A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Answers. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
|
|
|
- Albert Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Answers Name: Total Marks: Page 1
2 M1.(a) Measure with eyepiece graticule / scale; Calibrate with stage micrometer / scale on slide / object of known size; Repeats and calculate the mean; OR Use a ruler to estimate the field diameter under microscope; How many droplets go across the field; Repeats and calculate mean; Accept references to radius 3 (b) (i) Two mark for correct answer of 4 : 1;; One mark for incorrect answer but working shows that candidate has clearly attempted to compare values of r 2 / 6 2 and 3 2 / 36 and 9; Idea of comparing ratios A ratio of 1 : 4 should gain 1 mark 2 Small droplets have a larger surface area to volume ratio; More surface for lipase (to act), leading to faster digestion of triglycerides; Fatty acids are produced more quickly ph will drop more quickly in curve Y / with bile salts / less fatty acids in curve Z / without bile salts ph drop more slowly; 3 [8] M2.(a) C. Ignore name of organ 1 (b) E. Ignore name of organ 1 (c) 1. Active site (of enzyme) has (specific) shape / tertiary structure / active site complementary to substrate / maltose; Reject active site on substrate. Must have idea of shape Assume it = maltase Accept (specific) 3D active site Reject has same shape 2. (Only) maltose can bind / fit; Accept substrate for maltose 3. To form enzyme substrate complex. Accept E S complex 3 [5] M3. (a) Two marks for correct answer of / 64.3 / 64; (allow 1 mark for (8100 / ) / 37.8) 2 (b) dislve in / add ethanol then mix with water; emulsion / white colour indicates triglycerides present; 2 (c) (i) increase the surface area for abrption; (ignore wrong ref. to name) 1 R = tissue fluid / interstitial fluid / extracellular fluid / intercellular space; S = lymph(atic) vessel / lymph capillary / lacteal; 2 (iii) proteins are synthesised by U; involvement of ribomes; protein ilation / transport (inside RER); vesicle formation; Page 2
3 (iv) exocytosis / description of; because of size / too large to leave by other methods; 2 [11] M4.(a) High sucrose / starch diet leads to increase in lactase activity; 1 (b) Not valid / cannot be certain because overlap in SD between high sucrose and high starch; Study based on rats (not human) may not apply to human; 2 3] M5. (a) (i) Through alveolar epithelium; Through capillary epithelium / endothelium; Accept: Through lining / wall of alveolus and capillary for 1 mark Accept: squamous epithelial cells for epithelium Neutral: alveolar endothelium Neutral: references to diffusion Q Correct use of terminology; 2 (Thicker alveolar wall) no mark Neutral: less diffusion (So) Longer diffusion pathway / slower diffusion; Neutral: references to surface area 1 (b) (i) (In alveolus) Need the idea of air moving and oxygen concentration Brings in air containing a high(er) oxygen concentration; Neutral: reference to carbon dioxide concentration Removes air with a low(er) oxygen concentration; 2 Circulation of blood / moving blood; Neutral: blood Neutral: short diffusion pathway 1 (c) Long time between decrease in mining and increase in cases; Graph shows fluctuations; Correlation does not prove causation / there may be other causes of miner s lung; Improved diagnosis methods; Do not know number of cases / baseline before 1990; Not all cases reported / not all individuals with miner s lung visit a doctor; Accept: correct use of figures from graph for the first marking point: e.g. cases do not increase until after 2000 / / 10 years later. [8] Page 3
4 M6.(a) 1. Other gases / nitrogen / water vapour in atmosphere / A; 2. Only oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas mixtures / C and D; 3. Composition of / gases in A not controlled / composition of gas mixtures / C and D controlled. b) 1. Breathing rate lowest when no carbon dioxide / in (pure) oxygen / B; Idea of lowest must be stated. 2. (Generally) presence of carbon dioxide increases breathing rate / as concentration of carbon dioxide increases breathing rate increases / there is a positive correlation; A general point incorporating all concentrations. 3. Breathing rate increases when (carbon dioxide) higher than 0.1% / concentration in atmosphere / A; This MP requires a specific comparin to 0.1% or the atmospheric concentration. Accept gas mixtures 1 and 2 / C and D for higher carbon dioxide. 4. Breathing rate of grasshopper 3 falls in D / 16% / gas mixture 2 (whereas others increase). Restating data alone is insufficient for any mark point. 3 max c) (i) 54; OR 1. Correct data / column A chosen; A correct answer of 54 gets 2 marks. MP1 and MP2 allow a possible mark for an incorrect calculation or choice of wrong data. 2. Correct calculation of mean from data chosen; Check the three values must be from same column. 1. Small sample / only 3 (grasshoppers) may not be representative (of all grasshoppers / insects); 2. Grasshoppers are not the only insects / species; genetic / behavioural / metabolic differences; 3. (Insects) not all mature / are at different stages of development / different sizes; different metabolic rates; 4. Movement not restricted / not at rest in meadow; (rate of) respiration higher; 5. (Naturally-occurring) carbon dioxide concentration lower in meadow; breathing rate lower; Explanations required, therefore both parts of answer required for credit in each marking point. Accept appropriate converse answers. Accept respiration for metabolism and vice versa. 3 max [10] Page 4
5 M7. (a) Diaphragm (muscle) contracts; Flattens / Increases volume of chest; Reduced pressure allows air to enter; 3 (b) Allows comparin; As organs differ in size / as larger organs will need more blood; 2 (c) 2 marks for / 40.9 / 41 1 mark for / 59.1 / 59 2 (d) (i) Some oxygen still in lungs (which will enter the blood) / removal of carbon dioxide (from blood); 1 More blood available for other organs; Supplying oxygen / glucose / removing carbon dioxide; OR Diaphragm muscles not contracting (as not breathing); Will not require (as much) oxygen / glucose; 2 [10] M8.(a) Fish keep moving / swimming / movement of gill covers too fast to count (at higher temperatures). Accept converse. Reject pernal errors e.g. with counting. Neutral water not clear or difficult to see movement of gill covers. 1 (b) 1. There is only one dependent variable / there are not two dependent variables / water temperature is the independent variable / breathing rate is dependent on water temperature; Accept either approach for 1 mark. For independent accept manipulated. Reject need two continuous variables. 2. Water temperature plus breathing rate are not both properties of fish or water temperature plus breathing rate are not both properties of water. Accept reference to the two variables (instead of water temperature plus breathing rate) 1 max (c) (i) As (water) temperature increases, oxygen (concentration / lubility) falls and ventilation rate increases. MP requires all 3 aspects before credit is possible. The correct context is required for each aspect e.g. do not reward as oxygen concentration falls, water temperature increases or as temperature increases, ventilation rate increases and oxygen concentration falls As concentration / lubility of oxygen falls less oxygen flows over gills / less oxygen enters gills / less oxygen enters fish; For MP1 and MP2 accept converse. Both aspects needed for Page 5 mark.
6 2. (As a result) blood oxygen (concentration) falls / is lower; 3. An increase in ventilation rate increases / maintains the flow of oxygen / carbon dioxide across gills / into (or out of) fish; Accept idea in relation to either gas or gas exchange. 4. Maintains diffusion / concentration gradient(s) (in gills); Gradient(s) relates to either / both gas(es). 5. To maintain oxygen supply to cells / tissues / organs / to maintain respiration. Accept a named example of tissues e.g. muscle. 3 max [6] M9.(a) 1. Trachea and bronchi and bronchioles; 2. Down pressure gradient; 3. Down diffusion gradient; 4. Across alveolar epithelium. Capillary wall neutral 5. Across capillary endothelium / epithelium. 4 max (b) (About) 80.0%. 1 (c) 1. (Group B because) breathe out as quickly as healthy / have similar FEV to group A; 2. So bronchioles not affected; 3. FVC reduced / total volume breathed out reduced. Allow this marking point for group C 3 8] M10.(a) 1. (Carry) oxygen / glucose; Accept: oxygenated blood Ignore references to removing waste products Ignore references to arteries pumping blood 2. (To) heart muscle / tissue / cells / myocytes. Must be supply to heart or cardiac 2 (b) (i) A; H; Accept: A on its own even if outside box Reject if two (or more) letters given 1 Accept: H on its own even if outside box Reject if two (or more) letters given 1 (c) (Aorta) 1. (is) close / directly linked to the heart / ventricle / pressure is higher / is very high; 2. (Aorta has) elastic tissue; Accept elasticity Ignore reference to muscle 3. (Aorta has) stretch / recoil. Q Reject: contracts / relaxes / pumps Accept: for mp 2 and mp 3, converse for small arteries if qualified by little / less 3 [7] Page 6
7 M11. (a) (i) C and D; 1 left ventricle with thicker wall / more muscle / (muscle in) left ventricle contracts more forcefully / beats more strongly; 1 (b) higher in atria / lower in ventricles; atrioventricular valves / valves between atria and ventricles open; (position of valves must be identified. Do not accept an unqualified reference to valves. Assume pronouns refer to atria.) 2 (c) (i) allows blood to pass into ventricles / from atria / that atria can empty; before ventricles contract; 2 ventricle contracts from base / upwards; blood pushed through B and C / arteries / all blood ejected; 2 [8] M12.(a) 1. Many / more capillaries (than arterioles); 2. (Cross-sectional) area of capillaries (much) greater (than of arterioles). Note: maximum of 1 mark for this question 1 max (b) 1. Short pathway / short distance between blood and outside of capillary; Reference to blood and cells required 2. Large surface area (of blood) in contact with walls of capillaries; Idea is per unit volume of blood but candidates need not say this 3. Fast exchange / fast diffusion / fast osmosis. Must relate to increased speed (c) Width / size / diameter of blood cell. Accept named blood cell Reject platelet Accept idea that below a certain diameter friction becomes too great for blood to flow 1 (d) (Fluid) in tissue fluid / (fluid) in lymph. 1 5] M13. One mark for each correct row 3 Page 7
8 (b) 16; 1 (c) 1. Higher affinity / loads more oxygen at low / same / high partial pressure / po 2 ; 2. (Therefore) oxygen moves from mother / to fetus; 2 (d) 1. Low affinity / oxygen disciates; Assume it is adult haemoglobin 1. Accept: converse if fetal haemoglobin is clearly stated 2. (Oxygen) to respiring tissues / muscles / cells; 2. Q: Neutral respirate 2 (e) Enough adult Hb produced / enough oxygen released / idea that curves / affinities / Hb are similar / more red blood cells produced; Neutral: adult Hb is al produced as in the question stem Reject: curves / affinities / Hb are the same 1 [9] M14.(a) / / 17 (beats per minute). 1 (b) 13.6 / / 14; If answer is incorrect, 1 mark for the principle of difference (11) divided by initial heart rate (81). or for 1 mark Ignore + or signs 2 (c) 1. Allows comparin; 2. (Initial / resting) heart rates different (between males and females). 2 (d) 1. Cardiac output = stroke volume heart rate 1. Accept CO = SV HR 2. (So) stroke volume increases / increased size or volume of ventricles. 2. Neutral: more blood leaves heart 2. If the term stroke volume is not used, it must be defined [7] M15.(a) (i) Left ventricle; 1 Thick muscle / thick walls; Accept more muscle / more muscular. Ignore stronger muscle. 1 (b) (i) 85.7 / 86; Accept 85 Ignore additional decimal places. 1 Two marks for correct answer of ; Accept either formula or illustration with figures from table. Page 8
9 One mark for incorrect answer in which candidate provides evidence of multiplying heart rate by stroke volume; 2 (c) 1. Closed open; 2. Open closed; 2 [7] M16.(a) 1. (Overall) outward pressure of 3.2 kpa; 2. Forces small molecules out of capillary. 2 (b) Loss of water / loss of fluid / friction (against capillary lining). 1 (c) 1. High blood pressure = high hydrostatic pressure; 2. Increases outward pressure from (arterial) end of capillary / reduces inward pressure at (venule) end of capillary; 3. (So) more tissue fluid formed / less tissue fluid is reabrbed. Allow lymph system not able to drain tissues fast enough 3 (d) 1. Water has left the capillary; 2. Proteins (in blood) too large to leave capillary; 3. Increasing / giving higher concentration of blood proteins (and thus wp). 3 [9] M17. (a) More red blood cells; More haemoglobin; 2 (b) Given (only) salt lution; (Otherwise) treated the same way; Accept: Placebo in salt lution. Reference to salt lution is essential for first marking point. 2 (c) Allows comparin to be made; Different masses / weights (of volunteers) / different weeks / lengths of treatment; Accept: Both were different for one mark. Neutral: Size for second marking point. 2 (d) (e) To determine (most effective) dose / length of treatment / to find the most cost effective treatment; Investigate long term effect / toxicity / side effects; Do not credit marks for descriptions of the information in the table in terms of dose and length of treatment. 2 More haemoglobin / more red blood cells; (More) oxygen can be abrbed / transported (for) respiration / to respiring tissues / cells; (More) energy released / more ATP for muscle contraction; Delays anaerobic respiration / delays build up of lactate / lactic acid; Reject: Energy produced or made but allow energy made in form of ATP. 4 (f) Large sample / wide range (of individuals tested); Random (sampling); Tested at different times / more than Page 9 once;
10 Mean / average value determined; Idea of establishing a range for the normal concentration / reference to use of standard deviation; (g) Blood thicker / denser / more viscous / more concentrated / heart contraction greater / increases volume of blood; Accept: More blood cells in same volume / space. Neutral: more red blood cells / more blood on its own. Neutral: Heart pumps / beats more / harder. 1 [15] M18.(a) Open / use tap / add water from reservoir; 1 (b) 1. Seal joints / ensure airtight / ensure watertight; Answer must refer to precautions when setting up the apparatus Ignore: references to keeping other factors constant 2. Cut shoot under water; 3. Cut shoot at a slant; 4. Dry off leaves; 5. Insert into apparatus under water; 6. Ensure no air bubbles are present; 7. Shut tap; 8. Note where bubble is at start / move bubble to the start position; (c) 1. Water used for support / turgidity; Accept: water used in (the cell s) hydrolysis or condensation (reactions) for one mark. Allow a named example of these reactions 2. Water used in photosynthesis; 3. Water produced in respiration; 4. Apparatus not sealed / leaks ; (d) As number of leaves are reduced (no mark), Accept: converse arguments 1. Less surface area / fewer stomata; 3. Less evaporation / transpiration; 4. Less cohesion / tension / pulling (force); 3 [8] M19. (a) (i) unrestricted / free / quick / easy water flow / continuous column / maintains transpiration stream; 1 resists tension in water (column) / provides support / strength / maintains column of water / adhesion / prevents water loss Page 10
11 (allow waterproofing in correct context i.e. not abrbing); 1 (b) (i) as total area of stomata decreases the rate of water flow decreases / decrease is proportional; (reject proportional, as one goes up the other goes up and same shape ) 1 increasing / higher temperature causes increasing / higher rate of evaporation / transpiration; (not water loss) 1 (iii) lower plateau (start and finish at same point); (allow if curve sketched on original graph, reject curve is lower ) 1 (c) M20.(a) (b) conserves water / reduces water loss / reduces transpiration / reduces evaporation; high humidity (in pit) / reduced water potential gradient / less water blown away / increased diffusion pathway; 2 [7] (Scientists) used fully grown leaves / used five plants of each (species). Ignore other references to methodology. Reward only information provided in the Reurce. Do not accept reference to number of leaves different plants were used. 1 Either 1. Draw around leaf on graph paper; Mark as a trio MP1, MP2 and MP3 OR MP4, MP5 and MP6. Do not mix and match. Both aspects needed for mark drawing and type of paper. 2. Count squares (however described); There is no reward for additional detail e.g. dealing with part squares. 3. Multiply by 2 (for upper and lower leaf surface); OR 4. Draw around a leaf on paper of known mass (per unit area); Both aspects needed for mark drawing and mass of paper. 5. Cut out and weigh; 6. Multiply by 2 (for upper and lower leaf surface). 3 (c) (i) Species B (no mark) 1. Smaller surface area less evaporation / less heat abrbed; Correctly selected feature and the explanation required for 1 mark. In all marking points less water loss is insufficient as an explanation but accept transpiration for evaporation or diffusion. 2. Thicker leaves greater diffusion distance (for water); Accept thicker leaves more water storage. Page 11
12 3. Fewer stomata / lower stomatal density less diffusion / evaporation (of water); 4. Smaller surface area to volume ratio less evaporation. 1 max 1. Thick(er) cuticle increase in diffusion distance / slower (rate of) diffusion; Feature and explanation needed for each mark. Reject other features not related to leaves. Reject features related to water storage. Cuticle alone is insufficient (all leaves have a cuticle). Reject suggestion of less diffusion, for idea of slower diffusion, an idea of rate is required. 2. Hairs on leaves reduction in air movements / increase in humidity / decrease in water potential gradient; 3. Curled leaves reduction in air movements / increase in humidity / decrease in water potential gradient; 4. Sunken stomata reduction in air movements / increase in humidity / decrease in water potential gradient. (d) Small leaves / surface area (total) number of stomata is low. Both aspects needed for mark. 1 [8] M21. (a) (i) 1. Stomata open; Allow converse 2. Transpiration highest around mid-day as middle of day warmer / lighter; 2. Allow Sun is at its hottest 3. (Increased) tension / water potential gradient; Ignore pull, suck 3 (Inside xylem) lower than atmospheric pressure / (water is under) tension; Accept cohesion tension. Ignore vacuum 1 (b) (i) High pressure / smoothes out blood flow / artery wall contains more collagen / muscle / elastic (fibres) / connective tissue; Accept converse for pulmonary vein Incorrect function of artery disqualifies mark 1 1. (Aorta wall) stretches because ventricle / heart contracts / systole / Page 12
13 pressure increases; 1. Allow expand 2. (Aorta wall) recoils because ventricle relaxes / heart relaxes / diastole / pressure falls; 2. Allow spring back Reject any reference to contract / relax in MP1 and 2 3. Maintain smooth flow / pressure; 3 (iii) Aorta 1.2 / largest SD; Allow pulmonary vein provided candidate relates standard deviation to mean 1 (c) Formation 1. High blood / hydrostatic pressure / pressure filtration; 2. Forces water / fluid out; 2. Reject plasma, ignore tissue 3. Large proteins remain in capillary; Return 4. Low water potential in capillary / blood; 5. Due to (plasma) proteins; 6. Water enters capillary / blood; 7. (By) osmosis; 7. Osmosis must be in correct context 8. Correct reference to lymph; 6 max [15] M22.(a) (i) (Both) 1. Are polymers / polysaccharides / are made of monomers / of monosaccharides; 2. Contain glucose / carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; 3. Contain glycosidic bonds; 4. Have 1 4 links; Neutral: references to unbranched, inluble, formed by condensation, flexible and rigid Are made of the monomer glucose = MP 1 and 2 = 2 marks 5. Hydrogen bonding (within structure). Ignore reference to H bonds between cellulose molecules (Starch) 1. Contains α / alpha glucose; Assume it refers to starch Accept: converse arguments only if linked directly to cellulose Accept: forms α glycosidic bonds 2. Helical / coiled / compact / branched / not straight; 3. 1,6 bonds / 1,6 branching; 4. Glucoses / monomers same way up; Page 13
14 5. No H-bonds between molecules; 6. No (micro / macro) fibres / fibrils. (b) (i) 1. No / few organelles / very little cytoplasm / cytoplasm at edge / more room / hollow / large vacuole / large space / thick walls; Accept strong walls for thick walls 2. (So) easier / more flow / (thick / strong walls) resist pressure. Easier flow may be expressed in other ways e.g. lower resistance to flow 2 1. Mitochondria release energy / ATP / site of respiration; Q Reject: produce energy but accept produce energy in form of ATP 2. For active transport / uptake against concentration gradient. Note: no mark is awarded for simply naming an organelle OR: 3. Ribomes / rough endoplasmic reticulum produce(s) proteins; Concept of making proteins needed 4. (Proteins) linked to transport e.g. carrier proteins / enzymes. 2 [8] Page 14
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Gas Exchange, Transport, Circulation and Haemoglobin Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of lipase and a 3% bile salts solution
Carbohydrates. Mark Scheme. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Exam Board 3.1 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates. Page 1.
 Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Module Topic Booklet A Level Biology AQA 3.1 Biological Molecules 3.1. Carbohydrates Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /4 Percentage: /100 Grade
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport
 thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
thebiotutor.com AS Biology Unit 2 Exchange & Transport 1 Exchange of materials Oxygen and Carbon dioxide are obtained passively by simple diffusion Fick s law The rate of diffusion = concentration difference
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1)
 Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
Q1. The diagram shows a molecule of haemoglobin. (a) What is the evidence from the diagram that haemoglobin has a quaternary structure? (1) (i) A gene codes for the α-polypeptide chain. There are 43 bases
BYA6 Physiology and the Environment
 version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA6 Physiology and the Environment Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) C ; E ; A ; B ; 4 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance (b) (i) P wave combined with larger peak before QRS complex ; Note: - look
(i) N ; 1 IGNORE nitrogen
 (a) (i) N ; IGNORE nitrogen (a) (iii) (a) (iiii) polypeptide / protein ; name peptide (bond / link) ; DO NOT CREDIT n or N 2 Mark the first answer. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is
(a) (i) N ; IGNORE nitrogen (a) (iii) (a) (iiii) polypeptide / protein ; name peptide (bond / link) ; DO NOT CREDIT n or N 2 Mark the first answer. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
M1.(a) 1. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.
 M.(a). Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat oily fish; MP and Allow use of numbers.. Little / only
M.(a). Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat fish; Accept converse.. Fewer children / less likely that children with asthma eat oily fish; MP and Allow use of numbers.. Little / only
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Biology/ Human Biology A
 Biology/ Human Biology A Unit BYA1 Copyright 2003 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and
Biology/ Human Biology A Unit BYA1 Copyright 2003 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England and
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
GCE. Unit BYA6. Copyright 2002 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
 Mark scheme June 2002 GCE Biology A / Human Biology Unit BYA6 Copyright 2002 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee
Mark scheme June 2002 GCE Biology A / Human Biology Unit BYA6 Copyright 2002 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee
2.1.1 Biological Molecules
 2.1.1 Biological Molecules Relevant Past Paper Questions Paper Question Specification point(s) tested 2013 January 4 parts c and d p r 2013 January 6 except part c j k m n o 2012 June 1 part ci d e f g
2.1.1 Biological Molecules Relevant Past Paper Questions Paper Question Specification point(s) tested 2013 January 4 parts c and d p r 2013 January 6 except part c j k m n o 2012 June 1 part ci d e f g
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Cell Structure.
 Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
Version 1.0. General Certificate of Education (A-level) June Biology BIOL1. (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease. Final.
 Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
BYA1. BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 1 Molecules, Cells and Systems
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme. F211, AS Biology. May 2013 OCR
 Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
Martin Uckermann Unofficial Mark Scheme F211, AS Biology May 2013 OCR This mark scheme only deduce how the paper could be marked according to previous ones Question I. a.) i.) [2 marks] A nucleus B chloroplast
No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5]
![No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5] No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5]](/thumbs/81/83055588.jpg) 1. (a) Digestion/hydrolysis/breakdown of a disaccharide into monosaccharides; OR (glucose and galactose form lactose) glucose is a monosaccharide; max 1 (i) Dipeptidase / disaccharidase / named disaccharidase;
1. (a) Digestion/hydrolysis/breakdown of a disaccharide into monosaccharides; OR (glucose and galactose form lactose) glucose is a monosaccharide; max 1 (i) Dipeptidase / disaccharidase / named disaccharidase;
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
remove solution / liquid (on outside of worm) allow water variable amounts removed from each worm ignore reference to length of timing 1
 M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
M. (a) (i) variation in masses / more representative / more typical / more reliable / average / mean / reference to anomalies or one worm to light to measure change do not allow more accurate / more precise
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
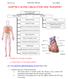 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance two marks for correct answer 1 (a) a single value between 67 and 80 ; ; max 2 If answer incorrect, allow one mark for appropriate working i.e. 60 divided
AS Biology 7401/2 PAPER 2. Mark scheme. June Version: 1.0 Final
 AS Biology 7401/2 PAPER 2 Mark scheme June 2017 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
AS Biology 7401/2 PAPER 2 Mark scheme June 2017 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 1
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
GCE AS and A Level. Biology. AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards. Unit 1: Specimen mark scheme. Version 0.2
 GCE AS and A Level Biology AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 1: Specimen mark scheme Version 0.2 Version 0.2: 0807 abc General Certificate of Education Biology BIOL1 Biology and disease
GCE AS and A Level Biology AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 1: Specimen mark scheme Version 0.2 Version 0.2: 0807 abc General Certificate of Education Biology BIOL1 Biology and disease
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Haemoglobin Revision. May minutes. 85 marks. Page 1 of 32
 Haemoglobin Revision May 103 97 minutes 85 marks Page 1 of 3 Q1. (a) The graph shows a dissociation curve for human haemoglobin at ph 7.4. The position of the curve is different at ph 7.. (i) (ii) Sketch
Haemoglobin Revision May 103 97 minutes 85 marks Page 1 of 3 Q1. (a) The graph shows a dissociation curve for human haemoglobin at ph 7.4. The position of the curve is different at ph 7.. (i) (ii) Sketch
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F211: Cells, Exchange and Transport Mark Scheme for June 2012 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
PMT GCE MARKING SCHEME SUMMER 2016 BIOLOGY - BY1 (LEGACY) 1071/01. WJEC CBAC Ltd.
 GCE MARKING SCHEME SUMMER 016 BIOLOGY - BY1 (LEGACY) 1071/01 INTRODUCTION This marking scheme was used by WJEC for the 016 examination. It was finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences
GCE MARKING SCHEME SUMMER 016 BIOLOGY - BY1 (LEGACY) 1071/01 INTRODUCTION This marking scheme was used by WJEC for the 016 examination. It was finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Q1. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor? (1)
 Q. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor?...... () Scientists investigated the link between pollution from vehicle exhausts and the number of cases of asthma.
Q. (a) Scientists who investigate disease may look at risk factors. What is a risk factor?...... () Scientists investigated the link between pollution from vehicle exhausts and the number of cases of asthma.
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
The cardiovascular and respiratory system
 The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
 3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
abc GCE 2005 January Series Mark Scheme Biology Specification A BYA1 Molecules, Cells and Systems
 version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Biology Specification A BYA1 Molecules, Cells and Systems Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant questions,
version 1.1 GCE 2005 January Series abc Biology Specification A BYA1 Molecules, Cells and Systems Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant questions,
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
SPECIFICATION CONTINUED Glucose has two isomers, α-glucose and β-glucose, with structures:
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Monosaccharides are the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made. Glucose, galactose and fructose are common monosaccharides. A condensation reaction between
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Monosaccharides are the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made. Glucose, galactose and fructose are common monosaccharides. A condensation reaction between
Kingdom Phylum Class Genus. Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta;
 1. (a) BIOLOGY BY2 Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Planta(e)/ plant(s); 4 Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta; (b) (i) A = Fungi; 2 B = Protoctist(a)/ protoctists/
1. (a) BIOLOGY BY2 Kingdom Phylum Class Genus Planta(e)/ plant(s); 4 Annelid(s)/ annelida Vertebrate/ vertebrata/ chordate/ chordata; Insect/ insecta; (b) (i) A = Fungi; 2 B = Protoctist(a)/ protoctists/
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
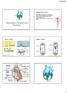 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
2 Organisation higher (import)
 2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
2 Organisation higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 56 minutes Marks: 56 marks Comments: Page of 2 The number of people in the UK with tumours is increasing. (a) (i) Describe how tumours form. () Tumours
Tuesday 21 May 2013 Afternoon
 Tuesday 21 May 2013 Afternoon AS GCE UMAN BIOLOGY F221/01 Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange *F210790613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Tuesday 21 May 2013 Afternoon AS GCE UMAN BIOLOGY F221/01 Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange *F210790613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION
 Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review
 Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
Laura - Bio 212 Exam 4 Review 1. Which of the following is not a factor that affects obesity.. a. Diet b. Leptin genes c. Economics d. Social interactions e. None of these 2. What was the difference in
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1072/01 BIOLOGY BY2 P.M. MONDAY, 2 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded 1. 15 2. 13 3. 10 1072 010001
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Blood Vessels. Over view. We have about 60,000 miles of blood vessels!
 Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016
 LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
LH8 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES SPORT PATHWAYS WITH FOUNDATION YEAR SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY MODULE NO: SRB3008 Date: Monday
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The exchange of substances 3 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba (below), do not need a circulatory
Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The exchange of substances 3 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba (below), do not need a circulatory
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
; Accept: Loads oxygen quicker, more readily, higher saturation, use of figures from graph for first point. Neutral: References to unloading.
 M. (a) High(er) affinity for oxygen / absorbs/loads more oxygen At lower partial pressure (of oxygen) / lower po Accept: Loads oxygen quicker, more readily, higher saturation, use of figures from graph
M. (a) High(er) affinity for oxygen / absorbs/loads more oxygen At lower partial pressure (of oxygen) / lower po Accept: Loads oxygen quicker, more readily, higher saturation, use of figures from graph
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and the Environment
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
TEST. Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F").
 TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
TEST Directions: Circle the letter indicating whether the following statements are either true ("T") or false ("F"). T F 1. A closed glass jar of pickles is a closed system. T F 2. Cellular respiration
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 www.tremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS General ertificate of Education dvanced Subsidiary Level and dvanced Level *2969235372* IOLOGY 9700/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November
www.tremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EMINTIONS General ertificate of Education dvanced Subsidiary Level and dvanced Level *2969235372* IOLOGY 9700/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November
OCR (A) Biology GCSE. Topic 1: Cell Level Systems
 OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
