Head & Neck Anatomical Dissection Course 8/14/07
|
|
|
- Jasper Hensley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Head & Neck Anatomical Dissection Course 8/14/07 Jason E. Portnof DMD, MD Chief Resident Division of Dentistry, Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical College
2 Muscles of Facial Expression
3 Muscles of Mouth, Lips, Cheek Circumoral Muscles Orbicularis oris Sphincter of oral aperture. Dilator Muscles Levator labii superioris alaque nasi Elevator of upper lip and alae of nose. Mentalis Raises skin of chin. Mentalis Buccinator Aids mastication by pressing the cheeks against the molar teeth during chewing.
4 Muscles of Mouth, Lips, Cheek Depressor anguli oris Levator anguli oris Zygomaticus major Zygomaticus minor Levator labii superioris Deprssor labii inferioris Risorius Platysma
5 Lymphatic Drainage of Lips Lymph from upper lip and lateral parts of lower lip drains to submandibular LN Lymph from middle part of lower lip drains to submental LN
6
7 Facial Nerve Main trunk emerges from Skull Base at Stylomastoid Foramen. Enters the Parotid Gland. 2 trunks emerge from the parotid and radiate anteriorly. Temporofacial Cervicalfacial 5 Terminal Branches Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Marginal Mandibular Cervical
8 Boundaries: Oral Cavity Extends from lips anteriorly to palatoglossal folds posteriorly (i.e., anterior to oropharynx). Structures: Tongue Teeth Alveolar Bone The oral vestibule is the space between the cheeks and the teeth/gums.
9
10
11 Pharynx Nasopharynx Oropharynx Hypopharynx (Laryngopharynx)
12 Pharyngeal Wall 5 Layers Mucosa Submucosa Pharyngobasilar fascia Muscular Layer Buccopharyngeal fascia
13 Oropharynx Boundaries of the oropharynx: Anteriorly: : junction of the hard and soft palate and circumvallate papillae of the tongue base. Superiorly: imaginary line drawn from the hard palate to the posterior oropharyngeal wall. Inferiorly: pharyngoepiglottic folds. Structures: Tonsils, tonsillar fossa, tonsillar pillars, tongue base and a portion of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
14 Oropharynx Structures Folds (or faucial pillars) Folds in the mucous lining of the oral cavity formed by the underlying palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal muscles. Palatoglossal folds run from the wall of the oral cavity to the approximate junction of the posterior 1/3 and anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
15 Oropharynx Structures Tonsils Palatine (faucial( faucial) ) tonsils are located immediately posterior to the palatoglossal folds and anterior to the palatopharyngeal folds; inferior to the soft palate and superior to the tongue; and a medial to the superior constrictors, the styloglossus,, and the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX). Nasopharyngeal (pharyngeal) tonsils are located on the posterior aspect of the nasopharynx. When enlarged these are referred to as the adenoids. Lingual tonsils are lymphoid tissue in the tongue. Continuous with the inferior pole of the palatine tonsil.
16
17 Nasopharynx Soft palate separates nasopharynx from oropharynx.
18 Adenoids Pharyngeal tonsils, nasopharyngeal tonsils Mass of lymphoid tissue situated in the roof of the nasopharynx
19 Palate Vasculature: (Bilateral) Greater palatine artery Branch of descending palatine artery Lesser palatine artery Branch of descending palatine artery Ascending palatine artery Branch of Facial Artery Veins of palate Tributaries of pterygoid venous plexus
20 Innervation of Palate Sensory nerves of palate are branches of pterygopalatine ganglion Greater palatine nerve supplies gingiva, mucous membrane, and glands of hard palate Nasopalatine nerve supplies mucous membrane of anterior part of hard palate Lesser palatine nerves supply soft palate
21 Hard Palate Palatine processes of maxilla and horizontal plates of the palatine bones. Periosteum of the hard palate is continuous into the soft palate (palatine aponeurosis), and is the insertion site of the palatal muscles. Landmarks Incisive Foramen Greater Palatine Foramen Lesser Palatine Foramen
22 Soft Palate Muscle Action Innervation Levator veli palatini elevates the soft palate Pharyngeal Plexus Tensor veli palatini Palatoglossus Palatopharyngeus Tenses the palate, opens mouth of auditory tube Elevates posterior tongue, draws soft palate into tongue Tenses soft palate. Pulls the pharynx superiorly, anteriorly, medially Mandibular Nerve V3 (medial pterygoid nerve) Pharyngeal Plexus Pharyngeal Plexus Musculus Uvulae Shortens uvula, pulls it superiorly Pharyngeal Plexus
23 Trigeminal Nerve
24 CN 5 Trigeminal Nerve Originates in Pons. Both motor and sensory nerve. Ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory. The mandibular nerve has both sensory and motor functions. Three large trunks originate from the semilunar ganglion (Gasserian( ganglion). Exit Skull at 3 different foramina V1: Superior Orbital Fissure V2: Foramen Rotundum V3: Foramen Ovale
25 Trigeminal Nerve Branches Opthalmic Nerve (V1) Nasociliary nerve Supraorbital nerve Lacrimal nerve Frontal nerve Supratrochlear nerve Infratrochlear nerve Maxillary Nerve (V2) Zygomatic nerve Posterior superior alveolar nerve Middle superior alveolar nerve Anterior superior alveolar nerve Infraorbital nerve Greater Palatine nerve Nasopalatine nerve Mandibular Nerve (V3) Auriculotemporal nerve Lingual nerve Buccal nerve Inferior alveolar nerve (Mental nerve)
26
27 CN V Dermatome Distribution
28
29
30 Maxilla Each half of the fused maxilla consists of: The body of maxilla Four processes Zygomatic process Frontal process Alveolar process Palatine process Infraorbital foramen
31
32 Mandible Condyle Sigmoid Notch Ramus Angle External Oblique Ridge Symphysis Mental Foramen
33 Mandible Sphenomandibular Ligament Stylomandibular Ligament
34 Muscle Attachments of the Muscles of Mastication Temporalis Masseter Lateral Pterygoid Medial Pterygoid Suprahyoid Muscles Geniohyoid Mylohyoid Digastric (anterior belly) Stylohyoid Genioglossus Mandible
35 Muscle Temporalis Origin Floor of temporal fossa, deep surface of temporal fascia. Insertion Coroniod process, anterior border of mandibular ramus. Function Elevates and retrudes mandible. Masseter Superficial portion- anterior 2/3 of inferior border of zygomatic arch. Deep portion- medial surface of zygomatic arch. Lateral surface of ramus, coronoid process, and angle of mandible. Elevates, protrudes, and retrudes mandible. Lateral Pterygoid Superior head- infratemporal surface of sphenoid greater wing. Inferior head- lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate. Anterior portion of condylar neck and TMJ capsule. Protrusion of mandible. Lateral movements of mandible. Medial Pterygoid Deep head- Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate; pyramidal process of palatine bone. Superficial head- maxillary tuberosity. Medial surface of ramus, inferior to mandibular foramen. Protrudes and elevates mandible. Lateral movements of mandible
36 Muscle Geniohyoid Origin Inferior genial tubercle on inner surface of mandibular symphysis. Insertion Body hyoid bone. Function Elevates tongue, FOM, and hyoid. Mylohyoid Line from last molar to mandibular symphysis. (mylohyoid line) Raphe and body of hyoid bone. Elevates base of hyoid bone. Raises floor of mouth and tongue. Digastric Posterior belly- mastoid notch (temporal bone). Anterior belly- digastric fossa (mandible). Intermediate tendon attached to hyoid bone by fibrous loop. Depresses mandible, Elevates the hyoid bone. Stylohyoid Posterior border of the styloid process. Body of hyoid bone. Elevates base of tongue and hyoid bone.
37 Accessory Muscles to the Muscles of Mastication Platysma Buccinator Posterior neck musculature Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Intrinsic neck muscles
38 Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
39 TMJ Classification: Ginglymoarthrodial Joint Translational (gliding) movement Rotational (hinging) movement Synovial Joint
40 TMJ Anatomy Articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone (TMJ fossa). Articular disc lies between condyle and fossa. Condyles Elliptically shaped. Long axis oriented mediolaterally. Articular Surface of Temporal Bone Functional aspect of TMJ. Dense fibrous connective tissue. Concave : Articular fossa (Glenoid Fossa, Mandibular Fossa) Convex : Articular eminence (tubercle)
41 Articular Disc Dense fibrocartilagenous connective tissue. Avascular and aneural. Nutrition of chondrocytes with the movement of synovial fluid is essential for maintenance of structure and function. Biconcave structure is a three dimensional space filler between the two convex surfaces of the condyle and articular eminence. Separates joint into inferior and superior joint spaces. Varies in thickness. Intermediate zone- thin (center of disc) Anterior and Posterior Bands- thick Posterior band is thicker and is attached to retrodiscal tissues (bilaminar( zone, posterior attachment). Anterior band is attached to the capsular ligament, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the condyle. Retrodiscal Tissues Loose connective tissues. Vascular and Innervated.
42 TMJ Disorders
43 TMJ Reconstruction
44 Boundaries Infratemporal Fossa Laterally: Ramus of Mandible Medially: Lateral Pterygoid Plate Anteriorly: : Posterior Aspect of Maxilla Posteriorly: : Tympanic Plate and the Mastoid and Styloid Processes of the Temporal Bone Superiorly: Inferior Surface of the Greater Wing of the Sphenoid Bone Inferiorly: Where the Medial Pterygoid Muscle Attaches to the Mandibular Angle
45 Infratemporal Fossa Contents: Inferior part of the temporal muscle Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles Maxillary artery Pterygoid venous plexus Mandibular,, Inferior alveolar, lingual, buccal, and chorda tympani nerves, and otic ganglion
46 Arteries of Face Artery Origin Course Distribution Facial External Carotid Artery Ascends deep to submandibular gland, rounds around inferior border of mandible and enters face Muscles of facial expression and face Inferior Labial Facial artery near angle of mouth Runs medially in lower lip Lower lip and chin Superior Labial Facial artery near angle of mouth Runs medially in upper lip Upper lip and ala and septum of nose Lateral nasal Facial artery as it ascends alongside nose Passes to ala of nose Skin on ala and dorsum of nose Angular Terminal branch of facial artery Passes to medial angle (canthus( canthus) ) of eye Superior part of cheek and lower eyelid
47 Arteries of Face Artery Origin Course Distribution Superficial temporal Smaller terminal branch of external carotid artery Ascends anterior to ear to temporal region and ends in scalp Facial muscles and skin of frontal and temporal regions Transverse facial Superficial temporal artery within parotid gland Crosses face superficial to masseter and inferior to zygomatic arch Parotid gland and duct, mauscles and skin of face Mental Terminal branch of Inferior alveolar artery Emerges from mental foramen and passes to chin Facial muscles and skin of chin
48 Maxillary Artery Arises from External Carotid Artery Arises posterior to neck of mandible Passes anteriorly (deep to neck of condyle)- 1 st part Passes superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle- 2 nd part Passes through pterygomaxillary fissure to enter infratemporal fossa- 3 rd part
49 st (Mandibular)) Part 1 st Deep auricular artery to external acoustic meatus Anterior tympanic artery to tympanic membrane Middle meningeal artery to dura mater and calvaria Accessory meningeal arteries to the cranial cavity Inferior alveolar artery to mandible, gingiva, teeth
50 2nd (Pterygoid Part) Deep temporal arteries,, anterior and posterior (supply temporal muscle) Pterygoid arteries (supply pterygoid muscles) Masseteric artery (supplies deep surface of masseter muscle) Buccal artery (supplies buccinator muscle)
51 rd (Pterygopalatine)) Part 3 rd Posterior superior alveolar artery supplies maxillary molar and premolar teeth, lining of maxillary sinus, gingiva Infraorbital artery supplies inferior eyelid, lacrimal sac, side of nose, superior lip Descending palatine artery supplies maxillary gingiva,, palatine glands, mucous membrane of roof of mouth Artery of pterygoid canal supplies superior part of pharynx, pharyngotympanic tube, tympanic cavity Pharyngeal artery supplies roof of pharynx, sphenoidal sinus, inferior part of pharyngotympanic tube Sphenopalatine artery supplies lateral nasal wall, nasal septum, paranasal sinuses
52 Veins of Face Vein Origin Termination Area Drained Facial Continuation of angular vein past inferior margin of orbit Internal jugular vein opposite or inferior to hyoid bone Anterior scalp and forehead, eyelids, external nose, anterior cheek, lips, chin, submandibular gland Deep facial Pterygoid venous plexus Enters posterior aspect of facial vein Infratemporal fossa (most areas supplied by maxilary artery)
53 Veins of Face Superficial temporal Begins from a widespread plexus of veins on side of scalp and along the zygomatic arch Joins the maxillary vein posterior to the neck of the mandible to form the retromandibular vein Side of scalp, superficial aspect of temporal muscle, external ear Retromandibular Formed anterior to the ear by union of superficial temporal and maxillary veins Unites with posterior auricular vein to form external jugular vein Parotid gland and masseter muscle
54 Salivary Glands Parotid Gland Sublingual Gland Submandibular Gland
55 Parotid Gland Stensen s Duct Pierces the buccal fat, buccopharyngeal fascia and buccinator muscle. Opens into the vestibule of the mouth opposite the maxillary 2nd molar tooth.
56 Floor of Mouth Sublingual Salivary Glands Sublingual folds (plica( sublingualis). Run anteroposterior alongside the frenulum,, one per side, converging just anterior to the root of the frenulum. Overly the sublingual salivary glands from which numerous ducts travel and open onto the top of each fold. Each gland does not have a single duct, but many which open directly into the oral cavity.
57 Floor Of Mouth Submandibular Gland Duct emanates from the posterior aspect of gland and travels deep to mylohyoid on the superficial surface of the hyoglossus and genioglossus muscles. At the anterior most extent of each sublingual fold, the opening for the duct of the submandibular salivary gland. (Wharton s s Duct)
58 Buccal Fat Pad Encapsuled mass of fat in the cheek on the outer side of the buccinator muscle Found in the space between the masseter muscle and the external surface of the buccinator
59 Pterygomandibular Raphe Tendinous band of the buccopharyngeal fascia Attached to: Hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate. Posterior end of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. Boundaries: medial surface is covered by the mucous membrane of the mouth. lateral surface is separated from the ramus of the mandible by adipose tissue. posterior border attaches to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. anterior border attaches to buccinator.
60
61 Tongue
62 Surface Anatomy Tongue Sulcus terminalis V-shaped line (with the point facing posteriorly) ) that separates the anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 of the tongue. At the point, a shallow pit named the foramen cecum is present (original location of thyroid diverticulum). Located posterior to a row of vallate papillae.
63 Lingual Tonsils Rounded masses of lymphatic tissue that cover the posterior region of the tongue. Located on the dorsal surface at the base of the tongue.
64 Anterior 2/3 Innervation Tongue Lingual Nerve (V3)- general sensation Chorda typmani (CN 7)- taste Posterior 1/3 Lingual branch glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)- general sensation, taste Lingual branch facial nerve- taste Internal laryngeal branch Vagus- general sensation, taste
65 Motor Innervation Tongue Palatoglossus- pharyngeal plexus (CN XI, CNX) All other muscles- CN XII (hypoglossal)
66 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Genioglossus Hyoglossus Styloglossus Palatoglossus
67 Genioglossus Muscle Origin: Superior part mental spine of mandible. Insertion: Dorsum of tongue, body of hyoid bone. Innervation: : CN 12 (Hypoglossal Nerve). Depresses tongue, posterior part pulls tongue anteriorly for protrusion
68 Hyoglossus Muscle Origin: Body and greater horn of hyoid Insertion: Side and inferior aspect of tongue Innervation: : CN XII Depresses and retracts tongue
69 Styloglossus Muscle Origin: Styloid process and stylohyoid ligament Insertion: Side and inferior aspect of tongue Innervation: : CN 12 Retracts tongue and draws it up to create trough for swallowing
70 Palatoglossus Muscle Origin: Palatine aponeurosis of soft palate Insertion: Side of tongue Innervation: : Cranial root of CN XI via pharyngeal branch of CN X and pharyngeal plexus Elevates posterior part of tongue
71 Intrinsic Muscles Tongue Superior Longitudinal Inferior Longitudinal Transverse Vertical
72 Tongue Vasculature Lingual artery (from external carotid artery) Dorsal lingual arteries Deep lingual artery Sublingual artery All veins terminate in the Internal Jugular Vein Dorsal lingual veins Deep lingual veins (ranine( veins) Sublingual vein
73 Lymph Drainage from Tongue Lymph from posterior 1/3 Superior deep cervical LN Lymph from medial part of anterior 2/3 Inferior deep cervical LN Lymph from lateral anterior 2/3 submandibular LN Apex submental LN Posterior 1/3 & area near midline drain bilaterally
74 Periodontal Anatomy Periodontium Gingiva Periodontal Ligament (PDL) Cementum Alveolar and supporting bone
75 Healthy Gingiva Evaluate Color, Contour, Tone and Consistency of Gingival Tissue
76 Gingiva Masticatory mucosa which cover the alveolar process and surround the cervical portion of teeth. Composed of connective tissue and epithelium. Epithelium can be divided into three histological distinct areas: Oral epithelium Continuous with epithelial lining of the attached gingiva. Composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Sulcular epithelium Non-keratinized Junctional epithelium Attached to the tooth by hemidesmosomes. Non-keratinized. Larger cells with increased intercellular spaces.
77 Gingival Fibers Composed of type I collagen. Support the gingiva and attach it to the tooth and alveolar bone. Gingival fibers are continuous with the periodontal ligament. Designated by their orientation. Dentogingival fibers Dentoperiosteal fibers Circular fibers Alveologingival fibers Transseptal fibers
78 Principal Fibers of the Periodontal Ligament (PDL) Bundles of collagen fibers grouped according to the direction they extend from the cementum of the root to the alveolar bone. Horizontal Fibers Alveolar Crest Fibers Oblique Fibers Apical Fibers Interradicular Fibers
79 Tooth Anatomy
80 Universal/National System for Permanent (Adult) Dentition (1-32) Maxillary Arch (1-16) 16) Mandibular Arch (17-32) 3 Molars, 2 Premolars, 1 Canine, 1 Lateral Incisor, 1 Central Incisor in each arch quadrant
81 The Universal/National System for the Primary (Baby) Dentition A T Upper case letters A through T No Premolars in the Primary Dentition
82 Sequence of Eruption Deciduous central/ lateral incisiors (6-9 9 months) First deciduous molar ( months) Deciduous canine ( months) Second deciduous molar (24-30 months First permanent molar, central/ lateral incisors (6-9 9 years) Permanent canine, first/ second premolars, second molar ( years) Permanent third molar (17-21 years)
83 Curve of Spee Curvature of the mandibular occlusal plane beginning at the tip of the lower cuspid and following the buccal cusps of the posterior teeth, continuing to the terminal molar. Anterior-posterior curve
84 Lateral curve Curve of Wilson
85 Occlusion Combination of Curve of Spee and Curve of Wilson create the Occlusal Plane Centric Relation Position Anatomic relationship of the TMJ joint. Muscles of Mastication are at rest.
86 Occlusion
87 Angle Classification of Occlusion Class I patient s I profile is characterized as normal. Class II patient s profile is deficient in chin length and characterized as a retruded (retrognathic) profile. Class III patient s profile is excessive in chin length and characterized as protruded (prognathic( prognathic) profile.
88 Overjet / Overbite: Horizontal and Vertical Overlap
89 Occlusal Surface of Teeth Canine= Cuspid Premolar= Bicuspid
90 Normal Cusp Relationship of Posterior Teeth Mesiofacial cusp of the maxillary first molar occludes in the facial groove of the mandibular first molar
91 Orthognathic Surgery Jaw Realignment and Correction of Facial Profile Maxillary (one multiple piece osteotomies) Mandibular osteotomies
92 Orthognathic Surgery
93 Cephalometric Analysis
94 Cepahalometric Analysis
95 Lefort 1 Osteotomy
96 BSR Mandibular ramus sagittal split osteotomy is the most common technique used for mandibular advancement
97 BSR
98 Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramusotomy
99 Vertical Ramus Osteotomy Vertical ramus osteotomy can be used to set the mandible posteriorly.
100 Genioplasty Anterior Mandibular Horizontal Osteotomy
101 Facial Trauma
102 Facial Trauma
103 R Zygomatic Arch Fracture
104 Distribution of Mandible Fractures
105 Mandible Fracture
106 Tx Mandible Fx
107 ORIF Mandible Fx
108 LeFort Fractures
109 Wisdom Teeth
110 Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars)
111 Extraction of Mandibular 3 rd Molar Tooth
112 Extraction of Mandibular 3 rd Molar Tooth
113 Thank You!
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
The Digestive System in the Head and Neck
 The Digestive System in the Head and Neck The Mouth The Lips The lips are two fleshy folds that surround the oral orifice They are covered on the outside by skin and are lined on the inside by mucous membrane
The Digestive System in the Head and Neck The Mouth The Lips The lips are two fleshy folds that surround the oral orifice They are covered on the outside by skin and are lined on the inside by mucous membrane
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
University of Palestine. Final Exam 1 st Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved
 HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
Today's lecture discuss : 1- the mouth. 5-the salivary glands
 Today's lecture discuss : 1- the mouth 3-the tongue 2-the teeth 4-the palates 5-the salivary glands ( u dnt have to refer to the slides, I've included everything in slides ( 1-27 ) except some figures.
Today's lecture discuss : 1- the mouth 3-the tongue 2-the teeth 4-the palates 5-the salivary glands ( u dnt have to refer to the slides, I've included everything in slides ( 1-27 ) except some figures.
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم
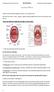 بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Today we will talk about digestive system in the head & neck We have the mouth, teeth, tongue, palate & salivary glands all of these are included in this lecture *First we will start
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Today we will talk about digestive system in the head & neck We have the mouth, teeth, tongue, palate & salivary glands all of these are included in this lecture *First we will start
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud
 Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德
 Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement
 Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
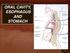 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Temporomandibular Joint. Dr Noman ullah wazir
 Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
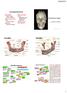 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically
 CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Anatomy 2. Parotid bed (V.imp): meaning that gland is sleeping on structures and they are:
 Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND. Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy
 FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy THE FACE THE SCALP The scalp is composed of five layers: Skin ConnecAve Assue Aponeurosis Loose connecave Assue Pericranium
FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy THE FACE THE SCALP The scalp is composed of five layers: Skin ConnecAve Assue Aponeurosis Loose connecave Assue Pericranium
Muscles of mastication [part 1]
![Muscles of mastication [part 1] Muscles of mastication [part 1]](/thumbs/76/73586850.jpg) Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Prosthodontics Dr.Yassen H.
 Prosthodontics Dr.Yassen H. Lecture -2- Anatomy & Physiology Related to Prosthodontics (Myology) Muscles are divided or classified into: 1. Muscles of facial expression. 2. Suprahyoid muscles. 3. Infrahyoid
Prosthodontics Dr.Yassen H. Lecture -2- Anatomy & Physiology Related to Prosthodontics (Myology) Muscles are divided or classified into: 1. Muscles of facial expression. 2. Suprahyoid muscles. 3. Infrahyoid
Mohammad Mohtaseb. Nour Hussein. Faisal Nimri
 2 Mohammad Mohtaseb Nour Hussein Faisal Nimri Muscles of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ and contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscle contains vertical, oblique, and transverse
2 Mohammad Mohtaseb Nour Hussein Faisal Nimri Muscles of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ and contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscle contains vertical, oblique, and transverse
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory fibers to the skin of the clavicular area
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
Upper Respiratory Tract
 Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
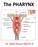 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
- Reem Akiely. -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh. - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -2 - Reem Akiely -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The palate: * Hard palate * Soft palate the Uvula: is a muscular structure present In the midline of the soft palate (اللهاة) The Hard
-2 - Reem Akiely -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The palate: * Hard palate * Soft palate the Uvula: is a muscular structure present In the midline of the soft palate (اللهاة) The Hard
