Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
|
|
|
- Beverly Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
2 PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most common opportunistic infection in persons infected with HIV.
3
4 CD4 Cell Count Pulmonary Infections.>500cellsmm3 Ac pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, TB cellsmm3 Recurrent bact pneumonia varicella zoster pneumonitis cells mm3 PCP Disseminated TB cells mm3 Fungal pneumonia.<50cells/mm3 - CMV retinits, Atypical mycobacteriosis
5 Pathophysiology Pneumocystis organisms are commonly found in the lungs of healthy individuals. Most children are believed to have been exposed to the organism by age 3 or 4 years, and its occurrence is worldwide. Animal studies have suggested that Pneumocystis organisms are communicable; airborne transmission has been reported. The organism is found in 3 distinct morphologic stages, as follows: The trophozoite (trophic form), in which it often exists in clusters The sporozoite (precystic form) The cyst, which contains several intracystic bodies (spores)
6
7 Pneumocystis carinii Genus/Species: Pneumocystis carinii Image Type: Microscopic Morphology Legend: An electron micrograph of P. carinii cyst from rat lung tissue. Title: EM Image of Pneumocystis carinii Disease(s): Pneumocystis pneumonia
8 Pneumocystis carinii Genus/Species: Pneumocystis carinii Image Type: Microscopic Morphology Legend: Title: EM Image of Pneumocystis carinii Disease(s): Pneumocystis pneumonia An electron micrograph of a P. carinii troph from rat lung tissue, showing its binding to a type I pneumocyte.
9 Disease occurs when both cellular immunity and humoral immunity are defective. Once inhaled, the trophic form of Pneumocystis organisms attach to the alveoli. Multiple host immune defects allow for uncontrolled replication of Pneumocystis organisms and development of illness, including the following: Activated alveolar macrophages without CD4+ cells are unable to eradicate Pneumocystis organisms. Increased alveolar-capillary permeability is visible on electron microscopy. Physiologic changes include the following: Hypoxemia with an increased alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient & permiability Respiratory alkalosis Impaired diffusing capacity Changes in total lung capacity and vital capacity
10 Frequency Prior to the widespread use of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), PCP occurred in 70-80% of patients with HIV infection. The frequency of PCP is decreasing with the use of PCP prophylaxis and HAART. PCP is still the 2 nd most common opportunistic infection in patients with HIV infection. Patients with HIV infection are more prone to PCP recurrence than patients not infected with HIV.
11 Mortality/Morbidity In patients with HIV infection In this population, PCP once carried a mortality rate of 20-40%, depending on disease severity at presentation. Currently, mortality rates of 10-20% are reported. PCP is still a major cause of death in patients with AIDS. In patients without HIV infection PCP carries a worse prognosis in persons without HIV infection; this has not changed significantly in the past 20 years. Mortality rates of 30-50% have been documented in several large studies. The higher mortality rate is likely a result of delayed diagnoses and initiation of appropriate treatment
12 Etiology & Risk Factors The following groups are at risk for PCP:
13 Clinical History The symptoms of P carinii pneumonia (PCP) are nonspecific. PCP in patients with HIV infection tends to run a acute or more often subacute indolent course and tends to present much later, often after several weeks of symptoms, compared with PCP associated with other immunocompromising conditions. Symptoms of PCP include the following: Progressive exertional dyspnea Fever Nonproductive cough Chest discomfort Weight loss Chills Hemoptysis (rare)
14 Physical The physical examination findings of PCP are nonspecific and include the following: Tachypnea Fever Tachycardia Pulmonary symptoms: Pulmonary examination may reveal mild crackles and rhonchi but may yield normal findings in up to half of patients. Additional findings in children with severe disease Cyanosis Nasal flaring Intercostal retractions Extrapulmonary manifestations: Although Pneumocystis infection rarely causes extrapulmonary manifestations, they may be present in patients receiving aerosolized pentamidine for prophylaxis or in patients with advanced HIV infection who are not taking any prophylaxis. They may also occur in the absence of lung involvement. Based on most well-documented findings, Pneumocystis infection may present in almost any organ system, as follows: CNS Bone marrow (may have necrosis with resultant pancytopenia) Lymphadenopathy Eyes (may have retinal cotton-wool spots) Thyroid (may present as a rapidly enlarging thyroid mass) GI tract
15 Differential Diagnoses Cytomegalovirus Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia Mycoplasma Infections viral Pneumonia Pulmonary Embolism Legionellosis Tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
16 Workup Laboratory Studies Lactic dehydrogenase study as part of the initial workup Lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) levels are usually elevated (>220 U/L) in patients with P carinii pneumonia (PCP). This study has a high sensitivity (78-100%). The LDH level is elevated in 90% of patients with PCP who are infected with HIV. This study has a much lower specificity because other disease processes result in an elevated LDH level. LDH levels appear to reflect the degree of lung injury. Consistently elevated LDH levels during treatment may indicate therapy failure and a worse prognosis. LDH levels should decline with successful treatment
17 Imaging Studies Chest radiography should be obtained in any immunocompromised patient with fever and/or respiratory signs or symptoms. Findings include the following: The chest radiographic findings may be normal in patients with early mild disease. Diffuse bilateral infiltrates extending from the perihilar region are visible in most patients with PCP. Less-common findings include patchy asymmetric infiltrates and pneumatoceles. Pleural effusions and intrathoracic adenopathy are rare. Pneumothorax may develop in patients using aerosolized pentamidine. Apical disease may also be found in patients using aerosolized pentamidine for prophylaxis. High-resolution CT scanning of the chest High-resolution CT scanning of chest (HRCT) is helpful when the chest radiography findings are equivocal. The typical appearance is patchy areas of ground-glass attenuation with a background of interlobular septal thickening. HRCT yields a high sensitivity for PCP in patients with HIV infection. Negative (normal or unchanged) CT scan findings alone do not rule out PCP.
18 Chest radiograph demonstrating diffuse bilateral infiltrates in a patient with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
19 This image shows the redistribution of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia to the upper lobes following aerosolized pentamidine prophylaxis.
20 This chest radiograph shows bilateral upper-lobe pneumatoceles after a Pneumocystis carinii infection in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
21 This chest radiograph shows left side pneumothorax after a Pneumocystis carinii infection in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
22 CT scan of chest, with classic patchy areas of ground-glass attenuation
23 Imaging Studies Gallium 67 scanning Gallium 67 scan demonstrates an increased diffuse symmetrical pulmonary uptake in patients with PCP. This study is highly sensitive (nearly 100%). The specificity is low (some studies report as low as 20%). The high cost and 2-day time delay in obtaining results have limited its use. A gallium 67 scan is potentially more useful in patients with suspected relapse, as BAL may be less diagnostic in such cases.
24 Other Tests Pulmonary function tests should be obtained as part of the initial noninvasive workup in patients with suspected PCP. Results may demonstrate a decreased diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO) of less than 75% predicted. Decreased DLCO has a high sensitivity (89-100%) but poor specificity (53%). PCP is unlikely if DLCO is normal. When combined with normal or unchanged HRCT findings, pulmonary function tests may be used to identify patients unlikely to have PCP; such patients may be managed with observation alone.
25 Procedures Obtain sputum sample by sputum-induction for histopathologic testing if PCP is strongly suspected. Pneumocystis organisms are frequently found in sputum induced by inhalation of a hypertonic saline solution. Expectorated sputum has a very low sensitivity and should not be submitted for diagnosis. Sputum induction is the quickest and least-invasive method for definitively diagnosing PCP.5 Sensitivity varies widely (<50% to >90%) and depends on proficiency in using the technique and the experience of the laboratory. Specificity is high (99-100%). This study may be less sensitive in patients without HIV infection, as the immunodeficiency caused by HIV infection typically leads to a greater alveolar load of Pneumocystis organisms. It may also be less sensitive in patients receiving aerosolized pentamidine for prophylaxis.
26 BAL is the most common invasive procedure used to diagnose PCP. BAL has a diagnostic yield that exceeds 90% (may be increased if multiple lobes are sampled).6 Obtain BAL if PCP is strongly suspected and the induced sputum sample findings are negative. BAL yields a lower sensitivity in patients receiving aerosolized pentamidine, in which case a transbronchial biopsy may be performed in conjunction with BAL.7 BAL may be used in patients who are unable to cooperate with an induced sputum sample (eg, because of altered mental status). BAL may be less useful in cases of suspected PCP relapse (see Imaging Studies). Open lung biopsy is the most invasive procedure and yields 100% sensitivity and specificity because it provides the greatest amount of tissue for diagnosis. However, this procedure is reserved for rare cases when bronchoscopy findings are nondiagnostic
27 Histologic Findings Because clinical and radiologic findings are not specific for PCP and because P jiroveci cannot be grown in vitro, histopathologic demonstration is necessary before a definitive diagnosis is established. The following are the staining techniques available for respiratory tract secretions: Cresyl violet, Giemsa, Diff-Quik, and Wright stain are used to detect both the trophozoite and cyst forms but not the cyst wall. Methenamine silver, toluidine blue, and Gram-Weigert selectively stain the wall of Pneumocystis cysts. Papanicolaou smear may demonstrate a foamy-appearing eosinophilic material surrounding Pneumocystis organisms. Some facilities prefer to use direct immunofluorescence using monoclonal antibodies to detect Pneumocystis organisms because it may be more sensitive than histologic staining.
28 Papanicolaou smear of Pneumocystis jiroveci
29
30 Further Inpatient Care All patients who require corticosteroids should be admitted to the hospital because of the risk of progressive respiratory compromise. Treatment of P carinii pneumonia (PCP) may be initiated before the workup is complete in severely ill high-risk patients. Appropriate histopathologic testing may still be used to confirm a diagnosis of PCP after treatment is initiated. Endotracheal tube aspirates from severely ill patients on mechanical ventilation may be submitted for diagnosis. Because of increasing evidence of possible human transmission the CDC Hospital Infection Control Practice Advisory Committee has recommended that patients with PCP not have direct contact with other immunocompromised patients.
31 Prevention Smoking cessation is strongly recommended in patients with HIV infection smokers are at an increased risk of PCP and have a more complicated treatment course. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for the following groups: Adults, adolescents, and pregnant patients with a CD4 count of less than 200/µL, oropharyngeal candidiasis, unexplained fever exceeding 100 F for more than 2 weeks, and a prior episode of PCP regardless of CD4 count should receive prophylaxis. Children born to mothers with HIV infection should receive prophylaxis with TMP-SMX beginning at age 4-6 weeks. The drug should be discontinued if they are subsequently determined not to be infected with HIV. Children who are determined to be HIV positive through the first year of life, then as determined by age-specific CD4 levels, should receive prophylaxis.
32 Chemoprophylaxis Two types of outpatient chemoprophylactic therapies exist, as follows: Primary prophylaxis is used in immunocompromised patients without a history of PCP. Secondary prophylaxis is used in patients with a prior bout of PCP. Prophylaxis may be discontinued in patients with HIV infection whose CD4 count exceeds 200/µL for 3 consecutive months while on HAART. Prophylaxis should be restarted if the CD4 count drops below 200/µL. Prophylaxis should be continued for life in patients who developed PCP while their CD4 level exceeded 200/µL.
33 immunocompromised patients without HIV Unlike in patients with HIV infection, no specific PCP prophylaxis guidelines exist for immunocompromised patients without HIV infection. In general, chemoprophylaxis should be considered in any of the following patients: Patients with an underlying primary immune deficiency (eg, SCID or hypogammaglobulinemia) Patients with a persistent CD4 count less than 200/µL Solid organ transplant recipients Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients, with prophylaxis administered (1) for 6 months after engraftment months or (2) for more than 6 months after HSCT in those who are still receiving immunosuppressive therapy (eg, prednisone, cyclosporine) or who have chronic graft versus host disease Patients receiving daily systemic corticosteroid therapy (at least 20 mg daily for at least 1 mo) Patients with cancer, vasculitides, or collagen vascular disorders and others receiving cytotoxic or immunosuppressive treatments such as cyclosporine or the purine analogs fludarabine or cladribine
34 Prophylactic regimens include Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Dose is one double-strength tablet (160 mg TMP to 800 mg SMX) daily. Dapsone: Dose is 100 mg by mouth daily if administered alone Dapsone with pyrimethamine (plus leucovorin Atovaquone Dose is 1500 mg by mouth once daily given with food Aerosolized pentamidine Dose is 300 mg in 6 ml sterile water via Respirgard nebulizer every 4 weeks
35 Complications & Prognosis Hypoxemia and respiratory failure A pathophysiologic process similar to ARDS may occur in patients with severe PCP. These patients may require intubation. This greatly diminishes the prognosis The prognosis of PCP is worse in patients who present with concurrent pulmonary disease, in patients who develop pneumothorax, and in patients who require mechanical ventilation. Other factors that affect prognosis include a delay in diagnosis that leads to to delayed treatment
36 HAART Before the availability of HAART[known as highly active antiretroviral therapy, HAART], patients who survived mechanical ventilatory support for PCP rarely lived longer than 1 year. With the use of HAART, the prospects for long-term survival are considerably more hopeful, especially if the patient has not yet received antiretroviral therapy [
37 Thank you
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Opportunistic infections
 Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review.
 HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
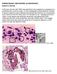 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
2. Clinical Manifestations (Pediatric HIV Infection)
 Page 1 of 6 HOUSTON ROMANIA SOUTHERN AFRICA MEXICO HOME CONTACT Friday, July 25, 2003 Pediatric HIV Infection by Mark W. Kline, M.D. 1. Introduction 2. Clinical Manifestations 3. Diagnosis 2. Clinical
Page 1 of 6 HOUSTON ROMANIA SOUTHERN AFRICA MEXICO HOME CONTACT Friday, July 25, 2003 Pediatric HIV Infection by Mark W. Kline, M.D. 1. Introduction 2. Clinical Manifestations 3. Diagnosis 2. Clinical
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Clinical Manifestations of HIV
 HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Lecture Notes. Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns
 Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
HIV-associated Pulmonary Disease. Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond QUESTION: HIV-associated Pulmonary Diseases
 Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia: High-Resolution CT Findings in Patients With and Without HIV Infection
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings
 Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational
Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
PNEUMONIA. I. Background 6 th most common cause of death in U.S. Most common cause of infection related mortality
 Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than
 TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP. Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital
 Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal transplant
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
5/15/2017. What Does HIV/AIDS Look Like in DC in Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections
 Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
 October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests
 medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
 January 2001 Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Brady Case, Harvard Medical School 1 Our Patient Nelson is a 40 year-old male who presents with a 6 month history of: progressive dyspnea on exertion dry cough
January 2001 Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Brady Case, Harvard Medical School 1 Our Patient Nelson is a 40 year-old male who presents with a 6 month history of: progressive dyspnea on exertion dry cough
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 03 Page March 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents
 Early Release March 24, 2009 / 58(Early Release);1-198 Early Release March 24, 2009 / 58(Early Release);1-198 Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults
Early Release March 24, 2009 / 58(Early Release);1-198 Early Release March 24, 2009 / 58(Early Release);1-198 Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults
AIDS at 25. Epidemiology and Clinical Management MID 37
 AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
Lung Injury after HCT
 Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Epidemiology and Management MID 37
 AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Radiological syndroms. Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome
 Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
OI prophylaxis When to start, when to stop. Eva Raphael, MD MPH Family and community medicine, pgy-2 University of California, San Francisco
 OI prophylaxis When to start, when to stop Eva Raphael, MD MPH Family and community medicine, pgy-2 University of California, San Francisco Learning Objectives o Recognize when to start OI prophylaxis
OI prophylaxis When to start, when to stop Eva Raphael, MD MPH Family and community medicine, pgy-2 University of California, San Francisco Learning Objectives o Recognize when to start OI prophylaxis
Inflammation class 2. Inflammation part 2. Rheumatic fever RF. Rheumatic fever - pathogenesis. Hypersensitivity reactions. Rheumatic fever RF
 Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I. December 5, 2012
 SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): Part 2
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): Part 2 Brian R. Wood, MD Medical Director, NW AETC ECHO Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Washington Presentation
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP): Part 2 Brian R. Wood, MD Medical Director, NW AETC ECHO Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Washington Presentation
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
 MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Dr. Lesego Mawela
 Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Dr. Lesego Mawela TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION IRIS Case Epidermiology Pathogenesis of IRIS Risk factors for IRIS Epidemiology of IRIS Health system burden of IRIS
Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Dr. Lesego Mawela TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION IRIS Case Epidermiology Pathogenesis of IRIS Risk factors for IRIS Epidemiology of IRIS Health system burden of IRIS
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
COPD exacerbation. Dr. med. Frank Rassouli
 Definition according to GOLD report: - «An acute event - characterized by a worsening of the patients respiratory symptoms - that is beyond normal day-to-day variations - and leads to a change in medication»
Definition according to GOLD report: - «An acute event - characterized by a worsening of the patients respiratory symptoms - that is beyond normal day-to-day variations - and leads to a change in medication»
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India Sonika Dahiya, Sandeep R. Mathur, Venkateswaran K. Iyer, Kusum Kapila
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India Sonika Dahiya, Sandeep R. Mathur, Venkateswaran K. Iyer, Kusum Kapila
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD
 Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study
 MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
 Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Treatment and Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in HIV-Infected Patients. 1 Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy.
 Teachers Topics Treatment and Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in HIV-Infected Patients Robert C. Stevens 1 School of Pharmacy, University of Tennessee, 26 South Dunlap Street, Memphis TN
Teachers Topics Treatment and Prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in HIV-Infected Patients Robert C. Stevens 1 School of Pharmacy, University of Tennessee, 26 South Dunlap Street, Memphis TN
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
 COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP
 Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Critical Care Nursing Theory. Pneumonia. - Pneumonia is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma
 - is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
- is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
Interstitial syndrome
 Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
 http://www.savinglivesuk.com/ HIV Awareness Study Morning 24 th November 2017 Agenda HIV Basics & Stages of HIV HIV Testing, Health Advising & Sexual Health Saving Lives Antiretroviral Medication Antenatal/Postnatal
http://www.savinglivesuk.com/ HIV Awareness Study Morning 24 th November 2017 Agenda HIV Basics & Stages of HIV HIV Testing, Health Advising & Sexual Health Saving Lives Antiretroviral Medication Antenatal/Postnatal
Index. B Biological factors, 2 Brain stem encephalitis, Burkitt s lymphoma, 83, 105
 Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) abdomen gallbladder complications, 97, 107 109 gastrointestinal complications, 96, 105 106 liver complications, 97, 107 109 neoplasm, 99, 110 111 pancreas
Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) abdomen gallbladder complications, 97, 107 109 gastrointestinal complications, 96, 105 106 liver complications, 97, 107 109 neoplasm, 99, 110 111 pancreas
Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012
 Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012 INTRODUCTION PNEUMOTHORAX HEMOPTYSIS RESPIRATORY FAILURE Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal Recessive Genetically
Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012 INTRODUCTION PNEUMOTHORAX HEMOPTYSIS RESPIRATORY FAILURE Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal Recessive Genetically
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia
 Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases
 Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS
 Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
COUGH Dr. A m A it i e t sh A g A garwa w l Le L ctu t rer Departm t ent t o f f M e M dic i in i e
 COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Treating Opportunistic Infections among HIV- Infected Adults and Adolescents: Recommendations from CDC, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association/Infectious
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Treating Opportunistic Infections among HIV- Infected Adults and Adolescents: Recommendations from CDC, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association/Infectious
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond
 PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Respiratory symptoms, including
 Matthew Fei, MD Laurence Huang, MD Respiratory symptoms, including cough, shortness of breath, labored breathing, and chest pain, are common complaints in the setting of HIV infection. The spectrum of
Matthew Fei, MD Laurence Huang, MD Respiratory symptoms, including cough, shortness of breath, labored breathing, and chest pain, are common complaints in the setting of HIV infection. The spectrum of
Measure #161: HIV/AIDS: Adolescent and Adult Patients with HIV/AIDS Who Are Prescribed Potent Antiretroviral Therapy
 Measure #161: HIV/AIDS: Adolescent and Adult Patients with HIV/AIDS Who Are Prescribed Potent Antiretroviral Therapy 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY DESCRIPTION:
Measure #161: HIV/AIDS: Adolescent and Adult Patients with HIV/AIDS Who Are Prescribed Potent Antiretroviral Therapy 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPTING OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY DESCRIPTION:
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
