5 COMMON CONUNDRUMS IN CODING KNEE SURGERY
|
|
|
- Bernadette Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 COMMON CONUNDRUMS IN CODING KNEE SURGERY Ruby O Brochta-Woodward, BSN, CPC, CPMA, CPB, COSC, CSFAC Clinical Technical Editor Decision Health AAPC Chapter Association Board of Directors Region Treasurer; Vice Chair 1
2 DISCLAIMER This presentation is for education purposes only. The information presented is not intended to be legal advice. The information presented was current at the time presented and when applicable, based upon guidelines published by the AMA, CMS, and NCCI. 2
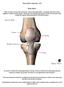
3 Knee Anatomy Skeletal anatomy Femur Condyles-medial and lateral Epicondyles-medial and lateral Patella Tibia Plateau Tibial spine Fibula 3
4 FEMUR Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle Lateral condyle Medial condyle Patellar surface 4
5 TIBIA AND FIBULA Intercondylar tubercles Intercondylar eminence 1. Lateral condyle 2. Fibula Apex Fibula Head Fibula Neck 3. Fibula 6. Tibia 7. Tibial tuberosity 8. Medial condyle 9. Medial and lateral facets (superior articular surfaces Gerdy s Tubercle-insertion of iliotibial tract 5
6 KNEE JOINT 1. Popliteus tendon 2. Fibular collateral ligament (lateral collateral) 3. Anterior cruciate 4. Arcuate popliteal ligament 5. Tibial collateral ligament 6. Suprapatellar bursa 7. Patella ligament/tendon 6
7 KNEE JOINT PCL Oblique Popliteal Ligament Lateral Meniscus Medial meniscus Iliotibial tract & capsule Synovial membrane ACL 7
8 KNEE JOINT Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) Lateral femoral condyle (LFC) Femur Medial femoral condyle (MFC) Fibular (lateral)collateral ligament LCL Medial meniscus Lateral meniscus Anterior cruciate ligament ACL Tibial (medial)collateral ligament MCL Patellar ligament/tendon Patella Tibia 8
9 CRUCIATE AND COLLATERAL LIGAMENTS 1. Anterior cruciate ligament 2. Popliteus tendon 3. Fibular collateral ligament 4. Lateral meniscus 5. Transverse ligament 6. Tibial collateral ligament 7. Lateral meniscus 8. ACL 9. Posterior cruciate ligament 10. Posterior cruciate ligament 11. Posterior meniscofemoral ligament (ligament of Wrisberg) 11 9
10 Ligaments Intracapsular ACL Weaker Tightens in extension, preventing hyperextension Attachment intercondylar tibia to LFC Tears occur when foot planted and knee rotates in hyperextension PCL Shorter and stronger than ACL Tightens during flexion Prevents anterior displacement of femur on tibia or posterior displacement tibia on femur Attachment posterior intercondylar tibia to MFC 10
11 Ligaments Intracapsular Meniscii Medial is larger than lateral Medial semicircular; lateral more circular Medial lies over the medial facet of tibia, attached to MCL Lateral lies over lateral facet of tibia Transverse ligament Binds and stabilizes meniscii Attaches anterior aspect of meniscii Posterior meniscofemoral Strong Attaches posterior lateral meniscus to MFC 11
12 Ligaments Extracapsular MCL Limits extension and abduction of the leg Attached to the medial meniscus Attached medial femoral epicondyle to medial tibial condyle LCL Limits extension and adduction of the leg Attached lateral femoral epicondyle to fibular head 12
13 Ligaments Extracapsular Patellar Acts in extension of quadriceps Also called patellar tendon Attaches patella to tibial tuberosity Arcuate popliteal Prevents posterior slipping of femur on tibia Torn in hyperextension Attaches fibular head to capsule Oblique popliteal Limits hyperextension and lateral rotation Attached semimembranosus tendon to posterior knee 13
14 Hamstring-Biceps Femoris Origin: Long head(2)- ischial tuberosity; Short head(1)- linea aspera Insertion: Head of fibula lateral side Action: Long head-extension of hip; Both heads-flexion of knee, lateral rotation of flexed knee Innervation: Long head-sciatic nerve tibial division (L5, S1,2); Short head-sciatic nerve peroneal division (L5, S1,2) Long head is one of 3 making up hamstrings which cross both the hip and knee joints Short head does not cross two joints 14
15 Hamstring-Semitendinosus Origin: Ischial tuberosity Insertion: Anterior proximal tibial shaft Action: Flexes knee, when knee flexed medially rotates tibia; thigh hip joint; when hip & knee both flexed, extends trunk Innervation: Sciatic nerve tibial division L5, S1,2 Has a long tendon of knee 15
16 Hamstring-Semimembranosus Origin: Ischial tuberosity Insertion: Posterior medial tibial condyle Action: Flexes knee, rotates flexed leg medially; extends hip; with hip & knee flexed extends trunk Innervation: Sciatic nerve tibial division L5, S1,2 Note Biceps femoris inserts knee; semitendinosus & semimembranosus insert medially 16
17 Tensor Fasciae Latae Origin: Anterior iliac crest & ASIS Insertion: Into iliotibial tract which inserts on lateral condyle of femur Action: flexes, abducts & medially rotates hip; w/ gluteus maximus stabilizes hip joint; stabilizes extended knee Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve L4,5 Braces the knee when walking Also known as the Iliotibial Band (ITB) 17
18 Sartorius Origin: ASIS Insertion: Upper medial tibial shaft Action: Flexor, abductor & lateral rotator of hip joint; flexor of knee joint; helps balance pelvis; not powerful Innervation: Femoral nerve L2,3 Longest muscle in the body Most superficial thigh muscle. Forms the lateral border of the femoral triangle Latin for tailor Crosses hip and knee joint 18
19 Rectus Femoris Origin: Two heads; anterior inferior iliac spine and ilium superior to acetabulum Insertion: Combines to insert into quadriceps tendon which inserts into base of patella & tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament Action: Action on knee is through patellar ligament; extends knee joint; helps iliopsoas flex hip Innervation: Femoral nerve L2,3,4 Only muscle of quadriceps group that crosses both the hip and knee joint 19
20 Vastus Lateralis Origin: Posterior aspect greater troch to lateral lip of linea aspera Insertion: Lateral patella & tendon of rectus femoris Action: Extension knee Innervation: Femoral Nerve L2,3,4 Vastus=immense Covers entire lateral portion of thigh 20
21 Vastus Intermedius Origin: Anterior & lateral aspect femoral shaft & lateral intermuscular septum Insertion: Posterior surface upper border patella; forms part of quadriceps tendon; inserts into tibial tuberosity via patella ligament Action: Extension knee joint Innervation: Femoral nerve L2,3,4 21
22 Vastus Medialis Origin: Intertroch line & medial lip linea aspera Insertion: Medial border of quadriceps tendon, some fibers insert directly into medial side of patella; tibial tuberosity via patella tendon Action: Extension of knee joint Innervation: Femoral nerve L2,3,4 Only muscle on the back of the upper arm 22
23 Extensor Mechanism Quadriceps tendon Patella Medial and lateral retinaculum Patellar tendon (ligament) 23
24 Medial & Lateral Retinculum "The medial retinaculum is far thinner than its lateral counterpart and is not felt to be as significant with respect to patella position and tracking. Deep to the medial retinaculum are patello-femoral, patello-meniscal and patello-tibial ligaments. The lateral retinaculum this thick structure lies along the lateral border of the patella and represents the confluence of many structures including the iliotibial band and lateral patellofemoral ligament. The superior geniculate artery and vein course in a medial-lateral direction along the ventral surface of the retinaculum near the superior pole of the patella."
25 Patellar realignment If the operation involves structures at or above the kneecap, it is called a proximal realignment. If the operation involves structures below the kneecap, it is called a distal realignment Elmslie Trillat Procedure - distal realignment procedure re-aligning the attachment of the patellar tendon (the tendon under the kneecap) to the underlying tibial tubercle. Also known as TTT or tibial tubercle transfer procedures Fulkerson osteotomy (or Fulkerson 'procedure') is an operation to realign the tibial tuberosity (lower bony attachment of the patellar tendon on the shinbone or
26 Patellar Realignment Feb 2010 Assistant Question: An orthopaedic surgeon performs a FULKERSON procedure. May code be reported? Answer: Yes. Code 27418, Anterior tibial tubercleplasty (eg, Maquet type procedure) may be reported with the Modifier 22, Increased procedural services. Modifier 22 is used to reflect the additional procedural work involved with the FULKERSON procedure, compared to the Maquet technique. While both procedures involve elevating the tubercle, the Maquet retains the distal part of the tubercle intact, which is then bent upward. The FULKERSON detaches the tubercle, moves it medially and elevates it." 26
27 7 MPFL Repair/Reconstruction Reconstruction of dislocating patella; with extensor realignment and/or muscle advancement or release (e.g., Campbell, Goldwaite type procedure) There is no scope code it would be 29999
28 Arthroscopy Arthroscopy, knee, diagnostic, with or without synovial biopsy (separate procedure) Included in ALMOST ALL Knee procedures Arthroscopy, knee, surgical; with lateral release If reconstruction/repair codes state include lateral release does not matter if open or scope it is included 28
29 Arthroscopy Just THREE compartments Medial Lateral Patellofemoral ACL considered patellofemoral Lateral release considered patellofemoral Must describe in operative note which one they are in
30 Arthroscopy Arthroscopy, knee, diagnostic, with or without synovial biopsy (separate procedure) Included in ALMOST ALL Knee procedures Arthroscopy, knee, surgical; with lateral release If reconstruction/repair codes state include lateral release does not matter if open or scope it is included 30
31 Arthroscopy Synovectomy (partial) Must be unrelated to other procedures Compartment doesn t matter Separate procedure Synovectomy (major) Need to be in at least 2 compartments and need to be different compartments Need to support major/extensive 31
32 Arthroscopy Chapter 1 CCI J. CPT "Separate Procedure" Definition - If a CPT code descriptor includes the term "separate procedure", the CPT code may not be reported separately with a related procedure. CMS interprets this designation to prohibit the separate reporting of a "separate procedure" when performed with another procedure in an anatomically related region often through the same skin incision, orifice, or surgical approach. 32
33 Arthroscopy Syovectomy partial AAOS January 2013 "CPT code 29875, limited synovectomy, is described as a separate procedure. This means that the work associated with this procedure is inclusive to more extensive procedures performed in the same anatomic site (the knee) and is not separately reportable. This code should only be reported if it is the only procedure performed; separate compartment rules do not apply. 33
34 Arthroscopy Synovectomy, MAJOR CCI CPT code may be reported for a medically reasonable and necessary synovectomy with another arthroscopic knee procedure on the ipsilateral knee if the synovectomy is performed in two compartments on which another arthroscopic procedure is not performed. For example, CPT code should never be reported for a major synovectomy with CPT code (knee arthroscopy, medial AND lateral meniscectomy) on the ipsilateral knee since knee arthroscopic procedures other than synovectomy are performed in two of the three knee compartments. 34
35 Arthroscopy Synovectomy, MAJOR Both AAOS and AMA believe you should be able to report and if a major synovectomy was done as long as there is documentation of underlying pathology Check with payer/carrier Indicator of 0 in CCI 35
36 Arthroscopy debridement/chondroplasty and loose body Medicare not to be reported with these codes at the same time as any other knee arthroscopic procedure Created G0289 Arthroscopy, knee, surgical, for removal of loose body, foreign body, debridement/shaving of articular cartilage (chondroplasty) at the time of other surgical knee arthroscopy in a different compartment of the same knee 36
37 Arthroscopy Loose Body G0289 reads separate compartment Size >5mm, separate incision is only AAOS Cannot override edit for Medicare and government payors based upon size or separate incision Separate incision is not enlarging the portal 37
38 G0289 with 29880/29881 With two exceptions HCPCS code G0289 (Surgical knee arthroscopy for removal of loose body, foreign body, debridement/shaving of articular cartilage at the time of other surgical knee arthroscopy in a different compartment of the same knee) may be reported with other knee arthroscopy codes. Since CPT codes and (Surgical knee arthroscopy with meniscectomy including debridement/shaving of articular cartilage of same or separate compartment(s)) include debridement/shaving of articular cartilage of any compartment, HCPCS code G0289 may be reported with CPT codes or only if reported for removal of a loose body or foreign body from a different compartment of the same knee. Requires 59 modifier HCPCS code G0289 should not be reported for removal of a loose body or foreign body or debridement/shaving of articular cartilage from the same compartment as another knee arthroscopic procedure. 38
39 Arthroscopy G0289 Must be separate compartment Per AMA may be reported more than once as long as different compartments Not for chondroplasty when done at the same operative session on the same knee as meniscectomy 39
40 Arthroscopy chondroplasty Describe it Where, tools used, condition of articular cartilage Frayed, flaked, exposed bone, Grade I, II, III 40
41 Arthroscopy Abrasion arthroplasty (includes chondroplasty where necessary) or multiple drilling or microfracture Debriding down to bleeding bone Includes Chondroplasty AND Lysis of Adhesions AND Synovectomy in same compartment August 2001 CPT assistant For example, when smoothing down the cartilage and/or drilling holes to create microfractures is also performed in addition to removal of foreign bodies or loose bodies of the bone or cartilage within the knee joint, code may be reported in addition to code only if performed in a separate knee compartment. Modifier -59 should be appended to indicate that a separate compartment was involved. 41
42 2 Arthroscopy August 2001 CPT Assistant Abrasion arthroplasty is usually performed to promote cartilage regeneration by creating access to blood and nutrients by smoothing down the cartilage and/or drilling holes to create microfractures. Code includes chondroplasty performed as part of the abrasion arthroplasty, so code should not be separately reported. If, however, chondroplasty is performed in a separate knee compartment, then code 29877/G0289 may be reported separately. Modifier -59, Distinct Procedural Service, should be appended to indicate that a separate compartment was involved. This code also includes resection of osteophytes and removal of loose or foreign bodies when performed in the same compartment.
43 Arthroscopy Meniscectomy and meniscal repair can be billed at same operative session if different meniscus with clear documentation of such Aetna policy Aetna considers arthroscopic partial meniscectomy medically necessary for traumatic meniscal tears. Aetna considers arthroscopic partial meniscectomy experimental and investigational for degenerative meniscal tears." 43
44 Revision ACL CPT Assistant November 2016 Question: Our surgeon performed a revision arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The patient previously had an arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction performed by another surgeon and sustained another injury that ruptured the graft. As part of the revision procedure, our surgeon removed the graft and fixation screws that were implanted by the other surgeon. In addition to reporting code 29888, Arthroscopically aided anterior cruciate ligament repair/augmentation or reconstruction, for the revision reconstruction, is it appropriate to report code 20680, Removal of implant; deep (eg, buried wire, pin, screw, metal band, nail, rod or plate), for removal of the screws? Answer: Yes, code may be separately reported for removal of the screws in addition to code
45 Revision ACL AAOS states either unlisted or If done by thermal shrinkage unlisted Harvesting and inserting the graft included in 29888, regardless of whether the graft is a patellar tendon or a hamstring tendon. If, however, the tendon is obtained from a distant site, such as the opposite leg, you may report the harvesting separately, using the most appropriate graft harvesting code (such as 2902X) Harvesting bone from the proximal tibia (e.g., from the bone tunnel) and grafting it to the patellar bone defect considered a local bone graft -included in the base procedure, and should not be reported. Reporting this as a harvest and transplant would be considered unbundling. AAOS April 2005 Bulletin 45
46 Open ACL CPT Assistant April 2009 Question: If a surgeon is reconstructing both the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament in the same knee, is it correct to report code x 2, or does the code take into account multiple ligamentous reconstructions? If the medial cruciate ligament also was reconstructed, would it be appropriate to report CPT code x 3 to represent each ligament reconstructed? Answer: It would be appropriate to report CPT code 27428, Ligamentous reconstruction (augmentation), knee; intra-articular (open), for the anterior cruciate ligament, code with modifier 59 for the posterior cruciate ligament, and code 27405, Repair, primary, torn ligament and/or capsule, knee; collateral, for the medial cruciate ligament. Both the second reporting of code and code are subject to modifier 51 to indicate multiple procedures. Sometimes, when repairing an ACL, the surgeon may chose to combine an intra-articular repair (i.e., bone-patella-bone) with an extra-articular repair (i.e., hamstrings). In that case code 27429, Ligamentous reconstruction (augmentation), knee; intra-articular, (open) and extra-articular, is the correct code to report 46
47 Cyclops Lesion Cyclops lesion=arthrofibrosis following ACL reconstruction CPT Arthroscopy, knee, surgical; with lysis of adhesions, with or without manipulation (separate procedure) ICD-10 M ankylosis, knee 47
48 Trephination CPT Assistant 2011 Question 3: What is the appropriate code to report arthroscopic trephination of the meniscus? Answer 3: Currently, there is no specific CPT code that describes arthroscopic trephination of the meniscus. Therefore, unlisted code 29999, Unlisted procedure, arthroscopy, should be reported. It is not appropriate to report either code or for the arthroscopic trephination of the meniscus procedure because these codes describe repair performed by a different technique. 48
49 Meniscal Transplant CPT Includes: Preparation of defected area Removal of damaged portion of meniscus Tibial tunnels or a bone trough created as stabilizing structures for the implant Insertion of the meniscal graft via arthrotomy Joint exploration Synovial biopsy Lavage drainage removal loose bodies Synovectomy Lysis of adhesions 49
50 0 Posterolateral Corner Question: What is the correct coding for a posterolateral corner repair/reconstruction of the knee involving the repair of the fibular collateral ligament (lateral collateral ligament), popliteus muscle, the popliteofibular ligament, and occasionally part of the posterolateral capsule? Answer: Code 27405, Repair, primary, torn ligament and/or capsule, knee; collateral, should be reported once when repair is performed. Code 27427, Ligamentous reconstruction (augmentation), knee; extra-articular, should be reported once when reconstruction is performed. The descriptor language of both codes and indicate that repair of the capsule is an inclusive component and is not reported separately. The posterolateral corner (PLC) of the knee is a complex area of the knee formed by the interaction of multiple structures. The arcuate complex, a component of the posterolateral corner, is composed of the arcuate ligament, the fibular collateral ligament, and the popliteus muscle and tendon.
51 1 Posterolateral Corner Additional elements of the posterolateral corner include the biceps femoris muscle and tendon (outside hamstring muscle), lateral collateral ligament, popliteofibular ligament, fabellofibular ligament, and posterolateral joint capsule. Because the open repair of multiple ligaments may occur, documentation of the specific ligaments should be described in detail to differentiate between repair and reconstruction and to help with accurate code choice. Dec 2012 CPT Assistant
52 Subchondroplasty What is it? Not fracture treatment! Minimally invasive surgery designed to treat subchondral defects associated with chronic bone marrow edema (BME) by filling them with a hard-setting, biomimetic bone void filler subchondroplasty Coding unlisted
53 CPT Assistant January 2014 Subchondroplasty Question: What Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ) code should be reported for a subchondroplasty procedure of the knee? Answer: The subchondroplasty procedure is a minimally invasive repair designed to treat subchondral bone defects associated with chronic bone marrow lesions by filling them with a bone-substitute material. There is no specific CPT code that accurately describes this service; therefore, unlisted code 27599, Unlisted procedure, femur or knee, should be reported. When reporting an unlisted code to describe a procedure or service, it is necessary to submit supporting documentation (e.g., procedure report) along with the claim to provide an adequate description of the nature, extent, and need for the procedure, and the time, effort, and equipment necessary to provide the service. 53
54 Subchondroplasty At this point, the diagnostic arthroscopy was completed. We turned our attention to the sub-chondroplasty. We utilized fluoroscopic imaging to obtain adequate radiographs to localize the entry point in AP and lateral planes. The AccuFill trocar and cannula were positioned appropriately. We used fluoroscopic imaging to position the femoral cannula, approximately 5 mm to 10 mm proximal to the joint line and centered over the bone marrow edema that was notable on the MRI scan which was essentially the weightbearing portion of the medial femoral condyle. We turned our attention to the positioning of tibial trocar as well. This was also centered in the weightbearing portion of the condyle and we advanced this with fluoroscopic imaging such that the fenestrations on the cannula were appropriately positioned within the bone. This was confirmed with both femoral and tibial cannulas. We then mixed the AccuFill appropriately and 5 ml of AccuFill were injected in a sequential manner in the femur with occasional repositioning and redirection of the cannula in order to distribute the AccuFill appropriately. Care was taken to confirm that there was no extrusion of any of the injected AccuFill. We then reinjected the plunger, distributing the remaining AccuFill within the cannula. In a similar manner, the tibia was treated with the same technique. During injection of the AccuFill, we were able to monitor the diffusion of the AccuFill within the medial femoral condyle and medial tibial plateau using fluoroscopic imaging. After allowing the femoral AccuFill to set for about 15 minutes and the tibia AccuFill to set for about 10 minutes, we were able to remove the trocars and cannulas and confirmed that there was no further extrusion of any of the AccuFill material. The knee was re-scoped and we noted no debris or AccuFill present. We turned our attention to closure. The portal sites were injected with Sensorcaine as was the AccuFill site. We then closed the small incisions with nylon suture. Dressings of Xeroform, fluffs, Kerlix, and Ace wrap were applied. The patient was awoken from anesthesia and transferred to the recovery room in stable condition. 54
55 Arthroplasty Arthro=joint + -plasty=repair or restoration of a part or function Combined simply means surgical repair of a joint in order to relieve pain, restore function, restore motion Generally done for arthritis, joint ankylosis always mean prosthetic placement Can involve partial removal of bone (osteophytes) to complete excision of bone(s) or joint surfaces Listed under Repair, Revision and/or Reconstruction subsection 55
56 Arthroplasty-Types Resection Without prosthetic replacement With partial prosthetic replacement With full prosthetic replacement Conversion Revision 56
57 Without mention of joint prosthesis Arthroplasty If no indication of placement of a joint prosthesis in op report look for CPT codes stating (arthro)plasty without notation of implant 27437, Arthroplasty patella, without prosthesis 27440, Arthroplasty, knee, tibial plateau 27442, Arthroplasty, femoral condyles or tibial plateau(s), kif no option look for ostectomy codes, excision bone cyst/benign tumors since arthroplasty is a resurfacing procedure of an arthritic/diseased joint 2012 CPT Assistant exostosis considered benign bone tumors; exostosis osteophyte 57
58 Types-Partial Uniarthroplasty One joint compartment is replaced with an artificial material Also referred to as a hemiarthroplasty Done in the medial or lateral compartment of the knee Arthroplasty, knee, condyle and plateau, medial OR lateral compartment 58
59 Types-Partial Uniarthroplasty Knee-MakoPlasty One joint compartment is replaced with an artificial material o o o o o o o o Uses robotic arm, bone resection, implant placement Pre-op 3-D CT(inclusive in procedure) Determines prosthesis size, placement, alignment Reduces amount of bone resection Outpatient, improved ROM, lower revision rate Done primarily in the medial compartment of the knee Arthroplasty, knee, condyle and plateau, medial OR lateral compartment plus 0055T computer assisted surgical navigation for musculoskeletal procedures, with image-guidance based upon CT/MRI images or computer assisted surgical navigation procedure imageless or S2900 surgical techniques requiring use of robotic surgical systems Check health plans for coverage 59
60 Types-Partial Resurfacing Patella Arthroplasty patella with prosthesis Only if no placement of femoral component Patellofemoral Compartment Arthroplasty-unlisted vs Check healthplan policies for coverage AHA Coding Clinics 2016 Q1 advises CPT Assistant advises arthroplasty. Femoral condyles or tibial plateau(s), knee and
61 Patellofemoral Question: When the physician performs a patellofemoral arthroplasty in which the prosthesis is inserted into the trochlear groove (and not into the femoral condyles), is it still appropriate to report code 27442, Arthroplasty, femoral condyles or tibial plateau(s), knee? Or would code 27599, Unlisted procedure, femur or knee, be reported because there is no CPT code that describes trochlear replacement? Answer: Yes, it is still appropriate to report code for the patellofemoral arthroplasty. Also, unlisted code may be reported for the trochlear resurfacing. When reporting an unlisted code to describe a procedure or service, it will be necessary to submit supporting documentation (eg, procedure report) along with the claim to provide an adequate description of the nature, extent, and need for the procedure; as well as the time, effort, and equipment necessary to provide the service Neither the femoral condyles nor the tibial plateaus are part of this procedure This doesn t address the patella 61
62 Types-Partial Bicompartmental knee arthroplasty Medial and patellofemoral compartments-journey Deuce Lateral and patella less common AMA instructs to use Check payer policies 62
63 Types-Partial Hemicap Femoral condyle year olds with isolated cartilage lesion Uses preoperative imaging Not covered by most healthplans Unlisted 63
64 Arthroplasty What is included? Synovectomy, joint debridement Removal loose body Tenotomy iliopsoas Acetabular reaming Excision of acetabular osteophytes Manipulation hip Trochanteric osteotomy and attachment Capsular release, repair, and/or reconstruction Insertion of femoral components with or without methylmethacrylate 64
65 Revision Arthroplasty Requires removal of previously placed prosthetic components and reinsertion of new components in a single surgical procedure Revision codes exist for shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, ankle Removal of the previously inserted prosthesis is included Previous primary procedure was total joint No time interval between primary arthroplasty and revision other than can t be billed on the same day Based upon which components are removed and replaced 65
66 Revision Arthroplasty Knee Revision of total knee arthroplasty, with or without allograft; 1 component Knee Revision of total knee arthroplasty, with or without allograft femoral and entire tibial component Includes removal of component Includes lateral release Includes manipulation, release of scar tissue Allows for bone grafting if harvested from a different site 66
67 CONVERSION What about conversion of Knee UKA to Total? Conversion of a unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to a total knee should be coded as revision two components CPT Assistant July
68 Staged Revision Stage one report using removal of prosthesis complicated Knee Removal of prosthesis, including total knee prosthesis, methylmethacrylate with or without insertion of spacer If non-biodegradable antibiotic beads are also inserted may also bill AMA considers temporary devices placed as a spacer (e.g.. PROSTLAC) as a spacer even if shaped like a prosthesis. Spacer is bundled into the prosthesis removal code and is NOT separately reportable. 68
69 Revision Arthroplasty Revision of total knee arthroplasty, with or without allograft; 1 component Revision of total knee arthroplasty, with or without allograft femoral and entire tibial component Includes removal of component Includes lateral release Includes manipulation, release of scar tissue Allows for bone grafting if harvested from a different site 69
70 Staged Revision Stage two Removal of spacer/temporary implant, joint debridement Knee Arthrotomy, knee, with exploration, drainage or removal of foreign body (e.g.. Infection) If non-biodegradable antibiotic beads are removed and reinserted also may bill (no global period) If reinsertion of antibiotic impregnated spacer w/o previously placed beads Nonbiodegradable means they eventually need to be removed 70
71 Staged Revision Final stage-infection resolved and final prosthesis to be inserted Knee Arthroplasty, knee, condyle and plateau, medial AND lateral compartments, with or without patella resurfacing (total knee arthroplasty) No conversion code exists for total knee arthroplasty Removal of spacer is included May report if separate placement of antibiotic impregnated beads AMA states that the reinsertion should not be billed as a revision arthroplasty since revision arthroplasty includes removal of the primary prosthesis. This step has already been done. 71
72 2 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Osteoarthritis/DJD M17. Primary = wear and tear, no prior trauma or disease Post-traumatic degenerative= occurs as a result of trauma around the joint o o Must be documented as post-traumatic degenerative/osteoarthritis Not the same as post-traumatic arthritis M12.5- Secondary = other causation such as AVN, infection Secondary due to hip dysplasia-hip only Laterality 1=right, 2=left o 5 th character Bilateral 4 th character zero
73 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis M05.- to M06.- Joint and laterality Comorbidities Presence of rheumatoid factor o Based upon guidelines default is without therefore if not documented code to RA without and body part AVN M87.- Laterality 1=right, 2=left Causation 73
74 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Include codes for genu valgum/varum M21.06-/ M as these can impact the difficulty of the procedure Requires laterality 74
75 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Uncomplicated Post-surgery encounters Aftercare following joint replacement Z47.1 Plus Z o Requires laterality If submitting claims for PT/OT post joint replacement, remember to add the Z96.6- series 75
76 ICD-10 Diagnosis Revision Revision arthroplasty= Complication Mechanical internal joint prosthesis o T broken internal joint prosthesis o T dislocation/instability/subluxation o T mechanical loosening/aseptic loosening 76
77 ICD-10 Diagnosis Revision Revision arthroplasty= Complication T peri-prosthetic fracture o i.e. fracture around the prosthesis o If a result of trauma use S series code in addition to T o October 2016 code revisions moves peri-prosthetic fracture codes to M97- M97.1- knee Joint specific require laterality 77
78 ICD-10 Diagnosis Revision Revision arthroplasty= Complication Mechanical internal joint prosthesis T peri-prosthetic osteolysis o + addl code for major osseous defect if present (M89.7-) T wear articular bearing surface T other mechanical complication/prosthetic failure Laterality 7 th character A PLUS Z96.6- code to define type of joint replaced Per Coding Clinics Q Manual only notes to append for other 78
79 ICD-10 Diagnosis Revision Revision arthroplasty= Complication Other specified complications of internal joint prosthesis T embolism T fibrosis T pain T stenosis T thrombosis T other specified No joint specificity No laterality 7 th character A Used for prosthesis, implants and graft complications PLUS Z96.6- code to define type of joint replaced 79
80 ICD-10 Diagnosis Infected/Staged Infected Stage One T84.5- Infection and inflammatory reaction due to internal knee prosthesis Laterality Z96.6- series to define joint Use additional code to identify infection 7 th character A Aftercare and subsequent stages INCLUDING encounter for reinsertion of prosthesis Z47.3 aftercare following explantation of joint prosthesis Subdivided for laterality and site (shoulder, hip, knee only) Should not use Z89.- series acquired absence of knee joint Excludes 1 note with Z47.3- Used if explanted but no plan for staged revision 4 th quarter 2011 Coding Clinic instructed to use 2015 Webinars did not include the use of Z89.- in revision instructions 80
81 81
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization
 evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
Hip, Knee and Shoulder Surgery
 Hip, Knee and Shoulder Surgery Policy Number: MM.06.030 Lines of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration; Medicare Advantage Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient Original Effective
Hip, Knee and Shoulder Surgery Policy Number: MM.06.030 Lines of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration; Medicare Advantage Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service: Outpatient; Inpatient Original Effective
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
MSK Covered Services. Musculoskeletal: Joint Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing, including acetabular and femoral components
 CPT CODE S2118 MSK Covered Services Musculoskeletal: Joint Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing, including acetabular and femoral components 23000 Removal of subdeltoid calcareous deposits, open 23020
CPT CODE S2118 MSK Covered Services Musculoskeletal: Joint Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing, including acetabular and femoral components 23000 Removal of subdeltoid calcareous deposits, open 23020
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
DOCUMENTATION REQUIREMENTS IN CODING HIP SURGERY
 DOCUMENTATION REQUIREMENTS IN CODING HIP SURGERY Ruby O Brochta-Woodward, BSN, CPC, CPMA, CPB, COSC, CSFAC Clinical Technical Editor Decision Health AAPC Chapter Association Board of Directors Region 7
DOCUMENTATION REQUIREMENTS IN CODING HIP SURGERY Ruby O Brochta-Woodward, BSN, CPC, CPMA, CPB, COSC, CSFAC Clinical Technical Editor Decision Health AAPC Chapter Association Board of Directors Region 7
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Presents ACL RECONSTRUCTION HAMSTRING METHOD. Multimedia Health Education
 HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
HAMSTRING METHOD Presents HAMSTRING METHOD Multimedia Health Education Disclaimer Stephen J. Incavo MD This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
Hip and Knee Approaches
 Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Posterior compartment of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking
 1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Why does it matter? Patellar Instability 7/23/2018. What is the current operation de jour? Common. Poorly taught. Poorly treated
 Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
Chapter 10. The Knee Joint. The Knee Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones. Bones. Knee joint. Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS
 The Knee Joint Chapter 10 The Knee Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 10-1 Knee joint largest joint in body very complex
The Knee Joint Chapter 10 The Knee Joint Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 10-1 Knee joint largest joint in body very complex
LOWER LIMB. As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs)
 LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Muscles of Gluteal Region
 1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee
 Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee I. Anatomy II. Assessment III. Treatment IV. Case Study V. Dissection Anatomy Not a hinge joint 6 degrees of freedom Flexion/Extension Rotation Translation Anatomy
Anatomy and Sports Injuries of the Knee I. Anatomy II. Assessment III. Treatment IV. Case Study V. Dissection Anatomy Not a hinge joint 6 degrees of freedom Flexion/Extension Rotation Translation Anatomy
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Your Practice Online
 Your Practice Online Disclaimer P R E S E N T S - PATELLAR TENDON This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction.
Your Practice Online Disclaimer P R E S E N T S - PATELLAR TENDON This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction.
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
1-Muscles: 2-Blood supply: Branches of the profunda femoris artery. 3-Nerve supply: Sciatic nerve
 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
Figure 3 Figure 4 Figure 5
 Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Patellofemoral Pathology
 Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy. Transcript for Volume Robert D Acland
 Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW?
 OTHER KNEE SURGERIES POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW? Written by Jacques Ménétrey, Eric Dromzée and Philippe M. Tscholl, Switzerland Injury of the posterolateral corner (PLC) is relatively
OTHER KNEE SURGERIES POSTEROLATERAL CORNER RECONSTRUCTION WHEN AND HOW? Written by Jacques Ménétrey, Eric Dromzée and Philippe M. Tscholl, Switzerland Injury of the posterolateral corner (PLC) is relatively
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
Hip joint and pelvic girdle. Lower Extremity. Pelvic Girdle 6/5/2017
 Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
ABSTRACT 2 Key Words: meniscus, tibiofemoral joint, osteoarthritis
 ABSTRACT In the United States, meniscal lesions represent the most common intra-articular knee injury. 1 In fact, the mean annual incidence of meniscal tears is approximately 60 to 70 per 100,000 patients.
ABSTRACT In the United States, meniscal lesions represent the most common intra-articular knee injury. 1 In fact, the mean annual incidence of meniscal tears is approximately 60 to 70 per 100,000 patients.
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
 BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants.
 Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
Learning IRM. The Knee: lateral ligaments and anatomical quadrants. Poster No.: C-1733 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Amador Gil, M. D. C. Jurado Gómez, V. de Lara Bendahan ;
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
lower limb Anterior Compartment: lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments:
 lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
Mohammad Ashraf. Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 - 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
- 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
