The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter 6. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
|
|
|
- Dwayne Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Skeletal System: Boe Tissue Chapter 6
2 Fuctios of Boe ad Skeletal System Support Protectio Assistace i Movemet Mieral Homeostasis Blood Cell Productio(Hemopoiesis) q Triglyceride Storage q Yellow boe marrow Triglycerides stored i adipose cells q Serves as a potetial chemical eergy reserve
3 Structure of Boe Log Boe Aatomy (Humerus) q Diaphysis q Epiphysis q Metaphysis Epiphyseal growth plate q Articular cartilage Perforatig fibers q Periosteum q Medullary cavity q Edosteum
4
5 Histology of Boe Tissue Extracellular matrix surroudig widely separated cells q Matrix 25% water 25% collage fibers 50% crystallized mieral salts The most abudat mieral salt is calcium phosphate
6 Histology of Boe Tissue A process called calcificatio is iitiated by boe-buildig cells called osteoblasts Mieral salts are deposited ad crystalize i the framework formed by the collage fibers of the extracellular matrix Boe s flexibility depeds o collage fibers
7 Histology of Boe Tissue Four types of cells are preset i boe tissue Osteogeic cells q Udergo cell divisio; the resultig cells develop ito osteoblasts Osteoblasts q Boe-buildig cells q Sythesize extracellular matrix of boe tissue Osteocytes q Mature boe cells q Exchage utriets ad wastes with the blood
8 Histology of Boe Tissue Osteoclasts q Release ezymes that digest the mieral compoets of boe matrix (resorptio) q Regulate blood calcium level
9 Histology of Boe Tissue Boe may be categorized as: q Compact q Spogy
10 Histology of Boe Tissue Compact Boe q Resists the stresses produced by weight ad movemet q Compoets of compact boe are arraged ito repeatig structural uits called osteos or Haversia systems q Osteos cosist of a cetral (Haversia) caal with cocetrically arraged lamellae, lacuae, osteocytes, ad caaliculi
11 Histology of Boe Tissue Osteo q Cetral caals ru logitudially through boe q Aroud the cetral caals are cocetric lamellae Rigs of calcified matrix (like the rigs of a tree truk) q Betwee the lamellae are small spaces called lacuae which cotai osteocytes q Radiatig i all directios from the lacuae are tiy caaliculi filled with extracellular fluid
12 Histology of Boe Tissue Osteo q Caaliculi coect lacuae, formig a system of itercoected caals Providig routes for utriets ad oxyge to reach the osteocytes q The orgaizatio of osteos chages i respose to the physical demads placed o the skeleto
13
14
15 Histology of Boe Tissue Spogy Boe q Lacks osteos q Lamellae are arraged i a lattice of thi colums called trabeculae Spaces betwee the trabeculae make boes lighter Trabeculae of spogy boe support ad protect the red boe marrow Hemopoiesis (blood cell productio) occurs i spogy boe
16 Histology of Boe Tissue Spogy Boe q Withi each trabecula are lacuae that cotai osteocytes q Osteocytes are ourished from the blood circulatig through the trabeculae q Iterior boe tissue is made up primarily of spogy boe q The trabeculae of spogy boe are orieted alog lies of stress helps boes resist stresses without breakig
17 Blood ad Nerve Supply of Boe Boe is richly supplied with blood q Periosteal arteries accompaied by erves supply the periosteum ad compact boe q Epiphyseal veis carry blood away from log boes Nerves accompay the blood vessels that supply boes q The periosteum is rich i sesory erves sesitive to tearig or tesio
18
19 Boe Formatio The process by which boe forms is called ossificatio Boe formatio occurs i four situatios: q 1) Formatio of boe i a embryo q 2) Growth of boes util adulthood q 3) Remodelig of boe q 4) Repair of fractures
20 Boe Formatio Formatio of Boe i a Embryo q Cartilage formatio ad ossificatio occurs durig the sixth week of embryoic developmet
21 Flat boe of skull Blood capillary Ossificatio ceter Mesechymal cell Osteoblast Madible Collage fiber 1 Developmet of ossificatio ceter Osteocyte i lacua Caaliculus Osteoblast Newly calcified boe matrix Mesechyme codeses Blood vessel Spogy boe trabeculae Osteoblast 2 Calcificatio 3 Formatio of trabeculae Periosteum Spogy boe tissue Compact boe tissue 4 Developmet of the periosteum
22 Boe Formatio Formatio of Boe i a Embryo q Boe formatio follows oe of two patters Itramembraous ossificatio q Flat boes of the skull ad madible are formed i this way q Soft spots that help the fetal skull pass through the birth caal later become ossified formig the skull Edochodral ossificatio q The replacemet of cartilage by boe q Most boes of the body are formed i this way icludig log boes
23 Perichodrium Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Distal epiphysis Hyalie cartilage Ucalcified matrix Calcified matrix Nutriet artery Periosteum Primary ossificatio ceter Spogy boe Ucalcified matrix Calcified matrix Periosteum (coverig compact boe) Medullary cavity Nutriet artery ad vei 1 Developmet of cartilage model 2 Growth of 3 Developmet of 4 cartilage model primary ossificatio ceter Developmet of the medullary cavity Secodary ossificatio ceter Epiphyseal artery ad vei Ucalcified matrix Articular cartilage Spogy boe Epiphyseal plate Nutriet artery ad vei 5 Developmet of secodary 6 ossificatio ceter Formatio of articular cartilage ad epiphyseal plate
24 Boe Growth Durig Ifacy, Childhood ad Adolescece Growth i Legth The growth i legth of log boes ivolves two major evets: q 1) Growth of cartilage o the epiphyseal plate q 2) Replacemet of cartilage by boe tissue i the epiphyseal plate
25 Boe Growth Durig Ifacy, Childhood ad Adolescece Osteoclasts dissolve the calcified cartilage, ad osteoblasts ivade the area layig dow boe matrix The activity of the epiphyseal plate is the way boe ca icrease i legth At adulthood, the epiphyseal plates close ad boe replaces all the cartilage leavig a boy structure called the epiphyseal lie
26
27 Boe Growth Durig Ifacy, Childhood ad Adolescece Growth i Thickess q Boes grow i thickess at the outer surface Remodelig of Boe q Boe forms before birth ad cotiually reews itself q The ogoig replacemet of old boe tissue by ew boe tissue q Old boe is cotiually destroyed ad ew boe is formed i its place throughout a idividual s life
28 Boe Growth Durig Ifacy, Childhood ad Adolescece A balace must exist betwee the actios of osteoclasts ad osteoblasts q If too much ew tissue is formed, the boes become abormally thick ad heavy q Excessive loss of calcium weakes the boes, as occurs i osteoporosis q Or they may become too flexible, as i rickets ad osteomalacia
29 Factors Affectig Boe Growth ad Boe Remodelig Normal boe metabolism depeds o several factors Mierals q Large amouts of calcium ad phosphorus ad smaller amouts of magesium, fluoride, ad magaese are required for boe growth ad remodelig Vitamis q Vitami A stimulates activity of osteoblasts q Vitami C is eeded for sythesis of collage q Vitami D helps build boe by icreasig the absorptio of calcium from foods i the gastroitestial tract ito the blood q Vitamis K ad B12 are also eeded for sythesis of boe proteis
30 Factors Affectig Boe Growth ad Boe Remodelig Hormoes q Durig childhood, the hormoes most importat to boe growth are growth factors (IGFs), produced by the liver IGFs stimulate osteoblasts, promote cell divisio at the epiphyseal plate, ad ehace protei sythesis q Thyroid hormoes also promote boe growth by stimulatig osteoblasts q Isuli promotes boe growth by icreasig the sythesis of boe proteis
31 Factors Affectig Boe Growth ad Boe Remodelig Hormoes q Estroge ad testosteroe cause a dramatic effect o boe growth Cause of the sudde growth spurt that occurs durig the teeage year Promote chages i females, such as wideig of the pelvis Shut dow growth at epiphyseal plates q Parathyroid hormoe, calcitriol, ad calcitoi are other hormoes that ca affect boe remodelig
32 Fracture ad Repair of Boe Fracture Types q Ope (compoud) fracture q q q q q q q The broke eds of the boe protrude through the ski Closed (simple) fracture Does ot break the ski Commiuted fracture The boe is splitered, crushed, or broke ito pieces Greestick fracture A partial fracture i which oe side of the boe is broke ad the other side beds Impacted fracture Oe ed of the fractured boe is forcefully drive ito aother Pott s fracture Fracture of the fibula, with ijury of the tibial articulatio Colles fracture A fracture of the radius i which the distal fragmet is displaced Stress fracture A series of microscopic fissures i boe
33 Fracture ad Repair of Boe
34 Fracture ad Repair of Boe Calcium ad phosphorus eeded to stregthe ad harde ew boe after a fracture are deposited oly gradually ad may take several moths The repair of a boe fracture ivolves the followig steps q q q q 1) Formatio of fracture hematoma Blood leaks from the tor eds of blood vessels, a clotted mass of blood forms aroud the site of the fracture 2) Fibrocartilagious callus formatio Fibroblasts ivade the fracture site ad produce collage fibers bridgig the broke eds of the boe 3) Boy callus formatio Osteoblasts begi to produce spogy boe trabeculae joiig portios of the origial boe fragmets 4) Boe remodelig Compact boe replaces spogy boe
35 Fracture ad Repair of Boe
36 Osteo Periosteum Compact boe Spogy boe Fracture hematoma Blood vessel Phagocyte Fracture hematoma Red blood cell Boe fragmet Osteocyte Fibroblast Phagocyte Fibrocartilagious callus Osteoblast Collage fiber Chodroblast Cartilage 1 Formatio of fracture hematoma 2 Fibrocartilagious callus formatio Boy callus Osteoblast Spogy boe New compact boe Osteoclast Osteocyte 3 Boy callus formatio 4 Boe remodelig
37 Boe s Role i Calcium Homeostasis Boe is the body s major calcium reservoir Levels of calcium i the blood are maitaied by cotrollig the rates of calcium resorptio from boe ito blood ad of calcium depositio from blood ito boe q Both erve ad muscle cells deped o calcium ios (Ca 2+ ) to fuctio properly q Blood clottig also requires Ca 2+ q May ezymes require Ca 2+ as a cofactor
38 Boe s Role i Calcium Homeostasis Actios that help elevate blood Ca 2+ level q Parathyroid hormoe (PTH) regulates Ca 2+ exchage betwee blood ad boe tissue PTH icreases the umber ad activity of osteoclasts PTH acts o the kideys to decrease loss of Ca 2+ i the urie PTH stimulates formatio of calcitriol a hormoe that promotes absorptio of calcium from foods i the gastroitestial tract
39 Boe s Role i Calcium Homeostasis
40 Boe s Role i Calcium Homeostasis Actios that work to decrease blood Ca 2+ level q The thyroid glad secretes calcitoi (CT) which ihibits activity of osteoclasts q The result is that CT promotes boe formatio ad decreases blood Ca 2+ level
41 Exercise ad Boe Tissue Boe tissue alters its stregth i respose to chages i mechaical stress q Uder stress, boe tissue becomes stroger through depositio of mieral salts ad productio of collage fibers by osteoblasts q Ustressed boes dimiishes because of the loss of boe mierals ad decreased umbers of collage fibers The mai mechaical stresses o boe are those that result from the pull of skeletal muscles ad the pull of gravity Weight-bearig activities help build ad retai boe mass
42 Agig ad Boe Tissue The level of sex hormoes dimiishes durig middle age, especially i wome after meopause q A decrease i boe mass occurs q Boe resorptio by osteoclasts outpaces boe depositio by osteoblasts Female boes geerally are smaller ad less massive tha males q Loss of boe mass i old age has a greater adverse effect i females
43 Agig ad Boe Tissue There are two pricipal effects of agig o boe tissue: q q 1) Loss of boe mass Results from the loss of calcium from boe matrix The loss of calcium from boes is oe of the symptoms i osteoporosis 2) Brittleess Results from a decreased rate of protei sythesis Collage fibers gives boe its tesile stregth The loss of tesile stregth causes the boes to become very brittle ad susceptible to fracture
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Skeletal System. Bones Protect. Bones. Bones Store. Bones Move SECTION 2: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 4/4/16
 Skeletal System Skeletal system: the orga system whose primary fuctio is to support ad protect the body ad to allow the body to move SECTION 2: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Boes The adult huma skeleto has 206 boes.
Skeletal System Skeletal system: the orga system whose primary fuctio is to support ad protect the body ad to allow the body to move SECTION 2: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Boes The adult huma skeleto has 206 boes.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Chapter 7: The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7: The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleto The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleto Chapter 7 Divisios of the Skeletal System Types of Boes Boe Surface Markigs Skull Hyoid Boe Vertebral Colum Thorax
Chapter 7: The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleto The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleto Chapter 7 Divisios of the Skeletal System Types of Boes Boe Surface Markigs Skull Hyoid Boe Vertebral Colum Thorax
Chapter 25 Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base homeostasis
 Chapter 25 Fluid, electrolyte, ad acid-base homeostasis Body Fluid Compartmets I lea adults, body fluids costitute 55% of female ad 60% of male total body mass Itracellular fluid (ICF) iside cells About
Chapter 25 Fluid, electrolyte, ad acid-base homeostasis Body Fluid Compartmets I lea adults, body fluids costitute 55% of female ad 60% of male total body mass Itracellular fluid (ICF) iside cells About
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
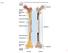 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Ossification = Osteogenesis
 Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
Ossification = Osteogenesis Ossification = Osteogenesis Parts of the fetal skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception By the end of the 8 th week, the skeletal pattern is formed : cartilage
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
The Skeletal S 1Jstem
 . / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
. / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Lecture 9. Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Lecture 9 Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Steroid Hormoes aall steroid hormoes are derived from cholesterol but their structure differ from the cholesterol (rig structure ad side chais) anomeclature: Steroids
Lecture 9 Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Steroid Hormoes aall steroid hormoes are derived from cholesterol but their structure differ from the cholesterol (rig structure ad side chais) anomeclature: Steroids
Basic Requirements. of meeting cow herd production and profitability goals for the beef cattle enterprise.
 Basic Requiremets It is imperative that cattle producers have a adequate uderstadig of the basic utriet requiremets of the cow herd to make iformed ad effective utritio-related decisios. by Matt Hersom,
Basic Requiremets It is imperative that cattle producers have a adequate uderstadig of the basic utriet requiremets of the cow herd to make iformed ad effective utritio-related decisios. by Matt Hersom,
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
LIPIDS. Biomolecules soluble in organic solvents but not water (hydrophobic). Important in: n Cell membranes. n Storage for energy.
 LIPIDS Biomolecules soluble i orgaic solvets but ot water (hydrophobic). Importat i: Cell membraes Storage for eergy Vitamis (Steroid) hormoes Classified ito: i. Simple lipids (oils/fats, wax) ii. Complex
LIPIDS Biomolecules soluble i orgaic solvets but ot water (hydrophobic). Importat i: Cell membraes Storage for eergy Vitamis (Steroid) hormoes Classified ito: i. Simple lipids (oils/fats, wax) ii. Complex
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
LIPIDS. Biomolecules soluble in organic solvents but not water (hydrophobic). Important in: n Cell membranes. n Storage for energy.
 LIPIDS Biomolecules soluble i orgaic solvets but ot water (hydrophobic). Importat i: Cell membraes Storage for eergy Vitamis (Steroid) hormoes Classified ito: i. Simple lipids (oils/fats, wax) ii. Complex
LIPIDS Biomolecules soluble i orgaic solvets but ot water (hydrophobic). Importat i: Cell membraes Storage for eergy Vitamis (Steroid) hormoes Classified ito: i. Simple lipids (oils/fats, wax) ii. Complex
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3.
 Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
Do Now: 1. Where, specifically, is blood created? Which part of the long bone? 2. Which structures are primarily associated with growth? 3. How could damage to these areas impact bone growth? WRITE AND
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Chapter 6. Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
BIOLOGY 11/3/2016. Animal Reproduction. Concept 46.1: Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 46 Aimal Reproductio CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cai Wasserma Miorsky Jackso Lecture Presetatio by Nicole Tubridge ad Kathlee Fitzpatrick Cocept 46.1: Both asexual ad sexual reproductio occur
46 Aimal Reproductio CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cai Wasserma Miorsky Jackso Lecture Presetatio by Nicole Tubridge ad Kathlee Fitzpatrick Cocept 46.1: Both asexual ad sexual reproductio occur
Ch 9 In-class Notes: Cell Reproduction
 Ch 9 I-class Notes: Cell Reproductio All cells grow, duplicate their DNA, ad divide to multiply. This is called the cell cycle. Most Prokaryotic cells divide via biary fissio. Most Eukaryotic cells divide
Ch 9 I-class Notes: Cell Reproductio All cells grow, duplicate their DNA, ad divide to multiply. This is called the cell cycle. Most Prokaryotic cells divide via biary fissio. Most Eukaryotic cells divide
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure
 Connexions module: m47981 1 Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure Donna Browne Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative
Connexions module: m47981 1 Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure Donna Browne Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
