Renal pathology II. Áron Somorácz MD PhD
|
|
|
- Tobias Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Renal pathology II. Áron Somorácz MD PhD
2 Urologic renal diseases I. Congenital abnormalities II. Cystic diseases of the kidney III. Urolithiasis IV. Obstructive uropathy V. Pyelonephritis VI. Tumors of the kidney
3 I. Congenital abnormalities 1. Agenesis of the kidney In utero detected bilateral agenesis indicates abortion 2. Hypoplasia of the kidney Smaller kidney with contralateral compensatory hypertrophy 3. Oligomeganephronia Reduced number of nephrons leading to end stage renal disease (ESRD) by the time of adolescence 4. Horseshoe kidney The most common congenital anomaly (1/ ) resulting from the fusion of lower (90%) or upper (10%) poles 5. Ectopic kidneys The kidney lies at the pelvic brim or within the pelvis
4 I. Congenital abnormalities 6. Duplication of the renal pelvis and the ureter 7. Ureteropelvic junction stenosis Usually unilateral, leads to hydronephrosis, early operation can save the kidney 8. Accessory renal artery 9. Multicystic renal dysplasia Developmental anomaly, NOT neoplastic process! Abnormal tissue elements (cartilage, undifferentiated mesenchyme) Cysts Unilateral or bilateral, complete or segmental Enlarged kidney with insufficent function
5 Horseshoe kidney Ureteral duplication
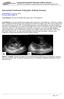
6 Ureteropelvic junction stenosis
7 Multicystic renal dysplasia
8 II. Cystic diseases of the kidney 1. Polycystic kidney disease A) Autosomal-dominant (ADPKD) Adulthood PKD1 and PKD2 genes (Polycystin-1 and -2) Prevalence 1/ Bilateral and marked enlargement Grape-like appearance Symptomes begin in early adulthood It is responsible for 5-10% of chronic renal failures Liver and pancreatic cysts, mitral valve prolapse, intracranial berry aneurysms
9 Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease
10 II. Cystic diseases of the kidney 1. Polycystic kidney disease B) Autosomal-recessive (ARPKD) Perinatal, neonatal, infantile, juvenile subcategories PKDH1 gene (fibrocystin) Markedly enlarged kidneys Lung hypoplasia, oligohydramnion Medullary and cortical elongated cysts, sponge-like appearance Usually leads to death within the first month of life
11 Autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease
12 II. Cystic diseases of the kidney 2. Cystic diseases of the renal medulla A) Medullary sponge kidney 1-3 mm medullary cysts of the collecting ducts Does not lead to renal failure B) Nephronophtysis Sporadic or familial Atrophic kidneys, cysts at the corticomedullary junction Leads to ESRD 3. Simple cysts Common finding, single or multiple, do not influence the renal function
13 II. Cystic diseases of the kidney 4. Acquired cystic disease of the kidney In case of long-standing dialysis 5. Glomerulocystic kidney disease 6. Cysts in hereditary syndromes von Hippel-Lindau syndrome Tuberous sclerosis
14 III. Urolithiasis Three factors: Salts that are capable of crystallization Core that triggers crystallizaton (cell debris, urinary cast) Lack of inhibitors of crystallization 1. Calcium stones 60-70% Calcium oxalate/calcium phosphate Hypercalciuria (with or without hypercalcemia), hyperoxaluria Brown-black, 1-2 cm, visible by X-ray
15 III. Urolithiasis 2. Struvite stones 15% Magnesium ammonium phosphate After infection (e.g., Proteus) Grey-yellow, staghorn calculi 3. Uric acid stones 15% Hyperuricemia (gout, rapid cell turnover e.g., leukemias) White or orange, radiolucent 4. Cystine stones 1-2% Cystinuria
16 Calcium stone Staghorn (struvite) stone
17 III. Urolithiasis Clinical features Uni- (80%) or bilateral Kidney stone attack: agonizing intense pain in the lower back (lumbal area) extending into the groin area Nausea, vomiting Smaller stones are more hazardous Hematuria Might be without symptomes Predisposes for infections
18 IV. Obstructive uropathy Obstruction predisposes for infections and stone formation Unrelieved obstruction leads to hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis: Dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces Progressive atrophy of the kidney
19 IV. Obstructive uropathy Causes: 1. Congenital anomalies 2. Calculi 3. Prostatic hyperplasia 4. Tumors 5. Lower urinary tract inflammations 6. Pregnancy 7. Uterine prolapse 8. Functional disorders
20 IV. Obstructive uropathy Clinical features: Acute obstruction usually provokes pain Partial obstruction may remain silent Partial bilateral obstruction leads to inabilty to concentrate the urine resulting in polyuria followed by chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis Complete bilateral obstruction leads oliguria or anuria
21 V. Pyelonephritis 1. Acute pyelonephritis Inflammation of the tubules, the interstitium, the calyces and the renal pelvis Caused by bacterias (E. coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella, Enterococcus) Usually consequence of an ascending urinary tract infection Less commonly result of a hematogenous spread In normal kidneys, or as a complication of urinary tract disorders (e.g. VUR) Predisposing factors: catheter, diabetes, pregnancy, lower urinary tract obstruction, immunsuppression
22 V. Pyelonephritis 1. Acute pyelonephritis Morphology: Sligthly enlarged kidney(s) 1-3 mm yellowish abscesses on the surface and in the parenchyme (pyelonpehritis apostematosa) The calyces and the renal pelvis are reddish Patchy interstitial suppurative inflammation, aggregates of neutrophils in the tubules, tubular necrosis Glomeruli are also affected in case of hematogenous origin
23 Acute pyelonephritis
24 Acute pyelonephritis
25 V. Pyelonephritis 1. Acute pyelonephritis Clinical features: Uni- or bilateral Sudden onset with high fever Pain at the costovertebral angle Leukocytosis, high sedimentation rate Pyuria, bacteruria Usually follows a benign course (with appropriate antibiotic therapy) Complicated cases can be fatal
26 V. Pyelonephritis 2. Chronic pyelonephritis Chronic injury of the interstitium and the tubules resulting in scar formation The renal pelvis and the calyces are also affected Causes: reflux nephropathy, chronic obstruction Recurrent infections Morphology: Kidneys are irregularly scarred, corticomedullary scars overlying dilated calyces, flattening of the papillae The calyces are dilated and their mucosa is thickened Focal interstitial fibrosis, atrophic tubules, tubular casts (thyroidization), lymphoid infiltration The mucosa of the calyces and pelvis is fibrotic and contains cronic inflammation
27 Chronic pyelonephritis
28 Chronic pyelonephritis
29 V. Pyelonephritis 2. Chronic pyelonephritis Clinical features: Uni- or bilateral Episodes of acute pyelonephritis, or silent clinical course leading to destruction Bilateral chronic pyelonephritis can result in hypertension and renal insufficiency 10% of patients on dialysis therapy have chronic pyelonephritis
30 V. Pyelonephritis 3. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis Middle-aged women with diabetes Usually unilateral Proteus mirabilis infection Tumor-like lesion Yellowish areas, extracapsular spread, infiltrative pattern Foamy histiocytes, giant cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils Indicates nephrectomy
31 Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
32 VI. Tumors of the kidney Tumor types Benign tumors Malignant tumors Pediatric tumors Genetic background Prognostic factors Clinical features
33 VI. Tumors of the kidney Histogenesis of renal tumors Tubular epithelium Papillary adenoma Oncocytoma Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (renal cell carcinoma: RCC) Multilocular cystic neoplasm Papillary RCC Chromophobe RCC Clear cell papillary RCC Mesenchyme Angiomyolipoma Metanephrogenic elements Metanephric adenoma Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor)
34 VI. Tumors of the kidney Benign tumors 1. Papillary adenoma Papillary tumor with low-grade tumors cells, 15 mm Grey-white, round nodule, can be multifocal Commonly incidental finding Cuboidal, monomorphic tumor cells, papillary architecture, psammoma bodies
35 VI. Tumors of the kidney Benign tumors 2. Oncocytoma 5% of renal tumors Mahogany brown, characteristic central scar Nested, trabecular architecture, degenerative signs Oncocytic, bland looking cells (large, granular eosinophilic cytoplasm), however, bizarre nuclei, extracapsular infiltration, vascular invasion might be encountered
36
37 VI. Tumors of the kidney Benign tumors 3. Angiomyolipoma PEComa: perivascular epithelioid cell tumor 1% of the resected renal tumors, but it is more common (by US detected tumors that are not operated) Well-circumscribed, usually fatty appearance Adipose tissue, thick-walled vessels, smooth muscle HMB45+, Melan A+ (melanocytic markers!!)
38
39 VI. Tumors of the kidney Benign tumors 4. Metanephric adenoma More common in females Average size is 5 cm Grey-brown, solid, cystic degeneration may be present Well-circumscribed but unencapsulated Tubulary, solid, or papillary architecture No mitoses WT1+, CD57+, CK7-, EMA-
40
41 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors 1. Clear cell RCC Most common type (approx. 80%) Characteristic golden yellow color Variable architecture: solid, tubular, papillary, microcystic, cystic Haemorrhages and necroses are usual Genetic/epigenetic alteration: 3p deletion, VHL mutation, VHL hypermetilation
42
43
44 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors 2. Multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential 2-3% of RCCs Middle-aged patients, usually incidentally detected Complex cystic lesion by radiological examination Composed exclusively of thin-walled cysts Clear cyst content Low-grade tumor cells: internal surface of cysts, small groups in the septums Excellent prognosis
45
46
47 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors 3. Papillary RCC Second most common (approx %) More commonly multifocal Type 1 Grey-white, well-circumscribed, encapsulated, haemorrhages Papillary, tubular, or solid architecture Cuboidal cells, foamy macrophages, psammoma bodies Type 2 Variable appearance, necroses, haemorrhages Larger cells, higher grade Characteristic genetic alteration: trisomies (7, 17, 12, 16 20), loss of Y, c-met mutation
48
49 Type 1 Type 2
50 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors 4. Chromophobe RCC Approx. 4-5% Well-circumscribed, grey-white Clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, distinct cell borders, binucleated figures, rasinoid nuclei, perinuclear halo Widespread chromosomal losses Better prognosis DD: oncocytoma
51
52 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors 5. Clear cell papillary RCC Originally descriped being associated with end-stage kidney disease 1-1,5% of renal cell tumors Well-circumscribed, encapsulated, grey-brown Solid and cystic areas Mostly branching tubular, less commonly papillary architecture Clear cells with low-grade morphology Subnuclear vacuolization Indolent behavior (no metastatic case has been published to date)
53
54
55 VI. Tumors of the kidney Malignant tumors Rare types Collecting duct (Bellini) carcinoma Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma-associated RCC MiT gene family translocation RCC Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient RCC Tubulocystic RCC Acquired cystic disease-associated RCC Mucinous tubular and spindle cell RCC Medullary RCC
56 VI. Tumors of the kidney Pediatric tumors 1. Nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor) Malignant tumor that derives from nephrogenic blastema cells 10% associated with congenital malformations (e.g. WAGR) 98% diagnosed prior to age 10 years, very rarely detected in adults Palpable abdominal mass, abdominal pain, haematuria 10% bilateral, greyish tumor, cystic areas Triphasic appearance: blastema cells, epithelial elements, stroma WT1 deletion in 1/3, as well as WT1 mutation in 1/10 of sporadic cases Usually good prognosis
57
58
59 VI. Tumors of the kidney Pediatric tumors 2. Mesoblastic nephroma Derives from nephrogenic mesenchyme Congenital tumor Indolent behavior 3. Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney Derives from nephrogenic mesenchyme Mean age of presentation is 2 years Bone metastases Poor outcome 4. Rhabdoid tumor of the kidney Large eosinophilic cytoplasma, excentric nuclei Prior to age 2 years Poor prognosis
60 VI. Tumors of the kidney Genetic background of RCCs VHL gene von Hippel-Lindau syndrome sporadic clear cell RCCs Degradation of HIF1 (hypoxia-inducible factor, HIF1α, HIF2 α) HIF target genes: MAPK pathway, mtor pathway, c-myc
61 Kidney Int Nov; 76(9):
62 VI. Tumors of the kidney Genetic background of RCCs MET gene Product: c-met/hgf receptor Hereditary papillary RCC Mutation of MET can be detected in a subset of type 1 papillary RCCs c-met inhibitor: foretinib TSC1/TSC2 Tuberous sclerosis complex Renal manifestation of tuberous sclerosis: angiomyolipoma, clear cell RCC mtor pathway
63 VI. Tumors of the kidney Genetic background of RCCs Folliculin Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome Fumarate hydratase Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma HIF1 accumulation Succinate dehydrogenase Paraganglioma, pheochromocytoma, RCC
64 VI. Tumors of the kidney Prognostic factors Tumor type Kuthi L et al. Pathol Oncol Res Jul;23(3):
65 VI. Tumors of the kidney Prognostic factors Stage pt: pt1 tumor 7 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the kidney (pt1a 4 cm, pt1b >4 cm) pt2 tumor >7 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the kidney (pt2a 10 cm, pt2b >10 cm) pt3 tumor extends into major veins (renal vein, VCI) or perinephric tissues (ERE) (pt3a renal vein invasion and/or ERE, pt3b VCI invasion below diaphragm, pt3c VCI invasion above diaphragm) pt4 tumor invades beyond the Gerota fascia (including contiguous extension into the ipsilateral adrenal gland)
66 VI. Tumors of the kidney Prognostic factors Grade: Fuhrman grade/isup grade Clear cell RCC, papillary RCC
67 VI. Tumors of the kidney Prognostic factors Grade: Fuhrman grade/isup grade Kuthi L et al. Pathol Oncol Res Jul;23(3):
68 VI. Tumors of the kidney Prognostic factors Kuthi L et al. Pathol Oncol Res Jul;23(3):
69 VI. Tumors of the kidney Clinical features 1. Symptomes Costovertebral pain Hematuria Palpable mass Fever (FUO) Weight loss Malaise Paraneoplastic syndromes (polycythemia, hypercalcemia, hypertension, hepatic dysfunction, feminization, masculinization, Cushing syndrome, eosinophilia, leukemoid reaction, amyloidosis) Symptomes of metastases (any organ can be affected)
70 VI. Tumors of the kidney Clinical features 2. Diagnostics Majority of renal tumors are discovered incidentally by abdominal imaging US, CT, MR Preoperative diagnostics: FNAB, core biopsy (US- or CT-guided)
71 VI. Tumors of the kidney Clinical features 3. Treatment Partial (pt1 tumors) or radical nephrectomy (open or laparoscopic surgery) Targeted therapy (metastatic cases): sunitinib,
72 Acknowledgement Eszter Székely For a subset of the pictures
Renal tumors of adults
 Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
Renal tumors of adults Urinary Tract Tumors 2%-3% of all cancers in adults. The most common malignant tumor of the kidney is renal cell carcinoma. Tumors of the lower urinary tract are twice as common
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder
 Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney.
 Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult. by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department
 Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology. Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford
 Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney:
 Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES
 DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Urological Tumours 1 Kidney tumours 2 Bladder tumours
 Urological Tumours 1 Kidney tumours 2 Bladder tumours Tim Bracey SpR Histopathology Derriford Hospital Kidney tumours What are we going to talk about?! Anatomy of urinary tract! Types of kidney tumours!
Urological Tumours 1 Kidney tumours 2 Bladder tumours Tim Bracey SpR Histopathology Derriford Hospital Kidney tumours What are we going to talk about?! Anatomy of urinary tract! Types of kidney tumours!
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM
 DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22
 Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms
 Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms د. BENIGN TUMORS : Benign renal tumors include adenoma, oncocytoma, angiomyolipoma, leiomyoma, lipoma, hemangioma, and juxtaglomerular tumors. Renal Adenomas : The adenoma is
Renal Parenchymal Neoplasms د. BENIGN TUMORS : Benign renal tumors include adenoma, oncocytoma, angiomyolipoma, leiomyoma, lipoma, hemangioma, and juxtaglomerular tumors. Renal Adenomas : The adenoma is
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Dr. Najla a Aldaoud. Omar Ayman Khasawneh
 Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers.!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1
 !! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
!! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
Table of Contents: OVERVIEW AND INTRODUCTION. Imaging Approaches RETROPERITONEUM. Introduction to the Retroperitoneum
 Table of ontents: OVERVIEW AND INTRODUTION Imaging Approaches RETROPERITONEUM Introduction to the Retroperitoneum Duplications and Anomalies of IV Inflammati Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Deg Pelvic Lipomatosis
Table of ontents: OVERVIEW AND INTRODUTION Imaging Approaches RETROPERITONEUM Introduction to the Retroperitoneum Duplications and Anomalies of IV Inflammati Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Deg Pelvic Lipomatosis
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
27-Apr-15 1 UAF ANOMALIES OF DEVELOPMENT RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED UAF UAF
 RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
RENAL SYSTEM - 1 DR. MUHAMMAD TARIQ JAVED Professor, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk RENAL AGENESIS Renal
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia. David Bingham MD
 Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia David Bingham MD typical malignant cytology of bladder washings 1 benign 2 malignant typical malignant cytology of bladder washings b Bladder tumor Non invasive papillary
Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia David Bingham MD typical malignant cytology of bladder washings 1 benign 2 malignant typical malignant cytology of bladder washings b Bladder tumor Non invasive papillary
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System
 A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
CLASSIFICATION OF RENAL DISEASE
 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Adelaide University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Adelaide University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Case Based Learning Program
 Case Based Learning Program The Department of Urology Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic Case Number 5 CBULP 2010 001 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editor:
Case Based Learning Program The Department of Urology Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic Case Number 5 CBULP 2010 001 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editor:
CT Imaging of the Kidney
 September 2001 CT Imaging of the Kidney Images: Netter, FH: Atlas of Human Anatomy, 2 nd ed. Novartis, 1997 Anthony Powell, HMS IV Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Images: BIDMC, Dept of Radiology,
September 2001 CT Imaging of the Kidney Images: Netter, FH: Atlas of Human Anatomy, 2 nd ed. Novartis, 1997 Anthony Powell, HMS IV Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Images: BIDMC, Dept of Radiology,
What s New in Pathology of Genitourinary Tumors. Jiaoti Huang, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Duke University School of Medicine
 What s New in Pathology of Genitourinary Tumors Jiaoti Huang, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Duke University School of Medicine Kidney Tumors Multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential
What s New in Pathology of Genitourinary Tumors Jiaoti Huang, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Duke University School of Medicine Kidney Tumors Multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential
Renal Disease. Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs
 Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
 Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) Introduction The most common solid renal tumor. Accounts for 2 3% of all adult malignancies. It is the 3 rd most common urological tumor in men and the 2 nd in women. It is th
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) Introduction The most common solid renal tumor. Accounts for 2 3% of all adult malignancies. It is the 3 rd most common urological tumor in men and the 2 nd in women. It is th
Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Case 1. Clinical history
 Case 1 Case 1 Clinical history 17-month-old boy with a kidney tumor found during routine childhood care program. CT scan showed a solid mass. Chemotherapy was given for 4 weeks using actinomycin D and
Case 1 Case 1 Clinical history 17-month-old boy with a kidney tumor found during routine childhood care program. CT scan showed a solid mass. Chemotherapy was given for 4 weeks using actinomycin D and
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Genetics & Imaging Srinivasa R Prasad University of Texas San Antonio
 Renal Cell Carcinoma: Genetics & Imaging Srinivasa R Prasad University of Texas HSC @ San Antonio No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Dr. Peter Choyke, NIH My Gurus @ MIR, MGH 2004 WHO Taxonomy of
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Genetics & Imaging Srinivasa R Prasad University of Texas HSC @ San Antonio No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Dr. Peter Choyke, NIH My Gurus @ MIR, MGH 2004 WHO Taxonomy of
Clinicopathologic Conference
 Participants: Mohammed Akhtar, MD*, Nabil Bissada, MD and William Cumming, MD Editor. John T. Godwin, MD, FCAP * Director, Electron Microscopy Section, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine;
Participants: Mohammed Akhtar, MD*, Nabil Bissada, MD and William Cumming, MD Editor. John T. Godwin, MD, FCAP * Director, Electron Microscopy Section, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine;
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline. Anatomy Coverings. Location. (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%)
 Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%) Anatomy Coverings true capsule perirenal fat surrounds capsule Gerota s fascia separates perirenal from extraperitoneal fat
Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%) Anatomy Coverings true capsule perirenal fat surrounds capsule Gerota s fascia separates perirenal from extraperitoneal fat
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain
 December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
Urinary tract pathology Renal syndromes Acute nephritic syndrome syndrome includes oliguria hematuria proteinuria edema hypertension typically occurs
 Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
RENAL NEOPLASMS: NEW ENTITIES & DIFFICULT DIAGNOSES
 RENAL NEOPLASMS: NEW ENTITIES & DIFFICULT DIAGNOSES Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Anatomic Pathology Kidney Tumors American Cancer Society Cancer Facts and Figures
RENAL NEOPLASMS: NEW ENTITIES & DIFFICULT DIAGNOSES Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Anatomic Pathology Kidney Tumors American Cancer Society Cancer Facts and Figures
Guidelines on Renal Cell
 Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma (Text update March 2009) B. Ljungberg (Chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction Renal cell carcinoma
Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma (Text update March 2009) B. Ljungberg (Chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction Renal cell carcinoma
Role of MDCT in Radiological evaluation of Renal Masses and its beneficial effects on patient management.
 International Journal of advances in health sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol2, Issue1, 2015, pp56-63 http://www.ijhsonline.com Research Article Role of MDCT in Radiological evaluation of Renal Masses
International Journal of advances in health sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol2, Issue1, 2015, pp56-63 http://www.ijhsonline.com Research Article Role of MDCT in Radiological evaluation of Renal Masses
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency
 Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder)
 Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
EDUCATIONAL CASES E1 & E2. Natasha Inglis 20/03/15
 EDUCATIONAL CASES E1 & E2 Natasha Inglis 20/03/15 CASE E1 79 year old female Rectum. Altemeier operation Histology Superficial erosions and mucosal congestion volcano lesion and pseudomembrane formation
EDUCATIONAL CASES E1 & E2 Natasha Inglis 20/03/15 CASE E1 79 year old female Rectum. Altemeier operation Histology Superficial erosions and mucosal congestion volcano lesion and pseudomembrane formation
SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS
 SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS NORMAL SMOOTH MUSCLE Cytology Immunohistochemistry Ultrastructure Masson Trichrome Smooth Muscle Ultrastructure Many myofilaments running parallel to the long axis of the smooth
SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS NORMAL SMOOTH MUSCLE Cytology Immunohistochemistry Ultrastructure Masson Trichrome Smooth Muscle Ultrastructure Many myofilaments running parallel to the long axis of the smooth
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Diseases of the Kidney. Janos Vasko
 Diseases of the Kidney Janos Vasko Congenital anomalies Glomerular diseases Tubulointerstitial diseases Infections Vascular diseases Stones Tumours POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE INFANTILE TYPE ADULT TYPE Autosomal
Diseases of the Kidney Janos Vasko Congenital anomalies Glomerular diseases Tubulointerstitial diseases Infections Vascular diseases Stones Tumours POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE INFANTILE TYPE ADULT TYPE Autosomal
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL
 Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD. Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K.
 PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K. RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD - CLASSIFICATION (2016) Nephroblastic tumours Mesenchymal tumours
PITFALLS AND TRAPS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING OF RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD Gordan M. Vujanić Cardiff, U.K. RENAL TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD - CLASSIFICATION (2016) Nephroblastic tumours Mesenchymal tumours
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
Updated Classification of Renal cell carcinoma
 Updated Classification of Renal cell carcinoma Suchin Worawichawong, M.D., FRCPath (Thailand) Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Incidence: Global: 338,000 new cases, 130,000
Updated Classification of Renal cell carcinoma Suchin Worawichawong, M.D., FRCPath (Thailand) Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Incidence: Global: 338,000 new cases, 130,000
Systemic Hypertension
 BCS Theme Session Cardiovascular Block Pathology of Hypertension Department of Pathology University of Sydney Systemic Hypertension Definition of Systemic hypertension: consistent blood pressure elevation
BCS Theme Session Cardiovascular Block Pathology of Hypertension Department of Pathology University of Sydney Systemic Hypertension Definition of Systemic hypertension: consistent blood pressure elevation
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
04/10/2018. What s new in renal tumor pathology what s important and why. Prognostic factors in RCC
 25th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA, April 26-29, 2018 What s new in renal tumor pathology what s important and why Kiril Trpkov, MD FRCPC Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine kiril.trpkov@cls.ab.ca
25th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA, April 26-29, 2018 What s new in renal tumor pathology what s important and why Kiril Trpkov, MD FRCPC Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine kiril.trpkov@cls.ab.ca
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018
 Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
1. Congenital Anomalies of Kidney and Ureter 1
 CONTENTS 1. Congenital Anomalies of Kidney and Ureter 1 1.1 Antenatal Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction 1 1.2 Bilateral Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction 3 1.3 Circumcaval Ureter 6 1.4 Crossed Renal
CONTENTS 1. Congenital Anomalies of Kidney and Ureter 1 1.1 Antenatal Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction 1 1.2 Bilateral Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction 3 1.3 Circumcaval Ureter 6 1.4 Crossed Renal
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
ESRD Dialysis Prevalence - One Year Statistics
 Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Kidney 1 Questions Please use the Q&A panel to submit your questions Send questions to All Panelist 2 Fabulous Prizes 3 NAACCR 2009 2010 Webinar
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
IMMUNOPROFILES OF THE MAJOR RENAL NEOPLASMS (%staining)
 Stain Clear Cell Papillary IMMUNOPROFILES OF THE MAJOR RENAL NEOPLASMS (%staining) Chromophobe Collecting Duct Carcinom a Sarcomatoid Xp11 Translocat ion Dr Jon Oxley See also www.jonoxley.com Page 1 MTSCC
Stain Clear Cell Papillary IMMUNOPROFILES OF THE MAJOR RENAL NEOPLASMS (%staining) Chromophobe Collecting Duct Carcinom a Sarcomatoid Xp11 Translocat ion Dr Jon Oxley See also www.jonoxley.com Page 1 MTSCC
Renal Masses in Patients with Known Extrarenal Primary Primary Cancer Primary Primary n Met Mets s RCC Beni L mphoma Lung Breast Others
 The Importance of Stuart G. Silverman, MD, FACR Professor of Radiology Harvard ard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA The Importance of
The Importance of Stuart G. Silverman, MD, FACR Professor of Radiology Harvard ard Medical School Director, Abdominal Imaging and Intervention Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA The Importance of
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD. Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018
 Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Nephrology Case Presentation for PCKD Douglas A. Stahura 24 January 2002 With update 2018 Case Presentation l 48 y/o WM presents with back pain Sharp, over L side/ribs Intermittent but severe 8/10 No radiation
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Kidney & Urinary Tract Neoplasms. Jaroslava Dušková Inst. Pathol.,1st Med. Faculty, Charles Univ. Prague
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Neoplasms Jaroslava Dušková Inst. Pathol.,1st Med. Faculty, Charles Univ. Prague Kidney & Urinary Tract Neoplasms - contents Kidney cancer epidemiology clinical symptoms classification
Kidney & Urinary Tract Neoplasms Jaroslava Dušková Inst. Pathol.,1st Med. Faculty, Charles Univ. Prague Kidney & Urinary Tract Neoplasms - contents Kidney cancer epidemiology clinical symptoms classification
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Problematic Renal Mass. Vikas Kundra, M.D., Ph.D.
 Problematic Renal Mass Vikas Kundra, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose. I WILL include discussion of investigational or off-label use of a product in my presentation.
Problematic Renal Mass Vikas Kundra, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose. I WILL include discussion of investigational or off-label use of a product in my presentation.
Pathology of Kidney Disorders
 Pathology of Kidney Disorders Anatomy-Kidney Components of Glomerulus: Capillary basement membrane Mesangium Bowman capsule Cells Endothelial Epithelial Mesangial Anatomy of Kidney Anatomic Compartments
Pathology of Kidney Disorders Anatomy-Kidney Components of Glomerulus: Capillary basement membrane Mesangium Bowman capsule Cells Endothelial Epithelial Mesangial Anatomy of Kidney Anatomic Compartments
Renal Neoplasia: Diagnostic Problems and Recently Recognized Entities
 Renal Neoplasia: Diagnostic Problems and Recently Recognized Entities John N. Eble, M.D. Department Pathology Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN Holger Moch, M.D. Department Pathology University Hospital
Renal Neoplasia: Diagnostic Problems and Recently Recognized Entities John N. Eble, M.D. Department Pathology Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN Holger Moch, M.D. Department Pathology University Hospital
Renal Cancer. By Jamie Calderwood
 Renal Cancer By Jamie Calderwood ("Kidney Cancer")*1 ("What are the different types of kidney mass?")*2 What is it? Renal cancer is more commonly known as kidney cancer. Wilms tumor Another name for kidney
Renal Cancer By Jamie Calderwood ("Kidney Cancer")*1 ("What are the different types of kidney mass?")*2 What is it? Renal cancer is more commonly known as kidney cancer. Wilms tumor Another name for kidney
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
