A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice
|
|
|
- Muriel Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami ABSTRACT Background The aim of our study is to determine circulating fibroblast growth factor (FGF21) levels in obese and diabetic db/db mice, and role of serotonin (5-HT) in the regulation of hepatic FGF21 expression and circulating FGF21 levels in relation to hepatic gluconeogenesis in obese and diabetic db/db mice. Methods and results Plasma FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 were significantly decreased in obese and diabetic db/db mice compared with age-matched C57BL6J mice. Treatment with p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), a tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor, for 3 days significantly increased plasma FGF21 levels, and decreased body weight and hyperglycemia in db/db mice while having no significant effect on plasma insulin levels. In addition, treatment with PCPA significantly increased expression of hepatic FGF21 and decreased expression of hepatic nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) in db/db mice, while having no significant effects on expression of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α, PPAR γ, and activating transcription factor 4. Moreover, treatment with PCPA significantly decreased phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, glucose 6-phosphatase, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate1, Nur77, forkhead box protein O1 and peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor γ coactivator-1α, which are involved in hepatic gluconeogenesis, in db/db mice. Conclusions These findings suggest that hepatic FGF21 production is decreased in db/db mice, and that a tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor increases expression of hepatic FGF21 production and decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis and hyperglycemia independently of insulin in db/db mice. Keywords FGF21, 5-HT, db/db mice, Gluconeogenesis, Tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor Department of Diabetes Technology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, Miyagi , Japan Author for correspondence: Katsunori Nonogaki, Professor, Division of Diabetes and Nutrition, New Industry Creation Hatchery Center, Tohoku University, 2-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi , Japan, Tel: ; Fax: ; katsu@trc.med.tohoku, ac.jp or knonogaki-tky@umin.ac.jp /Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychiatry (London) (2018) 8(4), p- ISSN e- ISSN
2 Katsunori Nonogaki Introduction Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is primarily secreted by the liver as an endocrine hormone [1]. Circulating FGF21 is elevated in fasted state [2], mice fed a high-fat diet, ob/ob mice [2-4], and obese humans [5]. Because mice lacking FGF21 fed a high-fat diet enhances insulin resistance [2], FGF21 is suggested as an insulin sensitizer. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), PPAR activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), and nuclear factor (erythroidderived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) are transcriptional factors of FGF21 in the liver [6-10]. Tryptophan hydroxylase (Tph) is the initial and rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of serotonin (5-HT). Systemic administration of p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), a Tph inhibitor, remarkably decreases serum and brain 5-HT levels in mice [11,12] and prevents obesity and impaired glucose tolerance in mice fed a highfat diet [13]. Circulating FGF21 levels in type 2 diabetic mice and the effect of a Tph inhibitor on hepatic FGF21 production and gluconeogenesis in type 2 diabetic mice, however, remains unclear. To determine hepatic FGF21 production in type 2 diabetic mice, we examined plasma FGF21 levels and hepatic FGF21 expression in db/db mice with impaired leptin receptors compared with C57BL6J mice matched for age. To determine the role of 5-HT in the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and FGF21 production in type 2 diabetic mice, we examined the effects of treatment with PCPA on food intake, body weight, blood glucose, plasma FGF21 and insulin levels, expression of hepatic genes involved in gluconeogenesis, and expression of hepatic FGF21 and the transcriptional factors of FGF21 in db/db mice. Materials and Methods General procedures Six-week-old male db/db mice and C57BL6J mice were purchased from Japan CLEA. The mice were individually housed in cages with free access to water and chow pellets in a lightand temperature-controlled environment (12 h on/12 h off, lights on at 08:00; 20 C -22 C). 9-week-old db/db mice and C57BL6J mice were decapitated and blood was obtained for the measurement of plasma FGF21 levels. The liver was excluded for determining mrna levels. Then, the 9-week-old mice were intraperitoneally injected with saline or PCPA (500 mg/kg) once daily for 3 days. Daily food intake and body weight changes were determined. At the fourth day, the animals were decapitated and blood was obtained for the measurement of blood glucose, plasma FGF21 and insulin levels. The liver was excluded for determining mrna levels. The experiment was performed between 9:00-12:00. PCPA was purchased from Sigma Chemical Co., Japan. The PCPA was suspended in 0.2 ml 1% Tween saline. The dose of PCPA (500 mg/kg) was selected based on evidences that treatment with PCPA for 3 days remarkably decreased brain 5-HT and serum 5-HT levels in mice [11,12]. Whole blood was mixed with EDTA-2Na (2 mg/ ml) and aprotinin (500 kiu/ml) to determine the plasma levels of FGF21. Plasma levels of FGF21 and insulin were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (rat/mouse FGF21 ELISA kits; R&D System, Tokyo, Japan, mouse Insulin ELISA KIT (TMB) (AKRIN-011T, Shibayagi, Gunma, Japan) as described previously [14,15]. Blood glucose levels were measured using glucose strips (blood glucose monitoring system; Accu- Check, Roche Diagnostics, Tokyo, Japan). The animal studies were conducted in accordance with the institutional guidelines for animal experiments at the Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) Total RNA was isolated from mouse liver using the RNeasy Midi kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer s instructions. cdna synthesis was performed using a Super Script III First-Strand Synthesis System for RT- PCR Kit (Invitrogen, Rockville, MD) with 1 g total RNA. cdna synthesized from total RNA was evaluated in a real-time PCR quantitative system (LightCycler Nano Instrument Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The primers used were listed in Table 1. The relative amount of mrna was calculated using -actin mrna as the invariant control. Data are shown as fold-change of the mean value of the control group, which received saline as described previously [14,15]. Statistical methods Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=6). Comparisons between two groups were 1477 Neuropsychiatry (London) (2018) 8(4)
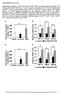
3 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Research Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice performed using Student s t-test. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Comparisons between more than two groups were performed using analysis of variance with Bonferroni s correction for multiple comparisons. Results Plasma FGF21 levels (Figure 1A) and hepatic FGF21 expression (Figure 1B) was significantly decreased in db/db mice compared with agematched C57BL6J mice. Intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (500 mg/ kg) for 3 days significantly decreased daily food intake (Figure 2A), body weight (Figure 2B) and blood glucose (Figure 2C) compared with saline controls in db/db mice while having no significant effect on plasma insulin levels (Figure 2D). On the other hand, intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (500 mg/kg) for 3 days significantly increased and plasma FGF21 levels compared with saline controls in db/db mice (Figure 2E). Intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (500 mg/kg) for 3 days had no significant effects on daily food intake, body weight changes, plasma FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 in C57BL6J mice (data not shown). Treatment with PCPA for 3 days significantly decreased phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), glucose 6-phosphatase (G6Pase), fructose 1,6-bisphosphate1 (Fbp1), Nur77, forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1 (PGC1 which are involved in hepatic gluconeogenesis (Figure 3A). In addition, treatment with PCPA for 3 days significantly increased expression of hepatic FGF21 (5.8-fold increase) and decreased expression of hepatic Nrf2 (35% decrease) while having no significant effects on expression of hepatic PPARα, PPAR, and ATF4 (Figure 3B). Discussion and Conclusion Although plasma FGF21 levels are reportedly elevated in obese rodents and human [2-5], the results of the present study demonstrated that plasma FGF21 levels and hepatic FGF21 expression were lower in obese and diabetic db/ db mice than normal C56BL6J mice matched for age. In addition, our results demonstrated that treatment with PCPA increased plasma FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 in db/db Table 1: The primers used for real-time RT-PCR. Gene Primer Sequence FGF21 sense CACCGCAGTCCAGAAAGTC ATCAAAGTGAGGCGATCCA PPAR sense CGGGTAACCTCGAAGTCTGA CTAACCTTGGGCCACACCT PPAR sense CTGCTCAAGTATGGTGTCCATGAG GAGGAACTCCCTGGTCATGAATC Nrf2 sense CAAGACTTGGGCCACTTAAAAGAC AGTAAGGCTTTCCATCCTCATCAC ATF4 sense AGACACCGGCAAGGAGGATG CGAAACAGAGCATCGAAGTCAAC Notch sense ATGTGGATGCTGCTGTTGTGCTCC CCGGTTGGCAAAGTGGTCCA FOXO1 sense GCGTGCCCTACTTCAAGGATAA TCCAGTTCCTTCATTCTGCACT G6Pase sense TGCAAGGGAGAACTCAGCAA GGACCAAGGAAGCCACAATG Nurr77 sense ATGCCT CCCCTACCAATCTTC TCACCTCCGGTGAGTCTGATC PGC1 sense GTAGCGACCAATCGGAAATC CTAGCAAGTTTGCCTCATTCTC Fbp1 sense TCTGCACCGCGATCAAAG GTTGAGCCAGCGATACCATAGAG PEPCK sense TTGTAACCAACTGGGACGATATGG GATCTTGATCTTCATGGTGCTAGG -actin sense TTGTAACCAACTGGGACGATATGG GATCTTGATCTTCATGGTGCTAGG mice. Moreover, our results demonstrated that treatment with PCPA decreased hyperglycemia independently of plasma insulin levels, and decreased hepatic gluconeogenesis via suppressing PGC1 and the downstream of Notch signaling [16-18] in db/db mice. From these findings, we raise a hypothesis that 5-HT might contribute to the decreases in plasma FGF21 levels and hepatic FGF21 expression, and the increases in blood glucose levels and hepatic gluconeogenesis in insulin-independent diabetic db/db mice. We have previously reported that treatment with PCPA for 3 days suppresses daily food intake, body weight gain and the increases in plasma FGF21 levels and insulin levels in C57BL6J mice fed a high-fat diet [19]. Moreover, treatment with PCPA significantly increases expression of hepatic Nrf2 and decreases expression of hepatic FGF21 in mice fed a high-fat diet [19]. Despite decreases in daily food intake and body weight, treatment with PCPA had different effects on plasma FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 and Nrf2 in mice fed a high-fat diet and 1478
4 Katsunori Nonogaki Figure 1: Plasma FGF21 levels (A) and hepatic FGF21 expression (B) in 9 wk-old db/db mice and C57BL6J mice. Basal body weights were 39.0 ± 1.5 g in db/db mice and 27.6 ± 0.34 g in C57BL6J mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=6/group). *P<0.05 Figure 2: Effects of intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (500 mg/kg) or 1% Tween in saline on daily food intake (A), body weight changes (B), blood glucose levels (C), plasma insulin (D), and FGF21 (E) levels in 9-wk old db/db mice. Basal body weights were 39.1 ± 1.6 g (controls) and 38.8 ± 1.5 g (PCPA-treated group) in db/db mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=6/group). *P<0.05. db/db mice. Thus, the different effect of PCPA on hepatic FGF21 production are independent of changes in daily food intake and body weight, and could be due to the differences in blood glucose levels and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Although mice fed a high-fat diet for 9 weeks display normal blood glucose levels [19], db/ db mice displayed remarkable hyperglycemia. Although plasma FGF21 levels and hepatic FGF21 expression are increased in obese mice fed a high-fat diet, they were decreased in diabetic db/db mice associated with increased hepatic gluconeogenesis. Thus, 5-HT could contribute to the pathophysiological mechanisms of diet Neuropsychiatry (London) (2018) 8(4)
5 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Research Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice Figure 3: Effects of intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (500 mg/kg) or 1% Tween in saline on expression of genes involved in hepatic gluconeogenesis (A) and expression of hepatic FGF21, PPAR PPAR ATF4, and Nrf2 (B) in db/db mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n=6/group). *P<0.05. induced obesity and type 2 diabetes in a different manner. Treatment with PCPA for 3 days remarkably decreases brain 5-HT and serum 5-HT levels in mice [11,12]. Although treatment with PCPA increases expression of hypothalamic 5-HT2C receptor and POMC, which may lead to feeding suppression [19], and increases energy expenditure via brown adipose tissues, which leads to weight loss [13], the present study demonstrated that changes in plasma FGF21 levels and hepatic FGF21 expression induced by treatment with PCPA were independent of decreases in food intake and body weight. Liver does not produce 5-HT and gut-derived 5-HT has substantially contributed to serum 5-HT levels. Gut-derived 5-HT may therefore contribute to the regulation of hepatic FGF21 production and gluconeogenesis in vivo. We, however, cannot completely rule out role of brain 5-HT in the regulation of hepatic FGF21 production and gluconeogenesis. In summary, these findings suggest that hepatic FGF21 production is decreased in db/db mice, and that a Tph inhibitor increases hepatic FGF21 production, and decreases hyperglycemia and hepatic gluconeogenesis in db/db mice. Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Acknowledgment This work was supported by a Grant in-aid for Scientific Research. References 1. Kharitonenkov A, DiMarchi R. FGF21 revolutions: recent advances illuminating FGF21 biology and medicinal properties. Trends. Endocrinol. Metab 26(11), (2015). 2. Markan KR, Naber MC, Ameka MK, et al. Circulating FGF21 is liver derived and enhances glucose uptake during refeeding and overfeeding. Diabetes 63(12), (2014). 3. Fisher FM, Chui PC, Antonellis PJ, et al. A. Obesity is a fibroblast growth factor 21(FGF21)-resistant state. Diabetes 59(1), (2010). 4. Hale C, Chen MM, Stanislaus S, et al. Lack of overt FGF21 resistance in two mouse models of obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 153(1), (2012). 5. Zhang X, Yeung DC, Karpisek M, et al. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 57(5), (2008). 6. Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, et al. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell. Metab 5(6), (2007). 7. Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, et al. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell. Metab 5(6), (2007). 8. Dutchak PA, Katafuchi T, Bookout AL, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-21 regulates PPARγ activity and the antidiabetic actions of thiazolidinediones. Cell 148(3), (2012). 9. Kim KH, Jeong YT, Kim SH, et al. Metformininduced inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory chain increases FGF21 expression via ATF4 activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 440(1), (2013). 10. Chartoumpekis DV, Ziros PG, Psyrogiannis AI, et al. Nrf2 represses FGF21 during longterm high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. 1480
6 Katsunori Nonogaki Diabetes 60(10) (2011). 11. Liu Y, Jiang Y, Si Y, et al. Molecular regulation of sexual preference revealed by genetic studies of 5-HT in the brains of male mice. Nature 472(7341), (2011). 12. Weng R, Shen S, Tian Y, et al. Metabolomics approach reveals integrated metabolic network associated with serotonin deficiency. Sci. Rep 5, (2015). 13. Oh C-M, Namkung J, Go Y, et al. Regulation of systemic energy homeostasis by serotonin in adipose tissues. Nat. Commun 6, 6794 (2015). 14. Nonogaki K, Hazama M, Satoh N. Liraglutide suppresses obesity and hyperglycemia associated with increases in hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 production in KKA y mice, Biomed. Res. Int , (2014). 15. Nonogaki K, Yamazaki T, Murakami M, et al. Ingestion of eicosapentaenoic acid in the early stage of social isolation reduces a fibroblast growth factor 21 resistant state independently of body weig ht in KKA(y) mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 464(2), (2015). 16. Diaz MB, Lemke U. Discovering orphans sweet secret: NR4A receptors and hepatic glucose production. Cell. Metab 4(5), (2006). 17. Pajvani UB, Shawber CJ, Samuel VT, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling ameliorates insulin resistance in a FoxO1-dependent manner. Nat. Med 17(8), (2011). 18. Czech MP. Obesity notched up fatty liver. Nat. Med 19(8), (2013). 19. Nonogaki K, Kaji T, Muarakami M. A tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitor decreases hepatic FGF21 expression and circulating FGF21 in mice fed a high-fat diet. Neuropsychiatry (London) 8(1), (2018) Neuropsychiatry (London) (2018) 8(4)
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression and Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet
 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami Abstract Background: Fibroblast growth
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami Abstract Background: Fibroblast growth
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21
 Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21 Dionysios V Chartoumpekis, 1* Ioannis G Habeos, 1* Panos G Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E Kyriazopoulou,
Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21 Dionysios V Chartoumpekis, 1* Ioannis G Habeos, 1* Panos G Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E Kyriazopoulou,
Molecular Medicine. Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic
 Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic stimulation by induction of FGF21 Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1, Ioannis G. Habeos, 1, Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E.
Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic stimulation by induction of FGF21 Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1, Ioannis G. Habeos, 1, Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E.
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin
 Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table 1. Tph1+/+ Tph1 / Analyte Supplementary Table 2. Tissue Vehicle LP value
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Implications of mitochondrial skeletal muscle metabolism on diabetes and obesity before and after weight loss
 GG2 Implications of mitochondrial skeletal muscle metabolism on diabetes and obesity before and after weight loss Dr Giacomo Gastaldi CHRU Montpellier Folie 1 GG2 19.10.2009 GG_PC; 12.10.2009 Plan Introduction
GG2 Implications of mitochondrial skeletal muscle metabolism on diabetes and obesity before and after weight loss Dr Giacomo Gastaldi CHRU Montpellier Folie 1 GG2 19.10.2009 GG_PC; 12.10.2009 Plan Introduction
Targeting Glucose Metabolism to Stop Strokes IRIS: Insulin Resistance In Stroke study
 Targeting Glucose Metabolism to Stop Strokes IRIS: Insulin Resistance In Stroke study Professor Gary Ford Chief Executive Officer, Oxford Academic Health Science Network Consultant Stroke Physician, Oxford
Targeting Glucose Metabolism to Stop Strokes IRIS: Insulin Resistance In Stroke study Professor Gary Ford Chief Executive Officer, Oxford Academic Health Science Network Consultant Stroke Physician, Oxford
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Supplemental Information. Intermittent Fasting Promotes. White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity. by Shaping the Gut Microbiota
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota Guolin Li, Cen Xie, Siyu Lu, Robert G. Nichols,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota Guolin Li, Cen Xie, Siyu Lu, Robert G. Nichols,
Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state
 Related Commentary, page 2267 Research article Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state Marc Foretz, 1,2 Sophie Hébrard,
Related Commentary, page 2267 Research article Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state Marc Foretz, 1,2 Sophie Hébrard,
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice
 Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat. day, cells were transduced with adenoviruses expressing GFP, MKP-3 or shgfp,
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
AMPK. Tomáš Kuc era. Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent
 Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R115 R132, 2001. Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent RUTH B. S. HARRIS, TIFFANY D. MITCHELL, XIAOLANG YAN, JACOB
Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R115 R132, 2001. Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent RUTH B. S. HARRIS, TIFFANY D. MITCHELL, XIAOLANG YAN, JACOB
Supplemental Information. FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating. Antibody Act on the Nervous System. to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO. Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu ABSTRACT
 Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Ruth B. S. Harris, Tiffany D. Mitchell, Xiaolang Yan, Jacob S. Simpson and Stephen M. Redmann, Jr.
 Metabolic responses to leptin in obesedb/db mice are strain dependent Ruth B. S. Harris, Tiffany D. Mitchell, Xiaolang Yan, Jacob S. Simpson and Stephen M. Redmann, Jr. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol
Metabolic responses to leptin in obesedb/db mice are strain dependent Ruth B. S. Harris, Tiffany D. Mitchell, Xiaolang Yan, Jacob S. Simpson and Stephen M. Redmann, Jr. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol
Supplementary Figure 1
 VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist. Research Summary:
 Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2014, 5(3): 32-36 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Study of the effect of ethanolic extract of Solanum xanthocarpum schrad &
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2014, 5(3): 32-36 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Study of the effect of ethanolic extract of Solanum xanthocarpum schrad &
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli
 BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli Symposium Co-Chairs: Bruce M. Spiegelman (Harvard/Dana Farber) and Sven Enerbäck (U.Gothenburg) April 17-23, 2015 Snowbird Resort,
BEIGE AND BROWN FAT: BASIC BIOLOGY AND NOVEL THERAPEUTICS Dr. Carl Ascoli Symposium Co-Chairs: Bruce M. Spiegelman (Harvard/Dana Farber) and Sven Enerbäck (U.Gothenburg) April 17-23, 2015 Snowbird Resort,
3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids?
 Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]
![TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1] TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]](/thumbs/89/99233308.jpg) ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
AMPK. Tomáš Kučera.
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis
 A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF. Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012.
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012. Title: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis and Type 2 Diabetes Complications Abstract
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012. Title: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis and Type 2 Diabetes Complications Abstract
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents
 Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Introduction. Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet
 Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets. James M. Ntambi Ph.D
 Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the. Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3 Huating Li, 1,2 Zhanguo Gao, 3 Jin Zhang, 3 Xin Ye, 3 Aimin Xu, 4,5
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3 Huating Li, 1,2 Zhanguo Gao, 3 Jin Zhang, 3 Xin Ye, 3 Aimin Xu, 4,5
glucagon receptor AgRP merged color map I corr = 0.76±0.024 glucagon receptor DAPI merged
 Hypothalamic glucagon signaling inhibits glucose production Patricia I. Mighiu*, Jessica T.Y. Yue*, Beatrice M. Filippi, Mona A. Abraham, Madhu Chari, Carol K.L. Lam, Clair S. Yang, Nikita R. Christian,
Hypothalamic glucagon signaling inhibits glucose production Patricia I. Mighiu*, Jessica T.Y. Yue*, Beatrice M. Filippi, Mona A. Abraham, Madhu Chari, Carol K.L. Lam, Clair S. Yang, Nikita R. Christian,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
FOR REVIEW. BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission. Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: BMB
 BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
Modifications of Pyruvate Handling in Health and Disease Prof. Mary Sugden
 Modifications of Handling Modifications of Handling Centre for Diabetes and Metabolic Medicine Institute of Cell and Molecular Science Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry 1 Potential
Modifications of Handling Modifications of Handling Centre for Diabetes and Metabolic Medicine Institute of Cell and Molecular Science Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry 1 Potential
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice.
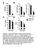 Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution
 Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Jaemin Lee, Ph.D. Department of New Biology Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST)
 Jaemin Lee, Ph.D. Department of New Biology Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) No Actual or Potential Conflict of Interest https://www.flickr.com/photos/luchoedu/2453267732/ 1985
Jaemin Lee, Ph.D. Department of New Biology Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) No Actual or Potential Conflict of Interest https://www.flickr.com/photos/luchoedu/2453267732/ 1985
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays
 Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) belongs to the. Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1 Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1 Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, 2
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
Targeting of the circadian clock via CK1δ/ε to improve glucose homeostasis in obesity
 Targeting of the circadian clock via CK1δ/ε to improve glucose homeostasis in obesity Peter S. Cunningham, Siobhán A. Ahern, Laura C. Smith, Carla S. da Silva Santos, Travis T. Wager and David A. Bechtold
Targeting of the circadian clock via CK1δ/ε to improve glucose homeostasis in obesity Peter S. Cunningham, Siobhán A. Ahern, Laura C. Smith, Carla S. da Silva Santos, Travis T. Wager and David A. Bechtold
Role of the ventromedial hypothalamic Steroidogenic Factor 1/ Adrenal 4. glucose metabolism in mice.
 Role of the ventromedial hypothalamic Steroidogenic Factor 1/ Adrenal 4 Binding Protein neurons in the regulation of whole body energy and glucose metabolism in mice. Eulalia Coutinho Department of Physiological
Role of the ventromedial hypothalamic Steroidogenic Factor 1/ Adrenal 4 Binding Protein neurons in the regulation of whole body energy and glucose metabolism in mice. Eulalia Coutinho Department of Physiological
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) belongs to the. Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1 Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nrf2 Represses FGF21 During Long-Term High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1 Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, 2
PXL770, a novel direct AMPK activator, improves metabolic disorders in a diet-induced mice model of obesity and diabetes
 PXL770, a novel direct AMPK activator, improves metabolic disorders in a diet-induced mice model of obesity and diabetes Sébastien Bolze 1 ; Sophie Hallakou-Bozec 1 ; Michael Roden 2, 3,4 ; Julien Roux
PXL770, a novel direct AMPK activator, improves metabolic disorders in a diet-induced mice model of obesity and diabetes Sébastien Bolze 1 ; Sophie Hallakou-Bozec 1 ; Michael Roden 2, 3,4 ; Julien Roux
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Characterization of a novel genetically obese mouse model demonstrating early onset hyperphagia and hyperleptinemia
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305: E451 E463, 2013. First published June 4, 2013; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00540.2012. Characterization of a novel genetically obese mouse model demonstrating early onset hyperphagia
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305: E451 E463, 2013. First published June 4, 2013; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00540.2012. Characterization of a novel genetically obese mouse model demonstrating early onset hyperphagia
Supplemental methods. Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and
 Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Diabesity. Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs
 Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism
 Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
University of Groningen. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba
 University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats 1 Kerstin Stemmer, 2 Maximilian Bielohuby, 3 Bernadette E. Grayson, 3 Denovan P.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery but not vertical sleeve gastrectomy decreases bone mass in male rats 1 Kerstin Stemmer, 2 Maximilian Bielohuby, 3 Bernadette E. Grayson, 3 Denovan P.
The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
 Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Identification of Binding Partners of Fibroblast Gro wth Factor221 in Cell Membrane of 3T32L1 Cells
 ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2008 7 24 (7) :667 673 3T32L1 FGF221 1), 1),, 3 (, 150030) (fibroblast growth factor,fgf)221 1, 2.,FGF221.,, 3T32L1, FGF221,
ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2008 7 24 (7) :667 673 3T32L1 FGF221 1), 1),, 3 (, 150030) (fibroblast growth factor,fgf)221 1, 2.,FGF221.,, 3T32L1, FGF221,
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Charalambous et al. 10.1073/pnas.1406119111 SI Experimental Procedures Serum and Tissue Biochemistry. Enzymatic assay kits were used for determination of plasma FFAs (Roche), TAGs
Supporting Information Charalambous et al. 10.1073/pnas.1406119111 SI Experimental Procedures Serum and Tissue Biochemistry. Enzymatic assay kits were used for determination of plasma FFAs (Roche), TAGs
The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided into five regions: cortex, hippocampus,
 Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Mamofillin New aesthetic perspective
 New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice
 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
7/31/2009. G.Y. Prince Used Cars 10 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland Drive..later that day. Would you buy a car without taking it for a spin first?
 7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
Leptin Intro/Signaling. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Ct=28.4 WAT 92.6% Hepatic CE (mg/g) P=3.6x10-08 Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
 a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes
 People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model. Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications. SDT fatty rats. SDT fatty rats
 Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
FGF21 Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance
 Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance The ICDM 213 & 5 th AASD Scientific Meeting Seoul, Korea, Nov 8, 213 Aimin Xu Dept of Medicine & Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacy The University
Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance The ICDM 213 & 5 th AASD Scientific Meeting Seoul, Korea, Nov 8, 213 Aimin Xu Dept of Medicine & Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacy The University
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
FGF21 Maintains Glucose Homeostasis by Mediating the Cross Talk Between Liver and Brain During Prolonged Fasting
 4064 Diabetes Volume 63, December 2014 Qingning Liang, 1,2 Ling Zhong, 1,2 Jialiang Zhang, 1,2 Yu Wang, 1,3 Stefan R. Bornstein, 4 Chris R. Triggle, 5 Hong Ding, 5 Karen S.L. Lam, 1,2 and Aimin Xu 1,2,3
4064 Diabetes Volume 63, December 2014 Qingning Liang, 1,2 Ling Zhong, 1,2 Jialiang Zhang, 1,2 Yu Wang, 1,3 Stefan R. Bornstein, 4 Chris R. Triggle, 5 Hong Ding, 5 Karen S.L. Lam, 1,2 and Aimin Xu 1,2,3
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to energy balance in dairy cows
 Xu et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:271 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0585-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to
Xu et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:271 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0585-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to
Metabolic Programming. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
Supplemental Fig. 1. Changes in fat and lean mass determined by DEXA. Fat mass in high fat-fed
 Supplemental Fig. 1. hanges in fat and lean mass determined by EXA. Fat mass in high fat-fed mice (A) and chow-fed controls (). Lean mass in high fat-fed mice () and chow-fed controls (). ata represent
Supplemental Fig. 1. hanges in fat and lean mass determined by EXA. Fat mass in high fat-fed mice (A) and chow-fed controls (). Lean mass in high fat-fed mice () and chow-fed controls (). ata represent
