JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
|
|
|
- Anne McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Module Title Introduction Target Students Duration Module Outcomes Departments DEPARTMENT/ SUBJECTS ANATOMY Spiral One Study Guide GIT & Hepatobiliary-1 Module This module is connected with and builds on the GIT module of semester 4. It provides in depth knowledge of gastrointestinal tract related disorders, their management and prevention where possible. The students will be introduced to the principles underlying diagnoses and therapy. Students will be exposed to the principles of using various investigative images for diagnoses. Students will also learn further about research. Semester IV Second year MBBS 8 weeks At the end of the module, the students will be able to: Explain the normal and abnormal gross and microscopic structures, functions and biochemical processes related to the GIT Provide explanations about common underlying pathologies of GIT Justify selection of medications for common GIT related disorders Perform relevant clinical examinations on simulated patients/ mannequins i. Anatomy ii. Biochemistry iii. Community Medicine iv. Pathology v. Pharmacology vi. Physiology vii. Radiology OBJECTIVES At the end of the week, the students should be able to: ANATOMY Introduction & divisions of GIT + abdominal quadrants: Describe the divisions and parts of digestive tract. Name the abdominal quadrants of GIT. GROSS ANATOMY Esophagus (Abdominal Part), Stomach Explain gross features of abdominal part of esophagus & stomach. Name their peritoneal & visceral relations. Explain their blood supply, lymphatic drainage & nerve supply.
2 HISTOLOGY General plan of G.I.T + Oesophagus List the divisions of digestive tract Describe the general histological features of GIT and especially of esophagus EMBRYOLOGY Development of GIT (derivatives of fore gut) &Congenital Anomalies of GIT (I) Describe the divisions of primitive gut Enumerate the derivatives of foregut Describe the development of foregut Describe the clinical aspect of derivatives of foregut Enumerate the congenital anomalies of GIT Discuss the features of the following congenital anomalies of GIT; i. Cleft lip or cleft palate ii. Hernias iii. Esophageal atresia, esophageal stenosis, congenital hypertorphoic pyloric stenosis, duodenal stenosis, atresia, anomalies of liver, extrahepatic, biliary artesia, annular pancreas, accessory pancreatic tissue, accessory spleen. HISTOLOGY of Stomach Describe the functions of the layers, component and cells in the wall of the digestive tract Explain how they differ in the pharynx, esophagus and stomach. Describe the microscopic features of gastric glands, their constituent cells and secretory product. ANATOMY Peritoneum describe the extent of peritoneum horizontally. explain the attachment of peritoneum on liver. describe the details about the boundaries of lesser sac. GROSS ANATOMY Small Intestine & large intestine Explain different parts of small and large intestine Describe the blood supply and nerve supply of intestine List the structural difference between small and large intestine Discuss the lymphatic drainage of small and large intestine
3 Discuss the Clinical conditions like volvulus & intussusceptions etc. EMBRYOLOGY Development Anatomy of GIT (2) (derivatives of mid and hind gut) :&Congenital Anomalies of GIT (II) List development of GIT(pharynx. esophagus stomach, intestine). Describe the derivatives of midgut and hindgut. Describe the formation of greater, lesser omentum and omental bursae. List the most common congenital anomalies of GIT. Describe the congenital anomalies of gut List the special features associated with common anomalies related to gut including I. Congenital omphalocele, umbilical hernia, gastroschisis, anomalies of midgut, internal hernia, stenosis, atresia of intestine, Mal-rotation of gut, Ileal diverticulum, duplication of intestine, anomalies of hindgut, Hirschsprung disease, imperforate anus, anal stenosis, rectal atresia HISTOLOGY Small intestine Explain the different layers of small intestine Discuss the cells present in the small intestine Describe the different glands present in the small intestine Define and explain Payers patches HISTOLOGY Large intestine Enumerate the different layers of large intestine Describe the cells and glands present in large intestine Explain the difference between small and large intestine GROSS ANATOMY of Liver and Gall bladder Describe liver with its anatomical positions. Identify lobes and surfaces of liver. Identify the segments of liver. Discuss the different components of biliary tract
4 GROSS ANATOMY Hepatic Portal System JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Identify and describe the venous drainage of the organs of GI tract Describe and identify the veins of hepatic portal system Describe and identify the clinical importance of the hepatic portal system and its connections EMBRYOLOGY Development of liver, Gall bladder and Pancreas Describe the Development of liver Discuss the formation of bile & hepatic cells Discuss the Molecular regulation of liver induction Explain the formation of gallbladder & cystic duct Enumerate the anomalies of Liver & gallbladder Discuss the formation of pancreatic bud and islet of Langerhan Discuss Molecular regulation of pancreas development Describe Pancreatic abnormalities HISTOLOGY of Liver and gall bladder Explain the histology of liver Explain the arrangement of liver parenchyma Draw and discuss the general concepts behind classical hepatic lobule, portal lobule and hepatic acinus Describe the microscopic structure of gall bladder GROSS ANATOMY pancreas Discuss the gross features of different parts of pancreas Describe the location, peritoneal relations, and morphological and secretory parts of Pancreas Describe the arterial supply, venous drainage and nerve supply of pancreas Discuss the clinical relevance of pancreas ANATOMY Posterior abdominal wall (boundaries, lumbar vertebrae Muscles, fascia) Enumerate the structures forming posterior abdominal wall Identify the boundaries of posterior abdominal wall
5 Discuss the general characteristics of lumbar vertebrae Describe the muscles and fasciae of posterior abdominal wall Discuss the clinical conditions associated with the posterior abdominal wall GROSS ANATOMY Anal Canal Describe the Ano-rectal junction Describe the Nerve supply and blood supply of anal canal Anal sphincters (External and internal) Describe Ano-rectal fistula, Polyps and diverticulum ANATOMY Abdominal Aorta + blood supply of abdomen Describe the course of abdominal aorta Enumerate the paired and unpaired branches of abdominal aorta Discuss the arteries which supply the abdominal walls. ANATOMY Inferior vena cavae + venous drainage of abdomen Describe the formation of inferior vena cava List the tributaries of inferior vena cava Explain the relations of inferior vena cava Discuss the clinical conditions associated with inferior vena cava ANATOMY: Lymphatic drainage and nerves of abdomen Explain the groups of lymph nodes draining the abdomen. Describe the following: lymphatic trunks, cistern chili, the thoracic duct and nerves supply of abdomen GROSS ANATOMY Surface anatomy of Abdomen Identify and palpate the bony landmarks of the abdomen Discuss the nine abdominal regions and quadrants and list the abdominal organs which are lying in each quadrant Discuss the surface anatomy of stomach and spleen in relation to anterior abdominal wall Discuss the surface anatomy of kidneys, ureters and spleen in relation to posterior abdominal wall. Identify the surface anatomy of liver Discuss the surface anatomy of diaphragm
6 Identify the level of vertebrae with respect to the three major orifices in the diaphragm BIOCHEMISTRY PHYSIOLOGY Discuss the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates Describe the digestion and absorption of proteins Explain the digestion and absorption of lipid Explain the glycolytic pathway of carbohydrates metabolism Discuss the TCA cycle of carbohydrates metabolism Describe the metabolism of glycogen with its disorders Explain the metabolic pathway of gluconeogenesis Describe the metabolic pathway of HMP shunt Describe the metabolic pathway of fructose and galactose Explain the biological oxidation of metabolic pathway Discuss the oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport change Discuss the metabolic role of liver and its detoxification Describe the degradation of hemoglobin and bilirubin metabolism Explain jaundice and its types and causes General principles of Gastrointestinal functions Describe characteristics of gastrointestinal wall Explain functional types of movements in gastrointestinal tract Briefly state the gastrointestinal blood flow Functions of the smooth muscle and their electrical properties List the electrical properties of smooth muscle Explain the mechanism of smooth muscle contraction Differentiate smooth muscle from skeletal muscle Describe genesis of BER and its role in GI motility Nervous and hormonal control of GIT Describe autonomic nervous system Explain Myenteric and Meissner s plexus List hormones of GIT and their role in process of digestion Describe the Gastrointestinal reflexes (gastro-colic, entero-gastric, colono-ileal reflexes) Secretion of saliva (composition, function and regulation) List the salivary glands and their functions Describe stimuli that increase salivary secretion Explain control of salivary secretion
7 Mastication & Deglutition reflex Describe mechanism of mastication Explain different phases of deglutition Explain lower esophageal tone and motility defects in esophagus Motor functions of stomach Describe motor functions of stomach Explain regulation of stomach emptying Gastric secretion (composition, function and regulation) List composition of secretions of gastric glands Describe role of gastric secretions in digestion Describe regulation of gastric secretion Secretions of small and large intestine List secretion of different enzymes in small and large intestines Describe regulation of small and large intestinal secretions Movements of small and large intestine Explain the following functions: Segmentation, Peristalsis, Mass movement and Defecation reflex Describe effects of autonomic system in modulating intestinal motility Pancreatic secretion (composition, function and regulation) Describe composition & secretions of pancreatic juice Explain phases of pancreatic secretion Describe regulation of pancreatic secretion Bile secretion (composition, function and regulation) List composition of bile and factors for its release Explain mechanism of conjugation and secretion of bile salts Describe role of bile acids and emulsification of fats Describe enterohepatic circulation of bile salts Vomiting & Defecation reflexes Explain vomiting reflex & its causes Explain defecation reflex & its regulation
8 COMMUNITY MEDICINE Introduction to Nutrient and Classification Provide Overview of the nutrient concept Classify nutrients Describe effects of nutrient deficiency on Health Explain process of control and prevention of nutrient deficiency Micro & Macro-nutrients with Diseases Classify micro and macronutrients Describe the role of Micronutrient in body metabolism List the disease caused by micronutrient deficiency Explain the process of prevention of micronutrient deficiency Diet, energy value and bioavailability of nutrient Balanced Define balanced diet Explain energy value and bioavailability of nutrient Describe the composition of macronutrient in balanced diet Calculate energy value from macronutrient Assessment of nutritional status- Growth Chart Describe the importance of Growth Chart List the tools for nutritional status Interpret Growth Charts Describe the uses of Growth charts Malnutrition and prevention Define malnutrition Classify malnutrition Explain the process of assessment of malnutrition Discuss the process of control and prevention of Malnutrition Hepatitis transmittable through ingestion and prevention Classify Hepatitis Describe the signs and symptoms of Hepatitis A and E Describe the agent, host and environment of Hepatitis A and E Describe the control and prevention of Hepatitis A and E Hepatitis transmittable through Parental route Describe signs and symptoms of Hepatitis B and C
9 Describe the agent, host and environment of Hepatitis B and C Explain the process of control and prevention of Hepatitis B and C Discuss the Hepatitis control programme in Pakistan Enteric Fever List the signs and symptoms of enteric fever Describe the assessment and diagnosis of enteric fever Explain the process of control and prevention of enteric fever Discuss the role of immunization in prevention of enteric fever Medical Entomology Define Entomology Describe the disease caused by entomology Classify Entomology Pharmacology Substance Abuse and Alcoholism Discuss risks for substance abuse and alcoholism Identify the risks and effects of substance abuse and alcohol Discuss control measures of substance abuse and alcoholism Discuss situation analysis in Pakistan regarding substance abuse and alcoholism Medical Parasitology Classify parasites Describe the medical importance of parasites in disease spread Discuss the process of control and prevention of Parasites Antacids List risk factors of acid peptic disease Classify drugs used to treat acid peptic disease Describe kinetics & dynamics of antacids Anti-secretory drugs: H2 receptor antagonists and mucosal protective agents Classify anti-secretory drugs Describe kinetics & dynamics of H2 receptor antagonists Explain pharmacology of mucosal protective agents sucralfate, colloidal bismuth compounds and prostaglandins Anti-secretory drugs: PPI & Treatment of H. Pylori
10 Enumerate PPIs and Describe their pharmacokinetics & dynamics Discuss treatment regimens for H.Pylori infection. Anti-diarrheal drugs Classify anti-diarrheal drugs Explain their basic & clinical Pharmacology Anti-emetics / Pro-kinetics Classify anti-emetics & Prokinetics. Describe mechanisms of action & clinical uses of these drugs Laxatives / Purgatives Distinguish between laxatives & purgatives based on their classification. Explain kinetics & dynamics of these drugs.
11 Developmental anomalies of GI JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Describe the congenital anomalies of GI including Atresia, fistulae, Diaphragmatic Hernia, Omphalocele and Gastroschisis. Describe Ectopia, Meckel diverticulum, Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, Hirschsprung disease Esophageal obstruction, varices, Achalasia, Esophagitis, Barrett s Esophagus Explain esophageal obstruction, varices and Achalasia. Classify esophagitis according to its types including Chemical and Infectious Esophagitis, Reflux Esophagitis, Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Esophageal Varices Discuss Barrett s esophagus, in relation to its risk factors, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features. Acute and chronic gastritis PATHOLOGY Discuss acute and chronic gastritis, its etiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, morphology and clinical features with special emphasis on H. Pylori gastritis and autoimmune gastritis Peptic ulcer & H.Pylori association Define Peptic ulcer Discuss its pathogenesis and its association with H.Pylori. Malabsorption and Diarrhea, Coeliac disease Define different malabsorption diseases, including cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, Environmental Enteropathy, Autoimmune enteropathy and lactase deficiency Discuss in detail the pathogenesis, risk factors, morphology and clinical features of celiac disease. Discuss different agents of diarrhea Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) & Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Define inflammatory bowel disease. Discuss its two types Ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease with relation to risk factors, pathogenesis, morphology, clinical features and diagnostic criteria
12 Explain in detail Irritable bowel syndrome Hepatic diseases and jaundice Explain the clinical features and laboratory diagnostics of hepatic diseases. Discuss patterns of hepatic injury, cholestasis, jaundice and portal hypertension Circulatory diseases of Liver Discuss various circulatory disorders of liver Liver failure and cirrhosis Explain liver failure, portal hypertension and cirrhosis. Discuss their clinical features and morphology Acute and chronic hepatitis Discuss acute and chronic hepatitis, their causes, clinical features and lab values Non tumorous conditions of Pancreas Describe non tumorous conditions of Pancreas including congenital anomalies, acute and chronic pancreatitis and non-neoplastic cysts Assessment of GIT RADIOLOGY Identify various parts of normal GIT on Plain X ray Identify common GI anatomical variances on Plain X ray Define Barium & Gastrografin studies
13 Histology Practical: Esophagus + stomach Identify the slides of esophagus and stomach under microscope Discuss the Structure of the gastrointestinal tract, GIT Histological features of layers of GIT Describe the microscopic Features of esophagus Discuss the Histological structure of each layer of esophagus Elaborate the different regions of stomach, grossly and histologically Discuss the various layers of the wall of stomach Discuss the different glands and the various kind of cells present in esophagus and stomach PRACTICALS Histology Practical Large Intestine Identify large intestine under microscope describe the important histological features of large intestine. differentiate between basic histological features of small and large intestines Identify the appendix on the basis of its distinguished features. Identify the histological features of anorectal regions Biochemistry 1. Estimate the following in serum: a. aminotransferase b. bilirubin c. glucose (by Kit method) 2. Interpret the reports of: a. Liver function test b. Serum aminotransferase c. Serum bilirubin d. Serum glucose Pathology
14 1. Histopathological lesions of lesions of oral cavity, salivary glands & esophagus. Describe the microscopic features of the conditions Discuss microscopic appearance of the given conditions 2. Histopathology of various types of gastritis Describe the microscopic features of benign peptic ulcer disease. Discuss microscopic appearance of gastric polyps, adenoma & adeno carcinoma 3. Histopathology of liver diseases Describe the principal histopathological changes typical of acute liver disease/chronic liver disease. Discuss the pathologic changes induced by hepatitis virus A, B, C. Define cirrhosis and describe the most important histological findings in the disease Discuss morphological features of hepatocellular carcinoma 4. Histopathology of intestinal tumors Recognize the various histopathological types of polyps and tumors of intestines Skills Lab i. NG Intubation 5. discuss the indications and contraindications for nasogastric tube insertion 6. demonstrate the correct technique of nasogastric tube insertion on a mannequin 2. Abdominal examination Perform complete abdominal examination on a mannequin Mode of Internal Assessment: Continuous monitoring of attendance and practical assessment in short groups. It will be in the form of BCQs, assignments, stages/sub-stages, projects, quiz or OSPE. Internal assessment carries 20% weightage in summative semester examination. Mode of terminal Examination: MCQs + EMQs and OSPE (observed + un observed).
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
LEARNING RESOURCES. 1. Anatomy: Gross Anatomy of The Liver and Gall Bladder Study from: Essential Moore, 5 th Ed., Pages: DEMO note.
 PROBLEM 1 (Hepatitis) 1. Anatomy: Gross Anatomy of The Liver and Gall Bladder Study from: Essential Moore, 5 th Ed., Pages: 158-166 + DEMO 2. Histology: Histology of The Liver and Gall Bladder Study from:
PROBLEM 1 (Hepatitis) 1. Anatomy: Gross Anatomy of The Liver and Gall Bladder Study from: Essential Moore, 5 th Ed., Pages: 158-166 + DEMO 2. Histology: Histology of The Liver and Gall Bladder Study from:
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
General description: Detailed description:
 18. Course Description: General description: This course focuses on Gastro Intestinal system to understand structures, biochemical aspects, physiological functions, pathological disorders, microbial, parasitic
18. Course Description: General description: This course focuses on Gastro Intestinal system to understand structures, biochemical aspects, physiological functions, pathological disorders, microbial, parasitic
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
ALIMENTARY SYSTEM MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 ALIMENTARY SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Alimentary System Objectives By the end of this system, students should recognize the followings: 1. The histological structure of the three
ALIMENTARY SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide Alimentary System Objectives By the end of this system, students should recognize the followings: 1. The histological structure of the three
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
CLASS 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 16 Tuesday, July 17 Wednesday, July 18 Thursday, July 19 Friday, July 20 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO SDL: Diseases of the Oral
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 16 Tuesday, July 17 Wednesday, July 18 Thursday, July 19 Friday, July 20 1. PATHOLOGY 3. PATHOLOGY 5. PATHOLOGY 7. PATHOLOGY 1. CELL BIOLOGY/PHYSIO SDL: Diseases of the Oral
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE
 GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
2. A digestive organ that is not part of the alimentary canal is the: a. stomach b. liver c. small intestine d. large intestine e.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Spleen indications of splenectomy complications OPSI
 Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Gastro Intestinal Pathology
 Duration: 04 weeks (20 days) Gastro Intestinal 3/SBM-4/01 Alimentation in health Topic/ Concept Objectives Time Dept. 1. recall digestion, absorption and metabolism relating to, carbohydrates, proteins,
Duration: 04 weeks (20 days) Gastro Intestinal 3/SBM-4/01 Alimentation in health Topic/ Concept Objectives Time Dept. 1. recall digestion, absorption and metabolism relating to, carbohydrates, proteins,
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Block 5 VIRGINIA CAMPUS Gastrointestinal and Renal Systems 2018
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
Block 5 VIRGINIA CAMPUS Gastrointestinal and Renal Systems 2018
 WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
WEEK 1 Time/Date Monday, July 23 Tuesday, July 24 Wednesday, July 25 Thursday, July 26 Friday, July 27 1. PATHOLOGY 4. PATHOLOGY Histology of the Mouth and Salivary Glands Histology of the Esophagus, Stomach,
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer
 Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Gastrointestinal System COM MS2 Fall 2017
 9/20/2017 Weeks Date Time Title Faculty Week 1 Monday, 9/25/17 8:00-12:00 pm SELF STUDY Monday, 9/25/17 12:00-1:00 pm LUNCH Gastrointestinal System COM 521 - MS2 Fall 2017 Monday, 9/25/17 1:00-2:00 pm
9/20/2017 Weeks Date Time Title Faculty Week 1 Monday, 9/25/17 8:00-12:00 pm SELF STUDY Monday, 9/25/17 12:00-1:00 pm LUNCH Gastrointestinal System COM 521 - MS2 Fall 2017 Monday, 9/25/17 1:00-2:00 pm
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System
 USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
OESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH CHAIR PERSON : Dr. Othman Al Harbi CO-CHAIR: Prof. Ali Somily
 WEEK 1 GASTROINTESTINAL & NUTRITION BLOCK (GNT 223) (Male Group A) Week (1) Starting: 19/11/2017 to 23/11/2017 OESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 19 November 2017 20 November 2017 8:00-9:00 am 21 November 2017 22
WEEK 1 GASTROINTESTINAL & NUTRITION BLOCK (GNT 223) (Male Group A) Week (1) Starting: 19/11/2017 to 23/11/2017 OESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 19 November 2017 20 November 2017 8:00-9:00 am 21 November 2017 22
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
ANATOMY. Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks)
 ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department 29/12/2015
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
The Digestive System 1
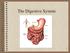 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
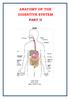 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم
 MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy
 The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System
 Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
