Lecture 7- Sound Waves Chapter 17
|
|
|
- Godwin Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Admin Wave Speed Questions 1 / 10 Lecture 7- Sound Waves Chapter 17 Prof. Noronha-Hostler PHY-124H HONORS ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IB Phys- 124H March 2 nd, 2018
2 Admin Wave Speed Questions 2 / 10 Housekeeping Homework 8 due 3/19/18 (because of lab) Projected grades on GradeBook. Have not yet dropped lowest homeworks/labs (only at the end) Shortened office hours (until 10:20am today).
3 Admin Wave Speed Questions 3 / 10 Recall the velocity of a string
4 Admin Wave Speed Questions 4 / 10 Derivation of speed of sound
5 Admin Wave Speed Questions 5 / 10 Sound through a tube
6 Admin Wave Speed Questions 6 / 10 Instrument size
7 Admin Wave Speed Questions 7 / 10 Beats
8 Admin Wave Speed Questions 8 / 10 Doppler Effect Train Whistle
9 Admin Wave Speed Questions 9 / 10 Beats
10 Admin Wave Speed Questions 10 / 10 Mach Cone
11 You are observing a thunderstorm. In the distance, you see a flash of lightning. Five seconds later, you hear thunder. How far away was the lightning flash? a) 1 mile (1.6 km) b) 0.5 mile (0.8 km) c) 2 miles (3.2 km) d) 0.25 mile (0.4 km) e) 5 miles (8.0 km)
12 You are observing a thunderstorm. In the distance, you see a flash of lightning. Five seconds later, you hear thunder. How far away was the lightning flash? a) 1 mile (1.6 km) b) 0.5 mile (0.8 km) c) 2 miles (3.2 km) d) 0.25 mile (0.4 km) e) 5 miles (8.0 km)
13 In a classroom demonstration, a physics professor breathes in a small amount of helium and begins to talk. The result is that the professor s normally low, baritone voice sounds quite high pitched. Which one of the following statements best describes this phenomena? a) The presence of helium changes the speed of sound in the air in the room, causing all sounds to have higher frequencies. b) The professor played a trick on the class by tightening his vocal cords to produces higher frequencies in his throat and mouth than normal. The helium was only a distraction and had nothing to do with it. c) The helium significantly alters the vocal chords causing the wavelength of the sounds generated to decrease and thus the frequencies increase. d) The wavelength of the sound generated in the professor s throat and mouth is only changed slightly, but since the speed of sound in helium is approximately 2.5 times larger than in air, therefore the frequencies generated are about 2.5 times higher.
14 In a classroom demonstration, a physics professor breathes in a small amount of helium and begins to talk. The result is that the professor s normally low, baritone voice sounds quite high pitched. Which one of the following statements best describes this phenomena? a) The presence of helium changes the speed of sound in the air in the room, causing all sounds to have higher frequencies. b) The professor played a trick on the class by tightening his vocal cords to produces higher frequencies in his throat and mouth than normal. The helium was only a distraction and had nothing to do with it. c) The helium significantly alters the vocal chords causing the wavelength of the sounds generated to decrease and thus the frequencies increase. d) The wavelength of the sound generated in the professor s throat and mouth is only changed slightly, but since the speed of sound in helium is approximately 2.5 times larger than in air, therefore the frequencies generated are about 2.5 times higher.
15 A particle of dust is floating in the air approximately one half meter in front of a speaker. The speaker is then turned on produces a constant pure tone of 226 Hz, as shown. The sound waves produced by the speaker travel horizontally. Which one of the following statements correctly describes the subsequent motion of the dust particle, if any? a) The particle of dust will oscillate left and right with a frequency of 226 Hz. b) The particle of dust will oscillate up and down with a frequency of 226 Hz. c) The particle of dust will be accelerated toward the right and continue moving in that direction. d) The particle of dust will move toward the right at constant velocity. e) The dust particle will remain motionless as it cannot be affected by sound waves.
16 A particle of dust is floating in the air approximately one half meter in front of a speaker. The speaker is then turned on produces a constant pure tone of 226 Hz, as shown. The sound waves produced by the speaker travel horizontally. Which one of the following statements correctly describes the subsequent motion of the dust particle, if any? a) The particle of dust will oscillate left and right with a frequency of 226 Hz. b) The particle of dust will oscillate up and down with a frequency of 226 Hz. c) The particle of dust will be accelerated toward the right and continue moving in that direction. d) The particle of dust will move toward the right at constant velocity. e) The dust particle will remain motionless as it cannot be affected by sound waves.
17 Two identical speakers are emitting a constant tone that has a wavelength of 0.50 m. Speaker A is located to the left of speaker B. At which of the following locations would complete destructive interference occur? a) 2.15 m from speaker A and 3.00 m from speaker B b) 3.75 m from speaker A and 2.50 m from speaker B c) 2.50 m from speaker A and 1.00 m from speaker B d) 1.35 m from speaker A and 3.75 m from speaker B e) 2.00 m from speaker A and 3.00 m from speaker B
18 Two identical speakers are emitting a constant tone that has a wavelength of 0.50 m. Speaker A is located to the left of speaker B. At which of the following locations would complete destructive interference occur? a) 2.15 m from speaker A and 3.00 m from speaker B b) 3.75 m from speaker A and 2.50 m from speaker B c) 2.50 m from speaker A and 1.00 m from speaker B d) 1.35 m from speaker A and 3.75 m from speaker B e) 2.00 m from speaker A and 3.00 m from speaker B
19 Natalie is a distance d in front of a speaker emitting sound waves. She then moves to a position that is a distance 2d in front of the speaker. By what percentage does the sound intensity decrease for Natalie between the two positions? a) 10 % b) 25 % c) 50 % d) 75% e) The sound intensity remains constant because it is not dependent on the distance.
20 Natalie is a distance d in front of a speaker emitting sound waves. She then moves to a position that is a distance 2d in front of the speaker. By what percentage does the sound intensity decrease for Natalie between the two positions? a) 10 % b) 25 % c) 50 % d) 75% e) The sound intensity remains constant because it is not dependent on the distance.
21 A girl is playing a trumpet. The sound waves produced are traveling through air to your ear. Which one of the following statements is false concerning this situation? a) A high-frequency sound that the trumpet produces is interpreted as a highpitched sound. b) Air molecules between the trumpet and your ear vibrate back and forth parallel to the direction the waves are traveling. c) The loudness of the sound wave involves the size of the oscillations in air pressure. d) The sounds from the trumpet are longitudinal waves. e) The sound travels at the speed of light to your ear.
22 A girl is playing a trumpet. The sound waves produced are traveling through air to your ear. Which one of the following statements is false concerning this situation? a) A high-frequency sound that the trumpet produces is interpreted as a highpitched sound. b) Air molecules between the trumpet and your ear vibrate back and forth parallel to the direction the waves are traveling. c) The loudness of the sound wave involves the size of the oscillations in air pressure. d) The sounds from the trumpet are longitudinal waves. e) The sound travels at the speed of light to your ear.
23 A soft drink bottle is 15 cm tall. Joey blows across that top of the bottle just after drinking the last of his drink. What is the approximate fundamental frequency of the tone that Joey generates? a) 230 Hz b) 570 Hz c) 680 Hz d) 810 Hz e) 1100 Hz
24 A soft drink bottle is 15 cm tall. Joey blows across that top of the bottle just after drinking the last of his drink. What is the approximate fundamental frequency of the tone that Joey generates? a) 230 Hz b) 570 Hz c) 680 Hz d) 810 Hz e) 1100 Hz
25 A child is swinging back and forth with a constant period and amplitude. Somewhere in front of the child, a stationary horn is emitting a constant tone of frequency f S. Five points are labeled in the drawing to indicate positions along the arc as the child swings. At which position(s) will the child hear the lowest frequency for the sound from the whistle? a) at B when moving toward A b) at B when moving toward C c) at C when moving toward B d) at C when moving toward D e) at both A and D
26 A child is swinging back and forth with a constant period and amplitude. Somewhere in front of the child, a stationary horn is emitting a constant tone of frequency f S. Five points are labeled in the drawing to indicate positions along the arc as the child swings. At which position(s) will the child hear the lowest frequency for the sound from the whistle? a) at B when moving toward A b) at B when moving toward C c) at C when moving toward B d) at C when moving toward D e) at both A and D
26.1 The Origin of Sound
 Chapter 26: Sound 26.1 The Origin of Sound All sounds are produced by the vibrations of material objects. Piano, violin, guitar: vibrating strings Saxophone: vibrating reed Flute: vibrating air around
Chapter 26: Sound 26.1 The Origin of Sound All sounds are produced by the vibrations of material objects. Piano, violin, guitar: vibrating strings Saxophone: vibrating reed Flute: vibrating air around
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
9.3 Sound The frequency of sound Frequency and pitch pitch Most sound has more than one frequency The frequency spectrum
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound. The frequency of sound. pitch - the perception of high or low that you hear at different frequencies of sound.
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
Sound Waves. and their characteristics. 1) Frequency (pitch) 2) Intensity (loudness) 3) Harmonic Content. May 10 11:45 AM
 Sound Waves and their characteristics 1) Frequency (pitch) 2) Intensity (loudness) 3) Harmonic Content May 10 11:45 AM 1 particle motion http://positron.ps.uci.edu/~dkirkby/music/html/demos/planewave/soundwave.html
Sound Waves and their characteristics 1) Frequency (pitch) 2) Intensity (loudness) 3) Harmonic Content May 10 11:45 AM 1 particle motion http://positron.ps.uci.edu/~dkirkby/music/html/demos/planewave/soundwave.html
Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations
 secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
NCERT solution for Sound
 NCERT solution for Sound 1 Question 1 Choose the correct answer. Sound can travel through (a) gases only (b) solids only (c) liquids only (d) solids, liquids and gases. (d) solids, liquids and gases. Question
NCERT solution for Sound 1 Question 1 Choose the correct answer. Sound can travel through (a) gases only (b) solids only (c) liquids only (d) solids, liquids and gases. (d) solids, liquids and gases. Question
Chapter 17 Sound Sound and Hearing. Properties of Sound Waves 1/20/2017. Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action
 Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it
 Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Dalkeith High School Level 4 Physics. Waves and Sound
 Dalkeith High School Level 4 Physics Waves and Sound By recording and analysing sound signals, I can describe how they can be manipulated and used in sound engineering. SCN 4-11a INSTRUCTIONS: Always put
Dalkeith High School Level 4 Physics Waves and Sound By recording and analysing sound signals, I can describe how they can be manipulated and used in sound engineering. SCN 4-11a INSTRUCTIONS: Always put
Low? High or. v vv \T\ \ C\ [ \(\(\(\(\ PITCH FREQUENCY CHAPTER4
 CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Wonderlab. Sound. The Statoil Gallery. The science and maths behind the exhibits LIGHT WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON
 Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Prisoner of Echo. 45 minutes. A sound wave needs a medium through which it is transmitted.
 LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
SOUNDS LIKE FUN SCIENCE GRADE 4 STELLA BIZZIO. TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class.
 SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
This test contains questions that are borrowed from other sources. It was not accepted to the exchange but is included in this folder because it was
 This test contains questions that are borrowed from other sources. It was not accepted to the exchange but is included in this folder because it was the only test submitted for this event. Sounds of Music
This test contains questions that are borrowed from other sources. It was not accepted to the exchange but is included in this folder because it was the only test submitted for this event. Sounds of Music
A Kazoo For You. Science Activity.
 A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics
 DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics Grade Level: 6 th -8 th Objectives: Students will be able to explain how dolphins use sound to communicate and navigate through their underwater environment. Florida Sunshine
DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics Grade Level: 6 th -8 th Objectives: Students will be able to explain how dolphins use sound to communicate and navigate through their underwater environment. Florida Sunshine
1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound
 1.34. Intensity and Loudness of Sound www.ck12.org 1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound Define intensity of sound and relate it to loudness. Compare decibel levels of different sounds. Identify factors
1.34. Intensity and Loudness of Sound www.ck12.org 1.34 Intensity and Loudness of Sound Define intensity of sound and relate it to loudness. Compare decibel levels of different sounds. Identify factors
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
LAST: intensity and loudness. READ: 6.3, (6.4,5 optional),
 Phys 1240: Sound and Music LAST: intensity and loudness TODAY: decibels NEXT: decibels, ears, and hearing READ: 6.3, (6.4,5 optional), Coming up: 6.6 (mostly, try to make sense of Fig 6.12!) CAPA 5 due
Phys 1240: Sound and Music LAST: intensity and loudness TODAY: decibels NEXT: decibels, ears, and hearing READ: 6.3, (6.4,5 optional), Coming up: 6.6 (mostly, try to make sense of Fig 6.12!) CAPA 5 due
Sound and Music. Acoustical Society of America 2
 Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
Name: Mode of Study: Student Number: Qualification: Instruction: Answer all the questions on the questions paper.
 Name: Mode of Study: Student Number: Qualification: Instruction: Answer all the questions on the questions paper. SECTION A: BIOLOGY QUESTION 1 [20 MARKS] Question Type: Multiple Choices. Each answer equals
Name: Mode of Study: Student Number: Qualification: Instruction: Answer all the questions on the questions paper. SECTION A: BIOLOGY QUESTION 1 [20 MARKS] Question Type: Multiple Choices. Each answer equals
The Nature of Sound. Section 1: What Is Sound? (p. 534)
 CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
Sound Waves. Sound waves can only travel through matter. The energy carried by a sound wave is transferred by the collisions between the
 Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Sound All Around. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th)
 Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
2015 Junior Entrance and Scholarship Examinations. Science Theory Paper. Time allowed: 60 minutes
 NAME: 2015 Junior Entrance and Scholarship Examinations Science Theory Paper Time allowed: 60 minutes You have 10 minutes reading time. In this time, you should look at the questions in the paper and choose
NAME: 2015 Junior Entrance and Scholarship Examinations Science Theory Paper Time allowed: 60 minutes You have 10 minutes reading time. In this time, you should look at the questions in the paper and choose
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy the clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet.
 Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
Sound Waves. Making Sound Waves
 Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Do you think the ultrasound experiments on mice were justified?
 Q1.(a) Explain what ultrasound is. (b) Ultrasound is used for pre-natal scanning. This is much safer than using X-rays. However, doctors were only sure ultrasound was safe after experiments on mice. Do
Q1.(a) Explain what ultrasound is. (b) Ultrasound is used for pre-natal scanning. This is much safer than using X-rays. However, doctors were only sure ultrasound was safe after experiments on mice. Do
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Hearing and Sound Study Guide
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
Sound. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 _ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
_ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
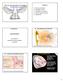 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
Science Year Unit 8L Sound and hearing About the unit Expectations At the end of this unit in terms of scientific enquiry most pupils will:
 Science Year 8 Unit 8L Sound and hearing About the unit In this unit pupils: build on their knowledge of sound and hearing explain how sound travels through media give an explanation of how the ear works,
Science Year 8 Unit 8L Sound and hearing About the unit In this unit pupils: build on their knowledge of sound and hearing explain how sound travels through media give an explanation of how the ear works,
Sounds Good to Me. Engagement. Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 Sounds Good to Me Students make a mental model of how frequencies are detected by the cochlear membrane. Using this model, students examine how cochlear implants can be used to help treat deafness. Next
Sounds Good to Me Students make a mental model of how frequencies are detected by the cochlear membrane. Using this model, students examine how cochlear implants can be used to help treat deafness. Next
Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted.
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Seminary 9 SOUND WAVES
 Seminary 9 SOUND WAVES SOUND WAVES Summary: 1/ When sound travels from air into water, does the frequency of the wave change? The speed? The wavelength? Explain your reasoning. 2/ Amplitude of a sound
Seminary 9 SOUND WAVES SOUND WAVES Summary: 1/ When sound travels from air into water, does the frequency of the wave change? The speed? The wavelength? Explain your reasoning. 2/ Amplitude of a sound
Clicker question. If a sound has an SIL of 0 db, is any energy transferred? a) Yes b) No c)??
 Clicker question If a sound has an SIL of 0 db, is any energy transferred? a) Yes b) No c)?? Phys 1240: Sound and Music www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1240 LAST TIME: Decibels. TODAY: Decibels. NEXT TIME:
Clicker question If a sound has an SIL of 0 db, is any energy transferred? a) Yes b) No c)?? Phys 1240: Sound and Music www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1240 LAST TIME: Decibels. TODAY: Decibels. NEXT TIME:
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Science - Year 4. Sound Block 4S. Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack
 Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Discrete Signal Processing
 1 Discrete Signal Processing C.M. Liu Perceptual Lab, College of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~cmliu/courses/dsp/ ( Office: EC538 (03)5731877 cmliu@cs.nctu.edu.tw
1 Discrete Signal Processing C.M. Liu Perceptual Lab, College of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~cmliu/courses/dsp/ ( Office: EC538 (03)5731877 cmliu@cs.nctu.edu.tw
(sound with frequency) above hertz / 20 khz. frequencies above (human) audible range. (sound) cannot be heard by humans 2
 M. (a) any two from: (sound with frequency) above 20 000 hertz / 20 khz frequencies above (human) audible range (sound) cannot be heard by humans 2 either two appropriate points gain mark each either both
M. (a) any two from: (sound with frequency) above 20 000 hertz / 20 khz frequencies above (human) audible range (sound) cannot be heard by humans 2 either two appropriate points gain mark each either both
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Spectrograms (revisited)
 Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
Diagnostic Ultrasound. Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D.
 Diagnostic Ultrasound Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D. Definition of Ultrasound Ultrasound is simply sound waves, like audible sound. High-frequency sound and refers to mechanical vibrations above 20 khz. Human
Diagnostic Ultrasound Sutiporn Khampunnip, M.D. Definition of Ultrasound Ultrasound is simply sound waves, like audible sound. High-frequency sound and refers to mechanical vibrations above 20 khz. Human
When hearing is painful. Can we damage our ears?
 When hearing is painful Can we damage our ears? What is the link? What is the link? Have you ever wondered what we learned from dolphins and use in submarines today? Objectives: To describe what noise
When hearing is painful Can we damage our ears? What is the link? What is the link? Have you ever wondered what we learned from dolphins and use in submarines today? Objectives: To describe what noise
Sound Workshop. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum
 Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Animal Senses 9/2/16
 Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
TERRESTRIAL S Traveling Noise
 Traveling Noise INTROD CTION In this exercise, students will experiment with their natural surroundings to discover what absorbs or reflects sound. Vegetation, topography, and atmospheric conditions all
Traveling Noise INTROD CTION In this exercise, students will experiment with their natural surroundings to discover what absorbs or reflects sound. Vegetation, topography, and atmospheric conditions all
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
Light/sound and hearing
 Medway LEA Advisory Service Light/sound and hearing 8K & 8L 26 min 27 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L4, Q4-L5, Q5-L5, Q6-L6 1. Thunder and lightning happen at the same time. (a) We see the flash of lightning
Medway LEA Advisory Service Light/sound and hearing 8K & 8L 26 min 27 marks Q1-L3, Q2-L4, Q3-L4, Q4-L5, Q5-L5, Q6-L6 1. Thunder and lightning happen at the same time. (a) We see the flash of lightning
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Table of Contents Science Action Labs
 Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
Table of Contents Science Action Labs 1: Vibrating Sound......................................5 2: Sound Fun..........................................8 3: How Sound Travels..................................11
THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist
 WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Lecture 9: Sound Localization
 Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
If sound waves needs molecules, how do astronauts in the vacuum of space talk to each other?
 Worksheet 16 A lesson from the Native Access to Engineering Programme Sound sound: saund (noun) 13 th century 1 a : a particular auditory impression : b : the sensation perceived by the sense of hearing
Worksheet 16 A lesson from the Native Access to Engineering Programme Sound sound: saund (noun) 13 th century 1 a : a particular auditory impression : b : the sensation perceived by the sense of hearing
Producing and Detecting Sound
 Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound /785 Spring 2017
 Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound 85-385/785 Spring 2017 Professor: Laurie Heller Classroom: Baker Hall 342F (sometimes Cluster 332P) Time: Tuesdays and Thursdays 1:30-2:50 Office hour: Thursday 3:00-4:00,
Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound 85-385/785 Spring 2017 Professor: Laurie Heller Classroom: Baker Hall 342F (sometimes Cluster 332P) Time: Tuesdays and Thursdays 1:30-2:50 Office hour: Thursday 3:00-4:00,
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Sound Localization PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 31. Audition
 Sound Localization PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 31 Physics and psychology. Audition We now have some idea of how sound properties are recorded by the auditory system So, we know what kind of information
Sound Localization PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 31 Physics and psychology. Audition We now have some idea of how sound properties are recorded by the auditory system So, we know what kind of information
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Conch Shell as an Omni Directional Speaker. Pratik Desai (ID # ) 9/12/14 Submitted to Dr. Rama Bhat.
 Conch Shell as an Omni Directional Speaker Pratik Desai (ID #6742866) 9/12/14 Submitted to Dr. Rama Bhat. CONCH SHELL AS A OMNIDIRECTIONAL SPEAKER Conch Shell is the protective cover of long sea snails
Conch Shell as an Omni Directional Speaker Pratik Desai (ID #6742866) 9/12/14 Submitted to Dr. Rama Bhat. CONCH SHELL AS A OMNIDIRECTIONAL SPEAKER Conch Shell is the protective cover of long sea snails
Outline. 4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
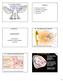 4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Loudness C. Perception of Pitch D. References Updated May 13, 01 Introduction 3 A. The Structure
4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Loudness C. Perception of Pitch D. References Updated May 13, 01 Introduction 3 A. The Structure
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Basic Ultrasound Physics Board Review Questions
 Basic Ultrasound Physics Board Review Questions Sidney K. Edelman, PhD ESP Ultrasound The Woodlands, TX Question 1 What is the wavelength of 2 MHz sound in soft tissue? 1. 1.54 mm 2. 0.75 mm 3. 0.75 cm
Basic Ultrasound Physics Board Review Questions Sidney K. Edelman, PhD ESP Ultrasound The Woodlands, TX Question 1 What is the wavelength of 2 MHz sound in soft tissue? 1. 1.54 mm 2. 0.75 mm 3. 0.75 cm
Honeybee. PSY 2364 Animal Communication. Honeybees. Honeybees. Honeybees. Sensory specialization
 PSY 2364 Animal Communication Honeybee Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Hymenoptera Family: Apiidae Genus: Apis Species: mellifera Honeybees Diploid animals (e.g. humans) 2 sets
PSY 2364 Animal Communication Honeybee Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Hymenoptera Family: Apiidae Genus: Apis Species: mellifera Honeybees Diploid animals (e.g. humans) 2 sets
whether or not the fundamental is actually present.
 1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Diagnostic Ultrasound: Physics and Equipment, 2nd ed., by Peter R. Hoskins (Editor), Kevin Martin (Editor),
ULTRASOUND IMAGING EE 472 F2018 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Diagnostic Ultrasound: Physics and Equipment, 2nd ed., by Peter R. Hoskins (Editor), Kevin Martin (Editor),
Technical Discussion HUSHCORE Acoustical Products & Systems
 What Is Noise? Noise is unwanted sound which may be hazardous to health, interfere with speech and verbal communications or is otherwise disturbing, irritating or annoying. What Is Sound? Sound is defined
What Is Noise? Noise is unwanted sound which may be hazardous to health, interfere with speech and verbal communications or is otherwise disturbing, irritating or annoying. What Is Sound? Sound is defined
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound
 Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound Sensing sound Experiencing sounds Science skills: Predicting Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should know: We use our senses to detect sound. We hear things with
Unit 1.P.2: Sensing Sound Sensing sound Experiencing sounds Science skills: Predicting Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should know: We use our senses to detect sound. We hear things with
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test. Grade 5, Chapter 5 Sound. Name. Date
 McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TKS Practice Test Grade 5, hapter 5 Sound Name ate Use the illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 3. 1 Why does the rubber band make
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TKS Practice Test Grade 5, hapter 5 Sound Name ate Use the illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 3. 1 Why does the rubber band make
group by pitch: similar frequencies tend to be grouped together - attributed to a common source.
 Pattern perception Section 1 - Auditory scene analysis Auditory grouping: the sound wave hitting out ears is often pretty complex, and contains sounds from multiple sources. How do we group sounds together
Pattern perception Section 1 - Auditory scene analysis Auditory grouping: the sound wave hitting out ears is often pretty complex, and contains sounds from multiple sources. How do we group sounds together
EKG and Sound.
 I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the supplemental. Visit the following website: blaufuss.org then click on the "START" button next to "Heart Sounds Tutorial." Do not worry so much about the
I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the supplemental. Visit the following website: blaufuss.org then click on the "START" button next to "Heart Sounds Tutorial." Do not worry so much about the
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price. Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized
 PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
Ultrasound: Past and Present. Lecturer: Dr. John M Hudson, PhD
 Ultrasound: Past and Present Lecturer: Dr. John M Hudson, PhD Disclosures 2 No conflicts of interest to declare Course Outline 3 1. Survey of ultrasound physics & applications 2. (Sep 21) 3. (Sep 28) 4.
Ultrasound: Past and Present Lecturer: Dr. John M Hudson, PhD Disclosures 2 No conflicts of interest to declare Course Outline 3 1. Survey of ultrasound physics & applications 2. (Sep 21) 3. (Sep 28) 4.
ISLAMABAD ACADEMY PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13)
 PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13) SHORT QUESTIONS How sound is produced? It is produced from a vibrating body which transfers in air from one place to other in the form of compression waves. A medium
PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13) SHORT QUESTIONS How sound is produced? It is produced from a vibrating body which transfers in air from one place to other in the form of compression waves. A medium
