1.4 Historical Particulars and General laws
|
|
|
- Martin Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 14 What Is Evolutionary Theory? Darwin had no evidence for his position; it means that his argument was more complex than might first appear. Matters are much more straightforward now. Modern biologists have observed speciation events. Indeed, diey have even caused them. As will be discussed in Chapter 6, one standard (though not uncontroversial) idea about species is that they are reproductively isolated from each other. Two contemporary populations are said to belong to different species if they cannot produce viable fertile offspring with each other. Botanists have found that the chemical colchicine causes ploidy a modification in the number of chromosomes found in an organism. For example, by administering colchicine, a botanist can produce tetraploid plants that are reproductively isolated from tlieir diploid parents. The daughter and parent populations satisfy the requirement of reproductive isolation. We now have observational evidence that species boundaries are not cast in stone. In summary, Darwin advanced a claim about pattern and a claim about process. The pattern claim was that all terrestrial organisms are related genealogically; life forms a tree in which all contemporary species have a common ancestor if we go back far enough in time. The process claim was that natural selection is the principal cause of the diversity we observe among life forms. However, neither of these claims was the straightforward report of what Darwin saw. This raises the question of how a scientist can muster evidence for hypotheses that go beyond what is observed directly. I'll address this problem in Chapter Historical Particulars and General laws Some sciences try to discover general laws; others aim to uncover particular sequences of historical events. It isn't that the "hard" sciences only do the former and the "soft" sciences strive solely for the latter. Each broad discipline contains subareas that differ in how they emphasize one task or the other. Within physics, compare the different research problems that a particle physicist and an astronomer might investigate. The particle physicist might seek to identify general principles that govern a certain sort of particle collision. The laws to be stated describe what the outcome of such a collision would be, no matter where and no matter when it takes place. It is characteristic of our conception of laws that they should be universal; they are not limited to particular regions of space and time. Laws take the form of if/then statements. Isaac Newton's universal law of gravitation says that the gravitational attraction between any two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The law does not say that the universe contains two, four, or any number of objects. It just says what would be true if the universe contained objects with mass. In contrast, astronomers typically will be interested in obtaining information about a unique object. Focusing on a distant star, they might attempt to infer its temperature,
2 What Is Evolutionary Theory? 15 density, and size. Statements diat provide information of this sort are not if/then in form. Such statements describe historical particulars and do not state laws. This division between nomothetic ("nomos" is Greek for law) and historical sciences does not mean that each science is exclusively one or the other. The panicle physicist might find that the collisions of interest often occur on the surface of the sun; if so, a detailed study of that particular object might help to infer the general law. Symmetrically, the astronomer interested in obtaining an accurate description of the star might use various laws to help make the inference. Although the particle physicist and the astronomer may attend to both general laws and historical particulars, we can separate their two enterprises by distinguishing means from ends. The astronomer's problem is a historical one because the goal is to infer the properties of a particular object; the astronomer uses laws only as a means. Particle physics, on the other hand, is a nomothetic discipline because the goal is to infer general laws; descriptions of particular objects are relevant only as a means. The same division exists within evolutionary biology. When a systematist infers that human beings are more closely related to chimps than tfiey are to gorillas, this phylogenetic proposition describes a family ttee that connects three species. The proposition is logically of the same type as the proposition that says that Alice is more closely related to Betty than she is to Carl. Of course, the family tree pertaining to species connects bigger objects than the family tree that connects individual organisms. But this difference merely concerns the size of the objects in the tree, not the basic type of proposition that is involved. Reconstructing genealogical relationships is the goal of a historical science. The same can be said of much of paleobiology. Examining fossils allows the biologist to infer that various mass extinctions have taken place. Paleobiologists identify which species lived through these events and which did not. They try to explain why the mass extinctions took place. Why did some species survive while others did not? In similar fashion, a historian of our own species might try to explain the mass death of South American Indians following the Spanish Conquest. Once again, the units described differ in size. The paleobiologist focuses on whole species; a historian of the human past describes individual human beings and local populations. Phylogenetic reconstruction and paleobiology concern the distant past. But historical sciences, as I am using that term, often aim to characterize objects that exist in the present as well. A field naturalist may track gene or phenotypic frequencies in a particular population. This is what Kettlewell (1973) did in his investigation of industrial melanism in the peppered moth (Biston betularia). The project was to describe and explain a set of changes. Field naturalists usually wish to characterize particular objects, not to infer general laws. Are there general laws in evolutionary biology? Although some philosophers (Smart 1963; Beatty 1981) have said no, I want to point out that there are many interesting if/then generalizations afoot in evolutionary theory.
3 16 What Is Evolutionary Theory? Biologists usually don't call them "laws"; "model" is the preferred term. When biologists specify a model of a given kind of process, they describe the rules by which a system of a given kind changes. Models have the characteristic if/then format that we associate with scientific laws. These mathematical formalisms say what will happen if a certain set of conditions is satisfied by a system. They do not say when or where or how often those conditions are satisfied in nature. Consider an example. R. A. Fisher (1930), one of the founders of population genetics, described a set of assumptions dial entails that the sex ratio in a population should evolve to 1:1 and stay there. Mating must be at random, and parental pairs must differ in the mix of sons and daughters they produce (and this difference must be heritable). Fisher was able to show, given his assumptions, that selection will favor parental pairs that produce just the minority sex. For example, if the offspring generation has more males than females, a parental pair does best by producing all daughters. If the population sex ratio is biased in one direction, selection favors traits that reduce that bias. The result is an even mix of males and females. Fisher's model considers three generations parents produce offspring who then produce grandoffspring. What mix of sons and daughters should a parent produce if she is to maximize the number of grandoffspring she has? If there are N individuals in the grandoffspring generation, and if the offspring generation contains m males and / females, then the average son has Nlm offspring and the average daughter has /V/yf offspring. A mother thereby gains a benefit of Nlm from each of her sons and a benefit of A///* from each of her daughters these "benefits" being the number of grandoffspring they give her. So individuals in the offspring generation who are in the minority sex on average have more offspring. Hence, the best strategy for a mother is to produce offspring solely of the minority sex. On the other hand, if the sex ratio in the offspring generation is 1:1, a mother cannot do better than die other mothers in the population by having an uneven mix of sons and daughters. A 1:1 sex ratio is a stable equilibrium. A more exact description of Fisher's argument is provided in Box 1.3. Fisher's elegant model is mathematically correct. If there is life in distant galaxies that satisfies his starting assumptions, then a 1:1 sex ratio must evolve. Like Newton's universal law of gravitation, Fisher's model is not limited in its application to any particular place or time. And just as Fishers model may have millions of applications, it also may have none at all. The model is an if/dien statement; it leaves open the possibility that the ifi are never satisfied. Field naturalists have the job of saying whether Fisher's assumptions apply to this or that specific population. In deciding whether something is a law or a historical hypothesis, one must be clear about which proposition one wishes to classify. For example, to ask whether "natural selection" is a law is meaningless until one specifies which proposition about natural selection is at issue. To say that natural selection is responsible for the fact that human beings have opposable thumbs is to state a historical hypothesis; but to say that natural selection will lead to an even sex ratio in the circumstances that
4 Box 1.3 Fishers Sex Ratio Argument The accompanying text provides a simplified rendition of Fisher's argument. In point of fact, Fisher did not conclude that there should be equal numbers of males and females but that there should be equal investment. A mother has a total package of energy (7} that she can use to produce, her mix of sons and daughters. Suppose p is the percentage of energy she allots to sons, that each son costs c m units of energy to raise, and that a son brings in b, units of benefit. With a similar representation of die costs and benefits of daughters, a mothers total benefit from her sons and daughters is bjp'tlcj b f f(i - p)t/c f J. Suppose all mothers (the "residents") residing in the population allocate p and (1 - p) of their resources to sons and daughters, respectively. When will a mother do better by departing from this behavior i.e., by allotting/>* and (1 -/>*) to sons and daughters (where/) 9*/*)? This novel mother does better than the other mothers precisely when bjp'tlcj + b f l(i - p*)t/c f \ > bjptlcj + b f [(, - p)t/c f J, which simplifies to (bjc, - b/c f )(p' - p) > o. Recall from the accompanying text that a son provides a benefit of Nlm and a daughter provides a benefit of N/f. Substituting these for the benefit terms in die above expression, we obtain (Nlmc m - N/fcfXp* - p) > o. When the residents invest equally in sons and daughters (mc, -fry), no mutant strategy can do better than the resident strategy. And when the residents invest /.^/equally, a mutant will do better than the residents by investing exclusively in the sex in which the residents have «W«invested. How does investment in the two sexes affect the numbers of sons and daughters produced? In human beings, males have a higher mortality rate, both prenatally and postnatally. This means that the average son costs less than the average daughter. In, this case, equal investment entails that an excess of males is produced at birth, which is what we observe. Fisher's argument assumes that there is random mating in the offspring generation. The import of this assumption was first explored by Hamilton (1967). If there is strict brother/sister mating, then a parent maximizes the number of grandoffspring she has by producing a female-biased sex ratio among her progeny.
5 18 What Is Evolutionary Theory? Fisher described is to state a law. (Evolutionary laws will be discussed further in Section 3.4.) Although inferring laws and reconstructing history arc distinct scientific goals, they often are fruitfully pursued together. Theoreticians hope their models are not vacuous; they want them to apply to the real world of living organisms. Likewise, naturalists who describe the present and past of particular species often do so with an eye to providing data that have a wider theoretical significance. Nomothetic and historical disciplines in evolutionary biology have much to learn from each other. An example of a particularly recalcitrant problem in current theory may help make this clear. We presently do not understand why sexual reproduction is as prevalent as it is. The problem is not that theoreticians cannot write models in which sexual reproduction is advantageous. There are lots of such models, each of them mathematically correct. Indeed, there also are many models that show that under specified conditions, sex will be ^/^advantageous. The difficulty is not that the models are wrong as if/then statements but that they often fail to apply to nature. In the real world, some species are sexual, whereas others are not. These different species live under a variety of conditions, and their phylogenetic backgrounds differ as well. What we would like is a model tfiat fits the diversity we observe. To date, no model can claim to do this. If model building (the pursuit of laws) proceeded independently of natural history, the evolution of sex would not be puzzling. A model can easily show how sex might have evolved; if the assumptions of the model were satisfied by some natural population, that population would evolve a sexual mode of reproduction. It is a historical question whether this or that population actually satisfied the assumptions in the model. Only by combining laws and history can one say why sex didevolve. 1.5 The Causes of Evolution Although die data of natural history are indispensable to evolutionary model building, there is a place for model building that floats free from the details of what we have observed. Fisher (1930, pp. viii-ix) put the point well when he remarked that "no practical biologist interested in sexual reproduction would be led to work out the detailed consequences experienced by organisms having three or more sexes; yet what else should he do if he wishes to understand why the sexes are, in fact, always two?" We often understand the actual world by locating it in a broader space of possibilities. Models map out the possible causes of evolution. What are these possible causes? I have already mentioned natural selection; heritable variation in fitness can produce evolution. And in Section 1.1,1 explained how the system of mating in a population can modify the frequencies of different genotypes. There are other possible causes as well. Gene frequencies can change because of mutation. A population that is 100 percent A can evolve away from this homogeneous state if A genes mutate into a genes. A
Special Supplement Part II. The AWAKENING Does Scientific Evidence Support the Existence of a Divine Creator?
 Special Supplement Part II The AWAKENING Does Scientific Evidence Support the Existence of a Divine Creator? The Flawed Theory of Evolution FACT:Although science has developed a vernacular, which include
Special Supplement Part II The AWAKENING Does Scientific Evidence Support the Existence of a Divine Creator? The Flawed Theory of Evolution FACT:Although science has developed a vernacular, which include
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 12 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 We want to understand the reasons
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 12 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 We want to understand the reasons behind the lifestyles of our non-human primate relatives
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 12 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 We want to understand the reasons behind the lifestyles of our non-human primate relatives
Bio 1M: Evolutionary processes
 Bio 1M: Evolutionary processes Evolution by natural selection Is something missing from the story I told last chapter? Heritable variation in traits Selection (i.e., differential reproductive success)
Bio 1M: Evolutionary processes Evolution by natural selection Is something missing from the story I told last chapter? Heritable variation in traits Selection (i.e., differential reproductive success)
Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example. 2 Patterns of evolution. Similarities and differences. History
 Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example Humans are an example of a biological species that has evolved Possibly of interest, since many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example Humans are an example of a biological species that has evolved Possibly of interest, since many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye
 Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2008 As we have seen before, the bottom line
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2008 As we have seen before, the bottom line in evolution is reproductive success reproductive success:
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2008 As we have seen before, the bottom line in evolution is reproductive success reproductive success:
Chapter 12: Evolutionary Invasion Analysis
 Supplementary material to: From: Chapter 1: Evolutionary Invasion Analysis A Biologist s Guide to Mathematical Modeling in Ecology and Evolution S. P. Otto and T. Day (005) Princeton University Press Supplementary
Supplementary material to: From: Chapter 1: Evolutionary Invasion Analysis A Biologist s Guide to Mathematical Modeling in Ecology and Evolution S. P. Otto and T. Day (005) Princeton University Press Supplementary
We are an example of a biological species that has evolved
 Bio 1M: Primate evolution (complete) 1 Patterns of evolution Humans as an example We are an example of a biological species that has evolved Many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Bio 1M: Primate evolution (complete) 1 Patterns of evolution Humans as an example We are an example of a biological species that has evolved Many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance
 Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns
Chapter 6 Patterns of Inheritance Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns Genetics can explain how these poodles look different. Section 10.1 Genetics Explains and Predicts Inheritance Patterns
Selection at one locus with many alleles, fertility selection, and sexual selection
 Selection at one locus with many alleles, fertility selection, and sexual selection Introduction It s easy to extend the Hardy-Weinberg principle to multiple alleles at a single locus. In fact, we already
Selection at one locus with many alleles, fertility selection, and sexual selection Introduction It s easy to extend the Hardy-Weinberg principle to multiple alleles at a single locus. In fact, we already
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation. Dr. Amjad Mahasneh. Jordan University of Science and Technology
 Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
A gene is a sequence of DNA that resides at a particular site on a chromosome the locus (plural loci). Genetic linkage of genes on a single
 8.3 A gene is a sequence of DNA that resides at a particular site on a chromosome the locus (plural loci). Genetic linkage of genes on a single chromosome can alter their pattern of inheritance from those
8.3 A gene is a sequence of DNA that resides at a particular site on a chromosome the locus (plural loci). Genetic linkage of genes on a single chromosome can alter their pattern of inheritance from those
Chapter 1 Review Questions
 Chapter 1 Review Questions 1.1 Why is the standard economic model a good thing, and why is it a bad thing, in trying to understand economic behavior? A good economic model is simple and yet gives useful
Chapter 1 Review Questions 1.1 Why is the standard economic model a good thing, and why is it a bad thing, in trying to understand economic behavior? A good economic model is simple and yet gives useful
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior
 Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
Chapter 02 Developing and Evaluating Theories of Behavior Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n): A. plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the
Walking upright Specific changes in chewing design: teeth, jaws and skull. Homonoidea, Hominidae, Hominininae, Hominini, Hominina, Homo
 Bio 1M: Hominins (complete) 1 Emergence Hominins refer to people and our upright ancestors Characterized by: Walking upright Specific changes in chewing design: teeth, jaws and skull Taxonomy Homonoidea,
Bio 1M: Hominins (complete) 1 Emergence Hominins refer to people and our upright ancestors Characterized by: Walking upright Specific changes in chewing design: teeth, jaws and skull Taxonomy Homonoidea,
Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y
 Name Date Period Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y Introduction: A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships.
Name Date Period Chapter 7: Pedigree Analysis B I O L O G Y Introduction: A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships.
Trait characteristic (hair color) Gene segment of DNA Allele a variety of a trait (brown hair or blonde hair)
 Evolution Change in DNA to favor certain traits over multiple generations Adaptations happen within a single generations Evolution is the result of adding adaptations together Evolution doesn t have a
Evolution Change in DNA to favor certain traits over multiple generations Adaptations happen within a single generations Evolution is the result of adding adaptations together Evolution doesn t have a
Authors Knowing something about the authors can illuminate the topic of the paper. Where does Robert Brooks work, and what does he usually research?
 Dissecting a scientific paper about evolutionary biology II Now that you ve had a guided tour of one scientific paper, it s time to attack another one with a little less assistance. The sections below
Dissecting a scientific paper about evolutionary biology II Now that you ve had a guided tour of one scientific paper, it s time to attack another one with a little less assistance. The sections below
Genes and Inheritance (11-12)
 Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Genes and Inheritance (11-12) You are a unique combination of your two parents We all have two copies of each gene (one maternal and one paternal) Gametes produced via meiosis contain only one copy of
Laboratory. Mendelian Genetics
 Laboratory 9 Mendelian Genetics Biology 171L FA17 Lab 9: Mendelian Genetics Student Learning Outcomes 1. Predict the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of a monohybrid cross. 2. Determine whether a gene is
Laboratory 9 Mendelian Genetics Biology 171L FA17 Lab 9: Mendelian Genetics Student Learning Outcomes 1. Predict the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of a monohybrid cross. 2. Determine whether a gene is
Hypothesis-Driven Research
 Hypothesis-Driven Research Research types Descriptive science: observe, describe and categorize the facts Discovery science: measure variables to decide general patterns based on inductive reasoning Hypothesis-driven
Hypothesis-Driven Research Research types Descriptive science: observe, describe and categorize the facts Discovery science: measure variables to decide general patterns based on inductive reasoning Hypothesis-driven
Pedigree Construction Notes
 Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
Name Date Pedigree Construction Notes GO TO à Mendelian Inheritance (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson3.html) When human geneticists first began to publish family studies, they used a variety
The Evolution of Sex. Or, why do we even need males?
 The Evolution of Sex Or, why do we even need males? Sexual VS Asexual reproduction Sexual Fewer offspring/individual Only half of genes passed on Good genotypes are lost Offspring are variable Asexual
The Evolution of Sex Or, why do we even need males? Sexual VS Asexual reproduction Sexual Fewer offspring/individual Only half of genes passed on Good genotypes are lost Offspring are variable Asexual
QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT
 Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Goals of Pedigree Analysis Basic Symbols More Symbols Y-Linked Inheritance
 Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
Pedigree Analysis Why do Pedigrees? Punnett squares and chi-square tests work well for organisms that have large numbers of offspring and controlled mating, but humans are quite different: Small families.
t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved
 t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You may print this text out and use
t-test for r Copyright 2000 Tom Malloy. All rights reserved This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You may print this text out and use
November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems. The evolution of sex ratio
 November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems The evolution of sex ratio - let us define sex ratio as the proportion of males to females. - in discussing the evolution
November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems The evolution of sex ratio - let us define sex ratio as the proportion of males to females. - in discussing the evolution
NAME: PID: Group Name: BioSci 110, Fall 08 Exam 3
 For questions 1 and 2 use the phylogeny to the right. 1. With what group of species do rodents share the most traits? a. amphibians b. dinosaurs and birds c. *primates d. ray-finned fish e. sharks 2. Which
For questions 1 and 2 use the phylogeny to the right. 1. With what group of species do rodents share the most traits? a. amphibians b. dinosaurs and birds c. *primates d. ray-finned fish e. sharks 2. Which
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 We want to understand the reasons
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 We want to understand the reasons behind the lifestyles of our non-human primate relatives
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 13 Mating: Primate females and males Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 We want to understand the reasons behind the lifestyles of our non-human primate relatives
Family Trees for all grades. Learning Objectives. Materials, Resources, and Preparation
 page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
The scope of perceptual content, II: properties
 The scope of perceptual content, II: properties Jeff Speaks November 16, 2009 1 What are the candidates?............................ 1 2 Arguments for inclusion............................. 2 2.1 From
The scope of perceptual content, II: properties Jeff Speaks November 16, 2009 1 What are the candidates?............................ 1 2 Arguments for inclusion............................. 2 2.1 From
Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs. Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs
 Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs Research by Gerhardt et al. (1996). Males call to attract females. Males call to attract females Ribbet! Figure 11.27 Tiny and super cute!
Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs Female Choice in Gray Tree Frogs Research by Gerhardt et al. (1996). Males call to attract females. Males call to attract females Ribbet! Figure 11.27 Tiny and super cute!
What we mean more precisely is that this gene controls the difference in seed form between the round and wrinkled strains that Mendel worked with
 9/23/05 Mendel Revisited In typical genetical parlance the hereditary factor that determines the round/wrinkled seed difference as referred to as the gene for round or wrinkled seeds What we mean more
9/23/05 Mendel Revisited In typical genetical parlance the hereditary factor that determines the round/wrinkled seed difference as referred to as the gene for round or wrinkled seeds What we mean more
The Nature of Behavior. By: Joe, Stephen, and Elisha
 The Nature of Behavior By: Joe, Stephen, and Elisha Genes- The Fundamentals Biology and its affects on us is most easily understood through starting small, molecular even, and working upwards until a whole
The Nature of Behavior By: Joe, Stephen, and Elisha Genes- The Fundamentals Biology and its affects on us is most easily understood through starting small, molecular even, and working upwards until a whole
Downloaded from
 Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and Variations Chapter No. Chapter Name Concepts Degree of imp. Ref. NCERT text book.: page nos Common errors 5 Principles of inheritance and variations 1. Mendel s
Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and Variations Chapter No. Chapter Name Concepts Degree of imp. Ref. NCERT text book.: page nos Common errors 5 Principles of inheritance and variations 1. Mendel s
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Name Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2. Explain the law
Name Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2. Explain the law
Biological scientists use a process of inquiry that has developed over centuries and involves the collaboration of a global community.
 Principles of Biology contents 3 Practicing Biology Biological scientists use a process of inquiry that has developed over centuries and involves the collaboration of a global community. Biologists study
Principles of Biology contents 3 Practicing Biology Biological scientists use a process of inquiry that has developed over centuries and involves the collaboration of a global community. Biologists study
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts
 Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Mendelian Genetics and Beyond Chapter 4 Study Prompts 1. What is a mode of inheritance? 2. Can you define the following? a. Autosomal dominant b. Autosomal recessive 3. Who was Gregor Mendel? 4. What did
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP!
 Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Are your feelings just another evolutionary adaptation? A discussion of the field of evolutionary psychology
 Are your feelings just another evolutionary adaptation? A discussion of the field of evolutionary psychology Psychology The study of behavior and mental function Goal is to understand behavior Evolutionary
Are your feelings just another evolutionary adaptation? A discussion of the field of evolutionary psychology Psychology The study of behavior and mental function Goal is to understand behavior Evolutionary
Mendelian Genetics. Gregor Mendel. Father of modern genetics
 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Father of modern genetics Objectives I can compare and contrast mitosis & meiosis. I can properly use the genetic vocabulary presented. I can differentiate and gather data
Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Father of modern genetics Objectives I can compare and contrast mitosis & meiosis. I can properly use the genetic vocabulary presented. I can differentiate and gather data
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy
 Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
Durkheim. Durkheim s fundamental task in Rules of the Sociological Method is to lay out
 Michelle Lynn Tey Meadow Jane Jones Deirdre O Sullivan Durkheim Durkheim s fundamental task in Rules of the Sociological Method is to lay out the basic disciplinary structure of sociology. He begins by
Michelle Lynn Tey Meadow Jane Jones Deirdre O Sullivan Durkheim Durkheim s fundamental task in Rules of the Sociological Method is to lay out the basic disciplinary structure of sociology. He begins by
EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly.
 Name: 1 NAME: EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly. 1) Describe the following concepts in a few sentences (2 points each)
Name: 1 NAME: EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly. 1) Describe the following concepts in a few sentences (2 points each)
GENETICS - NOTES-
 GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
Mechanisms of Evolution. Macroevolution. Speciation. MICROEVOLUTION - A change in the frequency of alleles. Review population genetics Ch. 23.
 Mechanisms of Evolution Macroevolution Speciation MICROEVOLUTION - A change in the frequency of alleles. Review population genetics Ch. 23. MACROEVOLUTION - Speciation (or emergence of higher taxonomic
Mechanisms of Evolution Macroevolution Speciation MICROEVOLUTION - A change in the frequency of alleles. Review population genetics Ch. 23. MACROEVOLUTION - Speciation (or emergence of higher taxonomic
Chapter 15 Review Page 1
 hapter 15 Review Page 1 1 ased on the results of this cross, you determine that the allele for round eyes is linked to the allele for no tooth. round eyes are dominant to vertical eyes, and the absence
hapter 15 Review Page 1 1 ased on the results of this cross, you determine that the allele for round eyes is linked to the allele for no tooth. round eyes are dominant to vertical eyes, and the absence
What Do You Call One Set Of Instructions For An Inherited Trait
 What Do You Call One Set Of Instructions For An Inherited Trait What would you like to do? Flag. What do scientist call instructions for an inherited traits? What do What do you call one set of instuctions
What Do You Call One Set Of Instructions For An Inherited Trait What would you like to do? Flag. What do scientist call instructions for an inherited traits? What do What do you call one set of instuctions
Ch. 24 Speciation BIOL 221
 Ch. 24 Speciation BIOL 221 Speciation Speciation Origin of new, is at the focal point of evolutionary theory Microevolution consists of adaptations that evolve within a population confined to one gene
Ch. 24 Speciation BIOL 221 Speciation Speciation Origin of new, is at the focal point of evolutionary theory Microevolution consists of adaptations that evolve within a population confined to one gene
Behavioral genetics: The study of differences
 University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Faculty Research and Publications http://opus.uleth.ca Lalumière, Martin 2005 Behavioral genetics: The study of differences Lalumière, Martin L. Department
University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Faculty Research and Publications http://opus.uleth.ca Lalumière, Martin 2005 Behavioral genetics: The study of differences Lalumière, Martin L. Department
CHAPTER 16 POPULATION GENETICS AND SPECIATION
 CHAPTER 16 POPULATION GENETICS AND SPECIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes a population? a. dogs and cats living in Austin, Texas b. four species of fish living in a pond c. dogwood
CHAPTER 16 POPULATION GENETICS AND SPECIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes a population? a. dogs and cats living in Austin, Texas b. four species of fish living in a pond c. dogwood
Chapter 3A: ESS in two easy lessons
 Chapter 3 Chapter 3A: ESS in two easy lessons The purpose of this chapter is to review some classical examples of evolutionary game theory models for behavior and life-history traits, and give an indication
Chapter 3 Chapter 3A: ESS in two easy lessons The purpose of this chapter is to review some classical examples of evolutionary game theory models for behavior and life-history traits, and give an indication
6. A theory that has been substantially verified is sometimes called a a. law. b. model.
 Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A theory is a(n) a. a plausible or scientifically acceptable, well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world. b. a well-substantiated explanation
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies
 Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook.
 This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook. Chromosomal basis of genes and linkage The majority of chapter 4 deals with the details of mitosis and meiosis. This
This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook. Chromosomal basis of genes and linkage The majority of chapter 4 deals with the details of mitosis and meiosis. This
Honors Biology Test Chapter 9 - Genetics
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 9 - Genetics 1. The exceptions to the rule that every chromosome is part of a homologous pair are the a. sex chromosomes. c. linked chromosomes. b. autosomes. d. linked autosomes.
Honors Biology Test Chapter 9 - Genetics 1. The exceptions to the rule that every chromosome is part of a homologous pair are the a. sex chromosomes. c. linked chromosomes. b. autosomes. d. linked autosomes.
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3
 Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Unit 7 Section 2 and 3 Evidence 12: Do you think food preferences are passed down from Parents to children, or does the environment play a role? Explain your answer. One of the most important outcomes
Models of Parent-Offspring Conflict Ethology and Behavioral Ecology
 Models of Parent-Offspring Conflict Ethology and Behavioral Ecology A. In this section we will look the nearly universal conflict that will eventually arise in any species where there is some form of parental
Models of Parent-Offspring Conflict Ethology and Behavioral Ecology A. In this section we will look the nearly universal conflict that will eventually arise in any species where there is some form of parental
Children s Ideas. Children s Ideas Page 1
 Children s Ideas Children come to science instruction with a diverse set of ideas about natural objects and events and how things work. These ideas are fairly tenacious after all, they were developed based
Children s Ideas Children come to science instruction with a diverse set of ideas about natural objects and events and how things work. These ideas are fairly tenacious after all, they were developed based
THE CHROMOSOME SHUFFLE Activity by Thomas Mueller - RHS (with reference to several articles) Modified by Larry Flammer
 THE CHROMOSOME SHUFFLE Activity by Thomas Mueller - RHS (with reference to several articles) Modified by Larry Flammer Anti- evolutionists suggest that evolution cannot be correct according to their naive
THE CHROMOSOME SHUFFLE Activity by Thomas Mueller - RHS (with reference to several articles) Modified by Larry Flammer Anti- evolutionists suggest that evolution cannot be correct according to their naive
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Name Period Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2.
Name Period Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2.
Chromosomes and Human Inheritance. Chapter 11
 Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Chapter 11 11.1 Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes and Human Inheritance Chapter 11 11.1 Human Chromosomes Human body cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 22 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Darwin s dilemma 8/14/2014. Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer Mitosis & Meiosis. The Modern Synthesis
 Darwin s dilemma 1 Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer 2014 How do organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring? The Modern Synthesis 2 Mitosis & Meiosis 3 1844 - Darwin essay on Natural Selection
Darwin s dilemma 1 Meiosis & Inheritance Lecture 18 Summer 2014 How do organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring? The Modern Synthesis 2 Mitosis & Meiosis 3 1844 - Darwin essay on Natural Selection
Q1.Darwin s theory of natural selection states that all living things have evolved from simple life forms.
 VARIATION AND EVOLUTION. NAME.. Q.Darwin s theory of natural selection states that all living things have evolved from simple life forms. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
VARIATION AND EVOLUTION. NAME.. Q.Darwin s theory of natural selection states that all living things have evolved from simple life forms. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
Psychology. Genes, Evolution, and Environment CHAPTER , 2011, 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Psychology CHAPTER3 Genes, Evolution, and Environment Unlocking the Secrets of Genes LO3.1 Explain how genes, chromosomes, DNA, genomes, and epigenetics all relate to one another. Evolutionary psychology
Psychology CHAPTER3 Genes, Evolution, and Environment Unlocking the Secrets of Genes LO3.1 Explain how genes, chromosomes, DNA, genomes, and epigenetics all relate to one another. Evolutionary psychology
Evolution of genetic systems
 Evolution of genetic systems Joe Felsenstein GENOME 453, Autumn 2013 Evolution of genetic systems p.1/24 How well can we explain the genetic system? Very well Sex ratios of 1/2 (C. Dusing, " 1884, W. D.
Evolution of genetic systems Joe Felsenstein GENOME 453, Autumn 2013 Evolution of genetic systems p.1/24 How well can we explain the genetic system? Very well Sex ratios of 1/2 (C. Dusing, " 1884, W. D.
This question is taken directly from the list of second test study questions (#6) it should not be a surprise...
 1. Female choice of males that have exaggerated characters has been explained by female choice of males that have better genes. Explain how female choice of higher quality males might lead to exaggerated
1. Female choice of males that have exaggerated characters has been explained by female choice of males that have better genes. Explain how female choice of higher quality males might lead to exaggerated
MECHANISMS AND PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION
 MECHANISMS AND PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION Evolution What is it again? Evolution is the change in allele frequencies of a population over generations Mechanisms of Evolution what can make evolution happen? 1.
MECHANISMS AND PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION Evolution What is it again? Evolution is the change in allele frequencies of a population over generations Mechanisms of Evolution what can make evolution happen? 1.
One Stop Shop For Educator
 One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance
 Chapter 3. Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance 1. Mendel s Study of Heredity 2. Applications of Mendel s Principles 3. Formulating and Testing Genetic Hypothesis 4. Mendelian Principles in Human
Chapter 3. Mendelism: the Basic principles of Inheritance 1. Mendel s Study of Heredity 2. Applications of Mendel s Principles 3. Formulating and Testing Genetic Hypothesis 4. Mendelian Principles in Human
To conclude, a theory of error must be a theory of the interaction between human performance variability and the situational constraints.
 The organisers have provided us with a both stimulating and irritating list of questions relating to the topic of the conference: Human Error. My first intention was to try to answer the questions one
The organisers have provided us with a both stimulating and irritating list of questions relating to the topic of the conference: Human Error. My first intention was to try to answer the questions one
By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES
 Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts)
 Biol 321 Quiz #2 Spring 2010 40 pts NAME See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance
Biol 321 Quiz #2 Spring 2010 40 pts NAME See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance
Heredity and Meiosis AP BIOLOGY. Heredity. Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142. Slide 4 / 142. Slide 3 / 142. Slide 6 / 142. Slide 5 / 142.
 Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142 AP BIOLOGY Heredity Slide 3 / 142 Slide 4 / 142 Heredity Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Heredity & Meiosis Law of Independent Assortment What Mendel Didn't
Slide 1 / 142 Slide 2 / 142 AP BIOLOGY Heredity Slide 3 / 142 Slide 4 / 142 Heredity Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Heredity & Meiosis Law of Independent Assortment What Mendel Didn't
Patterns of Inheritance
 1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
1 Patterns of Inheritance Bio 103 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Topics Mendel s Principles Variations on Mendel s Principles Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes 3 Experimental
Unit 4 Structure, Function and Information Processing
 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful
Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful
Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME
 Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME 1. (5 pts.) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance is excluded by the data C =
Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME 1. (5 pts.) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance is excluded by the data C =
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1
 Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Traits and Probability
 6.5 Traits and Probability KEY CONCEPT The inheritance of traits follows the rules of probability. S Punnett squares illustrate genetic crosses. A monohybrid cross involves one trait. A dihybrid cross
6.5 Traits and Probability KEY CONCEPT The inheritance of traits follows the rules of probability. S Punnett squares illustrate genetic crosses. A monohybrid cross involves one trait. A dihybrid cross
The Scientific Method
 Course "Empirical Evaluation in Informatics" The Scientific Method Prof. Dr. Lutz Prechelt Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Informatik http://www.inf.fu-berlin.de/inst/ag-se/ Science and insight
Course "Empirical Evaluation in Informatics" The Scientific Method Prof. Dr. Lutz Prechelt Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Informatik http://www.inf.fu-berlin.de/inst/ag-se/ Science and insight
THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS
 THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS HOW DOES A POPULATION OF PENGUINS EVOLVE? Every year, king penguins return to breed in the same colony in which they are born. These colonies help penguins to guard, protect
THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS HOW DOES A POPULATION OF PENGUINS EVOLVE? Every year, king penguins return to breed in the same colony in which they are born. These colonies help penguins to guard, protect
Schedule Change! Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution. Perplexing Observations. We owe much of our understanding of EVOLUTION to CHARLES DARWIN.
 Schedule Change! Film and activity next Friday instead of Lab 8. (No need to print/read the lab before class.) Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution Part 1: Darwin s Theory What is evolution?? And
Schedule Change! Film and activity next Friday instead of Lab 8. (No need to print/read the lab before class.) Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution Part 1: Darwin s Theory What is evolution?? And
Our genes are arrayed along 23 pairs of chromosomes. On rare occasion, a mutation can change their order.
 THE CHROMOSOME SHUFFLE Activity by Thomas Mueller - RHS (with reference to several articles) Creation Scientists (an oxymoron if ever there was one) suggest that Evolution cannot be correct according to
THE CHROMOSOME SHUFFLE Activity by Thomas Mueller - RHS (with reference to several articles) Creation Scientists (an oxymoron if ever there was one) suggest that Evolution cannot be correct according to
Natural Selection. Watch mec
 B Natural Selection Learning Outcome: 1. Variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve over time. 2. Natural selection (survival of the fittest) occurs when more offspring
B Natural Selection Learning Outcome: 1. Variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve over time. 2. Natural selection (survival of the fittest) occurs when more offspring
Audio: In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2
 Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
Overview of Animal Breeding
 Overview of Animal Breeding 1 Required Information Successful animal breeding requires 1. the collection and storage of data on individually identified animals; 2. complete pedigree information about the
Overview of Animal Breeding 1 Required Information Successful animal breeding requires 1. the collection and storage of data on individually identified animals; 2. complete pedigree information about the
Activity 19 Great Ideas in the History of Psychology. Purpose
 Activity 19 Great Ideas in the History of Psychology Purpose This activity will involve you in a search for information about when and why some of the great questions of psychology were first addressed
Activity 19 Great Ideas in the History of Psychology Purpose This activity will involve you in a search for information about when and why some of the great questions of psychology were first addressed
Advanced points about the Fisher model.
 Advanced points about the Fisher model. 1. Strictly speaking, the solution for a* is not an ESS, because the second derivative is equal to zero. That is a consequence of the assumption of infinite population
Advanced points about the Fisher model. 1. Strictly speaking, the solution for a* is not an ESS, because the second derivative is equal to zero. That is a consequence of the assumption of infinite population
Chapter 23. Population Genetics. I m from the shallow end of the gene pool AP Biology
 Chapter 23. Population Genetics I m from the shallow end of the gene pool 1 Essential Questions How can we measure evolutionary change in a population? What produces the variation that makes evolution
Chapter 23. Population Genetics I m from the shallow end of the gene pool 1 Essential Questions How can we measure evolutionary change in a population? What produces the variation that makes evolution
When the last member of a species dies without any surviving
 89 Here Today, Gone Tomorrow? TA L K I N G I T OV E R When the last member of a species dies without any surviving offspring, we say that that species has become extinct. Every species alive today is related
89 Here Today, Gone Tomorrow? TA L K I N G I T OV E R When the last member of a species dies without any surviving offspring, we say that that species has become extinct. Every species alive today is related
When the last member of a species dies without any surviving
 89 Here Today, Gone Tomorrow? ta l k i n g i t ov e r When the last member of a species dies without any surviving offspring, we say that that species has become extinct. Every species alive today is related
89 Here Today, Gone Tomorrow? ta l k i n g i t ov e r When the last member of a species dies without any surviving offspring, we say that that species has become extinct. Every species alive today is related
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design
 11-1 Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design Advantages and Limitations Comparing Two Groups Comparing t Test to ANOVA Independent Samples t Test Independent Samples ANOVA Comparing
11-1 Chapter 11. Experimental Design: One-Way Independent Samples Design Advantages and Limitations Comparing Two Groups Comparing t Test to ANOVA Independent Samples t Test Independent Samples ANOVA Comparing
Vocabulary. Bias. Blinding. Block. Cluster sample
 Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
Natural Selection: Peppered Moth Simulation and MRSA
 Name Date Period In this internet lesson, you will learn about a classic example of natural selection that occurred during the beginning of the industrial age and about modern issues with bacterial natural
Name Date Period In this internet lesson, you will learn about a classic example of natural selection that occurred during the beginning of the industrial age and about modern issues with bacterial natural
Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species
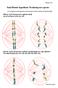 Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species Let us begin by reviewing the crucial moment in which mitosis and meiosis differ. Mitosis: Each chromosome replicates itself; one of each goes to the new
Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species Let us begin by reviewing the crucial moment in which mitosis and meiosis differ. Mitosis: Each chromosome replicates itself; one of each goes to the new
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs:
 Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Take a look at the three adult bears shown in these photographs: Which of these adult bears do you think is most likely to be the parent of the bear cubs shown in the photograph on the right? How did you
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1
 Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Chapter 10 Notes Patterns of Inheritance, Part 1 I. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) a. Austrian monk with a scientific background b. Conducted numerous hybridization experiments with the garden pea, Pisum sativum,
Evolutionary Psychology. by Elizabeth Anderson
 Evolutionary Psychology by Elizabeth Anderson Questions! What, according to Evolutionary Psychologists, do humans look for in a mate?! How might rape be explained according to Evolutionary Psychology?
Evolutionary Psychology by Elizabeth Anderson Questions! What, according to Evolutionary Psychologists, do humans look for in a mate?! How might rape be explained according to Evolutionary Psychology?
