Verruciform Xanthoma: An Unusual Lesion of Tongue A Case Report and Review of Literature
|
|
|
- Lynne Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
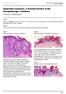
1 OMPJ G Rajalakshmi et al CASE REPORT /jp-journals Verruciform Xanthoma: An Unusual Lesion of Tongue A Case Report and Review of Literature 1 G Rajalakshmi, 2 Sankar Vinod, 3 R Anjana, 4 Pramod P Mathews, 5 Reeji Rajan ABSTRACT Verruciform xanthoma (VX) is a rare entity and we could procure only very few publications in the literature. This innocuous lesion with a sessile or pedunculated base is normal, reddish in color but occasionally pale or hyperkeratotic with rough or pebbly surface; 75% of VX occurs in masticatory mucosa, gingiva, and palate and very few occurs in buccal mucosa, floor of the mouth, and rarely in the tongue. Our case on the tongue exhibited papillary or verrucous proliferation of squamous epithelium associated with hyperkeratosis and with copious foamy cells confined to lamina propria papillae. The hallmark of VX is the presence of vacuolated foam or xanthoma cells. The xanthoma cells have been shown to be cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage. The exact etiopathogenesis of VX is not fully known, but various concepts have been postulated. Recurrence is unusual after surgical removal. Keywords: Recurrence, Verruciform xanthoma, Xanthoma cells. How to cite this article: Rajalakshmi G, Vinod S, Anjana R, Mathews PP, Rajan R. Verruciform Xanthoma: An Unusual Lesion of Tongue A Case Report and Review of Literature. Oral Maxillofac Pathol J 2018;9(1): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None INTRODUCTION Verruciform xanthoma was first described by Shafer. 1 It occurs mainly in the oral mucosa, with spasmodically extraoral cases being reported, inclusive of those on penis, 2 scrotum, 3 and vulva. 4 The term xanthoma is derived from the Greek word xanthos, meaning yellow. Originally, xanthoma was used to define a yellowish, slightly raised or flat lesion occurring on the skin, propounding an underlying illness. Oftentimes, lipid material accumulates in reticuloendothelial cells in various 1,3,5 Postgraduate Student, 2 Head, 4 Professor 1,3,5 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Mar Baselios Dental College, Ernakulam, Kerala, India 2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Mar Baselios Dental College, Ernakulam, Kerala, India 4 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Indira Gandhi Institute of Dental Sciences, Kothamangalam, Kerala, India Corresponding Author: G Rajalakshmi, Postgraduate Student, Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Mar Baselios Dental College, Ernakulam, Kerala, India, Phone: sites of the body. The phenomenon of xanthoma occurs beneath the epithelial surface, thus giving a yellow tan hue to the cutaneous lesions. 5 Most VX have been misdiagnosed clinically as papillomas and occasionally as verrucous carcinomas or squamous cell carcinomas. 6 Histologically, VX is characterized by papillary or verrucous proliferation of squamous epithelium associated with hyperparakeratosis and numerous foamy cells. These xanthoma cells are confined within lamina propria papillae and do not extend below rete pegs tips level. 1,7,8 Zegarelli et al 9 validated the presence of macrophages containing lipid in VX. The macrophagic nature of foamy cells has been confirmed by immunohistochemical studies. 8,10 The etiology and pathogenesis of VX still remain enigmatic. The presence of S100-positive Langerhans cells in the epithelium and connective tissue of lesions suggests that VX is at least relatively mediated by immune mechanism. 8,11 CASE REPORT A 35-year-old male patient presented with a white patch on the left side of his tongue which he spotted since 3 days. There was no associated pain, difficulty in mouth opening and chewing or articulating. He had history of smoking for 2 to 3 years back and later ceased. He also had a habit of keeping hans (a smokeless tobacco product) in the upper anterior gingiva and vestibule for the past 8 months. On intraoral examination, a white plaque-like lesion of approximate size cm was noticed on the left posterolateral aspect of tongue irt 36, 37 (Fig. 1). Shape and borders were irregular, the surrounding area was nonerythematous. On palpation, the lesion was nontender, nonscrapable, and was slightly firm in consistency with irregular borders. No induration was present, and the surface of the lesion was raised from adjacent normal mucosa. Based on history and clinical examination, we framed a provisional diagnosis of homogeneous leukoplakia. Later, an excisional biopsy was performed (Fig. 2). Histopathology revealed areas of parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium with elongated rete ridges at a uniform level (Figs 3 and 4). Epithelium also showed areas of koilocytic changes, dyskeratosis, and loss of cohesion. Subepithelial areas showed sheets of large foamy macrophages (xanthoma cells; Fig. 5). The cytoplasm of these cells seemed to be granular and the nuclei either 42
2 OMPJ Verruciform Xanthoma: An Unusual Lesion of Tongue Fig. 1: Plaque-like lesion on the left posterolateral aspect of the tongue Fig. 2: Excisional biopsy specimen Fig. 3: Papillary or verrucous proliferation of squamous epithelium associated with hyperkeratosis (10 view) Fig. 4: Numerous foamy cells confined to lamina propria papillae (10 view) Fig. 5: Xanthoma cells (40 view) Fig. 6: Large eosinophilic granular cells showing PAS positivity small round or were eccentrically placed. The connective tissue stroma showed a moderate subepithelial chronic inflammatory infiltration. The granules of foam cells were slightly periodic acid Schiff (PAS) positive (Fig. 6). DISCUSSION Data regarding the prevalence or incidence of oral VX are unexceptionally little. Verruciform xanthoma is a rare entity accounting for to 0.095% of all cases with an Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Journal, January-June 2018;9(1):
3 G Rajalakshmi et al unknown etiopathology. 12 From the available epidemiological data, oral VX is present in males below the age of 50, with a female-to-male ratio of 1:1.6 and the ratio reverses to 1:0.8 after the age of 50 years. Concerning the ethnic origin, oral VX is more common in Caucasians and rare in Asian population. The duration of lesion varies from a few weeks to 10 years. 13 Clinically, VX has been variously described, but principally, the oral lesions are described as asymptomatic, roughened, papillary or cauliflower-like lesions with sessile or rarely pedunculated base, and the size ranges from 0.2 to 4 cm. 14 Etiology and pathogenesis of oral VX are still far from being clarified, though reactive, immunological, infectious, and genetic mechanisms have been considered. The prominent accumulation of lipid-laden cells within the lesions has strongly suggested the association with systemic lipid abnormality. 14 But van der Waal et al 15 suggested that the lesion does not seem to be associated with systemic abnormality of lipid metabolism. Its association with the underlying inflammatory disorders of oral mucosa, such as blisters, lichen planus, pemphigus vulgaris supports that VX is a reactive process initiated by inflammatory reaction rather than a true neoplasm. But Travis et al 16 have reported a case associated with systemic unknown lipid storage disease. Zegarelli et al 9 put forward the concept that the cause of accumulation of lipid-containing macrophages was epithelial degeneration. The products of epithelial breakdown elicit an inflammatory response which is manifested by a predominant neutrophil infiltrate in the epithelium and the subsequent release of lipid material through the epithelium which is finally scavenged by macrophages. He also suggested that local irritant acts as an initiator in this process. Based on the fact that 70% or more of all VXs are located in the masticatory oral mucosa which is constantly subjected to the trauma of mastication as well as to the sensitizing agents of foodstuffs, this theory may seem quite plausible. The presence of inflammatory cells and colonies of microorganisms points toward an inflammatory response. Cobb et al 17 recommended that VX is inflammatory in origin as the lesion is predominantly present in masticatory mucosa. However, many authors suggest that VX is less common secondary to inflammation or irritation and foam cell deposition may be abundant where epithelial breakdown is limited. 16 Many authors substantiate that damage to squamous cells due to trauma, irritation, or infection can cause increased epithelial turnover results in epithelial breakdown, leading to inflammatory response and subsequent release of lipid material from the degenerated cells. 18 But VX has been reported in the oral regions, such as the floor of mouth and soft palate where trauma is minimal. The VX occurs in patients using snuff or indulging in the habit of chewing tobacco, possible etiological factors that Buchner et al could not subscribe to, as they denied the VX being inflammatory in nature. 19,20 Rowden et al 11 demonstrated dendritic cells among the mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate of VX lesions. These Langerhans cells were located at the base of the lesions and to a lesser extent among the foamy cells. Thus, they suggested that VX belongs to a new category of non-x histiocytosis in which the presence of Langerhans cells suggests an immunologic pathogenesis. Mostafa et al 8 validated the presence of macrophage marker (CD68) in the foamy cells of VX, thus determining the macrophagic nature of these cells. Mohsin et al 21 betokened human papillomavirus (HPV) as a putative pathogen because of the condylomalike architectural appearance of VX. However, most investigators have not found any evidence for the presence of HPV in oral VX. But only recently, Khaskhely et al 22 described an association of HPV with extraoral VX. Thus, a possible relationship between VX and HPV is not fully clarified. Neville and Weathers 19 noticed PASpositive fungal hyphae compatible with Candida albicans in parakeratotic layers. Recently, four cases of VX occurring within lichen planus of the oral mucosa have been reported. Based on their data, the authors recommended that the condition of altered epithelial turnover, as in repeated epithelial desquamation, would give rise to the VX. 23 Furthermore, VX and oral lichen planus may occur concomitantly without having a specific causal relationship between them. 24 Missense mutations in exon 6 of 3-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase have been reported in solitary VX. 25 Histopathologically, oral VX is characterized by a squamous epithelial surface of varying morphology covered with parakeratin, showing elongated rete pegs of relatively uniform depth. The most pathognomonic feature of this lesion is the presence of large swollen foam cells or xanthoma cells, which fill the connective tissue papillae between the rete pegs. 1 A variable degree of parakeratosis is observed that is usually marked in verrucous and papillary forms of VX with hyperparakeratosis present in the crypts in between papillae, although no increase in mitosois is observed. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is not usually seen, but connective tissue papillae are of variable length and thickness and often extend close to the surface. 26 Nowparast et al 5 demonstrated three different architectural appearances of oral VX on low-powered microscopy. Pattern A, a wart or verrucous appearance which 44
4 OMPJ Verruciform Xanthoma: An Unusual Lesion of Tongue is usually elevated, is well circumscribed but does not show thick stratum granulosum like verruca vulgaris. There is hyperparakeratosis, acanthosis, and elongation of rete ridges. Pattern B papillary or cauliflower architecture, which has many finger-like projections composed of stratified squamous epithelium containing connective tissue core, forming crypt-like spaces covered by parakeratin, often extends above the mucosal surface. Pattern C flat type, epithelial proliferation is seen below the surface with variable elongation of rete ridges which may be slender or of uniform depth. The connective tissue papillae extend almost to the surface only separated from the outer surface by a few parakeratotic cell layers. There is only a thin layer of parakeratin, although a wedge-shaped plugging phenomenon may often be recognized. Parakeratosis is more intense in verrucous and papillary form. Neville and Weathers 19 suggested that parakeratin exhibits an orange color in hematoxylin and eosin staining which sharply demarcates the remaining epithelium. Mostafa et al 8 suggested that elongation of epithelial rete ridges is illusory and is not a proliferation of epithelial cells with downgrowth of rete pegs, but rather results from the upward pushing effect of macrophages toward the epithelium. The side pressure exerted by the macrophages leads to the thinning of rete ridges through the compression of epithelial cells which may display a relatively spindle cell appearance rather than a polygonal one. Collections of microorganisms may present upon the epithelial surface and within the parakeratin invaginations. Neville and Weathers 19 noticed PAS-positive fungal hyphae compatible with C. albicans in the parakeratotic layers. A slight to moderate degree of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration consisting mainly of lymphocytes is observed in the subepithelial connective tissue. However, the hallmark feature of VX irrespective of intraoral or extraoral location is the presence of vacuolated foam cells or xanthoma cells. The PAS stains show many xanthoma cells to contain tiny PAS-positive granules in cytoplasm. Scharlach and Sudan III stains reveal an abundance of cytoplasmic lipid. No mucicarminophilic or alcinophilic material has been noted. 9 In most ultrastructural studies, these cells demonstrated oval or elongated irregular nuclei with peripheral condensation of chromatin and intense nucleoli, and a variable number of lipid droplets and lysosomal structures. Plasma membrane showed long thin filamentous processes. 9,17 Mostafa et al 5 suggested that the foam cells were stained intensively with monoclonal antimacrophage antibodies (CD68, KP1 and PG-M1), moderately with antileukocyte common antigen, faintly with antilysosome and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin antibodies. Some studies showed S100 positive dendritic cells in the lesional connective tissue. 11 However, as yet unrecognized factors may play a role in the development of VX, thus more comprehensive studies are needed to illustrate the nature of lesion. REFERENCES 1. Shafer WG. Verruciform xanthoma. Oral Surg 1971 Jun;31(6): Kraemer BB, Schmidt WA, Foucar E, Rosen T. Verruciform xanthoma of the penis. Arch Dermatol 1981 Aug;117(8): Kimura S. Verruciform xanthoma of the scrotum. Arch Dermatol 1984 Oct;120(10): Santa Cruz DJ, Martin SA. Verruciform xanthoma of the vulva. Report of two cases. Am J Clin Pathol 1979;71(2): Nowparast B, Howell FV, Rick GM. Verruciform xanthoma. A clinicopathologic review and report of fifty four cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1981;51(2): Toida M, Koizumi H, Verruciform xanthoma involving the lip: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993 Apr;51(4): Miller AS, Elzay RP. Verruciform xanthoma of the gingiva report of 6 cases. J Periodontol 1973 Feb;44(2): Mostafa KA, Takata T, Ogawa I, Ijuhin N, Nikai H. Verruciform xanthoma of the oral mucosa: a clinicopathological study with immunohistochemical findings relating to pathogenesis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1993 Jul;423(4): Zegarelli DJ, Zegarelli-Schmidt EC, Zegarelli EV. Verruciform xanthoma. A clinical, light microscopic, and electron microscopic study of two cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974 Nov;38(5): Orchard GE, Wilson Jones E, Russell Jones R. Verruciform xanthoma: an immunocytochemical study. Br J Biomed Sci 1994 Mar;51(1): Rowden D, Lovas G, Shafer W, Sheikh K. Langerhans cells in verruciform xanthomas: an immunoperoxidase study of 10 oral cases. J Oral Pathol 1986 Jan;15(1): Buchner A, Hansen LS, Merrell PW. Veruciform xanthoma of oral mucosa. Report of five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol 1981 Sep;117(9): Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Takata T, Ogawa I. Verruciform xanthoma biological profile of 282 oral lesions based on literature survey with nine new cases from Japan. Oral Oncol 2003 Jun;39(4): Shin HI, Choi KS, Nagatuka H, Murata M, Nagai N. Verruciform xanthoma of oral mucosa: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study of two cases. Oral Oncol 1997 Jul;33(4): van der Waal I, Kerstens HC, Hens CJ. Verruciform xanthoma of oral mucosa. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1985 Aug;43(8): Travis WD, Davis GE, Tosokos M, Lebovics R, Merrick HF, Miller SP, Gregg RE, Di Bisceglie AM, Parker RI, Ishak KG, et al. Multifocal verruciform xanthoma of upper aerodigestive tract in a child with systemic lipid storage disease. Am J Surg Pathol 1989 Apr;13(4): Cobb CM, Holt R, Denys FR. Ultrastructural features of the verruciform xanthoma. J Oral Pathol 1976 Jan;5(1): Shetty A, Nakhaei K, Lakkashetty Y, Mohseni M, Mohebatzadeh I. Oral verruciform xanthoma: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Dent 2013 Dec;2013: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Journal, January-June 2018;9(1):
5 G Rajalakshmi et al 19. Neville BW, Weathers DR. Verrucifrom xanthoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1980 May;49(5): Bhatt AP. Case of month. Verruciform xanthoma. J Indian Dent Assoc 1983 Dec;55(12): Mohsin SK, Lee MW, Amin MB, Stoler MH, Eyzaguirre E, Ma CK, Zarbo RJ. Cutaneous verruciform xanthoma: a report of five cases investigating the etiology and nature of xanthomatous cells. Am J Surg Pathol 1998 Apr;22(4): Khaskhely NM, Uezato U, Kamiyama T, Maruno M, Kariya KI, Oshiro M, Nonaka S. Association of human papilloma virus type 6 with a verruciform xanthoma. Am J Dermatopathol 2000 Oct;22(5): Miyamoto Y, Nagayama M, Hayashi Y. Verruciform xanthoma occurring within oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med 1996 Apr;25(4): Polonowita AD, Firth NA, Rich AM. Verruciform xanthoma and concomitant lichen planus of the oral mucosa a report of three cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1999 Feb;28(1): Regezi J, Sciubba J, Jordan R. Oral pathology: clinical pathologic correlations. 7th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier; Shafer WG, Hine MK, Levy BM, Shivapathasundaram B. Textbook of oral pathology. 8th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier; pp
Verruciform Xanthoma: A Retrospective Clinical and Histopathologic Analysis of 90 Cases
 Verruciform Xanthoma: A Retrospective Clinical and Histopathologic Analysis of 90 Cases Evan Santiago, DDS, Molly S. Rosebush, DDS, MS #, Jessica Owens, DMD, Kitrina G. Cordell, DDS, MS Department of Periodontics
Verruciform Xanthoma: A Retrospective Clinical and Histopathologic Analysis of 90 Cases Evan Santiago, DDS, Molly S. Rosebush, DDS, MS #, Jessica Owens, DMD, Kitrina G. Cordell, DDS, MS Department of Periodontics
Verruciform xanthoma of the palatal gingiva: a report of two cases
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.292 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Verruciform xanthoma of the palatal gingiva: a report of two cases Da Jung Ryu 1, Sang Hoon Lee 1, Jong In Yuk
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.292 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Verruciform xanthoma of the palatal gingiva: a report of two cases Da Jung Ryu 1, Sang Hoon Lee 1, Jong In Yuk
A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions
 Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS
 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Epidemiology Clinical presentation
 LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
The Gulf Journal of Oncology
 The Gulf Journal of Oncology ISSUE 10 JULY, 2011 Original Studies Table of Contents Mutations in EGFR Signal Pathway in Correlation with Response to Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers... 07 J. Neuwirthová,
The Gulf Journal of Oncology ISSUE 10 JULY, 2011 Original Studies Table of Contents Mutations in EGFR Signal Pathway in Correlation with Response to Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers... 07 J. Neuwirthová,
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma
 Benign tumors Epithelial origin Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma Squamous papilloma Exophytic
Benign tumors Epithelial origin Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma Squamous papilloma Exophytic
Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I)
 Introduction: Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I) Oral Epithelial Tumors may be: Benign tumors Sequamous cell Papilloma Malignant tumors Sequamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma
Introduction: Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I) Oral Epithelial Tumors may be: Benign tumors Sequamous cell Papilloma Malignant tumors Sequamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE
 CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
ORAL MELANOTIC NEVI: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 ORAL MELANOTIC NEVI: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Abstract: *V.T Beena **Isha Chauhan *** R. Heera ***R. Rajeev Oral melanotic nevi are uncommon oral lesions causing focal. Melanotic nevi are
ORAL MELANOTIC NEVI: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Abstract: *V.T Beena **Isha Chauhan *** R. Heera ***R. Rajeev Oral melanotic nevi are uncommon oral lesions causing focal. Melanotic nevi are
ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT
 Melanocytic Pigmentation: A Single Manifestation of Myriad of Pathologies [PP: 05-09] Dr. Swapna Honwad Department of Oral Pathology dr.swapnahonwad@gmail.com Dr. Elsy P. Simon Department of Endodontics
Melanocytic Pigmentation: A Single Manifestation of Myriad of Pathologies [PP: 05-09] Dr. Swapna Honwad Department of Oral Pathology dr.swapnahonwad@gmail.com Dr. Elsy P. Simon Department of Endodontics
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
A Speckled Lesion. Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD
 A Speckled Lesion Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD The following Case Challenge is provided in conjunction with the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Case Summary This
A Speckled Lesion Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD The following Case Challenge is provided in conjunction with the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Case Summary This
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies
 WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY
 Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
 International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
Conclusion: It was concluded that laser provides good coagulation, healing, reduces surgical time and prevents high-grade infection.
 Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Abstract Background: A wide variety of white lesions are encountered in general population and specially those people
 Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
WHITE LESIONS OF THE UPPER AIRWAY
 WHITE LESIONS OF THE UPPER AIRWAY WHITE LESION CONFIGURATIONS Solitary vrs Multifocal Flat Plaque Verrucous/rippled Lacey White with red component Papular (curdled milk plaques) Pseudomembranous PLAQUES
WHITE LESIONS OF THE UPPER AIRWAY WHITE LESION CONFIGURATIONS Solitary vrs Multifocal Flat Plaque Verrucous/rippled Lacey White with red component Papular (curdled milk plaques) Pseudomembranous PLAQUES
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
 MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
Pattern of oral lesions Cytohistopathological study in tertiary care centre.
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation
 CASE REPORT Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation M. Shaurya*, S. Ravindra, Sarvani Murthy *Post Graduate Student, Professor and Head, Department of Periodontics,
CASE REPORT Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation M. Shaurya*, S. Ravindra, Sarvani Murthy *Post Graduate Student, Professor and Head, Department of Periodontics,
Linear Leukoplakia on the Right Lateral Border of the Tongue
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Linear Leukoplakia on the Right Lateral Border of the Tongue Course Author(s): Anne Cale Jones, DDS; H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Michaell A. Huber, DDS Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-058
Continuing Education Brought to you by Linear Leukoplakia on the Right Lateral Border of the Tongue Course Author(s): Anne Cale Jones, DDS; H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Michaell A. Huber, DDS Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-058
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
Oral verruciform xanthoma and erythroplakia associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a rare case report and review of the literature
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-017-2952-7 BMC Research Notes Open Access CASE REPORT Oral verruciform xanthoma and erythroplakia associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a rare case report and review of
DOI 10.1186/s13104-017-2952-7 BMC Research Notes Open Access CASE REPORT Oral verruciform xanthoma and erythroplakia associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a rare case report and review of
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:140-146, 2009 Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia Sook-Bin Woo, DMD,* and Dorothy Lin Purpose: Morsicatio mucosae oris (MMO) presents
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:140-146, 2009 Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia Sook-Bin Woo, DMD,* and Dorothy Lin Purpose: Morsicatio mucosae oris (MMO) presents
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Kharidi U.A, Kodgi A, Biradar A, Kulkarni A
 Case Report Malignant Conversion of Oral Lichen Planus - A Case Report 1 2 3 4 Kharidi U.A, Kodgi A, Biradar A, Kulkarni A Kharidi U.A, Kodgi A, Biradar A, Kulkarni A. Malignant Conversion of Oral Lichen
Case Report Malignant Conversion of Oral Lichen Planus - A Case Report 1 2 3 4 Kharidi U.A, Kodgi A, Biradar A, Kulkarni A Kharidi U.A, Kodgi A, Biradar A, Kulkarni A. Malignant Conversion of Oral Lichen
HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report
 Case Report: HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report Dr Gopal Sharma, Dr Deepa Das, Dr Prachi Naik, Dr Jaya Mukherjee Oral Medicine and Radiology Department, YMT Dental College and
Case Report: HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report Dr Gopal Sharma, Dr Deepa Das, Dr Prachi Naik, Dr Jaya Mukherjee Oral Medicine and Radiology Department, YMT Dental College and
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Case Report Fibrolipoma of the Buccal Mucosa: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 5060964, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5060964 Case Report Fibrolipoma of the Buccal Mucosa: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Masayasu
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 5060964, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5060964 Case Report Fibrolipoma of the Buccal Mucosa: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Masayasu
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Oral histology. How is the oral mucosa different from skin?
 Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 04 ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION Romita Dilip Gaikwad 1,Mukta Bhagwandas Motwani 2,Kalpana Anil
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 04 ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION Romita Dilip Gaikwad 1,Mukta Bhagwandas Motwani 2,Kalpana Anil
ISPUB.COM. Giant Verruca Vulgaris-Rare Presentation. K Pandurengan, N R.M, R Chidambaram, S T.K INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number 2 K Pandurengan, N R.M, R Chidambaram, S T.K Citation K Pandurengan, N R.M, R Chidambaram, S T.K.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2010
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number 2 K Pandurengan, N R.M, R Chidambaram, S T.K Citation K Pandurengan, N R.M, R Chidambaram, S T.K.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2010
Papillary verrucous lesion of the oral mucosa: A need for detailed histopathological examination
 Case report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03163 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Papillary verrucous lesion
Case report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03163 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Papillary verrucous lesion
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA
 442 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA T. LEHNER From the Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London, S.E.1 Received for publication April 17, 197 SUMMARY.-The lymphocyte
442 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA T. LEHNER From the Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London, S.E.1 Received for publication April 17, 197 SUMMARY.-The lymphocyte
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report
 Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
 The Clinical Significance of Stratifying Vulval Squamous Carcinoma into HPV and Non-HPV Related Variants C. BLAKE GILKS MD FRCPC Dept of Pathology, University of British Columbia Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
The Clinical Significance of Stratifying Vulval Squamous Carcinoma into HPV and Non-HPV Related Variants C. BLAKE GILKS MD FRCPC Dept of Pathology, University of British Columbia Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Epidemiology of Oral Lichen Planus in a Cohort of South Indian Population: A Retrospective Study
 JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
JOURNAL OF CANCER PREVENTION Vol. 21, No. 1, March 2016 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-3-30 http://dx.doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2016.21.1.55 pissn
Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS
 J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report
 Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
R. Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: Evaluation.
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics. Mercè Jordà, University of Miami
 Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Mortality Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer incidence and mortality
Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Mortality Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer incidence and mortality
That. Name QUIZ. 60 SEPTEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com
 QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Cancers of the Oral Cavity.
 Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Oral verrucous hyperplasia versus oral verrucous carcinoma: A clinicopathologic dilemma revisited using p53 as immunohistochemical marker
 Original Article Oral verrucous hyperplasia versus oral verrucous carcinoma: A clinicopathologic dilemma revisited using p53 as immunohistochemical marker Preeti Sharma, Vijay Wadhwan, Pooja Aggarwal,
Original Article Oral verrucous hyperplasia versus oral verrucous carcinoma: A clinicopathologic dilemma revisited using p53 as immunohistochemical marker Preeti Sharma, Vijay Wadhwan, Pooja Aggarwal,
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other
 Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other disease. (Pindborg. 1978) Precancerous lesion
Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other disease. (Pindborg. 1978) Precancerous lesion
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report
 Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
Case Report Diagnosis of a granular cell tumour at the abdominal wall using fine needle aspiration cytology and histology: Case report Journal of International Medical Research 2015, Vol. 43(4) 592 596!
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report
 American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Case Report Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report Sivakumarashankari, Gaurav*, Jayanthi K and Kamala R Dept.
American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Case Report Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report Sivakumarashankari, Gaurav*, Jayanthi K and Kamala R Dept.
A clinical study on tongue lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients
 A clinical study on lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients Sura Ali Fuoad College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the frequency
A clinical study on lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients Sura Ali Fuoad College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the frequency
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Papillary and verrucous lesions of the oral mucosa
 Papillary and verrucous lesions of the oral mucosa Gareth J Thomas A William Barrett Abstract A variety of verrucous and papillary lesions affect the oral mucosa. Those which are benign and reactive, for
Papillary and verrucous lesions of the oral mucosa Gareth J Thomas A William Barrett Abstract A variety of verrucous and papillary lesions affect the oral mucosa. Those which are benign and reactive, for
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral leukoplakia
 Study Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral Minati Mishra, Janardan Mohanty*, Sujata Sengupta, Satyabrata Tripathy Department of Dermatology & Venereology, S.C.B. Medical College, *Department
Study Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral Minati Mishra, Janardan Mohanty*, Sujata Sengupta, Satyabrata Tripathy Department of Dermatology & Venereology, S.C.B. Medical College, *Department
Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic Bladder Biopsies -A Histopathological Study
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (2 ):1 3 2-1 3 6 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Spectrum of Lesions in Cystoscopic
A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS
 CASE REPORT A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS Chanchal Sareen 1, Aparna Pathak 2, Puneet Ahuja 3, Moulshree Kohli 4 1 Senior Lecturer, 3 Prof & Head,
CASE REPORT A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA: ORAL LICHEN PLANUS OR LICHENOID REACTION - A SERIES OF CASE REPORTS Chanchal Sareen 1, Aparna Pathak 2, Puneet Ahuja 3, Moulshree Kohli 4 1 Senior Lecturer, 3 Prof & Head,
Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity
 Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Cytoplasmic changes Nuclear changes
 The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
Pathology of Candida infection in oral HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma: a descriptive study.
 354 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no5a5 Pathology of Candida infection in oral HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma: a descriptive study. SADJ June 2018, Vol 73 no 5 p354 - p358 S Meer 1, A Sibda
354 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no5a5 Pathology of Candida infection in oral HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma: a descriptive study. SADJ June 2018, Vol 73 no 5 p354 - p358 S Meer 1, A Sibda
Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus
 Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus Girish HC* Sanjay Murgod**Savita JK*** *M.D.S, Professor & Head, **M.D.S, Professor,***M.D.S, Senior Lecturer,Dept of Oral Pathology, Raja Rajeswari Dental College
Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus Girish HC* Sanjay Murgod**Savita JK*** *M.D.S, Professor & Head, **M.D.S, Professor,***M.D.S, Senior Lecturer,Dept of Oral Pathology, Raja Rajeswari Dental College
AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT
 AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT Dr. R.S. Sathawane 1, Dr. Nikita Agrawal 2, Dr. Abhijeet Deoghare 3, Dr. Deepti Patel 2 1. Professor
AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT Dr. R.S. Sathawane 1, Dr. Nikita Agrawal 2, Dr. Abhijeet Deoghare 3, Dr. Deepti Patel 2 1. Professor
Penile cancer teams in UK. Common variants. Penile cancer teams. Basaloid squamous carcinoma. The Pathology of Penile Tumours
 The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus
 Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
