Author's accepted manuscript; final version published as:
|
|
|
- Lilian Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Mandible in An Eight Year-Old Girl with Noonan Syndrome (Noonan-Like/Multiple Giant Cell Lesions Syndrome) Paul C. Edwards 1 M.Sc., D.D.S., Joyce Fox 2 M.D., John E. Fantasia 1 DDS, Jeff Goldberg 3 DDS and Robert D. Kelsch 1 D.M.D. 1 Department of Dental Medicine, Division of Oral Pathology, Long Island Jewish Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, 2 Division of Human Genetics, Schneider Children s Hospital, Long Island Jewish Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, and 3 Private Practice, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Westbury, NY. Author's accepted manuscript; final version published as: Edwards PC, Fox J, Fantasia JE, Goldberg J, Kelsch RD. Bilateral central giant cell granulomas of the mandible in an 8-year-old girl with Noonan syndrome (Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod Mar;99(3):
2 Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Mandible in An Eight Year-Old Girl with Noonan Syndrome (Noonan-Like/Multiple Giant Cell Lesions Syndrome) Author's accepted manuscript; final version published as: Edwards PC, Fox J, Fantasia JE, Goldberg J, Kelsch RD. Bilateral central giant cell granulomas of the mandible in an 8-year-old girl with Noonan syndrome (Noonanlike/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod Mar;99(3):
3 Address reprint requests to: Dr. Paul C. Edwards and Dr. Robert D. Kelsch, Division of Oral Pathology, Department of Dental Medicine, Long Island Jewish Medical Center, th Avenue, New Hyde Park, NY, Tel: (718) Fax: (718) and
4 Abstract A number of conditions can present with lesions that histologically are indistinguishable from the central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) of bone, including brown tumors of hyperparathyroidism, cherubism, and, less commonly, a number of inherited syndromes. We report a case of an eight-year girl who presented with bilateral CGCGs of the posterior mandible. Characteristic facial features, reported increased post-operative bleeding and history of pulmonary stenosis led us to suspect a diagnosis of Noonan syndrome. A medical geneticist confirmed this on further evaluation. This case report will discuss the salient features of this diagnosis. 1
5 Case Presentation An eight-year-old girl (Fig. 1) was referred for evaluation after routine panoramic radiographic evaluation revealed well-defined bilateral multilocular radiolucencies of the posterior mandible associated with the developing third molars (Fig. 2). Each lesion measured more than 2.5 cm in greatest dimension. Also noted was displacement of the prematurely developing right and left mandibular third molar teeth. On axial computed tomographic examination, no cortical expansion was evident (Fig. 3). There was no history of prior trauma or surgery to the mandible. The patient was the product of a full-term uncomplicated pregnancy. At 10 days of age an atrial septal defect and pulmonic stenosis were detected. Her family history was unremarkable, with no record of jaw abnormalities or atypical facies among other family members. On physical examination she was at the 5 th percentile for weight, 10% for height and 50th percentile for head circumference. She had thick kinky hair and several pigmented nevi. She had brilliant blue eyes with slight ptosis of the left eye. The palpebral fissures were not downslanting. Her ears were low set and small with thickened helices bilaterally (Fig.1). The nose had a bulbous tip. Pectus excavatum was present. Her neck was not webbed. A systolic murmur was present at the right upper sternal border. The rest of her extra-oral examination was unremarkable, and no facial asymmetry or bony expansion was noted. A clinical and radiographic differential diagnosis was formulated (Table 1), and after excluding a vascular process via needle aspiration, incisional biopsies of the radiolucent lesions were performed. The patient s mother reported prolonged bleeding during the 2
6 immediate post-operative period. However, it was not significant enough to require additional intervention. Discussion Histopathologic examination of both lesions (Fig. 4) revealed a proliferation of giant cells in a fibrovascular connective tissue background, consistent with a giant cell granuloma. Based on the histopathology, the differential diagnosis was revised to include only lesions with a histology compatible with CGCG, as shown in Table 2. Central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) is a benign lesion of bone of variably aggressive nature that was first described by Jaffe 1. As defined by the World Health Organization, CGCG is a central lesion of bone with aggregates of multinucleated giant cells in a background of cellular fibrous connective tissue that contains multiple foci of hemorrhage with or without trabeculae of reactive bone. Initially termed giant cell reparative granuloma, these lesions are no longer believed to represent a reparative process 2. Various hypotheses have been proposed to explain their pathogenesis, including the possibility that these are related to intraosseous hemorrhage following trauma, develop in association with other pre-existing bone lesions (e.g. fibrous dysplasia), are of neoplastic nature or represent an idiopathic reactive process. The peak incidence of CGCG is in the second decade, with most cases appearing between the ages of 10 and 25 years. It is more common in females. The radiographic appearance of CGCG is not pathognomonic. Usually, a radiolucent lesion, which can be either unilocular (usually lesions less than 6 cm) or multilocular, is noted on routine radiographic examination. The borders are generally well defined. While it is frequently reported that lesions of CGCGs are usually located anterior to the mandibular first molar and often cross the 3
7 midline 3, a recent review of 80 cases suggested that there is an equal predilection for the posterior mandible 4. CGCGs can displace teeth and developing tooth follicles, but rarely cause tooth resorption. Most reported cases of multiple concurrent CGCGs are associated with some form of congenital syndrome or systemic disease, hence the possibility that these radiolucent lesions simply represented bilateral central giant cell granulomas was considered unlikely. Brown tumors of hyperparathyroidism are the result of excessive parathyroid hormone secretion. This can occur either primarily, due to hyperplasia or neoplasia of the parathyroid glands, or secondarily in association with renal osteodystrophy 5. Hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia and elevated parathyroid hormone blood levels characterize hyperparathyroidism. Radiographic findings are also characteristic. Besides multiple lytic lesions of bone, intraorally there is a loss of the lamina dura adjacent to the roots of the teeth and an altered trabecular pattern in the tooth bearing areas of the jaws. In our patient, an endocrine workup was unremarkable, effectively excluding this condition. Cherubism, an autosomal dominantly inherited condition with variable expressivity, is characterized by multiquadrant radiolucent lesions of the jaws. Clinically, cherubism is first noted between ages 1 and 4 years and is more common in males. There is usually a family history of similarly affected family members. It most commonly manifests as a progressive and symmetrical enlargement of the mandible and/or the maxilla. Mandibular swelling produces plump cheeks and maxillary enlargement causes 4
8 retraction of the lower eyelids and elevation of the pupils upward, resulting in an angel-like appearance reminiscent of the cherubs depicted in Renaissance art. Dental findings include marked displacement of developing second and third molars as well as premature exfoliation of primary teeth. Marked cervical lymphadenopathy is common. Regression is often seen following puberty 6. Currently cherubism is believed to be caused by a gain-of-function mutation in the gene coding a c-abl-tyrosine kinase-binding protein (SH3BP2) located on the short arm of chromosome 4 7. A number of congenital syndromes have been reported to be associated with giant cell lesions of the jaws, including Noonan syndrome 8, neurofibromatosis type-1 9 and Ramon syndrome (gingival fibromatosis, hypertrichosis, epilepsy, mental and somatic retardation and cherubism-like lesions) 10. Noonan-like syndrome, cherubism, and polyarticular pigmented villonodular synovitis is a congenital syndrome that includes additional findings of multiple lesions of pigmented villonodular synovitis affecting multiple bones, commonly the knees and ankles. It has been suggested 8 that some of these entities represent different levels of expression of a contiguous gene syndrome, resulting from defects or deletions of two or more genes that map near each other on the same region of a chromosome. Each defective or deleted gene is responsible for the overall characteristics of the syndrome. Thus, the overall phenotype seen would depend on the number and function of the specific genes affected. Noonan syndrome, one of the most common multiple congenital anomaly syndromes, occurs in approximately one out of every 1000 to 2500 live births 11. Noonan syndrome is also known as Turner-like syndrome, male Turner syndrome, female pseudo-turner 5
9 syndrome, Turner phenotype with normal karyotype, Bonnevie-Ullrich syndrome and pterygium colli syndrome. Noonan syndrome was initially described in 1963 by Jacqueline Noonan 12, a pediatric cardiologist. She had noticed that a number of her patients with cardiac anomalies (most commonly pulmonary stenosis and atrial and ventricular septal defects) were also of short stature and had atypical facies. Characteristic facial features include a broad or webbed neck, low set and posteriorly angulated ears, ptosis, hypertelorism, and downward slanting eyes. These manifestations tend to become less pronounced with increasing age. Since the initial discovery of this syndrome, a number of other associated features have been described (Table 3) 11. Similar to cherubism, Noonan syndrome is an autosomal dominantly inherited syndrome with variable expressivity. Cases can also occur sporadically; presumably the result of a spontaneous mutation. Tartaglia et al 13 reported that in slightly over 50% of 22 unrelated individuals tested, Noonan syndrome phenotype was associated with missense mutations in the gene PTPN11, which encodes the non-receptor tyrosine phosphatase protein SHP-2 located on the long arm of chromosome 12. This protein is involved in a number of signal transduction pathways that regulate several developmental pathways, including cardiac semilunar valve development 14. Recently, the same PTPN11 gene mutation was identified in two siblings in a family inheriting Noonan-like/ multiple giant cell lesions syndrome 15. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical criteria. Since many affected individuals have mild manifestations, many cases go undiagnosed. Prenatally, an association with fetal edema and cystic hygroma has been reported. Molecular genetic testing of the PTPN11 gene is now 6
10 clinically available, with mutations being identified in about 50% of patients. PTPN11 genetic testing was not available when this patient was initially evaluated. Based on our patient s clinical and radiographic presentation and histologic findings, our working diagnosis was that these giant cell lesions were a manifestation of Noonan syndrome. Molecular testing has been offered to the family, but to date they have opted not to undergo testing. Review of the Literature Cohen and Gorlin 8 published the first review detailing the association of central giant cell granuloma-like lesions of the jaws with Noonan syndrome in They reviewed previously published clinical and pathologic findings of 13 patients and included one patient that they had been following since Of the 14 total cases described, 7 also had polyarticular lesions of pigmented villonodular synovitis, which would place these cases under the spectrum of Noonan-like syndrome, cherubism, and polyarticular pigmented villonodular synovitis. Cohen and Gorlin believed that both of these types of giant cell lesions have a common pathogenesis. To date, excluding the 7 cases described by Cohen and Gorlin that also presented with polyarticular pigmented villonodular synovitis, fewer than 15 cases of Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome have been reported in the English language literature (Table 4). Significance and Management There are a number of potentially significant medical concerns that clinicians should be aware of prior to performing any surgical procedure on a patient with suspected Noonan 7
11 syndrome (Table 5). These risks include a high prevalence of congenital heart disease (as in our patient), bleeding diatheses (decreased coagulation factors XI and II, von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia, abnormal platelet function and stem cell dysfunction), an association with malignant hyperthermia and the potential of developing a life-threatening chylothorax. To rule out an occult bleeding diathesis, preliminary hematologic evaluation should include a complete blood count and differential, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and possibly measurement of factor XI levels. As the reported incidence of Noonan syndrome-associated giant cell lesions of the jaws is low, little is known of its natural history or what treatment approaches are most effective. Current treatment modalities have largely been extrapolated from published reports of the management of either conventional CGCGs of the jaws or cherubism. CGCGs of the jaws, especially smaller lesions, are commonly treated by surgical curettage. Aggressive lesions are occasionally treated by en bloc surgical resection. However, this approach can be disfiguring. Recent approaches for the treatment of large or multiple lesions have included weekly intralesional corticosteroid injection 16,17, daily subcutaneous 18 or intra-nasal 19 administration of calcitonin and the use of interferon alpha-2a 20. The principal disadvantage to these approaches is the necessity of continuing treatment over a prolonged period of time. Based on the apparent clinical and histologic similarity between patients with Noonan syndrome-associated giant cell lesions of the jaws and cherubism, the few reported cases that describe the management of these lesions have based treatment on the assumption that their 8
12 behavior and clinical course is also similar. Consequently, management has generally involved long term follow-up, with the assumption that these lesions will stabilize or regress during puberty. Treatment is reserved for patients with functional or cosmetic impairment. Our plan is to follow this patient on a biannual basis. Presently, she has no functional or cosmetic impairment and is asymptomatic. Conclusion Even though our patient was eight years old at the time of presentation and had a history of pulmonary stenosis, her Noonan syndrome had gone undiagnosed until she presented with bilateral giant cell lesions of the mandible. This case underscores the importance of formulating a thorough differential diagnosis of giant cell lesions of the jaws. The histologic findings must be interpreted in light of the radiographic and clinical findings to arrive at a correct diagnosis. As in our patient, children with Noonan syndrome are predisposed to having a wide array of health problems (including congenital heart disease, bleeding diatheses, malignant hyperthermia, lymphangiomatosis), making it essential that all practitioners involved in caring for these patients be aware of their special needs prior to performing any surgical procedure. 9
13 Figure 1: Clinical Photograph. The patient s ears were low set and small with thickened helices bilaterally. 10
14 Figure 2: Panoramic Radiograph. Note bilateral multilocular radiolucencies of the posterior mandible and anterior displacement of the prematurely developing mandibular third molar teeth. 11
15 Figure 3: Axial CT Scan. Note lack of significant cortical expansion. 12
16 Figure 4: High Power View of Histology. Numerous osteoclast-like giant cells in a background of spindle-shaped fibroblasts (Hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification 40x). 13
17 Table 1: Initial Clinical and Radiographic Differential Diagnosis Multiple odontogenic keratocysts (e.g. associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome) Central giant cell granuloma (CGCG), bilateral Cherubism Syndromes associated with CGCGs (e.g. Noonan syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1) Multiple dentigerous cysts Brown tumors of hyperparathyroidism Langerhans cell histiocytosis 14
18 Table 2: Bilaterally Occurring Central Giant Cell Lesions Of The Jaws Central giant cell granuloma, bilateral Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism Cherubism Noonan-like / multiple giant cell lesion syndrome Noonan-like syndrome, cherubism, and polyarticular pigmented villonodular synovitis Neurofibromatosis type 1 Ramon syndrome (cherubism, gingival fibromatosis, epilepsy, mental deficiency, hypertrichosis, and stunted growth) Note: Histologically and radiographically, all of these conditions are essentially indistinguishable 21. Clinical-radiological-pathologic correlation is required to arrive at the final diagnosis. 15
19 Table 3: Clinical Features of Noonan Syndrome Congenital heart defects (pulmonary stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ASD, VSD) Short stature Broad or webbed neck Low set, posteriorly angulated ears Ptosis, hypertelorism, downward slanting eyes Coarse +/- curly hair Pectus excavatum (depressed sternum) High arched palate Cherubism-like multiple giant cell lesions Cryptorchidism Conductive hearing loss Hypoplasia of lymphatics: potentially leading to chylothorax Bleeding diatheses: decreased factors XI and II, von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia, abnormal platelet function 22 Learning disabilities Tendency to develop keloids following surgery Association with multiple subcutaneous granular cell tumors 23 16
20 Table 4: Published Reports of Noonan Syndrome/Central Giant Cell Granuloma-Like Lesions of the Jaws Authors Year Number of Patients Chuong et al Dunlap et al Cohen and Gorlin Levine et al Betts et al Addante and Breen Ucar et al Bertola et al
21 Table 5: Surgical Risks in Patients with Noonan Syndrome Congenital heart disease Bleeding diatheses. Presurgical hematology work-up recommended Lymphangiomatosis of the pleura, lungs and chest wall; potentially leading to life-threatening chylothorax 32 Association with malignant hyperthermia (King syndrome) 18
22 REFERENCES 1 Jaffe HL. Giant cell reparative granuloma, traumatic bone cyst and fibrous (fibro-osseous) dysplasia of the jawbones. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. 6: (1953). 2 Sciubba JJ, Fantasia JE, Kahn LB. Nonodontogenic lesions. In: Atlas of Tumor Pathology: Tumors and Cysts of the Jaw. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Washington, D.C (2001). 3 Dorfman HD, Czerniak B. Giant cell lesions. In: Bone Tumors. Mosby Publishers, St. Louis, MI (1998). 4 Kaffe I, Ardekian L, Taicher S, Littner MM, Buchner A. Radiologic features of central giant cell granuloma of the jaws. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. Oral Radiol. Endo. 81: (1996). 5 Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral manifestations of systemic disease. In: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Second Edition. W.B. Saunders,Philadelphia PA (2002). 6 von Wovern N. Cherubism: A 36 year long-term follow-up of 2 generations in different families and review of the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. Oral Radiol. Endo. 90: (2000). 7 Ueki Y, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding c-abl-binding protein SH3BP2 cause cherubism. Nature Genetics. 28: (2001). 8 Cohen MM Jr, Gorlin RJ. Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genetics 40: (1991). 19
23 9 Ruggieri M, Pavone V, Polizzi A, Albanase S, Magro G, Merino M, Duray P. Unusual form of recurrent giant cell granuloma of the mandible and lower extremities in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. Oral Radiol. Endo. 87: (1999). 10 Pino-Neto JM, et al. Cherubism, gingival fibromatosis, epilepsy, and mental deficiency (Ramon syndrome) plus juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. Gen. 25: (1986). 11 Noonan JA. Noonan syndrome: An update and review for the primary pediatrician. Clinical Pediatrics. 33: (1994). 12 Noonan JA. Hypertelorism with Turner phenotype: A new syndrome with associated congenital heart disease. Am. J. Dis. Child. 116: (1963). 13 Tartaglia M, et al. Mutations in PTPN11, encoding the protein tyrosine phospatase SHP-2, cause Noonan syndrome. Nature Genetics. 29: (2001). 14 Chen B, et al. Mice mutant for Egfr and Shp2 have defective cardiac semilunar valvulogenesis. Nature Genetics. 24: (2000). 15 Tartaglia M, Kalidas K, Shaw A, Song X, Musat D, et al. PTPN11 mutations in Noonan syndrome: Molecular spectrum, genotype-phenotype correlation, and phenotypic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 70: (2002). 16 Terry BC, Jacoway JR. Central giant cell granulomas: An alternative to surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med Oral Path. 5: 572 (1988). 17 Kurtz M,Mesa M, Alberto P. Treatment of a central giant cell lesion of the mandible with intralesional glucocorticosteroids. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. Oral Radiol. Endo. 91: (2001). 20
24 18 Harris M. Central giant cell granulomas of the jaws regress with calcitonin therapy. British J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 31: (1993). 19 De Lange J, Rosenberg AJ, Van den Akker HP, Koole R, Wirds JJ, VandenBerg H. Treatment of central giant cell granuloma of the jaw with calcitonin. Int.J. Oral Maxillofac.Surg. 28: (1999). 20 Kaban LB, Mulliken JB, Ezekowitz RA, Ebb D, Smith PS, Folkman J. Antiangiogenic therapy of a recurrent giant cell tumor of the mandible with interferon alfa-2a. Pediatrics. 103: (1999). 21 Sapp JP, Eversole LR, Wosocki GP. Bone lesions. In:.Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Mosby Publishers, St. Louis, MI (1997). 22 Singer ST, Hurst D, Addiego,JE Jr. Bleeding disorders in Noonan Syndrome: Three case reports and review of the literature. J. Ped. Hem. and Onc. 19: (1997). 23 Lohmann DR, Gillessen-Kaesbach G. Multiple subcutaneous granular-cell tumors in a patient with Noonan syndrome. Clinical Dysmorphology. 9: (2000). 24 Chuong R, Kaban LB, Kozakewich H, Perez-Atayde A. Central giant cell lesions of the jaws: a clinicopathologic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44: (1986). 25 Dunlap C, Neville B, Vickers RA, O Neil D, Barker B. The Noonan syndrome/cherubism association. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. 67: (1989). 26 Cohen MM, Gorlin RJ. Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome. Amer. J. Med. Gen. 40: (1991). 27 Levine B, Skope L, Parker R. Cherubism in a patient with Noonan syndrome: Report of a case. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 49: (1991). 21
25 28 Betts NJ, Stewart JC, Fonseca RJ, Scott RF. Multiple central giant cell lesions with a Noonan-like phenotype. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Path. 76: (1993). 29 Addante RR, Breen GH. Cherubism in a patient with Noonan s syndrome. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 54: (1996). 30 Ucar B, Okten A, Mocan H, Ercin C. Noonan syndrome associated with central giant cell granuloma. Clin. Gen. 53: (1998). 31 Bertola DR, Kim CA, Pereira AC, Mota GF, Krieger JE, Vieira IC, Valente M, Loreto MR, Magalhaes RP, Gonzalez CH. Are Noonan syndrome and Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome distinct entities? Amer. J. Med. Gen. 98: (2001). 32 Yellon RF. Complications following airway surgery in Noonan Syndrome. Arch. Otolaryn. Head and Neck Surg. 123: (1997). 22
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
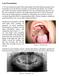 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case presentation. Central Giant Cell Granuloma. Case presentation
 Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case Report and Brief Review of Reported Cases
 J Oral Diag [online] 2017; 02:e20170005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aarfa Nasim 1 Ravi Prakash Sasankoti Mohan 1 * Nagaraju Kamarthi 1 Vijay Wadhwan 1 Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case
J Oral Diag [online] 2017; 02:e20170005 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Aarfa Nasim 1 Ravi Prakash Sasankoti Mohan 1 * Nagaraju Kamarthi 1 Vijay Wadhwan 1 Idiopathic Bilateral Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw- A Case
Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari
 Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Cherubism: Clinicoradiographic Features, Treatment, and Long-Term Follow-Up of 8 Cases
 CASE REPORTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:517-522, 2007 Cherubism: Clinicoradiographic Features, Treatment, and Long-Term Follow-Up of 8 Cases Edgard Carvalho Silva, DDS, PhD,* Guilherme Costa Carvalho Silva,
CASE REPORTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:517-522, 2007 Cherubism: Clinicoradiographic Features, Treatment, and Long-Term Follow-Up of 8 Cases Edgard Carvalho Silva, DDS, PhD,* Guilherme Costa Carvalho Silva,
Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic Features and Osseous-Dental Treatments
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 Dysanoor Maxillofacial Sujatha, surgery Naik Shobha CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Prof. PhD, The Oxford Dental College
Dysanoor Maxillofacial Sujatha, surgery Naik Shobha CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Prof. PhD, The Oxford Dental College
Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report.
 Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report. P.S Tripthi Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, ABSMIDS, Mangalore,
Case Report ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Giant Cell Granuloma of the Maxilla: A Rare Case Report. P.S Tripthi Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, ABSMIDS, Mangalore,
Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented as Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw Bones. A Report of Three Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports
 2018;24:182-186 The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2018007 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports Samir Abdelqader 1, Nicolas Roche 1,
2018;24:182-186 The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2018007 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Giant-cell granuloma: 2 case reports Samir Abdelqader 1, Nicolas Roche 1,
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report
 J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
Ramon s Syndrome: A Rare Entity
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1039 CASE REPORT 1 Alexander, 2 Sherry Peter, 3 Sheela Nampoothiri, 4 Latha Rao, 5 Ajith Nambiar 4 Ravi Veeraraghavan, 4 Ushass Puthalath WJD 1 Professor, Department of Oral Medicine
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1039 CASE REPORT 1 Alexander, 2 Sherry Peter, 3 Sheela Nampoothiri, 4 Latha Rao, 5 Ajith Nambiar 4 Ravi Veeraraghavan, 4 Ushass Puthalath WJD 1 Professor, Department of Oral Medicine
Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation
 Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology ISSN: Vol. 4 No. 4; April 2017
 Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Cherubism with multiple dental abnormalities: a rare presentation
 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 3 Department of
1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 3 Department of
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Loss of Heterozygosity in Tumor Cells of a Recurrent Mandibular Giant Cell Granuloma in Neurofibromatosis Type 1
 Loss of Heterozygosity in Tumor Cells of a Recurrent Mandibular Giant Cell Granuloma in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 REINHARD E. FRIEDRICH 1, VICTOR F. MAUTNER 1 and HANNA A. SCHEUER 2 1 Maxillofacial Surgery
Loss of Heterozygosity in Tumor Cells of a Recurrent Mandibular Giant Cell Granuloma in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 REINHARD E. FRIEDRICH 1, VICTOR F. MAUTNER 1 and HANNA A. SCHEUER 2 1 Maxillofacial Surgery
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Case Report Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Posterior Maxilla: First Expression of Primary Hyperparathyroidism
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2015, Article ID 170412, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/170412 Case Report Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Posterior Maxilla:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2015, Article ID 170412, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/170412 Case Report Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Posterior Maxilla:
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
Unexpected diagnosis for preauricular swelling - two case reports
 Unexpected diagnosis for preauricular swelling - two case reports Goran Roić 1, Vesna Posarić 1, Ante Marušić 1, Igor Borić 1, Tomislav Vlahović 2, Kristina Vrliček 3 1 Department of Paediatric Radiology,
Unexpected diagnosis for preauricular swelling - two case reports Goran Roić 1, Vesna Posarić 1, Ante Marušić 1, Igor Borić 1, Tomislav Vlahović 2, Kristina Vrliček 3 1 Department of Paediatric Radiology,
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 58-62 Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 58-62 Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
DISCUSSION ABSTRACT: Keywords: - Mandible, giant cell granuloma, reconstruction. INTRODUCTION.
 ABSTRACT: Giant Cell Granuloma is a rare benign disease. We present a case ofgiant Cell Granuloma involving mandible in a 7 year old boy. Rarity of the disease, difficulty in diagnosis along with surgical
ABSTRACT: Giant Cell Granuloma is a rare benign disease. We present a case ofgiant Cell Granuloma involving mandible in a 7 year old boy. Rarity of the disease, difficulty in diagnosis along with surgical
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible
 Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy
 Iranian Journal of Orthodontics Shirani, Arshad, Asefi 43 Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy Gholamreza Shirani a, Mahnaz Arshad
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics Shirani, Arshad, Asefi 43 Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy Gholamreza Shirani a, Mahnaz Arshad
SOS1 and PTPN11 mutations in five cases of Noonan syndrome with multiple giant cell lesions
 (2009) 17, 1216 1221 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1018-4813/09 $32.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg SOS1 and PTPN11 mutations in five cases of Noonan syndrome with multiple giant
(2009) 17, 1216 1221 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1018-4813/09 $32.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg SOS1 and PTPN11 mutations in five cases of Noonan syndrome with multiple giant
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Seyed Mohammad Razavi, Roya Yahyaabadi* Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF)
 CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Spectrum of clinical presentations
 Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Craniofacial Manifestations Of Eosinophilic Granuloma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 B Tümerdem Ulug, A Ar?nc?,? Ermi? Citation B Tümerdem Ulug, A Ar?nc?,? Ermi?.. The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2006 Volume 3
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 B Tümerdem Ulug, A Ar?nc?,? Ermi? Citation B Tümerdem Ulug, A Ar?nc?,? Ermi?.. The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2006 Volume 3
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report
 Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
CLINICALLY AGGRESSIVE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMAS IN TWO PATIENTS WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS 1
 * Manuscript CLINICALLY AGGRESSIVE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMAS IN TWO PATIENTS WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS 1 Paul C. Edwards 1 M.Sc., D.D.S., John E. Fantasia 2 DDS, Tarnjit Saini 3 DDS, MS, Tracey J. Rosenberg
* Manuscript CLINICALLY AGGRESSIVE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMAS IN TWO PATIENTS WITH NEUROFIBROMATOSIS 1 Paul C. Edwards 1 M.Sc., D.D.S., John E. Fantasia 2 DDS, Tarnjit Saini 3 DDS, MS, Tracey J. Rosenberg
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child
 Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Preface... Contributors... 1 Embryology... 3
 Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER. E Mail: Website:
 R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER Editor: Heather J. Stalker, M.Sc. Director: Roberto T. Zori, M.D. R.C. Philips Research and Education Unit Vol. XX No. 2 A statewide commitment to the problems of mental retardation
R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER Editor: Heather J. Stalker, M.Sc. Director: Roberto T. Zori, M.D. R.C. Philips Research and Education Unit Vol. XX No. 2 A statewide commitment to the problems of mental retardation
Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic and histological features
 (2005) 34, 313 318 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic
(2005) 34, 313 318 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report
 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Impacted third molars can be. Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report
 Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report Kevin E Lung, BSc, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C); Seema Ganatra, BSc, DDS, MSD, FRCD(C); Christopher
Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report Kevin E Lung, BSc, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C); Seema Ganatra, BSc, DDS, MSD, FRCD(C); Christopher
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Chapter 13. DiGeorge Syndrome
 Chapter 13 DiGeorge Syndrome DiGeorge Syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease caused by abnormal migration and development of certain cells and tissues during fetal development. As part of the developmental
Chapter 13 DiGeorge Syndrome DiGeorge Syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease caused by abnormal migration and development of certain cells and tissues during fetal development. As part of the developmental
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
