Social Psychology. Social Psychology. Friends agree that person is: Friends agree that person is:
|
|
|
- Duane Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Social Psychology Social Psychology Chapter 13 Impression formation and Attribution theory Study of the ways in which thoughts, feelings, perceptions, motives, and behavior are influenced by interactions with other people How we interpret the behavior of others How we form impressions of others How we form attitudes toward others/objects How others influence our own behavior How we establish relationships with others Social cognition: use of cognitive processes to understand others and ourselves Friends agree that person is: Industrious, intelligent, practical, warm, determined, cautious, skillful Rate overall impression of person Very favorable (1) Very unfavorable (7) Do you think this person is likable? Very likable (1) - Very unlikable (7 Y or N? Does this trait describe the individual? Generous Wise Good-natured Reliable Happy Important Friends agree that person is: Envious, stubborn, critical, fun-loving, irritating, artistic, clever, helpful Rate overall impression of person Very favorable (1) Very unfavorable (7) Do you think this person is likable? Very likable (1) - Very unlikable (7 Y or N? Does this trait describe the individual? Generous Wise Good-natured Reliable Happy Important 1
2 Friends agree that person is: Sensible, careful, cold, smart, skillful, productive, determined Rate overall impression of person Very favorable (1) Very unfavorable (7) Do you think this person is likable? Very likable (1) - Very unlikable (7 Y or N? Does this trait describe the individual? Generous Wise Good-natured Reliable Happy Important Friends agree that person is: Warm, cooperative, reckless, witty, active, spiteful, inflexible, judgmental Rate overall impression of person Very favorable (1) Very unfavorable (7) Do you think this person is likable? Very likable (1) - Very unlikable (7 Y or N? Does this trait describe the individual? Generous Wise Good-natured Reliable Happy Important Impression formation Person perception Did a single word change overall impression? Did change in order of positive / negative traits change overall impression? 1. Industrious, intelligent, practical, warm, determined, cautious, skillful 2. Envious, stubborn, critical, fun-loving, irritating, artistic, clever, helpful 3. Sensible, careful, cold, smart, skillful, productive, determined 4. Warm, cooperative, reckless, witty, active, spiteful, inflexible, judgmental First Impressions Serial position curve effects (primacy & recency) Anchor and adjustment heuristic Bottom up (features) Physical appearance Top down (schema) Social schema influence of knowledge Infer elements that may not have been present 2
3 What happened to cause this event? Woman spills her coffee at a restaurant You get an A on the exam A student takes a semester off from school You get pulled over by a cop for speeding A Mom hits the bottom of child in the mall Someone cuts you off on the highway Student drops food tray in Burwell You miss class You pull an all-nighter before a paper is due President is caught plagiarizing his speeches Attribution How people make sense about their own and others behavior Inferences of cause and effect Try to identify factors that give rise to outcomes Why do this? Make predictions about the future Process automatic and/or deliberate Covariation model of attribution Do they always do this in this situation? Do others do this in this situation? Do they do they do this in other situations? Attribution theory Explain event by attributing behavior to: Internal attribution: Disposition or personality Behavior is due to person s stable characteristics Can predict future behaviors External attribution: Situation or environment Behavior is due to outside forces Says little about future behaviors Attribution bias Good behavior Bad behavior Self Disposition Situation Other Situation Disposition 3
4 Biases in attribution Actor-Observer bias Own behavior external Others behavior - internal Fundamental attribution error: Others behavior Overestimate internal factors Underestimate external situational factors Self-serving bias : Own behavior Success = internal Failure = external Adaptive value vs. incorrect conclusions Jones & Nisbett (1970s) Had Ss write 4 essays Why do you/best friend like the person you date? Why did you/best friend choose your major? DV: coded for internal/external attribution Results: Self: more situational attributions (external) Best friend: more dispositional attributions (internal) Conclusions: Use it depends more in reference to self Actor-Observer bias Jones & Harris (1967) Fundamental attribution error Essay evaluation of either Pro or Anti-Castro Author chose/forced to take a side Guess author s true attitude Truly are pro-castro Choice Condition No Choice Pro-Castro Anti-Castro People tend to attribute action to internal factor Interpretation of actor-observer difference Motivation Cognitive dissonance Behavior/belief at odds with self-concept; inconsistency Try to reduce it when possible Festinger & Carlsmith (1959) Act in a way that contradicts true feeling/attitude IV: Paid $1 or $20 to lie (or no lie condition) DV: How enjoyable was the study Justification of effort Results 4
5 Festinger & Carlsmith (1959) Cognitive dissonance Interpretation of actor-observer difference enjoyable would participate similar control $1 $20 Cognitive interpretation Know ourselves better than know others Know only one situation for others Less dispositional attributions when know person better (best friend) Perceptual interpretation Different perspectives Can t see what actor is responding to Can t observe own behavior DV: Ratings from 5 to +5 Above-average effect (Harter, 1990) What are your strengths and weaknesses? College Board: 1 million HS students 70%: said above average on leadership 100%: above average for getting along with others 60% said above average in athletics People judge themselves as above-average on favorable characteristics Why? Memory is selective Protect self-image of themselves and others Consider: Why do we make attribution errors? Can you think of a recent example of this type of error in your own life? Relate your example to the terms: Fundamental attribution error Actor-observer effect Self-serving bias 5
6 Stereotypes Social Psychology Chapter 13 Stereotypes and prejudice Stereotypes Beliefs held about traits and behaviors that belong to a particular group and its members Most common: gender, race, age Prejudice Negative stereotype that leads people to negatively evaluate group members Emphasis on difference between groups Discrimination Prejudiced beliefs lead to behaviors Sources of stereotypes and prejudice Schemas or heuristics Organize and reduce amount of information Social learning Conformity to a social norm Media Social and economic conflict Social categorization Scapegoating or blaming the innocent Dissimilarity and social distance Blue-eyed vs. Brown-eyed example Thought paper Blue-eyed / Brown-eyed movie: What did you learn about stereotypes and prejudice from the movie? What other comments, thoughts, or questions do you have about the movie? 6
7 Effect of stereotypes and prejudice Self-fulfilling prophecies Beliefs cause the expected behavior Snyder et al. (1977): phone study Stereotype threat Expectation IQ test performance affects final score Activation of negative stereotype Automatic activation of stereotype Stereotype activation on action Behavior can be triggered automatically Wegner s white bear study Social behavior affected by unconscious thoughts Bargh, Chen, & Burrows (1996) Unscramble sentences about rudeness interrupt faster Flash words about aging walk slower Greenwald & Banaji (1995) (text pp.435) Flash negative stereotypes about African Americans fictional character evaluated as more aggressive Are our thoughts and behaviors under our control? Combating prejudice Education Possibly the least effective tool People usually avoid or discount information New role models Discussion forums Repeated positive exposure Intergroup cooperation Legislation Speak up against discriminatory behavior Examine your own beliefs be aware! Control requires awareness and motivation Consider: What are the conclusions of Keating s research? How are the conclusions different for children and adults? What does it tell us about attitude formation, persuasion, and leadership? 7
8 Conformity Social Psychology Chapter 13 Influence and obedience Look to others for behavior and attitudes Go along with group even when know they are wrong Why? Cognitive: Want to be right More likely to conform if unsure Ally effect: no conformity if 1 other has their answer Motivational: Want to be liked Fear ostracism from the group Avoid rejection Power of authority: Milgram (1963) Recruited for study of memory White-coated experimenter: examine effect of punishment on learning Run subjects in pairs: learner and teacher Learner was confederate Teacher watches: learner get strapped to chair electrodes attached to wrist 8
9 Power of authority: Milgram (1963) Teacher administered punishment when learner was incorrect (slight to severe shock) Increase punishment with each error If object to continuing: You must go on. How far do the participants go in obeying experimenter? Volt Reaction 75 Grunt 120 Shout in pain 150 Refuse to continue 200 Screams 300 No answer, heart 330+ Silence Milgram s quote I observed a mature and initially poised businessman enter the laboratory smiling and confident. Within 20min he was reduced to a twitching, stuttering wreck, who was rapidly approaching nervous collapse. He constantly pulled on his ear lobe and twisted his hands. At one point he pushed his fist into his forehead and muttered Oh God, lets stop it. And yet he continued to respond to every word of the experimenter, and obeyed to the end. Milgram s study of obedience Consider: Percentage of partcipants obeying command at each shock level slight moderate strong Why did 65% of the participants in the study deliver the highest level shock?! very strong intense extremely intense danger: severe shock 450 volts 65% willing to deliver highest level shock If you were to design a similar study, what variables would you change? Why? 9
10 Factors: Tendency to Obey Conformity High status of authority figure, prestige of Yale, for science Belief among subordinates that the source of the authority will be responsible for their actions not them Strong tendency to obey direct commands Absence of a clear-cut point for switching to disobedience The gradual nature of many obedience situations (mild consequences at first and only later are there harmful effects) Conclusion: Behavior not just due to personality due to situation too Obedience Ethics of Milgram s research? Participants mislead and were severely distressed Do the benefits outweigh the costs? Don t think Milgram s reasearch is real? McDonald s story: Police phone in to strip-search employee
Chapter 13. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Factors that affect interpersonal attraction:
 Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
CHAPTER 15. Social Psychology. Lecture Overview. Introductory Definition PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Social Cognition.
 Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology. What We Will Cover in This Section. Roles. PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
What is Social Psychology
 What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
Defining Social Psychology. informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people
 Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Chapter 14. Social Psychology. How Does the Social Situation Affect our Behavior? Social Psychology
 Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams
 Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
Social Psychology. Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations.
 Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008
 Name: Class: The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 In 1963, Stanley Milgram conducted a study on obedience. Using a series of social psychology experiments, Milgram measured participants willingness
Name: Class: The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 In 1963, Stanley Milgram conducted a study on obedience. Using a series of social psychology experiments, Milgram measured participants willingness
PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies
 PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies show? MYTH #1 NOTES GUIDE 1. Do you think there s truth to the statement, Psychology
PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies show? MYTH #1 NOTES GUIDE 1. Do you think there s truth to the statement, Psychology
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward
 Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
8 Diffusion of Responsibility
 Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS
 Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY. Social Influences on the Self. Self Concept. How do we see ourselves? How do we see others?
 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
F. Ellsworth 1972 Gaze aversion
 Impression Formation I. Impression Formation A. The process by which we integrate various sources of information about another into overall judgment. II. Guess Characteristics A. Major? B. Spare time?
Impression Formation I. Impression Formation A. The process by which we integrate various sources of information about another into overall judgment. II. Guess Characteristics A. Major? B. Spare time?
Person Perception. Forming Impressions of Others. Mar 5, 2012, Banu Cingöz Ulu
 Person Perception Forming Impressions of Others Mar 5, 2012, Banu Cingöz Ulu Person Perception person perception: how we come to know about others temporary states, emotions, intentions and desires impression
Person Perception Forming Impressions of Others Mar 5, 2012, Banu Cingöz Ulu Person Perception person perception: how we come to know about others temporary states, emotions, intentions and desires impression
MILGRAM EXPERIMENT. Research on people s obedience. Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School
 MILGRAM EXPERIMENT Research on people s obedience Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School October 14 th, 2014 ABSTRACT This paper is written in order to research and understand about the famous
MILGRAM EXPERIMENT Research on people s obedience Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School October 14 th, 2014 ABSTRACT This paper is written in order to research and understand about the famous
Defining Psychology Behaviorism: Social Psychology: Milgram s Obedience Studies Bystander Non-intervention Cognitive Psychology:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
What is Social Psychology
 The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
Ones Way of Thinking. Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will
 Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Introduction to Psychology Social Psychology Quiz
 MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
Social Psychology. Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions)
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions) Attribution Theory Tries to explain how people
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions) Attribution Theory Tries to explain how people
Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%)
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance
 Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern SoTL Commons Conference SoTL Commons Conference Mar 12th, 4:00 PM - 5:45 PM Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance Lugenia Dixon
Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern SoTL Commons Conference SoTL Commons Conference Mar 12th, 4:00 PM - 5:45 PM Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance Lugenia Dixon
Exam #4 Study Guide. Chapter 7 Memory
 Exam #4 Study Guide Chapter 7 Memory I. Memory Structural categorizations A. By length of time i. Sensory Store ii. Short Term Memory (working memory) iii. Long Term Memory B. By type of information i.
Exam #4 Study Guide Chapter 7 Memory I. Memory Structural categorizations A. By length of time i. Sensory Store ii. Short Term Memory (working memory) iii. Long Term Memory B. By type of information i.
AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology
 Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
33 Multiple choice questions
 NAME 33 Multiple choice questions 1. central route a. Aspect of persuasion, emotional appeals are quite powerful. Negative appeals play to the audience's b. Aspect of persuasion, whether or not someone
NAME 33 Multiple choice questions 1. central route a. Aspect of persuasion, emotional appeals are quite powerful. Negative appeals play to the audience's b. Aspect of persuasion, whether or not someone
Topics for today Ethics Bias
 HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
Social Psychology 10 (14)
 Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
attitude the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting the situation or the person's disposition attribution theory
 attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
Note:- Receptors are the person who receives any images from outer environment.
 Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 04/13/15. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 12.1 How Do We Form Our Impressions of Others? Nonverbal Actions and Expressions Affect our First Impressions We Make Attributions about Others Stereotypes
Social Psychology LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 12.1 How Do We Form Our Impressions of Others? Nonverbal Actions and Expressions Affect our First Impressions We Make Attributions about Others Stereotypes
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Authoritarian Personality.
 Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority.
 What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority. Resisting order or commands from people in authority. What is the core theory called? What does
What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority. Resisting order or commands from people in authority. What is the core theory called? What does
Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives. Chapter 3 Outline -Attitude Change
 Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives 1) An understanding of how both internal mental processes and external influences lead to attitude change 2) An understanding of when and how behavior which is inconsistent
Chapter 3-Attitude Change - Objectives 1) An understanding of how both internal mental processes and external influences lead to attitude change 2) An understanding of when and how behavior which is inconsistent
ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR
 ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LECTURE 3, CHAPTER 6 A process through which Individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment. PERCEPTION Why is Perception
ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR LECTURE 3, CHAPTER 6 A process through which Individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment. PERCEPTION Why is Perception
My Notebook. A space for your private thoughts.
 My Notebook A space for your private thoughts. 2 Ground rules: 1. Listen respectfully. 2. Speak your truth. And honor other people s truth. 3. If your conversations get off track, pause and restart. Say
My Notebook A space for your private thoughts. 2 Ground rules: 1. Listen respectfully. 2. Speak your truth. And honor other people s truth. 3. If your conversations get off track, pause and restart. Say
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations
 Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations Changing Perceptions at Camp FFIT - Camp FFIT is part of the Ottawa Fire Service s campaign to recruit more female firefighters - Aligning their
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations Changing Perceptions at Camp FFIT - Camp FFIT is part of the Ottawa Fire Service s campaign to recruit more female firefighters - Aligning their
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM
 CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
PERSON PERCEPTION September 25th, 2009 : Lecture 5
 PERSON PERCEPTION September 25th, 2009 : Lecture 5 PERSON PERCEPTION Social Information Attribution Self-serving Biases Prediction SOCIAL INFORMATION BEHAVIOURAL INPUT What Goes Into Person Perception?
PERSON PERCEPTION September 25th, 2009 : Lecture 5 PERSON PERCEPTION Social Information Attribution Self-serving Biases Prediction SOCIAL INFORMATION BEHAVIOURAL INPUT What Goes Into Person Perception?
Social Psychology. Studying the way people relate to others. Attitude. Group Behavior. Attraction Aggression
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
What is Social Cognition?
 Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
Tendencies to Distort Self and Social Reality Barriers to Critical Thinking
 1 Psychology 496 Dr. Patterson Tendencies to Distort Self and Social Reality Barriers to Critical Thinking Cognitive Biases and Errors Affecting Self and Social Perceptions, Social Beliefs, and Social
1 Psychology 496 Dr. Patterson Tendencies to Distort Self and Social Reality Barriers to Critical Thinking Cognitive Biases and Errors Affecting Self and Social Perceptions, Social Beliefs, and Social
Social Psychology. Social Psychology
 Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
Three Minute Review. critiques of Piaget s theories information processing perspective
 Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Three Minute Review. 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence
 Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. Recommended Homework
 Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Three Minute Review COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget s Stages 1. Sensorimotor Stage (0-2) physics, senses, movement, object permanence 2. Preoperational Stage (2-7) symbolic, egocentric, no conservation 3.
Lesson 12. Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior
 Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
PSYC 210 Social Psychology
 South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
SOCI 323 Social Psychology
 SOCI 323 Session 9 SOCIAL PERCEPTION Lecturer: Dr. Peace Mamle Tetteh, Department of Sociology Contact Information: ptetteh@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
SOCI 323 Session 9 SOCIAL PERCEPTION Lecturer: Dr. Peace Mamle Tetteh, Department of Sociology Contact Information: ptetteh@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
PSYC1001 NOTES. Science and Statistics
 PSYC1001 NOTES TOPICS PAGES Science and Statistics ---------------------------------------------------------------- 2-11 Personality Psychology -------------------------------------------------------------
PSYC1001 NOTES TOPICS PAGES Science and Statistics ---------------------------------------------------------------- 2-11 Personality Psychology -------------------------------------------------------------
AP Psych Unit 14 REVIEW
 Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
CHAPTER 3: SOCIAL PERCEPTION: UNDERSTANDING OTHER PEOPLE CHAPTER OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 3: SOCIAL PERCEPTION: UNDERSTANDING OTHER PEOPLE CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 3 covers three main topics: impressions others make on us, attribution processes and biases, and the impressions we make
CHAPTER 3: SOCIAL PERCEPTION: UNDERSTANDING OTHER PEOPLE CHAPTER OVERVIEW Chapter 3 covers three main topics: impressions others make on us, attribution processes and biases, and the impressions we make
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology. 4. What cultures do not make the fundamental attribution error as much?
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Conformity Asch study (1951) Which of the lines below is the same as the line to the right?
 a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
Exam #3 Review Sheet MAR 3503 Consumer Behavior Spring 2012
 Exam #3 Review Sheet MAR 3503 Consumer Behavior Spring 2012 These questions should help you organize your thoughts and prepare for the exam. The questions on these pages are, in general, much broader than
Exam #3 Review Sheet MAR 3503 Consumer Behavior Spring 2012 These questions should help you organize your thoughts and prepare for the exam. The questions on these pages are, in general, much broader than
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer
 -Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
Social Psychology Terms and Vocabulary. How one tends to act toward the object of an attitude.
 Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures)
 Traditional Persuasion Techniques A) Greater rewards lead to more responses B) Greater punishment leads to less responses C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures) D) Use of conformity
Traditional Persuasion Techniques A) Greater rewards lead to more responses B) Greater punishment leads to less responses C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures) D) Use of conformity
Introduction to Attitudes
 Introduction to Attitudes Learning Goals Understand the construct of attitudes Understand how are attitudes formed Attitudes Attitude: Positive or negative reaction to a person, object, or idea Good-bad
Introduction to Attitudes Learning Goals Understand the construct of attitudes Understand how are attitudes formed Attitudes Attitude: Positive or negative reaction to a person, object, or idea Good-bad
Actor-Observer Bias One of the most established phenomenon in social psychology YOUR behavior is attributed to OTHER S behavior is attributed to
 1 The Self in Social Psychology Disclaimer: there are many class demonstrations not included in the notes (to prevent ruining them); if you miss this lecture, you should get the notes from someone in the
1 The Self in Social Psychology Disclaimer: there are many class demonstrations not included in the notes (to prevent ruining them); if you miss this lecture, you should get the notes from someone in the
(TEST BANK for Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 7th Edition by Steven McShane, Mary Von Glinow)
 Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 7th Edition McShane Test Bank Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/organizational-behavior-emergingknowledge-global-reality-7th-edition-test-bank-mcshane-glinow/
Organizational Behavior Emerging Knowledge Global Reality 7th Edition McShane Test Bank Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/organizational-behavior-emergingknowledge-global-reality-7th-edition-test-bank-mcshane-glinow/
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles
 Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
A B C. Copyright Allyn and Bacon 2005
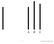 A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
Social Psychology. An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013
 Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
AP Psychology Summer Assignment. Book: Opening Skinner s Box by Lauren Slater
 AP Psychology Summer Assignment Book: Opening Skinner s Box by Lauren Slater One of the major themes of research in psychology is to answer the question what makes humans tick. Why do we love? Why are
AP Psychology Summer Assignment Book: Opening Skinner s Box by Lauren Slater One of the major themes of research in psychology is to answer the question what makes humans tick. Why do we love? Why are
Conformity ASCH S STUDY 12/8/2010 ASCH S STUDY. Social Psychology (581, ) Others Focus on Social Influences on Our Behavior
 Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
A First Look at Communication Theory
 16 Cognitive Dissonance Theory of Leon Festinger A First Look at Communication Theory 9 th edition Em Griffin Andrew Ledbetter Glenn Sparks Dissonance: Discord Between Behavior and Belief Slide 2 Cognitive
16 Cognitive Dissonance Theory of Leon Festinger A First Look at Communication Theory 9 th edition Em Griffin Andrew Ledbetter Glenn Sparks Dissonance: Discord Between Behavior and Belief Slide 2 Cognitive
Thinking and Intelligence
 Thinking and Intelligence Learning objectives.1 The basic elements of thought.2 Whether the language you speak affects the way you think.3 How subconscious thinking, nonconscious thinking, and mindlessness
Thinking and Intelligence Learning objectives.1 The basic elements of thought.2 Whether the language you speak affects the way you think.3 How subconscious thinking, nonconscious thinking, and mindlessness
Chapter 3: Perception and the Self in IPC 01/24/2012
 Chapter 3: Perception and the Self in IPC 01/24/2012 Section 1: The Self in Interpersonal Communication Self Concept Your self concept develops from at least four sources: Others Images: Cooley s concept
Chapter 3: Perception and the Self in IPC 01/24/2012 Section 1: The Self in Interpersonal Communication Self Concept Your self concept develops from at least four sources: Others Images: Cooley s concept
OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67,
 1 OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67, 371-378. If someone in a position of authority ordered you to deliver an electrical
1 OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67, 371-378. If someone in a position of authority ordered you to deliver an electrical
Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
 Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
Obedience to Authority
 Obedience to Authority Jan. 9, 2005 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.34 2005 David Schweingruber Milgram s experiment Experiment: research method designed to elicit some sort of behavior, typically conducted
Obedience to Authority Jan. 9, 2005 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.34 2005 David Schweingruber Milgram s experiment Experiment: research method designed to elicit some sort of behavior, typically conducted
Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research
 Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research Ten Points of the Nuremberg Code (1947) 1. The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential. This means that the person involved
Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research Ten Points of the Nuremberg Code (1947) 1. The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential. This means that the person involved
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: OBEDIENCE. Attitudes beliefs tinged with emotion cognitive dissonance
 Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology
 Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
Social Psychology. Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior. Studying the way people relate to others.
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Psychology and Social Change
 Psychology and Social Change Cognitive Dissonance and Paradigm Shifts Reminder from unit one: Psychologists focus on the individual Want to know how can you change someone's behaviour Cognitive Consistency
Psychology and Social Change Cognitive Dissonance and Paradigm Shifts Reminder from unit one: Psychologists focus on the individual Want to know how can you change someone's behaviour Cognitive Consistency
Name: Date: D) All of these answers are correct.
 Name: Date: 1. After months of deliberation, James decides to play football instead of joining the cross country team. According to the cognitive dissonance theory, when will James become more confident
Name: Date: 1. After months of deliberation, James decides to play football instead of joining the cross country team. According to the cognitive dissonance theory, when will James become more confident
Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being?
 Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
General Psychology Social Psych. Cognitive Bias. Bystander Effect. When others are present, less likely to help Fundamental Attribution Error
 General Psychology Social Psych Cognitive Bias Bystander Effect When others are present, less likely to help Fundamental Attribution Error Also called Correspondence Bias Attribution Effect We prefer dispositional
General Psychology Social Psych Cognitive Bias Bystander Effect When others are present, less likely to help Fundamental Attribution Error Also called Correspondence Bias Attribution Effect We prefer dispositional
Social Psychology. The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another.
 Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the situation
Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the situation
Self-Consciousness and its Effects on Dissonance-Evoking Behavior
 Self-Consciousness and its Effects on Dissonance 1 Self-Consciousness and its Effects on Dissonance-Evoking Behavior Erica Behrens Winona State University Abstract This study examines the effects of self-consciousness
Self-Consciousness and its Effects on Dissonance 1 Self-Consciousness and its Effects on Dissonance-Evoking Behavior Erica Behrens Winona State University Abstract This study examines the effects of self-consciousness
Breaking the Bias Habit. Jennifer Sheridan, Ph.D. Executive & Research Director Women in Science & Engineering Leadership Institute
 Breaking the Bias Habit Jennifer Sheridan, Ph.D. Executive & Research Director Women in Science & Engineering Leadership Institute P e r c e n t W o m e n Percent Women Bachelor's Degrees, Selected Fields
Breaking the Bias Habit Jennifer Sheridan, Ph.D. Executive & Research Director Women in Science & Engineering Leadership Institute P e r c e n t W o m e n Percent Women Bachelor's Degrees, Selected Fields
Conformity & Obedience
 Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
8/17/2012. Self-Concept Video. Cultural Differences in Defining the Self. Chapter 5. The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context
 Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
Social Psychology CHAPTER 14 CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
Emotion. I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression
 Emotion I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression Emotion Defined: Positive & negative feeling states consisting of patterns of: physiological arousal
Emotion I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression Emotion Defined: Positive & negative feeling states consisting of patterns of: physiological arousal
Social Psychology. The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another.
 Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. 1 Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the
Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. 1 Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the
Social Psychology. Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus (3 Credits) Lecturers: Dr. ZHANG Zhongyuan zhangzhongyuan@zju.edu.cn Dr. LV Jiaying Jiaying_lu@zju.edu.cn Dr. ZHOU Xinhong zxhzheda@zju.edu.cn Office Hours: Friday, 1330-1700, 805-01 central
Course Syllabus (3 Credits) Lecturers: Dr. ZHANG Zhongyuan zhangzhongyuan@zju.edu.cn Dr. LV Jiaying Jiaying_lu@zju.edu.cn Dr. ZHOU Xinhong zxhzheda@zju.edu.cn Office Hours: Friday, 1330-1700, 805-01 central
IMPLICIT BIAS: UNDERSTANDING AND ADDRESSING ITS IMPACT. ALGA Regional Training Dr. Markisha Smith October 4, 2018
 IMPLICIT BIAS: UNDERSTANDING AND ADDRESSING ITS IMPACT ALGA Regional Training Dr. Markisha Smith October 4, 2018 Develop and/or expand on an understanding of implicit bias. GOALS FOR TODAY S SESSION Consider
IMPLICIT BIAS: UNDERSTANDING AND ADDRESSING ITS IMPACT ALGA Regional Training Dr. Markisha Smith October 4, 2018 Develop and/or expand on an understanding of implicit bias. GOALS FOR TODAY S SESSION Consider
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES
 Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Psychology Ciccarelli and White
 1 Psychology Ciccarelli and White C H A P T E R 12: S O C I A L P S Y C H O L O G Y What is social psychology? It is the scientific study of how the individual functions as a result of being a part of
1 Psychology Ciccarelli and White C H A P T E R 12: S O C I A L P S Y C H O L O G Y What is social psychology? It is the scientific study of how the individual functions as a result of being a part of
Unconscious Bias: From Awareness to Action!
 Unconscious Bias: From Awareness to Action! Did you know that we all have unconscious bias, and that we each have a responsibility to prevent its unintended consequences? In this course, we will explore
Unconscious Bias: From Awareness to Action! Did you know that we all have unconscious bias, and that we each have a responsibility to prevent its unintended consequences? In this course, we will explore
