Familial dystonia with cerebral calcification
|
|
|
- Jeremy Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Familial dystonia with cerebral calcification case report and genetic update M. Signaevski, A.K. Wszolek, A.J. Stoessel, R. Rademakers, and I.R. Mackenzie Vancouver General Hospital, BC, Canada Mayo Clinic Jacksonville, Florida, USA Pacific Parkinson Research Centre, BC, Canada
2 nothing to disclose
3 Genealogy tree Canadian family with dystonia-plus syndrome and brain calcinosis: - followed since mid 80s - 6 generations - AD, highly penetrant Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67:
4 Family phenotype Symptoms - dystonia (oromandibular) +/- plus - dysarthria - chorea - ataxia - Parkinsonism - variable intellectual decline Cerebral calcifications: - basal ganglia - thalamus - subcortical white matter - cerebellum
5 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: symptomatic 8 asymptomatic
6 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: basal ganglia thalamus cerebellum WM 11 symptomatic 8 asymptomatic
7 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: basal ganglia thalamus cerebellum WM 11 symptomatic 8 - with dystonia all cases: range: 8-70 age at onset: mean ~19 dystonia+ cases range: 8-20 age of onset: mean ~ 13
8 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: basal ganglia thalamus cerebellum WM 11 symptomatic 8 asymptomatic
9 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: basal ganglia thalamus cerebellum WM 8 asymptomatic still asymptomatic in mid life age range mean =50
10 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67:
11 Wszolek et al, Neurology, 2006;67: Genealogy tree III-9
12 Clinical history 71 year old female with progressive movement disorder, dystonia, and intellectual decline age symptoms 10 - dysarthria and involuntary movements / oromabdibular 18 - right arm athetosis 28 - generalized involuntary movements 52 - CT scan: bilateral symmetric calcifications: - basal ganglia, thalamus, and cerebellum - subcortical white matter: occipital, temporal, parietal, frontal - frontal and parietal cortex 67 - follow up CT scan - no change - Ca, Cu, Phosphate, Fe - normal ~ generalized dystonia (predominantly upper body) - dysarthria, dysphagia - depression - repeated falls
13 CT scan, age 67
14 Gross pathology frontal WM lentiform
15 Gross pathology thalamus cerebellar dentate
16 Various parenchymal calcification patterns, H&E thalamus basal ganglia cerebellar dentate cerebellar WM & vessels
17 Cortical WM, H&E and von Kossa von Kossa
18 Vessel calcification patterns, H&E von Kossa
19 Pathology: striatum GFAP minor gliotic reaction to calcifications
20 Cerebellar vermis Cerebellar hemispheres Purkinje cells preserved in calcified and in non-calcified areas Purkinje cell loss and Bergmann s gliosis
21 Pathology: IHC Hippocampus: CA1 Hippocampus: alveus ubiquitin ubiquitin Negative: - tau - alpha-synuclein - FUS - TDP-43
22 Genetic considerations: background Historically: Familial Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification (IBGC, Fahr s disease): - movement abnormalities: dystonia, Parkinsonism, ataxia, chorea - may be asymptomatic To date: links to - Chr 14q (fibgc1) - Chr 2q37 (fibgc2) - Chr 8p21.1 (fibgc3*: various mutations in SLC20A2) Mayo Clinic study (co-authors): - mutation analysis of SLC20A2 in 27 cases of IBGC** - Mayo Clinic Jacksonville brain bank - including a member of Canadian IBGC family with dystonia-plus syndrome - brother of our case * Wang et al, Nature genetics, 2012, 4(3): ** Baker et al, Neurogenetics, 2014,15(1): 23-30
23 III-3 (brother) 85M with ~60-year history of progressive movement disorder and dystonia-plus Pathology: - same pattern as III-9: - parenchymal - vascular Baker et al., Neurogenetics March ; 15(1):
24 Genetic analysis Mayo genetic study*: - cohort of 27 cases, histologically proven IBGC - two with SLC20A2 mutations were identified: - one - novel C338G nonsense mutation - another - deletion on chromosome 8p Copy number analysis: - deleted ~563Kb region on 8p11.21 in this member of the family Sequencing: - complete deletion of 7 genes: - VDAC3, SLC20A2, c8orf40, CHRNB3, CHRNA6, THAP1, RNF170 - partially HOOK3 *Baker et al., Neurogenetics March ; 15(1):
25 SLC20A2 Gene: - SLC20A2 - chromosome 8p11.21 Protein: Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2 (PiT2) - homodimer - inorganic phosphate transport - pumps Phosphate into cell - ubiquitously expressed - highest in basal ganglia Mutations: loss-of-function - about 20 mutations in more than 40 families worldwide - truncated protein or loss of protein - explains 41% familial cases and 14% sporadic - excess of phosphate in the presence of Calcium => calcifications Disease: - idiopathic basal ganglia calcification - no dystonia phenotype is identified with isolated SLC20A2 loss.
26 THAP1 Gene: - THAP1 - chromosome 8p11.21 Protein: - THAP Domain Containing, Apoptosis Associated Protein 1 (THanatos Associated Protein 1) - DNA-binding transcription factor - endothelial cell proliferation - G1/S cell-cycle progression. - possible pro-apoptotic activity via TNF-induced apoptosis. Mutations: loss-of-function: - Over 90 point mutations - autosomal dominant, penetrance of 40 60% Disease: - causes dystonia (DYT6) - one of the two genetically determined dystonias
27 ~563Kb calcinosis dystonia
28 calcinosis dystonia? +/- plus: dysarthria chorea ataxia Parkinsonism intellectual decline
29 calcinosis dystonia?? +/- plus: dysarthria chorea ataxia Parkinsonism intellectual decline
30 calcinosis dystonia?? +/- plus: dysarthria chorea ataxia Parkinsonism intellectual decline
31 calcinosis dystonia??? +/- plus: dysarthria chorea ataxia Parkinsonism intellectual decline
32 ? calcinosis dystonia? +/- plus: dysarthria chorea ataxia Parkinsonism intellectual decline
33 Canadian family: - Cerebral Calcification +/- Dystonia-Plus syndrome - Autosomal Dominant - deletion on chromosome 8p11 - involving SLC20A2 and THAP1 genes Questions
34 Thank you
35
! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.
 UBC ! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.! cause unknown.! sporadic, familial or inherited.! degeneration of specific brain region! clinical syndrome.! pathology: abnormal accumulation
UBC ! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.! cause unknown.! sporadic, familial or inherited.! degeneration of specific brain region! clinical syndrome.! pathology: abnormal accumulation
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Clinicopathologic and genetic aspects of hippocampal sclerosis. Dennis W. Dickson, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida USA
 Clinicopathologic and genetic aspects of hippocampal sclerosis Dennis W. Dickson, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida USA The hippocampus in health & disease A major structure of the medial temporal
Clinicopathologic and genetic aspects of hippocampal sclerosis Dennis W. Dickson, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida USA The hippocampus in health & disease A major structure of the medial temporal
Epidural hematoma in Fahr s disease FAHR S DISEASE ACCOMPANIED BY EPIDURAL HEMATOMA: A CASE REPORT
 138 FAHR S DISEASE ACCOMPANIED BY EPIDURAL HEMATOMA: A CASE REPORT Kara H 1*, Bayir A 1, Ak A 1, Akinci M 1, Değirmenci S 1, Alp H 1 1. Selcuk University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine,
138 FAHR S DISEASE ACCOMPANIED BY EPIDURAL HEMATOMA: A CASE REPORT Kara H 1*, Bayir A 1, Ak A 1, Akinci M 1, Değirmenci S 1, Alp H 1 1. Selcuk University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine,
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs
 Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Stroke: clinical presentations, symptoms and signs Professor Peter Sandercock University of Edinburgh EAN teaching course Burkina Faso 8 th November 2017 Clinical diagnosis is important to Ensure stroke
Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado
 Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado Discuss an unusual case of CNS calcification encountered on an academic VA rheumatology service Summarize bilateral striatopallidodentate
Patrick R Wood, MD Fellow, Rheumatology University of Colorado Discuss an unusual case of CNS calcification encountered on an academic VA rheumatology service Summarize bilateral striatopallidodentate
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Neuroscience 410 Huntington Disease - Clinical. March 18, 2008
 Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
Neuroscience 410 March 20, 2007 W. R. Wayne Martin, MD, FRCPC Division of Neurology University of Alberta inherited neurodegenerative disorder autosomal dominant 100% penetrance age of onset: 35-45 yr
FRONTOTEMPORAL DEGENERATION: OVERVIEW, TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS
 FRONTOTEMPORAL DEGENERATION: OVERVIEW, TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS Norman L. Foster, M.D. Director, Center for Alzheimer s Care, Imaging and Research Chief, Division of Cognitive Neurology, Department of Neurology
FRONTOTEMPORAL DEGENERATION: OVERVIEW, TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS Norman L. Foster, M.D. Director, Center for Alzheimer s Care, Imaging and Research Chief, Division of Cognitive Neurology, Department of Neurology
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
An approach to movement disorders. Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London
 An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
An approach to movement disorders Kailash Bhatia, DM, FRCP Professor of Clinical Neurology Institute of Neurology Queen Square, London Neurology Diagnosis Two main questions: What parts of the nervous
Brain dissection protocol for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease
 Brain dissection protocol for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease Prepared by Approved by Approved by Revised by Name Signature Date Sampling and biomarker OPtimization and Harmonization
Brain dissection protocol for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease Prepared by Approved by Approved by Revised by Name Signature Date Sampling and biomarker OPtimization and Harmonization
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System
 Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy
 Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A
 CHCHD2 and Parkinson's disease Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A Published in: Lancet Neurology DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00095-2 2015 Link to
CHCHD2 and Parkinson's disease Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A Published in: Lancet Neurology DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00095-2 2015 Link to
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes
 Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, all types Revised Creutzfeldt-Jakob
Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, all types Revised Creutzfeldt-Jakob
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
NEUROPATHOLOGY BRAIN CUTTING MANUAL LAST UPDATED ON 6/22/2015
 NEUROPATHOLOGY BRAIN CUTTING MANUAL LAST UPDATED ON 6/22/2015 Neuropathology Faculty involved in Brain Cutting: Dr. Sandra Camelo-Piragua Dr. Andrew Lieberman (Chief of the Division) Dr. Kathryn A. McFadden
NEUROPATHOLOGY BRAIN CUTTING MANUAL LAST UPDATED ON 6/22/2015 Neuropathology Faculty involved in Brain Cutting: Dr. Sandra Camelo-Piragua Dr. Andrew Lieberman (Chief of the Division) Dr. Kathryn A. McFadden
Dystonia: Title. A real pain in the neck. in All the Wrong Places
 Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Focus on CME at the University of Western Ontario Dystonia: Title in All the Wrong Places A real pain in the neck By Mandar Jog, MD, FRCPC and; Mary Jenkins, MD, FRCPC What is dystonia? Dystonia is a neurologic
Objectives. RAIN Difficult Diagnosis 2014: A 75 year old woman with falls. Case History: First visit. Case History: First Visit
 Objectives RAIN Difficult Diagnosis 2014: A 75 year old woman with falls Alexandra Nelson MD, PhD UCSF Memory and Aging Center/Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease Recognize important clinical features
Objectives RAIN Difficult Diagnosis 2014: A 75 year old woman with falls Alexandra Nelson MD, PhD UCSF Memory and Aging Center/Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease Recognize important clinical features
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective
 Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective Samuel F Berkovic Epilepsy Research Centre, University of Melbourne Austin Health Epileptogenesis The process of development and sustaining the propensity to
Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective Samuel F Berkovic Epilepsy Research Centre, University of Melbourne Austin Health Epileptogenesis The process of development and sustaining the propensity to
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
ALLEN Human Brain Atlas
 TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: CASE QUALIFICATION AND DONOR PROFILES The case review process described here was employed for three components of the ALLEN Human Brain Atlas: (1) the Survey; (2) the Neurotransmitter
TECHNICAL WHITE PAPER: CASE QUALIFICATION AND DONOR PROFILES The case review process described here was employed for three components of the ALLEN Human Brain Atlas: (1) the Survey; (2) the Neurotransmitter
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Connections of basal ganglia
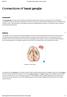 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY
 HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
CVA. Alison Atwater PA-C
 CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming. Morten Overgaard
 Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
II:3 III:1 III:2 III:3
 Assessment (Range) II:3 III:1 III:2 III:3 Age 54 Age 59 Age 27 Age 32 Age 23 Age 28 Age 18 Age 23 TRS (0-144) 10 11 9 9 NA 12 7 10 UPDRS part III (0-108) 3 6 1 3 5 6 4 6 UHDRS (0-124) 3 5 3 9 2 7 5 8 SARA
Assessment (Range) II:3 III:1 III:2 III:3 Age 54 Age 59 Age 27 Age 32 Age 23 Age 28 Age 18 Age 23 TRS (0-144) 10 11 9 9 NA 12 7 10 UPDRS part III (0-108) 3 6 1 3 5 6 4 6 UHDRS (0-124) 3 5 3 9 2 7 5 8 SARA
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS. Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan)
 Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Dementia Update. October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada
 Dementia Update October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada Outline New concepts in Alzheimer disease Biomarkers and in vivo diagnosis Future trends
Dementia Update October 1, 2013 Dylan Wint, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health Las Vegas, Nevada Outline New concepts in Alzheimer disease Biomarkers and in vivo diagnosis Future trends
NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium
 NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Test 3. Module 5 & 6
 Test 3 Module 5 & 6 Questions from the GVLS website Define the terms: Muscle- Involuntary- Voluntary- Striated- Smooth- Cardiac- Sarcomere - Actin - Myosin - Myofibril - Muscle Contraction - A-band - I-band
Test 3 Module 5 & 6 Questions from the GVLS website Define the terms: Muscle- Involuntary- Voluntary- Striated- Smooth- Cardiac- Sarcomere - Actin - Myosin - Myofibril - Muscle Contraction - A-band - I-band
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning
 Online supplementary information for: Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning Joel L. Voss, Brian D. Gonsalves, Kara D. Federmeier,
Online supplementary information for: Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning Joel L. Voss, Brian D. Gonsalves, Kara D. Federmeier,
Unusual Suspects of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) An Investigation for the Mechanism of the Motor Neuron Degeneration
 Unusual Suspects of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) An Investigation for the Mechanism of the Motor Neuron Degeneration Neurodegenerative Diseases Each neurodegenerative disease is characterized by
Unusual Suspects of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) An Investigation for the Mechanism of the Motor Neuron Degeneration Neurodegenerative Diseases Each neurodegenerative disease is characterized by
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia
 Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia Professor Tom Warner, Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological Studies UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square What
Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia Professor Tom Warner, Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological Studies UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square What
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia
 Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia Professor Tom Warner, Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological Studies UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square What
Diagnosis and treatment of dystonia Professor Tom Warner, Reta Lila Weston Institute of Neurological Studies UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square What
FTD Genetics: for patients and families. Kirk Wilhelmsen, M.D., Ph.D UNC
 FTD Genetics: for patients and families Kirk Wilhelmsen, M.D., Ph.D UNC UNC The Human Genome 22 Pairs of Chromosomes 2 Sex Chromosomes 3,300,000,000 basepairs of DN 7-14 picograms of DN per cell ~20,000
FTD Genetics: for patients and families Kirk Wilhelmsen, M.D., Ph.D UNC UNC The Human Genome 22 Pairs of Chromosomes 2 Sex Chromosomes 3,300,000,000 basepairs of DN 7-14 picograms of DN per cell ~20,000
USCAP Neuropathology. Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC
 USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases
 Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases Keith A. Josephs, MD, MST, MSc Professor of Neurology 13th Annual Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Symposium: Alzheimer and Non-Alzheimer
Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases Keith A. Josephs, MD, MST, MSc Professor of Neurology 13th Annual Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Symposium: Alzheimer and Non-Alzheimer
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease. David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology
 Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology Disclosures Dr. Standaert has served as a paid consultant
Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology Disclosures Dr. Standaert has served as a paid consultant
Lecture 42: Final Review. Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D.
 Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Lecture 42: Final Review Martin Wessendorf, Ph.D. Lecture 33 cortex Heilbronner 5 lobes of the cortex Lateral view (left side) Mid-saggital view (right side) Cellular organization of cortex White matter
Neurological Disorders and Purinergic Metabolic Disruption. By: Nhi, Alex, Teva, and Guadalupe
 Neurological Disorders and Purinergic Metabolic Disruption By: Nhi, Alex, Teva, and Guadalupe Lesch-Nyhan Disease Discovered by Michael Lesch and WIlliam Nyhan in 1964 Causes: Disruption of purine metabolism
Neurological Disorders and Purinergic Metabolic Disruption By: Nhi, Alex, Teva, and Guadalupe Lesch-Nyhan Disease Discovered by Michael Lesch and WIlliam Nyhan in 1964 Causes: Disruption of purine metabolism
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
On-line Table 1: Dementia diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a
 On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4
 Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior. Chapter 18 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior Behavior Most human behaviors are polygenic and have significant environmental influences Methods used to study inheritance include Classical methods of linkage and pedigree
Chapter 18 Genetics of Behavior Behavior Most human behaviors are polygenic and have significant environmental influences Methods used to study inheritance include Classical methods of linkage and pedigree
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of
 Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
The Neuropsychology of
 The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
The Neuropsychology of Stroke Tammy Kordes, Ph.D. Northshore Neurosciences Outline What is the Role of Neuropsychology Purpose of Neuropsychological Assessments Common Neuropsychological Disorders Assessment
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Memory. Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith
 Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
Relationship Between Intracranial Calcifications in Vein of Galen Malformations and Fahr s Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(2): 13-19 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160402.12 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Case Report Relationship Between Intracranial
Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(2): 13-19 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160402.12 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Case Report Relationship Between Intracranial
A Case of Vascular MCI
 A Case of Vascular MCI Charles DeCarli, MD Victor and Genevieve Orsi Chair in Alzheimer s Research Director Alzheimer s Disease Center University of California at Davis Initial Evaluation 78 y.o. Rt. Handed
A Case of Vascular MCI Charles DeCarli, MD Victor and Genevieve Orsi Chair in Alzheimer s Research Director Alzheimer s Disease Center University of California at Davis Initial Evaluation 78 y.o. Rt. Handed
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
SCL20A2 mutation presenting with acute ischemic stroke: a case report
 Zhang et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:11 DOI 10.1186/s12883-018-1012-9 CASE REPORT Open Access SCL20A2 mutation presenting with acute ischemic stroke: a case report Xiaoyu Zhang, Gaoting Ma, Zhangning Zhao
Zhang et al. BMC Neurology (2018) 18:11 DOI 10.1186/s12883-018-1012-9 CASE REPORT Open Access SCL20A2 mutation presenting with acute ischemic stroke: a case report Xiaoyu Zhang, Gaoting Ma, Zhangning Zhao
NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION
 E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER DISEASE
 ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER SEASE GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MECINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE
ADULT-ONSET (INFRATENTORIAL) LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY as PRESENTING MANIFESTATION of ERDHEIM-CHESTER SEASE GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MECINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
