ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Sports Massage Unit 27 Sports Massage
|
|
|
- Carmel Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Sports Massage Unit 27 Sports Massage Recommended Guided Learning Hours 100 Pre-requisite ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Holistic Massage or ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Body Treatments or equivalent QCA Qualification Accreditation Number: 100/2592/3 Unit 27 Sports Massage Theory Learning outcome Underpinning knowledge Students will be able to: 1) Understand and explain the changes Aerobic system that occur during exercise to the muscular Longer than 3 minutes to fatigue system Depletion of muscle glycogen and sugar Insufficient oxygen delivery VO 2 maximum Anaerobic glycolysis High intensity Short duration activities 1-3 minutes to fatigue Lactic acid build up causing rapid fatigue Creatine phosphate system Breakdown of glucose High intensity Short duration activities Less than 10 seconds to fatigue Define Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) production Define Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) production 2) Understand and explain the physiology of a muscle cell 3) Understand and explain (with the aid of diagrams) the Origin, Insertion and Action of each of the following muscles: Define Lactic Acid To include structure and function of the following: Cardiac Smooth Skeletal Muscle fibre type Fast and Slow twitch Myofibrils Actin and Myosin Sarcomeres Sliding filament theory Actinmyosin cross bridges Mitochondria Muscles of the Back and Neck Erector Spinae Scalenes Trapezius Latissimus Dorsi Teres Major Sternocleidomastoid Levator Scapulae Splenius Capitis Coracobrachialis Rhomboids Major and Minor Serratus Anterior Deltoid Rotator Cuff Muscles Infraspinatus, Supraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis Muscles of the Arm, Wrist and Hand Biceps Triceps Supinator Pronator Teres Brachialis Brachioradialis Aconeus Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Digitorum Extensor Digitorum Palmaris Longus Muscles of the Hip, Leg, Ankle and Foot Gluteus Maximus Gluteus Medius Gluteus Minimus Iliacus Psoas Major Iliopsoas Piriformis Tensor Fascia Lata Iliotibial Tract Sartorius Gracilis Quadriceps: Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Intermedius, Vastus Medialis Adductors: Brevis, Longus and Magnus Hamstrings: Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosis, Semimembranosis Popliteus Pectineus Tibialis Anterior Tibialis Posterior Peroneus Longus Peroneus Brevis Gastrocnemius Soleus Achilles Tendon Flexor Digitorum Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscles of Respiration and Abdominals Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Intercostals Rectus Abdominus Internal Obliques External Obliques Quadratus Lumborum Transverssus Abdominus ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 1
2 4) Understand and explain the effects of stress on muscles during sport 5) Understand and explain the changes that occur during exercise to the neurological system To include Fear, Fight and Flight : Adrenal cortex and medulla stimulated to secrete adrenaline Increase blood to the muscles Liver stimulates secretion of glucose for anaerobic energy production Salivary glands vasoconstrict Pupils dilate Digestive system slows down preventing energy wastage Butterflies Change in motor units Stimulation dependant on number of motor units contracting Fear, Fight and Flight Hypothalamus stimulates the Sympathetic Nervous System and the Endocrine System Adrenaline Cardiorespiratory System speeds up Blood is diverted to the muscles Digestive system slows down preventing energy wastage Liver secretes glucose for anaerobic energy production Salivary glands vasoconstrict Pupils dilate Butterflies 6) Describe in detail joint structures Synovial joints Cartilage Articular (Hyaline) Ligaments Synovial membrane Bursa 7) Understand and explain the possible stresses and strains put on the spine and other joints in sporting activities 8) Understand and explain in detail (with the aid of diagrams) the joint supporting systems 9) Understand and explain the possible causes and effects of the following diseases and disorders and their effect on specific sports: 10) Understand and explain the principles of training Inflexibility Lifting techniques Postural techniques Stress Environment Injury To include the following major joints: Atlanto-occipital Atlanto-axial Shoulder Sternoclavicular Elbow Wrist Hand Hip Sacro-iliac Knee Ankle Foot Osteo Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Shin splints Stress fractures Facet joint pain Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Rotator cuff injuries Chondromalacia patellae Calcaneal bursitis Periostitis Concussion Cramp Stitch Chronic muscle fatigue Sprain Strain Lateral epicondylitis Medial epicondylitis Adhesive capsulitis Dislocation Fractures Ruptured muscles Jogger s nipple Torn cartilage Fibrositis Fibrosis Impingement Muscle soreness Atony Atrophy Fasciitis Myositis Tendinitis Spasm Soft Tissue Injuries Exercise induced Asthma Diabetes Hay Fever Hyperventilation Osteoporosis Low Back Pain Heartburn Irritable Bowel Syndrome Haemorrhoids Hernias Amenorrhoea Heat stroke Heat exhaustion Kidney stones Dehydration Torticollis Myalgia Myotonia Black toe nails Runner s knee Plantar fasciitis Osgood Schlatters Compartment syndrome Frequency Intensity Duration Overload Specificity sport and individual Reversibility 11) Understand and explain over training Define over training Persistent muscle soreness Loss of co-ordination Prolonged fatigue Dizziness Performance inconsistency Elevated resting heart rate Tightness in the chest Heat stress 12) Understand the principles of force and motion 13) Understand and explain the principles of injury prevention and management Motive and Resistive forces Concentric Eccentric Isometric contractions Components of fitness Stamina Suppleness Strength Speed Skill ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 2
3 14) Understand and explain the stages of the healing process and the possible treatments available 15) Understand the preventative and rehabilitative training to reinforce massage treatments 16) Understand the effects and benefits of stretching 17) Understand and explain the use of stretching massage movements 18) Understand and explain the signs and symptoms of inflammation 19) Understand and explain the techniques of thermotherapy and cryotherapy(icer) and the rationale for choice 20) Understand and explain scar tissue and adhesions 21) Understand and explain the possible damage to the skin as a result of sporting activities on different types of surfaces, with regard to clothing, shoes, exposure to the sun, wind and other elements Specificity Psychological aspects Define Warm up/cool down Intrinsic/Personal Age Sex Somatotype Biomechanics Fitness to include Muscle balance Physical symmetry Joint integrity Motor skills Psychological factors Extrinsic/Environmental Organisation and Management Type of sport Training errors Environment Equipment Acute/inflammatory phase Repair phase Remodelling phase To include Passive Active Resistive forms of exercise and the frequency and duration of each Intensity Use of Free Weights and/or Resistive bands where appropriate Importance of Warm up/cool down Mental relaxation Muscular relaxation Increased flexibility Improved posture Prevention of lower back pain Improved fitness Relief of muscle soreness Relief of cramp Improved motor skills Prevention of injury Connective Tissue Massage (CTM) After injury Muscle reflexes preventing stretching overload Define inflammation to include: Increased temperature Redness Swelling Pain Loss of function Define thermotherapy to include the use of: Heat Pad Hot Compress for pain relief Increased elasticity of collagen fibres Define cryotherapy to include the use of: Ice for relief of pain Constriction of blood vessels Reduction of swelling Reduction of metabolism Reasons for contrast bathing Define Scar tissue Define Adhesions Blisters Grazes Sores Open wounds e.g. Lacerations Puncture wounds Abrasions Gravel burns Sun burns Wind burns Bruising Surfaces include: Grass Gravel Astroturf Stone Wood ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 3
4 22) Understand, explain and demonstrate methods of consultation 23) Understand, explain and demonstrate how to record information and store in a safe place and secure manner 24) Understand and recognise contraindications to sports massage with reasons why and when to refer to other health professionals An example of a consultation form can be found at Students should demonstrate knowledge of the importance of the following: Private comfortable area Positive body language Positioning of the client (no barriers between themselves and client) Good communication skills (asking open and/or closed questions where appropriate) Trust Professionalism, confidence and enthusiasm Confidentiality Any contraindications to treatment Client profile Importance of planning a treatment programme bearing in mind the clients religious, moral and social beliefs Determining the nature and extent of the clients needs Agreement to the course of action Ascertain the clients consent to the treatment (where the client is not in a position themselves ascertain from the appropriate companion s agreement to the treatment) Explanation of any possible side effects to the treatment Explanation how the programme will be evaluated and the review process Where applicable clarify with the client information, which may be available to other, e.g. relevant health care workers Obtain the client s signature (or that of the companion) Physical examination including: Head Shoulders Back Pelvis Legs Feet Body alignment/posture Range of motion/joint function Comparison of strength of the muscles on each side of the body Muscle definition Active, Passive and Resisted movement Palpation Any contraindications Area treated Type of injury Treatment given Any reactions Any exercises given Home care treatment Never treat unless the injury has been diagnosed and treatment has been recommended by a medical practitioner Pregnancy Cardio vascular conditions (thrombosis, phlebitis, hypertension, hypotension, heart conditions) Haemophilia Any condition already being treated by a GP or another health professional, e.g. Physiotherapist, Osteopath, Chiropractor, Coach Medical oedema Osteoporosis Arthritis Nervous/Psychotic conditions Epilepsy Recent operations Diabetes Asthma Any dysfunction of the nervous system (e.g. Muscular sclerosis, Parkinson s disease, Motor neurone disease) Bells Palsy Trapped/Pinched nerve (e.g. sciatica) Inflamed nerve Cancer Postural deformities Spastic conditions Kidney infections Whiplash Slipped disc Undiagnosed pain When taking prescribed medication Acute rheumatism Contraindications that restrict treatment Fever Contagious or infectious diseases Under the influence of recreational drugs or alcohol Diarrhoea and vomiting Skin diseases Undiagnosed lumps and bumps Localised swelling Inflammation Varicose veins Pregnancy (abdomen) Cuts Bruises Abrasions Scar tissues (2 years for major operation and 6 months for a small scar) Sunburn Hormonal implants ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 4
5 25) Understand, explain and ensure appropriate client care, client modesty and the correct use of towels at all times 26) Understand, explain and demonstrate correct hygiene procedures 27) Understand, explain and demonstrate the ability to ensure client is in a suitable position of comfort and support for different techniques applied to different parts of the body and range of conditions 28) Understand, explain and demonstrate the skills of palpation and physical examination compared with pre-massage states to measure the following: 29) Understand, explain and demonstrate the application and removal of the medium if required, appropriately and professionally 30) Understand and explain the effects of massage on muscle and other soft tissue 31) Understand, explain and demonstrate the classical massage movements where appropriate 32) Understand and explain the reasons for selecting the appropriate type of massage movement according to the client s conditions and needs Abdomen (first few days of menstruation depending how the client feels) Haematoma Hernia Recent fractures (minimum 3 months) Cervical spondylitis Gastric ulcers After a heavy meal Checking consultation and contraindications Explaining the treatment to the client Helping the client onto the couch/seat protecting the client s modesty at all times Ensure that all parts of the client are covered except the area being massaged Cleanse the feet with a medi-wipe or similar Wash own hands Keep ensuring that the client is comfortable Remove the massage medium at the end of the treatment if appropriate Help the client off the couch/seat protecting their modesty at all times Describe the most efficient form of sterilisation: In the sports clinic In situ at a sports event Describe the best form of waste removal (particularly when contaminated): In the sports clinic In situ at a sports event Reasons for good personal hygiene Wash own hands Wipe the clients feet Use clean towels for each client Put couch roll on top of towels Wear clean white professional work wear Socks/tights and full flat shoes Remove all jewellery (except wedding band) from self and client No nail enamel Clean short nails Hair tied back off collar and face Use appropriate supports e.g. under the ankles, chest and forehead, knees, head, or wherever a support is appropriate for the sports massage movement Passive, Active and Restricted Movement Range of Movement Degree of Swelling Variations in Tissue Temperature Muscle Tone and Bulk Adhesions Previous injury to the area Fatty Nodules Ensure the massage medium is removed at the end of the treatment if required Do not let the client walk around in bare feet Ensure all surfaces are lined with couch roll Wipe couch and trolley with surgical spirit or similar at the end of each day Speeds up healing of damaged tissues and muscles Increases fitness capabilities Increases performance potential Prevents future injury Helps clear out waste and toxins Breaks up adhesions Enables faster healing Improves flexibility Enables peak performance to be achieved more rapidly Effleurage Petrissage Frictions Tapotement Vibrations Specific Sports Massage Techniques Movements should be performed correctly and on areas appropriate for the injury and the clients needs Effleurage Petrissage Frictions Tapotement Vibrations Specific Sports Massage Techniques ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 5
6 33) Understand, explain and demonstrate sports massage techniques according to the clients condition and needs. 34) Understand and explain specific Sports Massage techniques for the following: 35) Understand, explain in detail and demonstrate the common sports injuries that can be treated after medical approval 36) Understand, explain and provide feedback and reassurance to the client 37) Understand, explain and advise on the use, application and benefits of self treatment 38) Understand, explain and demonstrate the heat sensitivity test 39) Understand, explain and provide feedback and reassurance of the client Manual Lymphatic Drainage Neuro-Muscular Technique (NMT) Muscle Energy Technique (MET) Soft Tissue Release (STR) Connective Tissue Massage (CTM) Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Treatment of injury Pre-event During/Between event Post event Corrective Preventative Conditioning massages Shin Splints Ilio tibial band release (Runner s knee) Muscle fatigue Lateral epicondylitis Medial epicondylitis Soft tissue injuries Sprains Rotator cuff injuries Strains Muscle soreness Cramp Myositis Spasm Stitch Fibrositis Fibrosis Atony Atrophy Hyperventilation Low back pain Carpal tunnel syndrome Calcaneal bursitis Chondromalacia patellae Adhesive capsulitis Torticollis Tendinitis of any muscle including: Achilles Flexor Biceps Supraspinatis Subscapularis Tibialis Anterior Superficial skin wounds including: Blisters Grazes Sores Open wounds e.g. Lacerations Puncture wounds Abrasions Gravel burns Sun burn Wind burn At the end of each treatment the client s feelings and any skin or other reactions should be recorded The following areas should be monitored: Outcomes achieved Effectiveness of the treatment Any change in demands Whether the treatment met the needs of the client Longer term needs of the client Encourage clients to express their feelings/requirement during the treatment Note client s reactions and make appropriate adjustments Thermotherapy Cryotherapy The use of alternating hot and cold test tubes on the appropriate part of the body At the end of each treatment the client s feelings and any skin or other reactions should be recorded The following areas should be monitored: Outcomes achieved Effectiveness of the treatment Any change in demands Whether the treatment met the needs of the client Longer term needs of the client Encourage client to express his/her feelings/requirements during the treatments Note client s reactions and make appropriate adjustments ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 6
7 Unit 27 Sports Massage Case Studies 5 clients must be treated 3 times each to make a total of 15 treatments Consultation including thorough medical history and general lifestyle Client profile (to include any current issues in their life) Rationale for the choice of treatment Details of how the therapist conducted the treatment Details of how the client felt during and after the treatment Details of home care advice given The following should also be documented for treatments 2 and 3 : The consultation should be checked and any changes noted Rationale for the choice of treatment Details of how the therapist conducted the treatment Details of how the client felt during and after the treatment Details of home care advice given An overall conclusion of the case should be recorded Reflective practice after each treatment* Signed by client *NB: Candidates should reflect on their own performance and the performance outcomes of the treatment ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 7
8 Mapping of Key Skills Unit 3 to ITEC Level 3 Unit 27 Sports Massage IT3.1 Plan and use different sources to Understand and explain methods of consultation search for and select information required Students are required to research and design a consultation for two different purposes form to be used for producing their case studies. Candidates may use a computer for this purpose. Understand and explain the issues surrounding consent, to include writing to GPs and other medical practitioners for consent to treatment Students are also required to understand the importance of producing a standard letter to send to GPs or other medical practitioners for consent to treatment. As students are required to study anatomy and physiology in detail, candidates may use the internet for researching the IT3.2 Explore, develop and exchange information and derive new information to meet two different purposes IT3.3 Present information from different sources for 2 different purposes and audiences Your work must include one example of text, one example of image and one example of numbers C3.1a Contribute to a group discussion about a complex subject C3.2 Read and synthesise information from two extended documents about a complex subject One of these documents should include at least one image subject Candidates are required to produce 15 case studies, i.e. they must treat 5 clients 3 times each, including taking a full consultation using their own form, gaining written consent where applicable, treatment plan, obtain information as to how the client felt before during and after the treatment and giving good after care advice. A computer may be used for this purpose. Understand and explain methods of consultation Students are required to research and design a consultation form to be used for producing their case studies and a computer may be used for this. Understand and explain the issues surrounding consent To include writing to GPs and other medical practitioners for consent to treatment IT skills may be used for this purpose. Throughout the course the use of sports massage techniques and their effects will be discussed in relevance to a variety of specific sports injuries and required case studies Students are required to understand the structure and function of the human body in detail in order to understand the effects of specific sports injuries, therefore they are required to read around the subject and research form the books on the ITEC recommended book list. They are also required to draw diagrams from memory of the human body and specifically the muscular system, joints and the possible reasons for the injuries ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 8
9 Mapping of other issues for ITEC Level 3 Unit 27 Sports Massage This unit deals with clients being consulted prior to selecting the appropriate sports massage treatment according to their requirements. As such, ethical issues are often raised relating to the massage treatment, the surroundings and whether the client should or should not be treated. For example: Understand, explain and demonstrate methods of consultation Understand, explain and demonstrate knowledge of the contraindications to sports massage and when to refer to other health professionals Understand, explain and ensure appropriate client care, client modesty and the correct use of towels at all times Social issues are often raised relating to the individual treatment of the client and ensuring that they are treated in an appropriate and acceptable way depending upon their particular cultural or religious background and the treatment being administered For example: Understand, explain and demonstrate the ability to ensure client is in a suitable position of comfort and support for different techniques applied to different parts of the body and range of conditions Understand, explain and provide feedback and reassurance to the client Understand, explain and ensure appropriate client care, client modesty and the correct use of towels at all times As the students will be working in a clinic environment they must ensure that it is safe and hygienic for themselves and any visiting clients. They must also ensure that it complies with the Health and Safety regulations and the Electricity at Work Act and that they never treat clients who may be contraindicated For example: Understand, explain in detail and demonstrate the common sports injuries that can be treated after medical approval Understand, explain and demonstrate correct hygiene procedures Understand, explain and demonstrate knowledge of the contraindications to sports massage and when to refer to other health professionals ITEC Unit 27 Sports Massage Syllabus September 2007 Page 9
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
The Massage Routine. Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position. Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes
 The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015 There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015 There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
1.1 To include: Arabic French Origins: Chinese Hippocrates Galen Dark ages Per Henrick Ling Johann Georg Mezger
 ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Sports Massage Therapy Unit 455 Sports Massage Treatments Recommended Learning Hours GLH 90 Credit Value 16 QCF Qualification Reference Number: T/506/7228 1. Understand the history
ITEC Level 3 Diploma in Sports Massage Therapy Unit 455 Sports Massage Treatments Recommended Learning Hours GLH 90 Credit Value 16 QCF Qualification Reference Number: T/506/7228 1. Understand the history
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
5 Specification Content
 5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
ITEC Unit 16 - Spa Treatments Recommended minimum guided learning hours 93
 ITEC Unit 16 - Spa Treatments Recommended minimum guided learning hours 93 Learning Outcome Students will be able to: 1. Understand and explain the history and concept of Spas 2. Understand and explain
ITEC Unit 16 - Spa Treatments Recommended minimum guided learning hours 93 Learning Outcome Students will be able to: 1. Understand and explain the history and concept of Spas 2. Understand and explain
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
4) The muscle protein that binds calcium used for muscle contraction is the. a) G actin b) Troponin c) Tropomyosin d) calmodulin e) B and D
 BIOL 2401 PRACTICE EXAM 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1) When acetylcholine binds to receptors at the motor end plate, the muscle membrane becomes. a) more permeable to sodium ions b) more permeable to
BIOL 2401 PRACTICE EXAM 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1) When acetylcholine binds to receptors at the motor end plate, the muscle membrane becomes. a) more permeable to sodium ions b) more permeable to
STRETCHING. Benefits of stretching
 STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Applied Human Biology for Exercise and Fitness Level 3 J/615/3220 MOCK PAPER
 Applied Human Biology for Exercise and Fitness Level 3 J/615/3220 MOCK PAPER There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out of 40 marks. All questions are multiple
Applied Human Biology for Exercise and Fitness Level 3 J/615/3220 MOCK PAPER There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out of 40 marks. All questions are multiple
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
National Fitness Leadership Alliance
 Exercise Theory s November 2005 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory s National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 1 Exercise Theory s November 2005 National Fitness Leadership Alliance
Exercise Theory s November 2005 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory s National Fitness Leadership Alliance (NFLA) 1 Exercise Theory s November 2005 National Fitness Leadership Alliance
The Muscular System home study course
 The Muscular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part of
The Muscular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part of
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
a. Demonstration & Practise of the Technique...4 b. Refining the Feel of the Technique...4 c. Practical Application to the Body Generally...
 Course Outline Course Overview Goltech Basic: Cross-Fibre Muscle Release...4 1. History & Development of Goltech...4 2. Musculo-Skeletal System as relevant to Goltech...4 3. Why Goltech cross-fibre muscle
Course Outline Course Overview Goltech Basic: Cross-Fibre Muscle Release...4 1. History & Development of Goltech...4 2. Musculo-Skeletal System as relevant to Goltech...4 3. Why Goltech cross-fibre muscle
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Muscle Energy Technique
 PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons
 SECTION 3 TRAUMATOLOGY Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons 58 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] TRAUMATOLOGY SECTION 3 59 IMPORTANT 3 comra therapy is particularly good for fractures, dislocations
SECTION 3 TRAUMATOLOGY Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons 58 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] TRAUMATOLOGY SECTION 3 59 IMPORTANT 3 comra therapy is particularly good for fractures, dislocations
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
Skeletal Muscle. Cardiac Muscle. Smooth Muscle. II. Muscular System. The Muscular System
 Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Chapter CHAPTER 8 8 The Muscular System College Prep NOTES Smooth Muscle Found in body organs,vessels, respiratory passages Not striated, tapered, single cell nucleus involuntary, peristaltic contractions
Learning Objective Lecture Content Suggested Resources Approximate Hours Introductory session
 SCHEME OF WORK APPLICATION FORM For each ITEC qualification, the lecturer/centre must complete a Scheme of Work indicating how the lecturer is planning to cover the ITEC syllabus throughout the course.
SCHEME OF WORK APPLICATION FORM For each ITEC qualification, the lecturer/centre must complete a Scheme of Work indicating how the lecturer is planning to cover the ITEC syllabus throughout the course.
Preface ORGANIZATION AND CONTENT
 Preface Today s massage, bodywork, and fitness professionals are increasingly becoming members of the healthcare team. These professionals collaborate with physicians, physical therapists, occupational
Preface Today s massage, bodywork, and fitness professionals are increasingly becoming members of the healthcare team. These professionals collaborate with physicians, physical therapists, occupational
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
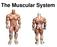 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley,
 Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED
 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training (Practitioner) - Sample Assessment Materials
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 5 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 5 Special Instructions: Level 3 Diploma
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 5 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 5 Special Instructions: Level 3 Diploma
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
SKABT18v2 Improve Body Condition Using Electro-Therapy
 Overview This unit is about improving body condition using electro-therapy. It covers the skills involved in providing a thorough consultation with the client to formulate a specific treatment plan. You
Overview This unit is about improving body condition using electro-therapy. It covers the skills involved in providing a thorough consultation with the client to formulate a specific treatment plan. You
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Personal Training Certificate. Anatomy and Physiology Mock Paper
 Candidate Name Date Personal Training Certificate Anatomy and Physiology Mock Paper Instructions: Make sure your name is in the box at the top, followed by the date you did the test Tick or highlight your
Candidate Name Date Personal Training Certificate Anatomy and Physiology Mock Paper Instructions: Make sure your name is in the box at the top, followed by the date you did the test Tick or highlight your
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit Number- 5470597 -Superclass- -Title- HK BODY TREATMENTS: MANUAL -----------------------------------------
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY HIGHER NATIONAL UNIT SPECIFICATION GENERAL INFORMATION -Unit Number- 5470597 -Superclass- -Title- HK BODY TREATMENTS: MANUAL -----------------------------------------
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals Chapter 1: Human Anatomy
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals Chapter 1: Human Anatomy 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 1 of ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals Chapter 1: Human Anatomy 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 1 of ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness
Lowe w r e r B ody Resistance Training
 Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and
 7.5 Muscles: Designed for Motion How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and o Muscles Muscles that are generally under control (usually ) o Muscles Muscles that not under
7.5 Muscles: Designed for Motion How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and o Muscles Muscles that are generally under control (usually ) o Muscles Muscles that not under
The Muscular System. Myology the study of muscles
 The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
Level 3 Diploma in Personal Training (Practitioner) - Sample Assessment Materials
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 4 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 4 Special Instructions: Level 3 Diploma
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 4 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 4 Special Instructions: Level 3 Diploma
Name Phone ( ) DOB. Address City State Zip. Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( Occupation Male Female Physician
 Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise. Unit Accreditation Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Reference Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy
 Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Assessment Strategy. Level 3 Certificate in Personal Training
 Assessment Strategy Level 3 Certificate in Personal Training 1 Contents page 1.0 Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 2.0 Criteria for using the SkillsActive fitness common units for the Level 3 Personal
Assessment Strategy Level 3 Certificate in Personal Training 1 Contents page 1.0 Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 2.0 Criteria for using the SkillsActive fitness common units for the Level 3 Personal
National Fitness Leadership Alliance
 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base 2015 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base These competencies are intended as
National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base 2015 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base These competencies are intended as
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional
 THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
