Lecture Notes - Consciousness. What are you happy to lose everyday but happier to find the next?
|
|
|
- Theodore Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 What are you happy to lose everyday but happier to find the next? Consciousness - again, we find a psychological concept that is nearly impossible to define - an awareness of our world and our own mental processes Ok that might work. But even it does, what about other people s consciousness? We might know we know our minds, but do we know other people are conscious? What about dogs? Chimps? Robots? And yes, zombies? we don t know if zombies, truly exist, but since you don t know another person s consciousness, you don t know if they are not a zombie! I mean a zombie can walk, pursue a goal and do most things we do, but are they alive? Aware? What about simply defining it as ourself who we the little person in our head that takes in info, processes the info and then acts (Nash, 2008). Ok, if we go with that, who is in that person s head? Cotard s syndrome belief that a person is dead, half-dead, or a part of their body is not working Theory of mind = empathy for others - insight for self Autism? Is it chemical? Some drugs can take away a person s consciousness. Can some drugs give a zombie consciousness?
2 2 Is your thought right now just a combination of 180 neural transmitters? If you give someone else the exact same chemical mix will they have your awareness It is not an on or off thing there are different types of consciousness but if we can t define one, how can we define subsections? There is one student right now who is not reading this because that student is daydreaming. What type of consciousness is that? The brain is working but usually on familiar things- default network This can be bad if the person is overly worrying about the same thing constantly Can you not day dream? thought suppression Very tough to do thought suppression rebound try to not think of your breathing pattern. o mindfulness OK, if we can t define consciousness, what about unconsciousness? Try not to read the following word. Try to sound it out or to use bottom up processing instead of having your unconscious just hand it to you. HELLO History 1. Rene Descartes Cartesian Theatre Dualism again the mind body problem Most people like this - religion Monism (materialism) mind is brain Modern view: The brain is what the mind does or vice versa
3 3 2. Wilhem Wundt through introspection wanted subjects to be able to report their own changing structure states of consciousness 3. William James wrote about functions of normal consciousness 4. Sigmund Freud argued about consciousness vs. unconsciousness 5. B.F. Skinner Behaviorism s -there is no consciousness, only Stimulus / Response More recently with advanced medical techniques: MRI, PET, CAT, EEG, fmri We can begin to study physiological representations of consciousness but a representation is not consciousness The insula and prefrontal cortex are the brain parts involved in consciousness The unconscious mind is active. Of course we don t know how active Freud said the unconscious mind was intelligent, motivated and steered our conscious mind but then -- -Freud said a lot of thingsespecially about your mother. -The unconscious is full of nasty, freaky things that we must never know so we repress it - Freudian Slip when you say one thing but mean your mother Modern psychologist agree the mind is active but aren t sure if it is as clever as Freud s depiction of it. 1. Maybe it is a dumb servant that does the routine work that we have already learned well walking, 2. But the problem is when the dumb servant makes decisions that are better left to our rational conscious mind.
4 4 Four basic properties - ADD 1. Intentionality being directed toward an object awareness can be directed 2. Unity resistance to division - cannot multitask Except for easy tasks attention can be divided a. practice makes tasks easy a. cerebellum B.B.B. b. procedural memory b. neural connections neurons that fire together wire together plasticity - long term potentiation Multitasking depends on the effort & practice of each task. Driving & cell phones 3. Selectivity to include some objects but not others filtering process ADD is trouble with ignoring stuff not a lack of attention Dichotic listening people cannot pay attention to two different messages at the same time o Bottleneck Donald Broadbent as soon as the two stimuli become complex or require thought we can t do both Broadbent s filter But say the word sex or mention someone s name and they notice it. cocktail party phenomenon 1. can you select the target of your attention 2. a person is aware of others conversation 3. bit of awareness even when our spotlight is on one thing, we can react to others outside the spotlight 4. Transience the mind wanders William James stream consciousness. Attention = consciousness = awareness? Consciousness as a spotlight Imagine attention as a battery, the more things you ask it to do, the less power each one gets!
5 5 ADD difficulty selecting targets like 10 people all talking to you at once It is not a deficit in attention! Red Blue Black Green Yellow Purple Brown Stroop Task Red Blue Black Green Yellow Purple Brown LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS 1. consciousness right now - 2. preconscious - in memory waiting to be accessed 3. subconscious dumb servant idea 4. unconscious Freud s idea -deep down can t be accessed but still affecting us 5. non-conscious life functions coma a. coma is a reduced state of awareness i. there are different types of coma b. little cerebral cortex activity c. can be caused by lots of things d. one man awoke after 19 years!
6 6 What is the relationship between conscious mind and physical brain? Mental processing without consciousness 1. Embodied Cognition unconscious perceptions trigger bodily reactions which trigger conscious thoughts and feelings 2. (chemical) state dependent learning process things emotionally 3. context dependent think different in different settings 3. Recovery room under anesthesia - 4. Priming getting someone ready to think in a certain way 5. Mere exposure effect - people like that which they have seen / heard before even subconsciously more often a person sees a stimulus, the more they will like it oh, snap yadda yadda fetch I feel you dawg don t go there you re fine sicing it ratchet Swerve fifty cant fade geekin gleesh frindle 6. Anterograde Amnesia pin study 7. Prosopagnosia people who have dain bramage and can not recognize familiar faces still have some physiological reaction to familiar people face blindness 8. Blind sight if damage done to visual processing area, the optic nerve can still be connected to other parts of the brain. People who cannot see things still react to visual stimuli
7 EEG patterns go from fast rhythms of low amplitude to slow rhythms of high amplitude Lecture Notes - Consciousness 7 SLEEP Sleep is active electro encephalagraph EEG measures electrical activity on the surface of of brain and measures consciousness (sort of) All people need sleep just as they need food Primitive animals don t need as much sharks, reptiles Sleep deprived people drive like they are drunk have hormone irregularity (insulin, thyroid, leptin) increased pain perception decreased immune response. Beta waves person is awake 12+Hz Low amplitude - high frequency Alpha waves very relaxed 8-12Hz High amplitude low frequency Theta Sleep 4-7Hz Delta Waves - largest - slowest 2-3Hz - in motor strip when we re Relaxed 8-12 Hz Related to intentionality & mirror neurons All people have all waves all the time Biofeedback an E.E.G. based machine that teaches people to change their brain waves for right level of consciousness
8 8 NON R.E.M. SLEEP NREM 1 (stage 1) hypnogogic transition from wakefulness to sleep waves are irregular high frequency - low amplitude ALPHA & THETA = irregular brain waves hallucinations spasm as you fall asleep o hypnagogic o hypnic jerk o myoclonic jerk slowed breathing. NREM 2 (stage 2) - Sleep spindles = bunches of EEG waves - K complexes = big dip/spike in waves - THETA waves Stage 3 pass through stage light sleep to deep sleep Some DELTA some THETA Stage 4 D.D.D. of sleep is the Deepest of Non R.E.M. sleep - DELTA waves - Drool - Cataplexy muscle weakness paralysis - Narcolepsy - Motor neurons are inhibited G.A.B.A. - Long time in beginning of night shorter towards morning - Good for repairing hard exercise - When lots of parasomnias happen sleepwalking - In sleepwalking people rarely trip- so that means people can process information unconsciously
9 9 R.E.M. SLEEP SACCADES - Paradoxical Characteristics Increasing sleep period towards morning EEG waves are Alpha but harder to wake than in stage 4 Skeletal muscles are paralyzed but twitching in face and hands genital arousal increased heart rate, rapid breathing muscles relax to the point of paralysis hard to wake Frontal Lobe (logic) inhibited activity in the motor cortex, movements efferent signal is blocked by the brainstem, activity of occipital and temporal brain areas story REM is when synapses are formed Entrainment - new neural connections = synapses rapid brain waves, Electrooculograph an instrument to measure eye
10 10 Theories of sleep 1. Adaptive theory cave people needed to be awake for 16 hours for our species to survive sleep is the mechanism that keeps the species from injuring itself when it is not involved in critical functions 2. Conserving energy for most species, except Americans, calories are difficult to get. Sleep conserves the precious resource 3. Restorative function sleep is necessary 1. restore body- stage 4 2. restore mind - R.E.M 3. new neural connections what was learned in day 4. remove waste delete wasteful info PONS heartbeat, breathing, vital life functions Reticular activating system controls activity level of brain while awake Ventrolateral preoptic nucleus activity level of brain while asleep Suprachiasmatic nucleus Along with hypothalamus and Melatonin hormone that helps you sleep Hypocretin hormone that helps you stay awake Narcolepsy Sleep is one of the best defenses against stress. Circadian Rhythms 24 hour cycle internal clock Teen hormones seem to mess with normal rhythm of sleep cycle There is a correlation between bad grades and lack of sleep confounding variables? Jet lag east to west is worse Seasonal affective disorder depression that happens in the winter due to longer nights (UV light). REM rebound repay yourself half of what you lost
11 11 DREAMS Activation-synthesis theory = (Crick and Mitchison) random firing of nerves that create dreams, dreams have no deep meaning- just an accidental occurrence we try to understand. Spiritual is this a way to connect with something bigger Cognitive - help you solve a problem Bio brain self-cleaning Sigmund Freud: 1 st major psychologist to consider dreams meaningful. Manifest/Surface Content: what your dream had in it Latent Content: what it symbolized a. Parents as emperors, empresses, kings, & queens b. Children (siblings) as small animals c. Birth as water d. Death as a journey e. Tunnels female genitals f. Snakes male genitals Dream therapy (Cartwright) people need the right amount of emotion in their dreams to help them be healthy in their emotional life Characteristics of Dreams 1. Intensely feel emotion 2. Dream Thought is illogical no continuity of time, place, or cause 3. Sensation is fully formed 4. Uncritical acceptance of thoughts and images (don t think) 5. Difficulty remembering 6. related to outside world except at the end of the night 7. usually more negative than positive 8. rarely about sex - men dream about sex more often Theories of Dreams A. spiritual world 1. Common Freudian dream symbols include:
12 12 2. Freud s analysis of dreams: an art, not a science no scientific method was used to prove theory PARASOMNIAS category of freaky sleep things - Non REM Night terrors (incubus attacks) in stage 4 Usually not remembered Nightmares = REM Sleepwalking = sonambulism stage 4 no real clear theory as to why Wife with a whistle - behavioralism Restless Leg syndrome Teeth Grinding - Bruxism Sleep Eating Sleep Apnea stopping breathing due to airway being blocked o cataplexy o Snoring!! 1.babies 2. obesity, age - increased blood pressure Insomnia correlation but no cause to mental illness Some healthy insomniacs can do well on as little as 3 hours Lucid Dreaming being able to control your dreams- be a super hero, rap star, athlete, model, each night. Your own fantasy land. It is possible with training Narcolepsy falling asleep into stage 4 suddenly Can be reduced with medication Genetic? What advantage is it to the species? Viral? Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) baby dying, o usually related to being smothered by blankets o sometimes neurological R.E.M. behavior disorder people act badly during sleep Dude attacking his wife
13 13
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
I. What Is Consciousness? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you. 3 Meanings of Consciousness
 I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 24 Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Module 24: Sleep,
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 24 Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Module 24: Sleep,
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
Sleep and Dreams UNIT 5- RG 5A
 Sleep and Dreams UNIT 5- RG 5A Goals for today Can you Discuss the circadian rhythm, what it is and how it effects us. Identify and explain each of the 5 stages of sleep. As well as the typical waves of
Sleep and Dreams UNIT 5- RG 5A Goals for today Can you Discuss the circadian rhythm, what it is and how it effects us. Identify and explain each of the 5 stages of sleep. As well as the typical waves of
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming. Elaine M. Hull
 Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Chapter Eleven. Sleep and Waking
 Chapter Eleven Sleep and Waking Sleep Are we getting enough. How z it work? Sleep Deprivation contributed to the Exxon Valdez, Challenger Explosion, and 3 Mile Island Deprivation is VERY common, and quite
Chapter Eleven Sleep and Waking Sleep Are we getting enough. How z it work? Sleep Deprivation contributed to the Exxon Valdez, Challenger Explosion, and 3 Mile Island Deprivation is VERY common, and quite
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Biological Psychology Unit Two AG Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Consciousness Consciousness is your awareness of how and why you react to your surroundings. During this lesson, you may realize
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams. Defined:
 Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
Consciousness, Stages of Sleep, & Dreams I. Consciousness Conscious is: Waking Consciousness Defined: Altered State of Consciousness Defined: Most of waking life Fuzzy, organized, bizarre thoughts Examples:
6/29/2009. Awareness of everything going on inside and outside of you CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS. Meaning of consciousness
 6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
6/29/2009 ness ness Links to Learning Objectives CONSCIOUSNESS, SLEEP & DREAMS HYPNOSIS LO 4.1 Meaning of consciousness LO 4.6 LO 4.2 Why people sleep LO 4.3 of sleep LO 4.4 disorders LO 4.5 Dreaming PSYCHOACTIVE
MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS
 MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS CONSCIOUSNESS Awareness of yourself and your environment. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS Biological rhythms (for example, of temperature and wakefulness) that
MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS CONSCIOUSNESS Awareness of yourself and your environment. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS Biological rhythms (for example, of temperature and wakefulness) that
March 14. Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part Dream Journal Assignment
 March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS. Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is our awareness of ourselves and our environment. - William James LEVELS OF CONSCIOUS AWARENESS Conscious (Controlled) Processes: Require full awareness, alertness
DUAL PROCESSING, SLEEP, AND DREAMS
 WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? DUAL PROCESSING, SLEEP, AND DREAMS Module 6 Our awareness of ourselves & our environment People who study consciousness: Cognitive Neuroscientists Sometimes we experience different
WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? DUAL PROCESSING, SLEEP, AND DREAMS Module 6 Our awareness of ourselves & our environment People who study consciousness: Cognitive Neuroscientists Sometimes we experience different
Chapter 6. Consciousness
 Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
Consciousness Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? The Value of Consciousness Setting Priorities for Mental Functioning Sleeping and Dreaming Altering Awareness: Psychoactive Drugs
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight What is Consciousness? William
Sleep Disorders. Sleep. Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep Disorders Sleep The Sleep Wakefulness Cycle: Circadian Rhythms Internally generated patterns of bodily functions that vary over a ~24-hour period Function even in the absence of normal cues 2 Circadian
Sleep Disorders Sleep The Sleep Wakefulness Cycle: Circadian Rhythms Internally generated patterns of bodily functions that vary over a ~24-hour period Function even in the absence of normal cues 2 Circadian
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight Levels of Consciousness
States of Consciousness Levels of Consciousness Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight Levels of Consciousness
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND
 Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Chapter 3 CONSCIOUSNESS AND THE TWO-TRACK MIND Forms of Consciousness Modern psychologists believe that consciousness is an awareness of ourselves and our environment. Consciousness is not whether or not
Unit 4: Sensation, Perception and States of Consciousness
 WHS AP Psychology Unit 4: Sensation, Perception and States of Consciousness Essential Task 4-9: Discuss aspects of sleep and dreaming: stages, characteristics of the sleep cycle and circadian rhythms.
WHS AP Psychology Unit 4: Sensation, Perception and States of Consciousness Essential Task 4-9: Discuss aspects of sleep and dreaming: stages, characteristics of the sleep cycle and circadian rhythms.
Consciousness. Encounters. Alien Abductions 1/8/2012. Chapter Six. Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens)
 Chapter Six Consciousness Encounters Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens) Almost 1 in 10 claim to have experienced or met an alien Are people being visited and abducted
Chapter Six Consciousness Encounters Approximately 20% of college students believe in extraterrestrials (aliens) Almost 1 in 10 claim to have experienced or met an alien Are people being visited and abducted
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to
 How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Week 4 Psychology. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding that they and others think, feel, perceive, and have private experiences.
 Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity.
 Sleep and Dreams What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity. A state we do not know we are in until we leave it. Characterized by
Sleep and Dreams What is sleep? A state of altered consciousness, characterized by certain patterns of brain activity and inactivity. A state we do not know we are in until we leave it. Characterized by
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis
 Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Module 22- Understanding Consciousness & Hypnosis - Fundamental, hard to define Psychological Concept - Difficulties in defining consciousness led those specializing in behaviorism to look at direct observations
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep.
 Brain wave frequency and amplitude This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u WYwMnMMEoU&feature=related
Brain wave frequency and amplitude This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u WYwMnMMEoU&feature=related
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
SLEEP THEORIES. Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed
 SLEEP THEORIES Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed about kept our ancestors out of harm s way. Sleep Recuperates: Sleep helps restore and repair brain tissue. Sleep Helps Remembering:
SLEEP THEORIES Sleep Protects: Sleeping in the darkness when predators loomed about kept our ancestors out of harm s way. Sleep Recuperates: Sleep helps restore and repair brain tissue. Sleep Helps Remembering:
Sleep and Dreaming Notes December 14, 2015
 an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
an altered state of consciousness Sleep serves as a restorative process of the body Scientists know the neurochemical melatonin plays a role in sleep and body restoration and repair. A definite cause effect
States of Consciousness
 1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
1 Unit 5 Review of Key Concepts and Terms States of Consciousness (2-4% of the AP exam/curriculum) Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our environment. Preconscious: something that is not in
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
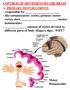 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind 1. When did the concept of consciousness begin to reemerge in the field of psychology? Explain why. Include all three explanations
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 3: Consciousness & the Two-Track Mind 1. When did the concept of consciousness begin to reemerge in the field of psychology? Explain why. Include all three explanations
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Sleep and Dreams. Sleep and Dreams. Brain Waves and Sleep Stages Typical Nightly Sleep Stages. Chapter 7 States of Consciousness
 Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
Chapter 7 States of Consciousness States of Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Fantasy Prone Personality imagines and recalls experiences with lifelike vividness
SPECIMEN MARK: NAME: / 54. Grade: Sleep and Dreaming. Answer all questions in this section (a) Identify an example of an exogenous zeitgeber.
 NAME: Sleep and Dreaming MARK: / 54 % Grade: Answer all questions in this section. 1. 9 (a) Identify an example of an exogenous zeitgeber. A C an endogenous pacemaker light pineal gland D sleep Your answer
NAME: Sleep and Dreaming MARK: / 54 % Grade: Answer all questions in this section. 1. 9 (a) Identify an example of an exogenous zeitgeber. A C an endogenous pacemaker light pineal gland D sleep Your answer
States of Consciousness:
 States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
States of Consciousness: Before the turn of the century Psychology was concerned primarily with the description and explanation of states of consciousness Because of problems with directly studying and
****REVISED 4/27/2015****
 Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Sleep and Dreaming. Sleep Deprivation Trivia
 Sleep and Dreaming Sleep Deprivation Trivia Peter Tripp stayed awake for 201 hours in 1959. Guinness Book of Records record is 18 days, 21 hours, 40 minutes. Sleep deprivation implicated in Three Mile
Sleep and Dreaming Sleep Deprivation Trivia Peter Tripp stayed awake for 201 hours in 1959. Guinness Book of Records record is 18 days, 21 hours, 40 minutes. Sleep deprivation implicated in Three Mile
Chapter 5/7. Variations in Consciousness
 Chapter 5/7 Variations in Consciousness -The Nature of Consciousness Consciousness is the awareness of internal and external stimuli. External: sound of my voice. Internal: heart beat Consciousness- it
Chapter 5/7 Variations in Consciousness -The Nature of Consciousness Consciousness is the awareness of internal and external stimuli. External: sound of my voice. Internal: heart beat Consciousness- it
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity.
 Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
CONSCIOUSNESS. Biological Clocks
 CONSCIOUSNESS Biological Clocks FREE RUNNING CYCLES Cycles set up by biological clocks that are under their own control ignore the environment Example: The kidney processes toxins all the time and gets
CONSCIOUSNESS Biological Clocks FREE RUNNING CYCLES Cycles set up by biological clocks that are under their own control ignore the environment Example: The kidney processes toxins all the time and gets
States of Consciousness
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 States of Consciousness "We do imagery work and talk about having that innovative mindset of being special," Wilson says. "We talk about being in the moment and increasing chaos
Myers PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 States of Consciousness "We do imagery work and talk about having that innovative mindset of being special," Wilson says. "We talk about being in the moment and increasing chaos
Thomas W. O Reilly, MS, PCC in cooperation with Lakeshore Educational and Counseling Services
 Thomas W. O Reilly, MS, PCC in cooperation with Lakeshore Educational and Counseling Services www.lakeshoresupport.com Humans have biological rhythms, known as Circadian Rhythms (CR) CR refers to cyclical
Thomas W. O Reilly, MS, PCC in cooperation with Lakeshore Educational and Counseling Services www.lakeshoresupport.com Humans have biological rhythms, known as Circadian Rhythms (CR) CR refers to cyclical
Lecture 8. Arousal & Sleep. Cogs17 * UCSD
 Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT.
 CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
What is Consciousness?
 What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, Hypnosis
 States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, Hypnosis Circadian Rhythm From the Latin meaning about a day Waxing and waning of consciousness/alertness Actually closer to 25 hour cycle in healthy young adults
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, Hypnosis Circadian Rhythm From the Latin meaning about a day Waxing and waning of consciousness/alertness Actually closer to 25 hour cycle in healthy young adults
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
 states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS
 Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Dreams and Dreaming. Michelle Zetoony, DO, FCCP, FACOI Board Certified Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Internal Medicine
 Dreams and Dreaming Michelle Zetoony, DO, FCCP, FACOI Board Certified Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Internal Medicine What are dreams? Varying definitions Varying experiences Generally classified
Dreams and Dreaming Michelle Zetoony, DO, FCCP, FACOI Board Certified Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Internal Medicine What are dreams? Varying definitions Varying experiences Generally classified
Electrooculogram (EOG): eye movements. Air flow measurements: breathing Heart rate.
 By: Ricardo Measurements and study of sleep: Sleep: absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness Measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics: Electromyogram (EMG): muscle activity
By: Ricardo Measurements and study of sleep: Sleep: absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness Measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics: Electromyogram (EMG): muscle activity
What is a dream? A succession of images, thoughts, or emotions passing through the mind during sleep
 Dreams What is a dream? A succession of images, thoughts, or emotions passing through the mind during sleep The Science of Dreaming http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xb7hqzc2p2y Stages of sleep Brain waves
Dreams What is a dream? A succession of images, thoughts, or emotions passing through the mind during sleep The Science of Dreaming http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xb7hqzc2p2y Stages of sleep Brain waves
Role of Biological Clocks
 Dreaming Role of Biological Clocks Biological Clocks Circadian Rhythm Ever notice Timing device Programmed to regulate physiological behaviors @ certain times. Type of bio. clock Programmed to regulate
Dreaming Role of Biological Clocks Biological Clocks Circadian Rhythm Ever notice Timing device Programmed to regulate physiological behaviors @ certain times. Type of bio. clock Programmed to regulate
States of Consciousness
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 7 States of Consciousness Waking Consciousness Consciousness our awareness of ourselves and our environments Sleep and Dreams Biological Rhythms periodic physiological
Unit 5 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The best predictor of an adolescent's pattern of drug usage is whether the adolescent A) grows up in an intact two-parent family. B) has religious beliefs. C) is a first or second child.
Name: Date: 1. The best predictor of an adolescent's pattern of drug usage is whether the adolescent A) grows up in an intact two-parent family. B) has religious beliefs. C) is a first or second child.
Key Knowledge. What is CONSCIOUSNESS? Consciousness is. Unit 3 ~ Chapter 2 ~ States of Consciousness. Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012
 Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012 Key Knowledge Consciousness as described by Rene Descartes & William James Normal Waking Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness Comparison of Normal & Altered
Chapter 2 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2012 Key Knowledge Consciousness as described by Rene Descartes & William James Normal Waking Consciousness Altered States of Consciousness Comparison of Normal & Altered
Consciousness. Mind-body Problem. Cartesian Substance Dualism 2/2/11. Fundamental issue addressed by psychologists Dualism. Monism
 Consciousness Mind-body Problem Fundamental issue addressed by psychologists Dualism Mind is immaterial Mind can exist separate from the body Monism Mind and body are different aspects of the same thing
Consciousness Mind-body Problem Fundamental issue addressed by psychologists Dualism Mind is immaterial Mind can exist separate from the body Monism Mind and body are different aspects of the same thing
Article printed from
 What Are Sleep Disorders? Sleep disorders are conditions that affect how much and how well you sleep. The causes range from poor habits that keep you awake to medical problems that disrupt your sleep cycle.
What Are Sleep Disorders? Sleep disorders are conditions that affect how much and how well you sleep. The causes range from poor habits that keep you awake to medical problems that disrupt your sleep cycle.
Activation-synthesis hypothesis. compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences. Addition. Amphetamines. Barbiturates.
 Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013
 Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013 Sleep is described as regularly occurring altered state of consciousness that typically occurs spontaneously and is characterised by a loss of conscious awareness Sleep occurs
Unit 3 Psychology ~ 2013 Sleep is described as regularly occurring altered state of consciousness that typically occurs spontaneously and is characterised by a loss of conscious awareness Sleep occurs
Physiology of Sleep. Dr Nervana
 Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness
 Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness Complete the following: I tasted I smelled I saw I touched I heard I remembered I felt I thought DEFINING
Brain, Body and Awareness Unit Two: Chapter 6 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 4: Consciousness Complete the following: I tasted I smelled I saw I touched I heard I remembered I felt I thought DEFINING
,.,
 States of Consciousness 5 -----.------.,.,----------------------------------- KEY TERMS Consciousness Sleep apnea Dissociation theory of Levels of consciousness Night terrors hypnosis Conscious level Dreams
States of Consciousness 5 -----.------.,.,----------------------------------- KEY TERMS Consciousness Sleep apnea Dissociation theory of Levels of consciousness Night terrors hypnosis Conscious level Dreams
HEALTHY LIFESTYLE, HEALTHY SLEEP. There are many different sleep disorders, and almost all of them can be improved with lifestyle changes.
 HEALTHY LIFESTYLE, HEALTHY SLEEP There are many different sleep disorders, and almost all of them can be improved with lifestyle changes. HEALTHY LIFESTYLE, HEALTHY SLEEP There are many different sleep
HEALTHY LIFESTYLE, HEALTHY SLEEP There are many different sleep disorders, and almost all of them can be improved with lifestyle changes. HEALTHY LIFESTYLE, HEALTHY SLEEP There are many different sleep
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS
 Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Chapter 5 CONSCIOUSNESS Section 1: The Study of Consciousness Section 2: Sleep and Dreams Section 3: Meditation, Biofeedback, and Hypnosis Section 4: Drugs and Consciousness 1 Section 1: The Study of Consciousness
Participant ID: If you had no responsibilities, what time would your body tell you to go to sleep and wake up?
 What does your sleep look like on a typical week? Total Sleep Time: Bedtime:, Sleep onset latency:, Number of Awakenings:, Wake time after sleep onset:, Rise time:, Out of bed:, Naps:? Notes: Is your sleep
What does your sleep look like on a typical week? Total Sleep Time: Bedtime:, Sleep onset latency:, Number of Awakenings:, Wake time after sleep onset:, Rise time:, Out of bed:, Naps:? Notes: Is your sleep
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
Subliminal Programming
 Subliminal Programming Directions for Use Common Questions Background Information Session Overview These sessions are a highly advanced blend of several mind development technologies. Your mind will be
Subliminal Programming Directions for Use Common Questions Background Information Session Overview These sessions are a highly advanced blend of several mind development technologies. Your mind will be
Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey
 Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey Thursday, October 5, 2017 10:59 AM How to Study and Measure Sleep Sleep: Absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness. -> measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics:
Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey Thursday, October 5, 2017 10:59 AM How to Study and Measure Sleep Sleep: Absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness. -> measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics:
AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness
 AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness 1. What is an example of synesthesia? Following a car accident, someone has the ability to see sounds and hear touch. 2. What is the most basic distinction
AP Psychology Chapter 09 Test Review: Consciousness 1. What is an example of synesthesia? Following a car accident, someone has the ability to see sounds and hear touch. 2. What is the most basic distinction
THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING
 THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING WRITTEN BY VALERIA CRUZ PUBLISHED 6 JUNE 2017 1 P a g e HISTORY Dreams are your subconscious creating a possible world. This, however, is not a new phenomenon. In fact,
THE ART OF DREAMS AND LUCID DREAMING WRITTEN BY VALERIA CRUZ PUBLISHED 6 JUNE 2017 1 P a g e HISTORY Dreams are your subconscious creating a possible world. This, however, is not a new phenomenon. In fact,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences
 BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
CONSCIOUSNESS AND IT ALTERED STAGES. Muhammad Rehan BSN,RN Lecturer
 CONSCIOUSNESS AND IT ALTERED STAGES Muhammad Rehan BSN,RN Lecturer What is CONSCIOUSNESS! Include all memories that remain within an individual s awarness. Event and experiences that are easily remembered.
CONSCIOUSNESS AND IT ALTERED STAGES Muhammad Rehan BSN,RN Lecturer What is CONSCIOUSNESS! Include all memories that remain within an individual s awarness. Event and experiences that are easily remembered.
Psychology - Mr. Duez Unit 3 - Part I Consciousness 3 - Dreams
 Psychology - Mr. Duez Unit 3 - Part I Consciousness 3 - Dreams Dreams A sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person s mind. Manifest Content: the remembered storyline of
Psychology - Mr. Duez Unit 3 - Part I Consciousness 3 - Dreams Dreams A sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person s mind. Manifest Content: the remembered storyline of
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Introduction Obstructive sleep apnea is an interruption in breathing during sleep. It is caused by throat and tongue muscles collapsing and relaxing. This blocks, or obstructs,
No Rest For the Weary: Some Common Sleep Disorders
 No Rest For the Weary: Some Common Sleep Disorders Student Activity 3G Activity Introduction: It seems Mom does know best ; sleep has been proven to be essential to our health and well-being. In order
No Rest For the Weary: Some Common Sleep Disorders Student Activity 3G Activity Introduction: It seems Mom does know best ; sleep has been proven to be essential to our health and well-being. In order
EMOTION Brain Areas Involved in Emotion
 Three Minute Review EMOTION Brain Areas Involved in Emotion two routes fast: senses amygdala frontal lobes slow: senses cerebral cortex frontal lobes amygdala frontal lobes Phineas Gage frontal lobotomies
Three Minute Review EMOTION Brain Areas Involved in Emotion two routes fast: senses amygdala frontal lobes slow: senses cerebral cortex frontal lobes amygdala frontal lobes Phineas Gage frontal lobotomies
CHAPTER 6 CONSCIOUSNESS, THOUGHT, AND LANGUAGE
 CONSCIOUSNESS, THOUGHT, AND LANGUAGE YOU KNOW YOU ARE READY FOR THE TEST IF YOU ARE ABLE TO! Define consciousness and discuss the different levels of consciousness.! Explain the factors that control sleep,
CONSCIOUSNESS, THOUGHT, AND LANGUAGE YOU KNOW YOU ARE READY FOR THE TEST IF YOU ARE ABLE TO! Define consciousness and discuss the different levels of consciousness.! Explain the factors that control sleep,
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep?
 4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 18 Basics of sleep medicine - Level 1 Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep? Rolf Fronczek Leiden,
4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 18 Basics of sleep medicine - Level 1 Normal sleep mechanisms & why do we sleep? Rolf Fronczek Leiden,
How Hypnosis Feels. P a g e 1 6
 How Hypnosis Feels Since everyone has experienced light levels of hypnosis at different times, don t be surprised if you don t feel hypnotized. All that is required to be hypnotized is a motivation to
How Hypnosis Feels Since everyone has experienced light levels of hypnosis at different times, don t be surprised if you don t feel hypnotized. All that is required to be hypnotized is a motivation to
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
CONSCIOUSNESS. Phil/Psych 256. Chris Eliasmith
 CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
Help I Have Problems with My Sleep!
 Help I Have Problems with My Sleep! Over An 85 Year Lifespan Sleep 31% Work 21% Exercise 1% Food and Drink 11% Sleep Is Important! You can survive without food for up to 2 months Without water 3-5 days
Help I Have Problems with My Sleep! Over An 85 Year Lifespan Sleep 31% Work 21% Exercise 1% Food and Drink 11% Sleep Is Important! You can survive without food for up to 2 months Without water 3-5 days
Is modern life making us tired?
 ENGLISH CONVERSATION WEDNESDAY 22ND AND THURSDAY 23RD JUNE 2016 18HOO Topic : Is modern life making us tired? From artificial lights, to late night TV, and now the ever-present glow of our smartphones,
ENGLISH CONVERSATION WEDNESDAY 22ND AND THURSDAY 23RD JUNE 2016 18HOO Topic : Is modern life making us tired? From artificial lights, to late night TV, and now the ever-present glow of our smartphones,
 Module 2: Booklet 5 http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/intro-to-statesof-consciousness.html#lesson (3:55) Different levels of awareness that occur each day (I.e. sleeping, dreaming, thinking, etc)
Module 2: Booklet 5 http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/intro-to-statesof-consciousness.html#lesson (3:55) Different levels of awareness that occur each day (I.e. sleeping, dreaming, thinking, etc)
SLEEP DISORDERS
 SLEEP DISORDERS 17.03.2013 Well this is a problem that is close to my heart, because for most of my life I have had problems sleeping. Many nights I have watched with envy as my husband goes to bed and
SLEEP DISORDERS 17.03.2013 Well this is a problem that is close to my heart, because for most of my life I have had problems sleeping. Many nights I have watched with envy as my husband goes to bed and
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Sleep problems 4/10/2014. Normal sleep (lots of variability at all ages) 2 phases of sleep. Quantity. Quality REM. Non-REM.
 Sleep problems Normal sleep (lots of variability at all ages) Quantity Newborns: 16-20 hrs/day 1-yr olds: 12 hrs/day 6-12 yr olds: 10-11 hrs/day Quality Newborns: distributed between day and night 3-months:
Sleep problems Normal sleep (lots of variability at all ages) Quantity Newborns: 16-20 hrs/day 1-yr olds: 12 hrs/day 6-12 yr olds: 10-11 hrs/day Quality Newborns: distributed between day and night 3-months:
