Bone Lengthening for Management of Type 1a Proximal Femoral Deficiency with or without Varus Deformity
|
|
|
- Leslie Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology (ARJOT) Volume 2016, 8 Pages Research Article Keywords: Bone lengthening, proximal, femoral deficiency, deformity. Introduction Open Access Bone Lengthening for Management of Type 1a Proximal Femoral Deficiency with or without Varus Deformity Adel Mohammed Salama, M. D. Assistant professor, orthopedic surgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt yousufmmkh@gmail.com Abstract: Background: The advances in bone lengthening for treatment of moderate congenital femoral deficiency have the advantages of preserving the limb function and decreasing the psychosocial burden on the patients. Patients and Methods: sixteen patients 10 males and 6 females with unilateral Paley Type 1A unilateral proximal femoral deficiency were treated with distraction osteogenesis bone lengthening. The mean follow up period in this prospective study was 36 months (range: months). The Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instruments (PODCI) score was used for clinical and functional outcome of the patients. The calculation of growth inhibition or stimulation in this study was began just after removal of the external fixator until 2 years after its removal. Results: The mean length gained at the end of the procedure was 6.5 cm (SD ±3; range, cm). The mean correction of femoral length discrepancy was 105 % (SD ± 45; range, 85% 165%) with overlengthening of 2-4 cm (average 3cm) in 6 patients (37.5 %). Ten patients (62.5 %) reached the equal femoral length in comparison to the normal femur. According to the PODCI score categories surveyed, the standardized and normative scores were accepted. Conclusion: The surgical technique of femoral lengthening in patients with Paley Type 1A proximal femoral deficiency is a successful and well tolerated technique. Aitken was the first to describe congenital femoral deficiency as a congenital deformities affecting the lower limb with specific attention to the proximal femur [1]. The deformities of the limb associated with the condition vary from very mild cases with normal short femur, severe coxa vara, and pseudoarthrosis of the proximal femur, valgus deformity of the distal femoral, ligaments hypoplasia, muscles hypoplasia, and abnormal vascularity [2 7]. The patients with Paley Type 1a and 1b congenital femoral deficiency were treated by femoral lengthening, while patients with Paley Type 2a treated with knee fusion and prosthetic fitting, Syme amputation, or rotationplasty [8-12]. The advances in bone lengthening for treatment of moderate congenital femoral deficiency have the advantages of preserving the limb function and decreasing the psychosocial burden on the patients [13, 14]. The tension on the soft tissues in bone lengthening surgery affects the adjacent physis which has an effect on bone growth [15, 16]. There is a controversy about the effect of limb lengthening on the growth of bone [12, 17-19]. In the literature, there is no well-established safe surgical technique for femoral lengthening in patients with proximal femoral deficiency. The clinical outcomes, patient function and psychosocial effects on the patients correlated to the lengthy surgical procedure are not well described in literature. The length which can be gained, the range of movements of the hip and knee joints, the effect of lengthening technique on the Page 1
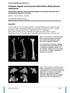
2 femoral growth, and specific complications have not been reported clearly in literatures. A recent study on distraction osteogenesis for femoral lengthening and reported effective lengthening without loss of hip or knee functions in 38 patients with congenital femoral deficiency [20]. Patients and Methods In the period from June 2009 to June 2015, 16 patients 10 males and 6 females with unilateral Paley Type 1A unilateral proximal femoral deficiency were treated with distraction osteogenesis bone lengthening. 14 from 16 patients had coxa vara which treated before lengthening by valgus osteotomy and plate fixation. Uniplanar external fixator was used for lengthening in all cases. The indications for this technique included stable hips and knees, unilateral cases, Paley type 1a, and limb length discrepancy more than 4 cm in comparison to normal leg. Four patients from 20 at the start of the study were excluded due to: one patient did not complete follow up, three patients previous stage of lengthening, so 16 patients completed the study a mean follow up period of 36 months (range: months) in this prospective study. All procedures using the same technique were performed at our institution with recording the postoperative clinical and radiological data. The surgical complications, the Range of Motion (ROM) were documented until last follow up. Surgical technique The surgical technique performed in all patients was distal femoral osteotomy with distraction osteogenesis using unipolar Limb Reconstructive System (LRS) external fixator and a mean distraction rate of 1 mm per day. The osteotomy was done at the distal metaphysis of the femur percutaneously through an anterolateral incision. Multiple drill holes were performed using 3.2 mm drill completed with an osteotome. If the hip subluxation was a risk before lengthening two schanz screws inserted in iliac bone to support the pelvis (Figure 1). Two 2mm crossing k-wires were inserted during application of external fixator in 12 patients and during follow up in 4 patients when noticed displacement in the osteotomy side with adjustment of the fixator (Figure 2). The physical therapy began soon after the operation by 1 hour daily until the ROM reaches an acceptable limits and the parents were taught to complete the therapy protocol at home. When tibiofemoral subluxation observed, the rate of lengthening was slowed or stopped temporarily and rate of physical therapy until regaining ROM or stop the lengthening. Fig1. Male patient 6 years old with left congenital short femur A) preoperative photo showing shortening of left leg; B) preoperative scanogram with 5 cm femoral shortening; C & D) intraoperative radiology; E) knee subluxation during lengthening; F)X-ray7 months postoperative; G& H) photo of the patient with equalized limb length in external fixator; I) x-ray 2 years postoperative showing the femur after lengthening and union. Page 2
3 Fig years old female with congenital short femur left side; A) preoperative x-ray showing left femoral shortening with coxa vara; B) x-ray after correction of coxa vara using plate fixation on valgus osteotomy of proximal femur; C) x-ray after second operation for lengthening with removal of the plate at the same sitting; D) x-ray after readjustment of fixator and insertion of 2 crossing k-wires for alignment. During follow up plain x-rays were taken every 2 weeks during the period of lengthening, then monthly during consolidation. After osteotomy consolidation, the plain x-rays were done every 6 months until the end of follow up. Care of the pins with gentle cleansing, if dry gauze wrapping to prevent motion at the pin-skin interface. Report of complications, obstacles, and surgical interference for these complications during follow up was done. Digital and traditional films for all patients with a magnification marker were done measuring overall limb length discrepancy. The formulae derived by Paley et al [21-25] to predict overall limb length discrepancy, and growth stimulation or inhibition were calculated for the patients included in this study. Serial radiographs at different time periods were used to measure the amount of growth inhibition or stimulation comparing that with the growth in the normal side as a percentage of normal growth. The calculation of growth inhibition or stimulation in this study was began just after removal of the external fixator until 2 years after its removal. The Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instruments (PODCI) score was used for clinical and functional outcome of the patients [13, 26]. Poor outcome/worse (PODCI) score is calculated as 0 and the best possible outcome is 100 points. Multiple scales of the PODCI including the upper extremity, global function, basic mobility, sports and physical functioning. Added to this the pain/comfort and happiness are included. The PODCI scores were recorded at least 2 years after completing the bone lengthening operation. The mean age of the patients at the time of lengthening was 7.5years (range: 5 10 years). In 14 patients the lengthening was months after correction of coxa vara (Figure 3). In 2 patients there was no prior hip surgery before lengthening (Figure 4). The goal of lengthening surgery was the temporary equalization of overall limb length expecting at least 4 cm length gaining or more by normal growth in 12 patients, and overlengthening of about 2 to 3 cm was done in four cases with cooperative child and parents and good tolerance. Page 3
4 Fig3. Male patient 5 years old with right side congenital short femur A) preoperative photo with short femur; B) x-ray after correction of coxa vara; C) x-ray 6 months postoperative with callus formation in the lengthened segment; D)X-ray photo after plate fixation due to fracture after removal of external fixator; E& F) X-ray with fracture femur after removal of the LRS; G) X-ray after plate fixation of fracture femur; H&I) photo of the patient with equalized lower limbs 2 years after plate fixation. Fig4. Male patient 6.5 years old with short right femur: A) preoperative scanogram with 4.5 cm shortening; B) x-ray after osteotomy and fixator; C) scanogram after finishing lengthening with2cm overlengthening; D) x-ray of femur after consolidation. Results The mean duration needed to get the expected lengthening was 203 days (SD ± 47; range, days). The mean length gained at the end of the procedure was 6.5 cm (SD ±3; range, cm). The mean correction of femoral length discrepancy was 105 % (SD ± 45; range, 85% 165%) with overlengthening of 2-4 cm (average 3cm) in 6 patients (37.5 %). Ten patients (62.5 %) reached the equal femoral length in comparison to the normal femur. Page 4
5 At the end of the bone lengthening procedure of the knee flexion ranged from 20 to 85 degrees (average 60 degrees) in a mean duration of 18 weeks. At the end of follow up, the flexion range of knee recovered to near normal range in all patients by a mean of 36 months (range: months). The range of hip flexion decreased to 80 degrees (range, degrees) at the end of the bone lengthening with recovery of normal range by the end of follow up. There was no significant reduction of hip ROM from preoperative to postoperative flexion or extension. The mean loss of knee extension by the end of follow up decreased by 10 degrees (5-15 degrees). In two patients, knee subluxation and antero-posterior displacement of the osteotomy appeared 10 weeks postoperative solved by reduction of the knee and correction of the osteotomy with external fixator adjustment, then continued lengthening and 2 crossing k-wires for alignment (Figure 2). In those patients limited knee ROM of 30 degrees and needed quadriceps plasty after complete union of lengthening site (42 weeks). The gained bone lengthening was greater in female patients than male patients (6.5 cm; range, cm in females and 5cm; range, cm in males), (p =0.023). Clinically According to the PODCI score categories surveyed, the standardized and normative scores were accepted (Table 1). It was noted that in the patients with femoral lengthening greater than 6 cm the global functioning scores were lower than that in the patients with less than 6 cm lengthening (88; SD ± 8 versus 94; SD ± 2 ; p = 0.056). The pain/comfort scores were less in patients needed lengthening of more than 25% of preoperative femoral length (74; SD ± 20 versus 90; SD ± 6; p = 0.032). Table 1. the PODCI score for all patients after completing the lengthening procedure PODCI category Standardized score Normative score Mean ± SD Range Mean ± SD Range Upper extremity 96 ± ± Basic mobility 95 ± ± Sports and physical functioning 85 ± ± Pain / comfort 90 ± ± Happiness 91 ± ± Global functioning 92 ± ± Complications The rate of complications was 50% (8 of 16) (Table 2). Knee subluxation and antero-posterior displacement of the osteotomy treated with correction of the osteotomy with external fixator adjustment, then continued lengthening. Table 2. complications during follow up period Complication Knee subluxation ( readjustment of fixator) 2 Pin tract infection ( conservative treatment) 5 Fracture after removal of fixator (plate fixation) 1 Discussion Number of patients The bone lengthening to correct the femoral length discrepancy is a procedure that may need a variety of surgical techniques and the published literature on heterogeneous groups of patients have mixed results and complications. Page 5
6 In a recent study conducted by Prince DE; et al 2015 they presented objective radiographic and clinical data reporting the patients function after performing lengthening with an external fixator plus intramedullary rodding and reported a mean lengthening of 6 cm and 1.3 months/cm lengthening index. Both hip and knee ROM, were maintained although 50% rate of complications during treatment. Aston et al. in their study achieved mean 6 cm femoral lengthening [13]. They incorporated the use of intramedullary rod fixation surgery and lengthening over the rods. Other authors recommended the rods fixation after lengthening at the time of external fixation removal, they recommended the rodding after removal of fixator to give the chance of using larger intramedullary nail to protect the entire lengthened bone to prevent fracture and deformity through the regeneration [20, 22, and 25]. In this study 16 patients with congenital femoral deficiency were treated with bone lengthening using unilateral external fixator with 2 intramedullary 2mm crossing k-wires at the same time of applying the fixator in a mean follow up of 36 months. The postoperative knee flexion, complication rates, and the amount lengthening obtained were similar to those of published literatures using the same technique [20-25]. Physical therapy is one of the main methods to regain hip and knee function and ROM. In this study the physical therapy was performed in our institute using the same modalities and techniques with the record of results by physical therapists. The serial x-rays were performed in radiology department of our institute using the same magnification markers to record the follow up changes. The reported healing index for every cm is 1.3 months in this study, and these results is comparable with published results of femoral lengthening for patients with congenital femoral deficiency Paley Type 1 [15, 17, and 18]. It is unclear to the authors why female patients have more length gaining than male patients (average 2 cm). It is claimed to be due to neurodevelopmental stage of each gender [20]. In this study, the range of motion (ROM) decreases during lengthening, but normal knee and hip ROM was regained at the end of follow up. These results are similar to Herzenberg et al study in a series of 25 patients who underwent lengthening of average 6 cm on isolated femoral shortening, in those patients knee ROM decreased to a minimum of 37 degrees at the end of lengthening, but increased to 69 degrees at last follow up [16]. Popkov et al. in their study using the Ilizarov technique for lengthening in 86 children (59 femoral and 55 tibial). The mean bone age was 8.5 years at time of lengthening for various congenital conditions. They published a comprehensive report on factors that influence postoperative growth after limb lengthening [18]. The average follow up period in their study was 4.5 years after fixator removal. The mean femoral lengthening was 5cm. Some reports in the literature found that in young patients there is a stimulatory effects [19], while others have found no change in growth rate in older patients [9, 15, 17, 28]. In this study we could not support the hypothesis of stimulation of growth in younger patients which may be due to the small number of cases and the relatively short follow up period. The authors used the PODCI scores reported that to maintain higher function and less pain after lengthening you should avoid excessive lengthening beyond 6 cm or more than 25% lengthening of the femur [20]. The rate of complications after lengthening surgery for congenital femoral shortening in this study are within the range of published reports [16, 29, and 30]. Complications were found in 50% of patients. Oostenbroek et al. reported a complication rate of 69% when the limb length discrepancy is the only predictor for complications after surgery [16]. Conclusion The surgical technique of femoral lengthening in patients with Paley Type 1A proximal femoral deficiency is a successful and well tolerated technique. The good results of the surgical technique of distraction osteogenesis Page 6
7 in younger patients, with 25% of the femur maximum lengthening is the key for preserving the knee and hip ROM. The qualified physical therapist doing and recording the intensive physiotherapy is one factor of gaining good function. The limitations of this study are the small number of the sample and short follow up period References Aitken GT. Proximal femoral focal deficiency definition, classification, and management. In: Aitken GT, ed. Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency. A Congenital Anomaly. Washington, DC, USA: National Academy of Sciences; 1969:1 22. Torode IP, Gillespie R. The classification and treatment of proximal femoral deficiencies. Prosthet Orthot Int. 1991; 15: Koman LA, Meyer LC, Warren FH. Proximal femoral focal deficiency: a50-year experience. Dev Med Child Neurol.1982; 24: Herring JA, Birch JG. Congenital femoral deficiency. In: Herring JA, Birch JG, eds. The Child With a Limb Deficiency. Rosemont, IL, USA: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; 1998: Gillespie R, Torode IP. Classification and management of congenital abnormalities of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983; 65: Amstutz HC, Wilson PD. Dysgenesis of the proximal femur (coxa vara) and its surgical management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962; 44: Ackman J, Altiok H, Flanagan A, Peer M, Graf A, Krzak J, Hassani S, Eastwood D, Harris GF. Long-term follow-up of Van Nes rotationplasty in patients with congenital proximal focal femoral deficiency. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95: Van Nes CP. Methods of treating pseudoarthrosis of the femoral neck, and their indications. Arch Chir Neerl. 1959:11: Westberry DE, Davids JR. Proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD): management options and controversies. Hip Int. 2009; 19 (Suppl 6):S Simpson-White RW, Fernandes JA, Bell MJ. King s procedure for Aitken B/Paley 2a proximal femoral focal deficiency with 19year follow-up a case report. Acta Orthop. 2013; 84: Stephens MM, Hsu LC, Leong JC. Leg length discrepancy after femoral shaft fractures in children. Review after skeletal maturity. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989; 71: Viehweger E, Pouliquen J-C, Kassis B, Glorion C, Langlais J. Bone growth after lengthening of the lower limb in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1998; 7: Aston WJS, Calder PR, Baker D, Hartley J, Hill RA. Lengthening of the congenital short femur using the Ilizarov technique: a single-surgeon series. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91: Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 250: Oostenbroek HJ, Brand R, van Roermund PM. Growth rate after limb deformity correction by the Ilizarov method with or without knee joint distraction. Acta Orthop. 2009; 80: Oostenbroek HJ, Brand R, van Roermund PM. Lower limb deformity due to failed trauma treatment corrected with the Ilizarov technique. Acta Orthop. 2009; 80: Hope PG, Crawfurd EJ, Catterall A. Bone growth following lengthening for congenital shortening of the lower limb. JPediatr Orthop. 1994; 14: Page 7
8 18. Popkov D, Journeau P, Popkov A, Pedeutour B, Haumont T, Lascombes P. Analysis of segmental residual growth after progressive bone lengthening in congenital lower limb deformity. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98: Sabharwal S, Paley D, Bhave A, Herzenberg JE. Growth patterns after lengthening of congenitally short lower limbs in young children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20: Prince DE, Herzenberg JE, Standard SC, and Paley D. Lengthening With External Fixation Is Effective in Congenital Femoral Deficiency. Clin Orthop Relat Res Oct; 473(10): Paley D, Bhave A, Herzenberg JE, Bowen JR. Multiplier method for predicting limb-length discrepancy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82: Paley D, Standard SC. Lengthening reconstruction surgery: for congenital femoral deficiency. In: Rozbruch SR, Ilizarov S, eds. Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press; 2006: Paley D, Tetsworth K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 280: Paley D, Tetsworth K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of multiapical frontal plane angular and bowing deformities of the femur and tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 280: Paley D. Principles of Deformity Correction. 1st ed. New York, NY, USA: Springer; 2003: Haynes RJ, Sullivan E. The Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America Pediatric Orthopaedic Functional Health Questionnaire: an analysis of normals. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001; 21: Herzenberg JE, Scheufele LL, Paley D, Bechtel R, Tepper S. Knee range of motion in isolated femoral lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; 301: McCarthy JJ, Kim H, Saluan P, Karsky D, Davidson RS. The effects of limb lengthening on growth. JP ediatr Orthop B.2003; 12: Nogueira MP, Paley D, Bhave A, Herbert A, Nocente C, Herzenberg JE. Nerve lesions associated with limb-lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85: Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A. Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994; 25: Citation: Adel Mohammed Salama, Bone Lengthening for Management of Type 1a Proximal Femoral Deficiency with or without Varus Deformity. American Research Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology;, 2016; pp:1-8 Copyright 2016 Adel Mohammed Salama, This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Page 8
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity
 Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring Fixator
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
A review of problems, obstacles and sequelae encountered during femoral lengthening : Uniplanar versus circular external fixator
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 628-635 ORIGINAL STUDY A review of problems, obstacles and sequelae encountered during femoral lengthening : Uniplanar versus circular external fixator Levent ERALP, Mehmet
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 628-635 ORIGINAL STUDY A review of problems, obstacles and sequelae encountered during femoral lengthening : Uniplanar versus circular external fixator Levent ERALP, Mehmet
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA
 ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
ANTERIOR MEDIAL AND POSTERIOR MEDIAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA 5 TH ANNUAL SLAOTI MEETING SAO PAOLO, BRAZIL OCTOBER 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research
Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing
 40 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, k. emara, 40-44 m. a. al kersh, a. k. emara ORIGINAL STUDY Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing Khaled Emara, Mohamed
40 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, k. emara, 40-44 m. a. al kersh, a. k. emara ORIGINAL STUDY Long term self esteem assessment after height increase by lengthening and then nailing Khaled Emara, Mohamed
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES
 LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES Jill C Flanagan, MD OBJECTIVES Evaluate the patient with a possible limb length difference (LLD) Understand general treatment principles when managing limb length differences
LIMB LENGTH DISCREPANCIES Jill C Flanagan, MD OBJECTIVES Evaluate the patient with a possible limb length difference (LLD) Understand general treatment principles when managing limb length differences
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Combined external fixation and intramedullary alignment in correction of limb length discrepancies
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 411-416 ORIGINAL STUDY Combined external fixation and intramedullary alignment in correction of limb length discrepancies Bojan Bukva, Radivoj Brdar, Dejan Nikolic, Ivana
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 411-416 ORIGINAL STUDY Combined external fixation and intramedullary alignment in correction of limb length discrepancies Bojan Bukva, Radivoj Brdar, Dejan Nikolic, Ivana
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening
 2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia. Case Report and Review of the Literature
 The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:19 24 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0241-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss Mootaz F. Thakeb 1 Mahmoud A.
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:19 24 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0241-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone transport for the management of severely comminuted fractures without bone loss Mootaz F. Thakeb 1 Mahmoud A.
Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications
 SHORT ARTICLE Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications Abstract Altaf A. Kawoosa, Suhail Majid*, Manzoor A. Halwai, Mohd. Ramzan Mir, G.R. Mir Femoral lengthening using Ilizarov
SHORT ARTICLE Femoral Lengthening by Ilizarov Technique: Results and Complications Abstract Altaf A. Kawoosa, Suhail Majid*, Manzoor A. Halwai, Mohd. Ramzan Mir, G.R. Mir Femoral lengthening using Ilizarov
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease
 Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening
 Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet
 J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
J Child Orthop (2007) 1:151 155 DOI 10.1007/s11832-007-0016-6 TECHNICAL NOTE A technique for calculating limb length inequality and epiphyseodesis timing using the multiplier method and a spreadsheet James
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D.,
 Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Reducing Limping by Tibial Lengthening Along Nails in Adult Unilateral Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip with High Dislocation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reducing Limping by Tibial Lengthening Along Nails in Adult Unilateral Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip with High Dislocation Shier-Chieg Huang, 1 Ting-Ming Wang, 2 Yang-Chen Chou, 1
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reducing Limping by Tibial Lengthening Along Nails in Adult Unilateral Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip with High Dislocation Shier-Chieg Huang, 1 Ting-Ming Wang, 2 Yang-Chen Chou, 1
Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children
 PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
Modified dome shaped proximal tibial osteotomy for treatment of infantile tibia vara
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities
 Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Kocaoglu, Mehmet MD; Eralp, Levent MD; Sen, Cengiz MD; Cakmak, Mehmet MD; Dincyürek, Hakan MD; Göksan, S. Bora MD
 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions?
 Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator.
 Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator. Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 TARGET AUDIENCE... 2 KEY CHANGES FROM PREVIOUS
Guidance for the Physiotherapy Management of Patients Undergoing Limb Reconstruction with a Circular Frame External Fixator. Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 2 TARGET AUDIENCE... 2 KEY CHANGES FROM PREVIOUS
Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail Surgical Technique
 183 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail
183 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail
Valgus osteotomy by external fixation for treatment for developmental coxa vara
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2013) 8:161 167 DOI 10.1007/s11751-013-0178-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Valgus osteotomy by external fixation for treatment for developmental coxa vara Hany Hefny Elhussein Mohamed Elmoatasem
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2013) 8:161 167 DOI 10.1007/s11751-013-0178-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Valgus osteotomy by external fixation for treatment for developmental coxa vara Hany Hefny Elhussein Mohamed Elmoatasem
Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Society AIM Index Reliably Assesses Lower Limb Deformity
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2609-8 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2609-8 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction
Large segmental defects of the tibia caused by highenergy. Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 219-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest Joachim HORN, Leif Pål KRISTIANSEN, Harald STEEN From the Department of Orthopaedics,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 219-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Deformity correction during growth after partial physeal arrest Joachim HORN, Leif Pål KRISTIANSEN, Harald STEEN From the Department of Orthopaedics,
Case Study: David. Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Age Range During Treatment 16 Years
 Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets. Limb deformity
 Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets Limb deformity Limb deformity Why do limbs become deformed? The limbs of dogs and cats, like the legs of people, are meant to be relatively straight.
Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets Limb deformity Limb deformity Why do limbs become deformed? The limbs of dogs and cats, like the legs of people, are meant to be relatively straight.
MANAGEMENT OF FIBULAR HEMIMELIA
 AMPUTATION OR LIMB LENGTHENING DOUGLAS NAUDIE, REGGIE C. HAMDY, FRANCOIS FASSIER, BENOIT MORIN, MORRIS DUHAIME From Shriners Hospital for Crippled Children, Montreal, Canada We reviewed retrospectively
AMPUTATION OR LIMB LENGTHENING DOUGLAS NAUDIE, REGGIE C. HAMDY, FRANCOIS FASSIER, BENOIT MORIN, MORRIS DUHAIME From Shriners Hospital for Crippled Children, Montreal, Canada We reviewed retrospectively
Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 451, pp. 177 181 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Knee Arthritis in Congenital Short Femur after Wagner Lengthening Changhoon Jeong, MD *, ; Muharrem
Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2469-6684.10001 Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw Ram Kewal
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2469-6684.10001 Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw Ram Kewal
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara
 Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Preliminary Outcome Using a New Free Motion Offloading KAFO for Postoperative Management of Hemiepiphysiodesis in Adolescent Tibia Vara Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency
 Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Lengthening and deformity correction about the knee using a magnetic internal lengthening nail
 SICOT J 2017, 3, 25 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2017 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017014 Special Issue: Deformity correction, limb lengthening and reconstruction Guest Editor: Y. ElBatrawy Available
SICOT J 2017, 3, 25 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2017 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017014 Special Issue: Deformity correction, limb lengthening and reconstruction Guest Editor: Y. ElBatrawy Available
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report
 Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Hemiepiphyseal stapling for treatment of genu valgum: A case report Nina Agrawal, BA, Danielle Cameron, BA, Lawrence Wells, MD Abstract A 12-year-old girl underwent a bilateral distal femoral and proximal
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Overview of the Use of the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD) as a Limb Lengthening Technique
 Overview of the Use of the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD) as a Limb Lengthening Technique Katherine E. Ludwig Introduction The intrameduallry skeletal kinetic distractor (ISKD) is a
Overview of the Use of the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD) as a Limb Lengthening Technique Katherine E. Ludwig Introduction The intrameduallry skeletal kinetic distractor (ISKD) is a
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Relocation of the radial head with minimal invasive approach using the Ilizarov technique in neglected Monteggia fracture
 2016; 2(2): 13-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2016; 2(2): 13-20 2016 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-09-2015 Accepted: 02-03-2016 Dr. Nishant Chaudhari Postgraduate resident in orthopaedics, Surat Municipal
2016; 2(2): 13-20 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2016; 2(2): 13-20 2016 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-09-2015 Accepted: 02-03-2016 Dr. Nishant Chaudhari Postgraduate resident in orthopaedics, Surat Municipal
Research Article. Abstract
 Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Leg-length discrepancy and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭
 and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency : congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
and Its management 성균관의대 삼성서울병원 심종섭 Etiology of Undergrowth Congenital limb deficiency : congenital femoral deficiency, congenital fibular deficiency, tibial hemimelia Asymmetrical neurological disorders
Medical Devices DYNAMIC MULTIAXIAL FIXATOR
 Medical Devices DDDAF DYNAMIC MULTIAXIAL FIXATOR DAF DYNAMIC MULTIAXIAL FIXATOR It is a single plan external fixation tool. The ball-joint structure connects the clamp to the fixator body as an articular
Medical Devices DDDAF DYNAMIC MULTIAXIAL FIXATOR DAF DYNAMIC MULTIAXIAL FIXATOR It is a single plan external fixation tool. The ball-joint structure connects the clamp to the fixator body as an articular
ISPUB.COM. Z Ali, L Khurshid, S Vakil, A Anjum, S Dhar OBJECTIVE METHOD PATIENTS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 22 Number 1 Prevalence Of Pin Tract Infection And Role Of Combined Saline And Povidone Iodine With Combined Spirit (Isopropyl Alcohol 70% V/V)
Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur
 CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
CASE REPORT Limb lengthening for radiation-induced growth arrest of the pelvis and femur Paul E. Matuszewski and S. Robert Rozbruch INTRODUCTION Aggressive treatment, including surgery and highdose irradiation,
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
AACPDM IC#21 DFEO+PTA 1
 Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
Roles of Distal Femoral Extension Osteotomy and Patellar Tendon Advancement in the Treatment of Severe Persistent Crouch Gait in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy Instructional Course #21
Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases
 Original article : Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases Rajendraprasad Butala *, Sunirmal Mukherjee, Prakash Samant, Ravindra Khedekar
Original article : Valgus subtrochanteric osteotomy for malunited intertrochanteric fractures : Our experience in 5 cases Rajendraprasad Butala *, Sunirmal Mukherjee, Prakash Samant, Ravindra Khedekar
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
, MD. physiologic. tibia varum. in utero (in. Disease in. variation. positioning. back and legs. instead of. Blount's. Infant with bowing in both legs
 North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
North Jersey Orthopaedic Institute Rutgers, The Statee University of New Jersey 140 Bergen Street, D1610 Newark, NJ 07101 973-972-2150 South Orange Ambulatory Center Hackensack Medical Plaza Overlook Medical
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams
 Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor Spatial Frame at Age of 16 Years
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 17 No. 1, pp: 67-78 (2010 A.D. / 1431 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 17-1.7 Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 17 No. 1, pp: 67-78 (2010 A.D. / 1431 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 17-1.7 Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Complex Deformity and Multiple Previous Surgeries Treated by Taylor
JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA
 JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
JOT Special Case Report Series CASE REPORTS www.jorthotrauma.com JOURNALOF ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF Orthopaedic Trauma Association Belgian Orthopaedic Trauma Association Canadian Orthopaedic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Large Distractor Femur
 Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual
 Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 419-425 ORIGINAL STUDY The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children Haridimos Tsibidakis, Anastasios D. Kanellopoulos,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 419-425 ORIGINAL STUDY The role of Taylor Spatial Frame for the treatment of acquired and congenital tibial deformities in children Haridimos Tsibidakis, Anastasios D. Kanellopoulos,
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara?
 Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
Khanfour Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2012, 7:23 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does langenskiold staging have a good prognostic value in late onset tibia vara? Ashraf Ahmad Khanfour * Abstract
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results. Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH
 New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH LLRS New York, NY July 19, 2013 Disclosures Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Paid Consultant
New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH LLRS New York, NY July 19, 2013 Disclosures Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Paid Consultant
