Combined Benign Odontogenic Tumors: CT and MR Findings and Histomorphologic Evaluation
|
|
|
- Percival Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22: , May 2001 Case Report Combined Benign Odontogenic Tumors: CT and MR Findings and Histomorphologic Evaluation Nadine Martin-Duverneuil, Marie-Hélène Roisin-Chausson, Anthony Behin, Estelle Favre-Dauvergne, and Jacques Chiras Summary: Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors and calcifying odontogenic cysts are rare, benign odontogenic tumors. We report two cases of an exceptional combination of these tumors with either an ameloblastic fibroodontoma or an odontoma. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors (CEOTs) and calcifying odontogenic cysts (COCs) are rare, benign odontogenic tumors. We report two cases of an exceptional combination of these tumors with either an ameloblastic fibroodontoma or an odontoma. Such a combination, which, to our knowledge, has not previously been reported, led us to review in detail the clinical, radiologic, and microscopic patterns of these tumors and to compare those findings with the present complex classification of CEOT and COC. Case Reports Case 1 A 10-year-old boy was referred for assessment of a large asymptomatic mandibular lesion that was discovered on a routine radiographic examination performed to evaluate an unerupted right first molar. Plain radiographs showed a large well-delineated expansile lesion of the mandibular angle with scattered irregular radiopacities with multiple pseudosepta (Fig 1A and B).On CT scans (Fig 1C and D), the lesion showed a combined pattern of a well-circumscribed unilocular radiolucency containing scattered flecks of calcification. Pseudosepta were seen with a large, smooth expansion of the thinned cortical plate, which appeared to be broken on the upper edge of the tumor. On surgical exploration, the lesion, which was located in the superior break of the cortical plate, appeared as a large, irregular, whitish mass with numerous hard nodules. The lesion was completely enucleated. Macroscopic examination revealed two fragments ( cm and cm, respectively) with variable consistency, sometimes soft, sometimes hard, with calcificlike areas. The microscopic sections (Fig 1E and F) showed two more or less intricate patterns: first, there were large areas of myxoid con- Received September 26, 2000; accepted after revision January 3, From thedepartments of Neuroradiology (N.M-D., M-H.R- C., A.B., J.C.) and Maxillofacial Surgery (E.F-D.), GH Pitié- La Salpêtrière, Paris, France. Address reprint requests to N. Martin-Duverneuil, Department of Neuroradiology, Charcot, GH Pitié-La Salpêtrière, 47, Bd de l Hôpital, Paris, France. American Society of Neuroradiology nective tissue containing spindle- or star-shaped cells. Found within these areas were ameloblastic crests or follicles with localized production of enamel, dentine organized in small teeth with a central pulp. Second, islands of epithelial cells were embedded within the latticework, sometimes with a clarified or ghostlike appearance and numerous calcifications. Some amount of an amorphous amyloidlike material was also present, which showed an apple green birefringence and positivity via the alkaline Congo red procedure, while under a fluorescent microscope it also revealed positive thioflavin T staining for amyloid. The diagnosis was combined ameloblastic fibroodontoma and CEOT. The patient is currently free of any recurrence 3 years after surgery, and follow-up plain radiography showed nearly complete healing of the lesion. Case 2 A 14-year-old girl presented with a lingual swelling on the left side of the mandible. Physical examination revealed a welldefined swelling, extending from the movable first molar to the angle, with slight pain at provocation. A plain radiograph (Fig 2A) revealed a large well-defined expansile unilocular radiolucency, containing several small peripheral radiopacities. Focal resorption of the first molar was noted with an inferior displacement of the unerupted second molar, while the germ of the third molar was ectopically placed in the upper ramus. CT specified the pattern of this cm well-delineated expansile lesion with a large smooth expansion of the thinned cortical plates seen predominately on the lingual edge; small peripheral calcifications were also present (Fig 2B). At MR imaging, the lesion showed a homogeneously and slightly hyperintense signal on noncontrast T1-weighted sequences (Fig 2C) and a markedly hyperintense signal on T2-weighted sequences after intravenous injection of contrast material (Fig 2D). On surgical exploration, the lesion appeared as a well-defined cyst containing brownish liquid with a nonadhering membrane covered with granulations thought to correspond to the radiographic calcifications. The lesion was completely enucleated. The surgical specimen was a cystic shell with several foci of calcifications. Pathologic examination (Fig 2E) revealed a stratified epithelial lining with an ameloblasticlike basal layer. Several groups of ghost cells were distinguished inside this lining and they were sometimes mineralized. Dentinoid was also noticed in contact with the basal layer of the epithelium. Close to this lining, a small odontoma with dental pulp, enamel, and dentine could also be seen. The diagnosis was combined COC and odontoma. The patient is currently free of any recurrence 3 years after surgery. Discussion Odontogenesis is a complex interplay between epithelial elements and those that are derived from ectomesenchyme. Tooth formation is initially evidenced by proliferation of the dental lamina, an ep- 867
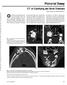
2 868 MARTIN-DUVERNEUIL AJNR: 22, May 2001 FIG 1. Case 1. A and B, Plain radiographs. Lateral plain radiograph (A) shows a large expansile mixed radiolucent/radiopaque lesion involving the right mandibular angle. Posteroanterior view of the right mandible (B) shows an anterior displacement of the first molar and a posterior displacement of the germ of the second molar. Scattered calcifications are seen. C and D, CT scans. Axial view of the mandible (C) shows a large expansile radiolucent lesion of the mandibular angle containing scattered calcifications. Coronal view (D) shows a localized rupture of the thinned cortical plate with a posterosuperior displacement of the germ of the second molar. E and F, Microscopic sections. These photomicrographs show the association of an ameloblastic fibroodontoma (E) with a CEOT (F) (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification 200). The ameloblastic fibroodontoma (E) has islands of epithelial cells that exhibit an enamel organlike arrangement (arrows) seen infiltrating the connective component of the tumor, similar to the dental pulp (asterisk). The CEOT (Pindborg tumor) (F) has epithelial cells (arrows) seen with foci of amyloidosis (asterisk). ithelial structure found in the primitive oral mucosal epithelium. This dental lamina can proliferate only in the presence of the underlying ectomesenchyme, which thus has an inductive effect on the dental lamina forming the enamel organ. The enamel organ is a three-dimensional structure that has four components: the inner enamel epithelium, the stratum intermedium, the stellate reticulum, and the outer enamel epithelium. A process called induction begins when the cells of the dental lamina closest to the inner enamel epithelium differentiate into odontoblasts and begin to form dentin. The formation of dentin again reciprocates in the inductive ability to stimulate the preameloblasts of the inner enamel epithelium, differentiating them into ameloblasts, which begin to secrete enamel. CEOT (also called Pindborg tumor) and COC are rare, benign tumors involving the odontogenic apparatus. Over the last decades, classification and individualization of the benign odontogenic tumors have seeded confusion and controversy in the literature. CEOT was only distinguished from ameloblastoma in 1955 by the Danish pathologist Pindborg (1), while COC was first described in 1962 by Gorlin et al (2). In 1971, a histologic typing of odontogenic tumours, jaw cysts, and allied lesions by the World Health Organization (WHO) classified neoplasms and other tumors of the odontogenic apparatus simply as benign or malignant (3). In 1992, a new WHO international classification system divided these benign tumors into three groups on the basis of their microscopic patterns, their embryonal origins, and their interactions with odontogenic tissues (4, 5) (Table). The first group included the epithelial tumors, in which there is odontogenic epithelium without odontogenic ectomesenchyme, such as CEOT (as in case 1); the second group included the mixed odontogenic tumors, in which there is odontogenic epithelium with odontogenic ectomesenchyme with or without dental hard tissue formation, such as ameloblastic fibroodontoma (as in case 1), COC (as in case 2), and complex odontoma (also as in case 2); and the third group included those tumors in which there is odontogenic ectomesenchyme with or without odontogenic epithelium. The odontogenic tumors thus seem to reproduce in a more or less acquired way the different steps
3 AJNR: 22, May 2001 ODONTOGENIC TUMORS 869 FIG 2. Case 2. A, Lateral plain radiograph of the mandible shows a large well-defined expansile radiolucency containing several small peripheral radiopacities. Focal resorption of the first molar with inferior displacement of the unerupted second molar is seen. Note the upper displacement of the germ of the third molar. B, Axial CT view of the mandible shows a well-delineated expansile lesion with a large, smooth expansion of the thinned cortical plates. Small peripheral calcifications are seen. C and D, MR images. Axial noncontrast spin-echo T1-weighted image (420/11/2) (C) shows a homogeneous, slightly hyperintense lesion. Axial fast spin-echo T2-weighted image (4000/104/1) (D) shows a markedly hyperintense lesion. E, Photomicrograph shows the characteristic patterns of a COC close to a small odontoma (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification 200). Epithelial cyst lining (thin arrows) is seen with focal areas of necrosis (asterisks). Dentinoid component of the odontoma (thick arrow) is associated. Benign neoplasms related to the odontogenic apparatus 1 Odontogenic epithelium without odontogenic ectomesenchyme 1.1 Ameloblastoma 1.2 Squamous odontogenic tumor 1.3 Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (Pindborg tumor) 1.4 Clear cell odontogenic tumor 2 Odontogenic epithelium with odontogenic ectomesenchyme, with or without dental hard tissue formation 2.1 Ameloblastic fibroma 2.2 Ameloblastic fibrodentinoma and ameloblastic fibroodontoma 2.3 Odontoameloblastoma 2.4 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor 2.5 Calcifying odontogenic cyst 2.6 Complex odontoma 2.7 Compound odontoma 3 Odontogenic ectomesenchyme with or without odontogenic epithelium 3.1 Odontogenic fibroma 3.2 Myoxma 3.3 Benign cementoblastoma Note. The pathologic processes in italics refer to case 1; those in boldface type refer to case 2. of odontogenesis. The first group of epithelial tumors is thought to be histologically related to remnants of the odontogenic epithelium (dental lamina, enamel organ, root sheath of Hertwig), while the second group of mixed tumors is composed of both epithelial- and mesenchymal-derived tissues (6 8). The critical factor in understanding the mixed odontogenic tumors as a group and their relationship with tooth formation is in recognizing the inductive and reciprocally inductive influences of one tissue on another. The present hypothesis is that the tumors included in the last group recapitulate some stages of odontogenesis, ranging from the earliest phase (ameloblastic fibroma) to that in which there is a high degree of histodifferentiation (odontomas). On the other hand, it is thought that the lesions in the first group of epithelial odontogenic tumors arise from residue of cells issued from actively growing dental lamina that are present within the jaws for a considerable time after birth. In this respect, our two cases, and in particular case 1, are interesting in that they represent an association of tumors histologically classified into two different groups. To our knowledge, no such association has
4 870 MARTIN-DUVERNEUIL previously been reported in the literature. Although the clinical, radiologic, and microscopic association of a COC with an odontoma has previously been described in detail (9 11). More rarely, COCs have been reported to be associated with other odontogenic tumors of its group. Such tumors have been considered to be part of the entire lesion and related to the ability of the COC to induce the formation of mature dental tissue. This combination of one tumor, considered to be an intermediate differentiated lesion of its mixed group, with an odontoma, considered to be the most differentiated lesion of this same group and therefore even considered to be a hamartoma, is today regarded as an important argument for evoking the hypothesis of a kind of histomorphologic filiation between all tumors of this group. Conversely, as in our case 1, the association of a CEOT with one of the intermediate mixed-group tumors (ie, ameloblastic fibroodontoma) is quite surprising. In both pathologic and radiologic examinations, these tumors appear within a single intricate lesion, with a homogeneous radiologic appearance, and on microscopic sections as a combination of the two different patterns embedded in the same lesion and not as two different lesions that developed in neighboring areas. This case can thus be related to the only other one described in the literature, in which the authors reported two cases of CEOTs in association with an adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (12). As in our case 1, the intricate tumor patterns (and not a collision of separate tumors in which the cells could not be expected to be so intermingled) suggests that these lesions represent primarily a mixed tumor (adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, or, in our case, an ameloblastic fibroodontoma), in which foci of CEOT had developed. It would not be surprising for this to occur, since these mixed tumors contain stratum intermedium. In such pathologic processes, it is clearly recognized today that a histologic diagnosis can be quite difficult and that a definitive diagnosis can only be made in conjunction with clinical and radiologic correlation (7). The four histologic specimens obtained in our two cases proved to be benign, slow-growing tumors, the clinical diagnosis of which is most often made in the presence of a (frequently) painless lesion, which may cause swelling or displacement of teeth or that prevents tooth eruption (7, 13). An analysis of demographic features shows that CEOT is considered to be a tumor of adults, with most patients between the ages of 30 and 50 years; however, in ameloblastic fibroodontoma, the mean age is 8 years (6, 7). The patient reported in case 1 was only 10 years old, and it would seem that this case not only represents a microscopic mixture, but also a hybrid clinical presentation. Similarly, the mean age of diagnosis of COCs is 30 years, while for patients with an odontoma-associated type, it is relatively lower (17 years) (9), and, in our case 2, the patient was 14 years old. AJNR: 22, May 2001 Most of the tumors represented in this classification are rare, and reports of such lesions are sparse. So, except for the most frequently occurring tumors, such as ameloblastomas or odontomas, their radiologic patterns have not been well characterized and, in most cases, are described on plain radiographs (6, 7, 9, 12 17). In our two cases, plain radiographs showed a well-delineated expansile lesion with thinned cortical plates, suggesting a benign slow-growing tumor. In case 1, a small break of the superior cortical plate was more apparent on CT scans as a fairly pronounced thinning of the cortical plate rather than as an aggressive rupture of the bone, owing to the progressive thinning of the bone, with an absence of any neighboring mucosal invasion. This focal bony rupture, which was also found on surgical examination, is quite rare in such benign odontogenic tumors, found in less than 7% of reported cases of COC (9). Such a pattern should be kept in mind as a possible feature of benign odontogenic lesions. Calcifications were present in our two cases, best detected on CT scans rather than on plain radiographs, appearing as more extensive scattered flecks in case 1 (CEOT with ameloblastic fibroodontoma) and as small peripheral calcifications in case 2 (COC with odontoma). Previous reports of CT patterns of such lesions are quite rare; however, CT may be beneficial in depicting such calcifications, whose presence may be characteristic of these lesions, as they may be obscured on plain radiographs by such surrounding structures as tooth or metal restoratives (14). Detection of such calcifications is essential to guide the differential diagnosis among the great variety of expansile radiolucent lesions of the jaws. Thus, CEOT may show considerable radiologic variations: its appearance may range from a diffuse, poorly demarcated, or well-circumscribed unilocular radiolucency to a combined pattern of radiolucency and radiopacity with small intralesional septa producing a multilocular pattern (6, 13). The more classical pattern, in which flecks of calcification are scattered in an area of radiolucency, appears quite superimposable to our case 1. In the rare reports of CT patterns in ameloblastic fibroodontoma, calcifications have been described as having two distinct patterns: either small calcifying nodules scattered through the lesion or calcifying spicules radiating from the center of the lesion and displaying a wheel-like appearance; with advancement in tumor maturation, these radiating spicules can fuse to form a massive calcification (7, 14). Despite the microscopic presence of the ameloblastic fibroodontoma in case 1, radiologically, it appeared to be more like a CEOT or, at best, as a hybrid of a CEOT and an ameloblastic fibroodontoma. However, calcifications, which can be suggestive of a diagnosis, may be absent in ameloblastic fibroodontoma, instead showing a totally radiolucent lesion; although dental hard tissues, by definition, must be formed. The degree of miner-
5 AJNR: 22, May 2001 ODONTOGENIC TUMORS 871 alization rather than the presence of the matrix accounts for the radiodensity of the lesion (7). COC is also known to display a variable radiologic pattern, appearing as a unilocular or, rarely, a multilocular radiolucency with variable amounts of radiopaque material ranging from tiny flecks (as seen in our case 2) to large masses (9, 16). In case 2, the characteristic patterns of odontoma were not found on radiologic examination owing to its small microscopic size. Detection of such calcifications is therefore crucial in the differential diagnosis of these odontogenic tumors. To our knowledge, the MR appearance of COCs has not previously been reported in the literature. Its relatively homogeneous, slightly hyperintense T1 signal and hyperintense T2 signal without enhancement after contrast injection seems to be well correlated with the macroscopic appearance, which shows a cystic lesion without a solid nodule; and the brownish appearance of the cystic liquid could be related to minimal bleeding beforehand, thus explaining the T1 signal. In both our cases, then, the presence of calcifications virtually excluded the diagnosis of ameloblastoma (the most frequent epithelial odontogenic tumor of the jaw, representing 1% of all tumors and cysts of the jaw), in which the presence of calcifications is quite exceptional. Moreover, ameloblastoma characteristically displays a large multilocularity with a mixed pattern of solid and cystic components and strong enhancement of the solid portions of the tumor. Diagnosis may be more difficult in small lesions; however, a solid, enhancing component without calcifications is the rule. The importance in differentiating ameloblastoma from the other odontogenic tumors lies in the different prognosis each tumor carries and therefore the different therapeutic implications (18 20). Similarly, the other epithelial odontogenic tumors, such as the exceptional and occasionally aggressive squamous odontogenic tumor, can be differentiated from our cases by their absence of calcification within a semicircular or triangular-shaped radiolucency between the roots of the teeth, with lysis of the lamina dura (21, 22). The recently individualized clear cell odontogenic tumor, however, appears radiologically indistinguishable from our cases as a purely radiolucent or as a mixed radiolucent/radiopaque uni- or multilocular lesion with either well-demarcated or poorly defined margins. Such findings are, however, not surprising, as the clear cell odontogenic tumor is today considered the neoplastic counterpart of COC (8). In the same manner, regarding mixed odontogenic tumors, the less differentiated ameloblastic fibroma can be excluded by the absence of calcifications. But the radiologic patterns of the exceptional odontoameloblastoma, like those of the equally rare adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, are indistinguishable from those of our two cases, which is also not surprising considering the steps of histodifferentiation they represent among mixed odontogenic tumors. Only the more anterior and maxillary location of the adenomatoid odontogenic tumor could elicit this diagnosis, since most of the other lesions predominate in the posterior part of the mandible. Clinical and microscopic correlations are therefore crucial, because the aggressive odontoameloblastoma shares a high risk of recurrence with ameloblastoma (23). Nonetheless, other tumors must still be considered in the differential diagnosis of lesions with mixed radiologic patterns, such as the odontogenic fibroma, which is most often located in the more anterior part of the maxilla (24), and the cementifying and ossifying fibromas, the dense calcified components of which usually show a more radiated appearance. Conclusion The radiologic, clinical, and microscopic findings in our two cases represent an unusual hybrid presentation that suggests the possibility of histomorphologic differentiation. In such cases, radiologic patterns can guide the diagnosis and perhaps be integrated into the classification of complex, benign odontogenic tumors. References 1. Pindborg JJ. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand (Suppl) 1955;111:71 2. Gorlin RJ, Pindborg JJ, Clausen FP, Vixkers RA. The calcifying odontogenic cyst: a possible analogue of the cutaneous epithelioma of Malherbe. Oral Surg 1962;15: Pindborg JJ, Kramer IRH. International Histological Classification of Tumours: Histological Typing of Odontogenic Tumours, Jaw Cysts and Allied Lesions. Geneva: World Health Organization, Kramer RH, Pindborg JJ, Shear M. International Histological Classification of Tumours: Histological Typing of Odontogenic Tumours. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; Kramer IRH, Pindborg JJ, Shear M. The WHO international histological classification of tumours: a commentary on the second edition. Cancer 1992;70: Melrose RJ. Benign epithelial odontogenic tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol 1999;16: Tomich CE. Benign mixed odontogenic tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol 1999;16: Ellis GL. Odontogenic ghost cell tumor. Semin Diagn Pathol 1999;16: Buchner A. The central (intraosseous) calcifying odontogenic cyst: an analysis of 215 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49: Buchner A, Merrell PW, Hansen LS, Leider AS. Peripheral (extraosseous) calcifying odontogenic cyst. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1991;72: Satomura K, Nakanishi H, Fujisawa K, Hayashi E, Nagayama M. Initiation of ectopic epithelial calcification in a calcifying odontogenic cyst. J Oral Pathol Med 1999;28: Damm DD, White DK, Drummond JF, Poindexter JB, Henry BB. Combined epithelial odontogenic tumor: adenomatoid odontogenic tumor and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor. Oral Surg 1983;55: Nelson SR, Schow SR, Read LA, Svane TJ. Treatment of an extensive calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1992;50: Sumi M, Yonetsu K, Nakamura T. CT of ameloblastic fibroodontoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1997;169: Villareal PM, Junquera LM, Albertos JM, Molina R, Gonzales S. Fibroondome améloblastique. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 1997;98: Devlin H, Horner K. The radiological features of calcifying odontogenic cyst. Br J Radiol 1993;66:
6 872 MARTIN-DUVERNEUIL 17. Gardner DG. The mixed odontogenic tumors. Oral Surg 1984; 57: Weissman JL, Snyderman CH, Yousem SA, Curtin HD. Ameloblastoma of the maxilla: CT and MR appearance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1993;14: Minami M, Kaneda T, Yamamoto H, et al. Ameloblastoma in the maxillomandibular region: MR imaging. Radiology 1992;184: Bonn GE, DeBoom GW. Multilocular radiolucent area of the posterior mandible. J Am Dent Assoc 1988;116: AJNR: 22, May Warnock GR, Correll RW, Pierce GL, Baker DA. Triangularshaped radiolucent area between roots of the mandibular right canine and first premolar. J Am Dent Assoc 1985;110: Goldblatt LI, Ellis GL. Squamous odontogenic tumor. Oral Surg 1982;54: Hooker SP. Ameloblastic odontoma: an analysis of twenty-six cases. Oral Surg 1967;24: Handlers JP, Abrams AM, Danforth R. Central odontogenic fibroma: clinicopathologic features of 19 cases and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1991;49:46 54
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth
 331 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 331-335, 2007 Case Report Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth Sílvia R. A. Reis
331 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 331-335, 2007 Case Report Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth Sílvia R. A. Reis
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy
 Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
WHO Histological typing of odontogenic tumors, A. Epithelial Odontogenic Tumors
 Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
06 Tooth Development and Eruption
 + 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
+ 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature
 Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference to their nature and interrelationship
 J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor A Case Report and Review on Diverse Presentation of the Tumor
 : J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
: J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of. the ethmoid sinus
 Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A Case Report and Review of Literature Sunil S, Nivia M, Devi Gopakumar
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(4):52-56 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(4):52-56 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1065 Kishore Sonawane et al CASE REPORT Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature Kishore Sonawane, Medhini Singaraju, Indra Gupta,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1065 Kishore Sonawane et al CASE REPORT Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature Kishore Sonawane, Medhini Singaraju, Indra Gupta,
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion
 DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma
 Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES
 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES CH Siar KHNg P Murugasu SYNOPSIS This paper represents a reappraisal of the gross and histological
SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES CH Siar KHNg P Murugasu SYNOPSIS This paper represents a reappraisal of the gross and histological
Središnja medicinska knjižnica
 Središnja medicinska knjižnica Čuković-Bagić I., Macan D., Dumančić J., Manojlović S., Hat J. (2010) Dilated odontome in the mandibular third molar region. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology,
Središnja medicinska knjižnica Čuković-Bagić I., Macan D., Dumančić J., Manojlović S., Hat J. (2010) Dilated odontome in the mandibular third molar region. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology,
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of a Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1472 Manikkath Aparna et al case report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of A Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma Manikkath Aparna, Mukund Gupta,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1472 Manikkath Aparna et al case report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of A Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma Manikkath Aparna, Mukund Gupta,
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature
 Case Report Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature Yash Agrawal 1, Giridhar S. Naidu 1, Ramanpal Singh Makkad 1, Ravleen Nagi 1, Supreet Jain 1, Dilip R. Gadewar 1,
Case Report Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature Yash Agrawal 1, Giridhar S. Naidu 1, Ramanpal Singh Makkad 1, Ravleen Nagi 1, Supreet Jain 1, Dilip R. Gadewar 1,
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Complex Odontome: A Review & Case Report Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2
 Complex Odontome: A Review & Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor & Head 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences
Complex Odontome: A Review & Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor & Head 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma in Maxilla and Its Literature Review
 Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(6):347-354 상악에서발생한법랑모세포섬유치아종 박원홍 1), 임원봉 1), 김지선 1), 김상우 1), Zheng Hui 1), Kou Ni 1), 전상미 1), 박지일 2), 최홍란 1), 김옥준 1) * 전남대학교치의학전문대학원구강병리학교실 1), 광주보건대학교치위생과
Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(6):347-354 상악에서발생한법랑모세포섬유치아종 박원홍 1), 임원봉 1), 김지선 1), 김상우 1), Zheng Hui 1), Kou Ni 1), 전상미 1), 박지일 2), 최홍란 1), 김옥준 1) * 전남대학교치의학전문대학원구강병리학교실 1), 광주보건대학교치위생과
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report
 155 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 1, 155-159, 2009 Case Report Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report Deepti Garg, Sangeeta Palaskar, V. P. Shetty and Anju Bhushan
155 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 1, 155-159, 2009 Case Report Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report Deepti Garg, Sangeeta Palaskar, V. P. Shetty and Anju Bhushan
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report
 Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54216 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54216 : Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation Fatima
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54216 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54216 : Case series of 14 with wide range of clinical presentation Fatima
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 18/May 05, 2014 Page 4859
 CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Odontogenic tumors: a review
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 57, 2011, 160 176 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Odontogenic tumors: a review PETER R. MORGAN Odontogenic tumors comprise
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 57, 2011, 160 176 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Odontogenic tumors: a review PETER R. MORGAN Odontogenic tumors comprise
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE TUMOUR AMELOBLASTOMA (A NON-CANCEROUS TUMOUR) Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information
 RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE TUMOUR AMELOBLASTOMA (A NON-CANCEROUS TUMOUR) Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Ameloblastoma
RESEARCH INFORMATION AWARENESS SUPPORT PRIMARY BONE TUMOUR AMELOBLASTOMA (A NON-CANCEROUS TUMOUR) Visit bcrt.org.uk for more information CONTENTS What is it? Who does it affect? Symptoms Types of Ameloblastoma
Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview
 Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Removal of a Complex Odontoma Associated With an Impacted Third Molar
 Removal of a Complex Odontoma Associated With an Impacted Third Molar Authored by Mohammad Hosein Kalantar Motamedi, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A
Removal of a Complex Odontoma Associated With an Impacted Third Molar Authored by Mohammad Hosein Kalantar Motamedi, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS
 ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Impeded Eruption of Mandibular Canine
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1434 Case Report Gauri S Lele, Darshan Modi Abstract Odontome, tumor of odontogenic origin, is associated with disturbances in the eruption of teeth such as impaction, delayed
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1434 Case Report Gauri S Lele, Darshan Modi Abstract Odontome, tumor of odontogenic origin, is associated with disturbances in the eruption of teeth such as impaction, delayed
