trees, deciduous and evergreen) Label parts of a plant Identify
Information for Parents/Carers SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST
 SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM
 FIRST NINE WEEKS CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM GRADE 2 Revised 2009 Identify words and construct meanings from text, illustrations, graphics, and charts. Acknowledge that people use scientific
FIRST NINE WEEKS CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM GRADE 2 Revised 2009 Identify words and construct meanings from text, illustrations, graphics, and charts. Acknowledge that people use scientific
Science skills progression KS2
 The principal focus of science teaching in lower key stage 2 is to enable pupils to broaden their scientific view of the world around them. They should do this through exploring, talking about, testing
The principal focus of science teaching in lower key stage 2 is to enable pupils to broaden their scientific view of the world around them. They should do this through exploring, talking about, testing
Class 3. Year A. Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Science Year 3 Magnets and friction
 Class 3 Year A Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Tomb Raiders (Egyptians) Fantastic Fenland Year 3 Magnets and friction Year 4 Sound Year 3 Plants compare
Class 3 Year A Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Tomb Raiders (Egyptians) Fantastic Fenland Year 3 Magnets and friction Year 4 Sound Year 3 Plants compare
Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler
 Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler Scientific enquiry Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Pupils describe or respond appropriately to simple features of objects, living things and events
Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler Scientific enquiry Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Pupils describe or respond appropriately to simple features of objects, living things and events
Science Skills Progression. Eden Park Primary School Academy
 Science Skills Progression Eden Park Primary School Academy In order to ensure broad and balanced coverage, we follow these principles: As much as is appropriate, link science in to Learning Experiences.
Science Skills Progression Eden Park Primary School Academy In order to ensure broad and balanced coverage, we follow these principles: As much as is appropriate, link science in to Learning Experiences.
Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers
 Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers Please note: Pennsylvania & Next Generation Science Standards as well as Instructional Resources are found on the SDP Curriculum Engine Prepared by:
Curriculum Guide for Kindergarten SDP Science Teachers Please note: Pennsylvania & Next Generation Science Standards as well as Instructional Resources are found on the SDP Curriculum Engine Prepared by:
Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP
 Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP Program description: Discover whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students will use
Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP Program description: Discover whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students will use
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2
 IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT
 Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
First Grade Science Report Card Rubric Fourth Nine Weeks
 Matter How Energy Changes Matter I can classify solid objects by properties. accurately sort the sample 1.5A objects by any of the following properties: shape, color, texture, relative size, or relative
Matter How Energy Changes Matter I can classify solid objects by properties. accurately sort the sample 1.5A objects by any of the following properties: shape, color, texture, relative size, or relative
Our Sense Organs Ears
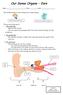 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Grade: 5 Science Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2
 Grade: 5 Science Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 55501 Time Allotted : 40 Mins
Grade: 5 Science Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 55501 Time Allotted : 40 Mins
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0982216887* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0982216887* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text.
 Learning Objective Name We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text. CFU What are we going to do? What does describe mean? Describe means. Activate Prior Knowledge Bethany did not go to school
Learning Objective Name We will describe 1 the cause-and-effect structure of text. CFU What are we going to do? What does describe mean? Describe means. Activate Prior Knowledge Bethany did not go to school
Tumwater School District FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials
 FOSS Investigation All Investigations All Investigations Standard FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials EALR 2 INQA Question Scientific investigations are designed to gain knowledge about the natural
FOSS Investigation All Investigations All Investigations Standard FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials EALR 2 INQA Question Scientific investigations are designed to gain knowledge about the natural
Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11. High School Biology 1
 Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11 High School Biology 1 Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11 High School Biology 1 Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
Haslingden High School Science Faculty HOMEWORK - Revision Questions Year 8 Block C
 Haslingden High School Science Faculty HOMEWORK - Revision Questions Year 8 Block C Name: Form: Teacher: Given: Hand in: Comment: Target: Haslingden High School 1 Year 8 Block C Homework Booklet Revision
Haslingden High School Science Faculty HOMEWORK - Revision Questions Year 8 Block C Name: Form: Teacher: Given: Hand in: Comment: Target: Haslingden High School 1 Year 8 Block C Homework Booklet Revision
Ecosystems and Microbiology Unit Study Guide
 Ecosystems and Microbiology Unit Study Guide 4.L.1 Understand the effects of environmental changes, adaptations and behaviors that enable animals (including humans) to survive in changing habitats. 4.L.1.1
Ecosystems and Microbiology Unit Study Guide 4.L.1 Understand the effects of environmental changes, adaptations and behaviors that enable animals (including humans) to survive in changing habitats. 4.L.1.1
SCIENCE POLICY. Date: March Signed: Review: March 2019
 SCIENCE POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science Policy T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science
SCIENCE POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science Policy T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
A Correlation of. Pearson Interactive Science Leveled Readers Grade 2
 A Correlation of Pearson Leveled Readers To Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas, 2011 to Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas,, 2011 This document was created as a service to Texas teachers to show the
A Correlation of Pearson Leveled Readers To Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas, 2011 to Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas,, 2011 This document was created as a service to Texas teachers to show the
Science. Area of Experience: Science. At Junior Certificate level the student can:
 Science Area of Experience: Science At Junior Certificate level the student can: 1 The Non-Living Environment Describe the characteristics and structures of different materials and explain how they change
Science Area of Experience: Science At Junior Certificate level the student can: 1 The Non-Living Environment Describe the characteristics and structures of different materials and explain how they change
Family Trees for all grades. Learning Objectives. Materials, Resources, and Preparation
 page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
Natural Sciences and Technology
 PLANNING & TRACKING Shuters Also available for download from www.shuters.com TOP CLASS Natural Sciences and Technology Grade 6 PHOTOCOPIABLE OS1001285 CUSTOMER SERVICES THIS SERIES IS ALSO AVAILABLE AS
PLANNING & TRACKING Shuters Also available for download from www.shuters.com TOP CLASS Natural Sciences and Technology Grade 6 PHOTOCOPIABLE OS1001285 CUSTOMER SERVICES THIS SERIES IS ALSO AVAILABLE AS
How Science Works. Grade 3. Module 2. Class Question: What variables affect ball motion? Group Color: Scientist (Your Name): Teacher s Name:
 Group Color: How Science Works Grade 3 Module 2 Class Question: What variables affect ball motion? Scientist (Your Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Volunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study of the
Group Color: How Science Works Grade 3 Module 2 Class Question: What variables affect ball motion? Scientist (Your Name): Teacher s Name: SciTrek Volunteer s Name: VOCABULARY Science: The study of the
Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science.
 End of Year Targets for Science 2018 Dear Parents and Carers, Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science. End of Year Targets for
End of Year Targets for Science 2018 Dear Parents and Carers, Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science. End of Year Targets for
Full of Mastery Level Items to be used as practice for the STAAR
 Full of Mastery Level Items to be used as practice for the STAAR Grade 3 Science CVP Answer Key Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 12) 7 A Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 13) 7 C Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 14) Lesson
Full of Mastery Level Items to be used as practice for the STAAR Grade 3 Science CVP Answer Key Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 12) 7 A Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 13) 7 C Lesson 1: Ecosystems (page 14) Lesson
... (1) ... (1) Drug manufacturers are spending less on research into new antibiotics.
 1 Different antibiotics destroy bacteria in different ways. Some antibiotics disrupt the bacterial cell membrane. Some antibiotics disrupt the bacterial cell wall. (a) Antibiotics that disrupt the bacterial
1 Different antibiotics destroy bacteria in different ways. Some antibiotics disrupt the bacterial cell membrane. Some antibiotics disrupt the bacterial cell wall. (a) Antibiotics that disrupt the bacterial
Objective 1.e. Justify whether an argument defending a conclusion is logical. Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide
 Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide Objective 1: Inquiry 1. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? 2. Why is skepticism an important part of science? 3. What is an inference?
Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide Objective 1: Inquiry 1. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? 2. Why is skepticism an important part of science? 3. What is an inference?
13+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION
 13+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION SAMPLE PAPER SCIENCE Read these instructions carefully You have one hour in which to complete this examination. Attempt all questions. You may use a calculator if you wish. Write
13+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION SAMPLE PAPER SCIENCE Read these instructions carefully You have one hour in which to complete this examination. Attempt all questions. You may use a calculator if you wish. Write
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
Autism, my sibling, and me
 ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
Matter and Energy Transfer
 Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants back.
Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants back.
This nonfiction book
 This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
PENTOUCH TRANSLATION & EDUCATION Utility Vehicles States of Matter
 States of Matter A. For many years, people did not know what matter was made of. The ancient Greeks tried to figure out what would happen if a rock were broken into smaller and smaller pieces. B. They
States of Matter A. For many years, people did not know what matter was made of. The ancient Greeks tried to figure out what would happen if a rock were broken into smaller and smaller pieces. B. They
Twenty First Century Science. PILOT Examination Questions. GCSE Science Jan 2005 Keeping healthy, Radioactive materials, Life on Earth (Higher Tier)
 Twenty First Century Science PILOT Examination Questions GCSE Science Jan 2005 Keeping healthy, Radioactive materials, Life on Earth (Higher Tier) Please note: These questions are not Sample Assessment
Twenty First Century Science PILOT Examination Questions GCSE Science Jan 2005 Keeping healthy, Radioactive materials, Life on Earth (Higher Tier) Please note: These questions are not Sample Assessment
Name. 1 st Expedition. Preview Questions
 Name 1 st Expedition 1. What percentage of the earth is covered by oceans? 2. Do you think more life exists in the oceans or on land? 3. What are some of the ways in which the ocean affects life on land?
Name 1 st Expedition 1. What percentage of the earth is covered by oceans? 2. Do you think more life exists in the oceans or on land? 3. What are some of the ways in which the ocean affects life on land?
Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1]
![Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1] Overview. Meeting Length 90 minutes. Senses [Meeting 1]](/thumbs/89/98894094.jpg) Overview Girls have fun exploring their five senses and how they use them in everyday life. They also learn about what life would be like without one of their senses. Note to Volunteers A few agenda activities
Overview Girls have fun exploring their five senses and how they use them in everyday life. They also learn about what life would be like without one of their senses. Note to Volunteers A few agenda activities
KIANGSU-CHEKIANG COLLEGE (SHATIN) Easter Holidays Assignment Form One Integrated Science. Total Marks: 100. Instructions:
 KIANGSU-CHEKIANG COLLEGE (SHATIN) Easter Holidays Assignment Form One Integrated Science Total Marks: 100 Instructions: 1. This paper consists of SIX sections. Attempt ALL questions. 2. Put all your answers
KIANGSU-CHEKIANG COLLEGE (SHATIN) Easter Holidays Assignment Form One Integrated Science Total Marks: 100 Instructions: 1. This paper consists of SIX sections. Attempt ALL questions. 2. Put all your answers
Correlation between Project Learning Tree Activities and the NAAEE Excellence in EE Guidelines for Learning: Grades (5-8)
 Correlation between Project Learning Tree Activities and the NAAEE Excellence in EE Guidelines for Learning: Grades (5-8) Correlation between Project Learning Tree Activities and the NAAEE Excellence in
Correlation between Project Learning Tree Activities and the NAAEE Excellence in EE Guidelines for Learning: Grades (5-8) Correlation between Project Learning Tree Activities and the NAAEE Excellence in
Organism Project. Asian Elephant. Abby-Rose Mannes
 Organism Project Asian Elephant Abby-Rose Mannes Asian Elephant Introduction I will be doing my Organism research project on the Asian Elephant, the Asian Elephants scientific name is Elephas Maximus.
Organism Project Asian Elephant Abby-Rose Mannes Asian Elephant Introduction I will be doing my Organism research project on the Asian Elephant, the Asian Elephants scientific name is Elephas Maximus.
Introduction. Help your students learn how to learn!
 Introduction Help your students learn how to learn! Lay a strong foundation in listening skills, the ability to follow directions, and in the ability to remember what one sees and hears important skills
Introduction Help your students learn how to learn! Lay a strong foundation in listening skills, the ability to follow directions, and in the ability to remember what one sees and hears important skills
A Correlation of. Pearson Interactive Science Content Leveled Readers Grade 1
 A Correlation of Pearson Content Leveled Readers To Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas, 2011 to,, 2011 This document was created as a service to Texas teachers to show the Content Leveled Readers that
A Correlation of Pearson Content Leveled Readers To Scott Foresman Reading Street Texas, 2011 to,, 2011 This document was created as a service to Texas teachers to show the Content Leveled Readers that
Ecology B/C Test. Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida
 Ecology B/C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Answers go on the team answer sheet. DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST SET. Principles of ecology 1. List 3 biotic and 3
Ecology B/C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Answers go on the team answer sheet. DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST SET. Principles of ecology 1. List 3 biotic and 3
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 1 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 1 Assessment 1. A student wants to find out if temperature affects the behavior of goldfish. He has four bowls and 20 goldfish. Which of the following
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit # 1 Assessment 1. A student wants to find out if temperature affects the behavior of goldfish. He has four bowls and 20 goldfish. Which of the following
SCIENCE GRADE 8 Navrachana International School, Vadodara ( ) GRADE 8 (SCIENCE) ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVE (based on Assessment Criteria)
 ATL / 12 TOPIC- Plant Nutrition AOI- Environments CONCEPTS 1. Structure of leaves and their adaptations for photosynthesis. 2. How plants make and use glucose they produce in photosynthesis. 3. Factors
ATL / 12 TOPIC- Plant Nutrition AOI- Environments CONCEPTS 1. Structure of leaves and their adaptations for photosynthesis. 2. How plants make and use glucose they produce in photosynthesis. 3. Factors
Name Teacher Hour
 http://www.citizenofthemonth.com/wp-content/images/frink.gif Name Teacher Hour www.mononagrove.org/faculty/ips/index.cfm Scientific Models What is a scientific model? The scientific process making observations,
http://www.citizenofthemonth.com/wp-content/images/frink.gif Name Teacher Hour www.mononagrove.org/faculty/ips/index.cfm Scientific Models What is a scientific model? The scientific process making observations,
A Kazoo For You. Science Activity.
 A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
Swadesh wordlist, categorised by semantic field.
 Swadesh wordlist, categorised by semantic field. 1. big adjective 2. long adjective 3. wide adjective 4. thick adjective 5. heavy adjective 6. small adjective 7. short adjective 8. narrow adjective 9.
Swadesh wordlist, categorised by semantic field. 1. big adjective 2. long adjective 3. wide adjective 4. thick adjective 5. heavy adjective 6. small adjective 7. short adjective 8. narrow adjective 9.
1a Materials come in different forms (states) including solids,
 Physical Sciences 1a Materials come in different forms (states) including solids, liquids, and gases. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know solids, liquids, and gases have different
Physical Sciences 1a Materials come in different forms (states) including solids, liquids, and gases. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know solids, liquids, and gases have different
Sea Turtle. Discovery. Teacher Resource Guide Grades K-2. Contents: Educational Objectives: Hello! Field Trip Information. Orlando.
 Hello! Sea Turtle Teacher Resource Guide Grades K-2 In this Resource Guide you will find an assortment of activities that correspond with Sea Turtle, our FREE education workshop, appropriate for Grades
Hello! Sea Turtle Teacher Resource Guide Grades K-2 In this Resource Guide you will find an assortment of activities that correspond with Sea Turtle, our FREE education workshop, appropriate for Grades
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
1. The nutrition information for four different brands of beans is listed in the table below.
 1. The nutrition information for four different brands of beans is listed in the table below. Which brand of beans would be best for a person on a low-sodium, high-fiber diet to eat? A) brand 1 B) brand
1. The nutrition information for four different brands of beans is listed in the table below. Which brand of beans would be best for a person on a low-sodium, high-fiber diet to eat? A) brand 1 B) brand
Grades K-2. Turtle Discovery Teacher Resource Guide. Contents: Welcome to SEA LIFE Orlando Aquarium! Educational Objectives:
 1 Turtle Discovery Teacher Resource Guide Grades K-2 Welcome to SEA LIFE Orlando Aquarium! Arrival and Entry Please allow ample time for parking and obtaining tickets. To book a FREE on-site educational
1 Turtle Discovery Teacher Resource Guide Grades K-2 Welcome to SEA LIFE Orlando Aquarium! Arrival and Entry Please allow ample time for parking and obtaining tickets. To book a FREE on-site educational
Mrs. Smith s Study Guide for the Alabama Science Assessment
 Mrs. Smith s Study Guide for the Alabama Science Assessment Plant Cell 5 3 2 6 7 4 1 Page 1 Mitochondria Cell Wall Cytoplasm Vacuole Nucleus Chloroplast Cell Membrane Mitochondria Cell Membrane Nucleus
Mrs. Smith s Study Guide for the Alabama Science Assessment Plant Cell 5 3 2 6 7 4 1 Page 1 Mitochondria Cell Wall Cytoplasm Vacuole Nucleus Chloroplast Cell Membrane Mitochondria Cell Membrane Nucleus
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY
 Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Grade 3 Science, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1. Force and Motion. Overview
 Grade 3 Science, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Force and Motion Overview Number of instructional days: 7 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Use prior knowledge and investigations in order to predict whether
Grade 3 Science, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Force and Motion Overview Number of instructional days: 7 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Use prior knowledge and investigations in order to predict whether
Name: Multiple Choice. Mark your answers on this test. Then carefully transfer your answers to the scan sheet provided
 Science 7 Name: Section: Mid-Term Review WS Date: Multiple Choice. Mark your answers on this test. Then carefully transfer your answers to the scan sheet provided 1. The diagram below represents four organisms.
Science 7 Name: Section: Mid-Term Review WS Date: Multiple Choice. Mark your answers on this test. Then carefully transfer your answers to the scan sheet provided 1. The diagram below represents four organisms.
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
Rising Scholars Academy 8 th Grade English I Summer Reading Project The Alchemist By Paulo Coelho
 Rising Scholars Academy 8 th Grade English I Summer Reading Project The Alchemist By Paulo Coelho Welcome to 8th grade English I! Summer is a time where you can relax and have fun, but did you know you
Rising Scholars Academy 8 th Grade English I Summer Reading Project The Alchemist By Paulo Coelho Welcome to 8th grade English I! Summer is a time where you can relax and have fun, but did you know you
Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie. Overview of the Book
 Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie Overview of the Book Five friends go on a quest to find out where food comes from and to gather
Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie Overview of the Book Five friends go on a quest to find out where food comes from and to gather
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8369008797* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/05 Paper 5 October/November
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8369008797* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/05 Paper 5 October/November
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System
 Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Standards Alignment...5 Safe Science...7 Scienti c Inquiry...9 Assembling Rubber Band Books...13
 Standards Alignment... Safe Science...7 Scienti c Inquiry...9 Assembling Rubber Band Books...13 Organization and Development of Living Organisms Parts...1 Brain Power... 2 Heart Smart... 3 A Look at Lungs...
Standards Alignment... Safe Science...7 Scienti c Inquiry...9 Assembling Rubber Band Books...13 Organization and Development of Living Organisms Parts...1 Brain Power... 2 Heart Smart... 3 A Look at Lungs...
Introduction Evolution of Metabolism
 2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan
 Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
FIFTH GRADE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
 FIFTH GRADE BUILT ENVIRONMENT 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES APPLIED SCIENCE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing
FIFTH GRADE BUILT ENVIRONMENT 3 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES APPLIED SCIENCE OVERVIEW OF FIFTH GRADE SCIENCE AND MATH WEEK 1. PRE: Interpreting data from a graph. LAB: Estimating data and comparing
Introduction to Oceanography Unit II: The Basics of Ocean Life (3 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Introduction to Oceanography Unit II (Topic 1A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Introduction to Oceanography Unit II: The Basics of Ocean Life (3 pts) Plankton Plankton are the
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Introduction to Oceanography Unit II (Topic 1A-2) page 1 Name: Section: Introduction to Oceanography Unit II: The Basics of Ocean Life (3 pts) Plankton Plankton are the
Recycle me! 4.7. Decomposers
 .7 Recycle me! Tyrannosaurus rex stalked the Earth over 6 million years ago. We have found the bones, but what happened to the atoms that made up its flesh? What will happen to the atoms in your body when
.7 Recycle me! Tyrannosaurus rex stalked the Earth over 6 million years ago. We have found the bones, but what happened to the atoms that made up its flesh? What will happen to the atoms in your body when
Grade Level Expectations for the Sunshine State Standards
 for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The kindergarten student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects have many different observable properties:
for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The kindergarten student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects have many different observable properties:
S1 to S3 - CfE SCIENCE. Rationale
 S1 to S3 - CfE SCIENCE Rationale The S1-S3 Science course has been designed to nurture and stimulate the curiosity and questioning of our pupils. The S1-S3 topics cover a broad range of outcomes in a thematic
S1 to S3 - CfE SCIENCE Rationale The S1-S3 Science course has been designed to nurture and stimulate the curiosity and questioning of our pupils. The S1-S3 topics cover a broad range of outcomes in a thematic
the Bone Teacher Pages Classroom Activities Grade Level 4-6
 Grade Level 4-6 Building Big Bones Students will work in pairs to investigate how the light, spongy layer around the bone s marrow makes the bones lighter for easier movement, by comparing cardboard tubes
Grade Level 4-6 Building Big Bones Students will work in pairs to investigate how the light, spongy layer around the bone s marrow makes the bones lighter for easier movement, by comparing cardboard tubes
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
Season 1. No Smoking. Study Guide
 Season 1 No Smoking Study Guide STUDY GUIDE CONTENTS No Smoking The Story Pages 1-10 Exercises Pages 11-25 Sasha loves to swim in the ocean in winter! He also likes to smoke. Helpful Information Pages
Season 1 No Smoking Study Guide STUDY GUIDE CONTENTS No Smoking The Story Pages 1-10 Exercises Pages 11-25 Sasha loves to swim in the ocean in winter! He also likes to smoke. Helpful Information Pages
Season 1. No Smoking. Study Guide
 Season 1 No Smoking Study Guide STUDY GUIDE CONTENTS The Story Pages 1-10 Exercises Pages 11-25 Helpful Information Pages 26-28 Dictionary Pages 29-30 Dear Sasha Page 31 Answers Page 32 Watch Read Learn
Season 1 No Smoking Study Guide STUDY GUIDE CONTENTS The Story Pages 1-10 Exercises Pages 11-25 Helpful Information Pages 26-28 Dictionary Pages 29-30 Dear Sasha Page 31 Answers Page 32 Watch Read Learn
Grade Five Science Winter Break Packet December 2008 January 2009 Teacher Booklet
 Grade Five Science Winter Break Packet December 2008 January 2009 Teacher Booklet Winter Break Packet Teacher Booklet Grade 5 i Table of Contents Page Note to Teacher... 1 Answers for Student Booklet...2-5
Grade Five Science Winter Break Packet December 2008 January 2009 Teacher Booklet Winter Break Packet Teacher Booklet Grade 5 i Table of Contents Page Note to Teacher... 1 Answers for Student Booklet...2-5
Science at West Chiltington Community School
 Empowerment Resilience Relationships First and foremost, children at our school should be immersed in a range of experiences which awaken their natural curiosity in the world. Alongside the structured
Empowerment Resilience Relationships First and foremost, children at our school should be immersed in a range of experiences which awaken their natural curiosity in the world. Alongside the structured
Nuclear Radiation Today
 CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution
 Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution I. 1. (a) Hydrogen peroxide has the molecular formula H 2 O 2. This means that there are two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms in one
Maharashtra State Board Class VII Science Board Paper 1 Solution I. 1. (a) Hydrogen peroxide has the molecular formula H 2 O 2. This means that there are two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms in one
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP!
 Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
I am sad. It is big. I set it on the pot. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. Mom will help. It is lost. It is red. My Cap. Name:
 My Cap It is red. It is big. I set it on the pot. It is lost. I am sad. Mom will help. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. 2 5 8 14 17 20 23 28 32 Day 1: What color is my cap? Day 2: What happened to my
My Cap It is red. It is big. I set it on the pot. It is lost. I am sad. Mom will help. Mom led me to it. Mom gets a hug. 2 5 8 14 17 20 23 28 32 Day 1: What color is my cap? Day 2: What happened to my
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A. Fall, 2012
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2012 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon- transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2012 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon- transforming
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Which two pieces of equipment should Josh use to carry out this step?
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/03/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 7 Science Inquiry & Application 1. In Josh's experiment, one step of the
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/03/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 7 Science Inquiry & Application 1. In Josh's experiment, one step of the
Wangari Maathai. Stop and think: What words would you use to describe Wangari? What words would you use to describe the women?
 Wangari Maathai l Reading Comprehension l Activity Read the paragraphs. Stop and think as you read. Stop and Think Good readers are active readers. Good readers stop and think about what they are reading.
Wangari Maathai l Reading Comprehension l Activity Read the paragraphs. Stop and think as you read. Stop and Think Good readers are active readers. Good readers stop and think about what they are reading.
5th Grade Ecosystem Dynamics
 Slide 1 / 89 Slide 2 / 89 5th Grade Ecosystem Dynamics 2015-11-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 89 Table of Contents: Ecosystem Dynamics Click on the topic to go to that section Food Webs Decomposers Cycles
Slide 1 / 89 Slide 2 / 89 5th Grade Ecosystem Dynamics 2015-11-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 89 Table of Contents: Ecosystem Dynamics Click on the topic to go to that section Food Webs Decomposers Cycles
PHOTOSYNTHESIS (7.5A)
 PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
PHOTOSYNTHESISS (7.5A) 1) What kind of energy is necessary to initiate the process of photosynthesis? A. radiant B. heat C. electrical D. wind 2) What happens to the radiant energy absorbed by plants during
STAR Student Test Questions Big Beetle Buzz. 1 From the information provided in the selection, the reader can conclude that ox beetles
 STAR Student Test Questions Big Beetle Buzz 1 From the information provided in the selection, the reader can conclude that ox beetles A prefer to live in rocky habitats B make a loud buzzing sound when
STAR Student Test Questions Big Beetle Buzz 1 From the information provided in the selection, the reader can conclude that ox beetles A prefer to live in rocky habitats B make a loud buzzing sound when
Scientific Investigation
 Scientific Investigation Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Scientific Investigation Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Connecting the Dots of Climate Change and Health: An Interactive Computer Lab
 Teacher s Guide Connecting the Dots of Climate Change and Health: An Interactive Computer Lab Incorporated Minnesota Standards: 7.1.3.4.1 8.1.1.2.1 8.1.3.4.1 8.3.4.1.2 Description: This lab incorporates
Teacher s Guide Connecting the Dots of Climate Change and Health: An Interactive Computer Lab Incorporated Minnesota Standards: 7.1.3.4.1 8.1.1.2.1 8.1.3.4.1 8.3.4.1.2 Description: This lab incorporates
The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings.
 WOODLEA W Science Y6 Essential Characteristics The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings. Confidence and competence
WOODLEA W Science Y6 Essential Characteristics The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings. Confidence and competence
SE: , 323. TECH: Student CD-Rom, Instructor s CD-Rom, A002: Interpret motto, emblem, and dress code for members SE:
 DUTY A: Career and Technical Student Organizations Task: A001: Discuss basic knowledge of national student organizations SE: 318-321, 323 TE: 376-381 TR: 218-220; Transparency 14-9 14-11 A002: Interpret
DUTY A: Career and Technical Student Organizations Task: A001: Discuss basic knowledge of national student organizations SE: 318-321, 323 TE: 376-381 TR: 218-220; Transparency 14-9 14-11 A002: Interpret
featured animals: Elephants
 Welcome to the Animal Action Education Programme from IFAW featured animals: Elephants Suitable for pupils aged 5-10 For more information and additional activities visit: www.ifaw.org/elephants-never-forget-uk
Welcome to the Animal Action Education Programme from IFAW featured animals: Elephants Suitable for pupils aged 5-10 For more information and additional activities visit: www.ifaw.org/elephants-never-forget-uk
The City School. Prep Section. PAF Chapter. Science. 2 nd Term. Class 8. Worksheets for Intervention Classes
 The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Science 2 nd Term Class 8 Worksheets for Intervention Classes Science Class 8 RESPIRATION AND CIRCULATION Q1. What is respiration? What are the types of respiration?
The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Science 2 nd Term Class 8 Worksheets for Intervention Classes Science Class 8 RESPIRATION AND CIRCULATION Q1. What is respiration? What are the types of respiration?
