Brain and nervous system disorders
|
|
|
- Gervase Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION NEUROLOGY Brain and nervous system disorders 8 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
2 NEUROLOGY SECTION 9 IMPORTANT In treating the heart area (4 th intercostal, left of sternum) NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. 3 A number of treatments in this user guide are complex treatments in which several standalone treatments have been combined to form one course of treatment. If in such cases more than one of the individual treatments calls for the heart area (4 th intercostal, left of sternum) to be treated, ensure that this is done only once. Do NOT use comra therapy on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. Pro NOTES Treatment times given in this user guide were designed for the home user with the Delta or Palm 980 nm laser to give a conservative starting point. Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience.
3 In treating the heart area NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. Do NOT use on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. SECTION NEUROLOGY 8 mins Treatment time. CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION DISORDERS STROKES 4 th intercostal, left of sternum (only once per day) Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Subclavian fossae 3 Supraclavicular fossae 4 Carotid arteries Frontotemporal per point Ultrasound OFF For points Suboccipital fossae 7 Spine (C-7) 8 Base of neck 0 x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest and repeat cycle. Repeat every 3 months until full health has been restored. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 0 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
4 NEUROLOGY SECTION
5 SECTION NEUROLOGY 8 mins Treatment time. Scan both sides of vertebral column, lumbosacral per side 000 ISCHIALGIA pain in the hips. Buttock piriformis on affected side Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. 3 Sub-buttock on affected side 4 Middle back of femur on affected side Popliteal fossa on affected side per point x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest before doing UNIVERSAL 4 (SB-). Thereafter repeat treatment if necessary, allowing for the periods of rest between courses. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
6 NEUROLOGY SECTION 3 3 4
7 The eyes must be closed during this treatment. SECTION NEUROLOGY 3 0 mins Treatment time. A Scan both sides of the face going from front of ears to the bottom of the jaw and up to the temporal area, as shown in the diagram per side 000 NEUROPATHY OF OPHTHALMIC NERVE eye ailments. Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. B Scan both sides of the head including the ear, as shown in the diagram x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest and repeat course if needed. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 4 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
8 NEUROLOGY SECTION A B
9 The eyes must be closed during this treatment. SECTION NEUROLOGY 4 0 mins Treatment time. TRIGEMINAL NERVE NEURALGIA TRIGEMINAL NERVE NEUROPATHY facial pain. Scan both sides of the face as shown in diagram 0 per side 0 Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest and repeat course if needed. 6 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
10 NEUROLOGY SECTION 7
11 SECTION NEUROLOGY 7 mins Treatment time. Place the tip of the Probe on each point shown in the diagram. Treat the points shown on both ears per point 000 DELIRIUM TREMENS withdrawal symptoms. Delta Probe Terminal with Extended Sheath. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. x daily for x days Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle as necessary. 8 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
12 NEUROLOGY SECTION 9
13 SECTION NEUROLOGY 6 8 mins Treatment time. Place the tip of the Probe on each point shown in the diagram. Point behind the ear should be done on both sides per point 000 ALCOHOLISM Delta Probe Terminal with Extended Sheath. Delta Meridian Terminal. Place Meridian Terminal over entire ear. Treat both ears Pro NOTES 3 per ear Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. x daily for x days Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle as necessary. 30 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
14 NEUROLOGY SECTION 3
15 SECTION NEUROLOGY 7 3 mins Treatment time. Place the tip of the Probe on each point shown in the diagram. 000 STUTTERING per point Using the Medical Terminal 0 Delta Probe Terminal with Extended Sheath. Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. 3 Using the Medical Terminal Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest and repeat course until improvement is noticed. Thereafter it is a matter of gaining confidence in not stuttering. 3 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
16 NEUROLOGY SECTION 33 3
17 In treating the heart area NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. Do NOT use on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. SECTION NEUROLOGY 8 6 mins Treatment time. 4 th intercostal, left of sternum (only once per day) EPILEPSY Elbow fossae per point Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. 3 Carotid Arteries per point 4 Suboccipital 0 Ultrasound OFF For point 4. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest and repeat course until condition is cured. Thereafter repeat course once every 6 months. 34 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
18 NEUROLOGY SECTION 3 3 4
19 SECTION NEUROLOGY 9 FIBROMYALGIA hr 3 mins ± Treatment time. PART EARLY MORNING As shown in the diagram per point per frequency then 0 Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. PART EARLY EVENING Apply UNIVERSAL 3 (BLOOD) every nd day x daily for x days Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle until improvement is noticed. Thereafter treat every 3 months if still necessary. PART 3 EVENING AFTER DINNER Apply UNIVERSAL (SB-) every day Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 36 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
20 NEUROLOGY SECTION 37
21 Conditions that display recurring areas of pain should additionally be treated locally, on and surrounding the area of pain at 0 Hz for mins per point. Where there has been muscle wastage, the appropriate muscles should also be treated, based on the treatment program set out in NEUROLOGY 3. SECTION NEUROLOGY 0 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS hr 3 mins ± Treatment time. PART EARLY MORNING & EVENING Apply UNIVERSAL (SB-) twice a day (morning and evening) PART MIDDAY Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. A Apply UNIVERSAL 3 (BLOOD) every nd day (alternating with B) B Apply CARDIOLOGY every nd day (alternating with A) Do continuously (without rest periods) until definite improvement is noticed. Thereafter treat for days, but doing only 3 courses of UNIVERSAL 4 (SB-), and allowing a period of weeks rest between courses. PART 3 EVENING AFTER DINNER Apply UNIVERSAL 4 (SB-) one part done once per day, every evening for 6 days. Having completed all 6 parts start again at the beginning. PART 4 EVENING AFTER DINNER From coccyx to occiput at 0 cm intervals 000 Along both sides of vertebral column through long extensors at 0 cm intervals per point 0 Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 38 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
22 NEUROLOGY SECTION 39
23 This treatment is best done last thing at night before going to sleep so as to ensure a good night s sleep. SECTION NEUROLOGY 3 mins Treatment time. WITTMAACK-EKBOM S SYNDROME (RESTLESS LEGS OR RESTLESS ARMS SYNDROME) LEGS For points -6 do first the one leg and then the other Scan both sides of vertebral column, lumbosacral per side 000 Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. x daily for x days Allow 3 weeks rest before doing UNIVERSAL 4 (SB-). Thereafter repeat treatment if necessary, allowing for the periods of rest between courses. Adrenal glands 3 Buttock piriformis 4 Sub-buttock per point Middle back of femur 6 Popliteal fossa 7 Below the calf muscle ARMS For points -6 do first the one arm and then the other Scan both sides of vertebral column, base of neck per side 000 Long head of triceps 3 Adrenal glands 4 Front of trapezius Pectoralis major per point 6 Anconeal arteries 7 Palmaris longus Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 40 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
24 NEUROLOGY SECTION 4 LEGS ARMS
25 In treating the heart area NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. Do NOT use on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. SECTION NEUROLOGY PARKINSON S DISEASE hr 0 mins ± Treatment time. PART EARLY MORNING A Apply UNIVERSAL 3 (BLOOD) every nd day (alternating with B) B Apply UNIVERSAL (SB-) every nd day (alternating with A) Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. PART * MIDDAY & EVENING AFTER DINNER * x daily for 30 x days Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle. Thereafter treat every 3 months if still necessary. Frontal (both sides) Temple (both sides) 3 Parietal lobes (both sides) 4 Suboccipital (both sides) From coccyx to occiput at 0 cm intervals 6 Along both sides of vertebral column through long extensors at 0 cm intervals per side per point th intercostal, left of sternum (only once per day) 8 Liver, points 0 cm apart 9 Pancreas, points 0 cm apart per point 0 Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 4 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
26 NEUROLOGY SECTION
27 To make the treatment of the muscles somewhat easier some of the muscles have been grouped where possible, so that one point of irradiation serves to irradiate more than one muscle. It is also of vital importance that as from the commencement of PLAN, the patient also undergoes a suitable physiotherapy program in order to rebuild the wasted muscle. SECTION NEUROLOGY 3 44 mins Treatment time. PLAN EARLY MORNING MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Sternocleidomastoid Deltoid Delta Aesthetic Terminal. 3 Pectoralis 4 Biceps x daily Do PLAN every day until definite improvement is noticed. Then allow a period of weeks rest before switching to PLAN. Brachioradialis 6 Flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus 7 Adductor longus and gracilis 8 Rectus femoris per point per frequency 0 then Variable (V) 9 Vastus lateralis 0 Vastus medialis Peroneus longus Continued overleaf comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
28 NEUROLOGY SECTION
29 hr 8 mins Treatment time. PLAN MIDDAY Trapezius Teres major Delta Aesthetic Terminal. 3 Latissimus dorsi/adrenal glands 4 Triceps, 3 points x daily Do PLAN every day until definite improvement is noticed. Then allow a period of weeks rest before switching to PLAN. 6 Flexor 7 Gluteus maximus 8 Adductor magnus 9 Iliotibial per point per frequency 0 then Variable (V) Extensor 0 Semitendinosus and biceps femoris Gastrocnemius Soleus 3 Achilles Continued overleaf comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
30 NEUROLOGY SECTION
31 In treating the heart area NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. Do NOT use on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. hr mins Treatment time. PLAN EARLY EVENING Frontal (both sides) Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Temple (both sides) 3 Parietal lobes (both sides) 4 Suboccipital (both sides) per side 0 Subclavian fossae per point Ultrasound OFF For points Supraclavicular fossae per point 7 4 th intercostal, left of sternum (only once per day) x daily Do PLAN every day until definite improvement is noticed. Then allow a period of weeks rest before switching to PLAN. 8 Liver 9 Spleen and pancreas per point 0 Solar plexus Coccyx to occiput at 0 cm intervals per point points along both sides of vertebral column, opposite scapulae per point per frequency 0 then 0 3 points below scapulae per point 4 Kidneys per point Scan both sides of vertebral column from mid back to lower back per side 000 PLAN LAST THING AT NIGHT Apply UNIVERSAL (SB-) every day Apply UNIVERSAL 3 (BLOOD) every nd day PLAN overleaf comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
32 NEUROLOGY SECTION
33 mins Treatment time. PLAN EARLY MORNING MONDAY, WEDNESDAY, FRIDAY Sternocleidomastoid Deltoid Delta Aesthetic Terminal. x daily for x days Monday, Wednesday and Friday. Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle until full recovery is achieved. 3 Pectoralis 4 Biceps Brachioradialis 6 Flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus 7 Adductor longus and gracilis 8 Rectus femoris 9 Vastus lateralis 0 Vastus medialis per point Variable (V) Peroneus longus Continued overleaf... 0 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
34 NEUROLOGY SECTION
35 34 mins Treatment time. PLAN EARLY MORNING TUESDAY, THURSDAY, SATURDAY Trapezius Teres major Delta Aesthetic Terminal. x daily for x days Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday. Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle until full recovery is achieved. 3 Latissimus dorsi/adrenal glands 4 Triceps, 3 points Extensor 6 Flexor 7 Gluteus maximus 8 Adductor magnus 9 Iliotibial 0 Semitendinosus and biceps femoris per point Variable (V) Gastrocnemius Soleus 3 Achilles Continued overleaf... comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
36 NEUROLOGY SECTION
37 In treating the heart area NEVER use a frequency other than Hz. Do NOT use on patients who have had heart transplants, who have hearts with artificial valves or who have cardiostimulators. hr mins Treatment time. PLAN EARLY EVENING MONDAY TO SATURDAY Frontal (both sides) Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Temple (both sides) per side 0 3 Parietal lobes (both sides) 4 Suboccipital (both sides) Subclavian fossae per point Ultrasound OFF For points Supraclavicular fossae per point 7 4 th intercostal, left of sternum (only once per day) 8 Liver 9 Spleen and pancreas per point 0 x daily for x days Monday to Saturday. Allow weeks rest and repeat cycle until full recovery is achieved. 0 Solar plexus 8 points from coccyx to occiput at 0 cm intervals 3 points along both sides of vertebral column, opposite scapulae per point 000 per point per frequency 3 points below scapulae per point 4 Kidneys per point then 0 Scan both sides of vertebral column from mid back to lower back per side 000 PLAN LAST THING AT NIGHT MONDAY TO SATURDAY A Apply UNIVERSAL (SB-) every nd day (alternating with B) Apply UNIVERSAL 3 (BLOOD) every nd day (alternating with A) Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 4 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
38 NEUROLOGY SECTION
39 The eyes must be closed during this treatment. SECTION NEUROLOGY 4 6 mins Treatment time. GLAUCOMA MACULAR DEGENERATION RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA Directly over each eye, gaze down per eye Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Scan both sides of the face as shown in the diagram per side 3 Occipital lobe (both sides) per side 4 Carotid artery (both sides) per side 0 Ultrasound OFF For point 3. Solar plexus, mid-distance between xiphoid process and umbilicus 6 Adrenal glands 0 per point per frequency then 0 x daily Until significant improvement is noticed. Then allow weeks rest and continue for 4 days. Repeat as necessary. Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 6 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
40 NEUROLOGY SECTION
41 SECTION NEUROLOGY 30 mins Treatment time. Tragus (both sides) Mastoid (both sides) per frequency then 0 TINNITUS Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Delta Probe Terminal with Extended Sheath. Ultrasound OFF For points 4 &. 3 Insert Probe towards tympanal (both sides) 4 Temporal lobes (both sides) Parietal lobes (both sides) 6 Carotid arteries (both sides) 7 Subclavian arteries (both sides) Pro NOTES 3 per ear 000 per side Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 0 x daily for 30 x days Allow weeks rest and repeat course if needed. 8 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
42 NEUROLOGY SECTION
43 SECTION NEUROLOGY 6 6 mins Treatment time. PART EARLY MORNING SPASTIC PARAPARESIS (LOWER) Scan along spine on both sides in the areas C-T and L-S 3 per side 0 Delta Medical Terminal or comra Palm. Lateral sides of knee 3 Area above kneecap 4 Area under kneecap x daily Until definite improvement is noticed. Then allow weeks rest and continue cycle as and when needed. Popliteal 6 Side of ankle 7 Front projection of ankle 8 Rear of ankle per point per side Variable (V) PART AFTERNOON 9 Scan calf and tendon 3 per side 0 0 Scan top of foot Scan bottom of foot per line Variable (V) Pro NOTES Treatments with the professional 90 nm laser are more intense, and therefore these treatment times may be shortened, and also the space between treatments extended further, as determined by feeling and experience. 60 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
44 NEUROLOGY SECTION
Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons
 SECTION 3 TRAUMATOLOGY Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons 58 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] TRAUMATOLOGY SECTION 3 59 IMPORTANT 3 comra therapy is particularly good for fractures, dislocations
SECTION 3 TRAUMATOLOGY Arthritis, muscles, joints and tendons 58 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] TRAUMATOLOGY SECTION 3 59 IMPORTANT 3 comra therapy is particularly good for fractures, dislocations
Thyroid and autoimmune diseases
 SECTION 14 AUTOIMMUNE Thyroid and autoimmune diseases 66 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] AUTOIMMUNE SECTION 14 67 IMPORTANT 1 In treating the heart area (4 th intercostal, left of sternum) NEVER use
SECTION 14 AUTOIMMUNE Thyroid and autoimmune diseases 66 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] AUTOIMMUNE SECTION 14 67 IMPORTANT 1 In treating the heart area (4 th intercostal, left of sternum) NEVER use
OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY SECTION 4. Ear, nose and throat. 104 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]
![OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY SECTION 4. Ear, nose and throat. 104 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY SECTION 4. Ear, nose and throat. 104 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0]](/thumbs/94/120361661.jpg) SECTION 4 OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY Ear, nose and throat 104 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY SECTION 4 105 IMPORTANT 1 2 3 All ear, nose and throat diseases are best treated by also using
SECTION 4 OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY Ear, nose and throat 104 comra user guide [ENGLISH, REV 4.0] OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY SECTION 4 105 IMPORTANT 1 2 3 All ear, nose and throat diseases are best treated by also using
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Lab Exercise 8. BIOPAC Exercise. Muscle Tissue. Muscles. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Figure 11-1: The lever-fulcrum principle is illustrated by flexion of the forearm.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
The Massage Routine. Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position. Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes
 The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
inerve Guide to Nerves 2009
 inerve Guide to Nerves 2009 A guide to self learning and self assessment Context: The following guide is intended to help interpret the sono-anatomy and follow a systematic stepwise approach to the practice
inerve Guide to Nerves 2009 A guide to self learning and self assessment Context: The following guide is intended to help interpret the sono-anatomy and follow a systematic stepwise approach to the practice
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley,
 Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
A-LEVEL PE SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 A-LEVEL PE - 2018 SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Physiological factors affecting performance is one of the units you will study in A Level Physical Education. Physiological factors affecting performance,
A-LEVEL PE - 2018 SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Physiological factors affecting performance is one of the units you will study in A Level Physical Education. Physiological factors affecting performance,
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body
 Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
S.A.F.E. Elements of Technique. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and STRENGTH ALIGNMENT FLEXIBILITY ENDURANCE
 Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
STRETCHING. Benefits of stretching
 STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Part 1: Communication between CNS & PNS
 Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS
 A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Anatomy Module Study Guide
 Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 12 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 381) 1. Surface anatomy is the study of the anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the body. 2. Visualization involves looking
Chapter 12 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 381) 1. Surface anatomy is the study of the anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the body. 2. Visualization involves looking
Electrode Placement. Skin Preparation. Frontalis (FRL) (Specific) Temporalis Anterior (TA) (Specific) Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) (Specific)
 Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
PAB Test Manual. Introduction
 PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST
 ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
BI 199 APWT Discussion 4
 BI 199 APWT Discussion 4 Heck Yeah! Fun again! I. Announcements No class Thursday. Next Monday night Treasure Hunt II in Anatomy Lab! Meet directly outside B63B Klamath again just prior to 8 pm. Q? II.
BI 199 APWT Discussion 4 Heck Yeah! Fun again! I. Announcements No class Thursday. Next Monday night Treasure Hunt II in Anatomy Lab! Meet directly outside B63B Klamath again just prior to 8 pm. Q? II.
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Rat Dissection Lab. Background
 Anatomy & Physiology Corvallis High School Rat Dissection Lab Name: Class Period: Background Dissection of any organism or organ allows a 3-dimensional look at structural connections within the body. It
Anatomy & Physiology Corvallis High School Rat Dissection Lab Name: Class Period: Background Dissection of any organism or organ allows a 3-dimensional look at structural connections within the body. It
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
5 Specification Content
 5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional
 THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
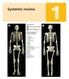 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Skeletal Muscle. Move your bones. Voluntary ( ) Over. Long. Cardiac Muscle. The muscle of the heart. Involuntary ( ) Works. Strongest. Only.
 Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS
 HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy
 Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
The Musculoskeletal system
 Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
2. Be able to define and give examples of each of the following planes:
 Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
