Progress Report for NJCSCR (Yu-Wen Chang)
|
|
|
- Nickolas Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Progress Report for NJCSCR (Yu-Wen Chang) Overall Plan Summary: Traumatic injury to the spinal cord initiates a cascade of degenerative processes, known as secondary injury, which include various inflammatory reactions. Anti-inflammatory drug Methylprednisolone (MP) has been a standard treatment to SCI patients and shown to preserve some neurological function if administered within 8 hours after the injury. In animal models, MP also has been shown to reduce lipid peroxidation, protect neurons, and promote functional recovery. Minocycline (MC), a tetracycline derivative, has been reported to have neuroprotective effects in animal models ofneurodegenerative diseases, ischemia, and brain injury. The major effect ofminocycline is to block cell death pathway and to reduce inflammation. In spinal cord injury models, minocycline reduces cell death and inflammation therefore improves functional recovery. Our previous study of acute transplantation ofrg3.6 showed improved functional recovery at early time points (~2d). Given the beneficial effects of anti-inflammatory therapy, we hypothesize that a combination of radial glial transplantation with anti-inflammatory treatment may yield greater improvement than either one alone. Our rationale is that stabilization of traumatized tissue by anti-inflammatory therapy in the acute phase will prevent trauma induced cell death and facilitate implanted radial glia function in a way similar to developing brain to bridge the injury, guide damaged axons, promote axonal regeneration, and further contribute to behavioral recovery. Progress Summary: During the reporting period, we have conducted acute administration of anti-inflammatory drug MP or MC followed by 9-day delayed transplantation of radial glial clone RG3.6 cells to rat with contused spinal cord injury. The purpose of this period of work was to select a better anti-inflammatory drug for chronic study. Migration of transplanted cells was measured and showed no significant difference in rats treated with or without anti-inflammatory drugs (Task 1). We proposed that acute administration ofmp or MC may reduce the number of activated macrophages, which may prevent secondary injury (Task 2). Locomotor recovery was determined by BBB score and only showed a slight increase in rats that received MP or MC at day 2 post-sci (Task 3). Spared white matter was quantitated and MP or MC treated rats preserved more white matter at rostral regions to the epicenter (Task 4). Oligodendrocyte labeling by CNPase antibody showed more oligodendrocytes in MP treated rats, suggesting MP reduces delayed oligodendrocyte death (Task 5). The behavior results did not show significant improvement, however histological observations indicate this combination therapy can protect oligodendrocytes and prevent Wallerian degeneration. Although NJCSCR has terminated this fellowship for the reminder of grant period, the results of oligodendrocytes and myelin preservation motivated us to continue this project and focus on optimizing the therapeutic time window to combine MP with transplantation ofrg3.6 cells. We modified our experiment design from 9 day delay radial glia transplantation to 0-2 day subacute transplantation with single injection ofmp following contusive spinal cord injury. In view of BBB scoring system can not represent as a whole recovery index, we also conducted footprint and grid walking testes to evaluate animals' walking improvement. In task 6, we conducted acute MP administration with acute or sub-acute RG3.6 transplantation after spinal cord injury. Significant improvement was observed in rats received acute MP and sub-acute RG3.6 transplantation. From footprints and grid walking results, we also found that 0-48 hours post injury is an effective window for radial glial transplantation. We did not continue any minocycline study because of severe liver fibrosis problem was found in some rats and may affect our evaluation on their recovery after spinal cord injury.
2 Specific tasks used in this project 18 rats were randomly assigned as 6 control rats which were given saline or PBS through neck external jugular or intraperitoneal injection, 6 MP rats which were injected with MP through jugular vein within 5 minutes after contusion, and 6 MC rats which were given MC through intraperitoneal injection within 5 minutes after contusion. 9 days post injury RG3.6 cells were injected to the injury site, and rats were euthanized 7 days after cell transplantation. (B) 7 6 ~5 ;;; 5,4 'iij 3 ;; 01 ;2 -' We proposed that immediate administration ofmp or MC can stabilize tissue after contusive injury and facilitate survival and migration of subsequent RG3.6 cells transplantation. 7 days after transplantation ofrg3.6, green fluorescent protein (GFP) signal was used to analyze transplant distribution and signal length from rostral to caudal was measured using fluorescent dissecting microscopy (A). RG3.6 cells appear to have similar migration extents in all conditions. (N=6 for each group, data present mean ± SEM) ''''-'~~ ~~~#~,,"~ ~~~ ~, "",*~.,y (,,,>~ RG3.6., _ Microglia or activated macrophages were immunostained by EDI antibody and showed no reduction in MC or MP treated rats 16 days post SCI (7 days after RG3.6 implantation). Scale bar = 500llm.
3 (3) Locomotor recovery measured by BBB score Locomotor recovery was measured using BBB score scale at day 2, week 1 (before cell transplantation) and week 2 (after cell -' Saline+RG3.6!R MP+RG3.6 Q MC+RG3.6 transplantation). There is atrend that MP or MC rats have higher scores than controls at day 2, but overall the results are not statistically significant. Our previous study of acute transplantation ofrg3.6 showed a score 8 to 9 at week 1 (plantar stepping to dorsal stepping) (Hasegawa, Chang et ai. day2 wk1 wk2 2005), however, in this study, we did not find that MP or MC alone increase the score significantly at 1 week. The combined results suggest that acute transplantation ofrg3.6 cells alone may be effective in protecting spinal cord from secondary damage and in promoting functional recovery. (N=6 for each group, data present mean± SEM). (4) White matter sparing (A) ~ Saline+RG3.6 d MC+RG3.6 d MP+RG3.6 ~E 5 E ~ 4 ~ 3 > Spared white matter was stained by Luxol fast blue and quantitated by Zeiss LSM software. 1 cm segment of the spinal cord with the injury site in the center was frozen sectioned at 20 11m and every 5 th section was taken. MC and MP both showed a trend to preserve more spared white matter at rostral regions, and only MC rats showed statistical significance at 1 mm rostral to lesion center (A). Spared white matter volume was reconstructed and showed that MC preserved more rostral spinal cord segment (R4-CT 4mm) than controls (B). 3D reconstruction ofluxol fast blue stained regions was obtained by Z-stack images of2d bright-field images taken with Zeiss Axiophot and processed through 3D rendering using Imaris software (C). (R: rostral, C: caudal, and CT: lesion center. N=3 per group, data present mean ± SEM)
4 (5) Oligodendrocytes preservation Ventral WM Dorsal Lateral WM Delayed oligodendrocytes death occurs about 2 weeks after injury. We used CNPase to immunostain olidodendrocytes to determine if treatment preserve more oligodendrocytes. Rostral sections were used in (A) and showed more CNPase positive staining in the ventral white matter (WM) which is indicated by the arrow in the adjacent luxol fast blue stained section, and dorsal lateral WM by the arrowhead. Lesion centers (Shown in B) also showed more CNPase positive cells in the ventral WM. Immuostained areas were indicated by the arrow in the adjacent sections in the lower panel. Scale = 20llm.
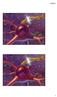
5 (5) Oligodendrocytes preservation (A) Footprint analysis ~..,..:; ~ ~r.a:acutergrf7 _8: 2dRG rf7 OC:acuteMedrF8 E3J D: 2d Med rf3 DE: acutemp+rg rf6 OF: acutemp+2d RG rf6.g: sham=4 Error steps 2.5 A: acute RG n=7 B:2dRG n=7 DC: acute Med n=8 EJ D: 2d Med n=3 o E:acute MP+RG n=6 o F: acute MP+2d RG n=6 (A) Animals were placed on a l-m long chamber, paws were inked and footprints were recorded on white paper strip. Animals with acute MP injection and sub-acute (2 d post injury) radial glia transplantation (Group F) have significant improved stepping, which is similar to naive rats with long stride length and short stride width. Acute radial glia transplantation (Group A) also showed better stepping but this beneficial effect was reduced when combined with acute MP administration (Group E). The recovery of stepping is also improved in subacute RG3.6 transplantation (Group B) and was enhanced by acute MP (Group F). Animals treated with medium DMEM+FI2 did not have functional recovery (Group C, D). (B) Animals were placed on a horizontal ladder with irregular gaps and failed steps were counted. Rats received acute or sub-acute RG3.6 transplantation show significant recovery with fewest dropped steps. *P<O.05, **P<O.OI, ***P<O.OOOI, Fisher's PLSD.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Helen R Barbour 2, Christine D Plant 1, Alan R Harvey 3 and Giles W Plant 1,2*
 Barbour et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:106 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Tissue sparing, behavioral recovery, supraspinal axonal sparing/regeneration following sub-acute glial transplantation in a model
Barbour et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:106 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Tissue sparing, behavioral recovery, supraspinal axonal sparing/regeneration following sub-acute glial transplantation in a model
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan, 2
 Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Is Spinal Cord Repair a Reality? Schwann Cell Transplantation for Subacute Spinal Cord Injury
 Is Spinal Cord Repair a Reality? Schwann Cell Transplantation for Subacute Spinal Cord Injury James Guest MD, PhD, FACS Clinical Professor of Neurological Surgery, Neurosurgery and the Miami Project to
Is Spinal Cord Repair a Reality? Schwann Cell Transplantation for Subacute Spinal Cord Injury James Guest MD, PhD, FACS Clinical Professor of Neurological Surgery, Neurosurgery and the Miami Project to
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI
 SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
Symptoms of spinal cord injury:
 Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Nerve Cells and Behavior
 Nerve Cells and Behavior 27 th September, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System and Behavior Nervous system
Nerve Cells and Behavior 27 th September, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System and Behavior Nervous system
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Figure S 1. S1. Histological evaluation of lateral hemisection.
 Dorsal Central Ventral Figure S1. Histological evaluation of lateral hemisection. Schematic Figure S1. Histological evaluation of lateral hemisection. Schematic representation of hemisection at. Dashed
Dorsal Central Ventral Figure S1. Histological evaluation of lateral hemisection. Schematic Figure S1. Histological evaluation of lateral hemisection. Schematic representation of hemisection at. Dashed
25/12/50. Delayed Transplantation of Adult Neural Precursor Cells Promotes Remyelination and Functional Neurological Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury
 2 Karimi-Abdolrezaee et al. J Neuroscience 26(13):3377-89; (2006) Delayed Transplantation of Adult Neural Precursor Cells Promotes Remyelination and Functional Neurological Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury
2 Karimi-Abdolrezaee et al. J Neuroscience 26(13):3377-89; (2006) Delayed Transplantation of Adult Neural Precursor Cells Promotes Remyelination and Functional Neurological Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Internship Research Paper. Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury. Completed at St.
 Internship Research Paper Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Completed at St. Joseph s Hospital Barrow Neurological Institute Dr. Thomas Hamm By Anivarya Kumar Introduction
Internship Research Paper Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Completed at St. Joseph s Hospital Barrow Neurological Institute Dr. Thomas Hamm By Anivarya Kumar Introduction
BioMed Central. Jeannette E Davies*, Christoph Pröschel, Ningzhe Zhang, Mark Noble, Margot Mayer-Pröschel and Stephen JA Davies* Research article
 BioMed Central Open Access Research article Transplanted astrocytes derived from BMP- or CNTF-treated glialrestricted precursors have opposite effects on recovery and allodynia after spinal cord injury
BioMed Central Open Access Research article Transplanted astrocytes derived from BMP- or CNTF-treated glialrestricted precursors have opposite effects on recovery and allodynia after spinal cord injury
Axon Guidance. Matthew Blewitt
 Axon Guidance Matthew Blewitt Overview Axonal development PNS regeneration CNS regeneration Future directions Brain Repair Axonal Development Neurite growth cone www.anatomy.unimelb.edu.au http://kalil.anatomy.wisc.edu/articles/kalil_dent_curropneurobiol_2005.pdf
Axon Guidance Matthew Blewitt Overview Axonal development PNS regeneration CNS regeneration Future directions Brain Repair Axonal Development Neurite growth cone www.anatomy.unimelb.edu.au http://kalil.anatomy.wisc.edu/articles/kalil_dent_curropneurobiol_2005.pdf
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the
 In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementary figure 1 (A) Quantitative analysis of F-actin signal intensity in NIH3T3 cells treated with PTD4-myc- RBD. NIH3T3 cells were treated with PTD4-myc-RBD as described. Please note the increase
Supplementary figure 1 (A) Quantitative analysis of F-actin signal intensity in NIH3T3 cells treated with PTD4-myc- RBD. NIH3T3 cells were treated with PTD4-myc-RBD as described. Please note the increase
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal
 glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor Promotes Functional Recovery in Primates after Spinal Cord Injury: past achievements and perspective for clinical trial
 Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor Promotes Functional Recovery in Primates after Spinal Cord Injury: past achievements and perspective for clinical trial Eurospine 2013 Kazuya Kitamura 1,2, Kanehiro Fujiyoshi
Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor Promotes Functional Recovery in Primates after Spinal Cord Injury: past achievements and perspective for clinical trial Eurospine 2013 Kazuya Kitamura 1,2, Kanehiro Fujiyoshi
regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries
 regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries primary and secondary events during SCI traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) main goal is to
regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries primary and secondary events during SCI traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) main goal is to
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
IVIg attenuates complement and improves spinal cord injury outcomes in mice
 RESEARCH ARTICLE IVIg attenuates complement and improves spinal cord injury outcomes in mice Faith H. Brennan 1, Nyoman D. Kurniawan 2, Jana Vukovic 1,3, Perry F. Bartlett 3, Fabian K asermann 4, Thiruma
RESEARCH ARTICLE IVIg attenuates complement and improves spinal cord injury outcomes in mice Faith H. Brennan 1, Nyoman D. Kurniawan 2, Jana Vukovic 1,3, Perry F. Bartlett 3, Fabian K asermann 4, Thiruma
Primary oligodendropathy is not a trigger of CNS autoimmunity
 Primary oligodendropathy is not a trigger of CNS autoimmunity Ari Waisman Institute for Molecular Medicine University Medical Center, JGU Mainz 1 How is an anti-myelin immune response initiated? Secondary
Primary oligodendropathy is not a trigger of CNS autoimmunity Ari Waisman Institute for Molecular Medicine University Medical Center, JGU Mainz 1 How is an anti-myelin immune response initiated? Secondary
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
New Approaches to Repair of Spinal Cord Injury
 New Approaches to Repair of Spinal Cord Injury 1 WHY IS THE SPINAL CORD SO VULNERABLE? Peripheral Nerve Spinal Cord Schwann Cell Myelin DRG Neuron Oligodendrocyte Myelin Collagen Axon 2 3 WHY IS THE SPINAL
New Approaches to Repair of Spinal Cord Injury 1 WHY IS THE SPINAL CORD SO VULNERABLE? Peripheral Nerve Spinal Cord Schwann Cell Myelin DRG Neuron Oligodendrocyte Myelin Collagen Axon 2 3 WHY IS THE SPINAL
Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair
 Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair YENFU CHEN, MD 1, YAO-LUNG KUO, MD 2,3,4, I-Ming Jou, Prof, 3. 1 Department of Orthopaedics, National Cheng Kung
Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair YENFU CHEN, MD 1, YAO-LUNG KUO, MD 2,3,4, I-Ming Jou, Prof, 3. 1 Department of Orthopaedics, National Cheng Kung
Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the. development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
Contact: Course outline: Contact for other times.
 Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
 Liu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:6 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0327-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
Liu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:6 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0327-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
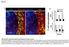 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
RECEIVED. W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ (732)
 Principal Investigator: Dongming Sun, W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 (732) 445-1832 RECEIVED NJ COMMISSION ON SPINAL CORD RESEARCH The overall
Principal Investigator: Dongming Sun, W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 (732) 445-1832 RECEIVED NJ COMMISSION ON SPINAL CORD RESEARCH The overall
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
~Dof. Zhou, Renping SCR-S-O. Final Report ~ Treating Spinal Cord Injury with Ginsenosides. Grant #: Period Covered: Data Submission Date:
 01-3003-SCR-S-O ~Dof Final Report ~ Grant Title: Treating Spinal Cord Injury with Ginsenosides Grant #: Period Covered: Data Submission Date: 01-3003-SCR-S-0 06/15/01-06/30/04 09/24/04 Renping Zhou Department
01-3003-SCR-S-O ~Dof Final Report ~ Grant Title: Treating Spinal Cord Injury with Ginsenosides Grant #: Period Covered: Data Submission Date: 01-3003-SCR-S-0 06/15/01-06/30/04 09/24/04 Renping Zhou Department
Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
CNS third year med students Summary of midterm material H Awad
 CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
Adult Nervous System
 Adult Nervous System What is the capacity of the PNS and CNS for repair? WHY? Why discuss this now? Potential for repair depends on cellular properties of nerve and glial cells. http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter09.html
Adult Nervous System What is the capacity of the PNS and CNS for repair? WHY? Why discuss this now? Potential for repair depends on cellular properties of nerve and glial cells. http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter09.html
M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination
 Supplemental Information Title: M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination Authors: Veronique E. Miron, Amanda Boyd, Jing-Wei Zhao, Tracy J. Yuen, Julia M.
Supplemental Information Title: M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination Authors: Veronique E. Miron, Amanda Boyd, Jing-Wei Zhao, Tracy J. Yuen, Julia M.
Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do?
 Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do? David Kahan, MD Fellow, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University Outline Wallerian Degeneration
Nerve Autografts, Allografts, Conduits, Wraps, and Glue. What Should I Do? David Kahan, MD Fellow, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University Outline Wallerian Degeneration
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46057 1 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
OpenStax-CNX module: m46057 1 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Protein as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Spinal Cord Injury
 Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Protein as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Spinal Cord Injury The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Protein as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Spinal Cord Injury The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Treatments for Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Jim Geddes Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Center University of Kentucky
 Treatments for Acute Spinal Cord Injury Jim Geddes Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Center University of Kentucky FDA Approved Drugs for Acute SCI Progress to date 5017 140 NIH funding ~$142 million/yr
Treatments for Acute Spinal Cord Injury Jim Geddes Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Center University of Kentucky FDA Approved Drugs for Acute SCI Progress to date 5017 140 NIH funding ~$142 million/yr
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Update on early management of acute spinal cord injuries. Mr Jonathon L Richards Orthopaedic & Spinal surgeon
 Update on early management of acute spinal cord injuries Mr Jonathon L Richards Orthopaedic & Spinal surgeon Overview: Aetiology/Cost Pathophysiology Early surgical intervention Emerging therapies Steroids
Update on early management of acute spinal cord injuries Mr Jonathon L Richards Orthopaedic & Spinal surgeon Overview: Aetiology/Cost Pathophysiology Early surgical intervention Emerging therapies Steroids
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS
 Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo. SI Figures and Legend
 Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Transplantation of D15A-Expressing Glial-Restricted- Precursor-Derived Astrocytes Improves Anatomical and Locomotor Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury
 78 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Biological Sciences 2013; 9(1):78-93. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5626 Transplantation of D15A-Expressing Glial-Restricted- Precursor-Derived
78 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Biological Sciences 2013; 9(1):78-93. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5626 Transplantation of D15A-Expressing Glial-Restricted- Precursor-Derived
Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain
 Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain Paul Durham, PhD Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology Director Center for Biomedical & Life Sciences Missouri State University Cluster Headache
Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain Paul Durham, PhD Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology Director Center for Biomedical & Life Sciences Missouri State University Cluster Headache
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Paclitaxel causes degeneration of both central and peripheral axon branches of dorsal root ganglia in mice
 DOI 10.1186/s12868-016-0285-4 BMC Neuroscience RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Paclitaxel causes degeneration of both central and peripheral axon branches of dorsal root ganglia in mice Aniqa Tasnim 1,3,
DOI 10.1186/s12868-016-0285-4 BMC Neuroscience RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Paclitaxel causes degeneration of both central and peripheral axon branches of dorsal root ganglia in mice Aniqa Tasnim 1,3,
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells
 University of Turin CNR Institute of Neuroscience Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells Roberta Parolisi Turin, December
University of Turin CNR Institute of Neuroscience Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells Roberta Parolisi Turin, December
25 Things To Know. Neurons
 25 Things To Know Neurons Neurons receive & transmit to other cells Neurons Many last your whole life Neurons Many last your whole life Other cells die and are replaced Most aren t replaced Neurons Hippocampus
25 Things To Know Neurons Neurons receive & transmit to other cells Neurons Many last your whole life Neurons Many last your whole life Other cells die and are replaced Most aren t replaced Neurons Hippocampus
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011
 Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice.
 Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Pathogenesis of Cervical Myelopathy in Chronic Cervical Cord Compression Model of Rat
 Pathogenesis of Cervical Myelopathy in Chronic Cervical Cord Compression Model of Rat Shigeru Kobayashi,MD,PhD 1, Masafumi Kubota, PT 1, Hisao Iwamoto, MD,PhD 2, Riya Kosaka,MD,PhD 3, Katsuhiko Hayakawa,MD,PhD
Pathogenesis of Cervical Myelopathy in Chronic Cervical Cord Compression Model of Rat Shigeru Kobayashi,MD,PhD 1, Masafumi Kubota, PT 1, Hisao Iwamoto, MD,PhD 2, Riya Kosaka,MD,PhD 3, Katsuhiko Hayakawa,MD,PhD
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline
 Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-77 TITLE: Translational Pharmacologic Efficacy Studies of Glial Growth Factor 2 (GGF2) in Spinal Cord Injury Models and in the Veterinary Clinical Setting PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-77 TITLE: Translational Pharmacologic Efficacy Studies of Glial Growth Factor 2 (GGF2) in Spinal Cord Injury Models and in the Veterinary Clinical Setting PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back
 Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Supplementary Materials
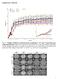 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Olfactory ensheathing glia
 Olfactory ensheathing glia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Neuroglia of the brain shown by Golgi's method. Olfactory ensheathing glia (OEG), also known as olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) or olfactory
Olfactory ensheathing glia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Neuroglia of the brain shown by Golgi's method. Olfactory ensheathing glia (OEG), also known as olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) or olfactory
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
Liz et al. BMC Biology 2014, 12:47
 Liz et al. BMC Biology 2014, 12:47 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neuronal deletion of GSK3β increases microtubule speed in the growth cone and enhances axon regeneration via CRMP-2 and independently of MAP1B and CLASP2
Liz et al. BMC Biology 2014, 12:47 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neuronal deletion of GSK3β increases microtubule speed in the growth cone and enhances axon regeneration via CRMP-2 and independently of MAP1B and CLASP2
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted
 Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted
