Loss of end- differentiated β- cell phenotype following pancreatic islet transplantation
|
|
|
- Austin Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received: 30 May 2017 Revised: 15 September 2017 Accepted: 16 September 2017 DOI: /ajt CASE REPORT Loss of end- differentiated β- cell phenotype following pancreatic islet transplantation S. J. Anderson 1 M. G. White 1 S. L. Armour 1 R. Maheshwari 1 D. Tiniakos 1,2 Y. D. Muller 3 E. Berishvili 3,4 T. Berney 3 J. A. M. Shaw 1 1 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK 2 Department of Pathology, Aretaieion Hospital, Medical School, National & Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece 3 Cell Isolation and Transplantation Center, Department of Surgery, Geneva University Hospitals and University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland 4 Institute of Medical Research, Ilia State University, Tbilisi, Georgia Correspondence James Shaw jim.shaw@ncl.ac.uk Funding information Diabetes UK Replacement of pancreatic β- cells through deceased donor islet transplantation is a proven therapy for preventing recurrent life- threatening hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Although near- normal glucose levels and insulin independence can be maintained for many years following successful islet transplantation, restoration of normal functional β- cell mass has remained elusive. It has recently been proposed that dedifferentiation/plasticity towards other endocrine phenotypes may play an important role in stress- induced β- cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Here we report loss of end-differentiated β- cell phenotype in 2 intraportal islet allotransplant recipients. Despite excellent graft function and sustained insulin independence, all examined insulin- positive cells had lost expression of the end- differentiation marker, urocortin- 3, or appeared to co- express the α- cell marker, glucagon. In contrast, no insulin + / urocortin-3 cells were seen in nondiabetic deceased donor control pancreatic islets. Loss of end- differentiated phenotype may facilitate β- cell survival during the stresses associated with islet isolation and culture, in addition to sustained hypoxia following engraftment. As further refinements in islet isolation and culture are made in parallel with exploration of alternative β- cell sources, graft sites, and ultimately fully vascularized bioengineered insulin- secreting microtissues, differentiation status immunostaining provides a novel tool to assess whether fully mature β- cell phenotype has been maintained. KEYWORDS clinical research/practice, diabetes: type 1, islet transplantation, tissue injury and repair 1 INTRODUCTION Following reproducible attainment of insulin independence through the Edmonton protocol, 1 islet transplantation has become an established therapy for prevention of recurrent life- threatening severe hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. 2 Although optimal islet grafts can restore nondiabetic glucose levels without adjuvant glucose- lowering therapy, detailed metabolic testing has revealed incomplete restoration of normal functional β- cell mass. 3 This is in contrast to vascularized whole pancreas transplant where normalization of β- cell secretory capacity has been confirmed. 4 During pancreas development, co- expression of insulin and the peptide hormone urocortin- 3 is a phenotypic marker of full β- cell maturation. 5 Maintenance of β- cell urocortin- 3 expression is required for physiological regulation of insulin secretion, with urocortin- 3 null mice having deficient insulin secretion during periods of high glucose. 6 β- cell dysfunction, defined by loss of mature end- differentiated phenotypic markers, including urocortin- 3, 7 and expression of nonβ- cell proteins, including glucagon, 8 has recently been postulated as an important contributor to impaired insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes. 9,10 We report abnormal β- cell phenotypes in 2 islet transplant recipients despite excellent graft function The American Society of Transplantation amjtransplant.com Am J Transplant. 2018;18: and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
2 2 METHODS Peripheral and central tissue blocks of right and left liver lobes were fixed in buffered formalin solution and embedded in paraffin following consent from donor s family (Patient 1) and the donor (Patient 2). Pancreata optimally retrieved during organ donation after brain stem death under Research Ethics Committee approval provided nondiabetic control tissue for staining of normal adult human islets in situ. Fourmicrometer- thick tissue sections were routinely stained with hematoxylin and eosin or immunostained with antibodies for endothelial (CD31, clone JC70A, Dako, Ely, UK) or lymphatic (podoplanin D2-40, clone D240, Ventana, Tucson, AZ) markers using Benchmark Ultra (Ventana) automated slide staining system. Due to the limited material available for immunohistochemistry, stains were not performed on serial sections. Indirect immunofluorescence was performed in more than 15 separate intrahepatic islets in both Patient 1 and Patient 2 in addition to control pancreata using guinea pig anti- insulin (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), rabbit anti- glucagon (Abcam), mouse anti- glucagon (Sigma, Gillingham, UK), and mouse anti- urocortin- 3 (Phoenix, Burlingame, CA) antibodies. Co- expression of insulin/urocortin- 3 and insulin/glucagon was confirmed by confocal microscopy Z- stack analysis. 751 deceased donors. 11 Islet transplantation was undertaken for recurrent life- threatening severe hypoglycemia with poor HbA1c (11.2%). 11 She attained insulin independence 3 months after transplant, maintaining nondiabetic oral glucose tolerance tests with HbA1c consistently <6% without any glucose- lowering agents on cyclosporin, mycophenolate mofetil, and low- dose steroid immunosuppression. Patient 2 was a 34- year- old woman with cystic fibrosis and previous lung transplant; she received a simultaneous liver and kidney transplant with islets from the same deceased donor infused into the transplant liver portal vein the following day. Induction was with thymoglobulin and ongoing immunosuppression with tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisolone (continued at a dose of 5 mg daily post lung transplant without weaning). Over the next 2 years she required 3 additional islet transplants with basiliximab induction to achieve and sustain insulin independence maintaining nondiabetic HbA1c (4.5%). Three years after the liver transplant, she developed arterial thrombosis of the graft, leading to ischemic lesions of intrahepatic bile ducts, cholangitic abscesses, and secondary hepatic failure. Despite maintained islet graft function (HbA1c 4.6%; basal C- peptide 5 ng/ ml), she was treated with supplementary low- dose exogenous insulin until graft hepatectomy. 3 CASE REPORTS Patient 1 was a 36- year- old woman with type 1 diabetes of 27 years duration who died following a cerebral hemorrhage 13 years after a single percutaneous infusion of isolated pancreatic islets pooled from 2 4 RESULTS 4.1 Histological analysis of transplanted islets Histological analysis of liver sections from Patient 1 demonstrated engrafted islets within portal tracts (Figure 1A) with mild congestive FIGURE 1 Islets engrafted within recipient liver. A C, Liver tissue from Patient 1. A, Portal tract with islet within portal venule (thick arrow), interlobular bile duct (white arrowhead), and hepatic arteriole profiles (black arrowhead). Hematoxylin & eosin (H&E), 200. B, Islet within thin- walled portal venule (thick arrow). Endothelial vascular lining is highlighted by CD31 immunostain (thin arrows), 200. C, Islet within inlet venule in a septal portal tract (thick arrow). D2-40 immunostain decorates lymphatic endothelium (black arrowheads) but not the endothelium of portal vein (PV) or the inlet venule, confirming intravenous localization of the engrafted islet, 200. D, Liver tissue from Patient 2. Portal tract with islet within portal venule (thick arrow), interlobular bile duct (white arrowhead), and hepatic arteriole profiles (black arrowheads). There is ductular cholestasis (*) and the periportal parenchyma shows hepatocellular cholestasis and mild macrovesicular steatosis, H&E 200 A C B P V * D * *
3 752 parenchymal changes. Immunostaining for the endothelial marker CD31 confirmed that islets were situated within terminal portal vein branches (Figure 1B) or inlet venules at the portal/parenchymal interface. Further evidence that the islets were situated within vein branches was obtained through absence of immunostaining with the lymphatic marker D2-40 (Figure 1C). Engrafted islets within the terminal portal venules were morphologically identified also in the liver explanted from Patient 2 (Figure 1D), which in addition showed evidence of ischemic and cholestatic changes in keeping with hepatic artery thrombosis, ductular cholestasis indicative of sepsis, and mild steatotic changes. There was no evidence of islet fibrosis or inflammation. 4.2 Differentiation status of transplanted islet β-cells Presence of the end- differentiated human islet β-cell/α-cell marker, urocortin- 3, was confirmed in all insulin- positive and glucagon- positive cells in normal adult islets in situ through immunofluorescence costaining of 5 nondiabetic control pancreata (Supplementary Figure S1). In contrast, despite co- expression of urocortin- 3 in all glucagonexpressing α- cells, loss of mature β- cell phenotype was confirmed through absent urocortin- 3 staining in all insulin- positive (glucagonnegative) cells within engrafted islets in Patient 1 (Figure 2A- E) and in Patient 2 (Figure 3A- E). In addition to loss of end- differentiation, endocrine cell plasticity was demonstrated by cells appearing to co- express insulin and glucagon in transplanted islets from both patients (Figure 2, 3F- H) with colocalization within single cells supported by spectral plot (Figure 3I) and Z- stack confocal microscopy (Supplementary Figure S2). /glucagon co- expressing cells were identified in all examined islets (>10 per donor). 5 DISCUSSION We have demonstrated immunofluorescence staining phenotypes indicating loss of β- cell end- differentiation in islets transplanted into the portal vein despite stable engraftment and long- term maintenance of normoglycemia. Metabolic outcomes after intrahepatic islet transplantation continue to improve, and this procedure can now reproducibly deliver virtually normal overall glycemia in tandem with absolute prevention of significant hypoglycemia. 12 Nevertheless, complete normalization of stimulated insulin and C- peptide secretion has remained elusive. 3 Loss of end-differentiated β- cell phenotype may provide at least partial explanation for subtle functional impairment, despite stable engraftment of sufficient β- cell mass to prevent hyperglycemia. Urocortin- 3 expression has been used to identify mature, fully functional β- cells during pancreas development 5 and is expressed at approximately equal levels in α- and β- cells in nondiabetic adult human pancreas. 13 Absence of detectable β- cell urocortin- 3 staining in all transplanted islets examined in the current study provides evidence for loss of end- differentiated phenotype despite maintained insulin expression and near- normoglycemia. Loss of urocortin- 3 has been reported in human β- cells in association with hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. 7,13 It has been proposed that urocortin- 3 loss is an adaptive response to β- cell stress/damage, enabling the damaged β- cell to maintain insulin secretion without negative feedback inhibition through urocortin- 3- mediated δ- cell somatostatin secretion. 13 Further mechanistic studies are required to determine whether adaptation of β- cells to acute stress evidenced by markers of dedifferentiation including urocortin- 3 loss is a direct cause of imperfect glucose control through impaired insulin secretion, or whether phenotypic changes are a reactive response to β- cell dysfunction primarily driven by other mechanisms. Further evidence for a phenotypic shift in intrahepatic transplanted islets was provided by identification of insulin and glucagon co- expressing cells. Each hormone appeared to be localized to different regions of the cytoplasm without incontrovertible direct overlay. In addition to confocal microscopy Z- stack imaging, spectral analysis supported the presence of bi- hormonal cells. It has been suggested that β- cell plasticity, leading to cells co- expressing insulin and glucagon, may contribute to abnormal glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetes. 9 Following islet transplantation, glucagon secretion in response to hypoglycemia remains impaired, even following replacement of nearnormal pancreatic β-cell mass. 14 Whether β- cell plasticity, with the presence of cells expressing and secreting both insulin and glucagon, plays a role in this residual abnormality of transplanted islet function requires further study. In the current case reports, β- cell pathology was not associated with decreasing functional β- cell mass over time or with high glucose. Amyloid deposition has been reported following intrahepatic islet transplantation, in association with failing grafts and elevated blood glucose levels. 15 We have previously reported near absence of amyloid deposits around islets from Patient 1, 16 in keeping with absence of ongoing β- cell stress due to maintained normoglycemia without evidence of attrition in islet function over time. Loss of end- differentiated phenotype may facilitate β-cell survival during the ex vivo stresses associated with islet isolation and culture, in addition to sustained hypoxia following engraftment, due to peripheral as opposed to central islet revascularization as reported by ourselves in Patient 1 17 and by others. 18 We have confirmed that islets remain in or at the periphery of the portal tracts at the portal parenchymal interface. Additional peri- and intra- islet microvasculature may reflect neovascularization from the hepatic artery. 17 Alternatively, the periislet microvasculature could correspond to dilated collateral venules associated with portal venopathy following intraportal islet infusion. A limitation of this study is the inability to absolutely quantify numbers of cells that have lost end- differentiated β- cell phenotype due to the limited tissue available within these unique samples. Nevertheless, absence of urocortin- 3 staining provided a reproducible marker of altered phenotype seen in all transplanted insulin- positive/glucagonnegative cells evaluated in both recipients. In contrast, this phenotype is absent in pancreata from organ donors without diabetes, where all insulin- positive cells expressed urocortin- 3. Confirmation of whether loss of urocortin- 3 staining and apparent bi- hormonal cells represent a true phenotypic shift will require deeper characterization of
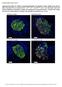
4 753 DAPI Glucagon UCN3 DAPI Glucagon UCN3 Glucagon A B C UCN3 D E DAPI Glucagon Glucagon F G H FIGURE 2 Changes in β- cell phenotype in Patient 1 following intraportal islet transplantation. Panel A demonstrates typical staining for insulin/glucagon/urocortin- 3 in an islet from Patient 1. Boxed region in A shows area magnified in B- E. Islet β- cells stained positive for insulin but all lacked urocortin- 3 (UCN3) co- expression (circle indicates insulin + /UCN3 cells). All glucagon + α- cells maintain UCN3 co- expression. Scale bars represent 20 μm in A and 10 μm in B- E. Panels F- H show islet cells (indicated by arrows) co- expressing insulin and glucagon. Scale bars represent 20 μm in F- H. Images representative of >10 transplanted islets insulin- positive cells, comprising staining for expression and subcellular localization of key β- cell transcription factors (including Pdx1 and Nkx6.1), examination of secretory granule ultrastructure by transmission electron microscopy, and transcriptomic analysis following laser capture microdissection. 19 Whether the phenotypic changes confirmed in the current study represent an irreversible adaptation to short- term reversible peritransplant stress, or a chronic response to ongoing β- cell metabolic, inflammatory, or immunosuppression- induced stress despite posttransplantation near normoglycemia remains unclear. Further studies are under way to assess whether loss of mature β- cell phenotype reflects an adaptive response to hypoxia. 20 Refinements in islet isolation and culture are ongoing in addition to innovations with the goal of fully vascularized engraftment,
5 754 DAPI Glucagon UCN3 DAPI Glucagon UCN3 Glucagon A B C UCN3 D DAPI Glucagon E E Glucagon F BG H I FIGURE 3 Changes in β- cell phenotype in Patient 2 following intraportal islet transplantation. Panel A demonstrates typical staining for insulin/glucagon/urocortin- 3 (UCN3) in an islet from Patient 2. Boxed region in A shows area magnified in B- E. Islet β- cells stained positive for insulin but lacked UCN3 co- expression (circle indicates insulin + /UCN3 cells). Glucagon + α- cells maintain UCN3 co- expression. Scale bars represent 20 μm in A and 10 μm in B- E. Panels F- H show islet cells (indicated by arrows) co- expressing insulin and glucagon. Scale bars represent 20 μm in F- H. Images are representative of >10 islets. Panel I shows a Spectral Plot (NIS Elements AR software) obtained from the cell circled in F- H confirming insulin and glucagon co- staining at the area indicated by the arrow in the microscopy images and line on the graph restoring entirely normal islet mass and function. 18 Evaluation of differentiation status through immunostaining co- localization protocols provides a novel tool to assess whether fully mature β- cell phenotype has been maintained without dedifferentiation/ plasticity following islet and isolated β- cell transplantation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS SJA was supported by PhD Studentship funding from Diabetes UK. The authors are grateful to the Newcastle University, Medical Research Council Molecular Pathology Node for tissue sectioning and automated staining.
6 755 DISCLOSURE The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the American Journal of Transplantation. REFERENCES 1. Shapiro AMJ, Lakey JRT, Ryan EA, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid- free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343: Brooks AM, Walker N, Aldibbiat A, et al. Attainment of metabolic goals in the integrated UK islet transplant program with locally isolated and transported preparations. Am J Transplant. 2013;13: Rickels MR, Liu C, Shlansky-Goldberg RD, et al. Improvement in betacell secretory capacity after human islet transplantation according to the CIT07 protocol. Diabetes. 2013;62: Rickels MR, Mueller R, Teff KL, Naji A. Beta- cell secretory capacity and demand in recipients of islet, pancreas, and kidney transplants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95: Blum B, Hrvatin S, Schuetz C, Bonal C, Rezania A, Melton DA. Functional beta- cell maturation is marked by an increased glucose threshold and by expression of urocortin 3. Nat Biotech. 2012;30: Li C, Chen P, Vaughan J, Lee K-F, Vale W. Urocortin 3 regulates glucose- stimulated insulin secretion and energy homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104: Blum B, Roose AN, Barrandon O, et al. Reversal of beta cell dedifferentiation by a small molecule inhibitor of the TGFbeta pathway. elife. 2014;3:e White MG, Marshall HL, Rigby R, et al. Expression of mesenchymal and alpha- cell phenotypic markers in islet beta- cells in recently diagnosed diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36: White MG, Shaw JAM, Taylor R. Type 2 diabetes: The pathologic basis of reversible β- cell dysfunction. Diabetes Care. 2016;39: Cinti F, Bouchi R, Kim-Muller JY, et al. Evidence of beta- cell dedifferentiation in human type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101: Berney T, Ferrari-Lacraz S, Buhler L, et al. Long- term insulinindependence after allogeneic islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes: Over the 10- year mark. Am J Transplant. 2009;9: Rickels MR, Peleckis AJ, Markmann E, et al. Long- term improvement in glucose control and counterregulation by islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101: van der Meulen T, Donaldson CJ, Caceres E, et al. Urocortin3 mediates somatostatin- dependent negative feedback control of insulin secretion. Nat Med. 2015;21: Robertson RP. Puzzling about partial glucagon responses to hypoglycemia in intrahepatic islet recipients: Missing pieces. Diabetes. 2015;64: Westermark GT, Davalli AM, Secchi A, et al. Further evidence for amyloid deposition in clinical pancreatic islet grafts. Transplantation. 2012;93: Muller YD, Morel P, Berney T. Absence of amyloid deposition in human islets transplantation after 13 years insulin independence. Transplantation. 2015;99:e31 e Muller YD, Gupta S, Morel P, et al. Transplanted human pancreatic islets after long- term insulin independence. Am J Transplant. 2013;13: Pepper AR, Gala-Lopez B, Ziff O, Shapiro AM. Revascularization of transplanted pancreatic islets and role of the transplantation site. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013: Gao T, McKenna B, Li C, et al. Pdx1 maintains β- cell identity and function by repressing an α-cell program. Cell Metab. 2014;19(2): Anderson SJ, Armour SL, White MG, et al. Evidence for beta-cell dedifferentiation as a cause for sustained graft dysfunction following peri-engraftment hypoxia in clinical islet transplantation. Late Breaking Abstract 76th American Diabetes Association meeting; June 2016; New Orleans, Abstract :p62 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional Supporting Information may be found online in the supporting information tab for this article. How to cite this article: Anderson SJ, White MG, Armour SL, et al. Loss of end- differentiated β- cell phenotype following pancreatic islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2018;18:
Future Therapies in the Treatment of Diabetes: Islet Transplantation
 Future Therapies in the Treatment of Diabetes: Islet Transplantation Michael R. Rickels, MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Medical Director,
Future Therapies in the Treatment of Diabetes: Islet Transplantation Michael R. Rickels, MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine Medical Director,
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Pancreas After Islet Transplantation: A First Report of the International Pancreas Transplant Registry
 American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 688 693 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi:
American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 688 693 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi:
β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation
 β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation Jyuhn-Huarng Juang, MD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung University and Memorial Hospital,
β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation Jyuhn-Huarng Juang, MD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung University and Memorial Hospital,
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Islet and Pancreas Transplantation
 Islet and Pancreas Transplantation Julie Wardle Specialist Nurse Coordinator Indication for Transplant Treatment option for a select groups of patients with type 1 diabetes Aged 18 years or over Recurrent
Islet and Pancreas Transplantation Julie Wardle Specialist Nurse Coordinator Indication for Transplant Treatment option for a select groups of patients with type 1 diabetes Aged 18 years or over Recurrent
Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro.
 Manuscript EMBO-2015-91058 Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. Holger A Russ, Audrey V Parent, Jennifer J Ringler, Thomas G Hennings, Gopika
Manuscript EMBO-2015-91058 Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. Holger A Russ, Audrey V Parent, Jennifer J Ringler, Thomas G Hennings, Gopika
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
islets scored 1 week month months
 Supplementary Table 1. Sampling parameters for the morphometrical analyses Time (post- DT) Control mice (age-matched) α-cells mice pancreatic surface (mm 2 ) scored DT-treated mice islets scored mice pancreatic
Supplementary Table 1. Sampling parameters for the morphometrical analyses Time (post- DT) Control mice (age-matched) α-cells mice pancreatic surface (mm 2 ) scored DT-treated mice islets scored mice pancreatic
Islet Cell Allo-Transplantation. Disclosure. Objectives
 Islet Cell Allo-Transplantation Gregory P. Forlenza, MD MCR Assistant Professor Barbara Davis Center University of Colorado Denver Special thanks to Melena Bellin, MD at The University of Minnesota who
Islet Cell Allo-Transplantation Gregory P. Forlenza, MD MCR Assistant Professor Barbara Davis Center University of Colorado Denver Special thanks to Melena Bellin, MD at The University of Minnesota who
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Figure legends Supplemental Fig.1. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Supplemental Fig. 2.
 Figure legends Supplemental Fig.. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Insulin secretory responses to.,., and. mm glucose (A) (n = 7-), and the insulin content in the islets
Figure legends Supplemental Fig.. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Insulin secretory responses to.,., and. mm glucose (A) (n = 7-), and the insulin content in the islets
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Eilandjes transplantatie. Eelco de Koning, LUMC 14 februari 2008
 Eilandjes transplantatie Eelco de Koning, LUMC 14 februari 2008 Pancreas or islets? What tissue do we wish to transplant? Is there competition for donor pancreas? How does the islet isolation and transplantation
Eilandjes transplantatie Eelco de Koning, LUMC 14 februari 2008 Pancreas or islets? What tissue do we wish to transplant? Is there competition for donor pancreas? How does the islet isolation and transplantation
Glucose Homeostasis. Liver. Glucose. Muscle, Fat. Pancreatic Islet. Glucose utilization. Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon
 Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Pancreas and Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation By: Kay R. Brown, CLCP
 Pancreas and Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation By: Kay R. Brown, CLCP Pancreas transplant recipients are usually under age 50. The majority of pancreas transplants are performed on diabetics, who are generally
Pancreas and Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation By: Kay R. Brown, CLCP Pancreas transplant recipients are usually under age 50. The majority of pancreas transplants are performed on diabetics, who are generally
Clinical Policy: Pancreas Transplantation Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.102
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.102 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 03/17 Revision Log Coding Implications Description This policy describes the medical necessity requirements for pancreas
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.102 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 03/17 Revision Log Coding Implications Description This policy describes the medical necessity requirements for pancreas
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium
 2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium The Future of Transplantation Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University of Toronto. Dr. Humar received his
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium The Future of Transplantation Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University of Toronto. Dr. Humar received his
Inhibition of DYRK1A stimulates human beta-cell proliferation
 Inhibition of DYRK1A stimulates human beta-cell proliferation Ercument Dirice 1,, Deepika Walpita 2,, Amedeo Vetere 2, Bennett C. Meier 2,5, Sevim Kahraman 1, Jiang Hu 1, Vlado Dančík 2, Sean M. Burns
Inhibition of DYRK1A stimulates human beta-cell proliferation Ercument Dirice 1,, Deepika Walpita 2,, Amedeo Vetere 2, Bennett C. Meier 2,5, Sevim Kahraman 1, Jiang Hu 1, Vlado Dančík 2, Sean M. Burns
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4)
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Monitoring of human uterus transplantation with cervical biopsies - a provisional scoring system for rejection. Johan Mölne
 Monitoring of human uterus transplantation with cervical biopsies - a provisional scoring system for rejection. Johan Mölne Department of Pathology and Genetics, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg,
Monitoring of human uterus transplantation with cervical biopsies - a provisional scoring system for rejection. Johan Mölne Department of Pathology and Genetics, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg,
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes
 MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren
 Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren Type 1 Diabetes is currently regarded as a T cell mediated autoimmune disease, a notion expressed in over 50 000 scientific publications. Acute
Är diabetes mellitus en autoimmun sjukdom? Olle Korsgren Type 1 Diabetes is currently regarded as a T cell mediated autoimmune disease, a notion expressed in over 50 000 scientific publications. Acute
Islet Transplantation. Description
 Subject: Islet Transplantation Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Islet Transplantation Description Autologous islet transplantation, performed in conjunction with pancreatectomy, is
Subject: Islet Transplantation Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Islet Transplantation Description Autologous islet transplantation, performed in conjunction with pancreatectomy, is
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver Colorado ******************** ******************
 University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver Colorado ******************** 1988-2005 ****************** Disclosures No disclosures Case 53 M presents with sudden onset of upper abdominal pain
University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver Colorado ******************** 1988-2005 ****************** Disclosures No disclosures Case 53 M presents with sudden onset of upper abdominal pain
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Kidney Transplantation
 Kidney Tran nsplantation Historical per rspective and current practice Piyanut Poo otracool, M.D. Departmen nt of Surgery, Ramathibo odi Hospital, Mahidol University Kidney Transplantation DDKT Adult deceased
Kidney Tran nsplantation Historical per rspective and current practice Piyanut Poo otracool, M.D. Departmen nt of Surgery, Ramathibo odi Hospital, Mahidol University Kidney Transplantation DDKT Adult deceased
Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment
 Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
The state of affairs of allogenic islet transplantation. William Bennet MD, PhD Fellow Division of Transplant Surgery UCHSC
 The state of affairs of allogenic islet transplantation William Bennet MD, PhD Fellow Division of Transplant Surgery UCHSC Global epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus IDDM NIDDM 1997 3 700 000 120 300 000
The state of affairs of allogenic islet transplantation William Bennet MD, PhD Fellow Division of Transplant Surgery UCHSC Global epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus IDDM NIDDM 1997 3 700 000 120 300 000
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection
 Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs
 Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
1030 Diabetes Care Volume 38, June 2015
 TYPE 1 DIABETES AT A CROSSROADS 1030 Diabetes Care Volume 38, June 2015 Islet Transplantation for Type 1 Diabetes, 2015: What Have We Learned From Alloislet and Autoislet Successes? Diabetes Care 2015;38:1030
TYPE 1 DIABETES AT A CROSSROADS 1030 Diabetes Care Volume 38, June 2015 Islet Transplantation for Type 1 Diabetes, 2015: What Have We Learned From Alloislet and Autoislet Successes? Diabetes Care 2015;38:1030
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study
 Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
Islet Transplantation
 Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 3/24/2017 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 3/24/2017 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Chapter 4 Section Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK), Pancreas-After-Kidney (PAK), And Pancreas-Transplant-Alone (PTA)
 Surgery Chapter 4 Section 24.7 Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK), Pancreas-After-Kidney (PAK), And Pancreas-Transplant-Alone Issue Date: February 5, 1996 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(5) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE
Surgery Chapter 4 Section 24.7 Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK), Pancreas-After-Kidney (PAK), And Pancreas-Transplant-Alone Issue Date: February 5, 1996 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(5) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE
Chapter 4 Section 24.7
 Surgery Chapter 4 Section 24.7 Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK), Pancreas-After-Kidney (PAK), And Pancreas-Transplant-Alone (PTA), And Pancreatic Islet Cell Transplantation Issue Date: February 5, 1996
Surgery Chapter 4 Section 24.7 Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK), Pancreas-After-Kidney (PAK), And Pancreas-Transplant-Alone (PTA), And Pancreatic Islet Cell Transplantation Issue Date: February 5, 1996
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis. Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland
 Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Pancreatitis Pancreas Pancreas - an organ that makes bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid, enzymes to digest
Diagnosis of chronic Pancreatitis Christoph Beglinger, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Pancreatitis Pancreas Pancreas - an organ that makes bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid, enzymes to digest
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Islet Transplantation
 Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 12/16/2016 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 12/16/2016 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Supplemental Information. b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous. Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Advancing Opportunities To Prevent Type 1 Diabetes
 Advancing Opportunities To Prevent Type 1 Diabetes Dr. Allison Green Centre for Immunology and Infection Hull York Medical School York University Type 1 Diabetes Insulin deficiency destabilizes regulation
Advancing Opportunities To Prevent Type 1 Diabetes Dr. Allison Green Centre for Immunology and Infection Hull York Medical School York University Type 1 Diabetes Insulin deficiency destabilizes regulation
Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes
 University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Haekwon Kim Dept. of Biotechnology Seoul Women s University Introduction Type I diabetes is caused by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic
Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Haekwon Kim Dept. of Biotechnology Seoul Women s University Introduction Type I diabetes is caused by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue
 Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
The regenerative therapy of type 1 diabetes mellitus 21April 2017 Girne, Northern Cyprus 53rd Turkish National Diabetes Congress
 The regenerative therapy of type 1 diabetes mellitus 21April 2017 Girne, Northern Cyprus 53rd Turkish National Diabetes Congress Thomas Linn Clinical Research Unit Centre of Internal Medicine Justus Liebig
The regenerative therapy of type 1 diabetes mellitus 21April 2017 Girne, Northern Cyprus 53rd Turkish National Diabetes Congress Thomas Linn Clinical Research Unit Centre of Internal Medicine Justus Liebig
Diabetes mellitus is a complex of syndromes characterized metabolically by hyperglycemia and altered glucose metabolism, and associated
 Diabetes mellitus is a complex of syndromes characterized metabolically by hyperglycemia and altered glucose metabolism, and associated pathologically with specific microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Diabetes mellitus is a complex of syndromes characterized metabolically by hyperglycemia and altered glucose metabolism, and associated pathologically with specific microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Transplanted Mouse Islets Labeled With Chitosan-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Transplanted Mouse Islets Labeled With Chitosan-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles J.-H. Juang, J.-J. Wang, C.-R. Shen, C.-H. Kuo, Y.-W. Chien, H.-Y. Kuo, Z.-T.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Transplanted Mouse Islets Labeled With Chitosan-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles J.-H. Juang, J.-J. Wang, C.-R. Shen, C.-H. Kuo, Y.-W. Chien, H.-Y. Kuo, Z.-T.
Pancreas Transplantation. Sonia Clarke-Swaby Recipient Kidney/pancreas Transplant Co-ordinator Guy s Hospital
 Pancreas Transplantation Sonia Clarke-Swaby Recipient Kidney/pancreas Transplant Co-ordinator Guy s Hospital Introduction Selection criteria, New innovation Complications, Success rates, Life expectancy
Pancreas Transplantation Sonia Clarke-Swaby Recipient Kidney/pancreas Transplant Co-ordinator Guy s Hospital Introduction Selection criteria, New innovation Complications, Success rates, Life expectancy
Transplantation in Nagasaki
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Evaluation of the Presumable Incide Transplantation in Nagasaki Tanaka, Takayuki; Kuroki, Tamotsu; Tatsuya; Ono, Shinichiro; Abiru, No Susumu
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Evaluation of the Presumable Incide Transplantation in Nagasaki Tanaka, Takayuki; Kuroki, Tamotsu; Tatsuya; Ono, Shinichiro; Abiru, No Susumu
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Islets of Langerhans consist mostly of insulin-producing β cells. They will appear to be densely labeled
 Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Islet Transplantation
 Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 07/01/2014 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Islet Transplantation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.07.027 07/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 07/01/2014 Section: Transplants Place(s) of Service: Inpatient I.
Pathways to Protecting from Autoimmunity the Resurrected/Regenerated Beta Cells. Jeffrey Bluestone, PhD Diabetes Center at UCSF
 Pathways to Protecting from Autoimmunity the Resurrected/Regenerated Beta Cells Jeffrey Bluestone, PhD Diabetes Center at UCSF Number of Transplants Is islet replacement a viable option? 2000 1800 1600
Pathways to Protecting from Autoimmunity the Resurrected/Regenerated Beta Cells Jeffrey Bluestone, PhD Diabetes Center at UCSF Number of Transplants Is islet replacement a viable option? 2000 1800 1600
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms?
 Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice
 Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Simple Measures to Monitor b -Cell Mass and Assess Islet Graft Dysfunction
 American Journal of Transplantation 2007; 7: 303 308 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2006 The Authors Journal compilation C 2006 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
American Journal of Transplantation 2007; 7: 303 308 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2006 The Authors Journal compilation C 2006 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
SELECTED ABSTRACTS. All (n) % 3-year GS 88% 82% 86% 85% 88% 80% % 3-year DC-GS 95% 87% 94% 89% 96% 80%
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Report on Pathology. Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques
 Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
Report on Pathology Study: The effect of Compound X on pancreatic islets in rhesus macaques Prepared for: Client Name Client Address January 1, 2013 Prepared by: Charter Preclinical Services 21 Main St.,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Baidal DA, Ricordi C, Berman DM, et al. Bioengineering of an
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Baidal DA, Ricordi C, Berman DM, et al. Bioengineering of an
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions
 2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
2013 Colorado Society of Pathology Pitfalls in the diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Hepatocellular adenoma: new WHO
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Using the cost effectiveness of allogeneic islet transplantation to inform induced pluripotent stem cell-derived β-cell therapy reimbursement
 For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Using the cost effectiveness of allogeneic islet transplantation to inform induced pluripotent stem cell-derived β-cell therapy reimbursement
For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Using the cost effectiveness of allogeneic islet transplantation to inform induced pluripotent stem cell-derived β-cell therapy reimbursement
Ch. 39 Endocrine System
 Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal and neonatal rat pancreases
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
Success with pancreatic islet transplantation in human. In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging of Transplanted Islets and Early Detection of Graft Rejection
 EXPERIMENTAL TRANSPLANTATION In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging of Transplanted Islets and Early Detection of Graft Rejection Xiaojuan Chen, Xiaomin Zhang, Courtney S. Larson, Marshall S. Baker, and Dixon
EXPERIMENTAL TRANSPLANTATION In Vivo Bioluminescence Imaging of Transplanted Islets and Early Detection of Graft Rejection Xiaojuan Chen, Xiaomin Zhang, Courtney S. Larson, Marshall S. Baker, and Dixon
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Pancreas Transplant File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: pancreas_transplant 1/2000 5/2017 5/2018 8/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Transplantation
Corporate Medical Policy Pancreas Transplant File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: pancreas_transplant 1/2000 5/2017 5/2018 8/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Transplantation
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes
 The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Records. Adult Kidney Pancreas Transplant Recipient Registration Worksheet. Recipient Information. Provider Information.
 Records Adult Kidney Pancreas Transplant Recipient Registration Worksheet FORM APPROVED: O.M.B. NO. 0915 0157 Expiration Date: 07/31/2020 Note: These worksheets are provided to function as a guide to what
Records Adult Kidney Pancreas Transplant Recipient Registration Worksheet FORM APPROVED: O.M.B. NO. 0915 0157 Expiration Date: 07/31/2020 Note: These worksheets are provided to function as a guide to what
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.03.10 Islet Transplantation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 7.03.10 Islet Transplantation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas. By Andrew Kringas
 Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Long-Term Immunosuppression After Solitary Islet Transplantation Is Associated With Preserved C-Peptide Secretion for More Than a Decade
 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Case Report C Copyright 21 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 1.1111/ajt.13383 Long-Term Immunosuppression After Solitary
Wiley Periodicals Inc. Case Report C Copyright 21 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 1.1111/ajt.13383 Long-Term Immunosuppression After Solitary
Paneth Cells. Road Map to the Finish. No Review this Friday. Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs. Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I
 Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation
 Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation Ron Shapiro, M.D. Professor of Surgery Surgical Director, Kidney/Pancreas Transplant Program Recanati/Miller Transplantation Institute
Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation Ron Shapiro, M.D. Professor of Surgery Surgical Director, Kidney/Pancreas Transplant Program Recanati/Miller Transplantation Institute
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
UEMS & EBS: DIVISION OF TRANSPLANT SURGERY
 CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS TRANSPLANTATION Module 1: Multi-organ retrieval Ability to evaluate donor suitability Ability to retrieve abdominal organs for transplantation Evaluation of donor/ organs suitability
CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS TRANSPLANTATION Module 1: Multi-organ retrieval Ability to evaluate donor suitability Ability to retrieve abdominal organs for transplantation Evaluation of donor/ organs suitability
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Allogeneic Pancreas Transplant
 Protocol Allogeneic Pancreas Transplant (70302) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14 The following
Protocol Allogeneic Pancreas Transplant (70302) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 09/11, 07/12, 05/13, 05/14 The following
C-Peptide and Exercise in people with Type 1 Diabetes. Guy Taylor
 C-Peptide and Exercise in people with Type 1 Diabetes Guy Taylor Produced in equal amounts to insulin C-Peptide Used to assess endogenous insulin secretion not injected with exogenous insulin Pathogenesis
C-Peptide and Exercise in people with Type 1 Diabetes Guy Taylor Produced in equal amounts to insulin C-Peptide Used to assess endogenous insulin secretion not injected with exogenous insulin Pathogenesis
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
