Prediction of genetic risk factors of atherosclerosis using various bioinformatic tools
|
|
|
- Arnold Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prediction of genetic risk factors of atherosclerosis using various bioinformatic tools H.X. Wang and Y.X. Zhao Department of Neurology, Department of Dermatology, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China Corresponding author: Y.X. Zhao Genet. Mol. Res. 15 (2): gmr Received September 21, 2015 Accepted November 19, 2015 Published April 4, 2016 DOI ABSTRACT. The aim of this study was to identify potential markers of atherosclerosis development in familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) patients. GSE13985 microarray data, generated using blood samples from 5 FH patients and 5 matched controls, was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between FH and controls were identified and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed. Module and hub proteins were screened in this network. The module genes were subjected to a gene ontology (GO) analysis, and a Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis was also performed. A total of 394 genes, including 125 up- and 269 down-regulated genes, were differentially expressed. Ribosomal proteins L9 (RPL9), L35 (RPL35), and S7 (RPS7) were designated as hub nodes in the PPI network. The DEGs were found to be significantly enriched in ribosomal and oxidative phosphorylation pathways. Ribosomal protein genes were found to be involved in the ribosomal pathway. The cytochrome-c oxidase (COX) genes COX subunit VIIa polypeptide 2 (COX7A2), COX subunit VIIb (COX7B), COX subunit VIIc (COX7C), and COX subunit VIc (COX6C) were enriched in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. Module analysis
2 H.X. Wang and Y.X. Zhao 2 and GO enrichment analysis identified ribosomal proteins as important regulators of FH. Ribosomal and oxidative phosphorylation pathways may be closely associated with atherosclerosis development. Ribosomal protein genes and cytochrome-coxidase genes may be potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis. Key words: Atherosclerosis; Familial hypercholesterolemia; Differentially-expressed genes; Bioinformatic analysis; Mechanism INTRODUCTION Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease caused by the deposition of lipid (mainly cholesterol and cholesterol esters) to the intima of the arterial wall, increasing its thickness (Moghadasian, 2002). Atherosclerosis contributes to high disease mortality in coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease worldwide. Patients in the initial stages of atherosclerosis are often asymptomatic, and can be so for decades. Therefore, very few cases of atherosclerosis are diagnosed early, increasing the need for methods to predict patients at a greater atherogenic risk. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a proven significant risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis (Cheung and Lam, 2010). FH is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically low-density lipoproteins (LDL). FH atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death worldwide. Many molecular biological studies have attempted to clarify the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in FH patients. High LDL-cholesterol is a risk factor for atherosclerosis, and deletion of the LDL receptor gene (LDLR) has been proven to be associated with FH (Hobbs et al., 1987). Smilde et al. (2001) reported that aggressive reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels was associated with a corresponding reduction in atherosclerosis progression in FH patients. Previous research at the genomic level has indicated that the over-expression of cholesteryl ester transfer protein reduces cholesterol levels in the body (Ishibashi et al., 1993). Moreover, a decrease in the production of interleukin-12, which links the 12/15-lipoxygenase pathway, was associated with reduced atherosclerosis in a mouse model of FH (Zhao et al., 2002). However, the molecular mechanism of atherosclerosis is not fully understood, and gene therapy available for atherosclerosis remains insufficient. This study utilized GSE13985 microarray data obtained from blood samples of FH patients and controls. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between FH and normal blood samples were analyzed using various bioinformatic methods. Significant DEGs and DEG-related functions and pathways were analyzed. The purpose of this study was to explore the potential markers of atherosclerosis in FH patients, and uncover specific targets that could prevent the development and progression of atherosclerosis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Affymetrix microarray data The public Gene Expression Omnibus was searched, and microarray data (GenBank accession No.: GSE13985) related to atherosclerosis were obtained. The dataset was deposited
3 Identifying genes and mechanisms affecting atherosclerosis 3 by Režen et al. (2008) in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, nlm.nih.gov/geo/) database on December 18, Gene expression data was developed from the white blood cells of 5 FH patients and 5 matched controls. Raw data and probe annotation information were downloaded using the platform GPL570 (Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array; Affymetrix Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). Data preprocessing and differential expression analysis Probe-level data in CEL files were converted to expression measures. The data were preprocessed using the Affy package ( affy.html) (Team RC, 2012) in the R language. If multiple probes corresponded to the same gene, the mean expression value was calculated to represent the gene expression level of that gene. The missing values were input using the K-nearest neighbors method (Troyanskaya et al., 2001). The obtained data were subjected to quantile normalization using the Affy package in R. The DEGs in blood cells of FH patients were compared against those of matched controls with Limma ( (Smyth, 2004). P value < 0.05 and fold change (FC) > 1.5 ( log 2 FC > 0.585) were defined as threshold values. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING, org/) (Szklarczyk et al., 2011) is a public database for the prediction of gene interactions with a confidence score. The interactions among DEGs were screened using STRING and the protein pairs with a confidence score > 0.9, in order to construct PPI networks. Connectivity degrees are the number of edges linked to a given node. Important nodes with high degrees in the network were analyzed as hub proteins. Interactions with confidence scores >0.9 were identified as candidates for further analysis. The PPI network was visualized using Cytoscape ( html) (Smoot et al., 2011). Module analysis for PPI network Gene products with similar functions are clustered in the same module to regulate the various biological processes (BPs). Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) (Bader and Hogue, 2003) is a method used to detect densely connected regions in PPI networks. MCODE was used to perform a module analysis of the PPI network. Modules with degree cutoffs 2 (each node in module with a degree of at least 2) and K-core values 2 (each node with at least 2 neighboring nodes) were identified. Gene Ontology (GO) database ( (Ashburner et al., 2000) is a large collection of annotated genes. The functions of the modules were determined by gene ontology (GO) analysis of the module genes using the Bingo plugin of Cytoscape (Maere et al., 2005). In this study, GO terms with fold discovery rate <0.05 were considered to be significant. Pathway analysis The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) knowledge database (
4 H.X. Wang and Y.X. Zhao 4 (Altermann and Klaenhammer, 2005), a major database assisting in pathway analysis, is used to identify significantly enriched metabolic or signal pathways for target genes. The Database for Annotation, Visualization, and integrated discovery (DAVID, ncifcrf.gov/) (Huang et al., 2009) is an online tool that provides a comprehensive set of functional annotations for a number of genes. DEGs in the PPI network were subjected to a KEGG pathway enrichment analysis using the DAVID online tool. P values < 0.05 were the cutoff criterion for functional enrichment analysis. RESULTS Identification of DEGs As shown in Figure 1, the raw expression data was normalized after preprocessing. A total of 394 DEGs, including 125 up-regulated and 269 down-regulated genes, were obtained. Figure 1. Box plots of data normalization. The x-coordinate represents samples; y-coordinate represents gene expression values. White boxes represent normal samples and gray boxes represent familial hypercholesterolemia samples. PPI network analysis The PPI network was constructed with 94 nodes (containing 25 up- and 69 down-regulated genes) and 220 edges (Figure 2). Genes with a high connectivity degree, such as ribosomal protein
5 Identifying genes and mechanisms affecting atherosclerosis 5 L9 (RPL9, degree = 22), ribosomal protein L35 (RPL35, degree = 20), ribosomal protein S7 (RPS7, degree = 19), and ribosomal protein L23 (RPL23, degree = 18), were selected as hub nodes in this network. All of the hub node genes were down-regulated. Figure 2. Protein-protein interaction network of differentially expressed genes. Triangles represent up-regulated genes and inverted triangles represent down-regulated genes. Module analysis Only one module was selected in the PPI network (Figure 3). The module network was constructed with 15 nodes. All DEGs in this module were ribosomal protein genes with high connectivity degrees. The results of GO functional annotation of the DEGs in this module are summarized in Table 1. The most significantly enriched GO BP term was translational elongation (P value = 8.03E- 34). Other significant GO BP terms included translation and cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process. KEGG pathway analysis The KEGG pathway analysis yielded 2 pathways (Table 2). The DEGs were significantly enriched in the ribosomal (P value = 4.89E-21) and oxidative phosphorylation (P value = 2.96E- 05) pathways. Twenty-one DEGs, including RPL9, RPL35, RPS7, and RPL23, were enriched in the ribosomal pathway, all of which were ribosomal protein-related genes. Some of the genes included in oxidative phosphorylation included cytochrome-c oxidase genes, such as cytochrome c oxidase (COX) subunit VIIa polypeptide 2 (COX7A2), COX subunit VIIb (COX7B), COX subunit VIIc (COX7C), and COX subunit VIc (COX6C).
6 H.X. Wang and Y.X. Zhao 6 Figure 3. Module selected from protein-protein interaction network. Inverted triangles represent down-regulated genes. Table 1. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of differentially expressed genes involved in the module. Category Description P value FDR BP Translational elongation 8.03E E-32 BP Translation 2.66E E-24 BP Cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process 6.70E E-16 BP Macromolecule biosynthetic process 9.08E E-16 BP Gene expression 1.38E E-15 BP Cellular biosynthetic process 1.10E E-13 BP Biosynthetic process 2.86E E-13 BP Cellular protein metabolic process 4.36E E-12 BP Protein metabolic process 7.96E E-11 BP Cellular macromolecule metabolic process 6.77E E-09 BP Macromolecule metabolic process 5.19E E-08 BP Cellular metabolic process 1.35E E-07 BP Primary metabolic process 3.23E E-06 BP Metabolic process 1.95E E-05 BP = biological process; FDR = false discovery rate. Table 2. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Term Count P value FDR hsa03010:ribosome E E-18 hsa00190:oxidative phosphorylation E Count = enriched gene number in the KEGG term; FDR = false discovery rate. DISCUSSION Atherosclerosis is a major cause of death worldwide; FH is an important risk factor for atherosclerosis (Cheung and Lam, 2010). Understanding the changes in FH gene expression is of critical importance towards understanding the mechanism of atherosclerosis procession. In this
7 Identifying genes and mechanisms affecting atherosclerosis 7 study, we analyzed the gene expression profiles of blood cells in FH patients, compared to the controls; moreover, we attempted to predict the biomarkers of atherosclerosis development. Three hundred and ninety five DEGs, including 125 up- and 269 down-regulated genes, were selected in this study. PPI network analysis identified several ribosomal proteins, such as RPL9, RPL35, and RPS7, as hub nodes. The KEGG pathway analysis revealed that DEGs were significantly enriched in ribosome and oxidative phosphorylation pathways. Ribosomal proteinrelated genes and cytochrome-c oxidase genes (COX7A2, COX7B, COX7C, and COX6C) were enriched in these pathways. Additionally, module analysis also identified ribosomal proteins as important proteins affecting FH. These significant DEGs and their functions were theorized to contribute to atherosclerosis development in FH patients. Ribosome is a large and complex organelle found in all living cells. We observed that the ribosomal pathway was significantly enriched by DEG function. Ribosomal protein-related genes, such as RPL9, RPL35, and RPS7, were identified in this pathway. Ribosomal proteins are reported to be associated with important biological processes, including protein synthesis (Ruvinsky and Meyuhas, 2006), cell proliferation (Volarević et al., 2000), and cell apoptosis (Khanna et al., 2003). Dzau et al. (2002) reported that vascular cell proliferation contributed to the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. RPL17, a member of the ribosomal protein family, is an inhibitor of vascular smooth muscle cell growth, and therefore is a potential therapeutic target used to limit the thickening of the carotid intima-media (Smolock et al., 2012). Limiting the thickening of the carotid intima-media could reduce the risk of atherosclerosis (Lorenz et al., 2006). Furthermore, ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6K) is the key mammalian target of the rapamycin (mtor) effector; the mtor pathway is a key regulator of cell growth through the regulation of protein synthesis (Jastrzebski et al., 2007). Mueller et al. (2008) reported that the mtor inhibitor strongly inhibited the development of atherosclerosis in LDLR -/- mice. In this study, ribosomal protein-related genes were down-regulated in the blood cells of FH patients; however, these genes functioned as the hub nodes in the PPI network. This suggested that the abnormal expression of ribosomal protein-related genes could increase the risk of atherosclerosis development through the ribosomal pathway. The oxidative phosphorylation pathway was found to be another important function enriched by DEGs. Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway wherein energy is released from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules in mitochondrial cells (Hatefi, 1985). The accumulation of reactive oxygen species causes an increase in oxidative stress in the cells (Scherz-Shouval and Elazar, Oxidative stress has been demonstrated to play an important role in the development of vascular diseases such as hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis (Magenta et al., 2013). In this study, cytochrome-c oxidase genes (COX7A2, COX7B, COX7C, and COX6C) were identified to perform this function. Cytochrome-c oxidase has been reported to regulate oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotic enzymes (Ludwig et al., 2001). Dutta et al. (2006) discovered COX7B to be a mitochondrial electron transport chain gene whose expression was down-regulated in multiple sclerosis patients, leading to reduced ATP production and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the development of cardiovascular diseases (including atherosclerosis) by inducing changes in the mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis (Williamson et al., 2010). Therefore, we speculated that cytochrome-c oxidases play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis. In this study, the expression of cytochrome-c oxidase genes was down-regulated in blood samples obtained from FH patients, suggesting that the aberrant expression of these genes may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis by regulating the oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
8 H.X. Wang and Y.X. Zhao 8 In summary, the results of our study indicate that the ribosomal and oxidative phosphorylation pathways may be closely associated with the development of atherosclerosis. Ribosomal protein genes and cytochrome-c oxidase genes may also function as potential markers for the development of atherosclerosis. However, further experiments with larger sample sizes are required to confirm our findings. Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES Altermann E and Klaenhammer TR (2005). PathwayVoyager: pathway mapping using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics 6: Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, et al.; The Gene Ontology Consortium (2000). Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 25: Bader GD and Hogue CW (2003). An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 4: 2. Cheung BM and Lam KS (2010). Is intensive LDL-cholesterol lowering beneficial and safe? Lancet 376: dx.doi.org/ /s (10) Dutta R, McDonough J, Yin X, Peterson J, et al. (2006). Mitochondrial dysfunction as a cause of axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis patients. Ann. Neurol. 59: Dzau VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC and Sedding DG (2002). Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: new perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 8: Hatefi Y (1985). The mitochondrial electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 54: Hobbs HH, Brown MS, Russell DW, Davignon J, et al. (1987). Deletion in the gene for the low-density-lipoprotein receptor in a majority of French Canadians with familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 317: NEJM Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA (2009). Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 4: Ishibashi S, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Gerard RD, et al. (1993). Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J. Clin. Invest. 92: org/ /jci Jastrzebski K, Hannan KM, Tchoubrieva EB, Hannan RD, et al. (2007). Coordinate regulation of ribosome biogenesis and function by the ribosomal protein S6 kinase, a key mediator of mtor function. Growth Factors 25: org/ / Khanna N, Sen S, Sharma H and Singh N (2003). S29 ribosomal protein induces apoptosis in H520 cells and sensitizes them to chemotherapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 304: Lorenz MW, von Kegler S, Steinmetz H, Markus HS, et al. (2006). Carotid intima-media thickening indicates a higher vascular risk across a wide age range: prospective data from the Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study (CAPS). Stroke 37: Ludwig B, Bender E, Arnold S, Hüttemann M, et al. (2001). Cytochrome C oxidase and the regulation of oxidative phosphorylation. ChemBioChem 2: Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M (2005). BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics 21: Magenta A, Greco S, Gaetano C and Martelli F (2013). Oxidative stress and micrornas in vascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14: Moghadasian MH (2002). Experimental atherosclerosis: a historical overview. Life Sci. 70: S (01) Mueller MA, Beutner F, Teupser D, Ceglarek U, et al. (2008). Prevention of atherosclerosis by the mtor inhibitor everolimus in LDLR-/- mice despite severe hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 198: atherosclerosis
9 Identifying genes and mechanisms affecting atherosclerosis 9 Režen T, Cvikl A, Brecelj N, Rozman D, et al. (2008). Atherosclerotic markers in human blood - a study in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Available at [ Ruvinsky I and Meyuhas O (2006). Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation: from protein synthesis to cell size. Trends Biochem. Sci. 31: Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z (2007). ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 17: Smilde TJ, van Wissen S, Wollersheim H, Trip MD, et al. (2001). Effect of aggressive versus conventional lipid lowering on atherosclerosis progression in familial hypercholesterolaemia (ASAP): a prospective, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 357: Smolock EM, Korshunov VA, Glazko G, Qiu X, et al. (2012). Ribosomal protein L17, RpL17, is an inhibitor of vascular smooth muscle growth and carotid intima formation. Circulation 126: CIRCULATIONAHA Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL, et al. (2011). Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27: Smyth GK (2004). Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. 3. Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, et al. (2011). The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 39: D561-D gkq973 Team RC (2012). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Troyanskaya O, Cantor M, Sherlock G, Brown P, et al. (2001). Missing value estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics 17: Volarević S, Stewart MJ, Ledermann B, Zilberman F, et al. (2000). Proliferation, but not growth, blocked by conditional deletion of 40S ribosomal protein S6. Science 288: Williamson CL, Dabkowski ER, Baseler WA, Croston TL, et al. (2010). Enhanced apoptotic propensity in diabetic cardiac mitochondria: influence of subcellular spatial location. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 298: H633-H org/ /ajpheart Zhao L, Cuff CA, Moss E, Wille U, et al. (2002). Selective interleukin-12 synthesis defect in 12/15-lipoxygenase-deficient macrophages associated with reduced atherosclerosis in a mouse model of familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Biol. Chem. 277:
A General Workflow to Analyze Key Cancer-Related Genes Based on NCBI illustrated by the case of gastric cancer
 A General Workflow to Analyze Key Cancer-Related Genes Based on NCBI illustrated by the case of gastric cancer Zhikuan Quan School of Statistics, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China 201511011114@bnu.edu.cn
A General Workflow to Analyze Key Cancer-Related Genes Based on NCBI illustrated by the case of gastric cancer Zhikuan Quan School of Statistics, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China 201511011114@bnu.edu.cn
Protein-protein interaction network analysis of osteoarthritis-related differentially expressed genes
 Protein-protein interaction network analysis of osteoarthritis-related differentially expressed genes Y.C. Zhu 1 *, B.Y. Deng 1 *, L.G. Zhang 1, P. Xu 3, X.P. Du 3, Q.G. Zhang 1 and B. Yang 2 1 Department
Protein-protein interaction network analysis of osteoarthritis-related differentially expressed genes Y.C. Zhu 1 *, B.Y. Deng 1 *, L.G. Zhang 1, P. Xu 3, X.P. Du 3, Q.G. Zhang 1 and B. Yang 2 1 Department
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and
 Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Karthik Ravi¹ and Inhan Lee². Journal of
 Journal of Upregulation of the Ribosomal Pathway as a Potential Blood-Based Genetic Biomarker for Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and PTSD Karthik Ravi¹ and Inhan Lee² ¹ International Academy,
Journal of Upregulation of the Ribosomal Pathway as a Potential Blood-Based Genetic Biomarker for Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and PTSD Karthik Ravi¹ and Inhan Lee² ¹ International Academy,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER
 EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome
 Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome Marta R. Hidalgo 1, Alicia Amadoz 2, Cankut Çubuk 1, José Carbonell-Caballero 2 and Joaquín Dopazo
Models of cell signalling uncover molecular mechanisms of high-risk neuroblastoma and predict outcome Marta R. Hidalgo 1, Alicia Amadoz 2, Cankut Çubuk 1, José Carbonell-Caballero 2 and Joaquín Dopazo
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Retinal expression of small non-coding RNAs in a murine model of proliferative retinopathy Chi-Hsiu Liu 1, Zhongxiao Wang 1, Ye Sun 1, John Paul SanGiovanni 2, Jing Chen 1, * 1 Department
Supporting Information Retinal expression of small non-coding RNAs in a murine model of proliferative retinopathy Chi-Hsiu Liu 1, Zhongxiao Wang 1, Ye Sun 1, John Paul SanGiovanni 2, Jing Chen 1, * 1 Department
1- Which of the following statements is TRUE in regards to eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
 Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
DeSigN: connecting gene expression with therapeutics for drug repurposing and development. Bernard lee GIW 2016, Shanghai 8 October 2016
 DeSigN: connecting gene expression with therapeutics for drug repurposing and development Bernard lee GIW 2016, Shanghai 8 October 2016 1 Motivation Average cost: USD 1.8 to 2.6 billion ~2% Attrition rate
DeSigN: connecting gene expression with therapeutics for drug repurposing and development Bernard lee GIW 2016, Shanghai 8 October 2016 1 Motivation Average cost: USD 1.8 to 2.6 billion ~2% Attrition rate
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Partial least squares-based gene expression analysis in preeclampsia
 Partial least squares-based gene expression analysis in preeclampsia F. Jiang 1 *, Y. Yang 1 *, J. Li 2, W. Li 3, Y. Luo 1, Y. Li 1, H. Zhao 1, X. Wang 1, G. Yin 1 and G. Wu 4 1 Department of Gynecology
Partial least squares-based gene expression analysis in preeclampsia F. Jiang 1 *, Y. Yang 1 *, J. Li 2, W. Li 3, Y. Luo 1, Y. Li 1, H. Zhao 1, X. Wang 1, G. Yin 1 and G. Wu 4 1 Department of Gynecology
Screening of genes related to acute coronary syndrome and identification of functional modules in the PPI network
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Screening of genes related to acute coronary syndrome and identification of functional modules in the PPI network W.-J. SHANGGUAN, L.-M. TANG, H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Screening of genes related to acute coronary syndrome and identification of functional modules in the PPI network W.-J. SHANGGUAN, L.-M. TANG, H.
Drug repurposing and therapeutic anti-mirna predictions in oxldl-induced the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell associated diseases
 Drug repurposing and therapeutic anti-mirna predictions in oxldl-induced the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell associated diseases Shun-Tsung Chen, Chien-Hung Huang, Victor C. Kok, Chi-Ying
Drug repurposing and therapeutic anti-mirna predictions in oxldl-induced the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell associated diseases Shun-Tsung Chen, Chien-Hung Huang, Victor C. Kok, Chi-Ying
Identifying Potential Prognostic Biomarkers by Analyzing Gene Expression for Different Cancers
 Identifying Potential Prognostic Biomarkers by Analyzing Gene Expression for Different Cancers Pragya Verma Department of Mathematics, Bioinformatics and Computer Applications Maulana Azad National Institute
Identifying Potential Prognostic Biomarkers by Analyzing Gene Expression for Different Cancers Pragya Verma Department of Mathematics, Bioinformatics and Computer Applications Maulana Azad National Institute
Copyright 2015 American College of Cardiology Foundation
 ,,nn Wisløff, U., Bye, A., Stølen, T., Kemi, O. J., Pollott, G. E., Pande, M., McEachin, R. C., Britton, S. L., and Koch, L. G. (2015) Blunted cardiomyocyte remodeling response in exercise-resistant rats.
,,nn Wisløff, U., Bye, A., Stølen, T., Kemi, O. J., Pollott, G. E., Pande, M., McEachin, R. C., Britton, S. L., and Koch, L. G. (2015) Blunted cardiomyocyte remodeling response in exercise-resistant rats.
Using the attract method to identify core pathways in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
 Using the attract method to identify core pathways in juvenile idiopathic arthritis J.S. Li 1, X.L. Gao 2, Y.R. Liu 3 and Y. Dong 4 1 Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Binzhou People s Hospital,
Using the attract method to identify core pathways in juvenile idiopathic arthritis J.S. Li 1, X.L. Gao 2, Y.R. Liu 3 and Y. Dong 4 1 Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Binzhou People s Hospital,
Topological centrality-based identification of hub genes and pathways associated with acute viral respiratory infection in infants
 Topological centrality-based identification of hub genes and pathways associated with acute viral respiratory infection in infants X.Y. Liu 1, G.Q. Li 2, Y. Ma 3 and L.J. Zhao 4 1 Department of Test Cabinet,
Topological centrality-based identification of hub genes and pathways associated with acute viral respiratory infection in infants X.Y. Liu 1, G.Q. Li 2, Y. Ma 3 and L.J. Zhao 4 1 Department of Test Cabinet,
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Data Alert. Vascular Biology Working Group. Blunting the atherosclerotic process in patients with coronary artery disease.
 1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
Gene expression profiles and protein protein interaction networks during tongue carcinogenesis in the tumor microenvironment
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 17: 165-171, 2018 Gene expression profiles and protein protein interaction networks during tongue carcinogenesis in the tumor microenvironment WEI SUN 1,2*, ZETING QIU 1,2*,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 17: 165-171, 2018 Gene expression profiles and protein protein interaction networks during tongue carcinogenesis in the tumor microenvironment WEI SUN 1,2*, ZETING QIU 1,2*,
Analysis of FOS, BTG2, and NR4A in the function of renal medullary hypertension
 Analysis of FOS, BTG2, and NR4A in the function of renal medullary hypertension Y.B. Wu 1, W.D. Zang 2, W.Z. Yao 3, Y. Luo 1, B. Hu 1, L. Wang 1 and Y.L. Liang 1 1 East Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai
Analysis of FOS, BTG2, and NR4A in the function of renal medullary hypertension Y.B. Wu 1, W.D. Zang 2, W.Z. Yao 3, Y. Luo 1, B. Hu 1, L. Wang 1 and Y.L. Liang 1 1 East Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/264/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Systems Approach for Decoding Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling Pathways Sehyun Chae, Byung Yong Ahn, Kyunghee Byun,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/264/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Systems Approach for Decoding Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling Pathways Sehyun Chae, Byung Yong Ahn, Kyunghee Byun,
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering. (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization)
 Reconstruction of Gene Regulatory Network to Identify Prognostic Molecular Markers of the Reactive Stroma of Breast and Prostate Cancer Using Information Theoretic Approach Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Dr.
Reconstruction of Gene Regulatory Network to Identify Prognostic Molecular Markers of the Reactive Stroma of Breast and Prostate Cancer Using Information Theoretic Approach Prof. Shanthi Mahesh 1, Dr.
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping
 Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies
 OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression
 Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression Nexus Copy Number provides user-friendly interface and functionalities to integrate copy number analysis with gene expression results for the purpose
Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression Nexus Copy Number provides user-friendly interface and functionalities to integrate copy number analysis with gene expression results for the purpose
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Dysfunctional HDL and Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE
 Dysfunctional HDL and Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE PIs and Members of HDL Project Wei Gao, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Chair Cardiology Third Hospital, PUHSC Yong Huo, M.D., Ph.D.
Dysfunctional HDL and Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE PIs and Members of HDL Project Wei Gao, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Chair Cardiology Third Hospital, PUHSC Yong Huo, M.D., Ph.D.
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Analysis of time course gene expression data. The time course data of the expression level of a representative gene is shown in the below figure. The trajectory of longitudinal expression
Supplementary Methods Analysis of time course gene expression data. The time course data of the expression level of a representative gene is shown in the below figure. The trajectory of longitudinal expression
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk COPYRIGHT. J. Peter Oettgen, MD
 Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Current Cholesterol Guidelines and Treatment of Residual Risk J. Peter Oettgen, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Preventive Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
Edge attributes. Node attributes
 HMDB ID input pane Network view Node attributes Edge attributes Supplemental Figure 1. Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator. The left pane is Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator (code name: rsmetabppi). User
HMDB ID input pane Network view Node attributes Edge attributes Supplemental Figure 1. Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator. The left pane is Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator (code name: rsmetabppi). User
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_ testing_ for_heterozygous_ familial_
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_ testing_ for_heterozygous_ familial_
Package leukemiaseset
 Package leukemiaseset August 14, 2018 Type Package Title Leukemia's microarray gene expression data (expressionset). Version 1.16.0 Date 2013-03-20 Author Sara Aibar, Celia Fontanillo and Javier De Las
Package leukemiaseset August 14, 2018 Type Package Title Leukemia's microarray gene expression data (expressionset). Version 1.16.0 Date 2013-03-20 Author Sara Aibar, Celia Fontanillo and Javier De Las
Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis
 Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis Mohamed Diwan M. AbdulHameed 1, Gregory J. Tawa 1, Kamal Kumar 1, Danielle L. Ippolito 2, John A. Lewis
Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis Mohamed Diwan M. AbdulHameed 1, Gregory J. Tawa 1, Kamal Kumar 1, Danielle L. Ippolito 2, John A. Lewis
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene expression in insulin resistance
 Gene expression in insulin resistance Name: Jules Jacobs Date: 4-7-2017 Supervisors: - Mirella Kalafati MSc - Dr. Lars Eijssen Department of Bioinformatics BACKGROUND Obesity Defined as: BMI > 30 kg/m
Gene expression in insulin resistance Name: Jules Jacobs Date: 4-7-2017 Supervisors: - Mirella Kalafati MSc - Dr. Lars Eijssen Department of Bioinformatics BACKGROUND Obesity Defined as: BMI > 30 kg/m
Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents
 Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents Rationale and recommendations for early identification and treatment European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Slide deck adapted from:
Familial hypercholesterolaemia in children and adolescents Rationale and recommendations for early identification and treatment European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Slide deck adapted from:
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
University of Groningen. Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise
 University of Groningen Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Hidradenitis suppurativa Dickinson-Blok, Janine Louise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Network-assisted data analysis
 Network-assisted data analysis Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Protein identification in shotgun proteomics Protein digestion LC-MS/MS Protein
Network-assisted data analysis Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Protein identification in shotgun proteomics Protein digestion LC-MS/MS Protein
A Network Partition Algorithm for Mining Gene Functional Modules of Colon Cancer from DNA Microarray Data
 Method A Network Partition Algorithm for Mining Gene Functional Modules of Colon Cancer from DNA Microarray Data Xiao-Gang Ruan, Jin-Lian Wang*, and Jian-Geng Li Institute of Artificial Intelligence and
Method A Network Partition Algorithm for Mining Gene Functional Modules of Colon Cancer from DNA Microarray Data Xiao-Gang Ruan, Jin-Lian Wang*, and Jian-Geng Li Institute of Artificial Intelligence and
In-Silico Screening of Biomarker Genes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using R/Bioconductor
 Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 2017; 5(3): 36-42 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cbb doi: 10.11648/j.cbb.20170503.12 ISSN: 2330-8265 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8281 (Online) In-Silico Screening
Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 2017; 5(3): 36-42 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cbb doi: 10.11648/j.cbb.20170503.12 ISSN: 2330-8265 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8281 (Online) In-Silico Screening
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Familial Hypercholesterolemia Dr.Ramzi Al-Mohammadi Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Cardiologist, Advanced HF and Transplant Consultant Classification of Hyperlipedemia Primary hyperlipedemia:
Familial Hypercholesterolemia Dr.Ramzi Al-Mohammadi Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Cardiologist, Advanced HF and Transplant Consultant Classification of Hyperlipedemia Primary hyperlipedemia:
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
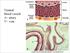 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer
 Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
fasting blood glucose [mg/dl]
![fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] fasting blood glucose [mg/dl]](/thumbs/80/82129652.jpg) SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Supplemental Figure I body weight [g] 5 5 5 fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] 5 5 5 C total cholesterol [mg/dl] 8 6 4 WT Has -/- Supplemental Figure I: Has-deficient mice exhibited no apparent
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Supplemental Figure I body weight [g] 5 5 5 fasting blood glucose [mg/dl] 5 5 5 C total cholesterol [mg/dl] 8 6 4 WT Has -/- Supplemental Figure I: Has-deficient mice exhibited no apparent
Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer
 S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes in the liver between Bai er layers and broilers
 Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes in the liver between Bai er layers and broilers Q.-G. Wang 1,2,4 *, H.-F. Zhang 1,2,3 *, S.-Z. Wang 1,2,3, G.L. Gao 1,2,4, L. Leng 1,2,3, W. Na 1,2,3
Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes in the liver between Bai er layers and broilers Q.-G. Wang 1,2,4 *, H.-F. Zhang 1,2,3 *, S.-Z. Wang 1,2,3, G.L. Gao 1,2,4, L. Leng 1,2,3, W. Na 1,2,3
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies
 Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer
 Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
MTB-1 MEDIATED GENE REGULATION SHOWS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS IN DMD PATIENT CELLS AND MDX MICE
 targeting mitochondria. advancing human health. MTB-1 MEDIATED GENE REGULATION SHOWS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS IN DMD PATIENT CELLS AND MDX MICE PPMD 2016 Annual Connect Conference George Mulligan, PhD VP Translational
targeting mitochondria. advancing human health. MTB-1 MEDIATED GENE REGULATION SHOWS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS IN DMD PATIENT CELLS AND MDX MICE PPMD 2016 Annual Connect Conference George Mulligan, PhD VP Translational
A quick review. The clustering problem: Hierarchical clustering algorithm: Many possible distance metrics K-mean clustering algorithm:
 The clustering problem: partition genes into distinct sets with high homogeneity and high separation Hierarchical clustering algorithm: 1. Assign each object to a separate cluster. 2. Regroup the pair
The clustering problem: partition genes into distinct sets with high homogeneity and high separation Hierarchical clustering algorithm: 1. Assign each object to a separate cluster. 2. Regroup the pair
CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets
 Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Journal: Nature Methods
 Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH AEROBIC RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
 HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11): /ISSN: /IJCEM Ying Sun, Meng Huo, Chunyan Zhang, Rengui Wang, Tingguo Wen
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):22194-22199 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0032775 Original Article Identification of genes associated with apoptosis-sensitive acute lymphoblastic leukemia responsive
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):22194-22199 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0032775 Original Article Identification of genes associated with apoptosis-sensitive acute lymphoblastic leukemia responsive
A two-step drug repositioning method based on a protein-protein interaction network of genes shared by two diseases and the similarity of drugs
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(2) A two-step drug repositioning method based on a protein-protein interaction network of genes shared by two diseases and the similarity of drugs Yutaka Fukuoka*,
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(2) A two-step drug repositioning method based on a protein-protein interaction network of genes shared by two diseases and the similarity of drugs Yutaka Fukuoka*,
Further insight into molecular mechanism underlying thoracic spinal cord injury using bioinformatics methods
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 7851-7858, 2015 Further insight into molecular mechanism underlying thoracic spinal cord injury using bioinformatics methods WEIGUO WANG 1*, RONGJUN LIU 2*, ZHANWANG XU 3,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 7851-7858, 2015 Further insight into molecular mechanism underlying thoracic spinal cord injury using bioinformatics methods WEIGUO WANG 1*, RONGJUN LIU 2*, ZHANWANG XU 3,
Integrating Genome and Functional Genomics Data to Reveal Perturbed Signaling Pathways in Ovarian Cancers
 Integrating Genome and Functional Genomics Data to Reveal Perturbed Signaling Pathways in Ovarian Cancers Songjian Lu, PhD, Xinghua Lu, MD. PhD Dept. Biomedical Informatics, Univ. Pittsburgh, PA 15232
Integrating Genome and Functional Genomics Data to Reveal Perturbed Signaling Pathways in Ovarian Cancers Songjian Lu, PhD, Xinghua Lu, MD. PhD Dept. Biomedical Informatics, Univ. Pittsburgh, PA 15232
Analysis of paired mirna-mrna microarray expression data using a stepwise multiple linear regression model
 Analysis of paired mirna-mrna microarray expression data using a stepwise multiple linear regression model Yiqian Zhou 1, Rehman Qureshi 2, and Ahmet Sacan 3 1 Pure Storage, 650 Castro Street, Suite #260,
Analysis of paired mirna-mrna microarray expression data using a stepwise multiple linear regression model Yiqian Zhou 1, Rehman Qureshi 2, and Ahmet Sacan 3 1 Pure Storage, 650 Castro Street, Suite #260,
Expanded View Figures
 Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Modern Lipid Management:
 Modern Lipid Management: New Drugs, New Targets, New Hope Kirk U. Knowlton, M.D Director of Cardiovascular Research Co Chief of Cardiology Why lower LDL C in those without evidence of CAD (primary prevention)
Modern Lipid Management: New Drugs, New Targets, New Hope Kirk U. Knowlton, M.D Director of Cardiovascular Research Co Chief of Cardiology Why lower LDL C in those without evidence of CAD (primary prevention)
Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis
 Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis Mohamed Diwan M. AbdulHameed 1, Gregory J. Tawa 1, Kamal Kumar 1, Danielle L. Ippolito 2, John A. Lewis
Systems Level Analysis and Identification of Pathways and Networks Associated with Liver Fibrosis Mohamed Diwan M. AbdulHameed 1, Gregory J. Tawa 1, Kamal Kumar 1, Danielle L. Ippolito 2, John A. Lewis
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona,
 Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS
 January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 21-25) VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS By Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA Groupe de Recherche en Valvulopathies (GRV), Hôpital Laval Research Centre
January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 21-25) VALVULO-METABOLIC RISK IN AORTIC STENOSIS By Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA Groupe de Recherche en Valvulopathies (GRV), Hôpital Laval Research Centre
Placebo-Controlled Statin Trials
 PREVENTION OF CHD WITH LIPID MANAGEMENT AND ASPIRIN: MATCHING TREATMENT TO RISK Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of
PREVENTION OF CHD WITH LIPID MANAGEMENT AND ASPIRIN: MATCHING TREATMENT TO RISK Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of
NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals?
 The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16
 38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16 PGAR: ASD Candidate Gene Prioritization System Using Expression Patterns Steven Cogill and Liangjiang Wang Department of Genetics and
38 Int'l Conf. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology BIOCOMP'16 PGAR: ASD Candidate Gene Prioritization System Using Expression Patterns Steven Cogill and Liangjiang Wang Department of Genetics and
Case Presentation. Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer
 Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
 1. Prevalence and prognostic significance of incidental cardiac troponin T elevation in ambulatory patients with stable coronary artery disease: data from the Heart and Soul study Hsieh, B.P., et al. Am
1. Prevalence and prognostic significance of incidental cardiac troponin T elevation in ambulatory patients with stable coronary artery disease: data from the Heart and Soul study Hsieh, B.P., et al. Am
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists.
 chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
Coronary artery disease remains the leading
 UNMET NEEDS IN THE TREATMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS: WHY ARE WE NOT DONE YET? * Evan A. Stein, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States. Despite advances in surgical,
UNMET NEEDS IN THE TREATMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS: WHY ARE WE NOT DONE YET? * Evan A. Stein, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States. Despite advances in surgical,
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Protein-protein interaction network and mechanism analysis of hepatitis C
 Protein-protein interaction network and mechanism analysis of hepatitis C Y. Tang 1, Q. Tang 2, C. Dong 1, X. Li 3, Z. Zhang 4 and F. An 5 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Jiyang Public Hospital,
Protein-protein interaction network and mechanism analysis of hepatitis C Y. Tang 1, Q. Tang 2, C. Dong 1, X. Li 3, Z. Zhang 4 and F. An 5 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Jiyang Public Hospital,
Bioenergetics. Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear.
 33 Bioenergetics Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc
33 Bioenergetics Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc
Single SNP/Gene Analysis. Typical Results of GWAS Analysis (Single SNP Approach) Typical Results of GWAS Analysis (Single SNP Approach)
 High-Throughput Sequencing Course Gene-Set Analysis Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Summer 28 Section Introduction What is Gene Set Analysis? Many names for gene set analysis: Pathway analysis Gene set
High-Throughput Sequencing Course Gene-Set Analysis Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Summer 28 Section Introduction What is Gene Set Analysis? Many names for gene set analysis: Pathway analysis Gene set
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Detecting robust gene signature through integrated analysis of multiple types of high-throughput data in liver cancer 1
 Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007 Dec; 28 (12): 2005 2010 Full-length article Detecting robust gene signature through integrated analysis of multiple types of high-throughput data in liver cancer 1 Xin-yu ZHANG
Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007 Dec; 28 (12): 2005 2010 Full-length article Detecting robust gene signature through integrated analysis of multiple types of high-throughput data in liver cancer 1 Xin-yu ZHANG
