Monoamine Systems. Susan R. Sesack. Professor, Neuroscience
|
|
|
- Laurence Barker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Monoamine Systems Susan R. Sesack Professor, Neuroscience
2 Nolte
3 Nolte
4 histidine decarboxylase Cooper, Bloom and Roth
5 Nolte
6 An underlying assumption in behavioral neurochemistry is that certain substances, neuroregulators, play a key role in communication among nerve cells. These compounds may be subdivided into those which convey information between adjacent nerve cells (neurotransmitters) and those which amplify or dampen neuronal activity (neuromodulators). J Barchas et al Science Neuromodulation...is taken to mean the enhancement, reduction, prolongation or curtailment of information processing by activity within these [monoamine] systems, often with only their minor participation in the computations of the neural networks they innervate. TW Robbins Each neuron has characteristic intrinsic response properties that result from the ensemble of ion channels found in its membrane. Modulatory substances can modify the type, number, and/or kinetic properties of these ion channels and thus change the excitability of the cell... Consequently, a single neuron can display a variety of intrinsic activity patterns and can switch between them, depending on the modulatory environment. E Marder
7 Purves
8 Nicoll et al., 1987
9 Wang et al., 2006 Neuron
10 Monoamine axons are thin and unmyelinated, placing them at the low end of the conduction velocity range (0.5 m/sec), consistent with their modulatory function. Netter, Ciba Series
11 Monoamine axon varicosities sometimes form recognizable synapses and sometimes do not, consistent with their use of both classical wiring transmission and volume transmission. Descarries; Sesack
12 Bezard and Gross, 1998
13 Fuxe and Agnati, 1991
14 Sanford Palay: "Topographic proximity of the pre- and postsynaptic elements is dispensed with in systems for which speed, efficiency, and precise focal interaction are not important." Non-synaptic transmission provides "an efficient way to produce generalized effects without directly and repetitiously contacting every single cell in a target area comparable to sounding a fire alarm instead of ringing the doorbell of every home in an area threatened by fire."
15 Limitations on volume transmission: amount of transmitter released tortuosity factors/glia receptor localization and affinity reuptake Sesack
16 Postsynaptic receptors for monoamines, such as these D1 receptors in a striatal dendrite, have been amply demonstrated at extrasynaptic sites and further shown to be functional (e.g. they internalize in response to agonist exposure). Dumartin et al., 1998, J Neurosci
17 Postsynaptic receptors for monoamines, such as these D1 receptors in a striatal dendrite, have been amply demonstrated at extrasynaptic sites and further shown to be functional (e.g. they internalize in response to agonist exposure). Dumartin et al., 1998, J Neurosci
18 Hersch et al., 1997, J Comp Neurol Plasma membrane transporters (e.g. DAT) are typically localized to the immediate perisynaptic area and at extrasynaptic sites all along monoamine axons. This is at least consistent with the possibility of extrasynaptic release. Sesack
19 wild type heterozygote knockout Giros et al., 1996, Nature The essential role played by monoamine transporters is evidenced by transgenic mice, such as the DAT knock-out mouse, which exhibits a hyperactive state associated with excessive extracellular DA levels, despite the system s many attempts at homeostasis.
20 Monoamine transmission is also typically regulated by autoreceptors located on axonal and somatodendritic membranes. The latter are consistent with dendritic release events.
21 Dopamine System Saper, 2000
22 Dopamine System Saper, 2000
23 Corticostriatal glutamate Medium Spiny Striatal Neuron Nigrostriatal dopamine Dopamine System In target areas, DA terminals frequently synapse onto spines and distal dendrites where they converge with glutamate inputs onto the same structures. adapted from Smith et al., 1990, TINS; and Sesack
24 Dopamine System DA modulates glutamate transmission by either attenuating or facilitating drive depending on receptor subtype and other factors. Mogenson
25 Dopamine System DA cells fire spontaneously due to pacemaker potentials. These slow depolarizing currents are voltage-dependent, carried by both Na+ and Ca2+ and are initiated upon the decay of the afterhyperpolarization. Grace, 1985/7 and 1995
26 Dopamine System Trulson, 1985 Many DA cells maintain a mean firing rate of 3-5 Hz (some populations are faster). DA neurons exhibit little variation in activity across different sleep-wake stages and are the only monoamine cells demonstrating such stability despite changes in behavioral state.
27 Dopamine System Grace, 1987 and 1995 In vivo, DA neurons fire in an irregular tonic mode that reflects excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs superimposed on the pacemaker activity. Strong excitatory drive leads to NMDAR-dependent bursts of action potentials that have a characteristic decreasing amplitude and increasing interspike interval within the burst. DA release from terminals during a burst is reportedly greater than during the same number of evenly spaced spikes. DA cells also show brief pauses after bursts or in response to strong synaptic inhibition.
28 Dopamine System In awake animals, the activity patterns of DA cells involve: activation to unpredicted rewards activation to conditioned stimuli that predict reward (but no longer to predictable rewards) inhibition when expected rewards are not delivered Hence, DA neurons appear to signal their targets with information regarding future expectancy. Schultz, 1998, J Neurophysiol
29 Historically, activation of forebrain DA systems has been associated with natural and drug rewards: food (presentation, not consumption) sex (preparation, not consummation) introduction of conspecifics to isolated animals cocaine amphetamine heroin nicotine alcohol Dopamine System Web images
30 DA cell firing is altered by: Natural and drug rewards (usually excitation) Conditioned stimuli predicting reward (usually excitation) Prediction of no reward (usually inhibition) Absence of predicted reward (usually inhibition) Stress and aversive/noxious stimuli (usually inhibition) Uncertainty (altered rate of tonic firing) Novel stimuli with fast rise times and high intensity (usually excitation): light flash, click, whistle, clap, hiss, strong odor, whisker stimulation, novel environment, etc. Dopamine System
31 DA cells are reticular! Dopamine System They are activated by conditions that cause the animal to: respond to the environment maintain a representation of the triggering event prepare for action Horvitz, 2000 DA cells are inhibited by conditions that call for halting action.
32 Norepinephrine & Epinephrine Saper, 2000
33 Norepinephrine System Saper, 2000
34 NE cells are reticular! are activated by multisensory stimuli are activated by acute stressors function in attention and arousal Norepinephrine System Tail shock Aston-Jones et al (1994) J Neurosci NE (pg/20 µl) Jedema et al (1999) Brain Res
35 Norepinephrine System Aston-Jones & Bloom, 1991 NE cells in the LC decrease activity progressively from waking to slowwave sleep and then shut off during REM sleep (i.e., REM-off cells).
36 Norepinephrine System LC neurons increase their activity during stressful events and in response to arousing stimuli. The LC operates like a central sympathetic system, cognitively preparing an animal by increasing attention and vigilance. In target areas, NE selectively enhances cell firing in response to sensory events that have high affective valence.
37 Activation of the LC NE system facilitates memory for emotionally disturbing events, which is better than for emotionally neutral events. Norepinephrine System
38 Norepinephrine System Alterations in the NE system also underlie certain anxiety disorders, including PTSD, that are characterized by hyper-vigilance and hyper-responsiveness.
39 NE dysfunction might also contribute to attention deficits seen in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Norepinephrine System
40 Serotonin System Saper, 2000
41 Serotonin System 5HT raphe cells fire around 3 Hz during active and quiet waking. They can fire up to 6 Hz by phasic stimuli (e.g. auditory clicks) linked to arousal. But they typically cannot be driven to fire faster, even by extreme stress. 5HT neurons show a progressive decline in activity through various stages of slow-wave sleep, and they shut off during REM sleep (i.e., REM-off cells).
42 Serotonin System BL Jacobs and CA Fornal: Serotonin is an enigma. It is at once implicated in virtually everything, but responsible for nothing. DA reward, approach/avoidance, response initiation NE vigilance 5HT - cardiovascular and respiratory activity, sleep, aggression and sexual behavior, nutrient intake, anxiety, mood, motor control, neuroendocrine secretion, and nociception and analgesia. Drugs that act on the serotonin system can be used to treat a range of disorders from migraines to obsessive compulsive disorder to depression, and they can cause side effects ranging from hallucinations to sexual dysfunction.
43 Serotonin System
44 Serotonin System Heninger, 1995
45 Histamine System Saper, 2000
46 Histamine System Sleep-Wake Cycles Histamine projections to the thalamus and cortex regulate arousal and consciousness. GABA neurons in the VLPO of the hypothalamus initiate non-rem sleep in part by shutting off the histamine neurons, mimicking the action of antihistamines. Web image
47 Acetylcholine System Reticular formation ACh neurons play a major role in sleep-wake cycles. Their extensive projections to thalamus provide diffuse activation signals that maintain thalamocortical activity in an awake state. These cells turn off during slow-wave sleep, then turn ON again in REM sleep (REM ON cells). This reactivation of thalamus and cortex maintains the awake EEG pattern characteristic of REM. Cooper, Bloom and Roth
48 Acetylcholine System Saper, 2000
49 Acetylcholine System Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are associated with learning, memory and attention. Drugs that are anti-muscarinics can produce amnesia (e.g. the twighlight sleep of scopolamine). Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons degenerate in Alzheimer s disease. Acetylcholine mediates increases in neuronal activity associated with enhanced demands for attentional processing. M Sarter Acetylcholine mediates the detection, selection, and processing of stimuli and associations, and the allocation of processing resources for these attentional functions J Bruno
50 Acetylcholine System Nicotinic receptors are associated with vigilance and concentration. Nicotine is the single most addictive substance known, almost certainly via its direct stimulant action on the midbrain DA system. Web images
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience Lecture 7: 02/02/16 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week:
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.thiscourse.com/ucsd/cogs107b/wi16 Lecture 7: 02/02/16 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: funcdonal anatomy neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.thiscourse.com/ucsd/cogs107b/wi16 Lecture 7: 02/02/16 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: funcdonal anatomy neurotransmitters: mediating information
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
Neurons have cell membranes that separate them from the environment outside the neuron.
 Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
Notes: Synapse. Overview. PSYC Summer Professor Claffey PDF. Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the
 PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters
 Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
ADHD Medications & How They Work. Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008
 ADHD Medications & How They Work Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008 Agenda How the (ADHD) Brain Works (or doesn t) Neurons and neurotransmitters NE & DA: the major players in ADHD Channel vs. state
ADHD Medications & How They Work Gail C. Rodin, Ph.D. January 21, 2008 Agenda How the (ADHD) Brain Works (or doesn t) Neurons and neurotransmitters NE & DA: the major players in ADHD Channel vs. state
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
COGS 269. Lecture 1 Spring 2018
 COGS 269 Lecture 1 Spring 2018 Psychological Experience Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Dissociation experiments (patients with brain damage) Neuroimaging experiments Computational modeling Brain damage
COGS 269 Lecture 1 Spring 2018 Psychological Experience Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Dissociation experiments (patients with brain damage) Neuroimaging experiments Computational modeling Brain damage
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e. Chapter 4: The action potential
 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Neurons: Structure and communication
 Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Human Brain and Senses
 Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Neurochemistry 2. Loewi s experiment
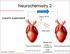 Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue
 9/12/11 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Overview of the nervous system Cells of the nervous system Electrophysiology of neurons Synapses Neural integration Subdivisions of the Nervous System 1 Subdivisions of
9/12/11 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Overview of the nervous system Cells of the nervous system Electrophysiology of neurons Synapses Neural integration Subdivisions of the Nervous System 1 Subdivisions of
Synapse. 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6.
 Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON
 UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
UNIT 3 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - DIVISIONs - THE NEURON CHARACTERISTICS COMPLEXITY: nerve cells connecting allow you to do EVERYTHING you will ever do INTEGRATION: brain pulls all information you get together
Nervous System (cont)
 Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
pdf NIH Overview Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from:
 1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Synapse. Structure & Function. Neurotransmitter Sequence. Integration. History: 10/4/12 original version
 Synapse History: 10/4/12 original version Structure & Function (This content is covered in Sinjin's presentation, see link in calendar) Neurotransmitters Synaptic cleft Post-synaptic potential Excitation
Synapse History: 10/4/12 original version Structure & Function (This content is covered in Sinjin's presentation, see link in calendar) Neurotransmitters Synaptic cleft Post-synaptic potential Excitation
Introduction to CNS 1
 Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other?
 LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION. Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre
 1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
Recreational Chemistry
 Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
Recreational Chemistry Well I'm fading away And I can't find the way to the door So I'll sit here on my bed all day While I'm whiling away The best part of a day on the floor I'll sit here on my head all
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (ACH) Deals with motor movement and memory. Too much and you will. Too little and you will Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer s disease. Serotonin Involved
TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (ACH) Deals with motor movement and memory. Too much and you will. Too little and you will Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer s disease. Serotonin Involved
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
 BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Warm-up. Warm-up. Warm-up. Chapter 48. Why do animals need a nervous system? 3/9/2012. Nervous System
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between cells' content and the extracellular fluid. Warm-up: Cells from this structure migrate to other parts
Warm-up Objective: Explain how membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between cells' content and the extracellular fluid. Warm-up: Cells from this structure migrate to other parts
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name. Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28
 Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28 Vocabulary acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), action potential,
Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28 Vocabulary acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), action potential,
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html What could possibly go wrong? n Causes of Narcolepsy Uncertain, but appears
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html What could possibly go wrong? n Causes of Narcolepsy Uncertain, but appears
Neurons. Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons.
 Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells. Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD
 Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering
 Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Notes are online at The Neuron
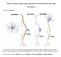 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
25 Things To Know. Neurotransmitters
 25 Things To Know Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters 300+ types Neurotransmitters Most Common In Brain Glutamate 90% GABA 9% Other 1% Other 1% Monoamines Dopamine Norepinephrine Epineprine Serotonin Acetylcholine
25 Things To Know Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters 300+ types Neurotransmitters Most Common In Brain Glutamate 90% GABA 9% Other 1% Other 1% Monoamines Dopamine Norepinephrine Epineprine Serotonin Acetylcholine
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Chapter 4: Biology of Behavior The Brain and Its Components Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord peripheral nervous system (PNS) nerves
 Chapter 4: Biology of Behavior A. The brain is the most complex organ that we know. It is responsible for many of the behaviors that humans are capable of I. The Brain and Its Components A. Basic Structure
Chapter 4: Biology of Behavior A. The brain is the most complex organ that we know. It is responsible for many of the behaviors that humans are capable of I. The Brain and Its Components A. Basic Structure
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
The Nervous System AP Biology
 The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Nervous System Notes
 Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Nervous System Notes The nervous system consists of a network of nerve cells or neurons. I. A nervous system is an important part of a cell s (or an organism s) ability to respond to the environment. A.
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
COGS 107B Systems Neuroscience. Week 6: Study Ques=ons
 COGS 107B Systems Neuroscience Week 6: Study Ques=ons Auditory System II Neuromodulators and Drugs of Abuse Auditory System Neurons in the primary auditory cortex (A1) are sensi=ve to of sounds. Neurons
COGS 107B Systems Neuroscience Week 6: Study Ques=ons Auditory System II Neuromodulators and Drugs of Abuse Auditory System Neurons in the primary auditory cortex (A1) are sensi=ve to of sounds. Neurons
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC
 BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
Brain Neurotransmitters
 Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Brain Neurotransmitters * Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane * Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane * Binds to and
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
NEUROTRANSMITTERS. Contraction of muscles to move our bodies Release hormones Psychological states of thinking and emotions
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
NEUROTRANSMITTERS NEURONS Neurons don t actually touch Separated by a tiny fluid-filled gap called a synapse Neural impulses must be ferried across the synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
Lujain Hamdan. Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test
 Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
