Radiographic Imaging. Standard Cervical Spine Series. Cervical Spine Imaging. Standard Cervical Spine Series. Cervical Spine Imaging 5/2/14
|
|
|
- Ruby George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiographic Imaging Hector RiveraMelo DC, DACBR Benefits Visualization of significant osseous and articular pathology Risks No safe amount of ionizing radiation Limitations Articular cartilage Soft tissues Early osseous and articular changes Cervical Spine Imaging Standard Cervical Spine Series AP Lower Cervical Lateral Standard radiographic series AP lower cervical AP open mouth Lateral Standard Cervical Spine Series AP Open Mouth Cervical Spine Imaging Accessory radiographic views Obliques Flexion/Extension 1
2 Accessory Cervical Spine Views Anterior Obliques Accessory Cervical Spine Views Extension Flexion Cervical Spine Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis Degenerative disc disease Facet arthrosis Uncovertebral arthrosis DISH Congenital annomalies Hangman s fracture (C2) Unilateral facet dislocation Cervical Spine Imaging Common pathology not seen on X-rays Disc herniations Chiari malformations Facet fractures* C1/2 Mach Effect Gives the appearance of a lucent line. An optical phenomenon from edge enhancement due to lateral inhibition in the retina. Occurs when two objects of similar but different densities overlap. 2
3 C1/2 Odontoid Fracture Question about C2/3 The facets at C2/3 are at a slightly different angle than the rest of the lower cervical spine facets. Pseudofusion appearance is very common. Lack of body involvement is a big clue. Congenital Block Vertebrae C2/3 C2/3 is a common location. Often accompanied by occipitalization of C1. Wasp-waist appearance anteriorly. Posterior element involvement Radiographic Features: Hypertrophy (enlargement) of the articular processes Sclerosis Anterior or posterior translations (advanced) Facet Arthrosis Nuchal Bones and C1 Accessory Ossicle with intercalary bones Nuchal Bones Ossicles within the nuchal ligament. Seen more commonly with increased age. Considered a normal variant. DDx: SP fracture 3
4 Nuchal Bones and C1 Accessory Ossicle with intercalary bones C1 Accessory Ossicle Accessory ossicle of no clinical significance. Considered a normal variant. DDx: HADD of the longus colli ALL calcification Nuchal Bones and C1 Accessory Ossicle with intercalary bones Intercalary Bones Degenerative calcification of the anterior fibers of the intervertebral disc. DDx: Calcification of the ALL (DISH). Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. Tear-Drop fracture. Old SP fracture of T1 66 yom with C/S pain AKA: Clay-shoveler s fracture Inferior displacement of fragment Parent/Donor site A stable injury DDx: Ununited growth center. Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis This is a common location for atherosclerosis. Will often look less tube-like and more globular. Will often see accompanying atherosclerosis of other large arteries. Jefferson Fracture Bonus: Tear-Drop Fracture 4
5 Jefferson Fracture Burst fracture of C1. Mechanism of injury usually axial loading. Classically see overhanging lateral masses of C1. Frequently accompanied by other C/S injuries. Tear-Drop Fracture Two mechanisms: Extension: A stable injury The result of an avulsion of anterior body by ALL. Flexion: A highly unstable injury The result of compressive forces, often with extensive damage to the posterior elements. Normal Pediatric C/S What s Wrong Here? Vertebral bodies are oddly shaped. Disc heights and joint spaces appear larger. Endplates appear to be separated. Right Sided Aortic Arch This is an uncommon congenital anomaly. (0.1% of the population) May be associated with other more serious congenital heart diseases. Thoracic Spine Imaging Standard radiographic series AP Lateral Of course, it s possible that the technician simply placed the marker on the wrong side 5
6 Standard Thoracic Spine Series AP Lateral Thoracic Spine Imaging Accessory radiographic views PA Chest Accessory Thoracic Spine Views PA Chest Thoracic Spine Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis Degenerative disc disease Facet arthrosis Costotransverse arthrosis Scoliosis Compression fractures Rib fractures Thoracic Spine Imaging Common pathology not seen on X-rays Early Infection Early osteoporosis Asthma Ununited TP Of T1 T1 Smooth/round borders Upper thoracic spine is a very common location. This is a very uncommon location for fractures. DDx: TP fracture Rib fracture HADD of the scalenes 6
7 20 yof with c/s and t/s pain Hair Artifacts What happened here? Multiple metallic curvilinear densities. Seen outside the chest. Here s another patient with the same mystery Acupuncture needles!! What went wrong? This is an unaltered (not cropped) image taken at a chiropractic office. Intended to be a lateral thoracic spine view. What went wrong? Cassette not pushed in all the way. Even digital machines use cassettes (CR) QUIZ Lumbar Spine Imaging 1) Which of the following levels o6en gives the false appearance of facet fusion? 2) Which of the following is considered a sign of pathology? Standard radiographic series AP (or PA) Lateral a) C1/2 b) C2/3 c) C3/4 d) C5/6 a) Nuchal bones b) Intercalary bones c) Mach bands d) Ununited growth centers 7
8 Standard Lumbar Spine Series AP Lateral Lumbar Spine Imaging Accessory radiographic views AP (or PA) L5/S1 spot Lateral L5/S1 spot Obliques Flexion/Extension Accessory Lumbar Spine Views Anterior or Posterior Obliques Accessory Lumbar Spine Views Flexion Extension R Accessory Lumbar Spine Views Lateral L5/S1 Spot AP L5/S1 Spot Lumbar Spine Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis Degenerative disc disease Facet arthrosis Ankylosing Spondylitis Compression fractures DISH Atherosclerosis of the Abdominal Aorta Congenital anomalies 8
9 Lumbar Spine Imaging 16yoF with lbp Common pathology not seen on X-rays Disc herniations Sciatica Piriformis Syndrome 16yoF with lbp Normal Transverse Processes 50yoF with lbp Metastatic Breast Cancer (Blastic) Ivory Vertebra DDx: Blastic Metastasis Lymphoma Pagets Disease Notice the osseous destruction of the TP. 9
10 56yom with lbp 48yom with lbp Limbus Bones 38yof with lbp Very common in the lumbar spine. Represent intravertebral disc herniations. Typically asymptomatic (especially if anterior). R Gall Stones 39yom with lbp following MVA Located in the right upper quadrant. Tend to be more dense around the periphery. Common in females over 40. May or may not be symptomatic. 10
11 Hydroxyapatite deposition disease Aka: Calcific tendinitis Cloud-like calcification Most common locations: Shoulder Hip Wrist Transitional Segment Commonly seen at the lumbosacral junction. 7 Subtypes: 35yom with lbp following MVA Swallowed Piercing Patient reported swallowing a piercing during car accident Doctor did not specify what kind of piercing. 29yom with lbp Ankylosing Spondylitis Common in young males. May just present with low back stiffness. Vertebral body squaring and erosions. SI joint fusion occurs in at least 50% of patients. Bilateral symmetry is classic. 11
12 Extremity Imaging Upper extremity Hector RiveraMelo, DC, DACBR Common indications for extremity imaging Unresponsive to care after 4 weeks Significant activity restriction >4 weeks Non-mechanical pain Osteoarthritis unrelieved by conservative care Suspected/known inflammatory arthritis Significant trauma Suspected physical abuse in children Extremity Imaging Red flag indicators Signs/symptoms or history of cancer Red skin, fever, immunosuppressed History of non-investigated trauma Unexplained significant sensory/motor deficit Shoulder Imaging Standard radiographic series AP internal rotation AP external rotation Baby arm Standard Shoulder Series AP Internal Rotation AP External Rotation Standard Shoulder Series Baby Arm 12
13 Shoulder Imaging Accessory Shoulder Views Axial Accessory radiographic views Axial Trans-scapular Y Accessory Shoulder Views Trans-scapular Y Shoulder Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Hydroxyapatite Deposition Disease (HADD) AC injuries (grades II-III) Glenohumeral dislocations Osteoarthritis (especially AC) Clavicular fractures Shoulder Imaging 44 Year-old M Common pathology not seen on X-rays Rotator cuff injury Adhesive capsulitis Impingement syndrome Labral injury AC injury (grade I) 13
14 44 Year-old M 44 Year-old M Absent 4 th Rib on the left 79yoM: Acute shoulder pain Examine the whole film: Don t forget the ribs on shoulder views. Potential causes include: Post-surgical Aggressive tumor Clavicle fx with multiple rib fxs Ribs 2 and 3 involved No pneumothorax Significant Osteoporosis 1) Which of the following is a common pathology seen on lumbar spine x- rays? QUIZ 2) Which of the following is a standard view of the thoracic spine? a) Disc hernialons b) Atherosclerosis c) SciaLca d) Piriformis Syndrome a) AP thoracic b) PA thoracic c) AP chest d) PA chest 14
15 Wrist Imaging Standard Wrist Series PA Lateral Standard radiographic series PA Lateral Medial oblique PA ulnar deviation Standard Wrist Series Medial Oblique PA Ulnar Deviation Wrist Imaging Accessory radiographic views Carpal Tunnel Angulated Scaphoid Accessory Wrist Views Carpal Tunnel Angulated Scaphoid Wrist Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis (especially 1 st CMC joint) Scaphoid fractures Distal radial fractures Instability Lunate dislocations Inflammatory arthritis Avascular necrosis 15
16 Wrist Imaging Common pathology not seen on X-rays Nerve entrapment syndromes Ganglion cysts Sprain/Strain Hand Imaging Standard radiographic series PA Lateral Medial oblique Standard Hand Series PA Lateral Medial Oblique Hand Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis (especially DIPs) Metacarpal fractures (especially 4 th & 5 th ) Interphalangeal fractures/dislocations Avulsion injuries Inflammatory arthritis (especially MCPs) Benign Enchondromas Penetrating injuries Hand Imaging 38yof w/ trauma and thumb pain Common pathology not seen on X-rays Nerve entrapment syndromes 16
17 Enchondroma with path fracture Benign cartilagenous lesion with very low rate of malignant degeneration. Represents the most common benign tumor of the hand. Lower extremity Typically asymptomatic until fracture occurs. Occasionally found incidentally. Hector RiveraMelo DC, DACBR Hip Imaging Standard Hip Series AP Pelvis Standard radiographic series AP Pelvis AP Spot Frog Leg Standard Hip Series AP Spot Frog Leg Hip Imaging Accessory radiographic views Judet Long bone study of the femur 17
18 Accessory Hip Views Judet Long bone study Hip Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis Avascular necrosis Hydroxyapatite Deposition Disease (HADD) Developmental dysplasia of the hip Femoral-acetabular impingement syndrome Femoral neck fractures Inflammatory arthritis Hip Imaging 65 yom 1 year post-surgery follow up Common pathology not seen on X-rays Sciatic or other nerve impingement syndromes (piriformis syndrome) Labral injuries Bursiits Muscle tears 65 yom 1 year post-surgery follow up Pre-Op Seen commonly in long bones. Nutrient Canal From the knee we flee! To the elbow we go! Typically will not see medullary involvement Smooth with no cortical offset. Post-Op 18
19 20of w/ hip pain Simple Bone Cyst AKA: Unicameral Bone Cyst Benign cystic lesion with no malignant degeneration. Common in long bones (humerus=mc location) Typically asymptomatic until fracture occurs. Occasionally found incidentally. QUIZ Knee Imaging 1) Which is the most common benign tumor of the hand? a) Osteoid Osteoma b) Osteochondroma c) Enchondroma d) Metastasis 2) Which of the following is a standard view of the hip? a) Frog- leg b) Lateral pelvis c) Lateral spot hip d) Judet Standard radiographic series AP Lateral Standard Knee Series AP Lateral Knee Imaging Accessory radiographic views Oblique Tangential (Sunrise) Intercondylar (Tunnel) Long bone studies 19
20 Knee Accessory Views Intercondylar (Tunnel) Knee Accessory Views Medial Oblique Long bone study Tangential (Sunrise) Knee Imaging: Ottawa Knee Rules Catch high percentage of fractures of the knee Order x-rays of the knee if there is trauma to the knee and any of the following: Age 55 Isolated tenderness at: Head of the fibula Patella Inability to flex knee >90 Inability to walk 4 weightbearing steps at presentation or at presentation Knee Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis Osteochondral defects (femur) Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD) Proximal fibular/tibial fractures Aggressive and benign 1 bone tumors Knee Imaging 59 yof with bilateral knee pain Common pathology not seen on X-rays Patellar tendinitis (Jumpers knee) Meniscal injury ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL injury Sprain/Strain Chondromalacia Patella Osgood-Schlatter disease* 20
21 49 yof with bilateral knee pain Osteoarthritis of the knees Age range is typically <45 Typically asymmetric involvement. Prominent osteophytes Medial joint compartment typically affected 1st. 31 yom with right knee pain Fabella A sesamoid bone. Located within the tendon of the lateral head of the gastrocnemious muscle. A very common normal variant. 41 yof with right knee pain Cyamella A sesamoid bone, similar to the fabella. Located within the tendon of the popliteus muscle. A normal variant 21
22 Meniscal Ossicle An accessory ossicle. Located within the meniscus. Typically seen posteriorly and medially May be triangular. An uncommon normal variant. 66 yom with left knee pain Popliteal Artery Atherosclerosis This is a common location for atherosclerosis. The popliteal artery is the most common location for peripheral aneurysms. Will often see accompanying atherosclerosis of other large arteries. 44 yom with bilateral knee pain 44 yom with bilateral knee pain 22
23 Synovial Osteochondromatosis 35 yom with right knee pain AKA: Synovial Chondrometaplasia, Synovial Chondromatosis Caused by flaking off of synovial lining. The knee is the most commonly affected joint May be 1 or 2 to osteoarthritis 2:1 Male:Female ratio Infrapatellar Fat Pad Syndrome 12yom with right leg pain AKA: Hoffa s Disease Rare cause of knee pain Caused by injury (acute or chronic) to the fat pad. May be pinched with full extension Seen in jumping and kneeling athletes. DDx for anterior knee pain: Patellar tendonitis Synovial chondromatosis Ganglion Cysts Chondromalacia Patella 12yom with right leg pain Lymphoma Abnormal periosteal reaction of tibia DDx. Osteosarcoma Ewing s Sarcoma Osteomyelitis Lymphoma Leukemia 23
24 More Acupuncture Needles!! Foot Imaging Standard radiographic series DP Lateral Medial oblique Standard Foot Series DP Medial Oblique Standard Foot Series Lateral Foot Imaging Accessory radiographic views Tangential Calcaneus (Harris-Beath) Accessory Foot Views Tangential Calcaneus (Harris-Beath) 24
25 Foot Imaging Common pathology seen on X-rays Osteoarthritis (especially 1 st MTP) Phalangeal fractures (especially 4 th & 5 th ) Interphalangeal fractures/dislocations Avulsion injuries Inflammatory arthritis (especially MCPs) Foot Imaging Common pathology not typically seen on X-rays Plantar fasciitis Mortons neuroma 38 yom with foot pain Os Peroneum And Os Intermetatarseum Os Peroneum A sesamoid bone within the peroneus longus tendon. Os Intermetatarseum An accessory ossicle which may form a synovial joint with the first or second metatarsal or medial cuneiform. 22 yom with foot pain Os Vesalianum Ossicle, representing an ununited secondary growth center at the styloid of the 5 th metatarsal. 25
26 27 yof with foot pain 5 th Metatarsal Fracture Avulsion fracture of the 5 th metatarsal styloid. Occurs at the insertion of the Peroneus brevis tendon. Relatively common among tennis players Generally respond well to conservative treatment (casting) QUIZ How to have your films read: 1) Which of the following is a pathologic finding in the knee? a) Fabella b) Cyamella c) Meniscal Ossicle d) Atherosclerosis 2) Which of the following is an accessory view of the knee? a) Intercondylar b) AP c) Lateral d) Femoral Head SCU hectormelo@scuhs.edu We re also on facebook! 26
Radiology 10/28/2013 COLLIMATION CAN IMPROVE YOUR IMAGES COLLIMATION CAN IMPROVE YOUR IMAGES REVIEW OF BASIC X-RAY PHYSICS
 Radiology Hector RiveraMelo, DC, DACBR Director, Center for Diagnostic Imaging Southern California University of Health Sciences COLLIMATION CAN IMPROVE YOUR IMAGES This film demonstrates limited collimation.
Radiology Hector RiveraMelo, DC, DACBR Director, Center for Diagnostic Imaging Southern California University of Health Sciences COLLIMATION CAN IMPROVE YOUR IMAGES This film demonstrates limited collimation.
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
& & 392 & C1-C2
 Abbreviations...424 Abdominal Aortic Aneur... 302 Abdominal Rapid DDx...401 AC Sprain... 140 Acetabular Labral Tear... 222 Achilles Tendinopathy... 286 ACL Sprain/Tear... 236 Advanced Wobble Board... 395
Abbreviations...424 Abdominal Aortic Aneur... 302 Abdominal Rapid DDx...401 AC Sprain... 140 Acetabular Labral Tear... 222 Achilles Tendinopathy... 286 ACL Sprain/Tear... 236 Advanced Wobble Board... 395
DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments
 DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments The DART Tool allows a user to obtain Treatment recommendations based on the disorder/condition. These recommendations are provided by ACOEM (American College of Occupational
DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments The DART Tool allows a user to obtain Treatment recommendations based on the disorder/condition. These recommendations are provided by ACOEM (American College of Occupational
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS. CMS Clinical Concepts
 CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb AP; Lat. PA. PA; Lat.: Obls.; Elongated PA with ulnar deviation
 Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Diagnostic Imaging Exams
 Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Guide for Chiropractors Diagnostic Imaging Exams CREATED FOR OUR CHIROPRACTIC PARTNERS This document has been prepared by the specialized, board-certified radiologists who interpret patient exams for Center
Functional Orthopedic Imaging Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion. Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy.
 Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Radiography Protocols
 Radiography Protocols Upper Limb Second through Fifth Digits (Standard 3 views) First Digit (Thumb) (Standard 3 views) Hand (Standard 3 views) Wrist (Standard 4 views) Forearm (Standard 2 views) Elbow
Radiography Protocols Upper Limb Second through Fifth Digits (Standard 3 views) First Digit (Thumb) (Standard 3 views) Hand (Standard 3 views) Wrist (Standard 4 views) Forearm (Standard 2 views) Elbow
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections
 WSCC Clinics Protocol Adopted: 3/05 Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections This document lists the routine, supplemental and alternative projections performed in the Diagnostic Imaging
WSCC Clinics Protocol Adopted: 3/05 Imaging Decision Making: Recommended Radiographic Projections This document lists the routine, supplemental and alternative projections performed in the Diagnostic Imaging
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks
 Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks _ The approach to examining the musculoskeletal system is the same no matter what joint or limb is being examined. The affected and contralateral region should both
Musculoskeletal Examination Benchmarks _ The approach to examining the musculoskeletal system is the same no matter what joint or limb is being examined. The affected and contralateral region should both
Special Instructions
 FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee
 Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
ABOS Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Examination Blueprint
 ABOS Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Subspecialty Examination, Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Combined Examination, and Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Practice Profiled Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of
ABOS Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Subspecialty Examination, Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Combined Examination, and Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Practice Profiled Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
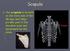 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES. Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM Academic
 WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Academic AM OC OC day CAM CAM PM with Dr. Lindley Wall Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Academic AM OC OC day CAM CAM PM with Dr. Lindley Wall Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of Common ICD-10 Codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of Common ICD-10 Codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park):
 Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Musculoskeletal and Orthopaedic Conditions Treated
 General category Sub-categories Often used diagnosis/common terms Muscle and tendon pain and injuries Strains, tears/ruptures, contusions, lacerations, muscle pain, myofascial pain Tendinopathy, tendinitis,
General category Sub-categories Often used diagnosis/common terms Muscle and tendon pain and injuries Strains, tears/ruptures, contusions, lacerations, muscle pain, myofascial pain Tendinopathy, tendinitis,
Objectives. The BIG Joint. Case 1. Boney Architecture. Presenter Disclosure Information. Common Knee Problems
 3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
3:30 4:15 pm Common Knee Problems SPEAKER Christopher J. Visco, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher J. Visco, MD: Speaker s Bureau
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
The examination of the painful knee. Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University
 The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
Sustained a sprained ankle
 Student Name : Student s Number : 3. Q 1. 2. Sustained a sprained ankle 1. List at least 3 key items you should ask during the history portion of an examination ( ) Possible Answers and Anything Else you
Student Name : Student s Number : 3. Q 1. 2. Sustained a sprained ankle 1. List at least 3 key items you should ask during the history portion of an examination ( ) Possible Answers and Anything Else you
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendonitis, criteria for full competition in, 164 165 description of, 164 patient education in, 165 prophylactic support in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles tendonitis, criteria for full competition in, 164 165 description of, 164 patient education in, 165 prophylactic support in,
An Introduction to Radiographic Views & Anatomy
 An Introduction to Radiographic Views & Anatomy Morey J. Kolber, PT, PhD, OCS, Cert MDT, CSCS*D An Introduction to Radiographic Views & Anatomy M.S.P.T. 1995-University of Miami Nova Southeastern University
An Introduction to Radiographic Views & Anatomy Morey J. Kolber, PT, PhD, OCS, Cert MDT, CSCS*D An Introduction to Radiographic Views & Anatomy M.S.P.T. 1995-University of Miami Nova Southeastern University
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans
 Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Standardised. knee. scanning of the. Basic pathology. Nemanja Damjanov. University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology
 Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Skeletal System. Bones & Joints
 Skeletal System Bones & Joints Vertebral Column Upper Limb Lower Limb OUTLINE Clinical Related Features Arrangements Features of the Joints Vertebral Column (Overview) Costal Element Regional Features
Skeletal System Bones & Joints Vertebral Column Upper Limb Lower Limb OUTLINE Clinical Related Features Arrangements Features of the Joints Vertebral Column (Overview) Costal Element Regional Features
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS AND PAIN
 Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO
 Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint injuries in football players, 318, 319 ALPSA. See Anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion. Anterior
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint injuries in football players, 318, 319 ALPSA. See Anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion. Anterior
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION
 COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES. Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM VA OR Wohl
 WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) VA OR Wohl Dr. Goldfarb CAM OC OC OR CAM CAM OR Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) VA OR Wohl Dr. Goldfarb CAM OC OC OR CAM CAM OR Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE
 ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 RA202 positioning class three- EXM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following hand projections would be used
RA202 positioning class three- EXM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following hand projections would be used
Take Pride in Performance
 2017 Take Pride in Performance Knee: Meniscal Tear FSE PD - Sagittal FSE PD - Coronal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: ACL Tibial Avulsion 3D SHARC ISO - Sagittal FSE PD - Sagittal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: Subchondral
2017 Take Pride in Performance Knee: Meniscal Tear FSE PD - Sagittal FSE PD - Coronal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: ACL Tibial Avulsion 3D SHARC ISO - Sagittal FSE PD - Sagittal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: Subchondral
SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011
 SUTTER MEDICAL FOUNDATION (SMF) 2800 L Street, 7 th Floor Sacramento, CA 95816 SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011 I. Shoulder Pain...Page
SUTTER MEDICAL FOUNDATION (SMF) 2800 L Street, 7 th Floor Sacramento, CA 95816 SMF PCP Treatment & Referral Guideline Orthopedics Developed February 1, 2003 Revised: October, 2011 I. Shoulder Pain...Page
Please differentiate an internal derangement from an external knee injury.
 Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities
 Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
CERVICAL SPINE: Radiographs and MRI Cases
 www.jprad.com Radiology reports with recommendations & clinical information - $30 per region, x-ray - $50 per MRI - Medpay Monthly Newsletter 700 East Redlands Blvd, Redlands CA 92373 909.353.9348 jpedley299@yahoo.com
www.jprad.com Radiology reports with recommendations & clinical information - $30 per region, x-ray - $50 per MRI - Medpay Monthly Newsletter 700 East Redlands Blvd, Redlands CA 92373 909.353.9348 jpedley299@yahoo.com
Outline. Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures
 C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
For more information call , or visit
 Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
TOP RYDE CHIROPRACTIC
 1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
