Diagnostic difficulties of primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report
|
|
|
- Pearl Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 CASE REPORT Diagnostic difficulties of primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report Youssef Mahdi 1,2*, Lamiaa Rouas 1,2, Abderrahmane Malihy 1, Najat Lamalmi 1,2 and Zaitouna Alhamany 1,2 Open Access Abstract Background: Angiosarcoma of the breast is a rare tumor, which may be primary or secondary to breast surgery or irradiation. It is characterized by polymorphic and nonspecific clinical and radiological features. A pathologist plays a key role in positive and differential diagnosis and in establishing the prognosis: only a histological examination can confirm the diagnosis, and the histologic grade is the most important prognostic factor. In fact, angiosarcomas of the breast constitute a very heterogeneous group and they are classified into three grades based on the degree of differentiation. We will illustrate diagnostic challenges through this new case of primary angiosarcoma of the breast. Microscopic findings were initially interpreted as a benign vascular tumor. We will also discuss the relevant medical literature. Case presentation: A 56-year-old Arabian woman presented with a palpable right breast mass that had been enlarging for 2 months, measuring 5 cm, without axillary lymphadenopathy. She had no personal or family history of breast surgery or breast irradiation. A mammography showed no evidence of spiculation. No suspicious calcifications were seen. A needle core biopsy was performed. Microscopic findings were initially interpreted as a benign vascular tumor. However, as the mass measured 5 cm, the diagnosis of angiosarcoma was more appropriate, and mastectomy without axillary dissection was performed. Microscopic examination found mild to moderately scattered pleomorphic cells, and scattered mitotic figures. It also showed papillary formations, solid foci of spindle cells, and hemorrhagic necrosis. The margins of the tumor were infiltrative. The diagnosis of primary intermediately differentiated angiosarcoma of the breast (grade II) was made. No distant metastases were found. Our patient was lost to follow-up and further treatment after mastectomy until she developed local tumor progression 4 months later. Conclusions: Through this case report, we emphasize the importance of clinicopathological confrontation in angiosarcoma of the breast. Keywords: Angiosarcoma, Breast, Pathology, Case report Background Angiosarcoma of the breast is a rare tumor. It is defined by the World Health Organization as a malignant tumor showing endothelial differentiation [1]. It can be either primary or secondary to breast tissue irradiation or chronic lymphedema after mastectomy [1 4]. It is characterized by polymorphic and nonspecific clinical and radiological features causing diagnostic errors. Thus, a pathologist plays a key role in positive and differential diagnosis. A pathologist also plays a major role in * Correspondence: ysf.mahdi@gmail.com 1 Department of Pathology, Gyneco-Obstetric and Pediatric Hospital, Ibn Sina University Hospital, Rabat, Morocco 2 Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Mohammed V University of Rabat, Rabat, Morocco establishing the prognosis by determining the grade. In fact, angiosarcomas of the breast are a heterogeneous group in which the grade is the most important prognostic factor. We will illustrate diagnostic challenges through this new case of primary angiosarcoma of the breast. Microscopic findings were initially interpreted as a benign vascular tumor. We will also discuss the relevant medical literature. Case presentation A 56-year-old Arabian woman presented to our institution with a palpable right breast mass (Fig. 1). Two months prior to presentation she complained of a painless right breast lump that quickly increased in size with bluish coloration of overlying skin. She had no personal The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 Page 2 of 6 or family history of cancer, breast surgery, or breast irradiation. A physical examination revealed a 5 cm ill-defined painless mass that overlapped two upper quadrants. The mass was firm and fixed to the skin which was bluish without ulceration. There was no nipple retraction, no axillary lymphadenopathy, and no signs of lymphedema. A mammography showed no evidence of spiculation. No suspicious calcifications were seen. A needle core biopsy was performed and showed anastomosing round-to-oval spaces which contained erythrocytes. Lining cells had thin, elongated but hyperchromatic nuclei, which sometimes protruded into the luminal spaces. The neoplastic vascular channels invaded adipose tissue. Immunohistochemical stains performed on the core biopsy revealed membranous reactivity of the tumor cells for CD31-related antigen and CD34-related antigen. These findings were initially interpreted as a benign vascular tumor. However, as the mass measured 5 cm, the diagnosis of angiosarcoma was more appropriate. A mastectomy without axillary dissection was performed since angiosarcoma was suspected. At gross examination, the tumor appeared ill-defined, spongy, and soft (Fig. 2). A microscopic examination revealed vascular channels lined by atypical endothelial cells with hyperchromatic, spindle-shaped or round nuclei (Fig. 3). There were mild to moderately scattered pleomorphic cells, and scattered mitotic figures (Fig. 4). Other sections showed papillary formations, solid foci of spindle cells, and hemorrhagic necrosis (Figs. 5 and 6). The margins of the tumor were infiltrative (Fig. 7). The diagnosis of primary intermediately differentiated angiosarcoma of the breast (grade II) was made. No distant metastases were found. She was lost to follow-up and further treatment after mastectomy until she developed local tumor progression 4 months later. Discussion and conclusions In terms of breast cancer, invasive carcinoma is by far the most common type. Angiosarcoma of the breast is a rare tumor; it accounts for 0.04% of all primary malignancies of the breast [1, 2, 5 7]. In our case, there was no axillary lymphadenopathy. The mammography showed no evidence of spiculation or suspicious calcifications. A biopsy showed anastomosing vascular spaces. Lining cells were almost bland. These results can be interpreted as a benign lesion. However, this did not correlate with the radiologic findings: 5 cm mass with ill-defined margins. Itmaybeprimaryorsecondarytobreastsurgeryor irradiation. Primary (de novo) angiosarcoma usually occurs in younger women [2, 5, 8] with an average age of 40 years [1, 8] compared to 67.5 years in secondary angiosarcoma [8]. The factors involved in carcinogenesis of primary angiosarcoma are exposure to vinyl chloride, arsenic and Thorotrast (thorium dioxide), chronic irritation induced by a foreign body, and local trauma [5]. Secondary angiosarcoma may occur in the skin and chest wall following radical mastectomy and local radiotherapy, and in the skin and breast parenchyma following breast conserving surgery and radiotherapy [1]. Furthermore, secondary angiosarcoma may occur in the skin and soft tissues of the arm following radical mastectomy and subsequent lymphedema (axillary dissection) [1]. Medical History 06/2015 First Admission 15/08/2015 Painless breast mass fastly increasing in size (2 months) Bluish coloration of overlying skin No history of cancer, breast surgery or breast irradiation Physical examination: a 5 cm ill-defined painless mass that overlaps two upper quadrants. It was firm and fixed to the skin. There was no axillary lymphadenopathy and no signs of lymphedema Mammography 20/08/2015 Biopsy 22/08/2015 Mastectomy 30/08/2015 Last Admission 02/01/2016 No evidence of spiculations and no suspicious calcifications Vascular tumor, without histological criteria of malignancy As the mass measured 5 cm, the diagnosis of angiosarcoma was more appropriate Diagnosis: intermediately differentiated angiosarcoma of the breast (grade II) Radiotherapy indicated (not received) Patient lost for follow-up Local tumour progression 4 months after removal Fig. 1 Case report timeline
3 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 Page 3 of 6 Fig. 2 Macroscopic appearance of the breast tumor: It is an ill-defined mass with hemorrhagic appearance It is manifested by a painless mass [2, 5, 6], sometimes with a pulsating character [5]. The overlying skin may have a bluish red discoloration, and there is no nipple retraction [2]. Axillary lymph node involvement is uncommon (0 to 5% of cases) [5] orevenabsent[2]. Mammography shows large, dense, and homogeneous mass, with sharp and sometimes polylobated contours [7]. There are no calcifications [5, 7] or spiculation whichareoftenseeninbreastcarcinomas[2, 5]. On sonography, angiosarcoma appears as a heterogeneous lesion [5, 7] with both hyperechoic and hypoechoic appearance [2, 7]. Hypoechoic areas represent hemorrhagic or necrotic changes [7]. Color Doppler sonography reveals marked hypervascularity of the lesion [5, 7]. This hypervascular character is confirmed by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging with intravenously administered contrast injection [7]. The signal on T2-weighted image is hyperintense [2, 5, 7], suggesting the presence of vascular channels containing slow flowing blood [2]. The tumors are deeply located in the breast parenchyma [1]. Size is always > 2 cm [5] and usually > 4 cm [2]. It is reported that 12% of patients present with diffuse breast enlargement [1]. In some cases, diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration cytology and needle core biopsy may be difficult. Chen et al. reported a percutaneous biopsy false-negative rate of 37% [9]. Given the vascular nature of these tumors, macrobiopsy is often difficult to perform, hence the need for surgical resection [2]. On macroscopic examination, angiosarcomas have a spongy hemorrhagic appearance with ill-defined borders [1]. Poorly differentiated tumors appear as a solid fibrous lesion [1]. Only a histological examination can confirm the diagnosis. Three groups are defined according to the classification proposed by Donnell et al. [10]. Grade I (well differentiated) contains open anastomosing vascular channels invading the breast fat and parenchyma. A single layer of endothelial cells lines these channels. The nuclei of the endothelial cells may be hyperchromatic. Solid areas of spindle cells, hemorrhage (known as blood lakes ), and necrosis are not present. In grade II (intermediately differentiated) 75% of the tumor is composed of the well-differentiated pattern seen in grade I, but there are additional solid cellular foci or papillary formations scattered throughout the tumor. Slightly increased mitotic activity is present. In grade III, solid areas of spindle cells and papillary formations are prominent. Mitoses are common. Areas of hemorrhage and necrosis are also seen. The constituent cells show immunoreactivity for endothelial markers: CD31, CD34, and factor VIII [1, 6]. CD31 remains the most sensitive and the most specific endothelial cell marker. The role of immunohistochemical study is to confirm the vascular nature of tumor proliferation. For grade I and II breast angiosarcoma, the differential diagnosis includes intramammary hemangioma, angiomatosis, and pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia Fig. 3 Representative micrograph of the breast tumor. Anastomosing vascular channels contain erythrocytes. Hematoxylin-eosin; a 100, b 200
4 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 Page 4 of 6 Fig. 4 Representative micrograph of the breast tumor. Vascular channels are lined by atypical endothelial cells with hyperchromatic, spindle-shaped or round nuclei (hematoxylin-eosin 400) Fig. 6 Representative micrograph of the breast tumor. There are also solid areas of spindle cells which invade adipose tissue (hematoxylin-eosin 40) (PASH) [4], especially in a core biopsy. Hemangioma is usually 2 cm or less and is sharply defined [4]. Angiomatosis is a diffuse angioma with hemangioma and lymphangioma-like channels growing diffusely in breast tissue but sparing lobules and without nuclear atypia. Unlike angiomatosis, angiosarcoma infiltrates and dissociates breast lobules [4]. PASH is a benign lesion comprising stromal myofibroblastic proliferation and having the appearance of anastomosing slit-like pseudovascular spaces lined by spindle-shaped cells [11]. These spaces do not contain red cells, and have a perilobular concentric arrangement with a densely collagenous stroma [4]. There is no destruction of the normal breast tissue, no necrosis, and no fat invasion [11]. The myofibroblasts in PASH are positive for CD34 but are negative for factor VIII and CD31 [4, 11]. The differential diagnosis of grade I and II breast angiosarcoma is summarized in Table 1. For grade III, sarcomatoid carcinoma and other types of high-grade sarcomas should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, hence the necessity of cytokeratin antibodies and endothelial markers [4]. The differential diagnosis of poorly differentiated angiosarcoma is summarized in Table 2. Angiosarcoma is an aggressive malignancy with high recurrence rates and poor overall survival [12]. According to Rosen and colleagues study [13], grade is an important prognostic factor. In fact, the 5 years disease-free survival rate was 76%, 70%, and 15% for grade I, grade II, and grade III tumors, respectively. Primary tumor size was not Fig. 5 Representative micrograph of the breast tumor. There are papillary formations (hematoxylin-eosin 100) Fig. 7 Anastomosing vascular channels in dense collagenous stroma engulfing breast elements (arrow). Hematoxylin-eosin 100
5 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 Page 5 of 6 Table 1 Differential diagnosis of grade I (well-differentiated) and grade II (intermediately differentiated) angiosarcomas of the breast Lesion Grade I angiosarcoma PASH Hemangioma Angiomatosis Size Always > 2 cm Variable < 2 cm Diffuse Anastomosing spaces True vascular channels contain erythrocytes Pseudovascular spaces, without erythrocytes True vascular channels contain erythrocytes True vascular channels contain erythrocytes Destruction of adjacent breast tissue, invasion of fat Yes No No No Dense hyaline stroma Absent Present Absent Absent Lining cells Atypical with prominent and hyperchromatic nuclei Without atypia (very rarely atypia and hyperchromasia) Without atypia Without atypia Factor VIII and CD31 Positive Negative Positive Positive PASH pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia Data in boldface: characteristic criteria for the differential diagnosis significantly related to the risk of recurrence or to survival. In contrast, Zelek et al. [14], by reviewing eight cases of breast angiosarcoma, found that the tumor size was correlated with the rate of disease-free survival at 10 years. The prognosis was even worse when the tumor size was greater than 10 cm. Primary angiosarcoma of the breast gives metastasis mainly to lungs, liver, bones, skin, and the contralateral breast [1, 2]. There are no treatment standards for breast angiosarcomas because of their rarity [2]. However, treatment is primarily surgical. Mastectomy with negative margins is the recommended treatment [2, 5], without axillary dissection [5, 6]. Complementary radiation therapy is necessary in case of tumorectomy [5]. Adjuvant radiation and chemotherapy improve survival outcomes in patients with tumor size > 5 cm [14, 15]. Chemotherapy is beneficial in high-grade lesions [3, 6] and in the metastatic setting [3]. Recently, with the exploitation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A and VEGF-C and the receptor VEGF-R1, anti-angiogenic treatment is certainly a highly promising therapeutic approach [2, 5]. Through this case report, we emphasize the importance of clinicopathological confrontation in angiosarcoma of the breast. This is especially true in cases of biopsy showing a well-differentiated angiosarcoma. It poses a problem of differential diagnosis with benign Table 2 Differential diagnosis of grade III (poorly differentiated) angiosarcoma of breast Grade III angiosarcoma Sarcomatoid carcinoma Other type of high-grade sarcomas Endothelial Positive Negative Negative markers Cytokeratin Negative Positive Negative Data in boldface: characteristic criteria for the differential diagnosis vascular pathology. It has a poor prognosis and presents therapeutic management difficulties. Abbreviations PASH: Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor Authors contributions YM analyzed and interpreted the patient data, drafted the manuscript, and made the figures. LR and NL performed the histological examination. LR proposed the study, supervised YM, and revised the manuscript. AM, NL, and ZA provided valuable insight during manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable for this section. Consent for publication Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 17 July 2017 Accepted: 9 July 2018 References 1. Fletcher CDM, MacGrogan G, Fox SB. Angiosarcoma. In: Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours of the breast. Lyon: IARC; p Bhosale SJ, Kshirsagar AY, Patil MV, Wader JV, Nangare N, Patil PP. Primary angiosarcoma of breast: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2013;4(4): Wang XY, Jakowski J, Tawfik OW, Thomas PA, Fan F. Angiosarcoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic analysis of cases from the last 10 years. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009;13(3): Mac Grogan G, Vincent-Salomon A, Arnould L. Angiosarcoma of the breast, Postgraduate teaching of breast pathology; p Champeaux-Orange E, Bonneau C, Raharimanana B, Favre A, Ibrahim M, Breteau N. Primary breast angiosarcoma: two case reports. Cancer Radiother. 2009;13(3): Georgiannos SN, Sheaff M. Angiosarcoma of the breast: a 30 year perspective with an optimistic outlook. Br J Plast Surg. 2003;56(2):
6 Mahdi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:228 Page 6 of 6 7. Chapiron C, Adjenou V, Arbion F, Potin J, Asquier E, Brunereau L. Breast angiosarcoma: sonographic, mammographic and MRI features. J Radiol. 2004;85(12 Pt 1): Hui A, Henderson M, Speakman D, Skandarajah A. Angiosarcoma of the breast: a difficult surgical challenge. Breast. 2012;21(4): Chen KT, Kirkegaard D, Bocian J. Angiosarcoma of the breast. Cancer. 1980; 46(2): Donnell RM, Rosen PP, Lieberman PH, Kaufman RJ, Kay S, Braun DW, Kinne DW. Angiosarcoma and other vascular tumors of the breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1981;5(7): Michal M, Badve S, Shin SJ. Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia. In: Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours of the breast. Lyon: IARC; p Ghareeb ER, Bhargava R, Vargo JA, Florea AV, Beriwal S. Primary and radiation-induced breast angiosarcoma: clinicopathologic predictors of outcomes and the impact of adjuvant radiation therapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2016;39(5): Rosen PP, Kimmel M, Ernsberger D. Mammary angiosarcoma: the prognostic significance of tumor differentiation. Cancer. 1988;62(10): Zelek L, Llombart-Cussac A, Terrier P, Pivot X, Guinebretiere JM, Le Pechoux C, Tursz T, Rochard F, Spielmann M, Le Cesne A. Prognostic factors in primary breast sarcomas: a series of patient with long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(13): Yin M, Mackley HB, Drabick JJ, Harvey HA. Primary female breast sarcoma: clinicopathological features, treatment and prognosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31497.
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report
 Bennani et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:66 CASE REPORT Open Access Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report Amal Bennani 1*, Layla Chbani 1, Meryem Lamchahab 1, Mouhcine Wahbi 2, Fatimazzahra
Bennani et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:66 CASE REPORT Open Access Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report Amal Bennani 1*, Layla Chbani 1, Meryem Lamchahab 1, Mouhcine Wahbi 2, Fatimazzahra
ISPUB.COM. Breast Angiosarcoma. C Lilaia, F Pereira, S André, B Cabrita INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 6 Number 2 C Lilaia, F Pereira, S André, B Cabrita Citation C Lilaia, F Pereira, S André, B Cabrita.. The Internet Journal of Gynecology
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics Volume 6 Number 2 C Lilaia, F Pereira, S André, B Cabrita Citation C Lilaia, F Pereira, S André, B Cabrita.. The Internet Journal of Gynecology
Diagnosis of Fibroepithelial and Mesenchymal Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy
 Diagnosis of Fibroepithelial and Mesenchymal Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy Emmanuel Agosto-Arroyo, MD Assistant Member Department of Anatomic Pathology 3/3/2018 Disclosure There are no conflicts of interest.
Diagnosis of Fibroepithelial and Mesenchymal Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy Emmanuel Agosto-Arroyo, MD Assistant Member Department of Anatomic Pathology 3/3/2018 Disclosure There are no conflicts of interest.
A case report of primary breast angiosarcoma with fatal pulmonary hemorrhage due to thrombocytopenia
 J Korean Surg Soc 2012;82:251-255 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.4.251 CASE REPORT JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 A case report of primary breast
J Korean Surg Soc 2012;82:251-255 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.4.251 CASE REPORT JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 A case report of primary breast
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Primary Angiosarcoma of the Breast: A Case Report Korean Breast Cancer Society. All rights reserved.
 CASE REPORT J Breast Dis 2018 December; 6(2): 73-78 JBD Journal of Breast Disease Primary Angiosarcoma of the Breast: A Case Report Ra Mi Kim, Hunkyoung Lee 1, Heebong Park 2 Kangnam Women s Hospital,
CASE REPORT J Breast Dis 2018 December; 6(2): 73-78 JBD Journal of Breast Disease Primary Angiosarcoma of the Breast: A Case Report Ra Mi Kim, Hunkyoung Lee 1, Heebong Park 2 Kangnam Women s Hospital,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Case Report Rare Presentation of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: A Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 331549, 5 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.331549 Case Report
IBIMA Publishing International Journal of Case Reports in Medicine http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/ijcrm/ijcrm.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 331549, 5 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.331549 Case Report
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report
 Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
American Journal of Cancer Case Reports. Invasive Papillary Carcinoma of Male Breast: A Rare Case Report
 American Journal of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr SantraAetal. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:56-61 Page 1 of 6 Vol 3 Article ID 20140617, 6 pages Case Report
American Journal of Cancer Case Reports http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr SantraAetal. American Journal of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:56-61 Page 1 of 6 Vol 3 Article ID 20140617, 6 pages Case Report
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Case Report Primary angiosarcoma of the breast: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2019;12(2):664-668 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085147 Case Report : a case report Soyoung Im 1, Byung Joo Chae 2, Sung Hun Kim 3, Bong-Joo Kang 3, Byung Joo Song 4, Ahwon
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2019;12(2):664-668 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085147 Case Report : a case report Soyoung Im 1, Byung Joo Chae 2, Sung Hun Kim 3, Bong-Joo Kang 3, Byung Joo Song 4, Ahwon
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Koebner Phenomenon in Radiation Associated Angiosarcoma of the Breast: Linear Metastasis in Split Skin Graft Donor Site
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Koebner Phenomenon in Radiation Associated Angiosarcoma of the Breast: Linear Metastasis in Split Skin Graft Donor Site A Chhabra, A Goyal, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Koebner Phenomenon in Radiation Associated Angiosarcoma of the Breast: Linear Metastasis in Split Skin Graft Donor Site A Chhabra, A Goyal, R
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
A rare case of rapidly progressing angiosarcoma of the breast with multiple metastases to the bone, liver, ovary, and gingiva
 Int Canc Conf J (2012) 1:159 163 DOI 10.1007/s13691-012-0032-3 CASE REPORT A rare case of rapidly progressing angiosarcoma of the breast with multiple metastases to the bone, liver, ovary, and gingiva
Int Canc Conf J (2012) 1:159 163 DOI 10.1007/s13691-012-0032-3 CASE REPORT A rare case of rapidly progressing angiosarcoma of the breast with multiple metastases to the bone, liver, ovary, and gingiva
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions. Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea
 Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT
 Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series
 18 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 18-23 Open Access Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series W.A. Donk *, R.J. Oostenbroek, R.K.
18 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 18-23 Open Access Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up; Description of a Case-Series W.A. Donk *, R.J. Oostenbroek, R.K.
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall
 Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Primary Stromal Sarcoma of Breast: A Rare Entity
 Case Report Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(5): 469-473: (Special Issue for Case Reports) Iranian Journal of Pathology ISSN: 2345-3656 Primary Stromal Sarcoma of Breast: A Rare Entity Sanjay Kumar, Jyoti Sharma*,
Case Report Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(5): 469-473: (Special Issue for Case Reports) Iranian Journal of Pathology ISSN: 2345-3656 Primary Stromal Sarcoma of Breast: A Rare Entity Sanjay Kumar, Jyoti Sharma*,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Pleomorphic adenoma of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari
 of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
Mousa. Israa Ayed. Abdullah AlZibdeh. 0 P a g e
 1 Mousa Israa Ayed Abdullah AlZibdeh 0 P a g e Breast pathology The basic histological units of the breast are called lobules, which are composed of glandular epithelial cells (luminal cells) resting on
1 Mousa Israa Ayed Abdullah AlZibdeh 0 P a g e Breast pathology The basic histological units of the breast are called lobules, which are composed of glandular epithelial cells (luminal cells) resting on
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Brief History. Identification : Past History : HTN without regular treatment.
 Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS. Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions
 SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
Invasive cystic hypersecretory carcinoma of the breast: a rare variant of breast cancer: a case report and review of the literature
 Sun et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5260-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Invasive cystic hypersecretory carcinoma of the breast: a rare variant of breast cancer: a case report
Sun et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5260-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Invasive cystic hypersecretory carcinoma of the breast: a rare variant of breast cancer: a case report
Malignant Phyllodes tumor with necrosis a rare case report
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 1 ~ Issue 1 (2014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Malignant Phyllodes
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 1 ~ Issue 1 (2014) pp: 01-06 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Malignant Phyllodes
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1753-1758, 2015 Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast: A report of nine cases and a review of the literature YIZI CONG *, GUANGDONG QIAO *, HAIDONG ZOU, JUN LIN, XINGMIAO WANG,
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
NAME/ AGE/57 SEX/Female AREA/Australia Visit 1: 5/8/2011. Right Breast Cancer Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma, no specific type, Grade 1 to 2.
 Breast Cancer-CAM Rx NAME/ AGE/57 SEX/Female AREA/Australia Visit 1: 5/8/2011 Case History Discussion Right Breast Cancer Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma, no specific type, Grade 1 to 2. Patient visited
Breast Cancer-CAM Rx NAME/ AGE/57 SEX/Female AREA/Australia Visit 1: 5/8/2011 Case History Discussion Right Breast Cancer Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma, no specific type, Grade 1 to 2. Patient visited
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
MALIGNANT PHYLLODES TUMOUR OF BREAST WITH LIPOSARCOMATOUS DIFFERENTIATION PRESENTING CLINICALLY AS FIBROADENOMA REPORT OF A RARE CASE
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 10 Section: Healthcare Category: Case Report Received on: 13/04/14 Revised on: 28/04/14 Accepted on: 13/05/14 MALIGNANT PHYLLODES TUMOUR OF BREAST WITH LIPOSARCOMATOUS DIFFERENTIATION
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 10 Section: Healthcare Category: Case Report Received on: 13/04/14 Revised on: 28/04/14 Accepted on: 13/05/14 MALIGNANT PHYLLODES TUMOUR OF BREAST WITH LIPOSARCOMATOUS DIFFERENTIATION
Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report
 Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
Int Surg 2017;102:294 298 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-17-00064.1 Solitary Pancreatic Metastasis From Breast Matrix-Producing Carcinoma: A First Case Report Yoshiyuki Kiyasu 1,2, Ken Hayashi 1, Go Miyahara 1,
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
RUTGERS CANCER INSTITUTE OF NEW JERSEY - ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON MEDICAL SCHOOL INTERDISCIPLINARY BREAST SURGERY FELLOWSHIP CORE EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
 RUTGERS CANCER INSTITUTE OF NEW JERSEY - ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON MEDICAL SCHOOL INTERDISCIPLINARY BREAST SURGERY FELLOWSHIP CORE EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES At the completion of Breast Fellowship training, the
RUTGERS CANCER INSTITUTE OF NEW JERSEY - ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON MEDICAL SCHOOL INTERDISCIPLINARY BREAST SURGERY FELLOWSHIP CORE EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES At the completion of Breast Fellowship training, the
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
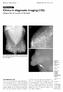 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction
 Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Recurrence following Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ with Skin-Sparing Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D., and Charles E. Butler, M.D. Houston, Texas Skin-sparing
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA
 + NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
+ NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast. Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist
 Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist * SCLs comprise a wide spectrum of diseases, ranging from reactive processes to aggressive malignant
Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist * SCLs comprise a wide spectrum of diseases, ranging from reactive processes to aggressive malignant
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis. Proliferative Breast Disease
 Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review
 Case Report Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review Nikolaos S. Salemis Breast Unit, 2nd Department of Surgery, Army General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Case Report Sinusoidal hemangioma of the breast: diagnostic evaluation management and literature review Nikolaos S. Salemis Breast Unit, 2nd Department of Surgery, Army General Hospital, Athens, Greece
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
