Usefulness of Intracranial CT Angiography with Spiral CT in Brain Death - A Preliminary Report -
|
|
|
- Herbert Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Usefulness of Intracranial CT Angiography with Spiral CT in Brain Death - A Preliminary Report - Jong-Ho Park, M.D., Hong-Ki Song, M.D., Dae-Young Yoon, M.D. Department of Neurology and Radiology*, Hallym University College of Medicine Background : The increasing implementation of organ transplantation requires an unequivocal diagnosis of brain death for moral and legal reasons. Among instrumental investigations, angiographic demonstration of absent intracranial blood flow is considered to be the most reliable test in diagnosing brain death. This test should be easily accessible since most brain dead patients are vitally unstable and have various life-supporting equipments besides their beds. To investigate the usefulness of an intracranial CT angiography (CTA) for the diagnosis of brain death, we performed CTA in comatose patients who were either clinically brain dead or not. Methods : Fourteen comatose patients (11 male and 3 female, aged from 17 to 63 years) with various brain insults were included in this study. Eleven patients were clinically brain dead. Among the remaining three patients, one showed subtle withdrawal movements in one extremity to noxious stimuli with absent brainstem reflexes, and the other two showed multifocal myoclonic seizures. CT scanning was performed with a table speed of 2 mm/sec, twenty seconds after beginning an injection of contrast media. The data were reformatted by maximum intensity projection (MIP) and shaded surface display (SSD) after the reconstruction of a 1 mm interval. A portable electroencephalography (EEG) was also taken serially in clinically brain dead patients except one. Results : Intracranial arterial blood flow was preserved in those who showed either a seizure, abnormal posture or intact brainstem reflexes. On the other hand, intracranial arteries were not visualized in all brain dead patients with electrocerebral silence (ECS) on their EEG with the exception of one patient whose EEG was difficult to determine a ECS due to excessive mechanical artifacts. However, in the clinically brain dead patients, the intracranial arterial flow was preserved in those who suffered from widespread brainstem and cerebellar infarction or whose EEG demonstrated periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges or a burst suppression pattern. Conclusions : Intracranial CTA seems to be a safe and noninvasive procedure for the determination of brain death that produces fast, reliable, and easy-to-interpret results. It can be used as an alternative method to the EEG when the EEG is not possible or difficult to interpret due to artifacts. J Kor Neurol Ass 17(4):554~560, 1999 Key Words : Brain Death, Intracranial CT Angiography Hong-Ki Song, M.D. 554 Copyright 1999 by the Korean Neurological Association
2 Table 1. Clinical and CT angiographic findings in 14 subjects Case Age/Sex Diagnosis Clinical State EEG CT Angiography 1 46/M Cerebral hypoxia BD ECS No CBF 2 38/M Cerebral hypoxia Seizure* Diffuse slowings preserved CBF BD ECS No CBF 3 49/F Cerebral hypoxia BD Burst suppression preserved CBF 4 57/M Basilar artery occlusion BD Many artifacts preserved CBF 5 45/M Cerebral hypoxia Seizure* -- preserved CBF 6 23/M ARDS BD ECS No CBF 7 38/M Lt. BG ICH with IVH BD ECS No CBF 8 35/M Lt. SDH BD ECS No CBF 9 33/M Rt. SDH BD ECS No CBF 10 17/M Lt. SDH BD ECS No CBF 11 19/M Cerebral hypoxia BD Sl Artifacts? No CBF 12 63/F Rt. EDH BD -- No CBF 13 25/M Cerebral hypoxia BD BiPLEDs preserved CBF 14 17/F Lt. SDH, SAH Withdrawal to pain -- preserved CBF BD ; brain dead ECS ; electrocerebral silence CBF ; cerebral blood flow BiPLEDs ; bilateral periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges ARDS ; acute respiratory distress syndrome SDH ; subdural hematoma EDH ; epidural hematoma ICH ; intracerebral hemorrhage IVH ; intraventricular hemorrhage SAH ; subarachroid hemorrhage * ; multifocal myoclonic seizure J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July,
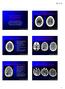
3 Figure 1. Case 1. Cerebral hypoxia due to asthmatic attack Spiral CT with enhancement(left) shows brain parenchymal swelling with gyral effacement. There is no evidence of cerebral arterial flow by MIP and SSD on CTA(right). A Figure 2-A, B. Case 2. Cerebral hypoxia due to epiglottitis (A) Initial CTA shows preserved intracranial arterial flow by MIP and SSD. (B) Seven days later, follow up CTA shows loss of cere - bral arterial flow. B 556 J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July, 1999
4 Figure 3. Case 3. Cerebral hypoxia due to hanging(suicide) Spiral CT with enhancement(left) and CTA by MIP and SSD(right) shows well-enhanced and preserved cerebral arteries, respectively. A Figure 4-A, B. Case 4. Basilar artery occlusion (A) Spiral CT with enhancement shows low intensity over brain stem, cerebellum, and posterior temporal regions. Obliteration of fourth ventricle and sulci markings are also noted. (B) CTA by MIP shows well enhanced and preserved cerebral arterial flow. B J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July,
5 Figure 5. Case 5. Cerebral hypoxia due to bronchospasm Spiral CT with enhancement(left) and CTA by MIP and SSD(right) show well-enhanced and pre - served cerebral arteries, respectively. 558 J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July, 1999
6 Table 2. ( ) (1) ( ) ( ) (2) ( ) (3) ( ) ( ) [ ( )( ( ) ( ) ] (4) [ ( ) 32 o C ] (5). (1) (2) (3) (4) ( ) :. () ( : light reflex) () ( : corneal reflex) () ( : oculo-cephalic reflex) () ( : vestibular-ocular reflex) () ( : cilio-spinal reflex) () ( : gag reflex) () (cough reflex) (5) ( ) (6) % (O 2 ) 95% (O 2 )5% (CO 2 )10 100% (O 2 )6 l /min, 10 ( PaCO 2 )50torr,. (7) : (1) (6) 6 (8) : (7) 30 (9) , (7) 48, 1 (8) (7) 24. J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July,
7 11. Kiyoshi I, Takehide O, Toshibumi K, Genzo S, Motonobu K, and Yasuko S Brain Death: MR and MR Angiography. AJNR 1996;17: ,,. C T C T : 1995 ; 33 ( 2 ): Schwartz RB. Neuroradiological applications of spiral CT. Semin Ultrasound, CT, MR 1992;13: Aoki S, Sasaki Y, Machida T, Ohkubo T, Minami M, Sasaki Y. Cerebral aneurysms : detection and delineation using 3-D CT angiography. AJNR 1992;13: Napel S, Marks MP, Rubin GD, et al. CT angiography with spiral CT and maximum intensity projection. R a d i o l o g y 1992 ; 185 : Schwartz, RB. Tice HM, Hooten SM, Hsu L, Stieg PE. Evaluation of cerebral aneurysms with helical CT : correlation with conventional angiography and MR angiography. Radiology 1994;192: A. Paolin, A. Manuali, F. Di Paola, F. Boccaletto, P. Caputo, R. Zanata, G. P. Bardin, G. Simini. Reliability in diagnosis of brain death. Intensive Care Med ; 2 1 : R. Nau, H. W. Prange, J. Klingelhofer, B. Kukowski, D.. Sander, R. Tchorsch, and K. Rittmeyer. Results of four technical investigations in fifty clinically brain dead patients. Intensive Care Med 1992;18: Holzman BH, Curless RG, Sfakianakis GN, Ajmone- Marsan C, Montes JE. Radionuclide cerebral perfusion in determination of brain death in children. N e u r o l o g y 1985;16: H. Wieler, K. Marohl, K. P. Kaiser, P. Klawski, and H. Frossler. Tc-99m HMPAO Cerebral Scintigraphy. A Reliable, Noninvasive Method for Determination of Brain Death. Clinical Nuclear Medicine 560 J Kor Neurol Ass / Volume 17 / July, 1999
Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No.
 3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
Brain Death: MR and MR Angiography
 Brain Death: MR and MR Angiography Kiyoshi Ishii, Takehide Onuma, Toshibumi Kinoshita, Genzo Shiina, Motonobu Kameyama, and Yasuko Shimosegawa Summary: Four patients in whom brain death was identified
Brain Death: MR and MR Angiography Kiyoshi Ishii, Takehide Onuma, Toshibumi Kinoshita, Genzo Shiina, Motonobu Kameyama, and Yasuko Shimosegawa Summary: Four patients in whom brain death was identified
BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience.
 BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience. Poster No.: C-1170 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Georgiou 1, V. KARTSOUNI 2, G. STAINHAUER 3, N.
BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience. Poster No.: C-1170 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Georgiou 1, V. KARTSOUNI 2, G. STAINHAUER 3, N.
The diagnosis of brain death must comply with the medicolegal
 CINICA REPORT BRAIN CT Perfusion for Confirmation of Brain Death J.J.S. Shankar and R. Vandorpe ABSTRACT SUMMARY: For pronouncing brain death, unlike CTP, the 2-phase CTA gives no functional information
CINICA REPORT BRAIN CT Perfusion for Confirmation of Brain Death J.J.S. Shankar and R. Vandorpe ABSTRACT SUMMARY: For pronouncing brain death, unlike CTP, the 2-phase CTA gives no functional information
뇌사의진단과진단을위한보조적검사 서울아산병원신경과. The Diagnosis and Ancillary Tests of Brain Death. Kim, Cheon-Sik
 대한임상검사학회지 : 36 권제 1 호, 64-68, 2004 뇌사의진단과진단을위한보조적검사 김천식 The Diagnosis and Ancillary Tests of Brain Death Kim, Cheon-Sik Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Asan Medical Center Brain death is defined
대한임상검사학회지 : 36 권제 1 호, 64-68, 2004 뇌사의진단과진단을위한보조적검사 김천식 The Diagnosis and Ancillary Tests of Brain Death Kim, Cheon-Sik Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Asan Medical Center Brain death is defined
Computed Tomogram Angiography, CTA
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 201-213 201 74 26 [1] 4.8% 2.6% 42.2% Sahs [2] 48 20% 40% 67% 2% 5% [3] 20% [4] 10% 15% 41% 48% [5] [6] 95 710 901 Computed Tomogram Angiography, 202 Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 201-213 201 74 26 [1] 4.8% 2.6% 42.2% Sahs [2] 48 20% 40% 67% 2% 5% [3] 20% [4] 10% 15% 41% 48% [5] [6] 95 710 901 Computed Tomogram Angiography, 202 Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Ancillary Testing in Death
 Ancillary Testing in Death MICHAËL CHASSÉ, MD, PHD, FRCPC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY AND CRITICAL CARE, UNIVERSITÉ LAVAL INTENSIVIST, DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY, DIVISION OF CRITICAL
Ancillary Testing in Death MICHAËL CHASSÉ, MD, PHD, FRCPC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY AND CRITICAL CARE, UNIVERSITÉ LAVAL INTENSIVIST, DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY, DIVISION OF CRITICAL
The Determination of Brain Death. James Zisfein, M.D. Chief, Division of Neurology Lincoln Medical Center, Bronx, NY
 The Determination of Brain Death James Zisfein, M.D. Chief, Division of Neurology Lincoln Medical Center, Bronx, NY James.Zisfein@nychhc.org The early history of brain death Until recently, death was determined
The Determination of Brain Death James Zisfein, M.D. Chief, Division of Neurology Lincoln Medical Center, Bronx, NY James.Zisfein@nychhc.org The early history of brain death Until recently, death was determined
Sample Guidelines for the Determination of Death: Including Death by Neurologic Criteria
 Sample Guidelines for the Determination of Death: Including Death by Neurologic Criteria A. SUBJECT: Guidelines for the Determination of Death: Including Death by Neurologic Criteria B. POLICY: The Medical
Sample Guidelines for the Determination of Death: Including Death by Neurologic Criteria A. SUBJECT: Guidelines for the Determination of Death: Including Death by Neurologic Criteria B. POLICY: The Medical
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN
 Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Traumatic Brain Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Emergency Department Stroke Registry Indicator Specifications 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates)
 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
What Are We Going to Do? Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy. Hydrocephalus and Effects of Interruption of CSF Flow. Tube Blockage Doctrine
 Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Dating Neurological Injury
 Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
New Biomedical Devices And Documentation Of Brain Death
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 1 Number 1 New Biomedical Devices And Documentation Of Brain Death G Litscher Citation G Litscher.. The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery. 2000 Volume
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 1 Number 1 New Biomedical Devices And Documentation Of Brain Death G Litscher Citation G Litscher.. The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery. 2000 Volume
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
Acute stroke imaging
 Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey. Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center
 Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center Past, present and future Past, present and future Cerebral Blood Flow Past, present and future
Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center Past, present and future Past, present and future Cerebral Blood Flow Past, present and future
Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17)
 Bilaga 4 Tabeller, beskrivning av studier Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17) Bilddiagnostik vid misstanke om total hjärninfarkt en systematisk litteraturöversikt, rapport 282 (2018) SBU Statens beredning för
Bilaga 4 Tabeller, beskrivning av studier Bilaga 4 till rapport 1 (17) Bilddiagnostik vid misstanke om total hjärninfarkt en systematisk litteraturöversikt, rapport 282 (2018) SBU Statens beredning för
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Scope. EEG patterns in Encephalopathy. Diffuse encephalopathy. EEG in adult patients with. EEG in diffuse encephalopathy
 Scope EEG patterns in Encephalopathy Dr.Pasiri Sithinamsuwan Division of Neurology Department of Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital Diffuse encephalopathy EEG in specific encephalopathies Encephalitides
Scope EEG patterns in Encephalopathy Dr.Pasiri Sithinamsuwan Division of Neurology Department of Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital Diffuse encephalopathy EEG in specific encephalopathies Encephalitides
Policy No: Title: Determination of Death by Brain Criteria Department: PATIENT CARE. Originated: May 1992
 Title: Determination of Death by Brain Criteria Department: PATIENT CARE Policy No: Page 1 of 6 Revised: April 2009 Previous revisions: 9/96, 7/99, 7/07 Reviewed: August 2010 Originated: May 1992 I. POLICY:
Title: Determination of Death by Brain Criteria Department: PATIENT CARE Policy No: Page 1 of 6 Revised: April 2009 Previous revisions: 9/96, 7/99, 7/07 Reviewed: August 2010 Originated: May 1992 I. POLICY:
Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
Non epileptiform abnormality J U LY 2 7,
 Non epileptiform abnormality S U D A J I R A S A K U L D E J, M D. C H U L A L O N G KO R N C O M P R E H E N S I V E E P I L E P S Y C E N T E R J U LY 2 7, 2 0 1 6 Outline Slow pattern Focal slowing
Non epileptiform abnormality S U D A J I R A S A K U L D E J, M D. C H U L A L O N G KO R N C O M P R E H E N S I V E E P I L E P S Y C E N T E R J U LY 2 7, 2 0 1 6 Outline Slow pattern Focal slowing
11/1/2018. Disclosure. Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium. Is NCCT good enough? Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options
 Disclosure Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options Kevin Abrams, M.D. Chief of Radiology Medical Director of Neuroradiology Baptist Hospital, Miami,
Disclosure Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke 2018 Neuro Symposium Keystone Heart Consultant, Stock Options Kevin Abrams, M.D. Chief of Radiology Medical Director of Neuroradiology Baptist Hospital, Miami,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Neurological Determination of Death Adult
 Approved by: Vice President and Chief Medical Officer Neurological Determination of Death Adult Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: VII-B-400 Date Approved June 9, 2015 Next Review (3 years from
Approved by: Vice President and Chief Medical Officer Neurological Determination of Death Adult Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: VII-B-400 Date Approved June 9, 2015 Next Review (3 years from
Chronic Brain-Dead Patients Who Exhibit Lazarus Sign
 CASE REPORT Korean J Neurotrauma 2017;13(2):153-157 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.153 Chronic Brain-Dead Patients Who Exhibit Lazarus Sign Department of Neurosurgery,
CASE REPORT Korean J Neurotrauma 2017;13(2):153-157 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.153 Chronic Brain-Dead Patients Who Exhibit Lazarus Sign Department of Neurosurgery,
Stroke Update. Lacunar 19% Thromboembolic 6% SAH 13% ICH 13% Unknown 32% Hemorrhagic 26% Ischemic 71% Other 3% Cardioembolic 14%
 Stroke Update Michel Torbey, MD, MPH, FAHA, FNCS Medical Director, Neurovascular Stroke Center Professor Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Objectives
Stroke Update Michel Torbey, MD, MPH, FAHA, FNCS Medical Director, Neurovascular Stroke Center Professor Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Objectives
DETERMINATION OF NEUROLOGIC DEATH IN ADULTS AND CHILDREN April 2010
 Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1 of 7 DETERMINATION OF NEUROLOGIC DEATH IN ADULTS AND CHILDREN April 2010 Key Content Expert: Medical Center Ethics Committee in consultation with Chiefs of Service for Neurology
Chicago, Illinois PAGE: 1 of 7 DETERMINATION OF NEUROLOGIC DEATH IN ADULTS AND CHILDREN April 2010 Key Content Expert: Medical Center Ethics Committee in consultation with Chiefs of Service for Neurology
Paul Gigante HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. Sept Mr. T s T s Headache. Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Sept 2005 Mr. T s T s Headache Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Mr. T s T s Presentation 45 year-old welder complains of sudden severe headache and witnessed seizure with loss of consciousness
Sept 2005 Mr. T s T s Headache Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Mr. T s T s Presentation 45 year-old welder complains of sudden severe headache and witnessed seizure with loss of consciousness
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Rerupture of intracranial aneurysms: a clinicoanatomic study
 J Neurosurg 67:29-33, 1987 Rerupture of intracranial aneurysms: a clinicoanatomic study ALBERT HIJDRA, M.D., MARINUS VERMEULEN, M.D., JAN VAN GIJN, M.D., AND HANS VAN CREVEL, M.D. Departments ~[ Neurology.
J Neurosurg 67:29-33, 1987 Rerupture of intracranial aneurysms: a clinicoanatomic study ALBERT HIJDRA, M.D., MARINUS VERMEULEN, M.D., JAN VAN GIJN, M.D., AND HANS VAN CREVEL, M.D. Departments ~[ Neurology.
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
YALE-NEW HAVEN HOSPITAL CLINICAL ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 YALE-NEW HAVEN HOSPITAL CLINICAL ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL Administrative Policy Title: Brain Death, Guidelines Determination of Death by Neurological Criteria in the Pediatric Patient Manual
YALE-NEW HAVEN HOSPITAL CLINICAL ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL Administrative Policy Title: Brain Death, Guidelines Determination of Death by Neurological Criteria in the Pediatric Patient Manual
Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling
 J Neurosurg 86:893 897, 1997 Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling Report of 11 cases ROHIT K. KHANNA, M.D., CHRISTOPHER J. PHAM, D.O., GHAUS M. MALIK,
J Neurosurg 86:893 897, 1997 Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling Report of 11 cases ROHIT K. KHANNA, M.D., CHRISTOPHER J. PHAM, D.O., GHAUS M. MALIK,
Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania POLICY MANUAL
 Page 1 of 8 KEY WORDS: Brain Death Coma # 1-6-11 Procedures Following Patient Death # 1-6-13 Organ Donation and Anatomical Donation and Pennsylvania s Anatomical Gift Act #1-6-17 Withholding and Withdrawing
Page 1 of 8 KEY WORDS: Brain Death Coma # 1-6-11 Procedures Following Patient Death # 1-6-13 Organ Donation and Anatomical Donation and Pennsylvania s Anatomical Gift Act #1-6-17 Withholding and Withdrawing
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System
 NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
8/29/2011. Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000. Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000
 Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography
 Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Retraction Retracted: Clinical Brain Death with False Positive Radionuclide Cerebral Perfusion Scans
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Volume 2016, Article ID 2057806, 1 page http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2057806 Retraction Retracted: Clinical Brain Death with False Positive Radionuclide Cerebral Perfusion
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Volume 2016, Article ID 2057806, 1 page http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2057806 Retraction Retracted: Clinical Brain Death with False Positive Radionuclide Cerebral Perfusion
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Neurological Prognosis after Cardiac Arrest Guideline
 Neurological Prognosis after Cardiac Arrest Guideline I. Associated Guidelines and Appendices 1. Therapeutic Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest 2. Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Algorithm II. Rationale
Neurological Prognosis after Cardiac Arrest Guideline I. Associated Guidelines and Appendices 1. Therapeutic Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest 2. Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Algorithm II. Rationale
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING
 ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Subhairline EEG Part II - Encephalopathy
 Subhairline EEG Part II - Encephalopathy Teneille Gofton September 2013 Objectives To review the subhairline EEG changes seen with encephalopathy To discuss specific EEG findings in encephalopathy To outline
Subhairline EEG Part II - Encephalopathy Teneille Gofton September 2013 Objectives To review the subhairline EEG changes seen with encephalopathy To discuss specific EEG findings in encephalopathy To outline
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Single Seizure of Unknown Cause
 S1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Seizures of Unknown Cause 1. Seizure or Epilepsy of Unknown Cause are the classifications used in these medical standards for a probable seizure(s),
S1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Seizures of Unknown Cause 1. Seizure or Epilepsy of Unknown Cause are the classifications used in these medical standards for a probable seizure(s),
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Severe traumatic brain injury. Fellowship Training Intensive Care Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre
 Severe traumatic brain injury Fellowship Training Intensive Care Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Primary focus of care Prevent ischemia, hypoxia and hypoglycemia Nutrient & oxygen supply Limited
Severe traumatic brain injury Fellowship Training Intensive Care Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Primary focus of care Prevent ischemia, hypoxia and hypoglycemia Nutrient & oxygen supply Limited
Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery
 Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery 2 Stroke Stroke kills almost 130,000 Americans each year. - Third cause of all deaths in Arkansas. - Death Rate is highest in
Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery 2 Stroke Stroke kills almost 130,000 Americans each year. - Third cause of all deaths in Arkansas. - Death Rate is highest in
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Coll Radiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke
 Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 57-62 Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 57-62 Evaluation of Craniocerebral Trauma Using Computed Tomography
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Brain Death Determination: Outline. Definition. Brain Death Determination. Brain Death Determination. No conflict of interest
 No conflict of interest : Outline Definition Definition Confounding factors Clinical examination Apnea test Confirmatory testing Communicating the diagnosis Ethical issues Brain death remains the preferred
No conflict of interest : Outline Definition Definition Confounding factors Clinical examination Apnea test Confirmatory testing Communicating the diagnosis Ethical issues Brain death remains the preferred
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash. Coding Documentation and Education Managers
 Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash Coding Documentation and Education Managers OBJECTIVES Review the basics of Diagnostic, CT, & MRI documentation Risk areas in radiology associated with Diagnostic, CT, &
Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash Coding Documentation and Education Managers OBJECTIVES Review the basics of Diagnostic, CT, & MRI documentation Risk areas in radiology associated with Diagnostic, CT, &
Determination of Death by Brain Death Criteria in Adults Page 1 of 10. All attending physicians certified to determine brain death.
 Page 1 of 10 Scope: All attending physicians certified to determine brain death. Statutory Background Uniform Determination of Death Act (Adopted in various forms in most states including Connecticut)
Page 1 of 10 Scope: All attending physicians certified to determine brain death. Statutory Background Uniform Determination of Death Act (Adopted in various forms in most states including Connecticut)
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury
 Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES
 ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES ENCEPHALOPATHY Encephalopathy is a general term that means brain disease, damage, or malfunction. The major symptom of encephalopathy is an altered
ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES ENCEPHALOPATHY Encephalopathy is a general term that means brain disease, damage, or malfunction. The major symptom of encephalopathy is an altered
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion. Updated: March 2011
 On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma.
 Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Determination of Death
 Policy Legal Standard UTMB physicians will determine death in accordance with this policy which is based on Texas law and the practice parameters recommended by the American Academy of Neurology for adults
Policy Legal Standard UTMB physicians will determine death in accordance with this policy which is based on Texas law and the practice parameters recommended by the American Academy of Neurology for adults
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012
 Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging. Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
 Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology Title of First Slide of Substance An Illustrative Case 2 Disclosures No financial disclosures Off-label uses of some
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging Ronald L. Wolf, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Radiology Title of First Slide of Substance An Illustrative Case 2 Disclosures No financial disclosures Off-label uses of some
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
 Demographic Data Group Study Cohort Control p N 60 20 Age, Mean (years) 36.3 64.4 < 0.001 Age, Median (years) 33.2 64 < 0.001 Male 41 (68.4%) 4 (20%) 0.001 Female 19 (31.6%) 16 (80%) 0.001 Mechanism of
Demographic Data Group Study Cohort Control p N 60 20 Age, Mean (years) 36.3 64.4 < 0.001 Age, Median (years) 33.2 64 < 0.001 Male 41 (68.4%) 4 (20%) 0.001 Female 19 (31.6%) 16 (80%) 0.001 Mechanism of
Comparison of outcome of etiological factors for non-traumatic coma in geriatric population in India
 Original article: Comparison of outcome of etiological factors for non-traumatic coma in geriatric population in India 1 DrAmit Suresh Bhate, 2 DrSatishNirhale, 3 DrPrajwalRao, 4 DrShubangi A Kanitkar
Original article: Comparison of outcome of etiological factors for non-traumatic coma in geriatric population in India 1 DrAmit Suresh Bhate, 2 DrSatishNirhale, 3 DrPrajwalRao, 4 DrShubangi A Kanitkar
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Frequency and Predictors of Nonconvulsive Seizures. continuous electroencephalographic
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Frequency and Predictors of Nonconvulsive Seizures During Continuous Electroencephalographic Monitoring in Critically Ill Children Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc; Jan Claassen, MD; Ronald
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Frequency and Predictors of Nonconvulsive Seizures During Continuous Electroencephalographic Monitoring in Critically Ill Children Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc; Jan Claassen, MD; Ronald
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
 INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
ACUTE STROKE TREATMENT IN LARGE NIHSS PATIENTS. Justin Nolte, MD Assistant Profession Marshall University School of Medicine
 ACUTE STROKE TREATMENT IN LARGE NIHSS PATIENTS Justin Nolte, MD Assistant Profession Marshall University School of Medicine History of Presenting Illness 64 yo wf with PMHx of COPD, HTN, HLP who was in
ACUTE STROKE TREATMENT IN LARGE NIHSS PATIENTS Justin Nolte, MD Assistant Profession Marshall University School of Medicine History of Presenting Illness 64 yo wf with PMHx of COPD, HTN, HLP who was in
TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH
 CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
Case 1. Case 5/30/2013. Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies
 Case 1 Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD 32 year old male s/p high speed MVA Difficult extrication Intubated at scene Case BP 75 systolic / palp GCS 3
Case 1 Traumatic Brain Injury : Review, Update, and Controversies Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD 32 year old male s/p high speed MVA Difficult extrication Intubated at scene Case BP 75 systolic / palp GCS 3
Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier
 Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier Abstract - Brain hemorrhage is a bleeding in or around the brain which are caused by head trauma, high blood pressure and intracranial
Automatic Hemorrhage Classification System Based On Svm Classifier Abstract - Brain hemorrhage is a bleeding in or around the brain which are caused by head trauma, high blood pressure and intracranial
SUBJECT: Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL, INC. Passion for excellence. Compassion for people. Effective Date: December 1, 2005 Proposed By: Samuel Picone III, MD, Trauma Medical Director Approval and Dates: Dr. Bunch,
ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL, INC. Passion for excellence. Compassion for people. Effective Date: December 1, 2005 Proposed By: Samuel Picone III, MD, Trauma Medical Director Approval and Dates: Dr. Bunch,
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE -!!
 INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE - Significance raised ICP main cause of death in severe head injury main cause of morbidity in moderate and mild head injury main target and prognostic indicator in the ITU setting
INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE - Significance raised ICP main cause of death in severe head injury main cause of morbidity in moderate and mild head injury main target and prognostic indicator in the ITU setting
acute-onset, severe, recurrent reversible vasoconstriction
 1 RCVS A clinical and radiologic syndrome Characterized by acute-onset, severe, recurrent headache and reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries RCVS accounts for most benign thunderclap headaches"
1 RCVS A clinical and radiologic syndrome Characterized by acute-onset, severe, recurrent headache and reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries RCVS accounts for most benign thunderclap headaches"
