Anatomical Characteristics of Infra-Lamina Ridge in Chinese Population
|
|
|
- Joan Maud Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Morphol., 32(2): , Anatomical Characteristics of Infra-Lamina Ridge in Chinese Population Características Anatómicas del Puente Infra-laminar en la Población China Xiao-he Li * ; Yong-qiang Cai * ; Xin Wang * ; Shang Gao * & Zhi-jun Li * LI, X. H.; CAI, Y. Q.; WANG, X.; GAO, S. & LI, Z. J. Anatomical characteristics of infra-lamina ridge in Chinese population. Int. J. Morphol., 32(2): , SUMMARY: The aim of our study was to observe the occurrence rate and morphological characteristics of Infra-Lamina ridge (ILR) in Chinese population and provide a comprehensive reference for its clinical implication. Vertebrae columns of 82 sets of Chinese adult skeletons were collected. The shape of ILR was classified into three types; the occurrence of it in different sides and sexes were counted. The length, width, thickness of ILR were measured using a caliper with 0.02 mm accuracy. The ILR was usually found to occur from C7 to L5, with its frequency higher from T8 to 12, and highest at T10 being up to 80.5%. There was significant statistical difference to the occurrence rate by side, sex and vertebral level. The largest values in its length and width were from T9 to T12. The ILR at T10 was largest in dimensions, being 4.1±2.1 mm in length and 4.4±2.3 mm in width. The ILR is more frequently detected in female and at the left side, at the lower thoracic spine with a larger dimension. KEY WORDS: Infra-lamina ridge; Vertebrae; Ossification; Ligamentum flavum; Morphological characteristics. INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHOD Ossification of the ligamentum flavum (OCLF) can often be seen at the thoracic segment, particularly at the thoracolumbar junction (T10/11, T11/12 and T12/L1), which was first studied systematically most by Japanese researchers in Japanese population through X-ray, CT or MRI, with rare reports about its epidemiology beyond Japanese population (van Oostenbrugge et al., 1999). Maigne et al. (1992), had measured the frequency and size of ossification in the caudal attachments of ligamentum flavum at the thoracic spine in Caucasians and analyzed its pathology. During our study of the dry skeletons of the human spine, we found some osseous processes inferior to the laminae at certain spinal segments, which are similar to the ossification of the ligmentum flavern described by van Ostenbrugge et al. and Maigne et al., and are provisionally named as the infralaminae ridge in our article. To date, there are no reports about the occurrence of infra-lamina ridge (ILR) in Chinese population (He et al., 2005), its side and sex prevalence, types and dimensions, hence this paper is proposed to present our observation and measurement about the morphological characteristics, dimension, side and sex prevalence, and the distributional pattern of the ILR, the manifestation of ILR in skeleton, at various spinal segments in Chinese population; Its clinical implication is also investigated. Eighty-two sets of intact skeletons of vertebral column without severe degenerative changes were obtained from our anatomy department, with 42 sets being male skeletons and 40 sets being female skeletons and 12 cadavers (5 male and 7 female) with intact spine were also used. Their age is listed in Table I. The occurrence of ILR, which is defined as the presence of ILR longer than 1.5 mm, was observed, and its presence on the left or right, male or female was respectively recorded. The shape was classified into three types (type A: inverted triangle; type B: saw-tooth shape; type C: spike shape) (Figs. 1, 2 and 3), the occurrence rate of which was calculated. The length, width and thickness of the ILR were measured using a caliper with 0.02 mm accuracy. Data and statistical analysis. The acquired data were processed with the Statistical Package for the social sciences (SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL). All the data were presented as mean ± SD. Comparison of the occurrence rate of the ILR between the left and right sides, between the male and female, and between the upper thoracic spine and lower thoracic spine by chi-square test all revealed significant statistical differences (p<0.01) Probability values of less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. * Department of Anatomy, Basic Medical College, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Huhhot, Inner Mongolia, P.R. China. 583
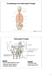
2 Table I. The age of skeletons (n). Age (years) Male Female Total < > RESULTS Fig. 1. Regional enlargement of infra- Lamina Ridge A: Type A. Fig. 2. Regional enlargement of infra- Lamina Ridge B: Type B. A total of 801 ILR were found in 1968 vertebrae. Data related to the length, width and thickness of ILR in each spinal segment were compared between the left and right, and the female and male using t test; No statistical differences were shown in terms of side and sex (p>0.05), therefore these data were combined for general analysis. Larger value of width and length of ILR were obtained from T9 to T12 segment, with its largest value being at T10. There was small fluctuation in the thickness of the ILR, ranging from 0.2 mm to 4.0 mm. The maximal value of length as 12 mm was found at T11, width as 13.8 mm at T10, thickness as 4.0 mm at T4 (Table II). The overall occurrence rate of the ILR, the occurrence rate of it with regard of sex and morphological type were listed in Figure 4. As the figure suggests, Type A and type B was more frequently present than type C; Type A was more often found in the upper thoracic spine (above T7) while type B appeared more frequently in the lower thoracic spine (below T7). In male, the ILR appeared at C7 to L5 with the exception of L2; in female, it appeared at T2 to L5 with the exception of L3 and L4. The ILR occurred most frequently on T10 with the occurrence rate up to 80.5% (76.2% in male and 85.0% in female). The ILR was rarely observed on cervical spine other than C7. In male, type A was frequently found at T1 to T8, type B at T9 to T12, while in female, type B was often found at T5 to T12 (Tables III and IV) (Fig. 4). DISCUSSION Fig. 3. Regional enlargement of infra- Lamina Ridge C: Type C. 584 Anatomical Characteristics of ILR. The ILR is located at the junction of the antero inferolateral border of the vertebral lamina and the superior part of the base of the inferior articular process. It is connected with the linea aspera
3 Table II. Data of ILR Mean±SD (min~max) mm (n=164). Vertebrae Length Width Thickness C7 3.0±1.2(1.9~3.9) 2.5±0.6(1.9~3.0) 1.5±0.6(0.9~2.0) T1 1.8±0.3(1.5~2.1) 1.8±0.3(1.5~2.0) 1.0±0.1(0.9~1.0) T2 2.5±0.9(1.5~6.0) 3.0±1.1(1.5~6.9) 1.4±0.6(0.8~2.8) T3 3.2±2.0(2.0~11.8) 3.6±1.8(1.0~8.0) 1.0±0.3(0.4~2.0) T4 3.1±1.6(1.5~10.0) 3.5±1.8(1.1~11.0) 1.0±0.6(0.2~4.0) T5 2.5±0.9(1.5~5.0) 2.7±1.0(1.0~6.1) 0.8±0.2(0.5~1.5) T6 3.1±1.2(1.5~7.0) 3.1±1.4(1.5~8.0)* 0.9±0.4(0.5~2.0) T7 3.0±1.0(1.5~5.1) 3.1±1.0(1.0~5.2)*# 0.9±0.4(0.3~2.0) T8 3.0±1.4(1.5~10.2)*# 3.5±1.5(1.2~10.0) 0.9±0.4(0.3~1.9) T9 4.0±2.2(2.0~10.0) 4.3±2.1(1.1~10.9) 1.1±0.6(0.3~3.0) T10 4.1±2.1(1.5~11.9) 4.4±2.3(1.5~13.8) 1.2±0.6(0.6~3.2) T11 3.8±1.5(1.6~12.0) 4.3±2.1(1.6~12.4) 1.1±0.5(0.4~3.0) *# T12 3.7±1.9(1.5~9.8) 4.3±2.0(1.0~12.0) 1.0±0.5(0.3~2.5) L1 2.5±0.9(1.5~6.0)* 3.0±1.1(1.5~7.0) 1.4±0.6(0.8~3.0) L2 3.0±1.4(2.0~3.9) 3.5±0.7(2.8~4.1) 0.8±0.1(0.7~0.9) # L3 1.9±0.0(1.9~1.9) 2.0±0.0(2.0~2.0) 2.1±0.0(2.1~2.1) L4 2.7±1.2(2.0~4.1) 3.6±0.6(2.9~3.8) 1.3±0.6(0.8~2.0) # L5 2.9±0.8(2.1~4.1)* 3.7±1.3(1.9~5.0)* 1.0±0.1(0.9~1.1) Total 3.4±1.7(1.5~12.0) 3.8±1.9(1.0~13.8) 1.1±0.5(0.2~4.0) * There is statistical significance for sexuality (p<0.05), # There is statistical significance for both sides (p<0.05). Table III. The occurrence rate and cases on three types of ILR in male. Vertebrae Left % (n) Right % (n) A* B* C* Total # A* B* C* Total# C (2) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 4.8 (2) (2) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 4.8 (2) T1 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) (2) 4.8 (2) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) (2) 4.8 (2) T (2) 33.3 (2) 33.3 (2) 14.0 (6) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) (4) 9.5 (4) T (7) 35.7 (5) 14.3 (2) 33.3 (14) 30.0 (3) 30.0 (3) 40.0 (4) 23.8 (10) T (4) 33.3 (4) 33.3 (4) 28.6 (12) 38.5 (5) 38.5 (5) 23.0 (3) 30.9 (13) T (9) 13.4 (3) 14.3 (2) 33.3 (14) 46.7 (7) 20.0 (3) 33.3 (5) 35.7 (15) T (7) 38.5 (5) 7.6 (1) 30.9 (13) 58.3 (7) 16.7 (2) 25.0 (3) 28.6 (12) T (8) 30.8 (4) 7.7 (1) 30.9 (13) 53.9 (7) 30.8 (4) 15.3 (2) 30.9 (13) T (8) 57.9 (11) 0.0 (0) 45.2 (19) 47.1 (8) 41.2 (7) 11.7 (2) 40.5 (17) T (12) 48.3 (14) 10.3 (3) 69.1 (29) 66.1 (18) 29.7 (8) 3.6 (1) 64.3 (27) T (11) 63.3 (19) 0.0 (0) 72.1 (30) 27.6 (8) 72.4 (21) 0.0 (0) 69.1 (29) T (9) 66.7 (18) 0.0 (0) 64.3 (27) 34.8 (8) 65.2 (15) 0.0 (0) 54.8 (23) T (6) 71.4 (15) 0.0 (0) 50.0 (21) 35.0 (7) 55.0 (11) 10.0 (2) 47.6 (20) L (2) 66.7 (6) 11.1 (1) 21.4 (9) 57.1 (4) 28.6 (2) 14.3 (1) 16.7 (7) L2 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) L (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.4 (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) L (2) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 4.8 (2) (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.4 (1) L (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.4 (1) (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.4 (1) *(The case of one type of ILR / The case of ILR) X 100%; #(The case of one type of ILR / Sample size ) X 100% 585
4 Fig. 4. The total occurence rate of Infra-Lamina Ridge. Fig. 5. The occurrence number on Infra-Lamina Ridge. 586 Table IV. The occurrence rate and cases on three types of ILR in female. Vertebrae Left % (n) Right % (n) A* B* C* Total # A* B* C* Total # C (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) T (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) T (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.5 (1) 0.0 (0) (1) 0.0 (0) 2.5 (1) T (3) 40.0 (2) 0.0 (0) 12.5 (5) (6) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 15.0 (6) T (2) 50.0 (3) 16.7 (1) 15.0 (6) 40.0 (2) 60.0 (3) 0.0 (0) 12.5 (5) T (1) 50.0 (4) 37.5 (3) 20.0 (8) 50.0 (4) 37.5 (3) 0.0 (0) 20.0 (8) T (3) 58.3 (7) 16.7 (2) 30.0 (12) 41.7 (5) 58.3 (7) 12.5 (1) 30.0 (12) T (6) 66.7 (1) 0.0 (0) 45.0 (18) 35.3 (6) 64.7 (11) 0.0 (0) 42.5 (17) T (10) 37.0 (1) 26.0 (7) 67.5 (27) 25.0 (5) 70.0 (14) 0.0 (0) 50.0 (20) T (14) 53.3 (1) 0.0 (0) 75.0 (30) 57.7 (15) 38.5 (10) 5.0 (1) 65.0 (26) T (10) 66.7 (2) 3.0 (1) 82.5 (33) 39.4 (13) 60.6 (20) 3.8 (1) 82.5 (33) T (8) 69.2 (1) 0.0 (0) 65.0 (26) 26.9 (7) 73.1 (19) 0.0 (0) 65.0 (26) T (5) 70.6 (1) 0.0 (0) 42.5 (17) 11.1 (2) 88.9 (16) 0.0 (0) 45.0 (18) L (2) 60.0 (3) 0.0 (0) 12.5 (5) 20.0 (1) 80.0 (4) 0.0 (0) 12.5 (5) L (1) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 2.5 (1) 0.0 (0) (1) 0.0 (0) 2.5 (1) L (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) L (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) L (3) 0.0 (0) 0.0 (0) 7.5 (3) 33.3 (1) 66.7 (2) 0.0 (0) 7.5 (3) *(The case of one type of ILR / The case of ILR) X100; #(The case of one type of ILR / Sample size) X 100%
5 of the ligamenta flava. The characteristics of ILR are as follows: 1) It diminishes in width form the upper side down; it is flat in anteroposterior view with the tip pointing to the vertebral canal; 2) The shapes of ILR can be defined as three types: inverted triangle, saw-tooth shape and spike shape; 3) The anterior surface of it is smooth while the posterior surface is rough; The outer margin is blunt while the inner margin is sharp and irregular; 4) It usually appears continuously on multiple segments of the vertebral column; sometimes it appears in intermittent segments, or even appears in one vertebra and one side of the vertebra; 5) There is a bony process on the lower vertebra that corresponds to the infra-lamina ridge. This bony process is projected from the base of the superior articular process with an irregular shape and its superior margin fused with the inner margin of infra-lamina ridge. This bony process is often present on both sides of the vertebra with an overall occurrence rate higher than that of the infra-lamina ridge. Since there is no standard anatomical terminology that can be retrieved in literature to our best knowledge, we name it as the medial ridge of the superior articular process, just as we do to the infra-lamina ridge. The relationship between the infra-lamina ridge and the adjacent anatomical structures. Similar to Maigne s report about ossifications in the caudal attachments of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine (Maigne et al.), the ILR is more frequently present in the lower thoracic spine with a relatively larger dimension, which is probably associated with the higher mobility of the small joints. There is a groove between the posterior aspect of the ILR and the inferior articular surface, where the tip of the superior articular process is wedged, probably leading to impediment of the mobility of small joints (Ruiz Santiago et al., 1997; Okuda et al., 2004). In addition, the ILR was found in 8 of the 12 cadavers, which is in contact with the anterior aspect of the articular capsule, leading to swelling of the capsule, and further to narrowness of the corresponding vertebral canal and compression of the adjacent nerve root (Yoshida et al., 1992; Xiong et al., 2001; Mak et al., 2002). It could be an important etiology in the clinically detected spinal stenosis. The relationship between the ILR and OCFL. When observed in 8 cadavers under the magnification coupe ( 10), the ligamentum flavum was found to cover the infra-lamina ridge with a hard texture, and there was a trace of ossification at its lateral margins. Therefore, the question arises: Is the ILR a structure where the ligamentum flavum is attached, or is it vestige of ossification of the ligamentum flavum? It has been reported in literature that OCLF most frequently happens in the lower thoracic spine where there is a large range of mobility of small joints and it often started from the lateral margins of the ligamentum flavum with the articular capsule involved (Pascal-Mousselard et al., 1998), which is similar to our observation. We also found in the cadavers that the infra-lamina ridge fused with the medial ridge of the superior articular process, together assuming an elongate shape, located lateral to the ligamentum flavum, which was similar to what we found in the skeletons. Therefore, we assume that the infra-lamina ridge and the medial ridge of the superior articular process are vestiges of ossification caused by the repetitive local strains and repair of the ligamentum flavum. The two ridges can be detected by various imaging modalities, which should be paid enough attention when the OCFL is to be diagnosed. CONCLUSION It is fundamentally important to observe the occurrence rate and morphological characteristics of Infra- Lamina Ridge (ILR) in Chinese population. In Chinese normal individuals, The ILR is more frequently detected in female and at the left side, and at the lower thoracic spine with a larger dimension. LI, X. H.; CAI, Y. Q.; WANG, X.; GAO, S. & LI, Z. J. Características anatómicas del puente infra-laminar en la población de China. Int. J. Morphol., 32(2): , RESUMEN: El objetivo de nuestro estudio fue observar la tasa de incidencia y características morfológicas del puente infralaminar (PIL) en la población china y ofrecer una referencia completa por su implicación clínica. Se utilizaron 82 series de vértebras pertenecientes a esqueletos adultos chinos. La forma del PIL se clasificó en tres tipos; además se cuantificó la presenciade la misma en diferentes lados y sexos. La longitud, ancho y grosor del PIL se midieron utilizando un caliper con 0,02 mm de precisión. Se encontró que el PIL por lo general se producía desde C7 a L5, con una mayor frecuencia entre T8 y T12, la más alta en T10 donde alcanzó el 80,5%. No hubo diferencia estadísticamente significativa en la tasa de ocurrencia según lado, sexo y el nivel de la vértebra. Los mayores valores de longitud y ancho fueron de T9 a T12. El PIL en T10 tuvo las mayores dimensiones, con una longitud de 4,1±2,1 mm y ancho de 4,4±2,3 mm. El PIL se detecta con mayor frecuencia en mujeres y la lado izquierdo, con una mayor dimensión en la columna torácica inferior. PALABRAS CLAVE: Puente infra-laminar; Vértebras; Osificación; Ligamento amarillo; Características morfológicas. 587
6 REFERENCES He, S.; Hussain, N.; Li, S. & Hou, T. Clinical and prognostic analysis of ossified ligamentum flavum in a Chinese population. J. Neurosurg. Spine, 3(5):348-54, Maigne, J. Y.; Ayral, X. & Guérin-Surville, H. Frequency and size of ossifications in the caudal attachments of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine: Role of rotatory strains in their development: An anatomic study of 121 spines. Surg. Radiol. Anat., 14(2):119-24, Mak, K. H.; Mak, K. L. & Gwi-Mak, E. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum in the cervicothoracic junction: case report on ossification found on both sides of the lamina. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 27(1):E11-4, Okuda, T.; Baba, I.; Fujimoto, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Sumida, T.; Manabe, H.; Hayashi, Y. & Ochi, M. The pathology of ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar disease. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 29(15): , Correspondence to: Zhi-jun Li Department of Anatomy, Basic Medical College Inner Mongolia Medical University Jinshan Economic Development Zone Huhhot Inner Mongolia P. R. CHINA @qq.com Received: Accepted: Pascal-Mousselard, H.; Smadja, D.; Cabre, P.; Raynaud, M. & Catonne, Y. Ossification of the ligamenta flava with severe myelopathy in a black patient. A case report. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 23(14):1607-8, Ruiz Santiago, F.; Alcázar Romero, P. P.; López Machado, E. & Garcia Espona, M. A. Calcification of lumbar ligamentum flavum and facet joints capsule. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 22(15):1734-5, van Oostenbrugge, R. J.; Herpers, M. J. & de Kruijk, J. R. Spinal cord compression caused by unusual location and extension of ossified ligamenta flava in a Caucasian male. A case report and literature review. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 24(5):486-8, Warwick, R. & Williams, P. L. Grey s Anatomy. 35 th ed. London, Longman Group Ltd., pp Xiong, L.; Zeng, Q. Y. & Jinkins, J. R. CT and MRI characteristics of ossification of ligamenta flava in the thoracic spine. Eur. Radiol., 11(9): , Yoshida, M.; Shima, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Tamaki, T. & Tanaka, T. Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Pathogenesis and morphologic and immunohistochemical observation. Spine (Phila. Pa. 1976), 17(11): ,
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
A morphometric study of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae
 Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 1, Issue: 4, July 2013, Pages
 Original article: Morphometry of first pedicle of sacrum and its clinical relevance Sinha Manisha B, Rathore Mrithunjay, Trivedi Soumitra, Siddiqui A U Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical
Original article: Morphometry of first pedicle of sacrum and its clinical relevance Sinha Manisha B, Rathore Mrithunjay, Trivedi Soumitra, Siddiqui A U Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population
 Original article Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population 1 Dr.Sreevidya.J, 2 Dr.Dharani.V, 3 Dr.Savithri.K, 4 Dr.Sudha Seshayyan 1Senior Assistant
Original article Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population 1 Dr.Sreevidya.J, 2 Dr.Dharani.V, 3 Dr.Savithri.K, 4 Dr.Sudha Seshayyan 1Senior Assistant
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Anatomy Lecture #19 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THORAX April 3, 2012
 Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Technique Guide. ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty.
 Technique Guide ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Table of Contents Introduction Overview 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications 5 Product Information
Technique Guide ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Table of Contents Introduction Overview 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications 5 Product Information
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
 J. Anat. (1999) 195, pp. 199 209, with 9 figures Printed in the United Kingdom 199 Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
J. Anat. (1999) 195, pp. 199 209, with 9 figures Printed in the United Kingdom 199 Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy.
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Osteology of the Thorax. Prof Oluwadiya K S
 Osteology of the Thorax Prof Oluwadiya K S www.oluwadiya.com The thoracic skeleton consists of the following: 12 pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages 12 thoracic vertebrae and their intervertebral
Osteology of the Thorax Prof Oluwadiya K S www.oluwadiya.com The thoracic skeleton consists of the following: 12 pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages 12 thoracic vertebrae and their intervertebral
Laminar Avulsion in a Cervical Vertebra
 Laminar Avulsion in a Cervical Vertebra CHRISTIAN V. CIMMINO AND DAVID W. SCOTT, III An unusual avulsion fracture involving the lamina of a cervical vertebra, most likely due to tear of a ligamentum flavum,
Laminar Avulsion in a Cervical Vertebra CHRISTIAN V. CIMMINO AND DAVID W. SCOTT, III An unusual avulsion fracture involving the lamina of a cervical vertebra, most likely due to tear of a ligamentum flavum,
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT.
 CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Laminar hook instrumentation in the cervical spine. An experimental study on the relation of hooks to the spinal cord
 Eur Spine J (2001) 10 :340 344 DOI 10.1007/s005860100251 ORIGINAL ARTICLE T. Fagerström R. Hedlund P. Bancel R. Robert B. Dupas Laminar hook instrumentation in the cervical spine. An experimental study
Eur Spine J (2001) 10 :340 344 DOI 10.1007/s005860100251 ORIGINAL ARTICLE T. Fagerström R. Hedlund P. Bancel R. Robert B. Dupas Laminar hook instrumentation in the cervical spine. An experimental study
ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty.
 ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Evaluation of Canal Diameter by MRI in Sudanese Population
 American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named.
 You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine. Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation
 Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques
 Dorsal Cervical Approaches Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Advantages Straightforward Easily
Dorsal Cervical Approaches Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Advantages Straightforward Easily
The sacrum is a complex anatomical structure.
 A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
A Morphometric study of lamina of lumbar vertebrae: A dry bone study conducted in RIMS, Imphal
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 11 Ver. 4 (November. 2018), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org A Morphometric study of lamina of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 11 Ver. 4 (November. 2018), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org A Morphometric study of lamina of
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE * QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries
 Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions:
 Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Am I eligible for the TOPS study? Possibly, if you suffer from one or more of the following conditions: Radiating leg pain Greater leg / buttock pain than back pain Severe pain sets in when walking as
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
The Thoracic Cage. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46350 1 The Thoracic Cage OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46350 1 The Thoracic Cage OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle. Suboccipital Triangle
 Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae
 Original Article Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae Gökflin fiengül Hakan Hadi KADIO LU ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: In this study, forty dried specimens of atlas and axis vertebrae were examined
Original Article Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae Gökflin fiengül Hakan Hadi KADIO LU ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: In this study, forty dried specimens of atlas and axis vertebrae were examined
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 117: 72 77 CASE REPORT Bilateral spondylolysis of inferior articular processes of the fourth lumbar vertebra: a case report TOMOAKI KOAKUTSU 1,2, NAOKI MOROZUMI
Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar spinal cord (conus medullaris) injuries
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-2011 Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 1-2011 Neurologic improvement after thoracic, thoracolumbar, and
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES
 AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
Sports Medicine Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
mild Devices Kit - Instructions for Use
 INDICATION FOR USE The Vertos mild Devices are specialized surgical instruments intended to be used to perform lumbar decompressive procedures for the treatment of various spinal conditions. CONTENTS AND
INDICATION FOR USE The Vertos mild Devices are specialized surgical instruments intended to be used to perform lumbar decompressive procedures for the treatment of various spinal conditions. CONTENTS AND
Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy. Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi. CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy
 Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy CVJ-Embryology SOMITE-The building block of vertebrae, skeletal muscle
Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy CVJ-Embryology SOMITE-The building block of vertebrae, skeletal muscle
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves in
A Patient s Guide to Neck Pain Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves in
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Thoracic Cooled-RF Training Presentation
 Thoracic Cooled-RF Training Presentation Patient Selection Anatomy Overview Neuroanatomy Lesion targets Technique Diagnostic Block Cooled-RF Precautions Summary Appendix AGENDA Patient Selection Thoracic
Thoracic Cooled-RF Training Presentation Patient Selection Anatomy Overview Neuroanatomy Lesion targets Technique Diagnostic Block Cooled-RF Precautions Summary Appendix AGENDA Patient Selection Thoracic
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
MD Bones & Joints of the Back. A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
Morphometry of Pedicle and Vertebral Body in a Mexican Population by CT and Fluroscopy
 Int. J. Morphol., 27(4):1299-1303, 2009. Morphometry of Pedicle and Vertebral Body in a Mexican Population by CT and Fluroscopy Morfometría del Cuerpo Vertebral y Pedículo en una Población Mexicana Mediante
Int. J. Morphol., 27(4):1299-1303, 2009. Morphometry of Pedicle and Vertebral Body in a Mexican Population by CT and Fluroscopy Morfometría del Cuerpo Vertebral y Pedículo en una Población Mexicana Mediante
