SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY I - VPM 222. Pathology of the Endocrine System. Lecture 1 General Mechanisms & Pituitary Gland (Web Review)
|
|
|
- Leona Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY I - VPM 222 Pathology of the Endocrine System Lecture 1 General Mechanisms & Pituitary Gland (Web Review) Paul Hanna Fall 2012
2 Reference Texts
3 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Others: chemoreceptor organs, testis/ovary, placenta, kidney, thymus, pineal, G-I tract (DNES)
4 ENDOCRINE GLANDS scattered / no physical continuity / diverse embryological origins synthesize / store / release hormones directly into the bloodstream hormones interact with target cells biological response (maintain homeostasis) From McGavin & Zachary: Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th ed disorders are manifest by derangement of target organ functions Clin Dx - laboratory tests (eg CBC, serum chemistry, specific hormone assays, etc)
5 Polypeptide Hormones RER synthesis secretory granule storage fusion to plasma membrane target cell membrane receptors (eg GPCR s) signal transduction pathways Growth hormone Basic Histology
6 Steroid Hormones continuous biosynthesis on SER diffuse through plasma membrane of target cell bind cytosolic receptors nucleus mrna transcription specific protein synthesis in target cells cortisol [Bloom & Fawcett: A textbook of Histology] Adrenal cortical cell
7 Catecholamines & Iodothyronine Hormones hormones derived from tyrosine catecholamines act like polypeptides iodothyronines act like steroids
8 Mechanisms of Endocrine Disease 1) Hyperactivity a) Primary hyperfunction autonomous hypersecretion of hormone due to endocrine tumor b) Secondary hyperfunction excess trophic hormone hypersecretion of hormones by the target organ c) Hyperactivity secondary to diseases of other organs d) Hypersecretion of hormones (hormone-like) by non-endocrine tumor e) Iatrogenic syndromes of hormone excess
9 Mechanisms of Endocrine Disease 2) Hypoactivity a) Primary Hypofunction subnormal hormone levels due to: destruction of secretory cells failure of development genetic defect in biosynthesis b) Secondary hypofunction destruction of one organ (pituitary) interferes with the secretion of trophic hormone hypofunction of target gland c) Endocrine dysfunction due to failure of target-cell response
10
11 Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) embryologic development oropharyngeal ectoderm + diencephalic neuroectoderm Figure Formation of the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland forms from two separate embryonic structures. (a): During the third week of development, a hypophyseal pouch (or Rathke s pouch, the future anterior pituitary) grows from the roof of the pharynx, while a neurohypophyseal bud (future posterior pituitary) forms from the diencephalon. (b): By late in the second month, the hypophyseal pouch detaches from the roof of the pharynx and merges with the neurohypophyseal bud. (c): During the fetal period, the anterior and posterior parts of the pituitary complete development.
12 Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Sella turcica (= Turkish saddle) is a saddle-shaped depression in the sphenoid bone
13 Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Figure (Zachary). Pituitary gland and brain stem, normal dog. Longitudinal section of the pituitary region illustrating the close relationship to the optic chiasm (O), hypothalamus (H), and overlying brain. The pars distalis (D) forms a major part of the adenohypophysis and completely surrounds the pars nervosa (N). The residual lumen of Rathke s pouch (arrow) separates the pars distalis and pars nervosa and is lined by the pars intermedia.
14 biology.clc.uc.edu Histology of feline pituitary gland
15 Neurohypophysis hormones from SO / PV nuclei pars nervosa by axonal processes terminate on fenestrated capillaries released to general circulation Basic Histology
16 Adenohypophysis Basic Histology
17 Basic Histology
18 Basic Histology Somatotroph of a cat Basic Histology Acidophils, basophils & chromophobes IHC for prolactin
19 Malformations Pituitary cysts Figure (Zachary). Cystic Rathke s pouch, brain, sagittal section, dog. A large, multiloculated cyst (C) is noted on the ventral aspect of this brain where the adenohypophysis would normally be located.
20 Malformations Pituitary cysts Cysts from failure of differentiation of oropharyngeal ectoderm of Rathke's pouch progressively enlarging cyst in the sella turcica complete or partial absence of adenohypophysis & compression of neurohypophysis * Cornell - CVM Close up of a pituitary cyst (*) from Rathke s pouch
21 Pituitary Dwarfism juvenile panhypopituitarism in German shepherd (AR) puppies stunted, retain juvenile hair, become alopecic & hyperpigmented secondary endocrine dysfunctions due to atrophy of thyroids, adrenals and gonads large cysts may cause diabetes insipidus Pituitary dwarfism A (top right) affected pup with normal littermate, at 5-months old. B (bottom right) stunted pup with juvenile partial alopecia of the haircoat
22 Inflammation 1) Pituitary Abscesses sporadically in ruminants and swine caused by bacteria or mycotic agents neurological signs due to local extension of the inflammation 2) Infiltration of mononuclear inflammatory cells in some viral and protozoan diseases as part of encephalitis or meningitis
23 Pituitary Abscesses * midsaggital section (above) and dorsal view through diaphragma sella (right) with abundant purulent exucate in both (asterisks) *
24 Diabetes Insipidus a) Hypophyseal form (= central DI) any lesion (neoplasm / cyst / trauma) that interferes with ADH synthesis / secretion Cross-section of normal axons with secretory granules Basic Histology Cross-section of axons of damaged neurons with reduced number of and empty (arrow) secretory granules
25 Diabetes Insipidus b) Nephrogenic form hereditary defects in the ADH receptor or occasionally in the water channel (AQP-2) collecting duct cells fail to respond to normal or elevated circulating ADH Note: There can be genetic defects in ADH (=V2) receptor or less frequently defects in the aquaporin 2 water channel. i) both forms PU/PD & urine of low osmolality (even after H 2 O deprivation) ii) exogenous ADH increase in urine osmolality in hypophyseal DI (not nephrogenic)
26 Hyperplasia / Neoplasia neoplasms may be functional (stimulate target organ) or nonfunctional (destructive to adjacent structures) nodular hyperplasia vs adenomas (larger, capsule, compression)
27 Adenomas of Pars Distalis a) ACTH-Secreting (Corticotroph) Adenoma esp dogs, tumors often small Figure (Zachary) Secondary hyperfunction of an endocrine organ, brain, pituitary gland and adrenal glands, dog. Corticotroph (adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH]-secreting) chromophobe adenoma (A) in the pituitary gland and bilateral enlargement of the adrenal glands. The chronic secretion of ACTH has resulted in hypertrophy and hyper plasia of secretory cells of the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis in the adrenal cortex (arrows) and excessive secretion of cortisol. Normal adrenal
28 Adenomas of Pars Distalis a) ACTH-Secreting (Corticotroph) Adenoma esp dogs, tumors often small Histology of a pituitary ACTH-secreting adenoma: cords and nests of proliferating neoplastic corticotrophs Immunohistochemistry: positive staining for ACTH.
29 Adenomas of Pars Distalis b) Nonfunctional Adenoma usually become large before causing clinical signs Figure (Zachary). Adenoma, pituitary gland, dog. A large pituitary adenoma (A) has extended dorsally and compresses the overlying brain. The optic chiasm (arrow) is also severely compressed. The adenohypophysis, neurohypophysis, and hypothalamus have been destroyed by the neoplasm.
30 b) Nonfunctional Adenoma Figure (Zachary) Secondary hypofunction of an endocrine gland, brain, pituitary gland and adrenal glands, dog. A large nonfunctional chromophobe adenoma (A) has invaded and completely destroyed the adenohypophysis and hypothalamus, and infiltrated into the thalamus. Destruction of the adenohypophysis has resulted in a lack of secretion of thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropin, and other pituitary trophic hormones. This resulted in severe trophic atrophy of the adrenal cortex (arrowheads), especially the adrenocorticotropic hormone dependent zona fasciculata and zona reticularis, and consequently, in a relatively more prominent medulla (M).
31 Adenomas of Pars Distalis c) Somatotroph Adenoma these tumors cause gigantism in the young and acromegaly in adults gigantism: six-foot-five-inch, 12 yr-old boy with his mother d) Adenomas of Lactotrophs, Gonadotrophs and Thyrotrophs excess prolactin secretion, reported in non-pregnant, lactating goats
32 Adenomas of Pars Intermedia in dogs: can be inactive or active in horses: often large and compress neurohypophysis and hypothalamus hirsutism, altered CHO metabolism, polyphagia, muscle atrophy / weakness, laminitis, intermittent hyperpyrexia, hyperhidrosis and PU/PD Hirsuitism due to failure of hair shedding associated with ademoma of the pars intermedia
33 Figure (Zachary). Adenoma, brain, pituitary gland, horse. The pituitary gland is notably enlarged because of an adenoma (A) of the pars intermedia. Cut surface of a pituitary adenoma of pars intermedia of a horse
34 Figure 41-1 (from Large Animal Internal Medicine 4 th edition). Physiology of the equine pituitary pars intermedia. The melanotropes of the pars intermedia produce the hormone precursor protein proopiomelanocortin (POMC), which in the pars intermedia is cleaved into the hormones - melanocytes-stimulating hormone ( -MSH), β- endorphin (β-end) and corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide (CLIP). Production of POMC in the pars intermedia is under inhibitory control by dopamine released from the nerve terminals of the periventricular neurons (cell bodies in hypothalmus). Figure 41-3 (from Large Animal Internal Medicine 4 th edition). Pathophysiology of equine pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction. Loss of functional dopaminergic periventricular neurons leads to a decrease in dopamine at the pars intermedia. This in turn results in disinhibition of the melanotropes of the pars intermedia. The outcome is hypertrophy and hyperplasia (and often adenomas) of the pars intermedia and increased systemic release of the pars intermedia POMCderived peptides -MSH, β-end and CLIP.
35 Adenomas of Pars Intermedia tumor cells produce excess proopiomelanocortin (POMC) aberrant posttranslational processing varying amounts of ACTH/CLIP, MSH, β-endorphin. PC1 = prohormone convertase I PC2 = prohormone convertase II Figure 41-2 (from Large Animal Internal Medicine 4 th edition). Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) processing. POMC is cleaved by prohormone convertase I into ACTH in the pars distalis and into - melanocytes-stimulating hormone ( -MSH), β-endorphin (β-end) and corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide (CLIP) by prohormone convertase I & II in the pars intermedia. Only a small amount of ACTH is produced by the normal pars intermedia.
36 Pituitary Carcinoma most inactive can lead to: panhypopituitarism, diabetes insipidus, CNS dysfunction, +/- metastasis Pituitary carcinoma showing destruction of normal pituitary and extension into overlying brainstem Histology of pituitary carcinoma showing local invasion (arrow) of adjacent neuroparenchyma (brain tissue).
37 Metastatic Tumors tumors metastasizing to the pituitary would be uncommon, but could also lead to panhypopituitarism, CNS signs, etc
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Diseases of pituitary gland
 Diseases of pituitary gland A brief introduction Anterior lobe = adenohypophysis Posterior lobe = neurohypophysis The production of most pituitary hormones is controlled in large part by positively and
Diseases of pituitary gland A brief introduction Anterior lobe = adenohypophysis Posterior lobe = neurohypophysis The production of most pituitary hormones is controlled in large part by positively and
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland
 Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY. Embryology cont. Embryology of the pituitary BY MISPA ZUH HS09A179. Embryology cont. THE PITUIYARY GLAND Anatomy:
 THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY BY MISPA ZUH HS09A179 Embryology of the pituitary The pituitary is formed early in embryonic life from the fusion of the Rathke s pouch (anterior) and the diencephalon ( posterior)
THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY BY MISPA ZUH HS09A179 Embryology of the pituitary The pituitary is formed early in embryonic life from the fusion of the Rathke s pouch (anterior) and the diencephalon ( posterior)
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones
 Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
Pituitary Gland and Tropic Hormones By Adeyomoye O.I Department of Physiology Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences Ondo, Ondo City. 11/9/2017 1 Introduction The hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Hypophysis. Organization
 Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
Hypophysis The hypophysis or pituitary is a complex endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, lying in the sella turcica, a small depression in the sphenoid bone. It is attached to the hypothalamic
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
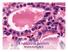 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D. Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline. Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
 Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
Pathophysiology of the th E d n ocr i ne S S t ys em B. Marinov, MD, PhD Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus
 Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB
 Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]
![BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ] BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]](/thumbs/87/96904971.jpg) BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
Pituitary Disorders. Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: /1/2019
 Pituitary Disorders Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 0915020385 31/1/2019 Objectives By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Understand basic Pituitary axis physiology State the common causes of
Pituitary Disorders Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 0915020385 31/1/2019 Objectives By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Understand basic Pituitary axis physiology State the common causes of
By: Mohammad Jomaa & Amer Al-Salamat. Lec:Pathology of pituitary gland. **Sheet contain the slide in Bold. **some book information in Red.
 By: Mohammad Jomaa & Amer Al-Salamat Lec:Pathology of pituitary gland **Sheet contain the slide in Bold. **some book information in Red. Pathology of pituitary gland Before we start :( from book) The endocrine
By: Mohammad Jomaa & Amer Al-Salamat Lec:Pathology of pituitary gland **Sheet contain the slide in Bold. **some book information in Red. Pathology of pituitary gland Before we start :( from book) The endocrine
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3.
 Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Original Research Article HISTOGENESIS OF HUMAN FOETAL PITUITARY AT VARIOUS GESTATIONAL AGES S. Babu Rao * 1, G. Geetha vani 2, V. Subhadra Devi 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research,
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
The Endocrine System. Qian XiaoJing. Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE QIAN
 The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
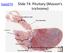 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
THE ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 THE ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the endocrine and reproductive systems. There are a bunch of tissues and topics that can be covered in these systems,
THE ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the endocrine and reproductive systems. There are a bunch of tissues and topics that can be covered in these systems,
Physiological processes controlled by hormones?
 : the study of hormones, their receptors, the intracellular signaling pathways they invoke, and the diseases and conditions associated with them. What are hormones? Major endocrine glands? Fig 7-2 Physiological
: the study of hormones, their receptors, the intracellular signaling pathways they invoke, and the diseases and conditions associated with them. What are hormones? Major endocrine glands? Fig 7-2 Physiological
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine part two. Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy
 Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
Biochemistry and Disorders of Hormones of the Hypothalamic and pituitary gland (hypothalamus and pituitary axis)
 Biochemistry and Disorders of Hormones of the Hypothalamic and pituitary gland (hypothalamus and pituitary axis) Objectives: 1. Describe the structure and function of the hypothalamus 2. List the hormones
Biochemistry and Disorders of Hormones of the Hypothalamic and pituitary gland (hypothalamus and pituitary axis) Objectives: 1. Describe the structure and function of the hypothalamus 2. List the hormones
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Fig The Endocrine System The connective tissue will be very well vascularized. Due to their need to distribute their products by the blood, the
 Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
The Endocrine System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris
 18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
18 The Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris NOTE: Presentations extensively modified for use in MCB 244 & 246 at the University of Illinois
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to
 Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS
 THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS They are two glands, present above the kidneys. One adrenal gland is sufficient for human beings/mammals (example: we also have two kidneys but one is sufficient). The Adrenal
THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLANDS They are two glands, present above the kidneys. One adrenal gland is sufficient for human beings/mammals (example: we also have two kidneys but one is sufficient). The Adrenal
Endocrine system. General principle of endocrinology. Mode of hormone delivery to target. Mode of hormone delivery to target
 Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY
 WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible. 15 Classification. Nomenclature
WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible. 15 Classification. Nomenclature
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland
 Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D.
 The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Construct the relationships between
The Posterior Pituitary Gland and Related Issues (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) R.J. Witorsch, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Construct the relationships between
Laurie A. Loevner, MD
 Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
ENDOCRINE GLANDS. Pituitary Gland
 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine (or internally secreting) glands are also named ductless glands, since they lack excretory ducts. Instead, the secretory cells release their products, hormones, into the extracellular
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. Some definitions. Receptor: Properties of receptors. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI.
 MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI. OUTLINE. Introduction Some definitions Hormone secretion, transport, and clearance from the blood. Feedback control of hormone secretion.
MECHANISM AND MODE OF HORMONE ACTION. PRESENTED BY MBUNKUR GLORY NKOSI. OUTLINE. Introduction Some definitions Hormone secretion, transport, and clearance from the blood. Feedback control of hormone secretion.
Introduction to the Endocrine System
 1 About This Chapter 2 Chapter 7a Hormones Introduction to the Endocrine System The classification of hormones Control of hormone release Hormone interactions Endocrine pathologies Hormone evolution Hormones:
1 About This Chapter 2 Chapter 7a Hormones Introduction to the Endocrine System The classification of hormones Control of hormone release Hormone interactions Endocrine pathologies Hormone evolution Hormones:
p171 - thyroid hyperplasia https://med-vmicro.med.illinois.edu/v/475/ p34 - prostate hyperplasia https://med-vmicro.med.illinois.
 THE ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the endocrine and reproductive systems. There are a bunch of tissues and topics that can be covered in these systems,
THE ENDOCRINE AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the endocrine and reproductive systems. There are a bunch of tissues and topics that can be covered in these systems,
Endocrine System. Collection of glands that secrete hormones.
 Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA
 RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
anterior lobe posterior lobe hypophyseal (Rathke s) pouch neuroectorderm neurohypophyseal bud
 Endocrine Glands I. Pituitary (L. Pituita - phlegm) A. Location and Anatomy 1. The pituitary gland or hypophysis hangs suspended from the hypothalamus and is protected by the sella turcica of the sphenoid
Endocrine Glands I. Pituitary (L. Pituita - phlegm) A. Location and Anatomy 1. The pituitary gland or hypophysis hangs suspended from the hypothalamus and is protected by the sella turcica of the sphenoid
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013
 panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
1. Changed level of a certain hormone Stimulation of the oxygen consumption 3. Decoupling of oxidative phosphorylation 2.
 1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis
 Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide
 Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed to help you recognize
Endocrine Lab In-Lab Guide The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed to help you recognize
See the latest estimates for new cases of pituitary tumors in the US and what research is currently being done.
 About Pituitary Tumors Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with a pituitary tumor or worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What
About Pituitary Tumors Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with a pituitary tumor or worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What
Metastasis. 57 year old with progressive Headache and Right Sided Visual Loss
 Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
