IMAGING NONODONTOGENIC TUMORS OF THE JAWBONES
|
|
|
- Angelica Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMAGING NONODONTOGENIC TUMORS OF THE JAWBONES N. Serman. Sept, 2002 W. & P Ch Stafne & Gibilisco Ch 15 Oral and Maxillofacial diagnostic Imaging Ch. 8 Non agenesis or non eruption of teeth often gives an indication regarding the time of onset of the lesion. The radiographic signs may - 1. May give an indication of the type of the lesion 2. Show evidence of features of the lesion 3. May provide specific diagnosis 4. Location of lesion may be a clue Benign tumors are often found incidentally on radiographs. In general they do not invade adjacent bone. Exception ameloblastoma Some have high incidence of recurrence Often are locally aggressive The majority of lesions discussed here do not produce pathopneumonic radiographic features that will allow one to use the radiograph as the sole basis for making a diagnosis. But then again, there is seldom such thing as only a radiographic diagnosis, implying that the findings observed on a radiograph always need to be correlated and interpreted with the clinical evaluation and other diagnostic aids If the radiograph reveals agenesis and non eruption of teeth in the region of a lesion, it generally can be assumed that the lesion had its onset prior to the normal time for development and eruption of these teeth A benign tumor is - 1. a new growth resembling the tissue of origin 2. has an insiduous onset 3. grows slowly 4. has a smooth outline 5. may displace adjacent structures such as teeth. 6. is usually painless 7. does not metastasize 8. is not life threatening 9. or forms septae or compartments 10. does not invade adjacent tissue - ameloblastoma the exception TECHNICAL PROCEDURES: Intra oral?: Occlusal radiographs Extra oral : Pan. P.A.; 0.M.; Tomographic radiographs, CT - hard tissue MRI - soft tissue Growth disturbances lacking the capacity for limitless growth proliferation are not true neoplasms but hyperplasias or hamartomas. CLASSIFICATION. 1. Tori and exostoses
2 2. Enostosis 3. Osteoma 4. Osteoid osteoma 5. Benign osteoblastoma 6. Chondroma 7. Neurogenic tumors 8. Calcifying peripheral fibroma 9. Central / Peripheral giant cell tumor 10. Central hemangioma 11. Arteriovenous shunt 12. Aneurysmal bone cyst 13. Dermoid cyst. Thyroglossal cyst Branchial cleft cyst. Definition: A bony formation on the inner surface of the periosteum extending into the edullary spaces. Radiographically some of the opacities within the jaws that are diagnosed as osteosclerosis actually represent enostoses. Since the advent of CT a difference is recognized between an enostosis [growing inward from the periodontium] and an enostosis [opacity] within the spongy bone. 3. OSTEOMAS: Rare in the jaws. Definition: Osteomas are benign tumors composed of bone. The bones of the face are subject to a variety of bony overgrowths that are difficult to classify. Osteomas vary greatly in size. May be attached by a pedicle; or may grow from a wide base. The pedenculated type occurs more frequently in the mandible. The skull is the most common site for the development of an osteoma, with the calvarium and frontal sinus areas being affected most frequently. Radiographically provides information concerning the shape and size and its relationship and attachment to the bone. If the tumor consists chiefly of dense, laminated bone with a few Haversian canals, the radiographic density is much greater than that of a tumor containing spongy bone and abundant marrow space. Osteomas of the mandible are rare. When found with associated supernumary teeth and sometimes with compound odontomas and hypercementosis may develop in patients with Gardner syndrome. Impacted supernumerary and permanent teeth seen with multiple polyposis of large intestine and epidermoid cysts of skin. Malignant change can occur in these polyps and the syndrome is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait. Thus, relatives of patients with the disease should be investigated 4. OSTEOID OSTEOMA: Rare Small, oval or roundish tumor-like nidus which is composed of osteoid and trabeculae of newly formed bone deposited within a substratum of highly vascularized osteogenic connective tissue. Clinically often severe pain Radiographically: A radiopaque nidus surrounded by a diffuse and irregular radiolucency, surrounded in turn by bone of increased radiographic density
3 5. BENIGN OSTEOBLASTOMA - RARE Some features distinguish the lesion from an apparently close relative, the osteoid osteoma but they are very similar. The benign osteoblastoma has the potential for becoming moderately large, whereas the osteoid osteoma usually is 1 cm or less in diameter. Radiographically well circumscribed radiolucent or mixed appearance. Sometimes large.
4 6. CHONDROMA - Rare in jaws Definition: A benign tumor composed of mainly of cartilage. The chondroma may become partially ossified and is then called as osteo-chondroma. Theoretically, complete replacement of the cartilage by bone could occur - producing an osteoma. Any cartilaginous lesion of the jaws must be treated as potentially malignant. A chondrosarcoma may arise from pre-existing chrondromatous tumors. Radiographically. Irregular radiolucent or mottled area of bone. NON specific appearance. A destructive lesion. May cause root resorption 7. NEUROGENIC TUMORS (NEURILEMMONA, NEUROFIBROMA) Benign neurogenic tumors are occasionally found centrally within the jaws. The neurilemmoma (Schwannoma) is usually encapsulated (lucency). The neurofibroma is not capsulated. Neurofibromas may occur as solitary nodules or they may be associated with von Recklinghausen's disease, in which there are multiple cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors, cafe-au-lait spots of melanin pigmentation, and occasional skeletal deformities. With von Recklinghausen's disease there may be widening of the mandibular canal unilaterally. Clinically. Occur at any age, and there appears to be no sex predilection. The majority of these lesions occur in the mandible. The lesions are relatively slow growing, and pain or parasthesia may be associated symptoms. Radiographically -findings vary considerably. May present as a solitary radiolucency associated with the inferior alveolar canal, or as a cystic multilocular radiolucency with extensive bone damage, cortical expansion, and perforation A neurofibroma adjacent to bone may produce a saucer-shaped erosive defect on the surface of the bone similar in appearance to other benign tumors Malignant peripheral nerve tumors are impossible to distinguish radiographically from other malignancies. TRAUMATIC NEUROMA (AMPUTATION NEUROMA) A traumatic neuroma is initiated by trauma to a nerve trunk, most commonly amputation (amputation neuroma). The tumor appears on the torn or cut end of the nerve, where it forms a ball or swelling varying in size, on the proximal termination of the nerve fiber. Radiographically. This tumor within bone produces a radiolucent defect of varied shape, but it has well-defined borders- non specific appearance. If small may not be seen. 8. CALCIFIED PERIPHERAL FIBROMA A peripheral fibroma arising from the fibrous connective tissue of the periodontium may demonstrate the odontogenic potential of that tissue. It rarely reaches a diameter of more than 2 cm. Calcified substances form in many of these tumors and may be bone, cementum, amorphous and nonspecific calcifications, or a combination of these. Clinically - seen on gingiva as a hard swelling, often between the teeth. Those in which extensive calcifications have taken place may become sufficiently radiopaque to permit visualization in the radiograph. 9. CENTRAL OR PERIPHERAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA (BENIGN GIANT CELL TUMOR: GIANT CELL REPARATIVE GRANULOMA)
5 It is not certain what the relationship is between the central and the peripheral type of jaw lesions and those found elsewhere. Giant cell granulomas are designated as peripheral or central in origin. The peripheral lesions occur equally in the maxilla or mandible and are located on the gingiva or alveolar process; have a predilection for edentulous areas, but may be located in dentate areas. Color : Deep red to blue. Age : plus or minus 30 years Sex : Female: Male 2 :1 Site : Mandible : maxilla 2:1 Radiographically Peripheral lesion may or may not involve the underlying bone. A superficial erosion or saucer-shaped concavity on the alveolar ridge is rarely seen. The central giant-cell granuloma occurs more often in children and young adults. The majority of these lesions occur in the region formerly occupied by deciduous teeth - that is, anterior to the molars. Frequently they cross the midline. Swelling may be the only presenting symptom Radiographically. CENTRAL LESION may be noted as an incidental finding on routine radiographic screening. Demonstrates two variations. One is osteolytic, unilocular lesion in which the cortex may be partially destroyed. The other type exhibits multiple osteolytic foci with bone trabeculations within the tumor [soapbubble appearance]; it may produce thinning and expansion of the cortex when it has become very extensive. In both types, malposition of teeth and resorption of the roots of the teeth upon which the lesion encroaches are not unusual findings Diff Diag. Ameloblastoma, Myxoma, cyst or central hemangioma. It is important to suspect parathyroid abnormality whenever a patient develops giant-cell lesions of the jaw, particularly if they are multiple or bilateral. There will then be a loss of the lamina dura radiographically to assist in differentiation. 10. CENTRAL HAEMANGIOMA OF BONE. Rare in jaws They are composed of blood channels of varied patterns that can be classified histologically as cavernous, capillary, or mixed Clinically - Usually no symptoms. May present as hard, non-tender swelling that slowly enlarges over months or years. Haemorrhaging around the necks of the teeth in the involved region or severe bleeding after extraction may give a clue to the nature of the lesion; clinical findings frequently encountered are mobility of the teeth, hyperthermia of the affected side, bruit and, less frequently, pain and parasthesia Females : Males 2 : 1 Age : Under 20 years Site : Usually Mandible Radiographically Large radiolucent lesions in the mandible, often reveal cystic spaces interspaced with trabecular patterns and thinned, expanded, cortices. Bone spicules.
6 may extend at right angles from the bone into the lesion, a feature that is pathognomonic of hemangioma. Sometimes a honeycomb appearance is seen. Diff Diagnosis: Ameloblastoma, myxoma, central giant cell granuloma, aneurysmal bone cyst 11. ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA / SHUNT An arteriovenous fistula is a direct communication between an artery and a vein, through which the blood bypasses the capillary circulation Early diagnosis and proper treatment of an arteriovenous fistula of the jaws is important to the dentist because of a simple extraction of a tooth could cause uncontrollable and fatal hemorrhage Clinically: Enlargement and abnormal warmth of the part, a palpable thrill, and an audible bruit are salient features. Also, there may be loosening of teeth at the site of the fistula and spontaneous hemorrhage from the mouth Radiographically: Peripheral - nothing unless radiopaque material injected. Central - honeycomb appearance or large radiolucency with trabeculations 12. ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST Aneurysmal bone cysts occur most frequently in the spinal column and long bones. Very rare in the mandible and maxilla. Occur during the first and second decades mainly in mandible. No sex predilection. An aneurysmal bone cyst may result from an overzealous attempt at repair in bone marrow Clinically: Progressive swelling of the jaw that may be associated with pain or tenderness. Teeth adjacent to the lesion may be deflected but remain vital. Often history of trauma. Lesion grows rapidly. Radiographically a well- circumscribed unilocular or multilocular cystyc lesion. As the lesion increases in size, there is marked expansion and thinning of the cortex, resulting in a ballooning that distends the jaw. Differential diagnosis: central myxoma, giant-cell lesion, odontogenic cysts or tumors. Central hemangioma. Too young for ameloblastoma 13. DERMOID CYSTS Definition: Dermoid cysts contain elements of dermis, such as epidermal tissue, hair, nails, sebaceous and sweat glands. They are benign, congenital tumors that may occur in the region near the pituitary gland, in the submaxillary region and in the sex glands, particularly the ovary. Many contain teeth, which permits a fairly reliable diagnosis to be made from the radiographic examination alone. Primary as well as permanent teeth may be present but are smaller than normal and jawbones may be seen as small rudimentary fragments.
7 II. MALIGNANT TUMORS. The two main types of malignant tumors are carcinoma and sarcoma. However, the most common malignancy seen in the bones of the jaws metastatic. CARCINOMA A carcinoma is a malignant tumor of epithelial origin. 1. SQUAMOUS-CELL carcinoma occurs most frequently in the oral cavity, and the sites of origin are the lip, tongue, floor of the mouth, palate, buccal surfaces, and gingivae. In rare instances the tumor may arise with in the jaws from cell rests remaining from the enamel organ and sheath of Hertwig Radiographically : Early stage - often N.A.D. Later stage - radiolucency with irregular and ill defined borders. Cortical destruction. Tilting / movement of teeth. Any ulcerated growth of the soft tissue beneath which there is radiographic evidence of destruction of bone should be suspected of being malignant. Moth eaten appearance. Differential diagnosis: simulates severe infection osteomyelitis Carcinomas that occur in the jaws as a result of metastases from lesions elsewhere most often arise in the central portion of the jaws, because red bone marrow appears to be the most frequent site of metastases to bone. The first evidence of metastasis may be radiographic signs of an osteolytic lesion in a jaw that, appears clinically to be normal. Seen as a poorly demarcated lucency. The lesions in the mandible may cause parasthesia of the lip; when this symptom is present, one should suspect that the lesion is malignant 2. MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA. Definition: Arises frequently in the salivary glands. The tumor may be found as a central lesion within the jaws. Either the maxilla or the mandible may be involved; the molar-premolar area is the usual site. Central lesions appear twice as frequently in women as in men, and the average age at diagnosis is 46 years Radiographically: A multilocular radiolucency similar to ameloblastoma; however, wide variations occur. Nothing will be seen where the lesion is limited to the soft tissue Clinically a slowly enlarging mass with or without pain 3. SARCOMA Definition: A sarcoma is a malignant tumor of connective tissue origin. May originate in fibrous tissue, cartilage, bone, muscle, fat, or endothelial tissue. Sarcomas tend to occur in a younger age group, have a greater propensity to metastasize via the bloodstream rather than the lymphatics; thus, distant sites of secondary tumor are observed more frequently. Radiographically: Early detection important. Produces changes in bone in the early stage of development. Irregular and diffuse destruction of bone and a patchy appearance at an early stage and there may be no line of demarcation from the normal surrounding bone.
8 A. FIBROSARCOMA The incidence of fibrosarcoma is less than that of osteosarcoma. In contrast to osteosarcoma, they are found uniformly in both young and older age groups. B. OSTEOSARCOMA (Osteogenic Sarcoma) The osteosarcomas may present a wide range of microscopic and radiographic findings. Divided into osteoblastic, osteoclastic, chondroblastic, and fibroblastic tumors, depending on the dominating element. The mean age at the time of the first-noted symptom related to the tumor is significantly greater (about a decade) than for osteosarcoma of other bones. Haemotagenous metastasis less frequently observed Clinically: Swelling of the involved area, with or without associated pain. Parasthesia, loose teeth, and bleeding. Nasal obstruction may be noted with maxillary lesions Radiographically: Destructive lesion with indistinct borders, may appear sclerotic or lytic, or there may be a combination of these findings. There may be a symmetrically widened periodontal membrane space associated with a few teeth. The osteoblastic variety may produce a sunburst / sunray affect C. CHONDROSARCOMA - Rare in jaws. Predilection for adulthood and older age groups Radiographically: Suggestive of malignancy, but no characteristic features that allow differentiation. Seen in head of condyle. D. MALIGNANT LYMPHOMA. The malignant lymphomas are a group of neoplasms that are derived from lymphocytes and reticulum cells in any of their developmental stages. Clinically: Present with swelling and pain of the involved area. Parasthesia is a frequent finding. No significant sex predilection, and all age groups are involved. Radiographically - usually nothing as it is usually limited to soft tissue E. MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Myeloma is a tumor of bone that arises from bone marrow constituents resembling plasma cells. These neoplasms are almost always multiple and may be widely distributed throughout the skeleton. Radiographically The lesion is seen most commonly in the skull on a lateral skull view. Fairly large, well demarcated radiolucencies describe as "punched out" lesions. Very rare in mandible or maxilla. There may be spotty distribution of lesions throughout the maxilla and the mandible. Tend to appear in the posterior regions, where the marrow spaces are largest. Tend to be multiple. The diagnosis of multiple myeloma is often aided by laboratory procedures. Many patients exhibit a hyperglobulinemia and an increase in serum protein. Bence Jones protein is noted in urine in patients with multiple myeloma. F. HISTIOCYTOSIS X. Related conditions of the reticulo-endothelial system.
9 LETTERER-SIWE. Acute form occurring in infants and is rapidly fatal. Radiographically large poorly demarcated lucencis seen on lateral skull view. HAND-SCHULLER-CHRISTIAN Chronic form affecting infants and young children. Radiology as above EOSINIPHILIC GRANULOMA Localized condition affecting children and young adults with a predilection for males Radiographically - sometimes poorly demarcated OR punched-out lesions in skull in young people; often multiple In the jaws non-specific lytic lesions may be seen in the bone or at the apices of the teeth that may resemble a peri-apical area or localized, advanced periodontal condition. The eosinophilic granuloma may appear as a poorly demarcated periapical lucency or a localized severe periodontal problem in young persons. G. Sickle cell anemia. Found mainly in young black males [early twenties]. Bleeding gingiva Radiographically - enlarged marrow spaces. Thalasemia. / Mediterranean disease : Fetal hemoglobin with short life span. Radiographically - large marrow spaces Metasteses - from prostate, ovaries, kidneys, stomach, breast etc. Commonly seen in the posterior region of the mandible in the region of the mandibular canal as a poorly demarcated lucency.
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone:
 Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS
 Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Oral Tumors in Dogs Gingival Enlargement
 Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Palatal Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 :
 Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity
 Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older
 Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
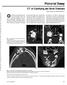 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
10/23/2014. features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means. interpretation vs. diagnosis. science or art? image investigation
 features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
University of Palestine. Final Exam 2 ed Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Bubbly Lesions of Bone
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month w79 08.18.09 Eisenberg Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Ronald L. Eisenberg 1 Eisenberg RL Keywords: bubbly lesions, fegnomashic, skeletal
Residents Section Pattern of the Month w79 08.18.09 Eisenberg Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Ronald L. Eisenberg 1 Eisenberg RL Keywords: bubbly lesions, fegnomashic, skeletal
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version -
 CHAPTER 21 BENIGN TUMORS OF THE JAWS as ameloblastic fioro-odontomas, when they are really developing odontomas. Clinical Features. The clinical features are similar to odontomas, often associated with
CHAPTER 21 BENIGN TUMORS OF THE JAWS as ameloblastic fioro-odontomas, when they are really developing odontomas. Clinical Features. The clinical features are similar to odontomas, often associated with
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Bone Tumours - a synopsis. Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009
 Bone Tumours - a synopsis Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009 Aims General approach to diagnosis Common entities.and not so common ones. Mini quiz Challenge of bone tumour diagnosis Bone tumours
Bone Tumours - a synopsis Dr Zena Slim SpR in Histopathology QAH 2009 Aims General approach to diagnosis Common entities.and not so common ones. Mini quiz Challenge of bone tumour diagnosis Bone tumours
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Grading of Bone Tumors
 Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review
 Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Limeme, N. Benzina, A. BelKhiria, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, N. Mallat, H.
Imaging Findings Of Bone Tumors: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Limeme, N. Benzina, A. BelKhiria, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, N. Mallat, H.
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp!
 APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
APMA 2018 Radiology Track Bone Tumors When to say Gulp! DANIEL P. EVANS, DPM, FACFAOM Professor, Department of Podiatric Medicine and Radiology Dr. Wm. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine Conflict of
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Bone tumors. RMG: jan
 Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
SAMPLE. Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS ICD-10. Cross Coder
 Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Swelling. Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal and transverse axis and if possible the depth)
 Swelling Inspection Site: exact anatomic position Number: single or multiple Shape: spherical, oval, kidney-shaped or irregular Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal
Swelling Inspection Site: exact anatomic position Number: single or multiple Shape: spherical, oval, kidney-shaped or irregular Size: measure exact size in cm using a tape measure (measure longitudinal
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Periodontal ligament
 Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
1/9/2013 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE. Introduction. Classification for Extramedullary Tumors
 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT
 Case Report Received : 23-07-2013 Review completed : 29-08-2013 Accepted : 04-09-2013 ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT V. V. N Pavan Kumar,* Madhumati Singh,** Sandeep Kashyap,*** Madan
Case Report Received : 23-07-2013 Review completed : 29-08-2013 Accepted : 04-09-2013 ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT V. V. N Pavan Kumar,* Madhumati Singh,** Sandeep Kashyap,*** Madan
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Oral Histology. Alveolar bone or process: Functions of alveolar bone: Chemical composition: Development of the alveolar process: Dr.
 Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses:
 Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses: Approaches to Diagnostic Imaging Nir J. Harish September 2007 Head and Neck Cancers Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Salivary glands Incidence
Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses: Approaches to Diagnostic Imaging Nir J. Harish September 2007 Head and Neck Cancers Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Salivary glands Incidence
5.1 Breast, Anatomy. 70
 Chapter 5 Breast 5.1 Breast, Anatomy Breasts, also called Mamma are mammary glands, subcutaneously placed on the ventral side of the trunk in mammalian species, and develop for the sole purpose of secreting
Chapter 5 Breast 5.1 Breast, Anatomy Breasts, also called Mamma are mammary glands, subcutaneously placed on the ventral side of the trunk in mammalian species, and develop for the sole purpose of secreting
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Department of Radiology, University of Szeged. Imaging of the skeleton
 Imaging of the skeleton Methods of examination: plain x-ray (radiography, densitometry) x-ray with contrast material (fistulography, angiography) ultrasound (b-mode, Doppler, color, duplex) computed tomography
Imaging of the skeleton Methods of examination: plain x-ray (radiography, densitometry) x-ray with contrast material (fistulography, angiography) ultrasound (b-mode, Doppler, color, duplex) computed tomography
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
