Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid. Chapter 133: Anatomy. Daniel O. Graney, Ronald C. Hamaker. Development of the Thyroid Gland
|
|
|
- Laureen Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid Chapter 133: Anatomy Daniel O. Graney, Ronald C. Hamaker Development of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland begins as an endodermal bud from the floor of the pharynx between the first and second branchial pouches. Elongation of this bud forms a tubular outgrowth, the thyroglossal duct. Further growth and migration of the thyroglossal duct continue inferiorly or caudally into the neck until the duct lies in a plane anterior to the developing tracheobronchial bud. As development progresses a bilobed organ connected by a midline isthmus is eventually formed. Ultimately the original connection with the floor of the mouth is lost except for a small pit, the foramen caecum, which can usually be seen on the adult tongue lying between the anterior two thirds and posterior one third of the tongue. Abnormalities in the pattern of thyroid development include arrested growth, accessory tissues, and cystic development of the thyroglossal duct. In the case of arrested development the thyroid gland may not migrate beyond its point of origin in the floor of the pharynx. In later life this may present as a lingual tumor but is, in fact, a lingual thyroid. Lingual thyroid may coexist with other thyroid tissue in the neck, varying from minimal tissue nodules to a hemithyroid or normal thyroid development (Bailey, 1925; Marshall and Becker, 1949). Even when there is normal development of the thyroid gland, there may be accessory thyroid tissue in the region of the neck at any point along the original track of the thyroid gland (Fig ) or beyond it in the mediastinal space and on rare occasions in the tracheal wall (Fish and Moore, 1963; Myers and Pantangco, 1974). Thyroglossal cysts are almost always midline masses of the neck and may lie anywhere along the migratory track of the gland from the foramen caecum to the suprasternal space. Thus they may present clinically as a lingual, sublingual, suprahyoid, infrahyoid, or suprasternal mass. The course of the thyroglossal duct during development is in close relationship to the mesenchymal masses of the second and third branchial arches, which eventually aggregate into the cartilaginous precursors of the hyoid bone. Keith (1933) described the course of the duct as traversing the hyoid precursor, whereas Frazer (1926) and Davies (1963) state that it courses anterior to the developing hyoid bone. The latter authors also describe it as having a recurrent course under the inferior surface of the body of the hyoid and passing inferiorly in contact with the thyrohyoid membrane. Because of the close association of the thyroglossal duct to the hyoid. Sistrunk (1920) recommended removal of the midportion or body of the hyoid bone at the time of surgical excision of a thyroglossal duct cyst to prevent recurrence of the cyst. In a histologic study of 200 laryngeal tissue blocks that included the tongue, Ellis and Van Nostrand (1977) found remnants of the thyroglossal duct in 7% of the specimens. Although the remnants were in some cases adherent to the hyoid bone, none were trapped within it, corroborating the descriptions of Frazer (1926) and Davies (1963). The "Sistrunk" operation is still current in its 1
2 original intent and the most effective technique of preventing recurrence of thyroglossal duct cysts (Deane and Telander, 1978). Development of the Parafollicular Cells In addition to the principal cells of the thyroid gland, which form the thyroid follicles and produce thyroglobulin, there is a second type of cell, which lies in the parafollicular space and is responsible for the secretion of thyrocalcitonin. These cells have had varied names such as parafollicular, clear, or "C" cells of the thyroid gland. Although in past years there were several hypotheses regarding both the embryologic origin and the function of these cells, it was not until the late 1960s that these were clarified (Pearse and Polak, 1971). Initially it was believed that the "C" cells were derived embryologically from the endoderm of the ultimobranchial body. The ultimobranchial body is variably described as being part of the fourth, fifth, or sixth pharyngeal pouch. This area of the pharynx has also been named the "caudal pharyngeal complex" by Grosser (1912), a term that is still used by some authors in current descriptions of this area (Davies, 1963; Warwick and Williams, 1980). More recently, it has been demonstrated that "C" cells are derived from neural crest cells that migrate ventrally, seeding the ultimobranchial body. Subsequently, they migrate into the ventral part of the neck and are incorporated into the thyroid gland (Pearse and Polak, 1971). Development of the Parathyroid Glands The parathyroid glands are also endodermal derivatives of the pharyngeal wall, but whereas the thyroid gland arises in the midline, the parathyroid glands are derived from the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches. The superior parathyroid gland (parathyroid IV) is derived from the fourth pouch, and the inferior parathyroid gland (parathyroid III) is derived from the epithelium of the superior portion of the third pouch. This seems paradoxical, but is explained on the basis of the additional migration by the cells in the third branchial pouch. As in the case of thyroid development, these cells may also be arrested in their migration or migrate beyond the thyroid gland into the mediastinum. Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland, as its Greek root implies, is shield shaped, although its form varies considerably, sometimes more H or U shaped (Fig ). Each of the elongated, lateral lobes of the thyroid gland consists of a superior and an inferior pole. In the average subject, the thyroid isthmus overlies the third tracheal ring, although in others it may be absent, so that the gland exists as two distinct lobes. It is usually firmly attached to the trachea by the visceral or pretracheal fascia, a division of the middle layer of deep cervical fascia. The firm attachment of the gland to the laryngotracheal skeleton is of assistance in differential diagnosis of neck masses, since thyroid masses will move with swallowing whereas branchial cysts and dermoid cysts will not. In addition to fascial coverings, there is a true capsule of fibrous tissue that sends interlacing septal fibers into the stroma of the gland. The superior pole of the thyroid gland may extend superiorly as far as the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, where it lies under cover of the 2
3 sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles. The inferior pole may extend inferiorly as far as the fifth or sixth tracheal ring. In some cases the distal part of the thyroglossal duct appears to serve as a guide for glandular development to proceed superiorly in the neck. This forms a pyramid-shaped lobe, extending from the isthmus or midportion of one of the lateral lobes, as far superiorly as the hyoid bone, to which it may be attached. On rare occasions there is a slip of muscle, the levator of the thyroid gland, which attackes the thyroid gland to the hyoid bone (Hollinshead, 1968). Anatomy of the Parathyroid Glands The parathyroid glands usually consist of four, flattened ovoid structures, measuring approximately 6 mm in height, 2 mm in width, and 1 to 2 mm in thickness. Size and number, however, are quite variable. The superior pair of glands are more constant in position, being located on the posterior aspect of the superior pole of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland and close to the recurrent laryngeal nerve (Fig ). The inferior parathyroid glands are substantially more varied in their position on the posterior aspect of the inferior pole of the thyroid gland. For this reason, pathologic enlargements of the inferior parathyroid glands may extend inferiorly either anterior to the trachea or posterior to the esophagus (see the reviews by Warwick and Williams, 1980). The primary role of the parathyroid hormone (PTH) is to maintain serum calcium and phosphorus levels and maintain a homeostatic concentration of extracellular calcium (Potts, 1977). This is accomplished by stimulating osteoclastic activity, mobilizing calcium from bone, and inhibiting renal tubular excretion of calcium ion. An equilibrium of serum calcium is maintained by the reciprocal action of thyrocalcitonin from thyroid parafollicular cells ("C" cells), which inhibits osteoclastic activity and stimulates calcium excretion in the kidney. Blood Supply of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland receives a dual blood supply, from the superior and inferior thyroid arteries, which have abundant collateral anastomoses with each other, both ipsilaterally and contralaterally (Fig ). Because of the common frequency of thyroidectomy and ligation of the thyroid blood supply, the pattern of its vascular pedicles is important to the surgeon. In addition, all arteries supplying the thyroid gland are accompanied by motor nerves to the larynx and thus are in jeopardy during ligation of the thyroid blood supply (Nordland, 1930). Superior thyroid artery The superior thyroid artery is the first anterior branch of the external carotid artery. In a small percentage of cases it may arise from the common carotid artery just before its bifurcation in the internal and external branches (see Fig ). Although this is of no consequence itself, it may confuse the surgeon, resulting in inadvertent ligation of the common carotid artery instead of the external carotid artery in certain operations. The superior thyroid artery descends the lateral 3
4 aspect of the neck under the cover of the superior belly of omohyoid and sternothyroid muscles. It is prominent on the anterior border of the lateral lobe as it runs superficially toward the isthmus to anastomose with the artery of the opposite side. Above the level of the superior pole of the thyroid gland, the artery is accompanied by the external laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. This nerve parallels the artery until it reaches the superior lobe of the thyroid gland, where it courses medially under the sternothyroid muscle to supply the cricothyroid muscle. High ligation of the superior thyroid artery places this nerve in jeopardy and in some cases the superior laryngeal nerve as well. Division of the external laryngeal nerve may produce dysphonia because it denervates the cricothyroid muscle, which assists in the regulation of pitch. In addition, it introduces an asymmetric rotatory force on the cricoid cartilage, which, in turn, causes an asymmetric tension in the vocal cords. If the superior laryngeal nerve is divided, there is, in addition to the motor deficit of external laryngeal nerve palsy, a sensory deficit affecting the distribution of the superior laryngeal nerve. This is also clinically important because the internal laryngeal nerve provides sensation to the mucosa of the piriform sinus and false vocal folds, which is the afferent portion of the protective reflex of the laryngeal inlet. Near the upper pole of the lateral lobe, the superior thyroid artery sends a small branch, the cricothyroid artery, across the cricothyroid muscle toward the midline (see Fig ). The vessel anastomoses with its opposite member in the midline on the surface of the median cricothyroid ligament. The vessel is important clinically because it may be lacerated during cricothyroidotomy or coniotomy either by the incision or the cannula as it is placed in the median cricothyroid ligament to provide an emergency airway. Inferior thyroid artery The inferior thyroid artery arises from the thyrocervical trunk, a branch of the first part of the subclavian artery at the level of the first rib (see Fig ). It ascends vertically for a short distance before turning medially, forming an arching loop and entering the tracheoesophageal groove (see Figs and 133-3). Most of its small branches penetrate the posterior aspect of the lateral lobe, but there is a longitudinal branch that anastomoses with the superior thyroid artery near the superior pole. In contrast, the superior thyroid artery lies on the anterior aspect of the lateral lobe, sending its branches deep into the substance of the gland. Because of the branching pattern of the inferior thyroid arteries, small vessels frequently intermingle with the recurrent laryngeal nerve as it occupies the tracheoesophageal groove before entering the larynx at the level of the cricoid cartilage. Small branches from the recurrent laryngeal nerve to the esophagus at this point also provide an intermingling of nerve and vascular branches. Nordland (1930) has described several variations in the relationship of the recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior thyroid artery. Surgery in this region is complicated by the tethering of the inferior pole of the lateral lobe to the trachea by the visceral fascia. Attempts to mobilize the lobe to either identify the recurrent laryngeal nerve or ligate the inferior thyroid artery are difficult. 4
5 Venous drainage of the thyroid gland Although the thyroid gland is supplied by two pairs of arteries, three pairs of veins provide venous drainage (Fig ). The superior thyroid vein parallels the course of the superior thyroid artery on the anterior surface of the thyroid as it ascends to become a tributary of the internal jugular vein. A middle thyroid vein, usually the shortest of the three pairs of veins, has a direct lateral course from the surface of the thyroid to the internal jugular vein. The inferior thyroid vein lies on the anterior surface of the thyroid gland compared with the posterior position of the inferior thyroid artery. It has an almost vertical course downward before entering the brachiocephalic vein. Innervation of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands The principal innervation of the thyroid and parathyroid glands is derived from the autonomic nervous system. Parasympathetic fibers are distributed from the vagus nerves, and sympathetic fibers descend from the superior, middle, and inferior sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. The specific role of the autonomic nervous system in relation to glandular secretion is not clearly understood, but it is postulated that most of the effect is on blood vessels and the perfusion rates of the glands. Surgeon's Viewpoint Recognition of the important aspects of the anatomy encountered in thyroidectomy help protect the superior laryngeal nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve, and parathyroid glands. If the disease permits, the thyroid isthmus is divided to expose the trachea and cricothyroid muscle at its anterior end. The trachea is always the reference point during surgery. The thyroid is then separated from the carotid sheath with division of the middle thyroid vein when present. The dissection is carried superiorly along the thyroid toward the superior pole. On the right side, a non-recurrent nerve (1% of population) can be identified crossing from the carotid sheath toward the thyroid and ultimately to the cricothyroid joint area. With this anatomy exposed, the superior pole of the thyroid is approached with care to protect the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. The superior pole is separated from the cricothyroid muscle fascia gently as the external branch of the nerve crosses this space to innervate the muscle. If the nerve is identified, then it must be cleared of the superior pole and the superior thyroid artery and vein. If the nerve is not seen crossing this space, then the superior vessels may be ligated at the superior aspect of the thyroid gland. The recurrent laryngeal nerve is identified by placing traction on the superior thyroid pole anteromedially. The left recurrent nerve lies in the tracheoesophageal groove, whereas the right approaches the gland from a more lateral approach. The nerve on either side can frequently be palpated. The nerve crosses over, under, or between branches of the inferior thyroid artery. The recurrent nerve can divide into two or more branches at or just inferior to the artery. This division increases the potential risk of injury and requires patience and precision. Isolation of the 5
6 artery and knowledge of the trachea and esophagus allow dissection of the nerve inferior to the artery. This is the common location for identification of the nerve; the dissection is then carried superiorly. After identification of the inferior thyroid artery and recurrent nerve, traction is placed on the inferior pole in an anteromedial direction. This allows inspection of the thyroid capsule for parathyroid tissue. Observation of the inferior thyroid artery branches can lead to the parathyroid glands. The lobe is dissected away from the nerve by separating the arterial branches to the thyroid gland. This protects the recurrent nerve and the parathyroid blood supply. At Berry's ligament, care must be taken because the nerve is held tightly to this area and because a branch of the artery is located adjacent to the ligament. Transection of this ligament frees the nerve and allows the thyroid gland to be removed from its bed. Thus for surgery of the thyroid compartment, the cricothyroid muscle, trachea, esophagus and inferior thyroid artery are essential landmarks in the preservation of the superior laryngeal nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve, and parathyroid glands. 6
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
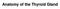 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
DEVELOPMENT & STRUCTURE OF THYROID GLAND DR TATHEER ZAHRA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANATOMY
 DEVELOPMENT & STRUCTURE OF THYROID GLAND DR TATHEER ZAHRA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANATOMY DEVELOPMENT OF THYROID Concept of pharyngeal arch 3 rd week 4 th week Adults 7 th week HISTOGENESIS OF THYROID GLAND
DEVELOPMENT & STRUCTURE OF THYROID GLAND DR TATHEER ZAHRA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANATOMY DEVELOPMENT OF THYROID Concept of pharyngeal arch 3 rd week 4 th week Adults 7 th week HISTOGENESIS OF THYROID GLAND
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
1. Thyroxine (inactive form) also called T4 (90% of the secretion). 2. Triiodothyronine (active form) also called T3 (10% of the secretion).
 A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Clinical Anatomy of the Thyroid and Adrenal Glands
 Clinical Anatomy of the Thyroid and Adrenal Glands Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 28 October 2003 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences College
Clinical Anatomy of the Thyroid and Adrenal Glands Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 28 October 2003 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences College
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands
 Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Chapter 28: The neck. Fascia of the neck
 Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Histology. Dr.shatarat
 Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Advanced Anatomy of the Neck
 AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery. John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe. Chapter 1: The Neck
 Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK
 REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK OUTLINE - EMBRYOLOGY UNDERLYING CLINICAL CONDITIONS I. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF FACE: CLEFT LIP, CLEFT PALATE, OBSTRUCTED NASOLACRIMAL DUCT II. BRANCHIAL ARCHES
REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK OUTLINE - EMBRYOLOGY UNDERLYING CLINICAL CONDITIONS I. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF FACE: CLEFT LIP, CLEFT PALATE, OBSTRUCTED NASOLACRIMAL DUCT II. BRANCHIAL ARCHES
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Ovid: Oxford Textbook of Endocrinology & Diabetes
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2002 Oxford University Press Wass, John A.H., Shalet, Stephen M., Gale, Edwin, Amiel, Stephanie A. Oxford Textbook of Endocrinology & Diabetes, 1st Edition Surgical procedure Part
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2002 Oxford University Press Wass, John A.H., Shalet, Stephen M., Gale, Edwin, Amiel, Stephanie A. Oxford Textbook of Endocrinology & Diabetes, 1st Edition Surgical procedure Part
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
 Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Development of the Pharyngeal Arches
 Development of the Pharyngeal Arches Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Recall the
Development of the Pharyngeal Arches Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Recall the
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Larynx. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Larynx Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb The Larynx Extends from the middle of C3 vertebra till the level of the lower border of C6 Continue as Trachea Above it opens into the laryngo-pharynx Suspended
The Larynx Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb The Larynx Extends from the middle of C3 vertebra till the level of the lower border of C6 Continue as Trachea Above it opens into the laryngo-pharynx Suspended
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus. Sarah Forsyth
 Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus Sarah Forsyth Embryology Basics Endoderm forms scaffolding of GIT Endoderm forms the lining of the yolk sac Derivative of foregut Wk 4 - Foregut develops
Embryology, anatomy and physiology of the oesophagus Sarah Forsyth Embryology Basics Endoderm forms scaffolding of GIT Endoderm forms the lining of the yolk sac Derivative of foregut Wk 4 - Foregut develops
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
DR. DARWISH H. BADRAN. Parathyroid glands
 Parathyroid glands History 1849 - Sir Richard owen provided 1st accurate description of normal parathyroid glands after examining Indian Rhinoceros 1879 - Anton Wölfer described tetany in a patient
Parathyroid glands History 1849 - Sir Richard owen provided 1st accurate description of normal parathyroid glands after examining Indian Rhinoceros 1879 - Anton Wölfer described tetany in a patient
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Chapter 20: Branchial cleft anomalies, thyroglossal cysts and fistulae. P. D. M. Ellis. Branchial cleft anomalies. Embryology
 Chapter 20: Branchial cleft anomalies, thyroglossal cysts and fistulae P. D. M. Ellis Branchial cleft anomalies and thyroglossal cysts and fistulae are the end result of defects in development in the neck
Chapter 20: Branchial cleft anomalies, thyroglossal cysts and fistulae P. D. M. Ellis Branchial cleft anomalies and thyroglossal cysts and fistulae are the end result of defects in development in the neck
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage.
 [ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
[ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
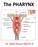 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
Anatomy Sheet #5. In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura.
 Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Difficult Problems in Thyroid Surgery
 Difficult Problems in Thyroid Surgery T he successful diagnosis and treatment of thyroid disease is based on a thorough understanding of the normal anatomic and physiologic features of the thyroid gland.
Difficult Problems in Thyroid Surgery T he successful diagnosis and treatment of thyroid disease is based on a thorough understanding of the normal anatomic and physiologic features of the thyroid gland.
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves)
 Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream
 1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology
 Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Agenesis of isthmus of thyroid gland and ectopic locations of the inferior parathyroid glands and thymus
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 12 (1): 127-132 (2008) Agenesis of isthmus of thyroid gland and ectopic locations of the inferior parathyroid glands and thymus R. Kalpana 1, C. Madhavi 1 and S. Apurva 2 1- Department
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 12 (1): 127-132 (2008) Agenesis of isthmus of thyroid gland and ectopic locations of the inferior parathyroid glands and thymus R. Kalpana 1, C. Madhavi 1 and S. Apurva 2 1- Department
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and incidence of malignancy in solitary nodule of thyroid
 International Surgery Journal Uday MM et al. Int Surg J. 2016 May;3(2):893-899 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20160943
International Surgery Journal Uday MM et al. Int Surg J. 2016 May;3(2):893-899 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20160943
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Lung & Pleura. The Topics :
 Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Objectives. Thoracic Inlet. Thoracic Inlet Boundaries. Thoracic Inlet Sagittal View ANTERIOR SCALENE ANTERIOR SCALENE
 Objectives Thoracic Inlet Deborah L. Reede M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center Learn the anatomy of the thoracic inlet (TI) Review the clinical and radiographic findings of common lesions encountered in
Objectives Thoracic Inlet Deborah L. Reede M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center Learn the anatomy of the thoracic inlet (TI) Review the clinical and radiographic findings of common lesions encountered in
Pharyngeal apparatus. - At the third week, it is a 3 layered structure: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This is called trilaminar disc
 Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Neck Ultrasound. Faculty Info: Amy Kule, MD
 Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Thyroglossal cyst our experience
 Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 Thyroglossal cyst our experience Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Ulaganathan Venkatesan 2 Geetha Ramamoorthy 1 1 Stanley Medical College 2 Meenakshi Medical College
Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 Thyroglossal cyst our experience Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Ulaganathan Venkatesan 2 Geetha Ramamoorthy 1 1 Stanley Medical College 2 Meenakshi Medical College
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (FIG. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
12 Larynx. I - Cartilages. Learning Objectives
 12 Larynx Learning Objectives By the end of this topic you should be able to: Identify the cartilages, membranes, muscles and nerves of the larynx. Describe the attachments of the larynx to other structures
12 Larynx Learning Objectives By the end of this topic you should be able to: Identify the cartilages, membranes, muscles and nerves of the larynx. Describe the attachments of the larynx to other structures
Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND
 STUDY COMPONENT Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System UNIT THEME 1: UNIT THEME 2: UNIT THEME 3: UNIT THEME 4: HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND THYROID AND PARATHYROID PANCREAS; ADRENAL GLANDS
STUDY COMPONENT Clinical Anatomy of the Endocrine System UNIT THEME 1: UNIT THEME 2: UNIT THEME 3: UNIT THEME 4: HYPOPTHALAMUS; HYPOPHYSIS; PINEAL GLAND THYROID AND PARATHYROID PANCREAS; ADRENAL GLANDS
Letty Moss-Salentijn DDS, PhD Dr. Edwin S.Robinson Professor of Dentistry (in Anatomy and Cell Biology)
 10. Pharyngeal Arches Revisited and the PHARYNGEAL POUCHES Letty Moss-Salentijn DDS, PhD Dr. Edwin S.Robinson Professor of Dentistry (in Anatomy and Cell Biology) E-mail: lm23@columbia.edu READING ASSIGNMENT:
10. Pharyngeal Arches Revisited and the PHARYNGEAL POUCHES Letty Moss-Salentijn DDS, PhD Dr. Edwin S.Robinson Professor of Dentistry (in Anatomy and Cell Biology) E-mail: lm23@columbia.edu READING ASSIGNMENT:
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
