Patients with immunoglobulin G4 related
|
|
|
- Gabriella Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMAJ CME An overview of the diagnosis and management of immunoglobulin G4 related disease Debashis Haldar MA MRCP, Paul Cockwell PhD, Alex G. Richter MD, Keith J. Roberts PhD, Gideon M. Hirschfield PhD Patients with immunoglobulin G4 related disease (IgG4-related disease) can present to any clinical specialty. It is an uncommon, immune-mediated, fibroinflammatory process that can progress to organ failure and death if untreated. Presentation is protean and can mimic other conditions, including systemic diseases (e.g., sarcoidosis), single-organ disorders (e.g., primary sclerosing cholangitis) and malignant disease (i.e., hematologic [lymphoma] and mass lesions [pancreatic cancer]). However, IgG4- related disease is eminently manageable; early treatment prevents organ damage and long-term morbidity. Nevertheless, recognition of IgG4- related disease is challenging and requires clinicians to have an awareness of the disease. We provide an overview of current understanding of the cause, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of IgG4-related disease, and we outline challenges to be addressed to improve care for patients (Box 1). What is IgG4-related disease? Immunoglobulin G4 related disease is a systemic immune-mediated fibroinflammatory disease that presents as organ dysfunction or mass lesions with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in single or multiple organs. It can result in organ failure or death if untreated. This disease has been recognized as a distinct clinical entity since the beginning of the 21st century, 1 when investigators in Japan reported that extrapancreatic manifestations of autoimmune sclerosing Box 1: Search strategy We searched publications in MEDLINE and PubMed from 2001 onwards (when the multisystem nature of the disease was recognized) using the key phrases IgG4, IgG4-related, IgG4-associated, IgG4 pancreatitis and autoimmune pancreatitis. Recommendations are based on information from international consensus guidelines. pancreatitis shared a distinct histopathologic signature with the parent disease. 2 Since then, the histologic features of infiltrative IgG4-positive plasma cells, storiform fibrosis and obliterative phlebitis have been reported in almost every organ (Table 1) 3 14 and share similar features with apparently unrelated pathologic entities, such as dacryoadenitis (Mikulicz disease) to retroperitoneal fibrosis (Ormond disease). What pathophysiologic mechanisms are involved in IgG4-related disease? The pathophysiology of IgG4-related disease is uncertain. Both genetic predisposition and environmental triggers may prompt aberrant immune pathways to perpetuate the disease. 15 An overview of current understanding of the disease is shown in Figure The pathology seems to be primarily affected by B cells. Patients with IgG4-related disease carry dominantly expanded clones of tissue B cells that produce immunoglobulins with greater antigen affinity and, preferentially, make more IgG4. However, the pathogenic role of IgG4 remains a contentious issue in view of its immune-modulating properties. 15,24 Expansion of regulatory T cells is observed, 22 which may contribute to fibrosis. Furthermore, a modified type 2 T-helper (Th2) cellular response 25 augments B-cell changes. 26,27 Maturation of B cells may also be directly stimulated by microbial components. 28 Key points Competing interests: None declared. This article has been peer reviewed. Correspondence to: Gideon Hirschfield Centre for Liver Research, g.hirschfield@bham.ac.uk CMAJ DOI: /cmaj IgG4-related disease is a multisystem fibroinflammatory disorder that can present to any clinical specialty and can lead to organ failure if left untreated. The pathophysiology is unclear but is likely to be affected by B-cell lineage with a modified type 2 T-helper cell response, supporting and contributing to fibrosis. The diagnosis requires prior awareness of the disease and a skillful correlation of clinical, biochemical, radiologic and histopathologic clues. IgG4-related disease is sensitive to glucocorticoid therapy, but the best way to maintain remission remains unclear Joule Inc. or its licensors CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13) 953
2 Certain serotypes of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) and non-hla polymorphisms of immunerelated genes may confer genetic predisposition to type-1 autoimmune pancreatitis, the pancreatic manifestation of IgG4-related disease However, the trigger mechanisms remain elusive. Molecular mimicry of Helicobacter pylori antigens with human counterparts 19 may act as a trigger most patients with autoimmune pancreatitis have antibodies against the plasminogen-binding protein of H. pylori 20 although this theory still requires confirmation. Only half of patients with autoimmune pancreatitis express autoantibodies. 16,33 (Figure 1). How does IgG4-related disease present? A detailed understanding of the geoepidemiology of IgG4-related disease will require the introduction and widespread use of easily accessible diagnostic tools or biomarkers. Studies of autoimmune pancreatitis involving patients in Japan showed that it is an uncommon disease, with an incidence and prevalence of 0.14 and 0.46 per population, respectively. 15,34 Patients usually present between the ages of 50 and 70 years and are more likely to be men (3:1). 35 However, this can vary between disease sites: a sex ratio of 1:1 has been reported for disease occuring in the head and neck. 36,37 IgG4-related disease can present as a consequence of organ involvement anywhere in the body. Therefore, it is within the remit of all adult medical and surgical specialties, although the organs most frequently involved are the pancreas, salivary and lacrimal glands, biliary tree, kidneys, thyroid and lungs. 38 The rarity, diverse presentation and lack of a gold standard test often result in delayed diagnosis, usually after investigation for malignant growths has occurred. 39,40 Thus, an understanding of the clinical, radiologic, laboratory tests (in particular serum concentrations of IgG4) and a focused histopathology examination are Table 1: Manifestations of IgG4-related disease in different organ systems Organ system Common clinical presentation Preferred name 3 Pancreas Lacrimal and salivary glands Orbits Lungs Thyroid gland Lymph nodes Arterial system Retroperitoneum Kidneys Biliary tree Painless obstructive jaundice and endocrine failure (secondary diabetes mellitus); frequently associated with IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis 4 Mikulicz disease: 5 bilateral dacryoadenitis, and enlargement of the parotid and submandibular glands with associated xerophthalmia and xerostomia Küttner tumour/chronic sclerosing sialadenitis: 6 hard indurated masses of submandibular (or parotid) glands; associated xerostomia is common Proptosis due to dacryoadenitis, local myositis or orbital pseudotumours; scleritis, uveitis and locoregional neuronal damage can occur from mass effect 7,8 Dyspnea, wheeze, cough Mild stridulous symptoms can be associated with upper respiratory tract (e.g., pharynx, trachea) inflammation; often diagnosed incidentally on imaging 9 Riedel thyroiditis: 10 stony goiter usually euthyroid or subclinical hypothyroid profile Nontender generalized lymphadenopathy or localized disease near other affected organs; often asymptomatic and diagnosed incidentally on imaging Aortitis of either the thoracic or abdominal aorta; aneurysmal disease can present with pain or vascular insufficiency but can also be acute and catastrophic. 11 Coronary arteritis may be associated with ischemic heart disease 12 Ormond disease: poorly localized lower back pain and chronic renal failure Ureteric obstruction, hydronephrosis and renal failure Diffuse renal enlargement and chronic renal failure; 13 commonly, tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with a profound hypocomplementemia Proteinuria due to coexistent glomerulonephritis (membranous) is common Jaundice, weight loss and abdominal pain that closely mimicks PSC or cholangiocarcinoma; associated cholecystitis is usually asymptomatic Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis* IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and IgG4-related sialadenitis IgG4-related ophthalmic disease IgG4-related lung disease IgG4-related thyroid disease IgG4-related lymphadenopathy IgG4-related aortitis or periaortitis IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis IgG4-related kidney disease IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis Meninges Headache, nerve palsies and radiculomyelopathy IgG4-related pachymeningitis Note: PSC = primary sclerosing cholangitis. Other involvement includes IgG4-related skin disease, prostatitis, mastitis, mesenteritis, mediastinitis and hypophysitis. *Should not be confused with type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis is also called idiopathic duct centric pancreatitis and is not related to IgG4-RD, affects younger patients with no sex preponderance, 14 is less common than type 1 but is also treated with steroids. 954 CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13)
3 Infectious agents Trigger (A) Autoantibodies Lactoferrin Trypsinogen Carbonic anhydrase II and IV Plasminogen-binding protein Heat shock protein 10 Amylase 2a Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor α-carbonic anhydrase Molecular mimicry Helicobacter pylori antigens Plasminogenbinding protein Carbonic anhydrase II UBR1 Microbial components Genetic susceptibility switching (B) HLA polymorphisms HLA-DRB1*0405 HLA-DRB1*0401 HLA-DQB1 Non-HLA polymorphisms CTLA-4 FcR-3 TNF-α promoter 863A Immune pathways (C) Th2 cells IL-5 Eosinophils B cells NODR/TLR2- mediated response IL-13 IgE Innate immunity T-reg cells IL-4 IL-10 Maturation Proliferation Ig class switching BAFF APRIL IgG4 Dendritic cells Basophil TGF-β Fibrosis Circulating plasmablast Figure 1: Mechanisms of pathogenesis for IgG4-related disease. (A) Antibodies versus antigens commonly found in exocrine organs may drive Th2-cell response. Most have only been investigated in type 1 AIP, are nonspecific, and none have been consistently found in active disease Molecular mimicry of Helicobacter pylori antigens with human counterparts may be a trigger for type 1 AIP. 19,20 Microbial components may stimulate innate immune mechanisms by activating NODR and TLR2 to produce BAFF and APRIL which lead to changes to B cells in a T cell independent manner. 21 (B) Polymorphisms of both HLA and non-hla antigens have been implicated in the development of type 1 AIP. 15 (C) A dominant Th2-cell (and associated cytokine) response occurs systemically and within affected organs. An expansion in T-reg cells may contribute to both B-cell Ig class switching and fibrosis. 22 A treatment-sensitive expansion in circulating plasmablasts is present in active disease, 23 although their exact role in pathogenesis remains unclear. Elevated levels of IgG4 in serum is a hallmark of the disease and is a consequence of a modified Th2-cell response. 15 Note: AIP = autoimmune pancreatitis, APRIL = a proliferation-inducing ligand, BAFF = B cell activating factor belonging to the TNF family, B cell = beta cell, HLA = human leucocyte antigens, Ig = immunoglobulin, NODR = nucleotidebinding oligomerization domain receptor, T cell = T lymphocyte cell, TGF = transforming growth factor, Th2 = type 2 T helper, TLR2 = toll-like receptor 2, T-reg = regulatory T cell, TNF = tumour necrosis factor, UBR1 = ubiquitin-protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 1. CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13) 955
4 required to ensure that IgG4-related disease has been considered in the differential diagnosis. 41,42 Organ-specific guidelines, such as the HISORt (histology, imaging, serology, other organ involvement, response to steroid therapy) criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis, facilitate this multimodal diagnostic approach but may blind specialists to clinical manifestations outside their area of interest. 41 In recognition of this, an international panel of experts described comprehensive consensus recommendations to aid clinicians in the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease (summarized in Figure 2). 43,44 The evolving nature of this novel disease means the research to guide the consensus was limited, and recommendations to instruct a diagnostic approach were supported by expert opinion and limited data. Organ-specific diagnostic criteria, such as those for IgG4-related pancreatitis, cholangiopathy, kidney disease and dacryoadenitis, should be used concurrently (Table 1 and Figure 2). Signs and symptoms Systemic symptoms can develop insidiously over several months; asthenia (26%) and weight loss (21%) were common in the patient populations of studies conducted in France 45 and China 46. Although most patients with IgG4- related disease have multiorgan involvement, 40% of patients have single-organ involvement at the time of diagnosis. 38 Abdominal symptoms are common: in a review of relevant articles published between Jan. 1, 2000, and Nov. 1, 2014, Stone and colleagues reported that pain, jaundice and diarrhea occurred in 40%, 23% and 6% of patients, respectively. 47 Sicca syndrome and respiratory symptoms were reported in 13% 15% of patients involved in the studies conducted in France and China. 45,46 Stone and colleagues reported that patients with head and neck disease usually presented with organ swelling, and they noted that swelling of the salivary and lacrimal glands, and lymphadenopathy were common sentinel signs. 47 Investigations Routine blood tests Routine blood tests may direct attention to the organs involved (e.g., abnormal results for liver function tests would prompt focused investigation of the liver and pancreas). However, such testing gives little indication to suggest an underlying diagnosis of IgG4-related disease. A study in Massachusetts involving patients with IgG4-related disease reported elevated counts for peripheral eosinophilia in 27% of these patients (mean 1062 cells/µl; normal count < 500 cells/µl). 48 Elevated levels of inflammatory markers (i.e., C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate) were reported in one-fifth of cases in a case series study conducted in Japan. 49 Clinical (and radiologic) Mass lesion in 1 or more organs Definite diagnosis All 3 criteria met Histopathologic Fibrosis and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate IgG4+ plasma cells > 10/HPF or IgG4:IgG > 40% Probable diagnosis Clinical and histopathologic criteria met Serologic Serum IgG4 > 1.35 g/l Possible diagnosis Clinical and serologic criteria met Figure 2: Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease. HPF = high-powered field. (Adapted from Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67: ) CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13)
5 Immunologic blood tests Stone and colleagues reported that polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia was detected in the sera of 80% of patients and an elevated level of IgE in 60% of patients. 47 One-third of patients have hypocomplementemia; this finding may be particularly associated with IgG4-related kidney disease, 13 presumably as a consequence of proteinuria. A systematic review that examined the clinical features of patients with a diagnosis of IgG4-related disease showed that only 32% and 20% of patients had detectable antinuclear antibodies and rheumatoid factor, respectively. 47,50 The presence of specific autoantibodies should prompt consideration of alternative diagnoses. 47 Serum IgG4 levels are elevated in as many as 84% of patients 47,50 with IgG4-related disease, and this is an important diagnostic tool; however, clinicians should be aware of the limitations of the test. 51 The reported sensitivity (80% 90%) of an elevated level of IgG4 in serum is likely to be inflated by selection bias. 51,52 In a study that required histologic proof of IgG4- related disease as an inclusion criterion, only 50% of the patients had elevated levels of serum IgG4 before treatment. 53 Elevated levels of IgG4 in serum can occur in many other conditions, including some pancreatobiliary diseases (e.g., primary sclerosing cholangitis, cholangiocarcinoma), hematologic malignant disease and infectious diseases (e.g., chronic sinusitis, recurrent pneumonia, aspergillosis). 51 An elevated IgG4 level in serum (upper limit of normal = 1.35 g/l) has low specificity and a positive predictive value under 40%. 52 Nevertheless, higher serum concentrations may suggest a positive diagnosis (mean = 6.70 g/l) over alternatives; 51 a threshold of four times the upper limit of normal provides a positive predictive value of 100% for the investigation of IgG4- Table 2: Radiographic findings in IgG4-related disease Organ system Pancreas 58 Salivary gland Orbits 61 Lungs 9 Arterial system 62 Retroperitoneum 63 Kidneys 64 Biliary tree Meninges and brain 8 Typical findings CT: focal (more common) or diffuse pancreatic enlargement with delayed enhancement and a low-density halo ; pancreatic atrophy is uncommon Cholangiography: diffuse irregular narrowing of the pancreatic duct CT: swelling is often bilateral and preferentially involves the submandibular glands US: 59 multiple hypoechoic lesions in affected glands MRI: 60 homogenous enhancement in hypointense or isointense T 2 -weighted imaging CT: involvement of any surrounding structures including lacrimal glands, nerves, extraocular muscles and maxillary and frontal bony structures CT: four major categories of findings (solid nodular masses, localized ground glass opacities, diffuse ground glass opacities associated with honeycomb lung and bronchovascular thickening); mediastinal lymphadenopathy is common Diffuse tracheal inflammation and subglottic stenoses may also be seen CT: adventitial sclerosing inflammation characterized by diffuse wall thickening and late-phase enhancement CT: perivascular fibrosis concentrates around the aorta, iliac vessels and vena cava. Occasionally, fibrotic disease will dominate perirectal and retrovesicular spaces. Associated lymphadenopathy and aortitis is common. CT: abnormalities noted in 70% of patients with renal disease include bilateral diffuse enlargement, solitary nodules and atrophy MRI: low-density lesions with T 2 -weighting hypointensity, with progressive enhancement pattern Cholangiography: stricturing disease is difficult to differentiate from other causes of sclerosing cholangitis. Common bile duct thickness of > 2.5 mm and continuous strictures can be suggestive of IgG4-RD rather than PSC; 65 4 patterns of stricturing disease have been described, but the clinical relevance of the different types is not obvious 66 Cholangioscopy: direct mucosal visualization may give diagnostic clues, although this requires thorough validation 67 CT: diffuse dural thickening or perineural masses as large as 3 cm in diameter; pituitary lesions require MRI Note: CT = computed tomography, IgG4-RD = immunoglobulin G4 related disease, MRI = magnetic resonance imaging, PSC = primary sclerosing cholangitis, US = ultrasonography. CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13) 957
6 related sclerosing cholangitis. 52 For moderately elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (up to 2 times the upper limit of normal; positive predictive value = 28%), the IgG1:IgG4 ratio in serum (> 0.24) may improve diagnostic yield for IgG4- related sclerosing cholangitis (positive predictive value = 55%; negative predictive value = 90%), although the use of IgG1:IgG4 ratios in serum has not been validated outside this setting. 52 Higher concentrations of IgG4 in serum are associated with multiorgan involvement (mean concentration: 6.99 g/l in multiorgan v g/l in single-organ disease) or a greater burden of localized disease that is prone to relapse after initial treatment. 51,54,55 Imaging studies Computed tomography (CT) may delineate a mass and identify the extent of multiorgan involvement; however, the assessment of multiorgan involvement may be better served by 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/ct. 56 Magnetic resonance imaging of affected areas generates a low signal on T 2 -weighted imaging. 57 An overview of the typical radiographic findings in different organs is described in Table 2. 8,9,58 67 Of these, only the classical CT findings of autoimmune pancreatitis Figure 3: Diffuse autoimmune pancreatitis. 68 (A) Axial computed tomography (CT) image in the pancreatic parenchymal phase of the typical enlarged and poorly enhanced pancreas in a patient with diffuse autoimmune pancreatitis 68 (arrow). Note the lack of inflammatory change around the organ, which differentiates the disease from acute pancreatitis and necrosis. (B) View of the pancreas using coronal T 2 -weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that shows low signal intensity in the pancreas (arrow) because of the diffuse fibrosis in the gland. (C) Coronal magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image showing a diffusely irregular pancreatic duct with stenosis distally in the pancreatic head (arrow). (D) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography image that confirms the MRI findings, including ductal stenosis (arrow). Images reproduced from reference 68 under Creative Commons licence 2.0 ( (i.e., a diffusely enlarged, sausage-shaped pancreas with an enhancing rim; Figure 3) 68 are pathognomonic, and may forego the need for histologic assessment 44 (Figure 3 and Table 2). Histologic assessment The purpose of histologic assessment of affected organs is to exclude other differential diagnoses (notably malignant disease) and to provide evidence of a diagnosis of IgG4-related disease before treatment starts. 43 Tissue procurement can be difficult with deep-seated disease, although modern techniques, such as endoscopic ultrasonography with fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic and biliary disease, have overcome some of these challenges. Nevertheless, needle biopsy and fine-needle aspiration often deliver insufficient tissue for assessment and can miss patchy disease. 69 Gross morphologic changes are often organ specific: a tumefactive mass is common in pancreatic involvement, with diffuse enlargement of the entire organ; 58 in organs such as salivary glands, discrete areas of disease are seen on a background of unaffected tissue even though no discernible difference in tissue constituency can be observed. 70 Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate laden with IgG4- positive plasma cells on a background of storiform fibrosis and obliterative phlebitis describes the distinctive histopathology that unifies the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease. 71 Thus, a comprehensive and meaningful assessment of tissue in this setting will require IgG4 immunostaining. In glandular organs, the infiltrate will typically concentrate around major ductal (biliary and bronchiolar) structures and can manifest as long regions of wall thickening. 71,72 Lymphocytes are prominent, with T cells distributed throughout and B cells organized in germinal centres. Although diffusely infiltrating IgG4- positive plasma cells are not specific to IgG4- related disease, they are a prerequisite for histopathologic diagnosis. 43,71 High relative density of IgG4-positive plasma cells has high diagnostic utility; some researchers have adopted an IgG4:IgG plasma cell ratio of greater than 40% (50% for aortic disease 73 ) as highly discriminatory when supported by clinical and pathologic features an approach supported in the consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. 71 Fibrosis is an early feature of IgG4-related disease and is arranged in radial fibres that interlace in a storiform pattern throughout the tissue. This storiform pattern may be absent in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis (although fibrosis is often dense) and lymphadenopathy, making the diagnosis in isolated lymph node disease challenging. 71,74 Obliterative phlebitis describes a partial or complete obliteration of medium-sized veins, which may look like an inflammatory nodule, in 958 CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13)
7 proximity to an unaffected artery. This is invariably present in pancreatic or submandibular disease but scarce in lacrimal gland disease. 71 In addition to the classical triad, an eosinophilic infiltration is common and can be dense. 72,75,76 Neutrophilic infiltration and granulomata are rare. 74 The phase of the disease may determine the predominant pathologic findings and predict response to treatment. Retroperitoneal disease is often diagnosed late, and histology shows a relatively paucicellular and dense fibrosis that does not respond well to glucocorticoid therapy. 77 Endstage or burnt-out disease of this type may manifest in different organ systems (e.g., cryptogenic cirrhosis, honeycomb lung, chronic pancreatitis). 34 How is IgG4-related disease treated? Currently, there are no robust data available to inform treatment guidelines, and recommendations are made based on expert opinion and limited data. A suggested treatment schematic based on the international consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease is shown in Figure The treatment model is to induce suppression of the inflammation and maintain the disease in a quiescent state. It should be started early in patients with clinical, biochemical or radiologic evidence of major organ involvement and/or symptomatic disease. 43 However, asymptomatic indolent disease in noncritical systems, such as IgG4-related lymphadenopathy, may only need monitoring. 15 At the other end of the spectrum, burnt-out fibrotic disease, as in some cases of retroperitoneal fibrosis, may be resistant to available treatments. 15 Occasionally, mechanical biliary drainage may be needed for urgent cases of autoimmune pancreatitis or cholangiopathy. 43 Induction IgG4-related disease is usually sensitive to glucocorticoid therapy, which is the recommended firstline treatment; a weight-based dosing regimen for prednisolone of 0.6 mg/kg body weight has been suggested in the treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. 78 A typical starting dose for prednisolone taken orally is 40 mg; 43 however, a nationwide Probable or definite diagnosis of IgG4-RD* Induction treatment Prednisolone 40 mg/d Treatment response (clinical, radiologic and biochemical markers) Assessment at 2 4 wk: Taper treatment if response is good; otherwise, consider alternative diagnosis or burnt-out disease Tapering treatment Duration 3 6 mo Relapse Reinduction: prednisolone AND maintenance treatment Maintenance treatment Low-dose prednisolone (2.5 5 mg/d) or azathioprine (2 2.5 mg/kg/d) or other agent Consider maintenance if the following are present: Multiorgan disease Substantially elevated serum IgG4 History of relapse System-specific markers Figure 4: Treatment schematic for IgG4-related disease. *As diagnosed by international consensus guidance. 43 Consider B-cell depletion if the patient is resistant to or intolerant of glucocorticoids and therapies available to the clinician. Other agents include calcineurin inhibitors, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil and methotrexate. B-cell depletion could be considered. Predictors of relapse in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis or autoimmune pancreatitis include coexisting diabetes, or a high burden of biliary involvement. Note: IgG4-RD = IgG4-related disease. CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13) 959
8 survey in Japan reported no significant differences in outcomes among patients treated with 30 or 40 mg of prednisolone. 79 Glucocorticoid tapering and discontinuation can be associated with disease relapse; however, there is little consistent guidance on how to taper glucocorticoids. Centres in North America aim to stop treatment with glucocorticoids within 11 weeks, 14 whereas some centres in Japan continue low-dose (5 mg) prednisolone for as much as three years. 78 International consensus is to take a pragmatic approach: start to taper the drug after two to four weeks of induction dosing and aim to stop treatment within three to six months, dependent on patient response. 78 Depletion of B cells by rituximab has been shown to be highly effective at inducing and maintaining remission in early phase two trials, and it may serve as an alternative for those with steroidrefractory disease. 43,80 However, B-cell depletion treatment is not readily available everywhere, and some specialists have little or no experience with its use. Thus, the consensus guidance statement suggested its use should be at the discretion and comfort of the prescribing physician. 43 The shortand medium-term safety of rituximab is well established for other autoimmune and hematologic malignant diseases However, long-term safety data are lacking, and concerns remain about longterm immunosuppression in certain populations, particularly among children. 84 There is little evidence to support the use of other induction agents. 21 Following treatment, relapsing disease occurs in about 30% 54% of patients and requires reinduction therapy. 35,78,79 The practice of adding a second agent (e.g., azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine or mycophenolate mofetil) is still common, but there is yet little evidence to suggest a relapse-free survival advantage. 85 Treatment response At present, there are no standardized outcomes by which to measure response to treatment. Serum Box 2: Future perspectives and unanswered questions Promising noninvasive diagnostic markers (e.g., flow cytometry for circulating plasmablasts) may circumvent the need for tissue diagnosis and skilled histopathologic assessment. 23,80,97 There is an urgent clinical imperative for validated specific outcome measures that will allow prognosis and treatment response to be monitored. Circulating plasmablast levels may fulfil this role, and an IgG4-responder index is currently under validation. 87 This will need to be linked to long-term studies to ascertain the optimal maintenance strategy for those patients who achieve remission. The pathophysiology of IgG4-related disease is elusive, and the links between the serologic and histologic findings are unclear. Treatment response (especially with B-cell depletion) and laboratory modelling of the disease may provide invaluable insights into the disease and interplay between immune pathways in other immune-mediated diseases. IgG4 levels do not reliably reflect disease activity, 86 and the utility of serum IgG4-positive plasmablast concentrations 23 and the IgG4-responder index 87 require validation studies. Clinicians must use clinical, laboratory and radiologic markers on a caseby-case basis to gauge response to treatment. Response is usually seen within two to four weeks. 88,89 A lack of improvement within this time frame should prompt a review of the diagnostic evidence and consideration of burnt-out disease 77 or other diagnoses, especially cancer. Maintenance The aim of maintenance treatment is to prevent recurrence of disease following remission. The risk factors for relapse are not well described, although anecdotal evidence suggests multiorgan disease, substantially elevated serum IgG4 concentrations and history of disease relapse are associated with recurrence after remission. 43 A higher burden of biliary involvement or coexisting diabetes in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis or IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis predicts a higher relapse rate. 78 Studies investigating the efficacy of low-dose prednisolone (2.5 5 mg/d) treatment showed a reduction in relapse rate from 34% to 23% compared with patients who were not receiving maintenance immunosuppression. 90 It is unclear how long to continue maintenance treatment with lowdose steroids, and risks related to long-term glucocorticoid treatment in older patients are not insignificant. 91 These issues will need further evaluation before any firm recommendations can be made. Several agents have been used as steroid-sparing maintenance treatment 85,92,93 after remission has been achieved. The use of azathioprine (2 2.5mg/kg body weight) is suggested, 94 although data to support the use of one agent over another are limited. 85 The use of rituximab as maintenance treatment for patients who are at high risk of relapse has been acknowledged in the international consensus guidance statement; however, the optimal frequency and duration of treatment with the drug are subject to further evaluation, 23,36,80,85,95,96 and its practical use is under the aforementioned caveats of physician preference and sparse long-term safety data (Figure 4). Conclusion In just over a decade since its recognition as a clinical entity, the diverse clinical presentation of IgG4-related disease has been mapped, and recent efforts have been geared to optimize its diagnosis and management. However, shortcomings in our understanding and approach persist (Box 2) 23,80,87,91 and need to be addressed. Awareness of the poten- 960 CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13)
9 tial for IgG4-related disease to mimic a range of disorders and an understanding of how to investigate and manage treatment in patients by the current criteria will lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes (Box 2). References 1. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2001;344: Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol 2003;38: Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64: Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: Do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28: Himi T, Takano K, Yamamoto M, et al. A novel concept of Mikulicz s disease as IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx 2012;39: Geyer JT, Ferry JA, Harris NL, et al. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner Tumor) Is an IgG4-associated disease. Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34: Ohno K, Sato Y, Ohshima K-I, et al. IgG4-related disease involving the sclera. Mod Rheumatol 2014;24: Inoue D, Zen Y, Sato Y, et al. IgG4-related perineural disease. Int J Rheumatol 2012: Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology 2009;251: Dahlgren M, Khosroshahi A, Nielsen GP, et al. Riedel s thyroiditis and multifocal fibrosclerosis are part of the IgG4-related systemic disease spectrum. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62: Zen Y, Kasashima S, Inoue D. Retroperitoneal and aortic manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Semin Diagn Pathol 2012;29: Inokuchi G, Hayakawa M, Kishimoto T, et al. A suspected case of coronary periarteritis due to IgG4-related disease as a cause of ischemic heart disease. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 2014;10: Pradhan D, Pattnaik N, Silowash R, et al. IgG4-related kidney disease a review. Pathol Res Pract 2015;211: Hart PA, Kamisawa T, Brugge WR, et al. Long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis: a multicentre, international analysis. Gut 2013;62: Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 2012;366: Aparisi L, Farre A, Gomez-Cambronero L, et al. Antibodies to carbonic anhydrase and IgG4 levels in idiopathic chronic pancreatitis: relevance for diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2005;54: Asada M, Nishio A, Uchida K, et al. Identification of a novel autoantibody against pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2006;33: Nishimori I, Miyaji E, Morimoto K, et al. Serum antibodies to carbonic anhydrase IV in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2005;54: Guarneri F, Guarneri C, Benvenga S. Helicobacter pylori and autoimmune pancreatitis: Role of carbonic anhydrase via molecular mimicry? J Cell Mol Med 2005;9: Frulloni L, Lunardi C, Simone R, et al. Identification of a novel antibody associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2009;361: Islam AD, Selmi C, Datta-Mitra A, et al. The changing faces of IgG4-related disease: clinical manifestations and pathogenesis. Autoimmun Rev 2015;14: Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology 2007;45: Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74: Maillette de Buy Wenniger LJ, Beuers U. Immunoglobulin G4-related cholangiopathy: clinical and experimental insights. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2015;31: Jeannin P, Lecoanet S, Delneste Y, et al. IgE versus IgG4 production can be differentially regulated by IL-10. J Immunol 1998;160: Deshpande V, Chicano S, Chiocca S, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: a systemic immune complex mediated disease. Am J Surg Pathol [published erratum in Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:328]. 2006;30: Detlefsen S, Bräsen JH, Zamboni G, et al. Deposition of complement C3c, immunoglobulin (Ig)G4 and IgG at the basement membrane of pancreatic ducts and acini in autoimmune pancreatitis. Histopathology 2010;57: Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T, et al. IgG4-related disease and its pathogenesis-cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity. Int Immunol 2014;26: Kawa S, Ota M, Yoshizawa K, et al. HLA DRB DQB10401 haplotype is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in the Japanese population. Gastroenterology 2002;122: Chang M-C, Chang Y-T, Tien Y-W, et al. T-cell regulatory gene CTLA-4 polymorphism/haplotype association with autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Chem 2007;53: Umemura T, Ota M, Hamano H, et al. Association of autoimmune pancreatitis with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103: Umemura T, Ota M, Hamano H, et al. Genetic association of Fc receptor-like 3 polymorphisms with autoimmune pancreatitis in Japanese patients. Gut 2006;55: Okazaki K, Uchida K, Fukui T. Recent advances in autoimmune pancreatitis: concept, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. J Gastroenterol 2008;43: Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, et al. IgG4-related disease. Lancet 2015;385: Raina A, Yadav D, Krasinskas AM, et al. Evaluation and management of autoimmune pancreatitis: experience at a large US center. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104: Yamamoto M, Yajima H, Takahashi H, et al. Everyday clinical practice in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and/or sialadenitis: results from the SMART database. Mod Rheumatol 2015;25: Guma M, Firestein GS. IgG4-related diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2012;26: Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, et al. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13: Kim S, Bae H, Choi M, et al. Isolated mass-forming IgG4-related cholangitis as an initial cinical presentation of systemic IgG4- related disease. J Pathol Transl Med 2016;50: Park HG, Kim KM. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the renal pelvis involving renal parenchyma, mimicking malignancy. Diagn Pathol 2016;11: Chari ST. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis using its five cardinal features: introducing the Mayo Clinic s HISORt criteria. J Gastroenterol 2007;42(Suppl 18): van Heerde MJ, Buijs J, Rauws EA, et al. A comparative study of diagnostic scoring systems for autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2014;43: Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67: Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), Mod Rheumatol 2012;22: Ebbo M, Daniel L, Pavic M, et al. IgG4-related systemic disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2012;91: Chen H, Lin W, Wang Q, et al. IgG4-related disease in a Chinese cohort: a prospective study. Scand J Rheumatol 2014;43: Stone JH, Brito-Zerón P, Bosch X, et al. Diagnostic approach to the complexity of IgG4-related disease. Mayo Clin Proc 2015;90: Della Torre E, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, et al. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia, and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy 2014;69: Kamisawa T, Anjiki H, Egawa N, et al. Allergic manifestations in autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;21: Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, et al. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13: Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, et al. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74: Boonstra K, Culver EL, de Buy Wenniger LM, et al. Serum immunoglobulin G4 and immunoglobulin G1 for distinguishing immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2014;59: Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in 125 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67: Matsubayashi H, Sawai H, Kimura H, et al. Characteristics of autoimmune pancreatitis based on serum IgG4 level. Dig Liver Dis 2011;43: CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13) 961
10 55. Kawa S, Ito T, Watanabe T, et al. The utility of serum IgG4 concentrations as a biomarker. Int J Rheumatol 2012;2012: Zhang J, Chen H, Ma Y, et al. Characterizing IgG4-related disease with 18 F-FDG PET/CT: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2014;41: Toyoda K, Oba H, Kutomi K, et al. MR imaging of IgG4- related disease in the head and neck and brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33: Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Farrell J, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: imaging features. Radiology 2004;233: Takagi Y, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, et al. IgG4-related Mikulicz s disease: ultrasonography of the salivary and lacrimal glands for monitoring the efficacy of corticosteroid therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2013;31: Katsura M, Mori H, Kunimatsu A, et al. Radiological features of IgG4-related disease in the head, neck, and brain. Neuroradiology 2012;54: Song YS, Choung H-K, Park S-W, et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4- related disease: CT and MRI findings. Br J Ophthalmol 2013;97: Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N, et al. IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Stone JH, et al. Rethinking Ormond s disease: idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2013;92: Takahashi N, Kawashima A, Fletcher JG, et al. Renal involvement in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiology 2007;242: Tokala A, Khalili K, Menezes R, et al. Comparative MRI analysis of morphologic patterns of bile duct disease in IgG4- related systemic disease versus primary sclerosing cholangitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014;202: Nakazawa T, Ohara H, Sano H, et al. Schematic classification of sclerosing cholangitis with autoimmune pancreatitis by cholangiography. Pancreas 2006;32: Okano N, Igarashi Y, Kishimoto Y, et al. Case of immunoglobulin G4-related cholangitis accompanying autoimmune pancreatitis: diagnosis by peroral cholangioscopy and treatment by endoscopic biliary stenting. Dig Endosc 2012;24(Suppl 1): Patel H, Khalili K, Kyoung KT, et al. IgG4 related disease a retrospective descriptive study highlighting Canadian experiences in diagnosis and management. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13: Morishima T, Kawashima H, Ohno E, et al. Prospective multicenter study on the usefulness of EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy for the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2016 Jan. 14 [Epub ahead of print]. 70. Asai S, Sato S, Okami K, et al. Sonographic evaluation of the treatment response in patients with immunoglobulin G4-related disease of the submandibular glands. J Ultrasound Med 2015;34: Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 2012;25: Deshpande V, Gupta R, Sainani N, et al. Subclassification of autoimmune pancreatitis: a histological classification with clinical significance. Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35: Stone JR. Aortitis, periaortitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis, as manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23: Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34: Deshpande V, Khosroshahi A, Nielsen GP, et al. Eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis is a form of IgG4-related systemic disease. Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35: Zamboni G, Lüttges J, Capelli P, et al. Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: a study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows Arch 2004;445: Shimizu Y, Yamamoto M, Naishiro Y, et al. Necessity of early intervention for IgG4-related disease delayed treatment induces fibrosis progression. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52: Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Amendment of the Japanese Consensus Guidelines for Autoimmune Pancreatitis, 2013 III. Treatment and prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 2014;49: Kanno A, Nishimori I, Masamune A, et al; Working Committee of the Japan Pancreas Society and the Research Committee for Intractable Pancreatic Disease supported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan. Pancreas 2012;41: Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74: Singh JA, Wells GA, Christensen R, et al. Adverse effects of biologics: a network meta-analysis and Cochrane overview. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;(2):CD Bauer K, Rancea M, Roloff V, et al. Rituximab, ofatumumab and other monoclonal anti-cd20 antibodies for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;(11): CD Lopez-Olivo MA, Amezaga Urruela M, McGahan L, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;(1):CD LaBarba S, Kaplan BM, Eberhard B. Prolonged immune suppression after rituximab use in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;137:AB Hart PA, Topazian MD, Witzig TE, et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut 2013;62: Sah RP, Chari ST. Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011;23: Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Deshpande V, et al. Development of an IgG4-RD responder index. Int J Rheumatol 2012;2012: Kamisawa T, Egawa N, Inokuma S, et al. Pancreatic endocrine and exocrine function and salivary gland function in autoimmune pancreatitis before and after steroid therapy. Pancreas 2003;27: Ko SBH, Mizuno N, Yatabe Y, et al. Corticosteroids correct aberrant CFTR localization in the duct and regenerate acinar cells in autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010;138: Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2009;58: Hirano K, Tada M, Isayama H, et al. Long-term prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis with and without corticosteroid treatment. Gut 2007;56: Buechter M, Klein CG, Kloeters C, et al. Tacrolimus as a reasonable alternative in a patient with steroid-dependent and thiopurine-refractory autoimmune pancreatitis with IgG4-associated cholangitis. Z Gastroenterol 2014;52: Bosco JJ, Suan D, Varikatt W, et al. Extra-pancreatic manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease: a single-centre experience of treatment with combined immunosuppression. Intern Med J 2013;43: Sah RP, Chari ST. Autoimmune pancreatitis: an update on classification, diagnosis, natural history and management. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2012;14: Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, et al. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62: Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;134: Della-Torre E, Feeney E, Deshpande V, et al. B-cell depletion attenuates serological biomarkers of fibrosis and myofibroblast activation in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74: Affiliations: Centre for Liver Research (Haldar, Hirschfield), National Institute for Health Research Liver Biomedical Research Unit, University of Birmingham; Department of Renal Medicine (Cockwell), Institute of Translational Medicine, Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, University Hospital Birmingham, Edgbaston; Institute of Immunology and Immunotherapy (Haldar, Richter, Hirschfield), College of Medical and Dental Sciences, University of Birmingham; Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery (Roberts), Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, University Hospital Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, UK Contributors: Debashis Haldar and Gideon Hirschfield contributed substantially to conception and design of the article. All of the authors drafted the article, reviewed it critically for intellectual content, gave final approval of the version to be published and agreed to act as guarantors of the work. Funding: Debashis Haldar was supported by a Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Fellowship Program. Debashis Haldar and Gideon Hirschfield were supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Birmingham Liver Biomedical Research Unit. This article presents independent research funded by the NIHR. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, the NIHR or the Department of Health. 962 CMAJ, September 20, 2016, 188(13)
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci
 CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
IgG4 Disease. General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman
 IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4-related sclerosing disease
 IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
Overview of the Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Spectrum
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore
 IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
How 5 Diseases Became One. Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University
 How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
 Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis of Other Etiology
 94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator
 Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease
 Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis
 REVIEW IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Emma L. Culver, B.Sc., M.B.Ch.B., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.,* and Eleanor Barnes, M.B.B.S., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.*,, BACKGROUND IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC)
REVIEW IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Emma L. Culver, B.Sc., M.B.Ch.B., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.,* and Eleanor Barnes, M.B.B.S., D.Phil., M.R.C.P.*,, BACKGROUND IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC)
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Korea
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Autoimmune Pancreatitis & Cholangiopathy. Goal and Objectives
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis & Cholangiopathy Kaveh Sharzehi, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Endoscopy Section of Gastroenterology Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University
Autoimmune Pancreatitis & Cholangiopathy Kaveh Sharzehi, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Endoscopy Section of Gastroenterology Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University
Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term Outcome of Autoimmune Pancreatitis after Oral Prednisolone Therapy Takayoshi Nishino 1, Fumitake Toki 2,HiroyasuOyama 3, Kyoko Shimizu 1 and Keiko Shiratori 1 Abstract Objective
Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation
 ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
IgG4 Related disease a retrospective descriptive study highlighting Canadian experiences in diagnosis and management
 Patel et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:168 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IgG4 Related disease a retrospective descriptive study highlighting Canadian experiences in diagnosis and management Harshna
Patel et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:168 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IgG4 Related disease a retrospective descriptive study highlighting Canadian experiences in diagnosis and management Harshna
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin G4-related Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Sjögren s Syndrome
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy
 Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
IgG4-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients
 IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
Autoimmune pancreatitis
 Review Article Autoimmune pancreatitis Ayodeji Oluwarotimi Omiyale Department of Cellular Pathology, Maidstone Hospital, Maidstone, Kent, UK Correspondence to: Ayodeji Oluwarotimi Omiyale. Department of
Review Article Autoimmune pancreatitis Ayodeji Oluwarotimi Omiyale Department of Cellular Pathology, Maidstone Hospital, Maidstone, Kent, UK Correspondence to: Ayodeji Oluwarotimi Omiyale. Department of
Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Autoimmune Pancreatitis, Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Imaging Findings
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis, Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Imaging Findings Poster No.: R-0074 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Stegeman, A. Borsaru; Clayton/AU Keywords: Education
Autoimmune Pancreatitis, Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Imaging Findings Poster No.: R-0074 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Stegeman, A. Borsaru; Clayton/AU Keywords: Education
Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease: Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Extrapancreatic
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 CASE REPORT Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas Involving Type 1 Localized Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Normal Serum IgG4 Levels Successfully Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided
CASE REPORT Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas Involving Type 1 Localized Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Normal Serum IgG4 Levels Successfully Diagnosed by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided
IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review
 www.rarediseasesjournal.com Journal of Rare Diseases Research & Treatment Mini review Open Access IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review Ramy Sedhom 1*, Daniel Sedhom 1 and Roger Strair 2 1 Department of
www.rarediseasesjournal.com Journal of Rare Diseases Research & Treatment Mini review Open Access IgG-4 related disease: A mini-review Ramy Sedhom 1*, Daniel Sedhom 1 and Roger Strair 2 1 Department of
The most common presentation of autoimmune pancreatitis. A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc. Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz
 Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) was described more than a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4
 238 & 2015 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/15 $32.00 Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4 Phil
238 & 2015 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/15 $32.00 Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis without IgG4 tissue infiltration or serum IgG4 elevation: IgG4-related disease without IgG4 Phil
The newly recognized fibroinflammatory condition. An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases
 case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease
 International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
International Rheumatology Volume 2, Article ID 283459, pages doi:1.1155/2/283459 Clinical Study Evaluation and Clinical Validity of a New Questionnaire for Mikulicz s Disease Motohisa Yamamoto, 1 Hiroki
Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 591360, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/591360 Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 591360, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/591360 Case Report IgG4-Seronegative Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Sclerosing Cholangitis
Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
 2007 년도대한췌담도학회추계학술대회 Session II: Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria for AIP: Japan, USA & Korea Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National
2007 년도대한췌담도학회추계학술대회 Session II: Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria for AIP: Japan, USA & Korea Overview of Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Pancreatitis Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National
Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features.
 'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features. Poster No.: C-2649 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. P. Patel, T. M. Chandler, S. Barrett, J.
'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features. Poster No.: C-2649 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. P. Patel, T. M. Chandler, S. Barrett, J.
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Renal Pathology Case Conference. Case 2
 Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Associated with Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
 CASE REPORT A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Associated with Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Koushiro Ohtsubo 1, Hiroyuki Watanabe 1, Tomoya Tsuchiyama 1, Hisatsugu Mouri 1, Yasushi Yamaguchi 1, Yoshiharu Motoo
CASE REPORT A Case of Autoimmune Pancreatitis Associated with Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Koushiro Ohtsubo 1, Hiroyuki Watanabe 1, Tomoya Tsuchiyama 1, Hisatsugu Mouri 1, Yasushi Yamaguchi 1, Yoshiharu Motoo
Differentiating Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis from Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 2, March 2013, pp. 234-238 ORiginal Article Differentiating Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis from Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma Taku Tabata*, Terumi Kamisawa*, Seiichi
Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 2, March 2013, pp. 234-238 ORiginal Article Differentiating Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis from Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma Taku Tabata*, Terumi Kamisawa*, Seiichi
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) can be defined as a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus
 Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4-
 Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease
 Original Article Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease Lu Cao, Yi-Bing Chen, Da-Hui Zhao, Wen-Fang Shi, Song Meng, Li-Xin Xie Department of
Original Article Pulmonary function tests findings and their diagnostic value in patients with IgG4-related disease Lu Cao, Yi-Bing Chen, Da-Hui Zhao, Wen-Fang Shi, Song Meng, Li-Xin Xie Department of
Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis
 REVIEW Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:841-850 https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2018.018 Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis George Goodchild, Stephen P. Pereira, and George Webster Department of
REVIEW Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:841-850 https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2018.018 Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis George Goodchild, Stephen P. Pereira, and George Webster Department of
Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7816-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Yoji Komiya 1, Makoto Soejima
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7816-16 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Early Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Yoji Komiya 1, Makoto Soejima
Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone Phenomenon in Patients With IgG4-Related Disease
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp 213 217 DOI 10.1002/art.38193 2014, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Spuriously Low Serum IgG4 Concentrations Caused by the Prozone
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), a clinical entity originally
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Multiorgan Disease Presenting a Conundrum for Clinicians in the West Eileen Kim, MD, Rebecca Voaklander, MD, Franklin E. Kasmin, MD, William H. Brown, MD, Rifat Mannan, MD, and
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Multiorgan Disease Presenting a Conundrum for Clinicians in the West Eileen Kim, MD, Rebecca Voaklander, MD, Franklin E. Kasmin, MD, William H. Brown, MD, Rifat Mannan, MD, and
Localized autoimmune pancreatitis mimicking pancreatic cancer: Case report and literature review
 Case Report Localized autoimmune pancreatitis mimicking pancreatic cancer: Case report and literature review Journal of International Medical Research 2018, Vol. 46(4) 1657 1665! The Author(s) 2018 Reprints
Case Report Localized autoimmune pancreatitis mimicking pancreatic cancer: Case report and literature review Journal of International Medical Research 2018, Vol. 46(4) 1657 1665! The Author(s) 2018 Reprints
Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Key words: diagnosis, immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin G4-related diseases, immunohistochemistry, pseudolymphoma. CASE HISTORY
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
IgG4-Related Disease
 IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease that produces sclerotic, tumefactive masses containing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in immunoglobulin (Ig)
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease that produces sclerotic, tumefactive masses containing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in immunoglobulin (Ig)
Successful Treatment of Multi-system IgG4-related Disease with Cyclophosphamide: A Case Report X Zhang, W Qin, J Zhou, L Yang ABSTRACT
 Successful Treatment of Multi-system IgG4-related Disease with Cyclophosphamide: A Case Report X Zhang, W Qin, J Zhou, L Yang ABSTRACT Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is increasingly recognized
Successful Treatment of Multi-system IgG4-related Disease with Cyclophosphamide: A Case Report X Zhang, W Qin, J Zhou, L Yang ABSTRACT Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is increasingly recognized
Case Report The Challenging Diagnosis of Pancreatic Masses: Not All Tumors Are Cancers
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 832463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/832463 Case Report The Challenging Diagnosis of Pancreatic Masses: Not All Tumors Are Cancers Alessandro
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 832463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/832463 Case Report The Challenging Diagnosis of Pancreatic Masses: Not All Tumors Are Cancers Alessandro
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT
 J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass
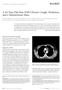 [ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
[ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction
 Clin Exp Nephrol (2016) 20:87 93 DOI 10.1007/s10157-015-1140-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction Takako Saeki
Clin Exp Nephrol (2016) 20:87 93 DOI 10.1007/s10157-015-1140-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recovery of renal function after glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-related kidney disease with renal dysfunction Takako Saeki
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis
 Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
Hideaki Miura, Yasutaka Miyachi. Department of Internal Medicine, Social Insurance Central General Hospital. Tokyo, Japan
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Retroperitoneal Fibrosis and Sclerosing Cholangitis Independent of Autoimmune Pancreatitis. A Recurrent Case after a 5-Year History of Spontaneous Remission Hideaki Miura, Yasutaka
CASE REPORT IgG4-Related Retroperitoneal Fibrosis and Sclerosing Cholangitis Independent of Autoimmune Pancreatitis. A Recurrent Case after a 5-Year History of Spontaneous Remission Hideaki Miura, Yasutaka
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL
 TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Succinct Overview
 REVIEW ARTICLE Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Succinct Overview Juan Putra, Xiaoying Liu Department of Pathology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, One Medical Center Drive Lebanon, NH 03756, USA ABSTRACT
REVIEW ARTICLE Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Succinct Overview Juan Putra, Xiaoying Liu Department of Pathology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, One Medical Center Drive Lebanon, NH 03756, USA ABSTRACT
Wang et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:65
 Wang et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1567-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Failure of remission induction by glucocorticoids alone or in combination with
Wang et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1567-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Failure of remission induction by glucocorticoids alone or in combination with
Clinical profile and treatment outcomes in autoimmune pancreatitis: a report from North India
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-7 Clinical profile and treatment outcomes in autoimmune pancreatitis: a report from North India Surinder S. Rana a, Rajesh Gupta b, Ritambhra Nada
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-7 Clinical profile and treatment outcomes in autoimmune pancreatitis: a report from North India Surinder S. Rana a, Rajesh Gupta b, Ritambhra Nada
Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular Glands and Extraocular Muscles
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Crohn s Disease
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0213-17 Intern Med 57: 2957-2962, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Crohn s Disease Yoon Suk Lee, Nam-Hoon Kim, Jun Hyuk Son, Jung Wook
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0213-17 Intern Med 57: 2957-2962, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Crohn s Disease Yoon Suk Lee, Nam-Hoon Kim, Jun Hyuk Son, Jung Wook
IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal
 CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 232960, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/232960 Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 232960, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/232960 Clinical Study Spectrum of Disorders Associated with Elevated Serum IgG4 Levels Encountered in Clinical Practice
Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Medicine 2015 Vol 15, No 2: 130 4 Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease Authors: Deepak Joshi, A Rolf Jager, B Steven Hurel, C Stephen P Pereira, D Gavin J Johnson, E
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Medicine 2015 Vol 15, No 2: 130 4 Cerebral involvement in IgG4-related disease Authors: Deepak Joshi, A Rolf Jager, B Steven Hurel, C Stephen P Pereira, D Gavin J Johnson, E
gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features
 gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features Poster No.: C-2603 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Kawamura, Y. Kikuchi, I.
gg4-related inflammatory pseudotumour of the trigeminal nerve: imaging findings and clinical features Poster No.: C-2603 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. Kawamura, Y. Kikuchi, I.
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):803-807 Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):803-807 Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture. J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc.
 Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc Outline What defines a refractory biliary stricture Endoscopic
Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc Outline What defines a refractory biliary stricture Endoscopic
Longstanding IgG4-related Ophthalmic Disease Dramatically Improved after Steroid Therapy
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0300-17 Intern Med 57: 2879-2883, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Longstanding IgG4-related Ophthalmic Disease Dramatically Improved after Steroid Therapy Yoko Hirata
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0300-17 Intern Med 57: 2879-2883, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Longstanding IgG4-related Ophthalmic Disease Dramatically Improved after Steroid Therapy Yoko Hirata
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease, a systemic,
 IgG4-Related Disease of the Gastrointestinal Tract A 21st Century Chameleon Vikram Deshpande, MD Context. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease is a systemic fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting
IgG4-Related Disease of the Gastrointestinal Tract A 21st Century Chameleon Vikram Deshpande, MD Context. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease is a systemic fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting
Incidence of Malignancy in Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incidence of Malignancy in Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis Junko Tahara 1, Kyoko Shimizu 1, Junichi Akao 1, Yukiko Takayama 1, Katsutoshi Tokushige 1, Masakazu Yamamoto 2 1 Department of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incidence of Malignancy in Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis Junko Tahara 1, Kyoko Shimizu 1, Junichi Akao 1, Yukiko Takayama 1, Katsutoshi Tokushige 1, Masakazu Yamamoto 2 1 Department of
Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients C.A. Tiegs-Heiden, L.J. Eckel, C.H. Hunt, F.E. Diehn, K.M. Schwartz, D.F. Kallmes, D.R. Salomão,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Immunoglobulin G4 Related Disease of the Orbit: Imaging Features in 27 Patients C.A. Tiegs-Heiden, L.J. Eckel, C.H. Hunt, F.E. Diehn, K.M. Schwartz, D.F. Kallmes, D.R. Salomão,
IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Kazuichi Okazaki 1 and Hisanori Umehara Introduction. 2. The Concept of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 357071, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/357071 Review Article Are Classification Criteria for IgG4-RD Now Possible?
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease
 CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
CASE REPORT A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Coexisting with IgG4-related Disease Hirofumi Takei 1, Hayato Nagasawa 1, Ryota Sakai 1, Koji Nishimura 1, Takahiko
IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: all we need to know
 J Gastroenterol (2016) 51:295 312 DOI 10.1007/s00535-016-1163-7 REVIEW IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: all we need to know Yoh Zen 1 Hiroshi Kawakami 2 Jung Hoon Kim 3 Received: 24 December 2015 /
J Gastroenterol (2016) 51:295 312 DOI 10.1007/s00535-016-1163-7 REVIEW IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: all we need to know Yoh Zen 1 Hiroshi Kawakami 2 Jung Hoon Kim 3 Received: 24 December 2015 /
IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report
 Zhang et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:44 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0041-6 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report Hui Zhang
Zhang et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:44 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0041-6 CASE REPORT Open Access IgG4-related kidney disease from the renal pelvis that mimicked urothelial carcinoma: a case report Hui Zhang
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Diagnosis of tumor extension in biliary carcinoma has. Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP Sun Young Choi 1, Sanghui Park 2
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
