REFERENCES. Hemispheric Processing Asymmetries: Implications for Memory
|
|
|
- Gertrude Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TENNET XI 135 Results Allocentric WM. There was no difference between lesioned and control rats; i.e., there was an equal proportion of rats from the two groups in the target quadrant (saline, 100%; lesioned, 80%, n.s.). Egocentric WM. Lesioned rats were less frequently found in the target quadrant compared to control rats (saline, 50%; lesioned, 9%, Z 2 (17.67, df = 1), p <.00003). Lesioned rats were neither found in the previous trial's target quadrant. Rather, 9/11 (88.1%) of the lesioned rats were found in the starting quadrant. Discussion We found no difference between control and lesioned rats in the allocentric WM while mpfc rats were impaired in the egocentric WM. In the egocentric WM test, behavioral analysis showed that lesioned rats were neither located in the previous trial's target quadrant, suggesting that they also did not use an allocentric navigation strategy as an alternative. The fact that they were located back in the starting quadrant could suggest that rats with a lesion of the mpfc are not capable of correcting a deficient navigational strategy as it is being elaborated and that they choose to home the starting position upon navigational strategy difficulties. REFERENCES de Bruin, J. P. C., Swinkels, W. A. M., & de Brabander, J. M. (1997). Response learning of rats in a Morris water maze: Involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex. Behavioural Brain Research, 85, Hemispheric Processing Asymmetries: Implications for Memory Margaret G. Funnell, Paul M. Corballis, and Michael S. Gazzaniga Center.for Cognitive Neuroscience, Dartmouth College Recent research has demonstrated that memory for words elicits left hemisphere activation, faces right hemisphere activation, and nameable objects bilateral activation. This pattern of results was attributed to dual coding of information, with the left hemisphere employing a verbal code and the right a nonverbal code. Nameable objects can be encoded either verbally or nonverbally and this accounts for their bilateral activation. We investigated this hypothesis in a callosotomy patient. Consistent with dual coding, the left hemisphere was superior to the right in memory for words, whereas the right was superior for faces. Contrary to prediction, perlormance on nameable pictures was not equivalent in the two hemispheres, but rather resulted in a right hemisphere superiority. In addition, memory lbr pictures was significantly better than for either words or faces. These findings suggest that the dual code hypothesis is an oversimplification of the processing capabilities of the two hemispheres Academic Press Observations of patients with unilateral brain lesions hint at a multitude of functional asymmetries between the two hemispheres of the brain. Paul Broca first noted the left hemisphere's dominance for language after an autopsy on his famous aphasic patient, Tan. Other syndromes resulting from unilateral brain damage also sparked interest in the specialized functions of the two cerebral hemispheres. Patients with
2 136 TENNET XI right parietal damage would ignore the right half of visual space and, to the amazement of their families and doctors, might only dress one half of their bodies or put makeup on the right side of their faces. These types of startling patient profiles led many researchers to begin to think about functional differences between the two hemispheres. Research with patients who have undergone surgical separation of the two cerebral hemispheres, so-called "split-brain" patients, has confirmed and extended many of the findings from lesion patients and revealed much about the specialized functions of the two hemispheres. Early investigations confirmed the left hemisphere's specialization for language and demonstrated the right hemisphere's superiority for visuospatial functions. These differences in the way that the two hemispheres process information have potential implications for the way information is encoded. The two hemispheres might "remember" different aspects of events and split-brain patients might demonstrate deficits in various memory tasks. Although early studies demonstrated that callosotomy does not result in any general decrement in memory, subsequent research revealed specific memory functions that are affected by hemispheric separation. Phelps, Hirst, and Gazzaniga (1991) demonstrated that although callosotomy patients are not impaired in recognition memory, they are impaired in free recall. They speculate that the two hemispheres process and store different aspects of events, and therefore disconnecting the two hemispheres results in a degradation of the resulting mnemonic representation. A number of researchers have further investigated the effect of hemispheric processing differences on memory. Kroll and colleagues tested callosotomy patients on memory for different types of stimuli (Jha, Kroll, Baynes, & Gazzaniga, 1997). They found that callosotomy patients are not impaired on verbal memory tasks, but do demonstrate significant deficits in memory for pictorial information. The authors conclude that the left hemisphere encodes the elements of verbal memories independently of the right hemisphere whereas memory for pictorial information requires integration between the two hemispheres. Consequently, callosotomy is detrimental to memory for pictorial information but not verbal information. This finding is consistent with previous research demonstrating differences in verbal and nonverbal memory in patients with unilateral brain lesions (Kroll, Knight, Metcalfe, et al., 1996). Recent research by Kelley and colleagues is consistent with the idea of a dual coding of stimuli (verbal and nonverbal). They investigated the neural substrates of memory encoding using functional brain imaging (Kelley, Miezin, McDermott, et al., 1998). Subjects were presented with words, line drawings of common objects, and pictures of unfamiliar faces and asked to try to remember them for a subsequent memory test. Each category of stimuli elicited activation in dorsal frontal regions, but the lateralization of the activation differed depending on the type of stimuli being encoded. Encoding of words resulted in left frontal activation whereas encoding of faces resulted in fight hemisphere activation. The line drawings of common objects, however, resulted in bilateral activation. The authors conclude that the left hemisphere is dominant for encoding of verbal information, whereas the fight is superior for nonverbal encoding. Pictures of nameable objects can be encoded both visually and verbally, so both hemispheres have a mechanism available for encoding of this class of stimuli. Based on these findings, it would be expected that the left hemisphere of split-brain patients would be superior to the right in memory for verbal information, whereas the fight hemisphere would be dominant in memory for unfamiliar faces. There should be no significant difference between the two hemisphere in memory for line drawings of common objects since these can be encoded both visually and verbally. These predictions were tested in a series of experiments with a patient with a complete callosotomy.
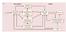
3 TENNET Xl 137 Methods Callosotomy patient J.W. participated in the reported experiments. J.W. is a 46- year-old right-handed man who underwent two-stage resection of the corpus callosum for the relief of intractable epilepsy in Further details of his medical history can be found in Gazzaniga, Nass, Reeves, and Roberts (1984). The study sets consisted of 10 items presented center field for 3 s each. There was a 1.5-s interval between study items. Following each study set, there was a 4-min interval in which J.W. was asked to make simple visual discriminations as part of a separate experiment. J.W. was then presented with a test set which included the 10 items he had studied and 10 new items. Each item appeared once in the right visual field and once in the left, resulting in a total of 40 items in the test set. On each trial J.W. indicated whether he recognized the item as belonging to the study set by pressing a button on the computer keyboard. J.W. was seated approximately 57 cm in front of a computer screen and told to fixate a central cross-hair. Stimuli were flashed to either the right (RVF) or left visual field (LVF) for 150 ms to ensure that stimuli are perceived only by the hemisphere contralateral to the visual field of the presentation. There were a total of six study/test sets: two each of pictures, faces, and words. The pictures and words were taken from the set published by Snodgrass and Vanderwart (1980). The faces were provided courtesy of M. J. Tarr (Brown University, Providence, RI). J.W. was tested on each set four times, with at least 1 week between each testing session. The hand used to respond was counterbalanced between blocks. Results and Discussion Only responses made with the hand ipsilateral to the stimuli were analyzed. In other words, for left-hand blocks only responses to left-visual-field stimuli were included in the analysis and vice versa. This helped to ensure that the stimulated hemisphere generated the response. J.W.'s response accuracy for stimuli presented to each visual field in each task is shown in Fig. 1. Because this experiment involves analysis of data collected from a single observer in which each hemisphere serves as a control for the other, statistical tests were carried out on J.W.'s responses using a hierarchical )~: analysis (Winer, Brown, & Michels, 1991). The factors in this analysis were Condition (old vs new), Response ("old" vs "new"), Visual Field (LVF vs RVF), and Task (pictures vs words vs faces). In this analysis, response accuracy is indexed by the contingency between Condition and Response, and "interactions" involving accuracy are indexed by higher-order contingencies between Condition, Response, and other factors. The ;~2 analysis revealed a significant contingency between Condition and Response ()~2 (1) = 90.13, p <.001), which indicates that J.W. was performing the memory task accurately overall (overall accuracy =.717). The contingencies between Task, Condition, and Response (Z 2 (2) = 22.82, p <.001) and Task, Field, Condition, and Response (g2 (2) = 7.35, p <.05) were also significant. The first of these reflects different overall levels of response accuracy in the three tasks (pictures,.868; words,.663; faces,.619). The four-way contingency reflects the fact that the effect of visual field on response accuracy was not the same in each task. In the pictures and faces tasks responses were more accurate for LVF stimuli than for RVF stimuli (pictures, LVF =.938, RVF =.800; faces, LVF , RVF =.550). By contrast, in the words task performance was more accurate for RVF stimuli (.725) than for LVF stimuli (.600). Post hoc tests were carried out in which the data from
4 13 8 TENNET XI J.W. Recognition Memory 0.9 P(correct] ,5 i= Pictures Words Faces Task rjrvf IILVF FIG. 1. J.W.'s recognition performance in the pictures, words, and faces tasks. The proportion of correct responses in each task is shown separately for each visual field. each task were removed from the calculation in turn. This analysis revealed that the four-way contingency between Task, Field, Condition, and Response was statistically significant for the comparisons between the words and pictures 0~ 2 (1) = 5.51, p <.05) and words and faces (Z 2 (1) = 5.51, p <.05), but not between pictures and faces 0~ 2 (1) = 0.00, n.s.). Thus it appears that the original four-way contingency was driven exclusively by the difference between the words task and the other two tasks--the effects of Visual Field on accuracy did not differ between the pictures and faces tasks. These results suggest that the memory trace for words is lateralized differently from those for faces and pictures. As predicted, memory performance for words is better when the test stimuli are presented to the RVF (left hemisphere) than when they are presented to the LVF (right hemisphere). The opposite pattern was obtained for the faces task and, somewhat surprisingly, for the pictures task. For both these tasks test stimuli presented to the LVF (right hemisphere) resulted in better recognition than stimuli presented to the RVF (left hemisphere). Although pictures were recognized better than faces, the lack of a significant four-way contingency between Task, Field, Condition, and Response for the comparison between pictures and faces suggests that the memory traces are similarly lateralized. General Discussion At the outset of the experiment we anticipated that the left-hemisphere specialization for language would result in an advantage for recognizing words. Similarly, we expected that the fight hemisphere would exhibit stronger memory for faces. Both these expectations were confirmed. However, we also anticipated that the hemispheres would be equivalent for the pictures task since both verbal and nonverbal codes would be available. Instead, we found that the lateralization pattern of recognition memory for nameable pictures was similar to that for faces, with the right-hemisphere recognition
5 TENNET XI 139 performance superior to the left. Levels of accuracy in both hemispheres, however, were significantly higher for pictures than for either words or faces. The results of this experiment suggest that a dual-code model may be an oversimplification of the processing capabilities of the two hemispheres. Instead, each hemisphere brings to bear a variety of processing resources, with each contributing to the memory trace. If the left hemisphere had only the verbal code available, then there should be no difference in level of accuracy on words and pictures. The pictures should simply be stored as verbal labels. This, however, was not the case in this experiment. Similarly, if the right hemisphere had only a single nonverbal code available, then there should be no difference in recognition for faces and nameable objects. Because both hemispheres were better able to remember nameable objects than either words or faces, this suggests that each hemisphere has a variety of processing capabilities, and these are reflected in the memory trace for different categories of stimuli. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This research was supported by Grants 1 F32 NS from NIH to M.G.F., RG 0161/1999-B from the Human Frontiers Science Program to P.M.C., and 1 R01 MH from NIH to M.S.G. REFERENCES Gazzaniga, M. S., Nass, R., Reeves, A., & Roberts, D. (1984). Neurologic perspectives on right hemisphere language following surgical section of the corpus callosum. Seminars in Neurology, 4~ Jha, A. P., Kroll, N. E. A., Baynes, K., & Gazzaniga, M. S. (1997). Memory encoding following complete callosotomy. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 9(1 ), Kelley, W. M., Miezin, F. M., McDermott, K. B., Buckner, R. L., Raichle, M. E., Cohen, M. J., Ollinger, J. M., Akbudak, E,, Conturo, T. E., Snyder, A. Z., & Petersen, S. E. (1998). Hemispheric specialization in human dorsal frontal cortex and medial temporal lobe tbr verbal and nonverbal memory encoding. Neuron, 20, Kroll, N. E. A., Knight, R. T., Metcalfe, J., Wolf, E. S., & Tulving, E. (1996). Cohesion failure as a source of memory illusions. Journal ~fmemory and Language, 135, Phelps, E. A., Hirst, W., & Gazzaniga, M. S. (1991). Deficits in recall following partial and complete commissurotomy. Cerebral Cortex, 1, Snodgrass, J. G., & Vanderwart, M. (1980). A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity, and visual complexity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning & Memoo,, 6(2), Winer, B. J., Brown, D. R., & Michels, K. M. (1991 ). Statistical principles in experimental design (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw Hill. Imagined and Actual Limb Selection: A Test of Preference Carl Gabbard and Casi Rabb Department of Health & Kinesiology, Texas A &M University Imagined and actual motor performance were compared to determine what factor(s) drive limb selection for programming movements in contralateral hemispace. Forty right-handed blindfolded subjects were asked to 'reach' via auditory stimulus for a small object placed at multiple locations in hemispace. Two conditions were included: arms uncrossed and arms crossed. With the uncrossed condition, responses were similar. With arms crossed, subjects had the choice of keeping the limbs crossed, reacting to proximity, or uncrossing the arms to reach ipsilaterally. In this condition subjects 'imagined' that they would maintain the crossed
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Deficits in Recall Following Partial and Complete Commissurotomy
 Deficits in Recall Following Partial and Complete Commissurotomy Elizabeth A. Phelps, 1 William Hirst, 2 and Michael S. Gazzaniga 3 1 Center for Neural Science, New York University, New York, New York
Deficits in Recall Following Partial and Complete Commissurotomy Elizabeth A. Phelps, 1 William Hirst, 2 and Michael S. Gazzaniga 3 1 Center for Neural Science, New York University, New York, New York
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
A dissociation between spatial and identity matching in callosotomy patients
 Cognitive Neuroscience, 8±87 (999) ALTHOUGH they are structurally similar, the two hemispheres of the human brain have many functional asymmetries. Some of these, such as language and motor control, have
Cognitive Neuroscience, 8±87 (999) ALTHOUGH they are structurally similar, the two hemispheres of the human brain have many functional asymmetries. Some of these, such as language and motor control, have
EVIDENCE FOR PARACALLOSAL VERBAL TRANSFER AFTER CALLOSAL SECTION
 Brain (1982), 105,53-63 EVIDENCE FOR PARACALLOSAL VERBAL TRANSFER AFTER CALLOSAL SECTION A POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCE OF BILATERAL LANGUAGE ORGANIZATION by MICHAEL S. GAZZANIGA, JOHN J. SIDTIS, BRUCE T. VOLPE,
Brain (1982), 105,53-63 EVIDENCE FOR PARACALLOSAL VERBAL TRANSFER AFTER CALLOSAL SECTION A POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCE OF BILATERAL LANGUAGE ORGANIZATION by MICHAEL S. GAZZANIGA, JOHN J. SIDTIS, BRUCE T. VOLPE,
PSY 215 Lecture 17 (3/28/2010) (Lateralization in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215
 PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Insights into the functional specificity of the human corpus callosum
 Brain (2000), 123, 920 926 Insights into the functional specificity of the human corpus callosum Margaret G. Funnell, Paul M. Corballis and Michael S. Gazzaniga Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Dartmouth
Brain (2000), 123, 920 926 Insights into the functional specificity of the human corpus callosum Margaret G. Funnell, Paul M. Corballis and Michael S. Gazzaniga Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Dartmouth
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions. Michael E. Goldberg, M.D.
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy
 Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy Jeff Ojemann, MD Department of Neurological Surgery University of Washington Children s Hospital & Regional
Frontal Contributions to Memory Encoding Before and After Unilateral Medial Temporal Lobectomy Jeff Ojemann, MD Department of Neurological Surgery University of Washington Children s Hospital & Regional
PsychoBrain. 31 st January Dr Christos Pliatsikas. Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading
 PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception. Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital.
 Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language
 Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Published 21 May 2009 Cite this as: BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi: /bcr ] Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
![Published 21 May 2009 Cite this as: BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi: /bcr ] Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. Published 21 May 2009 Cite this as: BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi: /bcr ] Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.](/thumbs/75/72410127.jpg) Published 21 May 2009 Cite this as: BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0593] Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. Right hemisphere dominance for understanding the intentions of others:
Published 21 May 2009 Cite this as: BMJ Case Reports 2009 [doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0593] Copyright 2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. Right hemisphere dominance for understanding the intentions of others:
shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all of the above.
 Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Functional Neuroanatomy. IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya
 Functional Neuroanatomy IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya What is/are the function(s) of the nervous system? Sensation Perception Visceral activities (Homeostasis) Behavior
Functional Neuroanatomy IBRO ISN African Neuroscience School 4-13 th Dec 2014 Nairobi, Kenya What is/are the function(s) of the nervous system? Sensation Perception Visceral activities (Homeostasis) Behavior
1--One Brain...or Two?--2
 Página 1 de 5 1--One Brain...or Two?--2 Left How many brains do you have - one or two? Actually, this is quite easy to answer...you have only one brain. However, the cerebral hemispheres are divided right
Página 1 de 5 1--One Brain...or Two?--2 Left How many brains do you have - one or two? Actually, this is quite easy to answer...you have only one brain. However, the cerebral hemispheres are divided right
Cognitive Neuroscience
 Gazzaniga Ivry Mangun Cognitive Neuroscience FOURTH EDITION Chapter 4 Hemispheric Specialization Science debate: Is it true? Are the followings true? Left and right hemispheres perform different functions.
Gazzaniga Ivry Mangun Cognitive Neuroscience FOURTH EDITION Chapter 4 Hemispheric Specialization Science debate: Is it true? Are the followings true? Left and right hemispheres perform different functions.
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Hemispheric Specialization (lateralization) Each lobe of the brain has specialized functions (Have to be careful with this one.)
 Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Sensorimotor Functioning. Sensory and Motor Systems. Functional Anatomy of Brain- Behavioral Relationships
 Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm
 Author's response to reviews Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm Authors: Julia Miro (juliamirollado@gmail.com) Pablo Ripollès (pablo.ripolles.vidal@gmail.com)
Author's response to reviews Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm Authors: Julia Miro (juliamirollado@gmail.com) Pablo Ripollès (pablo.ripolles.vidal@gmail.com)
Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis
 97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
Right hemisphere. Left hemisphere. Demonstration: Contralateral processing. Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space
 Week 6 Lab: Hemispheric Functions - Contralateral processing Back to Index Right hemisphere Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space Left hemisphere Motor functions on right side
Week 6 Lab: Hemispheric Functions - Contralateral processing Back to Index Right hemisphere Motor functions on left side of body Perceives left side of space Left hemisphere Motor functions on right side
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems
 Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Cortical and subcortical contributions to the representation of temporal information
 Neuropsychologia 41 (2003) 1461 1473 Cortical and subcortical contributions to the representation of temporal information Todd C. Handy a,, Michael S. Gazzaniga a, Richard B. Ivry b a Department of Psychological
Neuropsychologia 41 (2003) 1461 1473 Cortical and subcortical contributions to the representation of temporal information Todd C. Handy a,, Michael S. Gazzaniga a, Richard B. Ivry b a Department of Psychological
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION. Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni
 FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
UPRIGHT AND INVERTED FACES: THE RIGHT HEMISPHERE KNOWS THE DIFFERENCE!
 UPRIGHT AND INVERTED FACES: THE RIGHT HEMISPHERE KNOWS THE DIFFERENCE! Susan Leehey, Susan Carey, Rhea Diamond and Andrew Cahn (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) INTRODUCTION Existing evidence suggests
UPRIGHT AND INVERTED FACES: THE RIGHT HEMISPHERE KNOWS THE DIFFERENCE! Susan Leehey, Susan Carey, Rhea Diamond and Andrew Cahn (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) INTRODUCTION Existing evidence suggests
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Supplementary Data for "Single-trial learning of novel stimuli by individual. neurons of the human hippocampus-amygdala complex"
 Supplementary Data for "Single-trial learning of novel stimuli by individual neurons of the human hippocampus-amygdala complex" Figure S1. Behavioral performance of all subjects. Recognition performance
Supplementary Data for "Single-trial learning of novel stimuli by individual neurons of the human hippocampus-amygdala complex" Figure S1. Behavioral performance of all subjects. Recognition performance
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture. Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D.
 Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University
 Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Support for lateralization of the Whorf effect beyond the realm of color discrimination
 Brain and Language xxx (2007) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/b&l Support for lateralization of the Whorf effect beyond the realm of color discrimination Aubrey L. Gilbert a,b, *, Terry Regier d, Paul
Brain and Language xxx (2007) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locate/b&l Support for lateralization of the Whorf effect beyond the realm of color discrimination Aubrey L. Gilbert a,b, *, Terry Regier d, Paul
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Frontal steady-state potential changes predict long-term recognition memory performance
 International Journal of Psychophysiology 39 2000 79 85 Frontal steady-state potential changes predict long-term recognition memory performance Richard B. Silberstein, Philip G. Harris, Geoffrey A. Nield,
International Journal of Psychophysiology 39 2000 79 85 Frontal steady-state potential changes predict long-term recognition memory performance Richard B. Silberstein, Philip G. Harris, Geoffrey A. Nield,
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
The frontal lobe role in memory: a review of convergent evidence and implications for the Wada memory test
 Epilepsy & Behavior 3 (2002) 309 315 Review The frontal lobe role in memory: a review of convergent evidence and implications for the Wada memory test Jeffrey G. Ojemann a, * and William M. Kelley b a
Epilepsy & Behavior 3 (2002) 309 315 Review The frontal lobe role in memory: a review of convergent evidence and implications for the Wada memory test Jeffrey G. Ojemann a, * and William M. Kelley b a
Specific Sulci/Fissures:
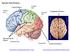 Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Theories of memory. Memory & brain Cellular bases of learning & memory. Epileptic patient Temporal lobectomy Amnesia
 Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet?
 Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet? Two types of AVA: 1. Deficit at the prephonemic level and
Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet? Two types of AVA: 1. Deficit at the prephonemic level and
9.00 BLINDSIGHT & NEGLECT. Professor John Gabrieli
 9.00 BLINDSIGHT & NEGLECT Professor John Gabrieli Objectives Blindsight what it is brain basis unconscious perception Neglect what it is brain basis construction of visual attention Left optic tract Left
9.00 BLINDSIGHT & NEGLECT Professor John Gabrieli Objectives Blindsight what it is brain basis unconscious perception Neglect what it is brain basis construction of visual attention Left optic tract Left
central sulcus parietal lobe frontal lobe occipital lobe Sylvian fissure temporal lobe
 frontal lobe central sulcus parietal lobe occipital lobe Sylvian fissure temporal lobe The lobes of the brain. Note that the crease along the top of the temporal lobe is the Sylvian fissure, which divides
frontal lobe central sulcus parietal lobe occipital lobe Sylvian fissure temporal lobe The lobes of the brain. Note that the crease along the top of the temporal lobe is the Sylvian fissure, which divides
Notes: Organization. Anatomy of the Nervous System. Cerebral cortex. Cortical layers. PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall Professor Claffey
 PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Organization Version: 10/30/12 - original version Anatomy of the Nervous System Content covered in Hans's lecture: CNS & PNS Directions/Planes
PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Organization Version: 10/30/12 - original version Anatomy of the Nervous System Content covered in Hans's lecture: CNS & PNS Directions/Planes
Neuroscience of Consciousness II
 1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness II Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive Contents
1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness II Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive Contents
It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple
 It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple 6 th Annual Northern Kentucky TBI Conference March 23, 2012 www.bridgesnky.org James F. Phifer,
It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple 6 th Annual Northern Kentucky TBI Conference March 23, 2012 www.bridgesnky.org James F. Phifer,
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1
 Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Language Speech. Speech is the preferred modality for language.
 Language Speech Speech is the preferred modality for language. Outer ear Collects sound waves. The configuration of the outer ear serves to amplify sound, particularly at 2000-5000 Hz, a frequency range
Language Speech Speech is the preferred modality for language. Outer ear Collects sound waves. The configuration of the outer ear serves to amplify sound, particularly at 2000-5000 Hz, a frequency range
THE PERFORMANCE OF TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY (TLE) PATIENTS ON VERBAL AND NONVERBAL SELECTIVE REMINDING PROCEDURES: PRE AND POSTOPERATIVE COMPARISONS
 THE PERFORMANCE OF TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY (TLE) PATIENTS ON VERBAL AND NONVERBAL SELECTIVE REMINDING PROCEDURES: PRE AND POSTOPERATIVE COMPARISONS Gail L. Risse, PhD Robert C. Doss, PsyD Ann M. Hempel,
THE PERFORMANCE OF TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY (TLE) PATIENTS ON VERBAL AND NONVERBAL SELECTIVE REMINDING PROCEDURES: PRE AND POSTOPERATIVE COMPARISONS Gail L. Risse, PhD Robert C. Doss, PsyD Ann M. Hempel,
Direct Comparison of Prefrontal Cortex Regions Engaged by Working and Long-Term Memory Tasks
 NeuroImage 14, 48 59 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0791, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Direct Comparison of Prefrontal Cortex Regions Engaged by Working and Long-Term Memory Tasks Todd
NeuroImage 14, 48 59 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0791, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Direct Comparison of Prefrontal Cortex Regions Engaged by Working and Long-Term Memory Tasks Todd
Collaboration between the hemispheres of a callosotomy patient Emerging right hemisphere speech and the left hemisphere interpreter
 Brain (1996), 119, 1255-1262 Collaboration between the hemispheres of a callosotomy patient Emerging right hemisphere speech and the left hemisphere interpreter Michael S. Gazzaniga, James C. Eliassen,
Brain (1996), 119, 1255-1262 Collaboration between the hemispheres of a callosotomy patient Emerging right hemisphere speech and the left hemisphere interpreter Michael S. Gazzaniga, James C. Eliassen,
Experimental Design!
 Experimental Design! Variables!! Independent Variables: variables hypothesized by the experimenter to cause changes in the measured variables.!! Conditions: Different values of the independent variables!!
Experimental Design! Variables!! Independent Variables: variables hypothesized by the experimenter to cause changes in the measured variables.!! Conditions: Different values of the independent variables!!
Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions
 Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
Lab 12 Nervous System II
 Lab 12 Nervous System II Laboratory Objectives Identify the structural components of the central nervous system Label the functional areas of human cerebral cortex. Given a deficit affecting one or more
Lab 12 Nervous System II Laboratory Objectives Identify the structural components of the central nervous system Label the functional areas of human cerebral cortex. Given a deficit affecting one or more
2. Area of the brain affected by the seizures.
 Learning Through Storms When discussing learning, we sometimes refer to cognition, or one s ability to think, learn and use information. Seizures can impact cognition, learning and behaviour in a variety
Learning Through Storms When discussing learning, we sometimes refer to cognition, or one s ability to think, learn and use information. Seizures can impact cognition, learning and behaviour in a variety
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Summarized by. Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
"False tagging mechanism False Tagging Theory All idea initially believed Doubt occur when prefrontal cortex tags it as false Provides doubt and
 Ventromedial Notes Frontal lobe Prefrontal cortex 1. dorsolateral cortex Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility Planning 2. Orbitofrontal cortex Controls
Ventromedial Notes Frontal lobe Prefrontal cortex 1. dorsolateral cortex Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility Planning 2. Orbitofrontal cortex Controls
Are there Hemispheric Differences in Visual Processes that Utilize Gestalt Principles?
 Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Dietrich College Honors Theses Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences 2006 Are there Hemispheric Differences in Visual Processes that Utilize
Carnegie Mellon University Research Showcase @ CMU Dietrich College Honors Theses Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences 2006 Are there Hemispheric Differences in Visual Processes that Utilize
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Takwa Adly Gabr Assistant lecturer of Audiology
 Mismatch Negativity as an Objective Tool for the Assessment of Cognitive Function in Subjects with Unilateral Severe to Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss Takwa Adly Gabr Assistant lecturer of Audiology
Mismatch Negativity as an Objective Tool for the Assessment of Cognitive Function in Subjects with Unilateral Severe to Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss Takwa Adly Gabr Assistant lecturer of Audiology
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning
 Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
Brain Imaging Applied to Memory & Learning John Gabrieli Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Institute for Medical Engineering & Sciences McGovern Institute for Brain Sciences MIT Levels of Analysis
Prof. Greg Francis 5/23/08
 Brain parts The brain IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 02 The source of cognition (consider transplant!) Weighs about 3 pounds Damage to some parts result in immediate death or disability
Brain parts The brain IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis Lecture 02 The source of cognition (consider transplant!) Weighs about 3 pounds Damage to some parts result in immediate death or disability
Speeded right-to-left information transfer: the result of speeded transmission in right-hemisphere axons?
 Neuroscience Letters 380 (2005) 88 92 Speeded right-to-left information transfer: the result of speeded transmission in right-hemisphere axons? Kylie J. Barnett, Michael C. Corballis Research Centre for
Neuroscience Letters 380 (2005) 88 92 Speeded right-to-left information transfer: the result of speeded transmission in right-hemisphere axons? Kylie J. Barnett, Michael C. Corballis Research Centre for
Memory. Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith
 Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Cortical Visual Symptoms
 대한안신경의학회지 : 제 6 권 Supplement 2 ISSN: 2234-0971 Jeong-Yoon Choi Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea Jeong-Yoon Choi. MD. PhD. Department of Neurology, Seoul
대한안신경의학회지 : 제 6 권 Supplement 2 ISSN: 2234-0971 Jeong-Yoon Choi Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea Jeong-Yoon Choi. MD. PhD. Department of Neurology, Seoul
The effects of bilateral presentations on lateralized lexical decision
 Brain and Cognition 64 (2007) 60 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/b&c The effects of bilateral presentations on lateralized lexical decision Leonardo Fernandino a, *, Marco Iacoboni b,c, Eran Zaidel a,c a Department
Brain and Cognition 64 (2007) 60 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/b&c The effects of bilateral presentations on lateralized lexical decision Leonardo Fernandino a, *, Marco Iacoboni b,c, Eran Zaidel a,c a Department
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
The Biological Basis of Behavior
 The Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Chapter Overview I. Introduction II. Neurons III. The Human Nervous System IV. The Brain I. Introduction A. Announcement: The Brain Game B. Phrenology I. Introduction
The Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Chapter Overview I. Introduction II. Neurons III. The Human Nervous System IV. The Brain I. Introduction A. Announcement: The Brain Game B. Phrenology I. Introduction
Disorders affecting region: depression anxiety
 Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom //
 Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Using immersive virtual reality to test allocentric spatial memory impairment following unilateral temporal lobectomy
 Using immersive virtual reality to test allocentric spatial memory impairment following unilateral temporal lobectomy G Morris, D Parslow and M D ecce 3 Neuropsychology Unit, Institute of Psychiatry, De
Using immersive virtual reality to test allocentric spatial memory impairment following unilateral temporal lobectomy G Morris, D Parslow and M D ecce 3 Neuropsychology Unit, Institute of Psychiatry, De
Vision and Action. 10/3/12 Percep,on Ac,on 1
 Vision and Action Our ability to move thru our environment is closely tied to visual perception. Simple examples include standing one one foot. It is easier to maintain balance with the eyes open than
Vision and Action Our ability to move thru our environment is closely tied to visual perception. Simple examples include standing one one foot. It is easier to maintain balance with the eyes open than
Distinguishing between Category-based and Similarity-based Induction
 Distinguishing between Category-based and Similarity-based Induction Tracey Miser (miser.4@osu.edu) Department of Psychology, 1835 Neil Avenue Columbus, OH43210 USA Vladimir Sloutsky (sloutsky.1@osu.edu)
Distinguishing between Category-based and Similarity-based Induction Tracey Miser (miser.4@osu.edu) Department of Psychology, 1835 Neil Avenue Columbus, OH43210 USA Vladimir Sloutsky (sloutsky.1@osu.edu)
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex. 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations. 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage
 Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.
 Stimulus versus Face Recognition in Laterally Displayed Stimuli Author(s): Raymond Bruyer, Hervé Abdi, Jeannine Benoit Source: The American Journal of Psychology, Vol. 100, No. 1 (Spring, 1987), pp. 117-121
Stimulus versus Face Recognition in Laterally Displayed Stimuli Author(s): Raymond Bruyer, Hervé Abdi, Jeannine Benoit Source: The American Journal of Psychology, Vol. 100, No. 1 (Spring, 1987), pp. 117-121
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology. Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm
 Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm Lecture 2. Functional Organisation of the Nervous System Lecture Outline 1.1 Introduction
Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm Lecture 2. Functional Organisation of the Nervous System Lecture Outline 1.1 Introduction
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
FREE RECALL OF VERBAL AND NON-VERBAL STIMULI
 Q. JI exp. Psychol. (1970) 22, 215-221 FREE RECALL OF VERBAL AND NON-VERBAL STIMULI JEFFREY R. SAMPSON Department of Computing Science, The University of Alberta In two experiments, 40 and 72 male subjects
Q. JI exp. Psychol. (1970) 22, 215-221 FREE RECALL OF VERBAL AND NON-VERBAL STIMULI JEFFREY R. SAMPSON Department of Computing Science, The University of Alberta In two experiments, 40 and 72 male subjects
Sample Copyright. Academic Group SELF 1 2. Syllabus Checklist. On completion of this chapter you should be able to understand:
 SELF 1 2 Syllabus Checklist On completion of this chapter you should be able to understand: 2.1 Biological influences/bases of behaviour functions of the major parts of the brain hindbrain midbrain forebrain
SELF 1 2 Syllabus Checklist On completion of this chapter you should be able to understand: 2.1 Biological influences/bases of behaviour functions of the major parts of the brain hindbrain midbrain forebrain
The Neural Substrates of Visual Implicit Memory: Do the Two Hemispheres Play Different Roles?
 The Neural Substrates of Visual Implicit Memory: Do the Two Hemispheres Play Different Roles? N. E. A. Kroll 1, A. P. Yonelinas 1, M. M. Kishiyama 1, K. Baynes 1, R. T. Knight 2, and M. S. Gazzaniga 3
The Neural Substrates of Visual Implicit Memory: Do the Two Hemispheres Play Different Roles? N. E. A. Kroll 1, A. P. Yonelinas 1, M. M. Kishiyama 1, K. Baynes 1, R. T. Knight 2, and M. S. Gazzaniga 3
 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Neurobiology and Behavior, Ph.D. in progress University of California, Irvine; Irvine, CA
 Zachariah M. Reagh CONTACT INFORMATION Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 211 Qureshey Research Laboratory University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA 92617 Phone: 949-824-0314 Cell: 205-936-0608
Zachariah M. Reagh CONTACT INFORMATION Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 211 Qureshey Research Laboratory University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA 92617 Phone: 949-824-0314 Cell: 205-936-0608
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding
 Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
