This is the first histology lecture for the respiratory tract system.
|
|
|
- Stephen Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
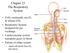
1 This is the first histology lecture for the respiratory tract system. Respiratory tract starts with nose and ends with lungs, the respiratory tract is divided into upper part ( conducting ) like the nose, larynx, trachea and bronchi and lower part ( respiratory ) which include gases exchange like the bronchioles, alveoli. As we said the respiratory tract is divided into : conducting : for passage of air only respiratory : for gases exchange, it starts by the respiratory bronchioles then alveolar duct, alveolar sac and alveoli (where largest capillary network is found around the alveoli ) we have also the transitional area separating the conducting from the respiratory and always the transitional areas are site of cancers,the transitional area here doesn t appear suddenly, it appears gradually. The common epithelium in the respiratory tract is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, but as we reach the bronchioles it is transformed to simple columnar ciliated and as we go distally it changes into simple cuboidal ciliated epithelium and more distally toward the lungs, it changes into clara cells ( no cilia ) and finally in the wall of the alveoli it becomes simple squamous ( for gases exchange )
2 Goblet cells start with large number but as we go distally, the number is reduced, and once we reach the bronchioles, they become scattered and finally disappear. Also there are seromucous gland with the same story, they decrease in number as we go distally. Cartilage also changes, in the nose there is some cartilage and bone ( nasal bone ), and in the larynx there are hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage, and in trachea there is C shaped hyaline cartilage to prevent the collapse to keep the passage of air, but when we go distally until we reach the bronchioles there are no cartilage, no goblet cells, no glands BUT the elastic fibers increase, and they are found with high amount at the lungs because they are needed for inflation and deflation. In the lungs we have lobes ( three lobes and two fissures in the right and two lobes with one fissure in the left ), primary and secondary bronchus enter the lobes, then the secondary becomes tertiary. Inside the lobes, there are lobules and each lobule is surrounded by connective tissue, which has it s own blood supply, venous drainage and lymphatics so these days the surgeon is able to remove the lobule only not the whole lobe. the doctor is advising us not to SMOKE, 90% of lung cancers are due to smoking, because smoking affects a protein called dynein, which is responsible for the movement of cilia ( from inside to outside ), so by affecting the dynein will lead to prevent this movement, leading to some disease like bronchitis and eventually to cancers. again and again, the doctor is talking about the two parts of the respiratory tract, and he mentioned that as we go distally the diameter is decreasing, starting from the trachea which is like tip of the finger and reaching the large bronchioles which is 1 mm in diameter and eventually in terminal bronchioles.5 mm, in the respiratory part it is less than.5 mm and the wall here is simple squamous epithelium. The conducting part : 1 ) Nose 2 ) Pharynx ( which we have taken in the GI and it is required with it s three parts; oropharynx, ) مش راح ارجعله nasopharynx and laryngopharynx 3 ) Larynx which has true vocal cords that are responsible for the production of voice. for your information : the ( inspiration ) inhalation process is considered as an active process need energy and it is caused by stimulation of phrenic nerve so the diaphragm will decends downward with the result that the intrathoracic pressure will become less that the atmospheric pressure so this will cause gush of air through the nose filling the two lungs with oxygen.however, the expiration is a passive process ; the diaphragm ascends upwards increasing the intrathoracic pressure letting to deflation of lung so the air will goes outside the lungs through the larynx. when the expired air is going outside through the larynx it faces the true vocal cords making a column of air under pressure under the vocal cords, and when it assends between them, it causes vibration and thus
3 production of voice. Sudden opening after closure of these cords will cause the coughing ( a protection process ) also when anyone tried to lift heavy object, the vocal cords will adduct to produce pressure column of air so he won t breath till putting it off. 4 ) Bronchi, and we have main bronchus on the right and other one on the left, each is going to it s lung - to the hilum - ( extrapulmonary), the main bronchus is the primary, the secondary is lobar, three in the right lung and two in the left lung ( inside the lung > intrapulmonary ) bronchi to the lobes, and then the tertiary ( segmental or bronchopulmonary segment 10 on the right and 10 on the left but at birth, you will find 8 on the left and 10 on the right ) which is also intrapulmonary. 5 ) Bronchioles, the diameter is smaller and they are intrapulmonary, no cartilage, no glands, no goblet cells and there is changes in epithelium, they are of two kinds, conducting ends with terminal and respiratory.
4 Section in the trachea : any part of the respiratory tract has the following layers : 1 ) mucosa which has lining epithelium which is - pseudostratified ciliated columnar in general -, lamina propia muscularis mucosa also 2 ) submucosa which has connecting tisse, glands ( seromucous ), blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics 3 ) supportive layer which has cartilage like the hyaline cartilage, elastic fibers, blood vessels, glands, smooth muscles and lymphatics ( smooth muscles increase as we go distally, and they are spiral in bronchioles - the doctor mentioned the cause of asthma that is contraction of the smooth muscles which will cause narrowing the lumen of bronchioles with the result that the patient will have difficulty in breathing and wheezing during breathing, treatment will be by taking smooth muscle relaxant like adrenaline ) 4 ) adventitia which is connecting tissue and can be found as serosa in pleura which surrounds the lung which is simple squamous epithelium ( mesothelium like the peritoneum ). there are more functions for the conducting part other than conduction of air, like cleaning, moistening and warming. we will notice that at the beginning, in the nose there is hair which will clean the air from the dust, and also there is venous blood in the mucosa and submucosa which will cause warming and moistening to the air as a protecting mechanism. The doctor mentioned again the conducting and the respiratory part of the tract -,- and the alveolar duct will end with the alveolar sac, and the whole wall is the alvioli which do the principle function of the reparatory tract. Gases Exchange : The oxygen concentration which will reach the cappilary is low almost 40, but after the gases exchange, the hemoglobin takes the oxygen,so the oxygen concentration increase.
5 as we know from the cardiovascular system, the deoxygenated blood comes to the lung through the pulmonary artery and after the gases exchange it goes out through the pulmonary vein which has the highest oxygen concentration - saturated - ( 95 mm Hg to 105 mm Hg, whereas the concentration of CO2 can reach 45 mm Hg in the alveoli. We will take the alveoli in details later on, which has alveolar type one (simple squamuos ) and type two - which secretes surfactant factor which decrease the surface tension of the alveoli so it will be inflated as the baby is born and then the respiration starts -. Between the wall of the capillary and the wall of the alveolus there is very thin layer of basal lamina,and both walls ( alveolar and capillary ) are simple squamous epithelium for the gases exchange.
6 The carbon dioxide has three walls to pass to the capillaries : a ) only 7% is dissolved in the plasma b ) 23% is combined with hemoglobin forming carbaminohemglobin c ) 70% is converted to protons by carbonic anhydrase and combines to hemoglobin (reversible reaction) ( H2O+CO2= H2CO3 ) Respiratory epithelium : the most important layer is the lining epithelium that is pseudostartified ciliated columnar epithelium and it has five types of cells laying on the thick basement membrane ( it is not necessary to reach the surface ) as we said the major part is psuedostratified ciliated columnar cells, but there are also other types of cells : goblet cells which is unicellular gland found also in GI, and it s most important function that it s secretion will cause the stuck of the dust, bacteria and viruses and also it moistening to the respiratory tract. Brush cell ( called Brush because it has microvilli and receptors ) serous cells with serous secretory granules Diffuse Neuroendocrine cells ( DNES ) kluchitsky cells, found on the base stem cells ( or basal cells ) reservoir with mitotic division to replace other cells.
7 Glands are found in the submucosa and have ducts which open at the surface. Each cell has special characteristics for example the ciliated cells, each cell has about 300 cilia found on the surface connected with basal bodies, also cilia is surrounded by mitochondria, so at the apex of the cells there is a large number of mitochondria for the production of ATP, also there is Dynein which is important for ciliary movement, nicotine that we get during smoking will cause damage and prevent the formation of dynein and the disease in this case is Immotile cilia syndrome (Kartagner syndrome) which includes immobility of cilia and infection ( chronic respiratory tract infection ), we also found that it causes infertility and sterility in males not females ( unlike the mumps affecting the parotid gland which causes sterility in females not males ) Goblet Cells ( Apical mucous droplets ) : they are unicellular, includes polysaccharides and glycoprotein. Brush cells : called like this because they have microvilli, and there is sensory receptors there. Basal ( short ) cells - stem cells - : small rounded cells, and considered as reserve cells, for mitotic activity. Cells of the DNES (diffuse neuroendocrine system) : small granule cells, also called Kulchitsky Cells, regulates locally the excretions or secretions of mucous and serous glands in the respiratory tract layers : mentioned before ( mucosa, submucosa, supporting and adventitia ) NASAL cavity : if we take section in the nose, we will find it s beginning as vestibule ( anterior nares, the space directly after the opening ) it is characterized by having thick and short hair ( vibrissae ) for air filtration, the
8 epithelium is stratified squamous non keratinized, and has sebaceous and sweat gland ( like the skin ) ONLY the vestibule. P.s : the doctor said that it is non keratinized, but according to Wikipedia, it is keratinized. Then the respiratory area, three conchae like shelf ( process ), three meatuses ( groove under them ) and one recess lateral wall The respiratory area is were the respiration occurs, the epithelium is pseudostratified ciliated columnar with seromucos gland, and what characterize it is having venous blood plexus within the submucosa for warming the air for protection. The last area is olfactory which is responsible for smell sensation found under the cribriform plate of ethmoid ( called like this because olfactory filaments enter through it ) plate of ethmoid, on the roof and septum. And there is respiratory mucosa in addition to olfactory epithelium with bipolar cells which are responsible to convert the odor stimulus from chemical to mechanical then to electrical impusle. bipolar means it has two poles - two ends -, one has hair leads and the other is nerve fibers forming olfactory filaments - appear from the base - then olfactory bulb then tract, around them there is supportive or sustintacular cells supporting the bipolar, also there is gland called bowmans glad secrete
9 watery seromucous to dissolve the odor. what we are concerned about is knowing that thre is center in the base of the temporal lobe responsible for the sensation of smell, so all odors we smell since birth are saved in this center. Sinuses : in the nose there is air sinuses which are spaces in some bones of the skull like in the frontal bone ( frontal air sinuses ), in the maxilla ( maxillary air sinuses - the largest- ), in the ethmoid ( ethmoidal air sinuses ), sphenoid ( sphenoidal air sinuses ) all are pairs except the ethmoid are six ( 3+3 ) they are spaces covered by thin mucosa and contain air, their most important function is resonance of the air to determine the tone of the voice, that s why all air sinuses have ducts which open in the lateral wall of the nose. When there is sinusitis ( infection ), the secretion of the duct increases, and in chronic cases it becomes yellow with bad odor. the nasal sinuses as we said has mucosa but it is thin and contains few goblet cells, and also submucosa also thin connected with periosteum. The lamina propria contains only a few small glands continuous with the underlying periosteum.
10 the last four words in the lecture :P the most important thing the respiratory tract is knowing the histological changes along the tract ; we started in the nasal vestibule as non keratinized ( skin ) then it becomes respiratory, and then olfactory where we added bipolar cells. When we go downward to the trachea : as we go distally : goblet cell number decreases gland number decreases cartilage is absent in bronchioles smooth muscles increase elastic fiber number increases lymphocyte becomes nodules after being scattered trachea ends at the level of sternal angle. Each large bronchiole ( 1 mm ) gives 5 to 7 terminal ones with smaller diameter the trachea has C shaped hyaline cartilage and closed posteriorly by brachialis muscle which is smooth muscle separate it from esophagus and if the trachea was complete ring it will stop the bolus. trachea has seromucus gland and all type of cells when we go to bronchi, it the same like trachea but the cartilage is plates ( pieces of hyaline cartilage ) and spiral smooth muscle increases when we go distally, also has the five parts of cells.
11 PLEASE REFER TO the slides especially the last parts, the doctor didn t mention everything. P.S : excuse me for the bad editing but I have done this sheet online and the editing options are not enough. Done by : Mohammad Abu Dosh.
12
The Respiratory System. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
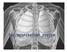
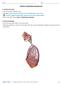
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
Includes : - the lung - a system of tube
 FYH - ERDS 1 Includes : - the lung - a system of tube Divided into 2 principal regions : - conducting portion : nasal cavity, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles & terminal bronchioles -
FYH - ERDS 1 Includes : - the lung - a system of tube Divided into 2 principal regions : - conducting portion : nasal cavity, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles & terminal bronchioles -
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
SCPA602 Respiratory System
 SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Upper Respiratory Histology
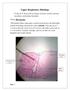 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
RESPIRATORY LAB. Introduction: trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
 RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
The Respiratory System:
 The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
General Human Histology. The Respiratory System
 General Human Histology Lecture 5 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Respiratory System The respiratory system includes the lungs and a system of tubes that link the sites of gas exchange with the external
General Human Histology Lecture 5 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Respiratory System The respiratory system includes the lungs and a system of tubes that link the sites of gas exchange with the external
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E
 MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
MH1001 Larynx, Monkey, H&E - False vocal fold : ciliated pseuodostratified columnar epithelium - True vocal fold : nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium vocalis muscle, vocal ligament - Thyroid
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Read Me. We are the Learning Lab. to look
 Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Epithelial Tissue. By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: different types of epithelial membranes.
 Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Anatomy #1; Respiratory Nose and the Nasal Cavity December 1st, 2013
 Note #1: the doctor skipped some slides in the lecture. Those slides are not included in this sheet and so you will have to review the slides to study them. The reason they were not included is because
Note #1: the doctor skipped some slides in the lecture. Those slides are not included in this sheet and so you will have to review the slides to study them. The reason they were not included is because
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The RESPIRATORY System
 The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
Development of the nasal cavity :
 Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
CHAPTER 24. Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
a. dissolved gases b. nutrients c. globulins d. surfactants e. hormones
 Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
Example Lecture Test: Blood, Respiratory Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
